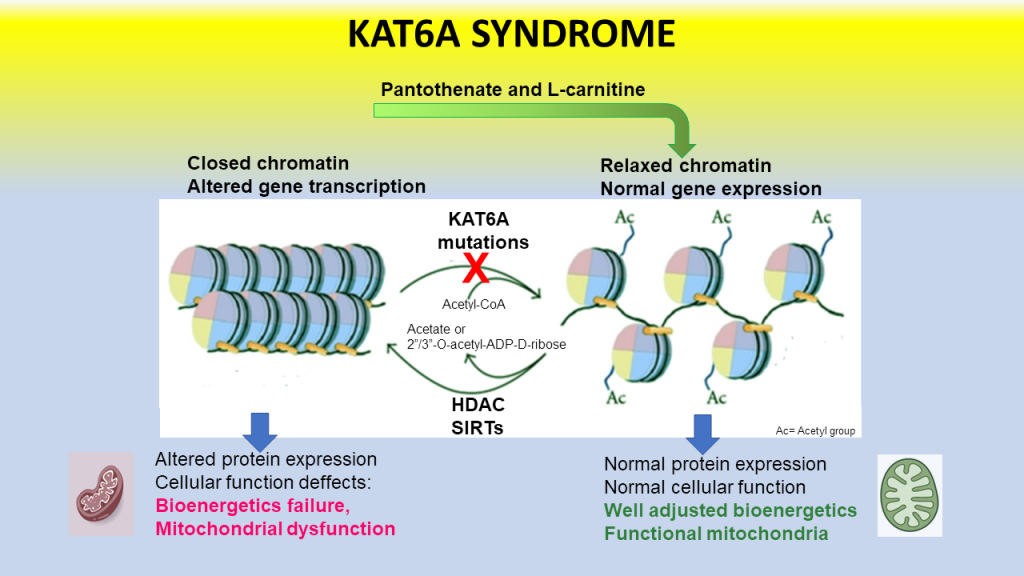
Autism Spectrum disorder (ASD) and intellectual disability (ID) are the most frequent develop-mental disorders with a prevalence between 3% and 5% of the population. In addition, both ASD and ID can be found in the same patient. Mutations in several genes involved in the epigenetic regulation of gene expression have been linked to different ID associated with ASD features including alterations of the ly-sine-acetyltransferase 6A (KAT6A) gene in KAT6A syndrome. KAT6A enzyme participates in a wide range of critical cellular functions such as chromatin remodeling, gene expression, protein synthesis, cell metabolism, and replication. In this manuscript, we examined the pathophysiolog-ical alterations in fibroblasts derived from three patients harboring KAT6A mutations. We ad-dressed survival in stress medium, histone acetylation, protein expression patterns and tran-scriptome analysis as well as cell bioenergetics. In addition, we evaluated the therapeutic effec-tiveness of epigenetic modulators and mitochondrial boosting agents such as pantothenate and L-carnitine in correcting the mutant phenotype. Pantothenate and L-carnitine treatment increased histone acetylation and corrected protein and transcriptomic expression patterns in mutant KAT6A cells. Furthermore, cell bioenergetics of mutant cells was significantly improved. Our results suggest that pantothenate and L-carnitine can significantly correct the mutant phe-notype in cellular models of KAT6A syndrome.