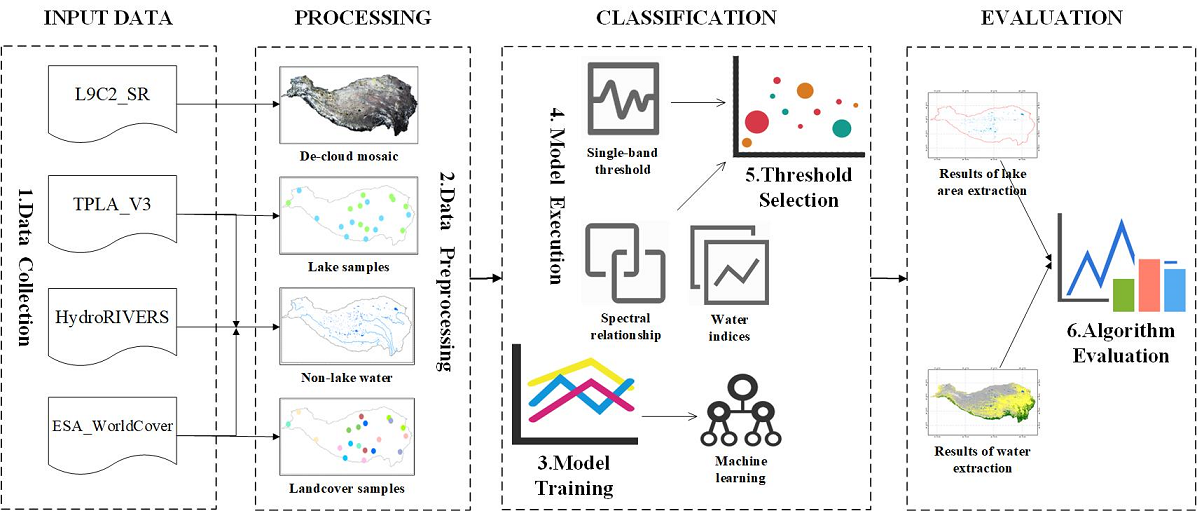
The monitoring of lake waterbody area in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau (QTP) is of great significance to deal with global climate change. As the latest generation of Landsat series satellites, Landsat-9 data not only have higher radiometric resolution, but also cooperate with other Landsat satellites to greatly improve the temporal resolution. It has great application potential in lake waterbody area monitoring. In order to explore the performance of different algorithms for extracting waterbody and lake waterbody area in Landsat-9 data under large-scale QTP regions, this study relies on Google Earth Engine (GEE) platform and selects 10 waterbody extraction algorithms as the basis to realize the quantitative evaluation of QTP lake waterbody area extraction results. The results show that the Random Forest (RF) algorithm performs best in all models. The overall accuracy of waterbody extraction is 95.84%, and the average error of lake waterbody area extraction is 1.505%. Among the traditional threshold segmentation waterbody extraction algorithms, the overall accuracy of the NDWI waterbody extraction method is 89.89%, and the average error of lake waterbody area extraction is 3.501%, which is the highest performance model in this kind of algorithms. This study proves that Landsat-9 data can effectively classify QTP waterbodies. With the development of cloud computing technologies such as Gee, more complex models such as RF can be selected to improve the extraction accuracy of water body and Lake area in large-scale research.