Submitted:
01 January 2023
Posted:
03 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Generation of Optical Microcombs
2.1. Device Platforms
2.1.1. Material Platforms
2.1.2. High-Volume Manufacturing
2.2. Device Architectures
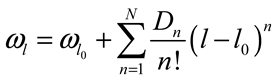
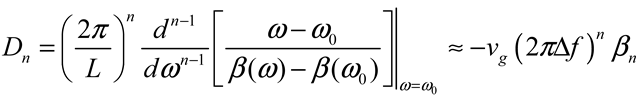
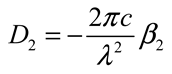
2.3. Soliton Classes
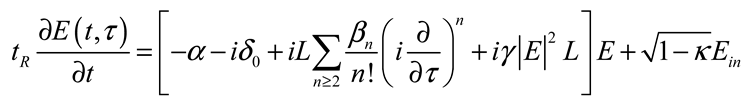
2.4. Driving Mechanisms
3. Microwave Photonics Based on Optical Microcombs
3.1. Frequency Synthesizers
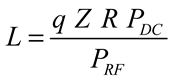
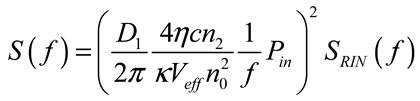
3.2. Microwave Photonic Filters
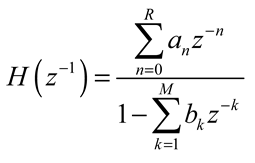
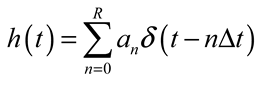
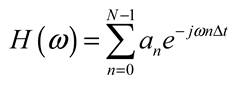
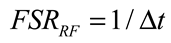
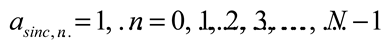
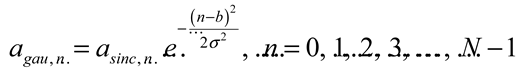
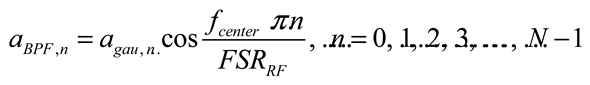
3.3. Microwave Photonic Signal Processors
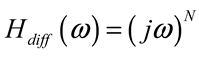

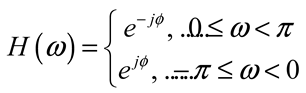
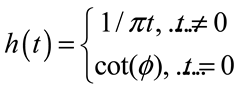
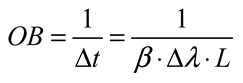
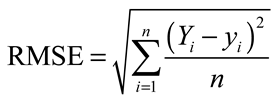
4. Optical Communications Based on Optical Microcombs
4.1. Coherent Optical Communications
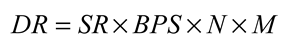
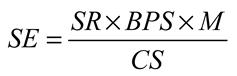
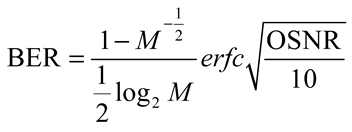
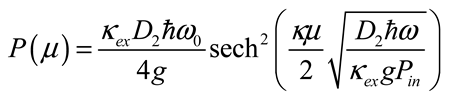
4.2. Intensity Modulation - Direct Detection Optical Communications
5. Precision Measurements Based on Optical Microcombs
5.1. Dual-Comb Spectroscopy
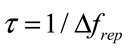
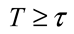
5.2. Ranging
5.3. Astrocombs
5.4. Frequency Measurements
5.5. Spectrum Channelizers
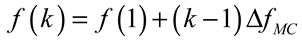
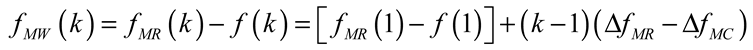
6. Neuromorphic Computing Based on Optical Microcombs
6.1. Single Neurons
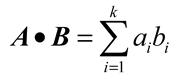
6.2. Neural Networks
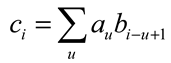
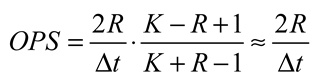
7. Quantum Optics Based on Optical Microcombs
7.1. Generation of Single / Entangled Photons
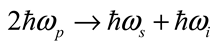
7.2. Generation of Squeezed Light
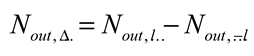
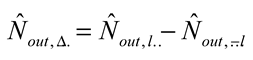
8. Challenges and Perspectives
9. Conclusions
Conflict of interest
References
- Chen, Z.; Segev, M. Highlighting photonics: looking into the next decade. eLight 2021, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Bai, N.; Zhao, N.; Xia, C. Space-division multiplexing: the next frontier in optical communication. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2014, 6, 413–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, Z.; Kudyshev, Z.A.; Boltasseva, A.; Cai, W.; Liu, Y. Deep learning for the design of photonic structures. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, T.; Baumann, E. 20 years of developments in optical frequency comb technology and applications. Communications Physics 2019, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, B.J.; Tait, A.N.; Ferreira de Lima, T.; Pernice, W.H.P.; Bhaskaran, H.; Wright, C.D.; Prucnal, P.R. Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, G.; Sorger, V.J.; Blumenthal, D.J.; Juodawlkis, P.W.; Loh, W.; Sorace-Agaskar, C.; Jones, A.E.; Balram, K.C.; Matthews, J.C.F.; Laing, A.; et al. 2022 Roadmap on integrated quantum photonics. Journal of Physics: Photonics 2022, 4, 012501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, T.W. Nobel Lecture: Passion for precision. Reviews of Modern Physics 2006, 78, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.L. Nobel Lecture: Defining and measuring optical frequencies. Reviews of Modern Physics 2006, 78, 1279–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.A.; Vahala, K.; Udem, T. Optical frequency combs: Coherently uniting the electromagnetic spectrum. Science 2020, 369, eaay3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del'Haye, P.; Schliesser, A.; Arcizet, O.; Wilken, T.; Holzwarth, R.; Kippenberg, T.J. Optical frequency comb generation from a monolithic microresonator. Nature 2007, 450, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquazi, A.; Peccianti, M.; Razzari, L.; Moss, D.J.; Coen, S.; Erkintalo, M.; Chembo, Y.K.; Hansson, T.; Wabnitz, S.; Del’Haye, P. Micro-combs: A novel generation of optical sources. Physics Reports 2018, 729, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kippenberg, T.J.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M.; Gorodetsky, M.L. Dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Science 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic-chip-based frequency combs. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.J.; Diddams, S.A.; Ranka, J.K.; Stentz, A.; Windeler, R.S.; Hall, J.L.; Cundiff, S.T. Carrier-envelope phase control of femtosecond mode-locked lasers and direct optical frequency synthesis. Science 2000, 288, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.A.; Jones, D.J.; Ye, J.; Cundiff, S.T.; Hall, J.L.; Ranka, J.K.; Windeler, R.S.; Holzwarth, R.; Udem, T.; Hansch, T.W. Direct link between microwave and optical frequencies with a 300 THz femtosecond laser comb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 5102–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, R.; Udem, T.; Hansch, T.W.; Knight, J.C.; Wadsworth, W.J.; Russell, P.S.J. Optical frequency synthesizer for precision spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2264–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.A. The evolving optical frequency comb [Invited]. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2010, 27, B51–B62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devgan, P.S. Applications of Modern RF Photonics; Artech House: 2018.
- Marković, D.; Mizrahi, A.; Querlioz, D.; Grollier, J. Physics for neuromorphic computing. Nature Reviews Physics 2020, 2, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lee, H.; Chen, T.; Vahala, K.J. Low-Pump-Power, Low-Phase-Noise, and Microwave to Millimeter-Wave Repetition Rate Operation in Microcombs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, D.T.; Drake, T.; Briles, T.C.; Stone, J.; Sinclair, L.C.; Fredrick, C.; Li, Q.; Westly, D.; Ilic, B.R.; Bluestone, A.; et al. An optical-frequency synthesizer using integrated photonics. Nature 2018, 557, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Lucas, E.; Lihachev, G.; Lobanov, V.E.; Guo, H.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Spectral Purification of Microwave Signals with Disciplined Dissipative Kerr Solitons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, E.; Brochard, P.; Bouchand, R.; Schilt, S.; Südmeyer, T.; Kippenberg, T.J. Ultralow-noise photonic microwave synthesis using a soliton microcomb-based transfer oscillator. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, W.; Kaszubowska Anandarajah, A.; Liu, J.; Anandarajah, P.M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Frequency division using a soliton-injected semiconductor gain-switched frequency comb. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Tan, M.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Broadband Microwave Frequency Conversion Based on an Integrated Optical Micro-Comb Source. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2020, 38, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lucas, E.; Raja, A.S.; He, J.; Riemensberger, J.; Wang, R.N.; Karpov, M.; Guo, H.; Bouchand, R.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic microwave generation in the X- and K-band using integrated soliton microcombs. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Morgan, J.S.; Sun, K.; Jahanbozorgi, M.; Yang, Z.; Woodson, M.; Estrella, S.; Beling, A.; Yi, X. Towards high-power, high-coherence, integrated photonic mmWave platform with microcavity solitons. Light: Science & Applications 2021, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsumoto, T.; Nagatsuma, T.; Fermann, M.E.; Navickaite, G.; Geiselmann, M.; Rolland, A. Optically referenced 300 GHz millimetre-wave oscillator. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Xuan, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Wang, J.; Leaird, D.E.; Qi, M.H.; Weiner, A.M. Programmable Single-Bandpass Photonic RF Filter Based on Kerr Comb from a Microring. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2014, 32, 3557–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Advanced Adaptive Photonic RF Filters with 80 Taps Based on an Integrated Optical Micro-Comb Source. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2019, 37, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. High performance RF filters via bandwidth scaling with Kerr micro-combs. APL Phontonics 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; He, J.; Liu, J.; Raja, A.S.; Karpov, M.; Lukashchuk, A.; Kippenberg, T.J.; Brès, C.-S. Reconfigurable radiofrequency filters based on versatile soliton microcombs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Chang, L.; Tao, Y.; Shen, B.; Xie, W.; Jin, M.; Netherton, A.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.; et al. Microcomb-driven silicon photonic systems. Nature 2022, 605, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.G.; Shoeiby, M.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Integrated frequency comb source based Hilbert transformer for wideband microwave photonic phase analysis. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 22087–22097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. Microwave and RF Photonic Fractional Hilbert Transformer Based on a 50 GHz Kerr Micro-Comb. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2019, 37, 6097–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Boes, A.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Lowery, A.J.; Morandotti, R.; et al. Highly Versatile Broadband RF Photonic Fractional Hilbert Transformer Based on a Kerr Soliton Crystal Microcomb. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2021, 39, 7581–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. RF and Microwave Fractional Differentiator Based on Photonics. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2020, 67, 2767–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Corcoran, B.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. Photonic RF and Microwave Integrator Based on a Transversal Filter With Soliton Crystal Microcombs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Boes, A.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. Photonic RF Arbitrary Waveform Generator Based on a Soliton Crystal Micro-Comb Source. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2020, 38, 6221–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Corcoran, B.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. Photonic RF Phase-Encoded Signal Generation With a Microcomb Source. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2020, 38, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifle, J.; Brasch, V.; Lauermann, M.; Yu, Y.; Wegner, D.; Herr, T.; Hartinger, K.; Schindler, P.; Li, J.; Hillerkuss, D. Coherent terabit communications with microresonator Kerr frequency combs. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Palomo, P.; Kemal, J.N.; Karpov, M.; Kordts, A.; Pfeifle, J.; Pfeiffer, M.H.; Trocha, P.; Wolf, S.; Brasch, V.; Anderson, M.H. Microresonator-based solitons for massively parallel coherent optical communications. Nature 2017, 546, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, A.; Mazur, M.; Lorences-Riesgo, A.; Helgason, O.B.; Wang, P.; Xuan, Y.; Leaird, D.E.; Qi, M.; Andrekson, P.A.; Weiner, A.M.; et al. High-order coherent communications using mode-locked dark-pulse Kerr combs from microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, B.; Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Boes, A.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A. Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, S.; Tanaka, S.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kogure, S.; Wada, K.; Kumazaki, H.; Tasaka, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Araki, T.; et al. Dissipative Kerr soliton microcombs for FEC-free optical communications over 100 channels. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 1351–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trocha, P.; Karpov, M.; Ganin, D.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Kordts, A.; Wolf, S.; Krockenberger, J.; Marin-Palomo, P.; Weimann, C.; Randel, S.; et al. Ultrafast optical ranging using microresonator soliton frequency combs. Science 2018, 359, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.G.; Vahala, K.J. Soliton microcomb range measurement. Science 2018, 359, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemensberger, J.; Lukashchuk, A.; Karpov, M.; Weng, W.; Lucas, E.; Liu, J.; Kippenberg, T.J. Massively parallel coherent laser ranging using a soliton microcomb. Nature 2020, 581, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chu, S.T.; Zhao, W.; Little, B.E.; et al. Long-distance ranging with high precision using a soliton microcomb. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 1964–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrzud, E.; Rainer, M.; Harutyunyan, A.; Anderson, M.H.; Liu, J.; Geiselmann, M.; Chazelas, B.; Kundermann, S.; Lecomte, S.; Cecconi, M.; et al. A microphotonic astrocomb. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.G.; Yi, X.; Lai, Y.H.; Leifer, S.; Grudinin, I.S.; Vasisht, G.; Martin, E.C.; Fitzgerald, M.P.; Doppmann, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Searching for exoplanets using a microresonator astrocomb. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, T.; McCracken, R.A. Astrocombs: Recent Advances. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 2019, 31, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roztocki, P.; Morandotti, R. Astrocombs for extreme-precision spectroscopy. Nature Astronomy 2019, 3, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Boes, A.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; et al. Photonic Perceptron Based on a Kerr Microcomb for High-Speed, Scalable, Optical Neural Networks. Laser Photon. Rev. 2020, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Youngblood, N.; Karpov, M.; Gehring, H.; Li, X.; Stappers, M.; Le Gallo, M.; Fu, X.; Lukashchuk, A.; Raja, A.S.; et al. Parallel convolutional processing using an integrated photonic tensor core. Nature 2021, 589, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Corcoran, B.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Hicks, D.G.; Morandotti, R.; et al. 11 TOPS photonic convolutional accelerator for optical neural networks. Nature 2021, 589, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kues, M.; Reimer, C.; Lukens, J.M.; Munro, W.J.; Weiner, A.M.; Moss, D.J.; Morandotti, R. Quantum optical microcombs. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspani, L.; Xiong, C.; Eggleton, B.J.; Bajoni, D.; Liscidini, M.; Galli, M.; Morandotti, R.; Moss, D.J. Integrated sources of photon quantum states based on nonlinear optics. Light: Science & Applications 2017, 6, e17100–e17100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.; Kues, M.; Roztocki, P.; Wetzel, B.; Grazioso, F.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Johnston, T.; Bromberg, Y.; Caspani, L.; et al. Generation of multiphoton entangled quantum states by means of integrated frequency combs. Science 2016, 351, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.G.; Yang, Q.; Yang, K.; Yi, X.; Vahala, K.J. Microresonator soliton dual-comb spectroscopy. Science 2016, 354, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chembo, Y.K. Kerr optical frequency combs: theory, applications and perspectives. Nanophotonics 2016, 5, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, T.; Wabnitz, S. Dynamics of microresonator frequency comb generation: models and stability. Nanophotonics 2016, 5, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Haye, P.; Herr, T.; Gavartin, E.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Holzwarth, R.; Kippenberg, T.J. Octave Spanning Tunable Frequency Comb from a Microresonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquazi, A.; Caspani, L.; Peccianti, M.; Clerici, M.; Ferrera, M.; Razzari, L.; Duchesne, D.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Moss, D.J.; et al. Self-locked optical parametric oscillation in a CMOS compatible microring resonator: a route to robust optical frequency comb generation on a chip. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 13333–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, T.; Brasch, V.; Jost, J.D.; Wang, C.Y.; Kondratiev, N.M.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Temporal solitons in optical microresonators. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Zhang, L.; Matsko, A.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, G.; Agarwal, A.M.; Kimerling, L.C.; Michel, J.; Maleki, L.; et al. Nonlinear conversion efficiency in Kerr frequency comb generation. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6126–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovach, A.; Chen, D.; He, J.; Choi, H.; Dogan, A.H.; Ghasemkhani, M.; Taheri, H.; Armani, A.M. Emerging material systems for integrated optical Kerr frequency combs. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2020, 12, 135–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzari, L.; Duchesne, D.; Ferrera, M.; Morandotti, R.; Chu, S.; Little, B.E.; Moss, D.J. CMOS-compatible integrated optical hyper-parametric oscillator. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.S.; Gondarenko, A.; Foster, M.A.; Turner-Foster, A.C.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. CMOS-compatible multiple-wavelength oscillator for on-chip optical interconnects. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, I.H.; Okawachi, Y.; Gaeta, A.L. Theoretical and experimental investigation of broadband cascaded four-wave mixing in high-Q microspheres. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 16209–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, S.B.; Del’Haye, P.; Diddams, S.A. Mechanical Control of a Microrod-Resonator Optical Frequency Comb. Phys. Rev. X 2013, 3, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Savchenkov, A.A.; Matsko, A.B.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Seidel, D.; Maleki, L. Generation of near-infrared frequency combs from a MgF2 whispering gallery mode resonator. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 2290–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Herr, T.; Del’Haye, P.; Schliesser, A.; Hofer, J.; Holzwarth, R.; Hänsch, T.W.; Picqué, N.; Kippenberg, T.J. Mid-infrared optical frequency combs at 2.5 μm based on crystalline microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Savchenkov, A.A.; Xie, Z.D.; McMillan, J.F.; Burkhart, J.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Wong, C.W.; Matsko, A.B.; Maleki, L. Miniature multioctave light source based on a monolithic microcavity. Optica 2015, 2, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudinin, I.S.; Yu, N.; Maleki, L. Generation of optical frequency combs with a CaF2 resonator. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savchenkov, A.A.; Matsko, A.B.; Liang, W.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Seidel, D.; Maleki, L. Kerr combs with selectable central frequency. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Diallo, S.; Henriet, R.; Jacquot, M.; Chembo, Y.K. Barium fluoride whispering-gallery-mode disk-resonator with one billion quality-factor. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 6009–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriet, R.; Lin, G.; Coillet, A.; Jacquot, M.; Furfaro, L.; Larger, L.; Chembo, Y.K. Kerr optical frequency comb generation in strontium fluoride whispering-gallery mode resonators with billion quality factor. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.G.; Lau, R.K.W.; Cardenas, J.; Okawachi, Y.; Mohanty, A.; Fain, R.; Lee, Y.H.D.; Yu, M.; Phare, C.T.; Poitras, C.B.; et al. Silicon-chip mid-infrared frequency comb generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Okawachi, Y.; Griffith, A.G.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Mode-locked mid-infrared frequency combs in a silicon microresonator. Optica 2016, 3, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okawachi, Y.; Saha, K.; Levy, J.S.; Wen, Y.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Octave-spanning frequency comb generation in a silicon nitride chip. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3398–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Varghese, L.T.; Metcalf, A.J.; Xue, X.; Wang, P.H.; Han, K.; Jaramillo- Villegas, J.A.; Al Noman, A.; Wang, C.; et al. High-Q silicon nitride microresonators exhibiting low-power frequency comb initiation. Optica 2016, 3, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, X.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. RF Photonics: An Optical Microcombs’ Perspective. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 2018, 24, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Xiong, C.; Fong, K.Y.; Zhang, X.; Tang, H.X. Optical frequency comb generation from aluminum nitride microring resonator. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2810–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausmann, B.J.M.; Bulu, I.; Venkataraman, V.; Deotare, P.; Loncar, M. Diamond nonlinear photonics. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Ottaviano, L.; Semenova, E.; Yvind, K. Efficient frequency comb generation in AlGaAs-on-insulator. Optica 2016, 3, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xie, W.; Shu, H.; Yang, Q.; Shen, B.; Boes, A.; Peters, J.D.; Jin, W.; Xiang, C.; Liu, S.; et al. Ultra-efficient frequency comb generation in AlGaAs-on-insulator microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moille, G.; Chang, L.; Xie, W.; Rao, A.; Lu, X.; Davanço, M.; Bowers, J.E.; Srinivasan, K. Dissipative Kerr Solitons in a III-V Microresonator. Laser Photon. Rev. 2020, 14, 2000022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiles, J.; Nader, N.; Hickstein, D.D.; Yu, S.P.; Briles, T.C.; Carlson, D.; Jung, H.; Shainline, J.M.; Diddams, S.; Papp, S.B.; et al. Deuterated silicon nitride photonic devices for broadband optical frequency comb generation. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fang, Z.; Yi, A.; Yang, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Shen, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, R.; et al. High-Q microresonators on 4H-silicon-carbide-on-insulator platform for nonlinear photonics. Light: Science & Applications 2021, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Yu, S.P.; Carlson, D.R.; Drake, T.E.; Briles, T.C.; Papp, S.B. Tantala Kerr nonlinear integrated photonics. Optica 2021, 8, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.J.; Schneider, K.; Hönl, S.; Anderson, M.; Baumgartner, Y.; Czornomaz, L.; Kippenberg, T.J.; Seidler, P. Integrated gallium phosphide nonlinear photonics. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Buscaino, B.; Wang, C.; Shams Ansari, A.; Reimer, C.; Zhu, R.; Kahn, J.M.; Lončar, M. Broadband electro-optic frequency comb generation in a lithium niobate microring resonator. Nature 2019, 568, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ling, J.; Luo, R.; Liang, H.; Li, M.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Vahala, K.; Lin, Q. Self-starting bi-chromatic LiNbO3 soliton microcomb. Optica 2019, 6, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; Zhu, R.; Hu, H.; Loncar, M. Monolithic lithium niobate photonic circuits for Kerr frequency comb generation and modulation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del’Haye, P.; Arcizet, O.; Schliesser, A.; Holzwarth, R.; Kippenberg, T.J. Full Stabilization of a Microresonator-Based Optical Frequency Comb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 053903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Haye, P.; Papp, S.B.; Diddams, S.A. Hybrid Electro-Optically Modulated Microcombs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 263901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Stoll, R.; Guo, X.; Fischer, D.; Tang, H.X. Green, red, and IR frequency comb line generation from single IR pump in AlN microring resonator. Optica 2014, 1, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Xuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.H.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Leaird, D.E.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Mode-locked dark pulse Kerr combs in normal-dispersion microresonators. