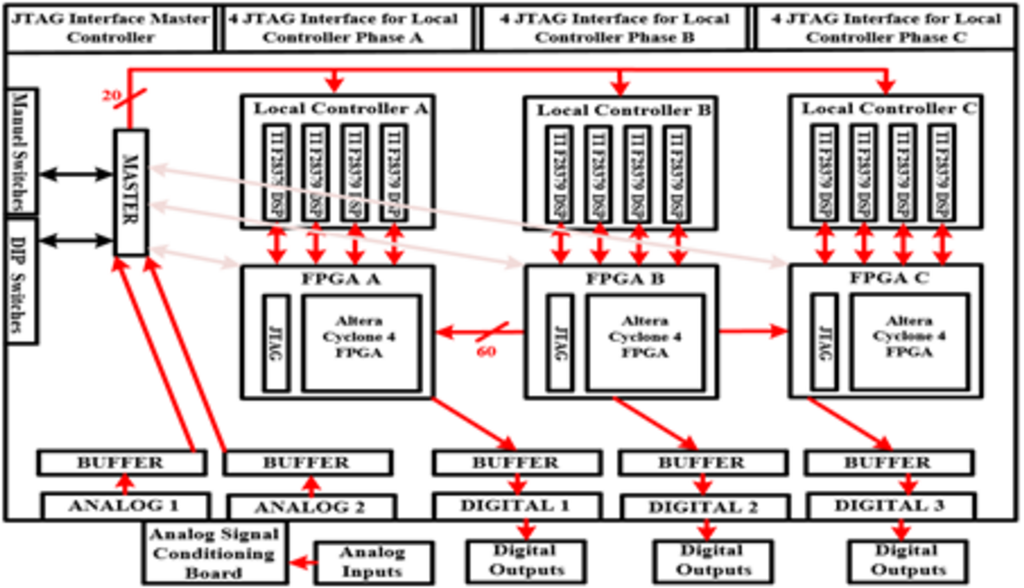
Centralized control algorithm limits the hardware flexibility of a Modular Multilevel Converter (MMC). Therefore, industrial MMC applications have started adopting distributed control structures. Even though distributed controller reduces a single point of failure risk compared to the centralized controller, the failure risk of the entire control systems increases due to the number of local controllers. However, the distributed controller can be programmed in such a way as to bypass the faulty local controller and take care of the power modules with the adjacent local controllers. This paper implements a modular distributed fault-tolerant controller for a scaled laboratory MMC prototype. Experimental results show that an MMC can operate without interruption, even under two local controller failures. Besides, the experimental results are verified with the Opal-RT, a real-time simulator with the same controller in a Control Hardware in Loop (CHIL) environment.