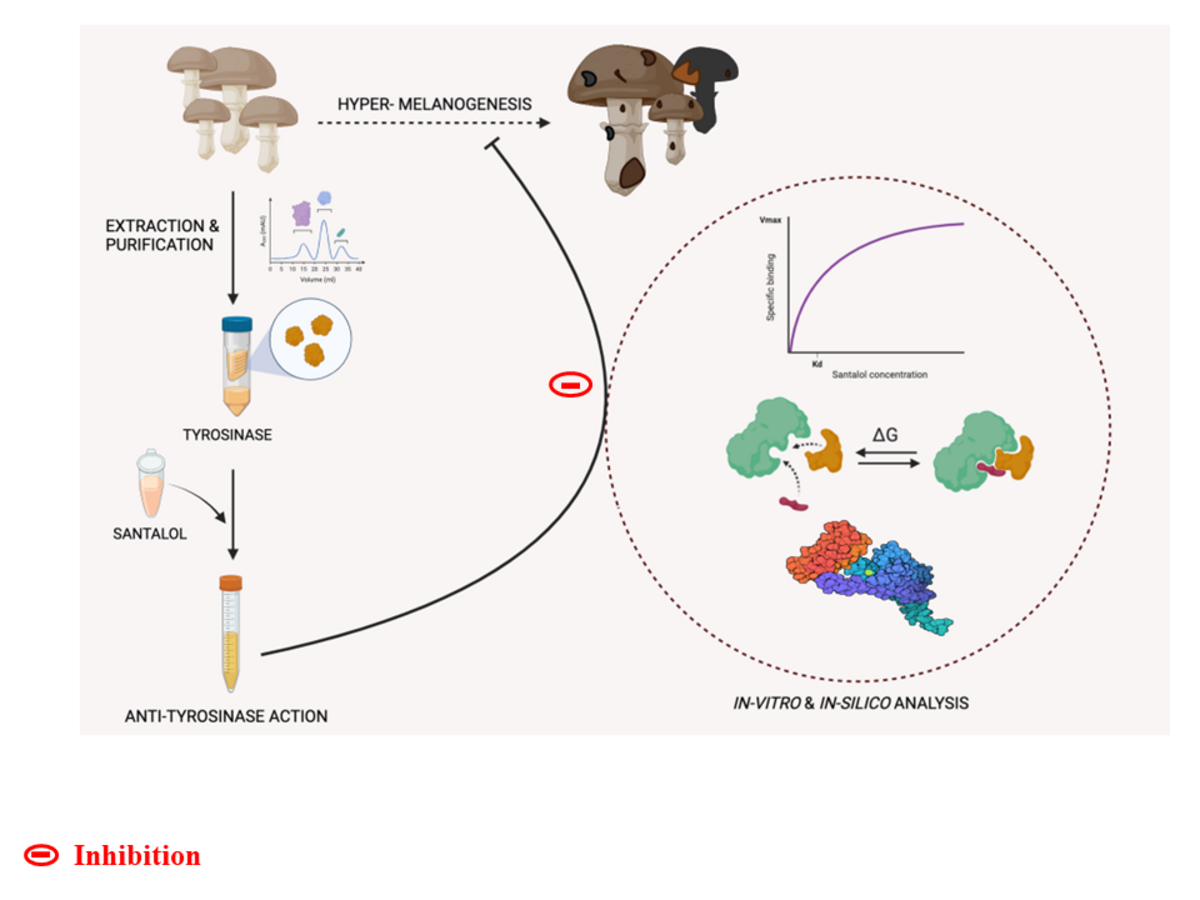
This research work focuses on the potential application of an organic compound, santalol obtained from santalum album in the inhibition of the enzyme tyrosinase which is actively involved in the biosynthesis of the melanin pigment. Over-production of melanin causes undesirable pigmentation in humans as well as other organisms that significantly downgrade their aesthetic value. The study is designed to explain the purification of tyrosinase from the mushroom Agaricus bisporus, followed by activity assay and enzyme kinetic to give insight into the santalol modulated tyrosinase inhibition in a dose dependent manner. The multi-spectroscopic techniques like UV-vis, fluorescence, and isothermal calorimetry are employed to deduce the efficiency of santalol as potential candidate against the tyrosinase enzyme activity. Experimental results are further verified by molecular docking. Santalol derived from the essential oils of santalum album, is widely used as remedy for skin disorders and potion for fair complexion since ancient times. Based on enzyme kinetics and biophysical characterization, this is the first scientific evidence where santalol inhibits tyrosinase, which may be employed in agriculture, food, and cosmetic industries by prevent excess melanin formation or browning.