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Herkommer, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; Karpov, M.; Lucas, E.; Zervas, M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Octave-spanning dissipative Kerr soliton frequency combs in Si3N4 microresonators. Optica 2017, 4, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Leo, F.; Xuan, Y.; Jaramillo Villegas, J.A.; Wang, P.H.; Leaird, D.E.; Erkintalo, M.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Second-harmonic-assisted four-wave mixing in chip-based microresonator frequency comb generation. Light: Science & Applications 2017, 6, e16253–e16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, D.C.; Lamb, E.S.; Del’Haye, P.; Diddams, S.A.; Papp, S.B. Soliton crystals in Kerr resonators. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Vinod, A.K.; Choi, C.; Hoff, M.; Li, Y.; Yu, M.; Feng, Z.; Kwong, D.-L.; et al. Gate-tunable frequency combs in graphene–nitride microresonators. Nature 2018, 558, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpov, M.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Liu, J.; Lukashchuk, A.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic chip-based soliton frequency combs covering the biological imaging window. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Wang, L.; Xie, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; et al. Robust soliton crystals in a thermally controlled microresonator. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2002–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Cooper, A.; Rowley, M.; Di Lauro, L.; Totero Gongora, J.S.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Oppo, G.-L.; Morandotti, R.; Moss, D.J.; et al. Laser cavity-soliton microcombs. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayson, N.L.B.; Bi, T.; Ng, V.; Pham, H.; Trainor, L.S.; Schwefel, H.G.L.; Coen, S.; Erkintalo, M.; Murdoch, S.G. Octave-spanning tunable parametric oscillation in crystalline Kerr microresonators. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ling, J.; Li, M.; Lin, Q. Perfect Soliton Crystals on Demand. Laser Photon. Rev. 2020, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ji, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Cao, Q.; Gong, Q.; Yi, X.; Xiao, Y. Chaos-assisted two-octave-spanning microcombs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Chang, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Xiang, C.; Wang, R.; He, J.; Liu, T.; Xie, W.; et al. Integrated turnkey soliton microcombs. Nature 2020, 582, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ji, X.; Kim, B.Y.; Donvalkar, P.S.; Jang, J.K.; Joshi, C.; Yu, M.; Joshi, C.; Domeneguetti, R.R.; Barbosa, F.A.S.; et al. Visible nonlinear photonics via high-order-mode dispersion engineering. Optica 2020, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, W.; et al. Synthesized soliton crystals. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruch, A.W.; Liu, X.; Gong, Z.; Surya, J.B.; Li, M.; Zou, C.; Tang, H.X. Pockels soliton microcomb. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jang, J.K.; Dave, U.D.; Corato-Zanarella, M.; Joshi, C.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. Exploiting Ultralow Loss Multimode Waveguides for Broadband Frequency Combs. Laser Photon. Rev. 2021, 15, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, D.J.; Morandotti, R.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. New CMOS-compatible platforms based on silicon nitride and Hydex for nonlinear optics. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S. GaAs, AlAs, and AlxGa1−xAs: Material parameters for use in research and device applications. Journal of Applied Physics 1985, 58, R1–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, J.S.; Hutchings, D.C.; Kang, J.U.; Stegeman, G.I.; Villeneuve, A. The nonlinear optical properties of AlGaAs at the half band gap. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 1997, 33, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrahi, V.; DeLong, K.W.; Stegeman, G.I.; Saifi, M.A.; Andrejco, M.J. Two-photon absorption as a limitation to all-optical switching. Opt. Lett. 1989, 14, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, M.; Hu, H.; Ottaviano, L.; Semenova, E.; Vukovic, D.; Oxenløwe, L.K.; Yvind, K. Ultra-Efficient and Broadband Nonlinear AlGaAs-on-Insulator Chip for Low-Power Optical Signal Processing. Laser Photon. Rev. 2018, 12, 1800111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, E.; Mahony, P.; Starbuck, A.; Pomerene, A.; Trotter, D.C.; DeRose, C.T. Effect of precursors on propagation loss for plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition of SiN x: H waveguides. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 2892–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Song, B.-S.; Asano, T.; Noda, S. Silicon carbide-based photonic crystal nanocavities for ultra-broadband operation from infrared to visible wavelengths. Applied Physics Letters 2011, 99, 201102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhan, M.; Wang, G.; Xuan, H.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Chen, X. 4H-SiC: a new nonlinear material for midinfrared lasers. Laser Photon. Rev. 2013, 7, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.S.; Asano, T.; Jeon, S.; Kim, H.; Chen, C.; Kang, D.D.; Noda, S. Ultrahigh-Q photonic crystal nanocavities based on 4H silicon carbide. Optica 2019, 6, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidry, M.A.; Yang, K.Y.; Lukin, D.M.; Markosyan, A.; Yang, J.; Fejer, M.M.; Vučković, J. Optical parametric oscillation in silicon carbide nanophotonics. Optica 2020, 7, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Li, Q. Octave-spanning microcomb generation in 4H-silicon-carbide-on-insulator photonics platform. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempe, G.; Thompson, R.J.; Kimble, H.J.; Lalezari, R. Measurement of ultralow losses in an optical interferometer. Opt. Lett. 1992, 17, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Huang, J.Y.; Ou, D.H.; Liao, T.W.; Chiu, Y.J.; Shih, M.H.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chu, A.K.; Lee, C.K. Efficient wavelength conversion with low operation power in a Ta2O5-based micro-ring resonator. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4804–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawala, P.A.; Sawai, M.; Tatsuta, T.; Tsuji, O.; Fujita, S.; Fujita, S. Structural and Electrical Properties of Ta2O5 Grown by the Plasma-Enhanced Liquid Source CVD Using Penta Ethoxy Tantalum Source. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 1993, 32, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukli, K.; Aarik, J.; Aidla, A.; Kohan, O.; Uustare, T.; Sammelselg, V. Properties of tantalum oxide thin films grown by atomic layer deposition. Thin Solid Films 1995, 260, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkuhn, M.H.; Foster, L.M. Green Luminescence from Solution-grown Junctions in GaP Containing Shallow Donors and Acceptors. IBM Journal of Research and Development 1966, 10, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, K.; Lin, Z.; Hatami, F.; Masselink, W.T.; Vučković, J. Second harmonic generation in gallium phosphide photonic crystal nanocavities with ultralow continuous wave pump power. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 22609–22615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, A.J.; Torres-Company, V.; Leaird, D.E.; Weiner, A.M. High-Power Broadly Tunable Electrooptic Frequency Comb Generator. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 2013, 19, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Tang, H.X. Near-octave lithium niobate soliton microcomb. Optica 2020, 7, 1275–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, F.; Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.; Ferrari, A.C. Graphene photonics and optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Chang, L.; Wang, R.N.; Weng, W.; Peters, J.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Z.; Riemensberger, J.; et al. Laser soliton microcombs heterogeneously integrated on silicon. Science 2021, 373, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, C.; Guo, J.; Jin, W.; Wu, L.; Peters, J.; Xie, W.; Chang, L.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.-F.; et al. High-performance lasers for fully integrated silicon nitride photonics. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.; Pavlov, N.G.; Jost, J.D.; Lihachev, G.; Liu, J.; Morais, T.; Zervas, M.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Highly efficient coupling of crystalline microresonators to integrated photonic waveguides. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2106–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, Q.F.; Yi, X.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Vahala, K. Bridging ultrahigh-Q devices and photonic circuits. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, B.; Ji, X.; Okawachi, Y.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. Battery-operated integrated frequency comb generator. Nature 2018, 562, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.S.; Voloshin, A.S.; Guo, H.; Agafonova, S.E.; Liu, J.; Gorodnitskiy, A.S.; Karpov, M.; Pavlov, N.G.; Lucas, E.; Galiev, R.R.; et al. Electrically pumped photonic integrated soliton microcomb. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Silver, J.M.; Bi, T.; Del’Haye, P. Spectral extension and synchronization of microcombs in a single microresonator. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Yang, K.Y.; Jeon, S.; Painter, O.; Vahala, K.J. Chemically etched ultrahigh-Q wedge-resonator on a silicon chip. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Tran, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.Y.; Wu, L.; Bao, C.; Bowers, J.; Yariv, A.; et al. Vernier spectrometer using counterpropagating soliton microcombs. Science 2019, 363, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Jeong, D.; Jeon, I.; Lee, H.; Kim, J. Ultrastable microwave and soliton-pulse generation from fibre-photonic-stabilized microcombs. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Silver, J.M.; Del Bino, L.; Copie, F.; Woodley, M.T.M.; Ghalanos, G.N.; Svela, A.Ø.; Moroney, N.; Del’Haye, P. Sub-milliwatt-level microresonator solitons with extended access range using an auxiliary laser. Optica 2019, 6, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Gong, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, Y. Soliton microwave oscillators using oversized billion Q optical microresonators. Optica 2022, 9, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Kaszubowska-Anandarajah, A.; He, J.; Lakshmijayasimha, P.D.; Lucas, E.; Liu, J.; Anandarajah, P.M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Gain-switched semiconductor laser driven soliton microcombs. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Okawachi, Y.; Griffith, A.G.; Picque, N.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Silicon-chip-based mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Xuan, Y.; Wang, P.H.; Liu, Y.; Leaird, D.E.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Normal-dispersion microcombs enabled by controllable mode interactions. Laser Photon. Rev. 2015, 9, L23–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Han, K.; Wang, C.; Jaramillo-Villegas, J.A.; Xue, X.; Bao, C.; Xuan, Y.; Leaird, D.E.; Weiner, A.M.; Qi, M. Dispersion engineering and frequency comb generation in thin silicon nitride concentric microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgason, Ó.B.; Arteaga Sierra, F.R.; Ye, Z.; Twayana, K.; Andrekson, P.A.; Karlsson, M.; Schröder, J.; Victor, T.C. Dissipative solitons in photonic molecules. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.W.; Li, B.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Vinod, A.K.; Wang, K.; Yu, M.; Kwong, D.L.; Wang, H.T.; et al. Real-time transition dynamics and stability of chip-scale dispersion-managed frequency microcombs. Light: Science & Applications 2020, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, M.A.; Turner, A.C.; Sharping, J.E.; Schmidt, B.S.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Broad-band optical parametric gain on a silicon photonic chip. Nature 2006, 441, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jia, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Jia, B.; Moss, D.J. Graphene Oxide for Integrated Photonics and Flat Optics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, Z.; Wada, K.; Kimerling, L.C.; Agarwal, A.M.; Michel, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, L. Power-efficient generation of two-octave mid-IR frequency combs in a germanium microresonator. Nanophotonics 2018, 7, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, C.; Singh, V.; Mu, J.; Yang, C.; Agarwal, A.M.; Kimerling, L.C.; Michel, J. Generation of two-cycle pulses and octave-spanning frequency combs in a dispersion-flattened micro-resonator. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 5122–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Kimerling, L.C.; Michel, J.; Agarwal, A.M.; Li, G.; Zhang, L. Robust cavity soliton formation with hybrid dispersion. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moille, G.; Li, Q.; Briles, T.C.; Yu, S.P.; Drake, T.; Lu, X.; Rao, A.; Westly, D.; Papp, S.B.; Srinivasan, K. Broadband resonator-waveguide coupling for efficient extraction of octave-spanning microcombs. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 4737–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Geng, Y.; Cui, W.; Huang, S.W.; Zhou, Q.; Qiu, K.; Wei Wong, C. Soliton bursts and deterministic dissipative Kerr soliton generation in auxiliary-assisted microcavities. Light: Science & Applications 2019, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yang, Q.F.; Yang, K.Y.; Vahala, K. Imaging soliton dynamics in optical microcavities. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, L.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W. Program-controlled single soliton microcomb source. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Liu, J.; Afridi, A.A.; Li, J.; Dai, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Donegan, J.F.; Guo, W. Directly accessing octave-spanning dissipative Kerr soliton frequency combs in an AlN microresonator. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Jang, J.K.; Okawachi, Y.; Griffith, A.G.; Luke, K.; Miller, S.A.; Ji, X.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Breather soliton dynamics in microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E.; Karpov, M.; Guo, H.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Breathing dissipative solitons in optical microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Niu, R.; Wang, Z.Y.; Peng, J.L.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Guo, G.C.; Zou, C.L.; Dong, C.H. Frequency stabilization and tuning of breathing solitons in Si3N4 microresonators. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, Y.K.; Wu, L.; Oh, D.Y.; Shen, B.; Lee, S.H.; Vahala, K. Dirac solitons in optical microresonators. Light: Science & Applications 2020, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.F.; Yi, X.; Yang, K.Y.; Vahala, K. Stokes solitons in optical microcavities. Nature Physics 2017, 13, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Q.; Ding, S.; Qin, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, M. Brillouin-Kerr Soliton Frequency Combs in an Optical Microresonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, M.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Guo, H.; Weng, W.; Liu, J.; Kippenberg, T.J. Dynamics of soliton crystals in optical microresonators. Nature Physics 2019, 15, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Zhao, J.; Xie, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Raman self-frequency-shift of soliton crystal in a high index doped silica micro-ring resonator [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Bouchand, R.; Lucas, E.; Obrzud, E.; Herr, T.; Kippenberg, T.J. Heteronuclear soliton molecules in optical microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Wang, P.-H.; Xuan, Y.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Microresonator Kerr frequency combs with high conversion efficiency. Laser Photon. Rev. 2017, 11, 1600276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemensberger, J.; Hartinger, K.; Herr, T.; Brasch, V.; Holzwarth, R.; Kippenberg, T.J. Dispersion engineering of thick high-Q silicon nitride ring-resonators via atomic layer deposition. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 27661–27669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Kordts, A.; Brasch, V.; Zervas, M.; Geiselmann, M.; Jost, J.D.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic Damascene process for integrated high-Q microresonator based nonlinear photonics. Optica 2016, 3, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lucas, E.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Karpov, M.; Anderson, M.; Liu, J.; Geiselmann, M.; Jost, J.D.; Kippenberg, T.J. Intermode Breather Solitons in Optical Microresonators. Phys. Rev. X 2017, 7, 041055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccianti, M.; Pasquazi, A.; Park, Y.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Moss, D.J.; Morandotti, R. Demonstration of a stable ultrafast laser based on a nonlinear microcavity. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Wang, L.R.; Zhang, W.F. Advances in soliton microcomb generation. Advanced Photonics 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidry, M.A.; Lukin, D.M.; Yang, K.Y.; Trivedi, R.; Vučković, J. Quantum optics of soliton microcombs. Nat. Photonics 2022, 16, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, M.; Guo, H.; Kordts, A.; Brasch, V.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Zervas, M.; Geiselmann, M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Raman Self-Frequency Shift of Dissipative Kerr Solitons in an Optical Microresonator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 103902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Bruch, A.; Shen, M.; Guo, X.; Jung, H.; Fan, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; et al. High-fidelity cavity soliton generation in crystalline AlN micro-ring resonators. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 4366–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Yang, Q.F.; Yang, K.Y.; Suh, M.G.; Vahala, K. Soliton frequency comb at microwave rates in a high-Q silica microresonator. Optica 2015, 2, 1078–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, V.; Geiselmann, M.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Kippenberg, T.J. Bringing short-lived dissipative Kerr soliton states in microresonators into a steady state. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 29312–29320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, V.; Geiselmann, M.; Herr, T.; Lihachev, G.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic chip-based optical frequency comb using soliton Cherenkov radiation. Science 2016, 351, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Karpov, M.; Lucas, E.; Kordts, A.; Pfeiffer, M.H.; Brasch, V.; Lihachev, G.; Lobanov, V.E.; Gorodetsky, M.L.; Kippenberg, T.J. Universal dynamics and deterministic switching of dissipative Kerr solitons in optical microresonators. Nature Physics 2017, 13, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strekalov, D.V.; Yu, N. Generation of optical combs in a whispering gallery mode resonator from a bichromatic pump. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 79, 041805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, T.; Wabnitz, S. Bichromatically pumped microresonator frequency combs. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 013811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Pasquazi, A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Dual-pump Kerr Micro-cavity Optical Frequency Comb with varying FSR spacing. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 28501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, S.B.; Del’Haye, P.; Diddams, S.A. Parametric seeding of a microresonator optical frequency comb. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 17615–17624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, S.B.; Beha, K.; Del'Haye, P.; Quinlan, F.; Lee, H.; Vahala, K.J.; Diddams, S.A. Microresonator frequency comb optical clock. Optica 2014, 1, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Haye, P.; Beha, K.; Papp, S.B.; Diddams, S.A. Self-Injection Locking and Phase-Locked States in Microresonator-Based Optical Frequency Combs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 043905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Eliyahu, D.; Ilchenko, V.S.; Savchenkov, A.A.; Matsko, A.B.; Seidel, D.; Maleki, L. High spectral purity Kerr frequency comb radio frequency photonic oscillator. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, M.; Hanzard, P.-H.; Cutrona, A.; Bao, H.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Moss, D.J.; Oppo, G.L.; Totero Gongora, J.S.; et al. Self-emergence of robust solitons in a microcavity. Nature 2022, 608, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, C.; Jang, J.K.; Luke, K.; Ji, X.; Miller, S.A.; Klenner, A.; Okawachi, Y.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Thermally controlled comb generation and soliton modelocking in microresonators. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del'Haye, P.; Coillet, A.; Fortier, T.; Beha, K.; Cole, D.C.; Yang, K.Y.; Lee, H.; Vahala, K.J.; Papp, S.B.; Diddams, S.A. Phase-coherent microwave-to-optical link with a self-referenced microcomb. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasch, V.; Lucas, E.; Jost, J.D.; Geiselmann, M.; Kippenberg, T.J. Self-referenced photonic chip soliton Kerr frequency comb. Light: Science & Applications 2017, 6, e16202–e16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gong, Z.; Bruch, A.W.; Surya, J.B.; Lu, J.; Tang, H.X. Aluminum nitride nanophotonics for beyond-octave soliton microcomb generation and self-referencing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Klenner, A.; Ji, X.; Okawachi, Y.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Synchronization of coupled optical microresonators. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Lucas, E.; Raja, A.S.; Lihachev, G.; Wang, R.N.; He, J.; Liu, T.; Anderson, M.H.; Weng, W.; et al. Monolithic piezoelectric control of soliton microcombs. Nature 2020, 583, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.H.; Bouchand, R.; Liu, J.; Weng, W.; Obrzud, E.; Herr, T.; Kippenberg, T.J. Photonic chip-based resonant supercontinuum via pulse-driven Kerr microresonator solitons. Optica 2021, 8, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moille, G.; Perez, E.F.; Stone, J.R.; Rao, A.; Lu, X.; Rahman, T.S.; Chembo, Y.K.; Srinivasan, K. Ultra-broadband Kerr microcomb through soliton spectral translation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moille, G.; Lu, X.; Rao, A.; Li, Q.; Westly, D.A.; Ranzani, L.; Papp, S.B.; Soltani, M.; Srinivasan, K. Kerr-Microresonator Soliton Frequency Combs at Cryogenic Temperatures. Physical Review Applied 2019, 12, 034057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Zou, C.L.; Dong, C.H.; Zhao, B.; et al. Deterministic generation and switching of dissipative Kerr soliton in a thermally controlled micro-resonator. AIP Advances 2019, 9, 025314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrzud, E.; Lecomte, S.; Herr, T. Temporal solitons in microresonators driven by optical pulses. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeds, A.J. Microwave photonics. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 2002, 50, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, T.M.; Kirchner, M.S.; Quinlan, F.; Taylor, J.; Bergquist, J.C.; Rosenband, T.; Lemke, N.; Ludlow, A.; Jiang, Y.; Oates, C.W.; et al. Generation of ultrastable microwaves via optical frequency division. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, A.; Diddams, S.A.; Oates, C.W.; Wilpers, G.; Bergquist, J.C.; Oskay, W.H.; Hollberg, L. Femtosecond-laser-based synthesis of ultrastable microwave signals from optical frequency references. Opt. Lett. 2005, 30, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Rodriguez, J.D.; Leopardi, H.; Sherman, J.A.; Fortier, T.M.; Xie, X.; Campbell, J.C.; McGrew, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, Y.S.; et al. Coherent optical clock down-conversion for microwave frequencies with 10-18 instability. Science 2020, 368, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlabs. SMART-COMB - Compact Fully-Automated Optical Frequency Comb datasheet. Available online: https://www.thorlabs.com/drawings/a9701f46e62cd263-5ED71E17-CC29-C5DE-DD9F78B026058207/SMART-COMB-SpecSheet.pdf.
- Thorlabs. FC1500-ULNPLUS - Ultra Low Noise Optical Frequency Comb datasheet. Available online: https://www.thorlabs.com/drawings/a9701f46e62cd263-5ED71E17-CC29-C5DE-DD9F78B026058207/FC1500-ULNPLUS-SpecSheet.pdf.
