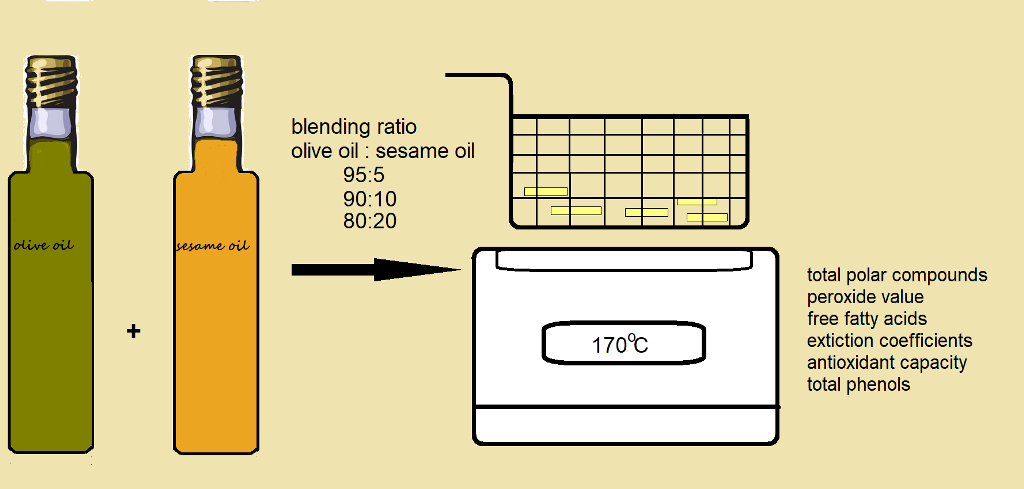
Fresh potatoes were deep-fried in olive oil (OO) & extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) and their blends with 5%, 10% and 20% v/v sesame oil (SO). This is the first report on the use of sesame oil as natural source of antioxidant for olive oil deep-frying. Oil was evaluated for Peroxide Value (PV), Free Fatty Acids (FFA), K232, K270, Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC) and Total Phenols (TP) until Total Polar Compounds (TPCs) reached 25%. Sesame lignan transformations were monitored through Reverse-phase HPLC. While TPCs in olive oils increased at a steady rate, the addition of 5%, 10% and 20% v/v SO created a time window lasting 1, 2 and 3 hours, respectively, where TPCs were constant. SO addition to OO increased the total frying time. Furthermore, the addition of SO reduced the peroxides formation rate for both OO and EVOO. EVOO was more resistant to oxidation than OO as measured by TPCs and TEAC, while frying time raised from 21.5 to 25.25 h when EVOO replaced OO. The increase in frying time for olive oil but not for extra virgin olive oil, after SO addition, is pointing out a niche market for extra virgin olive oil in deep-frying.