- Millo, J.; Boudot, R.; Lours, M.; Bourgeois, P.Y.; Luiten, A.N.; Coq, Y.L.; Kersalé, Y.; Santarelli, G. Ultra-low-noise microwave extraction from fiber-based optical frequency comb. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 3707–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, K.; Chembo, Y.K. On the phase noise performance of microwave and millimeter-wave signals generated with versatile Kerr optical frequency combs. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25043–25056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Moein, T.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Photonic microwave true time delays for phased array antennas using a 49 GHz FSR integrated optical micro-comb source Invited. Photonics Res. 2018, 6, B30–B36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Bouchand, R.; Nicolodi, D.; Giunta, M.; Hänsel, W.; Lezius, M.; Joshi, A.; Datta, S.; Alexandre, C.; Lours, M.; et al. Photonic microwave signals with zeptosecond-level absolute timing noise. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capmany, J.; Ortega, B.; Pastor, D.; Sales, S. Discrete-time optical processing of microwave signals. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2005, 23, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Li, Z.; Yao, J. A Microwave Bandpass Differentiator Implemented Based on a Nonuniformly-Spaced Photonic Microwave Delay-Line Filter. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2011, 29, 3470–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigyes, I.; Seeds, A.J. Optically generated true-time delay in phased-array antennas. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 1995, 43, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Shoeiby, M.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Advanced RF and microwave functions based on an integrated optical frequency comb source. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Xuan, Y.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, B.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Microcomb-Based True-Time-Delay Network for Microwave Beamforming With Arbitrary Beam Pattern Control. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2018, 36, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Lu, L.; Shan, W.; Xu, W.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J. Silicon integrated microwave photonic beamformer. Optica 2020, 7, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Peng, J.; Liu, B.; Pan, T.; Zhou, H.; Mao, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Su, Y. Passive silicon photonic devices for microwave photonic signal processing. Optics Communications 2016, 373, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Choudhary, A.; Marpaung, D.; Eggleton, B.J. Integrated microwave photonic filters. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2020, 12, 485–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Microcomb-Based Photonic RF Signal Processing. Ieee Photonics Technology Letters 2019, 31, 1854–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. RF and microwave photonic temporal signal processing with Kerr micro-combs. Advances in Physics-X 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Shoeiby, M.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Reconfigurable broadband microwave photonic intensity differentiator based on an integrated optical frequency comb source. APL Phontonics 2017, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Sun, S.; Yi, X. Radio-frequency line-by-line Fourier synthesis based on optical soliton microcombs. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poularikas, A.D. Transforms and applications handbook; CRC press: 2018.
- Toprak, A.; Güler, İ. Impulse noise reduction in medical images with the use of switch mode fuzzy adaptive median filter. Digital Signal Processing 2007, 17, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Lou, Y.; Ye, H.; Qiu, M.; Ruan, Z.; Fan, S. Plasmonic computing of spatial differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Kravchenko, I.I.; Valentine, J. Flat optics for image differentiation. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Guo, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Orenstein, M.; Ruan, Z.; Fan, S. Topological optical differentiator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh Nejad, F.; Sounas, D.L.; Alu, A.; Fleury, R. Analogue computing with metamaterials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, T.; Qiang, L.; Ye, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, M.; Su, Y. Compact optical temporal differentiator based on silicon microring resonator. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 15880–15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, M.; Park, Y.; Razzari, L.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Morandotti, R.; Moss, D.J.; Azaña, J. On-chip CMOS-compatible all-optical integrator. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, K.A.; Duchesne, D.; Strain, M.J.; Morandotti, R.; Sorel, M.; Azaña, J. Ultrafast all-optical temporal differentiators based on CMOS-compatible integrated-waveguide Bragg gratings. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 19514–19522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, P.; Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Tremblay, C.; Su, Y. Compact tunable silicon photonic differential-equation solver for general linear time-invariant systems. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 26254–26264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Yao, J. Photonic Generation of Phase-Coded Millimeter-Wave Signal Using a Polarization Modulator. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 2008, 18, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, S. Generation of phase-coded microwave signals using a polarization-modulator-based photonic microwave phase shifter. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shi, Z.; Li, M.; Zhu, N.H.; Li, W. Simultaneous frequency upconversion and phase coding of a radio-frequency signal for photonic radars. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhu, N.H.; Cao, Z.Z.; Li, W. Photonic generation of background-free binary phase-coded microwave pulses. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Chi, H.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J. Photonic Generation of Phase-Coded Microwave Signal With Large Frequency Tunability. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 2011, 23, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, L.; Yao, J. Photonic generation of triangular waveforms based on a polarization modulator in a Sagnac loop. In Proceedings of 2013 IEEE International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics (MWP), 28-31 Oct. 2013; pp. 68–71.
- Chou, J.; Han, Y.; Jalali, B. Adaptive RF-photonic arbitrary waveform generator. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 2003, 15, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundiff, S.T.; Weiner, A.M. Optical arbitrary waveform generation. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidinejad, A.; Li, Y.; Weiner, A.M. Recent Advances in Programmable Photonic-Assisted Ultrabroadband Radio-Frequency Arbitrary Waveform Generation. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 2016, 52, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamanaka, S.; Matsuura, A.; Kawakami, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishihara, K.; Masuda, H. 102.3-Tb/s (224 × 548-Gb/s) C- and extended L-band all-Raman transmission over 240 km using PDM-64QAM single carrier FDM with digital pilot tone. In Proceedings of OFC/NFOEC, 4-8 March 2012; pp. 1–3.
- G.694.1: Spectral grids for WDM applications: DWDM frequency grid. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-G.694.1-202010-I/en.
- Hillerkuss, D.; Schmogrow, R.; Schellinger, T.; Jordan, M.; Winter, M.; Huber, G.; Vallaitis, T.; Bonk, R.; Kleinow, P.; Frey, F.; et al. 26 Tbit s-1 line-rate super-channel transmission utilizing all-optical fast Fourier transform processing. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataie, V.; Temprana, E.; Liu, L.; Myslivets, E.; Kuo, B.P.; Alic, N.; Radic, S. Ultrahigh Count Coherent WDM Channels Transmission Using Optical Parametric Comb-Based Frequency Synthesizer. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2015, 33, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, C.; Schindler, P.C.; Palmer, R.; Wolf, S.; Bekele, D.; Korn, D.; Pfeifle, J.; Koeber, S.; Schmogrow, R.; Alloatti, L.; et al. Silicon-organic hybrid (SOH) frequency comb sources for terabit/s data transmission. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 3629–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifle, J.; Vujicic, V.; Watts, R.T.; Schindler, P.C.; Weimann, C.; Zhou, R.; Freude, W.; Barry, L.P.; Koos, C. Flexible terabit/s Nyquist-WDM super-channels using a gain-switched comb source. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.; Suh, M.G.; Fülöp, A.; Schröder, J.; Company, V.T.; Karlsson, M.; Vahala, K.; Andrekson, P. High Spectral Efficiency Coherent Superchannel Transmission With Soliton Microcombs. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2021, 39, 4367–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Han, X.; Cui, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Deng, G.; Zhou, Q.; Qiu, K. Coherent optical communications using coherence-cloned Kerr soliton microcombs. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capmany, J.; Novak, D. Microwave photonics combines two worlds. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J. Microwave Photonics. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2009, 27, 314–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoshi, T.; Kikuchi, K. Coherent optical fiber communications; Springer Science & Business Media: 1988; Vol. 4.
- Li, G. Recent advances in coherent optical communication. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2009, 1, 279–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, J.R.; Lee, E.A. Performance of coherent optical receivers. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1369–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freude, W.; Schmogrow, R.; Nebendahl, B.; Winter, M.; Josten, A.; Hillerkuss, D.; Koenig, S.; Meyer, J.; Dreschmann, M.; Huebner, M.; et al. Quality metrics for optical signals: Eye diagram, Q-factor, OSNR, EVM and BER. In Proceedings of 2012 14th International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), 2-5 July 2012; pp. 1–4.
- Schmogrow, R.; Nebendahl, B.; Winter, M.; Josten, A.; Hillerkuss, D.; Koenig, S.; Meyer, J.; Dreschmann, M.; Huebner, M.; Koos, C.; et al. Error Vector Magnitude as a Performance Measure for Advanced Modulation Formats. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 2012, 24, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, A.; Joshi, C.; Ji, X.; Cardenas, J.; Okawachi, Y.; Luke, K.; Gaeta, A.L.; Lipson, M. On-chip dual-comb source for spectroscopy. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Shen, B.; Sung, K.; Leifer, S.; Lin, Q.; Vahala, K. Interleaved difference-frequency generation for microcomb spectral densification in the mid-infrared. Optica 2020, 7, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Newbury, N.R. Coherent dual-comb spectroscopy at high signal-to-noise ratio. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 82, 043817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Lu, B.; Pan, W.; Yan, L.; Stöhr, A.; Yao, J. Photonics for microwave measurements. Laser Photon. Rev. 2016, 10, 711–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Newbury, N.; Swann, W. Dual-comb spectroscopy. Optica 2016, 3, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, L.; Suh, M.G.; Wang, H.; Lin, Q.; Vahala, K.J. Architecture for microcomb-based GHz-mid-infrared dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.S.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Yu, M.; Kwong, D.L.; Wong, C.W. Nanometric Precision Distance Metrology via Hybrid Spectrally Resolved and Homodyne Interferometry in a Single Soliton Frequency Microcomb. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2021, 126, 023903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, E.S.; Carlson, D.R.; Hickstein, D.D.; Stone, J.R.; Diddams, S.A.; Papp, S.B. Optical-Frequency Measurements with a Kerr Microcomb and Photonic-Chip Supercontinuum. Physical Review Applied 2018, 9, 024030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yi, X. Vernier frequency division with dual-microresonator solitons. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Precise dynamic characterization of microcombs assisted by an RF spectrum analyzer with THz bandwidth and MHz resolution. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 2153–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Broadband RF channelizer based on an integrated optical frequency Kerr comb source. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2018, 36, 4519–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, M.; Wu, J.; Boes, A.; Nguyen, T.G.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Mitchell, A.; Moss, D.J. Broadband Photonic RF Channelizer With 92 Channels Based on a Soliton Crystal Microcomb. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2020, 38, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideguchi, T.; Poisson, A.; Guelachvili, G.; Picqué, N.; Hänsch, T.W. Adaptive real-time dual-comb spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehravar, S.; Norwood, R.A.; Peyghambarian, N.; Kieu, K. Real-time dual-comb spectroscopy with a free-running bidirectionally mode-locked fiber laser. Applied Physics Letters 2016, 108, 231104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yan, G.; Zhou, S.; An, N.; Peng, B.; Soavi, G.; Rao, Y.; Yao, B. Multispecies and individual gas molecule detection using Stokes solitons in a graphene over-modal microresonator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoshima, K.; Matsumoto, H. High-accuracy measurement of 240-m distance in an optical tunnel by use of a compact femtosecond laser. Appl. Opt. 2000, 39, 5512–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coddington, I.; Swann, W.C.; Nenadovic, L.; Newbury, N.R. Rapid and precise absolute distance measurements at long range. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urmson, C.; Anhalt, J.; Bagnell, D.; Baker, C.; Bittner, R.; Clark, M.; Dolan, J.; Duggins, D.; Galatali, T.; Geyer, C. Autonomous driving in urban environments: Boss and the urban challenge. Journal of field Robotics 2008, 25, 425–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozpour, B.; Sandborn, P.A.; Wu, M.C.; Boser, B.E. Lidar system architectures and circuits. IEEE Communications Magazine 2017, 55, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Zeitouny, M.G.; Bhattacharya, N.; van den Berg, S.A.; Urbach, H.P. Long distance measurement with femtosecond pulses using a dispersive interferometer. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 6549–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, S.A.; van Eldik, S.; Bhattacharya, N. Mode-resolved frequency comb interferometry for high-accuracy long distance measurement. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, R.A.; Charsley, J.M.; Reid, D.T. A decade of astrocombs: recent advances in frequency combs for astronomy [Invited]. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 15058–15078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.T.; Udem, T.; Holzwarth, R.; Sizmann, A.; Pasquini, L.; Araujo-Hauck, C.; Dekker, H.; D'Odorico, S.; Fischer, M.; Hänsch, T.W.; et al. High-precision wavelength calibration of astronomical spectrographs with laser frequency combs. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2007, 380, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, T.; Wilken, T.; Araujo-Hauck, C.; Holzwarth, R.; Hänsch, T.W.; Pasquini, L.; Manescau, A.; D'Odorico, S.; Murphy, M.T.; Kentischer, T.; et al. Laser Frequency Combs for Astronomical Observations. Science 2008, 321, 1335–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Benedick, A.J.; Fendel, P.; Glenday, A.G.; Kärtner, F.X.; Phillips, D.F.; Sasselov, D.; Szentgyorgyi, A.; Walsworth, R.L. A laser frequency comb that enables radial velocity measurements with a precision of 1 cm s-1. Nature 2008, 452, 610–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Yi, X.; Yang, K.Y.; Vahala, K. Counter-propagating solitons in microresonators. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, M.; Reimer, C.; Pasquazi, A.; Peccianti, M.; Clerici, M.; Caspani, L.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; Morandotti, R.; Moss, D.J. CMOS compatible integrated all-optical radio frequency spectrum analyzer. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 21488–21498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Ai, S.; Wang, X.; Davidson, R.R.; Wu, Y.; Morandotti, R.; Little, B.E.; Moss, D.J.; et al. All-optical RF spectrum analyzer with a 5 THz bandwidth based on CMOS-compatible high-index doped silica waveguides. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1574–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Dai, Y.; Ji, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Lin, J. Broadband Photonic Radio-Frequency Channelization Based on a 39-GHz Optical Frequency Comb. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters 2012, 24, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Davis, R.L.; Jung, T.J.; Lodenkamper, R.; Lembo, L.J.; Brock, J.C.; Wu, M. Characterization of a coherent optical RF channelizer based on a diffraction grating. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 2001, 49, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D.B.; Edvell, L.G.; Englund, M.A. Wideband Microwave Photonic Channelised Receiver. In Proceedings of 2005 International Topical Meeting on Microwave Photonics, 14-14 Oct. 2005; pp. 249–252.
- Rhodes, W.T. Acousto-optic signal processing: Convolution and correlation. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnall, S.T.; Lindsay, A.C.; Austin, M.W.; Canning, J.; Mitchell, A. A microwave channelizer and spectroscope based on an integrated optical Bragg-grating Fabry-Perot and integrated hybrid Fresnel lens system. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 2006, 54, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, C. Neuromorphic electronic systems. Proc. IEEE 1990, 78, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, C.D.; Potok, T.E.; Patton, R.M.; Birdwell, J.D.; Dean, M.E.; Rose, G.S.; Plank, J.S. A survey of neuromorphic computing and neural networks in hardware. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.06963 2017. arXiv:1705.06963 2017.
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. Large Margin Classification Using the Perceptron Algorithm. Machine Learning 1999, 37, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, J.; Youngblood, N.; Wright, C.D.; Bhaskaran, H.; Pernice, W.H.P. All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities. Nature 2019, 569, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, D.; Brady, D.; Gu, X.G.; Lin, S. Holography in artificial neural networks. Nature 1990, 343, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Harris, N.C.; Skirlo, S.; Prabhu, M.; Baehr Jones, T.; Hochberg, M.; Sun, X.; Zhao, S.; Larochelle, H.; Englund, D.; et al. Deep learning with coherent nanophotonic circuits. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ma, S.Y.; Wright, L.G.; Onodera, T.; Richard, B.C.; McMahon, P.L. An optical neural network using less than 1 photon per multiplication. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Rivenson, Y.; Yardimci, N.T.; Veli, M.; Luo, Y.; Jarrahi, M.; Ozcan, A. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks. Science 2018, 361, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, A.N.; de Lima, T.F.; Zhou, E.; Wu, A.X.; Nahmias, M.A.; Shastri, B.J.; Prucnal, P.R. Neuromorphic photonic networks using silicon photonic weight banks. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 7430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sande, G.V.d.; Brunner, D.; Soriano, M.C. Advances in photonic reservoir computing. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.G.; Jayasuriya, S.; Yang, J.; Stephen, J.; Sivaramakrishnan, S.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Molnar, A. ASP vision: Optically computing the first layer of convolutional neural networks using angle sensitive pixels. In Proceedings of Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; pp. 903–912.
- Chang, J.; Sitzmann, V.; Dun, X.; Heidrich, W.; Wetzstein, G. Hybrid optical-electronic convolutional neural networks with optimized diffractive optics for image classification. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miscuglio, M.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; George, J.K.; Capanna, R.; Dalir, H.; Bardet, P.M.; Gupta, P.; Sorger, V.J. Massively parallel amplitude-only Fourier neural network. Optica 2020, 7, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X. Optronic convolutional neural networks of multi-layers with different functions executed in optics for image classification. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 5877–5889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Wu, H.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.; Qian, H. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature 2020, 577, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, S.; Giles, C.L.; Ah Chung, T.; Back, A.D. Face recognition: a convolutional neural-network approach. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 1997, 8, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspani, L.; Reimer, C.; Kues, M.; Roztocki, P.; Clerici, M.; Wetzel, B.; Jestin, Y.; Ferrera, M.; Peccianti, M.; Pasquazi, A.; et al. Multifrequency sources of quantum correlated photon pairs on-chip: a path toward integrated Quantum Frequency Combs. Nanophotonics 2016, 5, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibfried, D.; Blatt, R.; Monroe, C.; Wineland, D. Quantum dynamics of single trapped ions. Reviews of Modern Physics 2003, 75, 281–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoret, M.H.; Schoelkopf, R.J. Superconducting Circuits for Quantum Information: An Outlook. Science 2013, 339, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeas, F.; Traetta, M.; Bentivegna, M.; Kaiser, F.; Aktas, D.; Zhang, W.; Ramos, C.A.; Ngah, L.A.; Lunghi, T.; Picholle, É.; et al. High-quality photonic entanglement for wavelength-multiplexed quantum communication based on a silicon chip. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 28731–28738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.H.; Alexander, R.N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. Quantum computing with multidimensional continuous-variable cluster states in a scalable photonic platform. Physical Review Research 2020, 2, 023138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chembo, Y.K. Quantum dynamics of Kerr optical frequency combs below and above threshold: Spontaneous four-wave mixing, entanglement, and squeezed states of light. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 033820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.; Caspani, L.; Clerici, M.; Ferrera, M.; Kues, M.; Peccianti, M.; Pasquazi, A.; Razzari, L.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; et al. Integrated frequency comb source of heralded single photons. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6535–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.; Kues, M.; Caspani, L.; Wetzel, B.; Roztocki, P.; Clerici, M.; Jestin, Y.; Ferrera, M.; Peccianti, M.; Pasquazi, A.; et al. Cross-polarized photon-pair generation and bi-chromatically pumped optical parametric oscillation on a chip. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo Villegas, J.A.; Imany, P.; Odele, O.D.; Leaird, D.E.; Ou, Z.Y.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. Persistent energy-time entanglement covering multiple resonances of an on-chip biphoton frequency comb. Optica 2017, 4, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kues, M.; Reimer, C.; Roztocki, P.; Cortés, L.R.; Sciara, S.; Wetzel, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cino, A.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; et al. On-chip generation of high-dimensional entangled quantum states and their coherent control. Nature 2017, 546, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imany, P.; Jaramillo-Villegas, J.A.; Odele, O.D.; Han, K.; Leaird, D.E.; Lukens, J.M.; Lougovski, P.; Qi, M.; Weiner, A.M. 50-GHz-spaced comb of high-dimensional frequency-bin entangled photons from an on-chip silicon nitride microresonator. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 1825–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, C.; Sciara, S.; Roztocki, P.; Islam, M.; Romero Cortés, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fischer, B.; Loranger, S.; Kashyap, R.; Cino, A.; et al. High-dimensional one-way quantum processing implemented on d-level cluster states. Nature Physics 2019, 15, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnabel, R. Squeezed states of light and their applications in laser interferometers. Physics Reports 2017, 684, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, D.F. Squeezed states of light. Nature 1983, 306, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Okawachi, Y.; Jang, J.K.; Ji, X.; Lipson, M.; Gaeta, A.L. Near-Degenerate Quadrature-Squeezed Vacuum Generation on a Silicon-Nitride Chip. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 193601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, A.; Luke, K.; Manipatruni, S.; Gaeta, A.L.; Nussenzveig, P.; Lipson, M. On-Chip Optical Squeezing. Physical Review Applied 2015, 3, 044005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otterpohl, A.; Sedlmeir, F.; Vogl, U.; Dirmeier, T.; Shafiee, G.; Schunk, G.; Strekalov, D.V.; Schwefel, H.G.L.; Gehring, T.; Andersen, U.L.; et al. Squeezed vacuum states from a whispering gallery mode resonator. Optica 2019, 6, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.D.; Morrison, B.; Helt, L.G.; Shahrokshahi, R.; Mahler, D.H.; Collins, M.J.; Tan, K.; Lavoie, J.; Repingon, A.; Menotti, M.; et al. Broadband quadrature-squeezed vacuum and nonclassical photon number correlations from a nanophotonic device. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba9186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Menotti, M.; Tan, K.; Vaidya, V.D.; Mahler, D.H.; Helt, L.G.; Zatti, L.; Liscidini, M.; Morrison, B.; Vernon, Z. Squeezed light from a nanophotonic molecule. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Jahanbozorgi, M.; Jeong, D.; Sun, S.; Pfister, O.; Lee, H.; Yi, X. A squeezed quantum microcomb on a chip. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, D.Y.; Yang, Q.F.; Shen, B.; Wang, H.; Yang, K.Y.; Lai, Y.H.; Yi, X.; Li, X.; Vahala, K. Towards visible soliton microcomb generation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kumar, R.R.; Zhong, K.; Tsang, H.K. Near-infrared frequency comb generation from a silicon microresonator. Journal of Optics 2021, 23, 10LT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrera, M.; Razzari, L.; Duchesne, D.; Morandotti, R.; Yang, Z.; Liscidini, M.; Sipe, J.E.; Chu, S.; Little, B.E.; Moss, D.J. Low-power continuous-wave nonlinear optics in doped silica glass integrated waveguide structures. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, A.S.; Kondratiev, N.M.; Lihachev, G.V.; Liu, J.; Lobanov, V.E.; Dmitriev, N.Y.; Weng, W.; Kippenberg, T.J.; Bilenko, I.A. Dynamics of soliton self-injection locking in optical microresonators. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shen, Z.X.; Loh, K.P.; Tang, D.Y. Atomic-Layer Graphene as a Saturable Absorber for Ultrafast Pulsed Lasers. Advanced Functional Materials 2009, 19, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, K.; Lee, C.; Zhang, H.; He, J. Recent Progress in 2D Material-Based Saturable Absorbers for All Solid-State Pulsed Bulk Lasers. Laser Photon. Rev. 2020, 14, 1900240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cao, P.; Pan, T.; Hu, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, L.; Su, Y. High-speed fourth-order photonic differentiator based on silicon self-coupled optical-waveguide resonator. In 2014 Ieee 11th International Conference on Group Iv Photonics, Ieee: New York, 2014.
- Yang, T.; Dong, J.; Lu, L.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, A.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. All-optical differential equation solver with constant-coefficient tunable based on a single microring resonator. Scientific Reports 2014, 4, 5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Peng, J.; Mao, J.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, C.; Tremblay, C.; Su, Y. On-Chip Tunable Second-Order Differential-Equation Solver Based on a Silicon Photonic Mode-Split Microresonator. Journal of Lightwave Technology 2015, 33, 3542–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.; Guzzon, R.S.; Norberg, E.J.; Parker, J.S.; Lu, M.; Coldren, L.A.; Yao, J. A fully reconfigurable photonic integrated signal processor. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, D.G.; Bian, Z.; Shakouri, A. Ring resonator lasers using passive waveguides and integrated semiconductor optical amplifiers. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 2007, 13, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.H.; Shen, H.; Xuan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, S.; Leaird, D.E.; Weiner, A.M.; Qi, M. Ultrabroad-bandwidth arbitrary radiofrequency waveform generation with a silicon photonic chip-based spectral shaper. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, A.J.; Kim, H.J.; Leaird, D.E.; Jaramillo Villegas, J.A.; McKinzie, K.A.; Lal, V.; Hosseini, A.; Hoefler, G.E.; Kish, F.; Weiner, A.M. Integrated line-by-line optical pulse shaper for high-fidelity and rapidly reconfigurable RF-filtering. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 23925–23940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Bertrand, M.; Shams-Ansari, A.; Chandrasekhar, S.; Winzer, P.; Lončar, M. Integrated lithium niobate electro-optic modulators operating at CMOS-compatible voltages. Nature 2018, 562, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molony, A.; Lin, Z.; Williams, J.A.R.; Bennion, I.; Edge, C.; Fells, J. Fiber Bragg-grating true time-delay systems: discrete-grating array 3-b delay lines and chirped-grating 6-b delay lines. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 1997, 45, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, J.; Liu, J.; Kimerling, L.C. High-performance Ge-on-Si photodetectors. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Fazal, I.M.; Ahmed, N.; Yan, Y.; Huang, H.; Ren, Y.; Yue, Y.; Dolinar, S.; Tur, M.; et al. Terabit free-space data transmission employing orbital angular momentum multiplexing. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, M. On-chip noninterference angular momentum multiplexing of broadband light. Science 2016, 352, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashtiani, F.; Geers, A.J.; Aflatouni, F. An on-chip photonic deep neural network for image classification. Nature 2022. [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, N.K.; Scott, R.P.; Yang, C.; Geisler, D.J.; Heritage, J.P.; Okamoto, K.; Yoo, S.J.B. Compact 10 GHz loopback arrayed-waveguide grating for high-fidelity optical arbitrary waveform generation. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 1714–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnieli, A.; Arie, A. Frequency domain Stern-Gerlach effect for photonic qubits and qutrits. Optica 2018, 5, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roztocki, P.; Kues, M.; Reimer, C.; Wetzel, B.; Sciara, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cino, A.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Moss, D.J.; et al. Practical system for the generation of pulsed quantum frequency combs. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 18940–18949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J. Rubidium chip-scale atomic clock with improved long-term stability through light intensity optimization and compensation for laser frequency detuning. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2016, 33, 1756–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, P.J.; Riemensberger, J.; Skehan, J.C.; Ho, J.J.; Pfeiffer, M.H.P.; Liu, J.; Hauger, C.; Lasser, T.; Kippenberg, T.J. Soliton microcomb based spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajraszewski, T.; Wojtkowski, M.; Szkulmowski, M.; Szkulmowska, A.; Huber, R.; Kowalczyk, A. Improved spectral optical coherence tomography using optical frequency comb. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 4163–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, S.J.; Brasch, V.; Szabados, J.; Obrzud, E.; Jia, Y.; Lecomte, S.; Buse, K.; Breunig, I.; Herr, T. Frequency comb up- and down-conversion in synchronously driven χ(2) optical microresonators. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 5745–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zou, C.L.; Jung, H.; Gong, Z.; Bruch, A.; Jiang, L.; Tang, H.X. Efficient Generation of a Near-visible Frequency Comb via Cherenkov-like Radiation from a Kerr Microcomb. Physical Review Applied 2018, 10, 014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
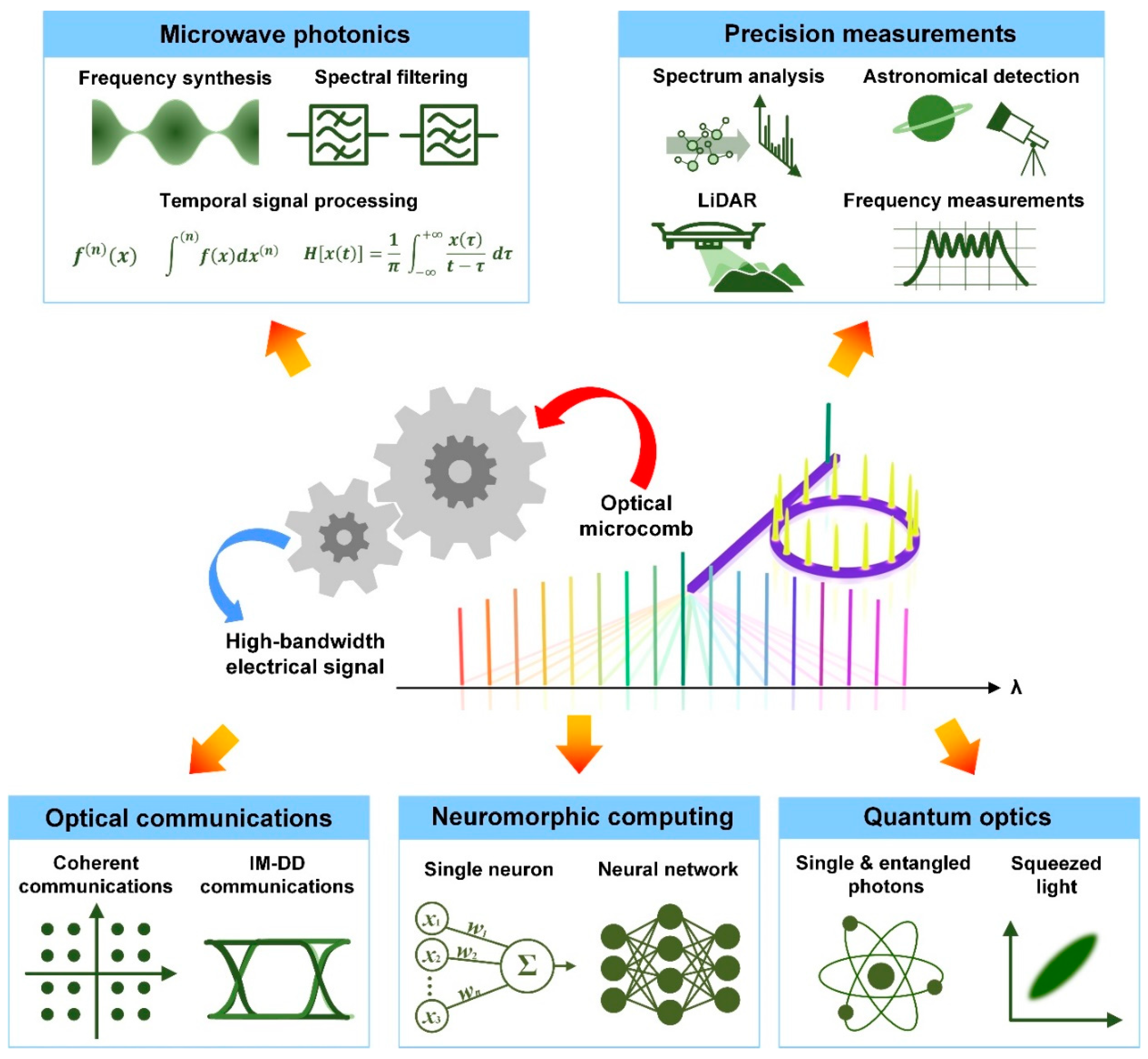
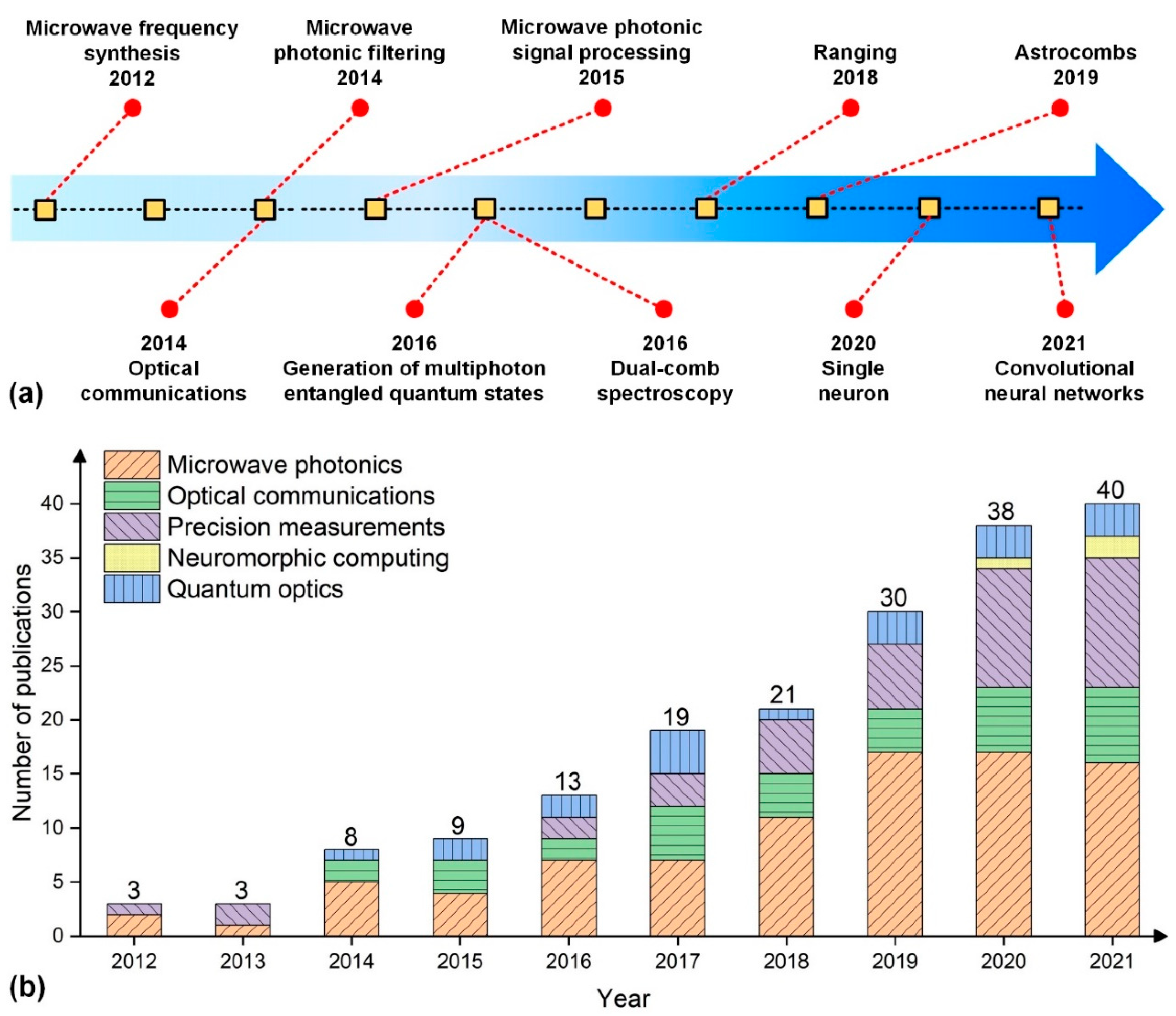
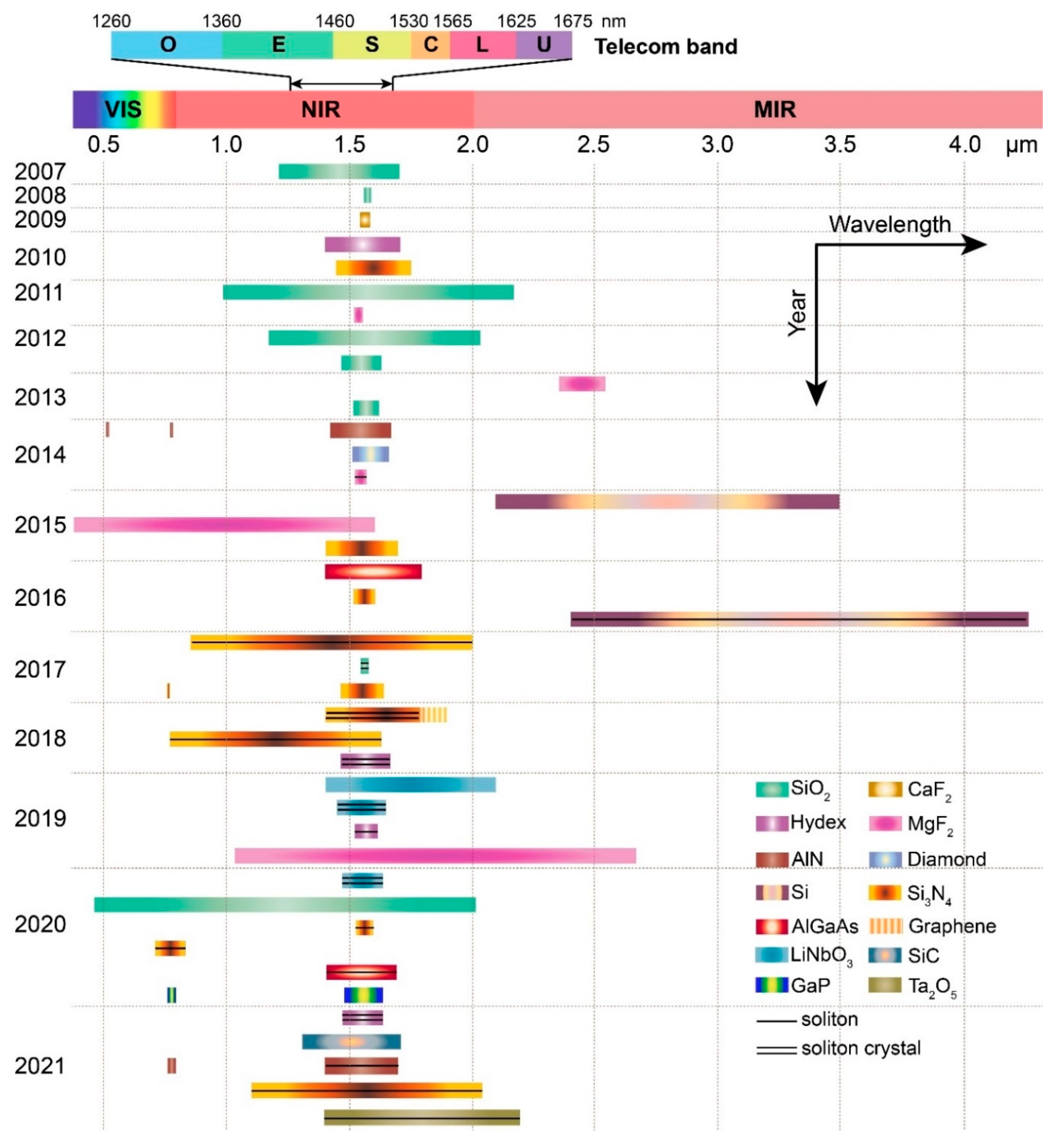
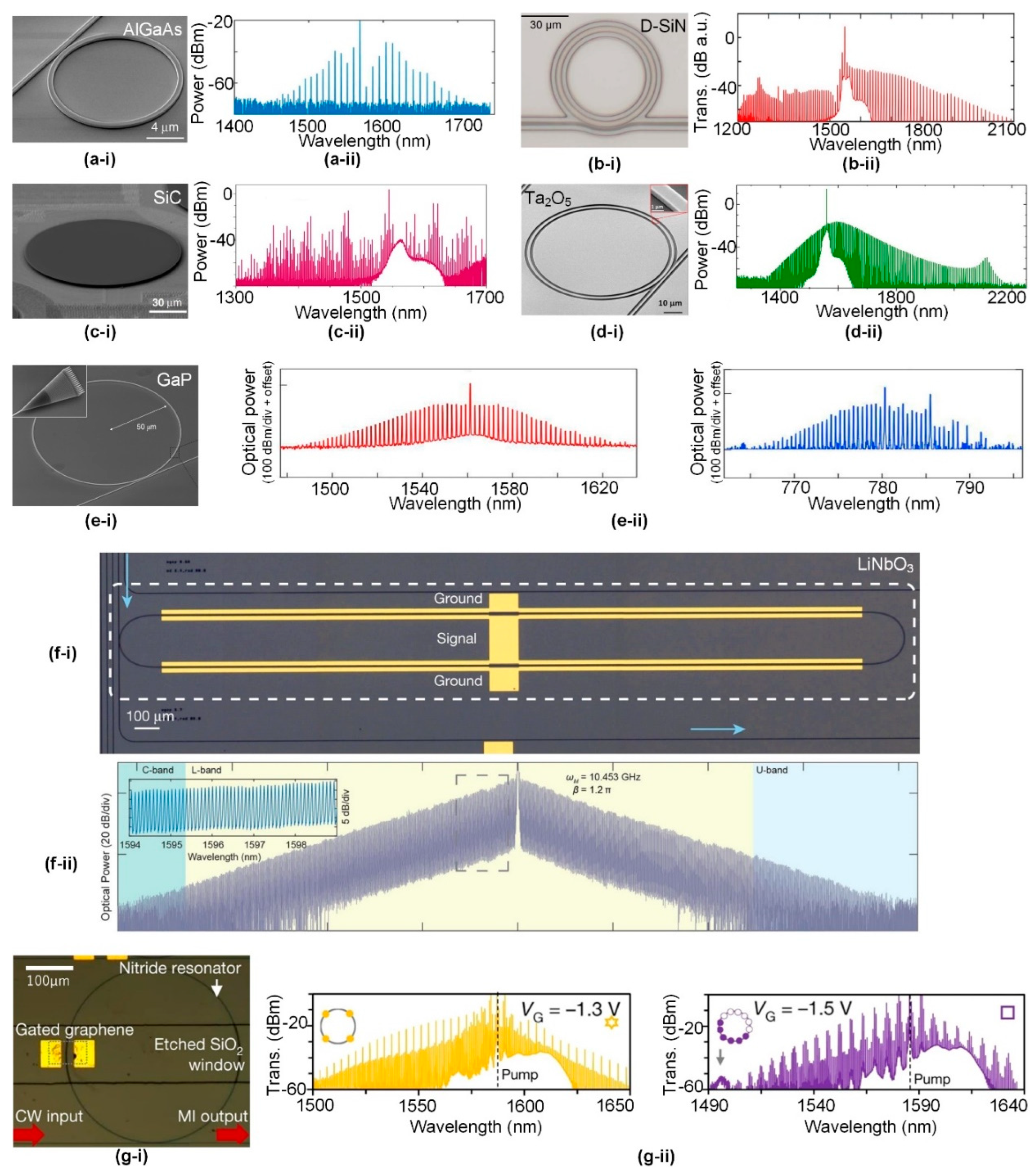
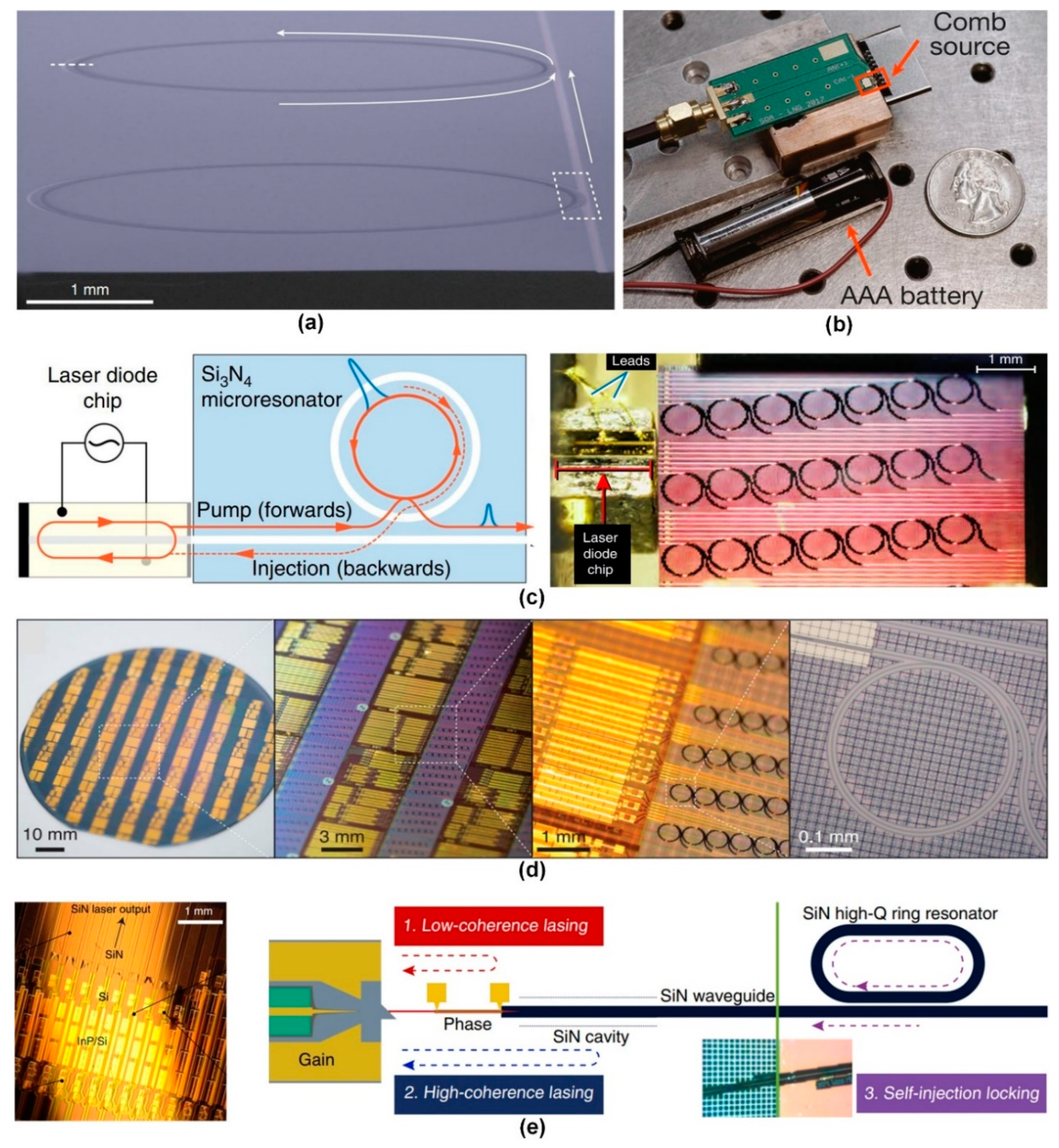
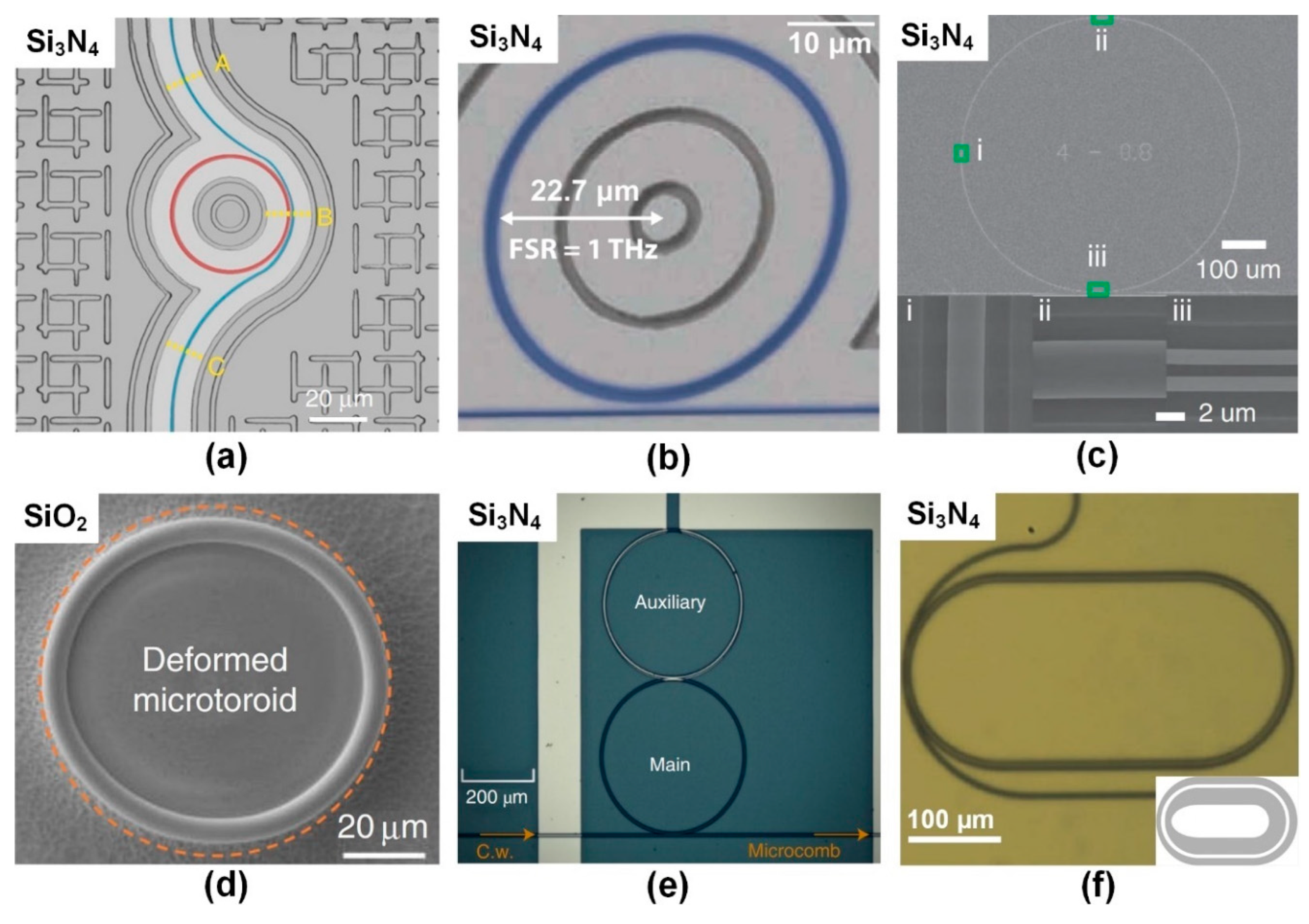
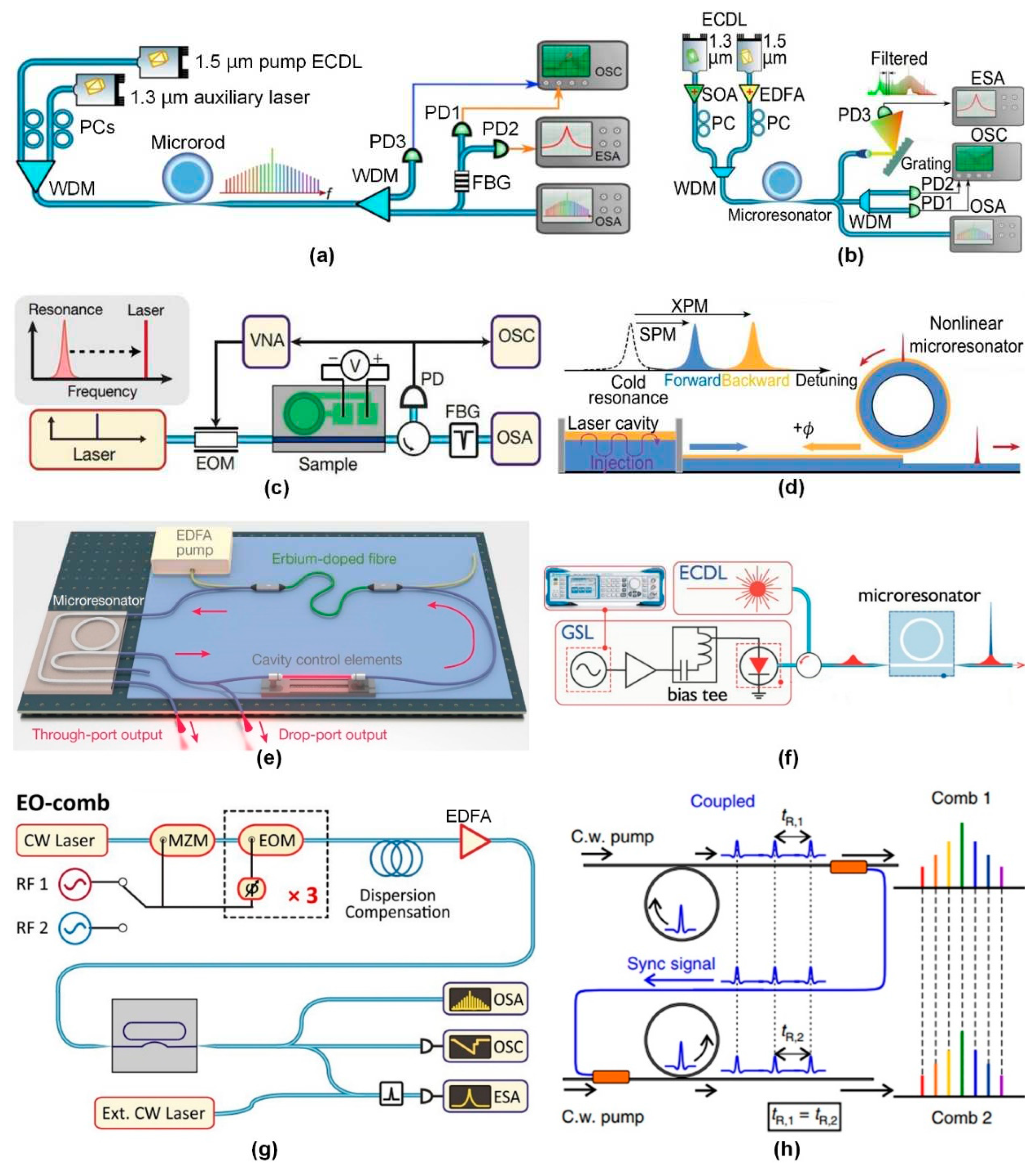
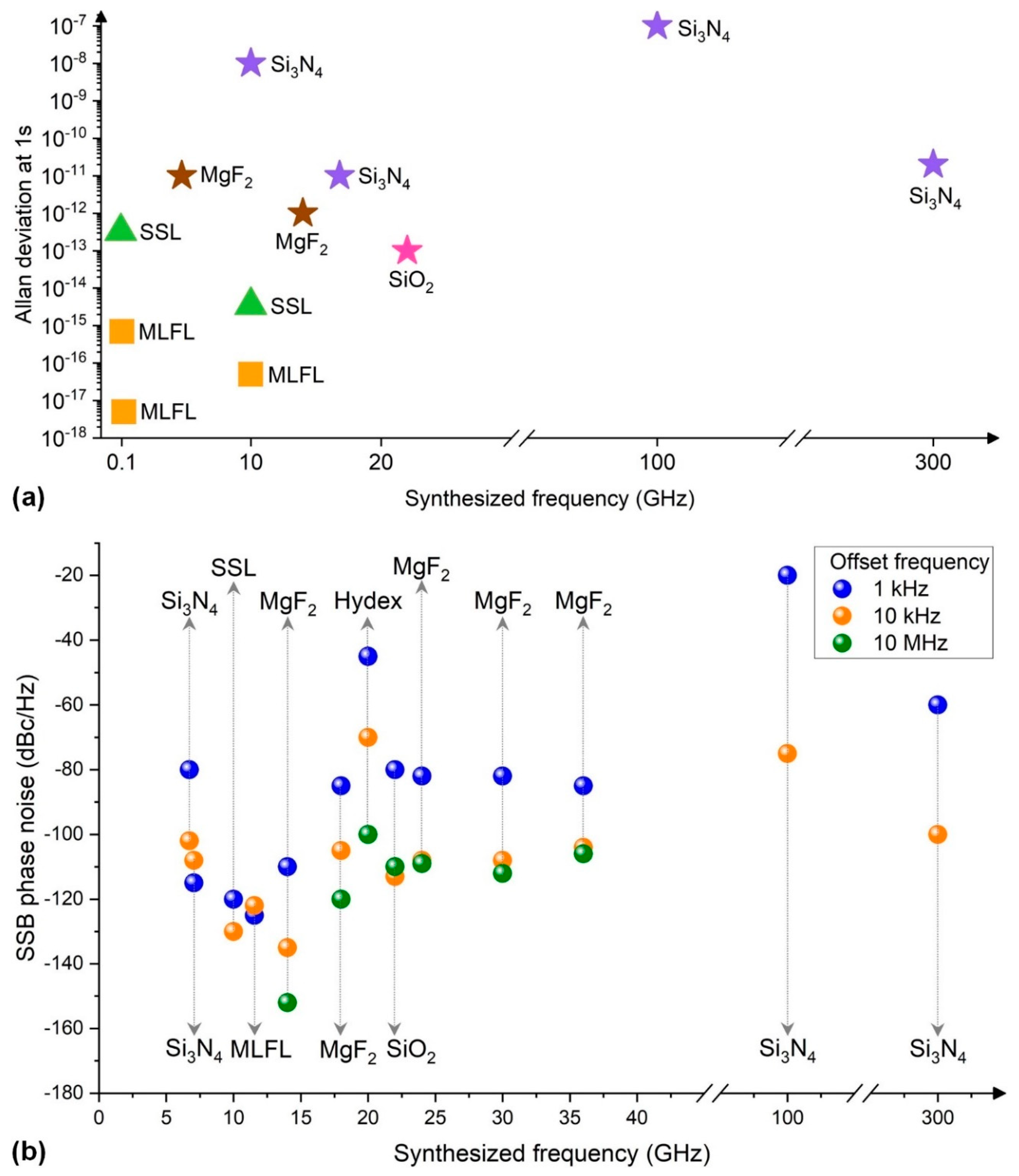
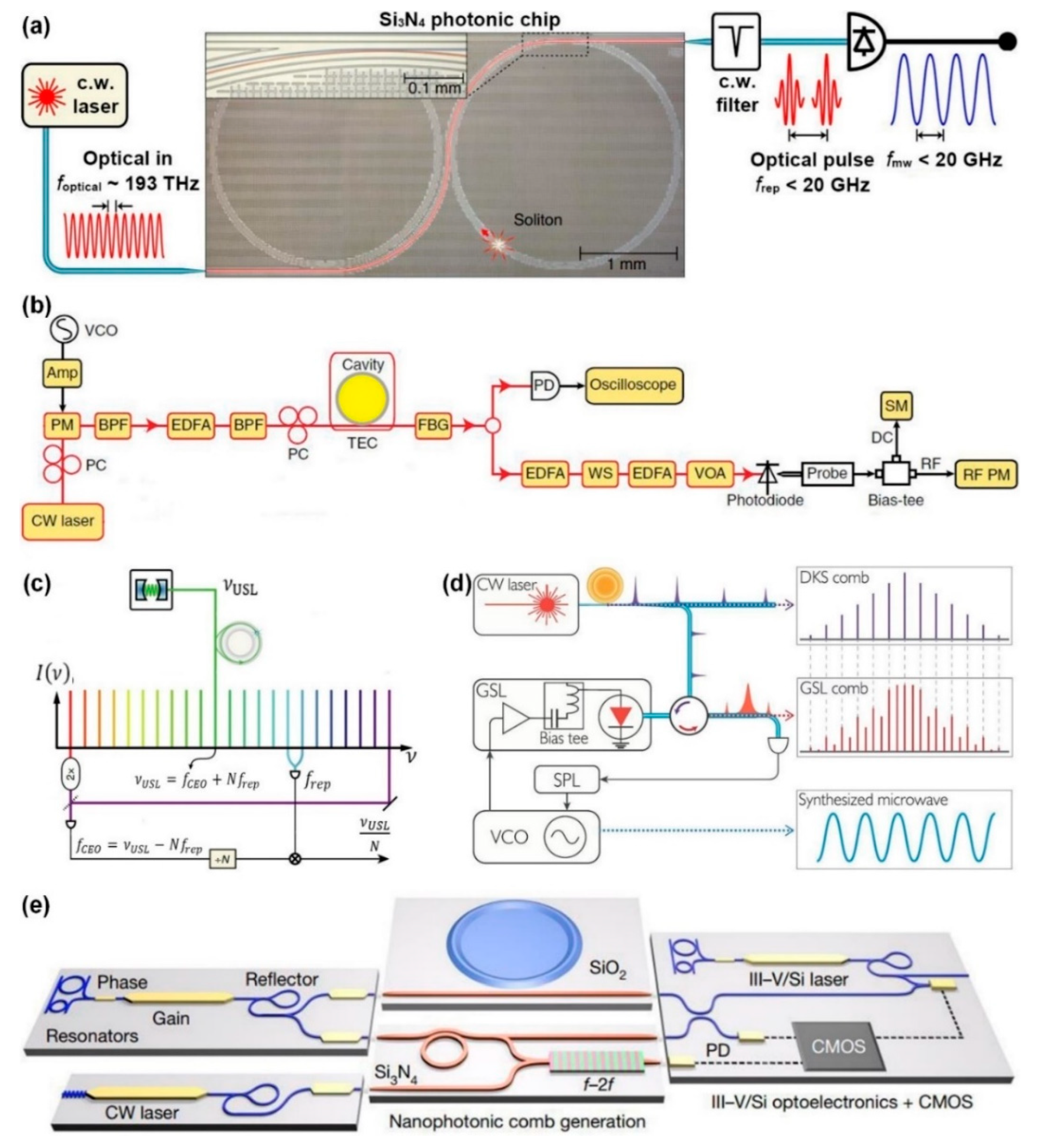
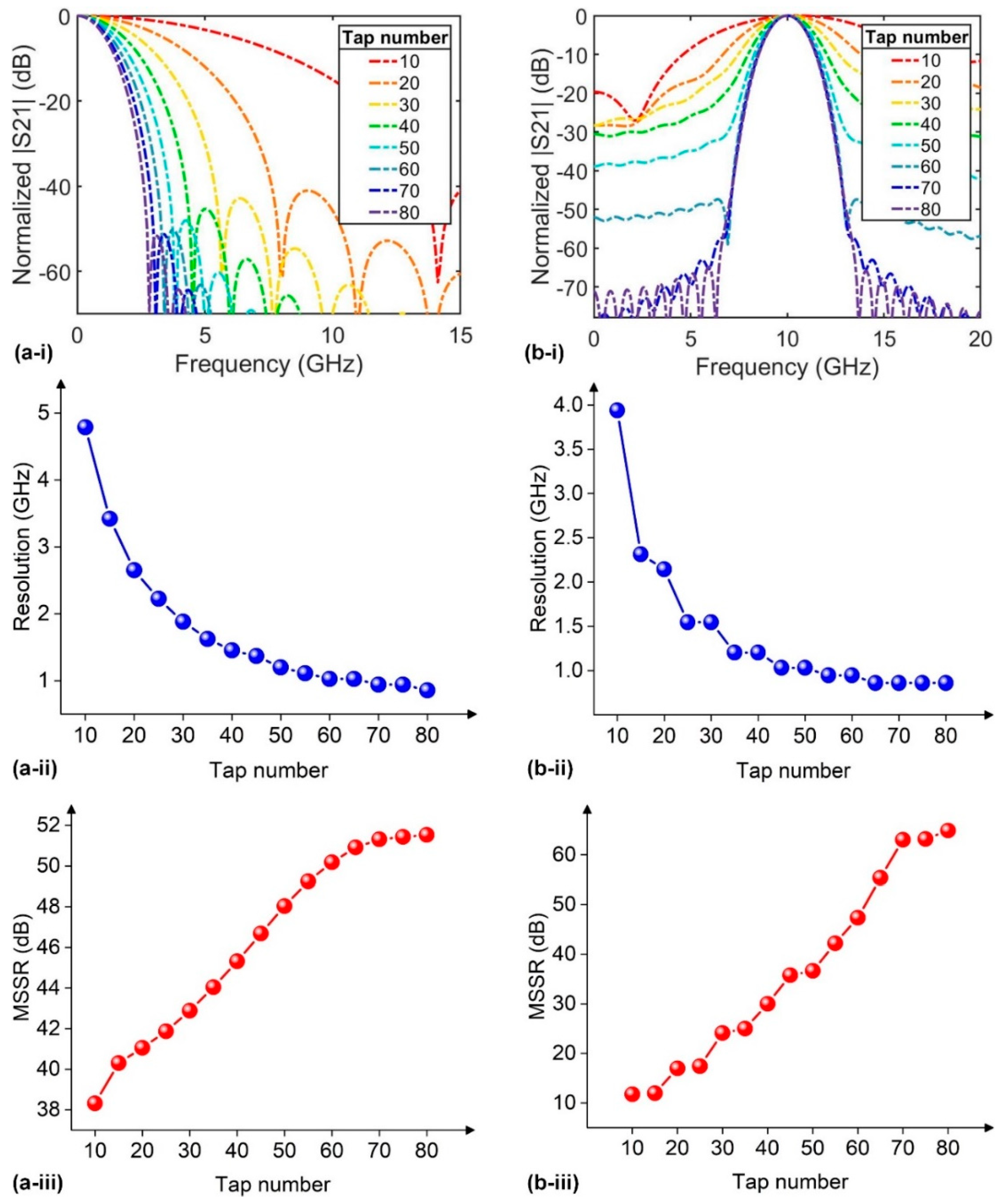
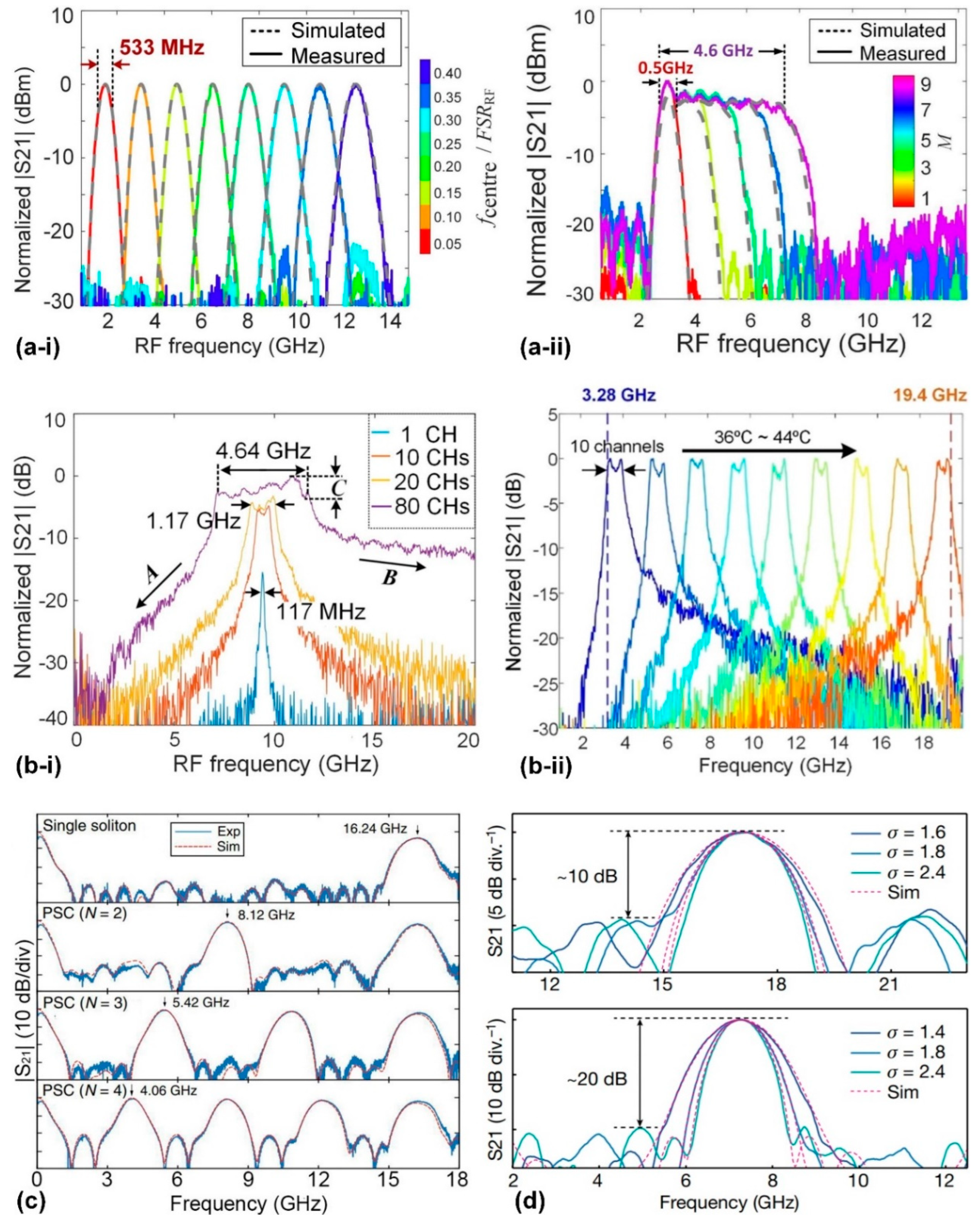
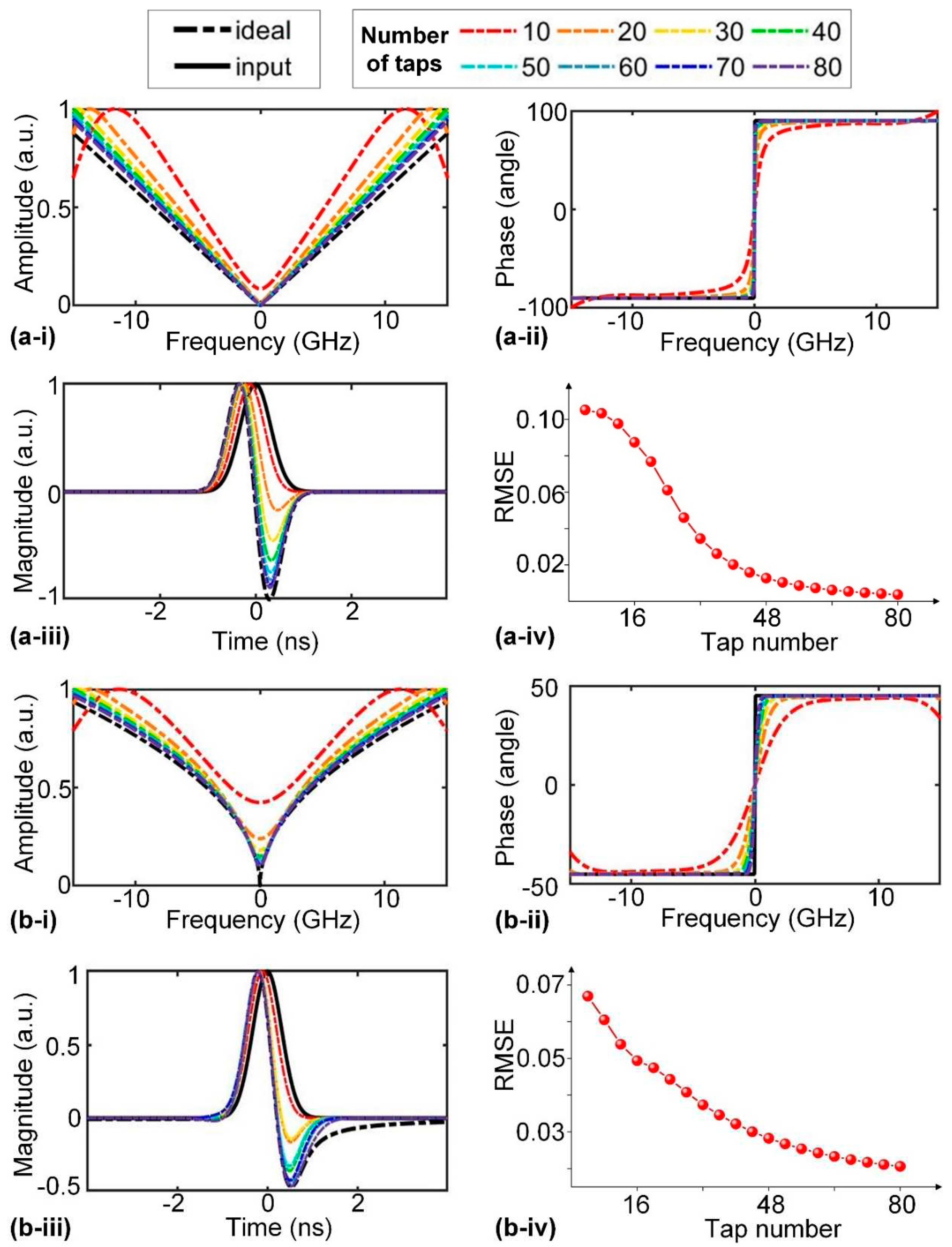
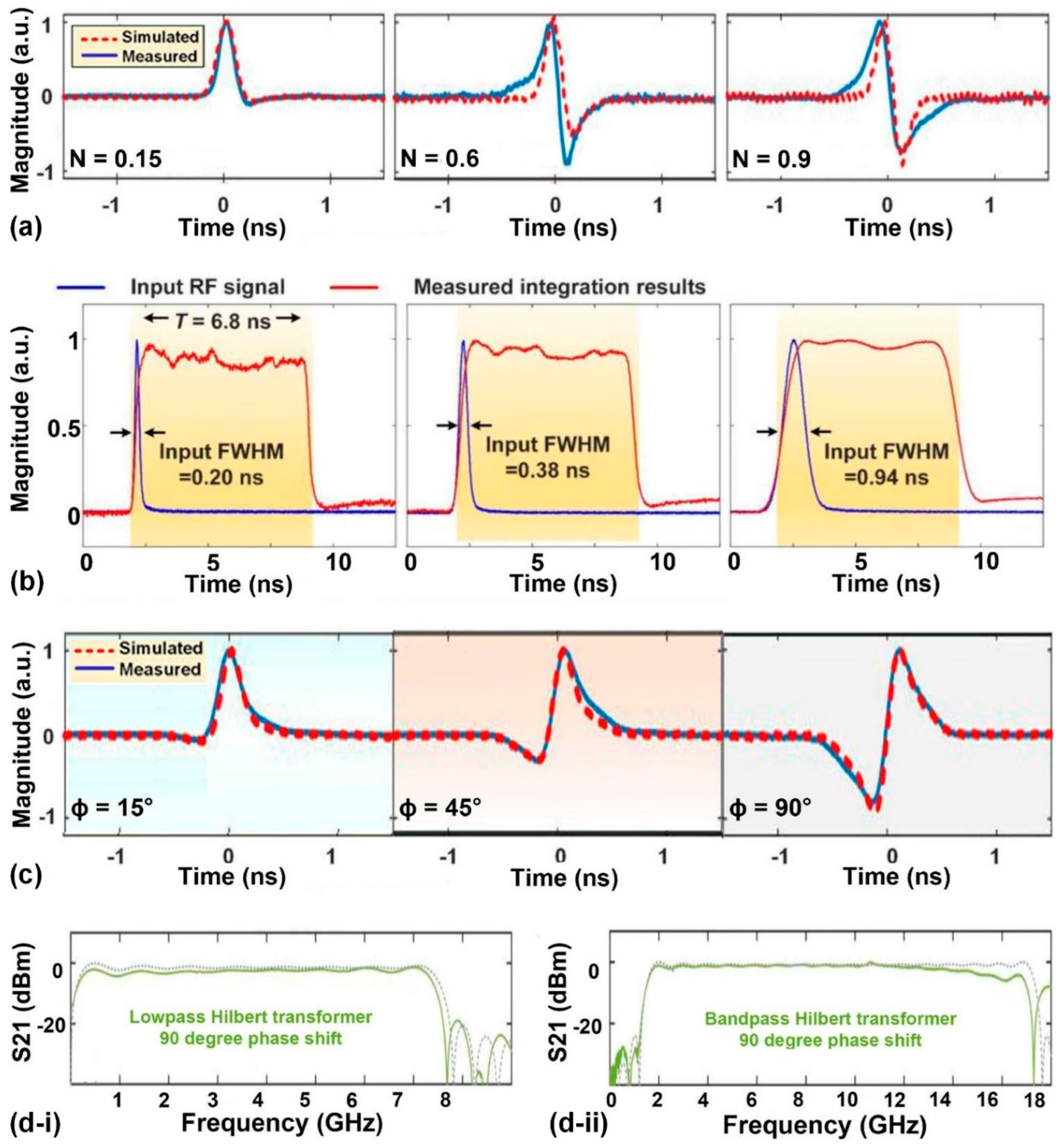
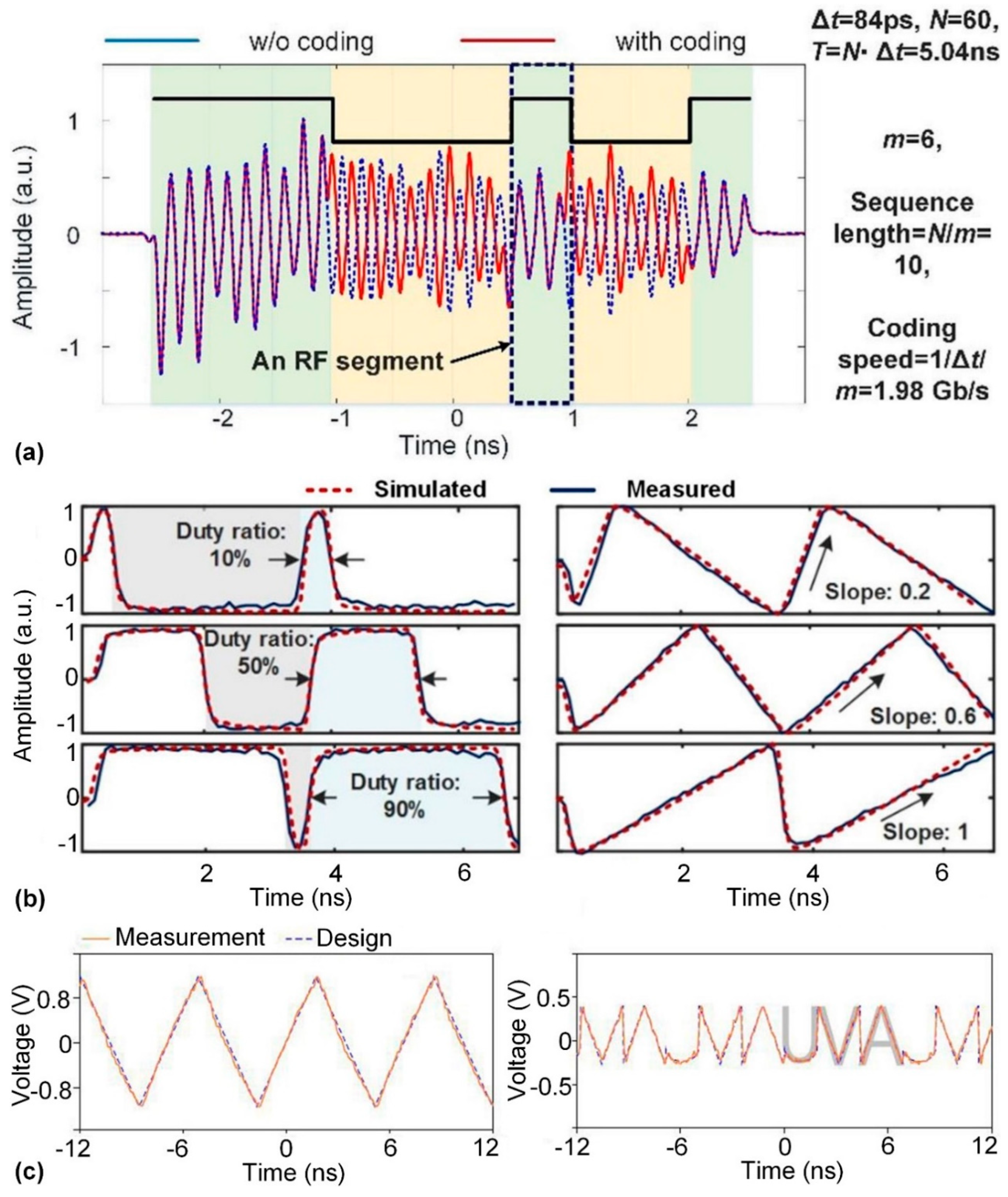
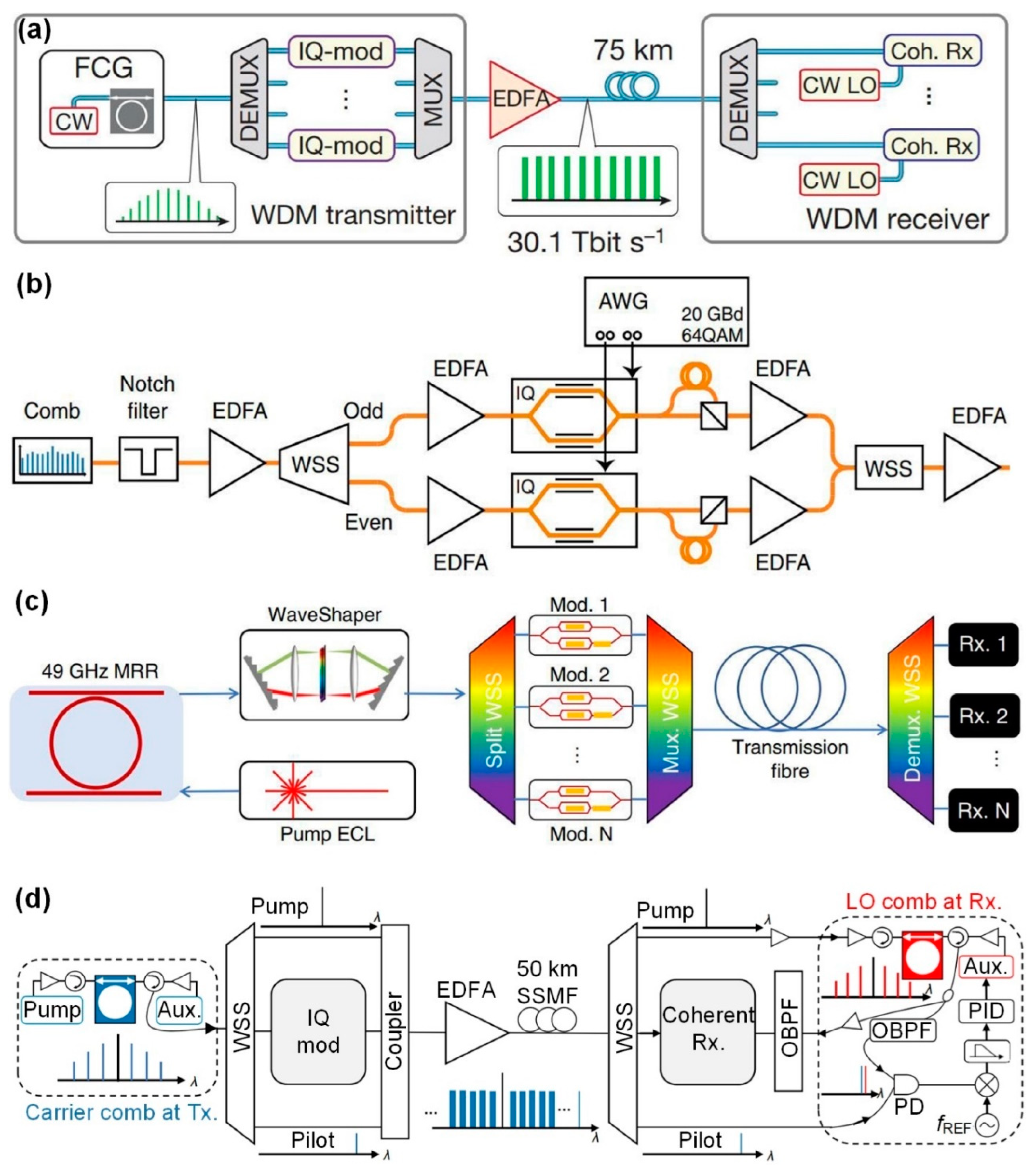
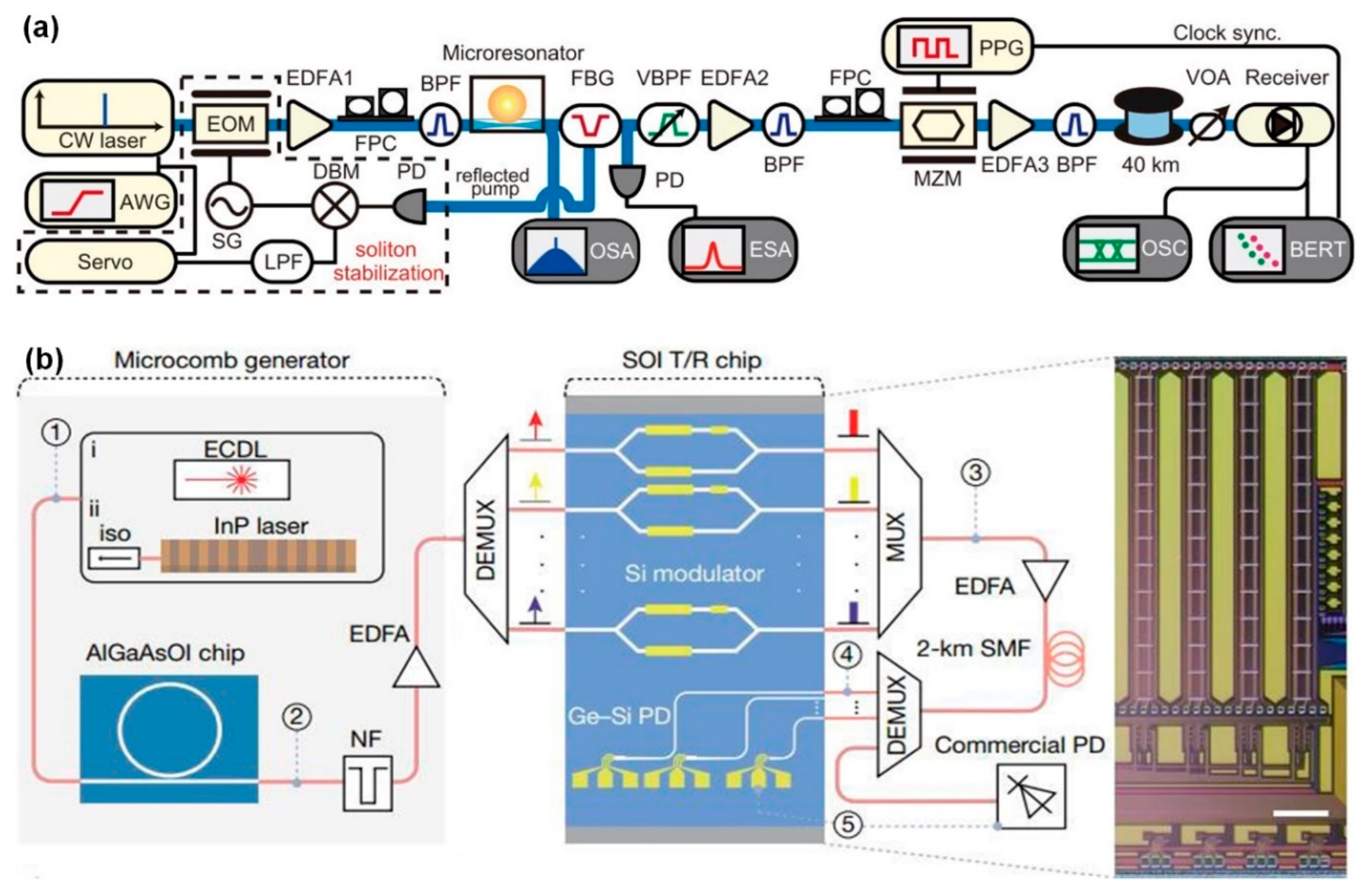
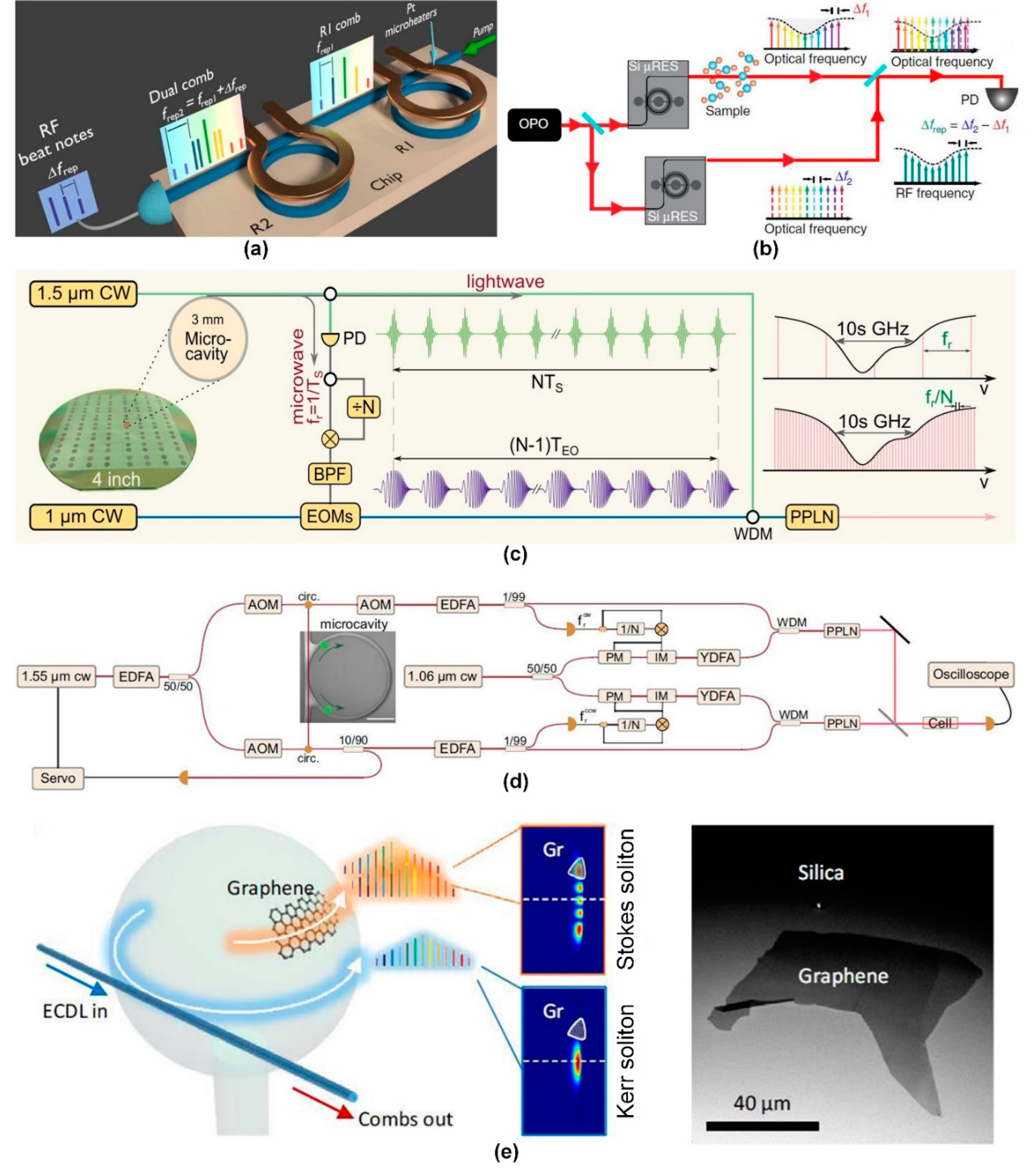
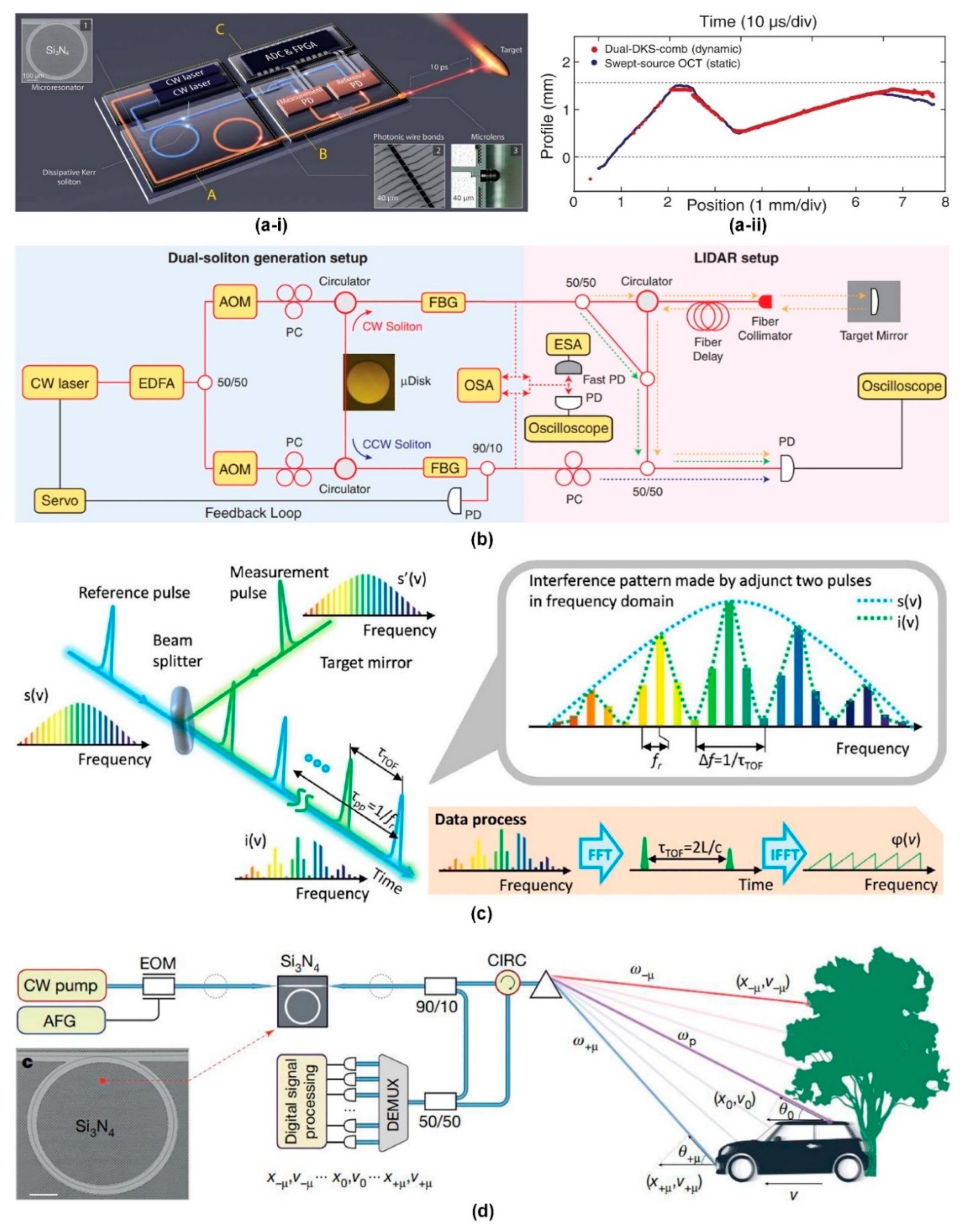
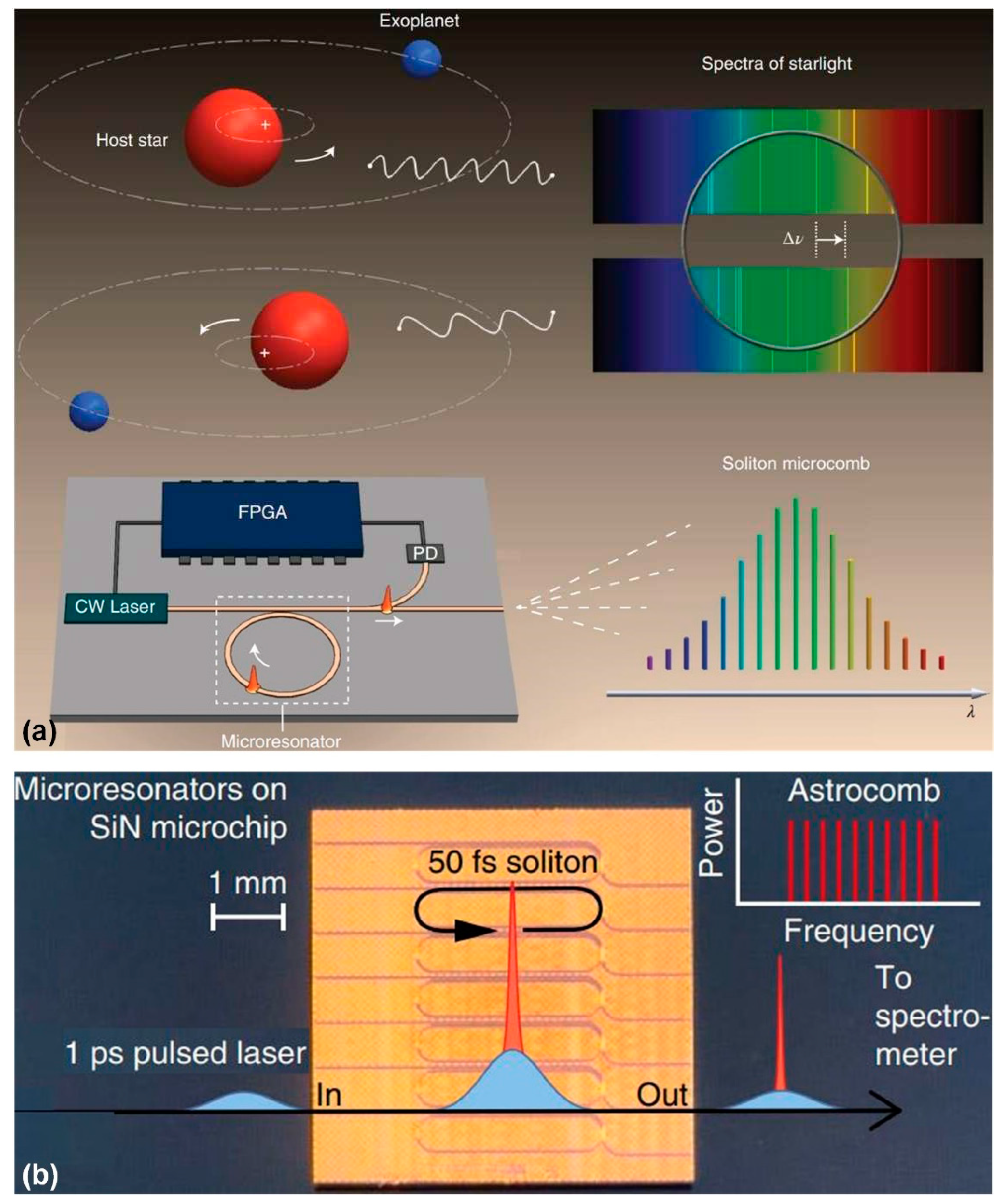
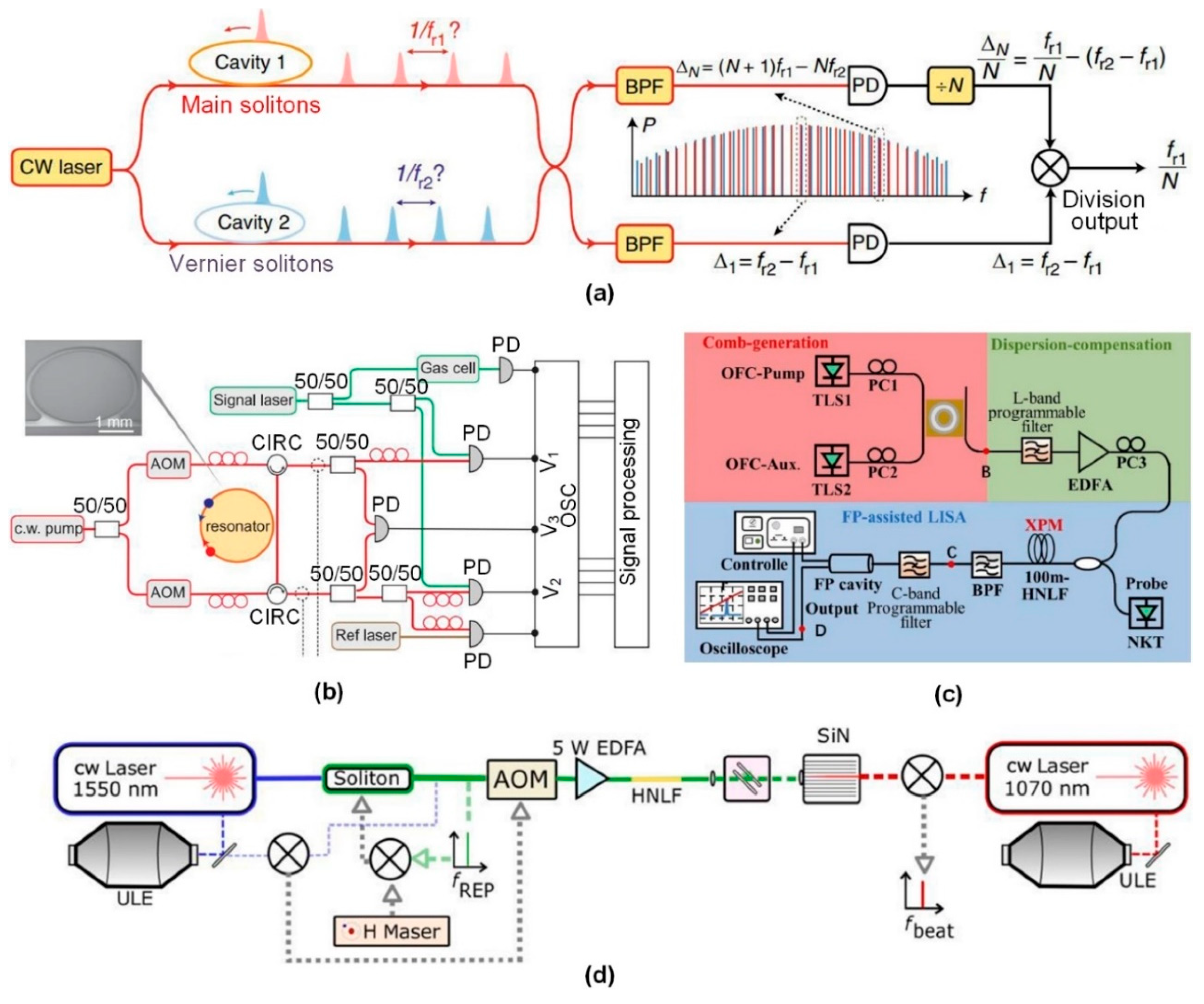
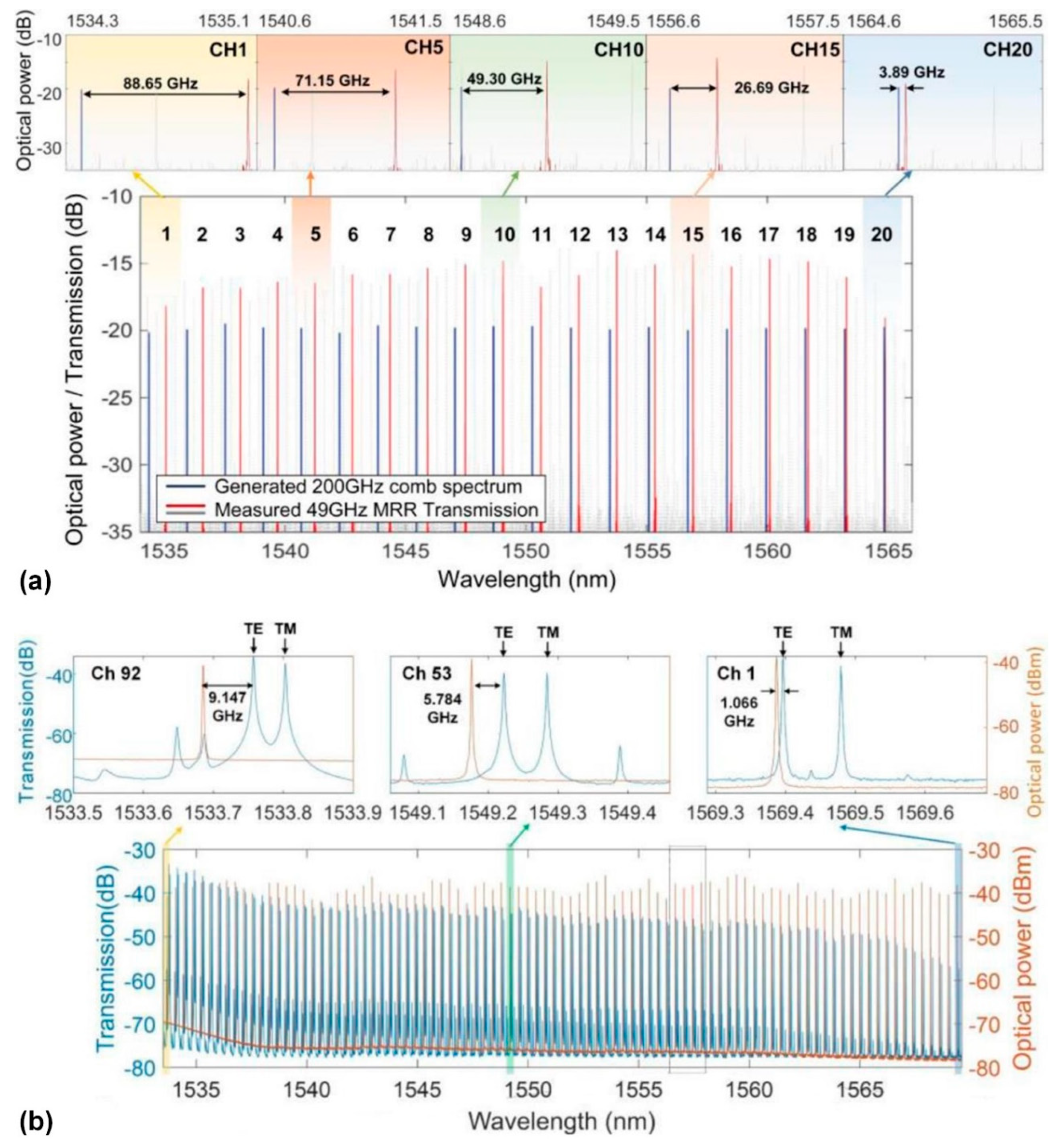
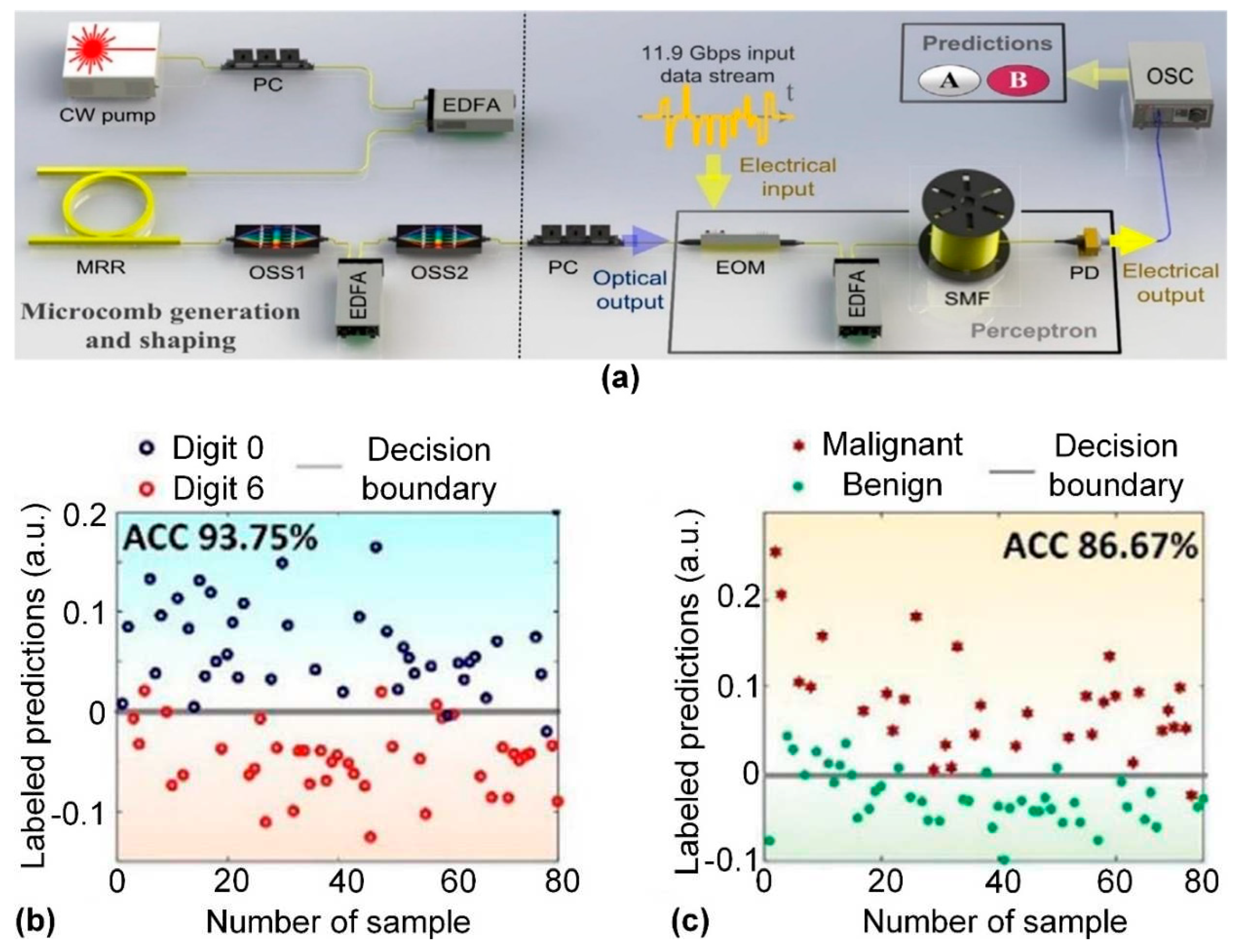

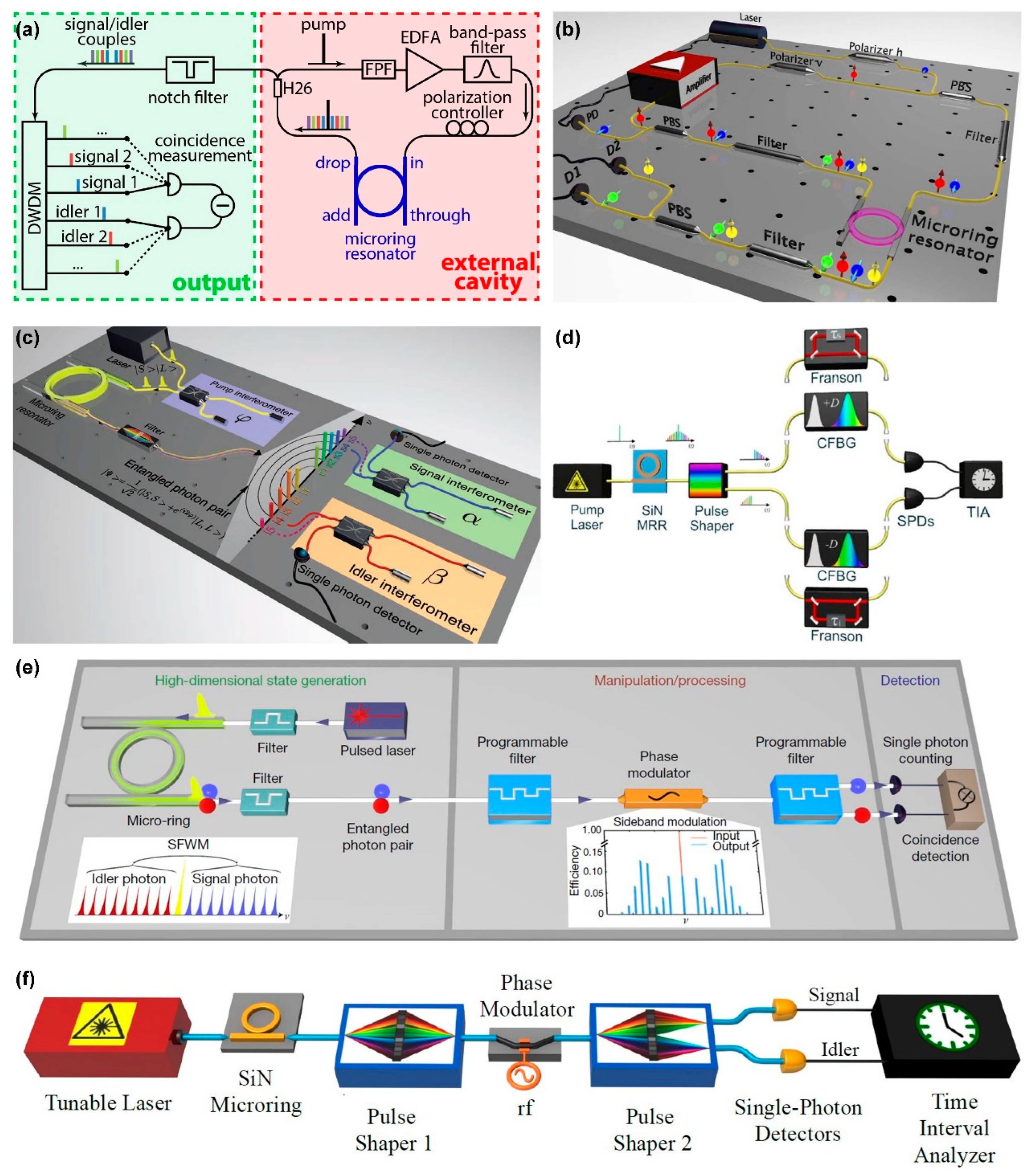
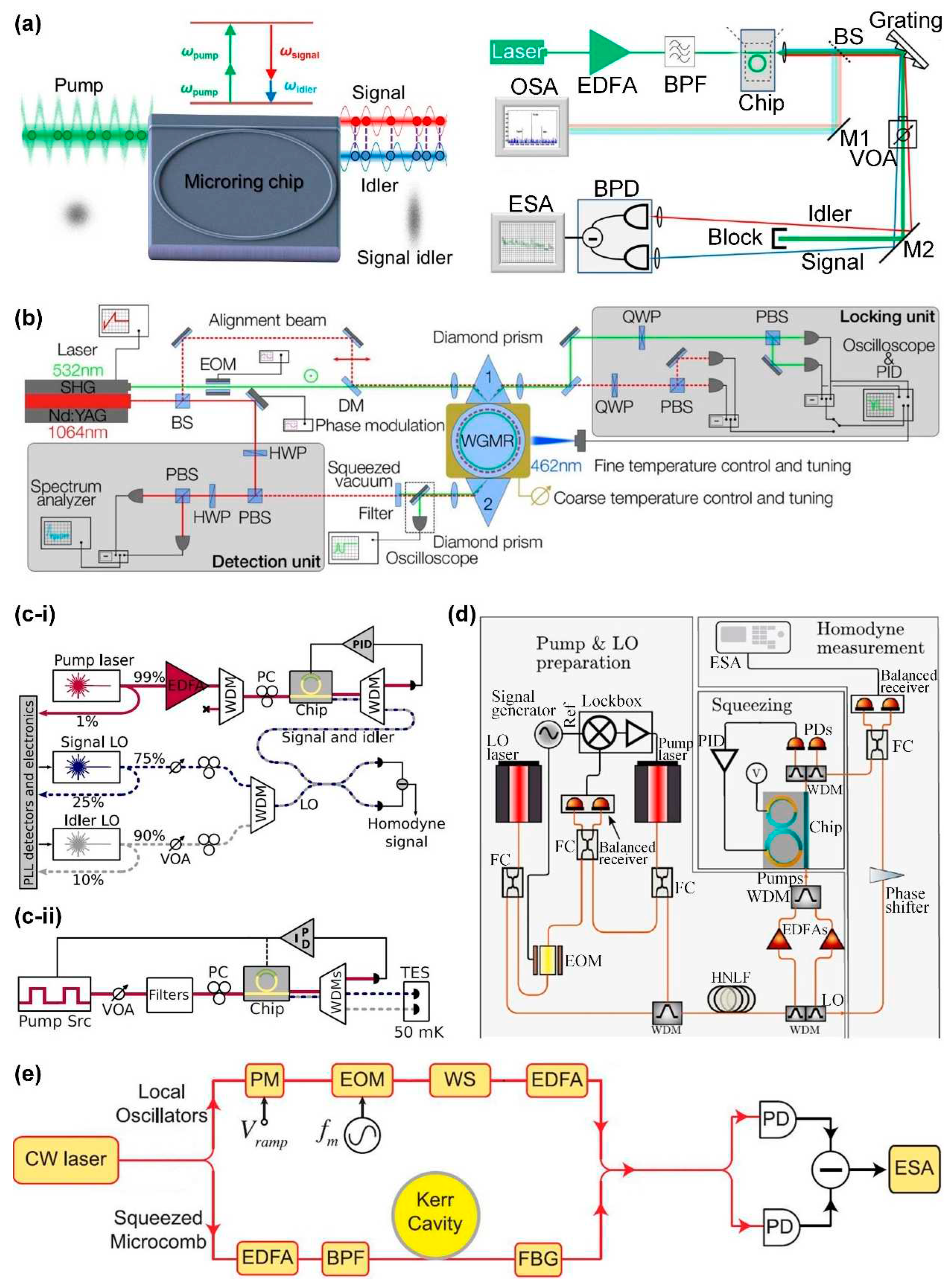
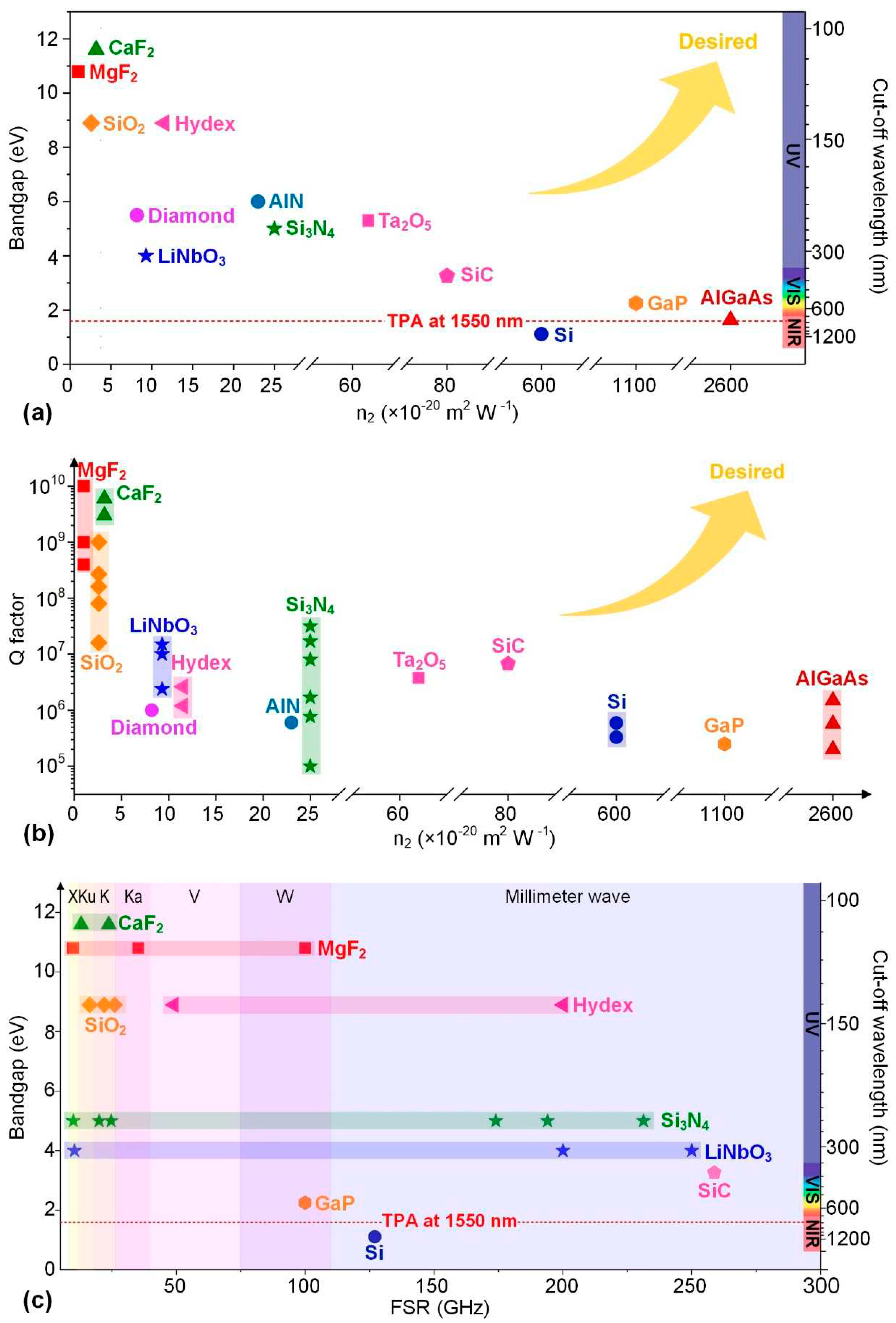
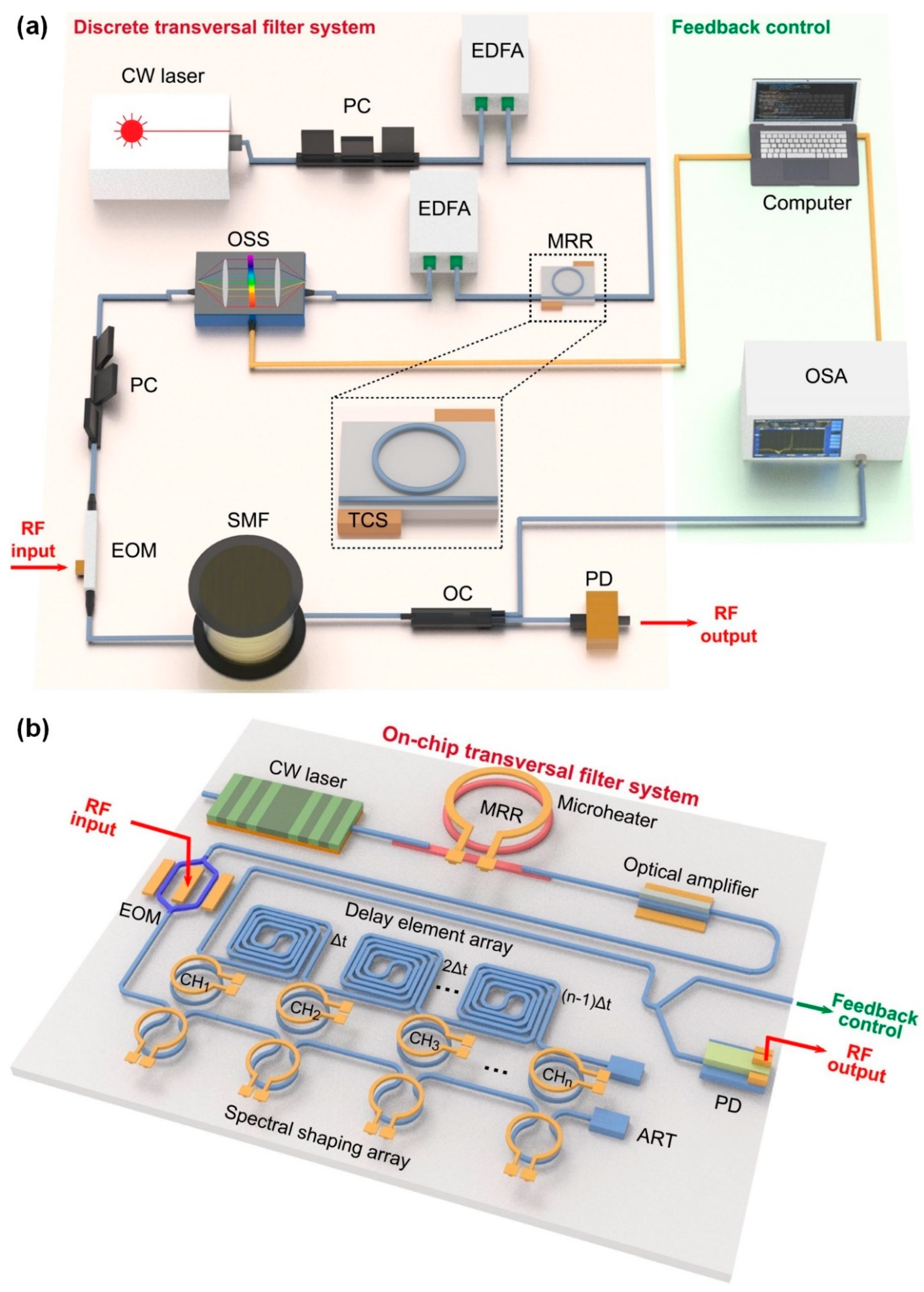
| Resonator Structure |
Q factor |
Repetition rate (GHz) | On-chip integration |
Material platforms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toroid | 108 – 1010 | 101 – 102 | No | SiO2 [10,63,109,141], MgF2 [72,73,74], CaF2 [75,76] |
| Wedge | 108 | 100 – 101 | Yes | SiO2 [47,142,143,144] |
| Ridge | 108 | 101 | Yes | SiO2 [138] |
| Sphere | 107 | 102 | No | SiO2 [70] |
| Disk | 106 – 108 | 100 – 102 | Yes | SiO2 [21,51,60], SiC [90] |
| Rod | 108 – 109 | 101 – 102 | No | SiO2 [71,145,146], MgF2 [22,23,24,147] |
| Single ring | 105 –107 | 101 – 103 | Yes | Si3N4 [26,55,89,104,114,135,139,140,150,152], Hydex [56,68,83,112], Si [148], LiNbO3 [93,95,108], AlGaAs [33,88], AlN [98,113], Diamond [85], GaP [92], Ta2O5 [91] |
| Multiple rings | 105 – 106 | 102 | Yes | Si3N4 [149,150,151] |
| Soliton classes | Characteristics | Dispersion | Platform | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright solitons | Generated by using a red-detuned pump to excite a microresonator with anomalous dispersion. | Anomalous | MgF2 Si3N4 SiO2 Hydex AlN AlGaAs Si |
[65] [110,159] [109,160] [106,161] [113,162] [88] [80] |
| Dark solitons | Generated by using a blue-detuned pump to excite a microresonator with normal dispersion. | Normal | Si3N4 | [43,99] |
| Breather solitons | Generated in presence of dynamical instabilities, where bright or dark solitons experience periodic variation in amplitude and duration. | Both | Si3N4 MgF2 Si |
[163,164,165] [164] [163] |
| Dirac solitons | Generated by engineering dispersion induced by nonlinear coupling between TE and TM modes on the basis of DKS. | Both | SiO2 | [166] |
| Stokes solitons | Generated through Kerr-effect trapping and Raman amplification created by initially formed DKS. | Anomalous | SiO2 | [167] |
| Brillouin-Kerr solitons | Generated by using a blue-detuned pump to excite red-detuned Brillouin lasing in a microresonator. | Anomalous (Brillouin mode) | SiO2 | [168] |
| Soliton crystals | Self-organized ensembles of multiple co-propagating solitons with a crystal-like profile in the angular domain. | Anomalous | SiO2 Si3N4 Hydex LiNbO3 |
[102] [103,169] [105,112,170] [94,108] |
| Soliton molecules | Bound states of solitons are achieved when there is a balance between attractive and repulsive effects. | Anomalous | MgF2 | [171] |
| Laser cavity solitons | Generated based on filter-driven four-wave mixing in a gain fiber loop with a nested microresonator. | Anomalous | Hydex | [106] |
| Mechanisms | Methods | Year a) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency scanning | Sweeping the pump from blue to the red-detuned regime before the microresonator is heated up by the thermo-optic effect. | 2007 | SiO2 [10], MgF2 [65], Si3N4 [179], AlN [180] |
| Two-colour pumping | Using two pumps at different wavelengths to generate microcombs based on cascaded FWM. | 2009 | MgF2 [185,186], Hydex [187] |
| Filter-driven FWM |
Embedding a four-port MRR in a gain fiber laser loop to generate LCS microcombs based on passive laser mode locking. | 2012 | Hydex [106,176] |
| EO modulation | Stabilizing a microcomb by locking the comb spacing to the spacing of EO modulated pump sidebands. | 2012 | SiO2 [97,188,189] |
| Self-injection locking | Locking a microcomb by narrowing the pump linewidth via the self-injection locking effect and keeping light within the resonance. | 2014 | MgF2 [74,191] |
| Power kicking | Stabilizing the pump in short soliton steps by using modulators to accurately control the pump power and timing sequence. | 2015 | Si3N4 [182,183], SiO2 [181] |
| Integrated heaters | Using integrated heaters to assist mode selection, control of mode interactions, or passive thermal locking in microcomb generation. | 2015 | Si3N4 [99,149,193] |
| Self-referencing | Stabilizing a microcomb based on phase locking of the carrier-envelope offset frequency via self-referencing. | 2016 | SiO2 [194], Si3N4 [195], AlN [196] |
| Forward and backward tuning | First sweeping the pump forward and then backward at a slow speed to generate deterministic single soliton microcombs. | 2017 | MgF2 [184], Si3N4 [184] |
| Auxiliary laser | Using an auxiliary laser located at blue-detuned regime to compensate the decrease of intracavity heat during the generation of soliton microcombs. | 2019 | Si3N4 [159], SiO2 [141,145], Hydex [202] |
| Cryogenic cooling | Stabilizing a microcomb by cryogenic cooling the microresonator to quench the thermorefractive effects. | 2020 | AlGaAs [88] |
| Piezoelectric control | Using integrated actuators to achieve a large actuation bandwidth and realize rapid and dynamic pump tuning. | 2020 | Si3N4 [198] |
| Turnkey operation |
Achieving turnkey mode locking of a microcomb by exploiting backscattered light from the microresonator to the pump laser cavity. | 2020 | Si3N4 [110] |
| Pulse pump | Using optical pulses as the pump for microcomb generation to reduce the power consumption and improve the conversion efficiency. | 2021 | MgF2 [147], Si3N4 [147,199] |
| Self-starting oscillation | Generating robust self-emergence microcombs in a microresonator-filtered fiber laser system by tailoring the slow nonlinearities in such system. | 2022 | Hydex [192] |
| Resonator for generating microcombs | Frequency range | Phase noise (dBc/Hz) a) |
Allan deviation b) | Year | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 microdisk resonator | 2.6 ‒ 220 GHz | -113 at 104 Hz | ‒ | 2012 | [20] |
| MgF2 WGM resonator | ~9.9 GHz | -170 at 107 Hz | ~10−11 | 2015 | [191] |
| MgF2 WGM resonator | 6 GHz, 12 GHz, 18 GHz, 24 GHz, 30 GHz, and 36 GHz | <-100 at 104 Hz | ‒ | 2016 | [211] |
| Si3N4 MRR and SiO2 microdisk resonator |
4 THz around 1550 nm | ‒ | 9.2 × 10−14 | 2018 | [21] |
| MgF2 crystalline resonator | ~14 GHz | -130 at 104 Hz | ~10−12 | 2019 | [22] |
| MgF2 crystalline resonator | ~14 GHz | <-135 at 104 Hz | ‒ | 2020 | [23] |
| MgF2 crystalline resonator Si3N4 MRR |
4.7 GHz, 7.05 GHz, 6.73 GHz, 10.09 GHz, 16.82 GHz |
<-115 at 103 Hz <-60 at 103 Hz |
~10−11 | 2020 | [24] |
| Si3N4 MRRs | ~10 GHz ~20 GHz |
-110 at 104 Hz | ~10−8 | 2020 | [26] |
| Hydex MRR | 8.9 ‒ 25.9 GHz | -70 at 104 Hz | ‒ | 2020 | [25] |
| Si3N4 MRR | ~100 GHz | <-60 at 104 Hz | ~10−7 | 2021 | [27] |
| Si3N4 MRR | ~300 GHz | -100 at 104 Hz | 2 × 10−11 | 2021 | [28] |
| SiO2 wedge resonator | ~22 GHz | -110 at 103 Hz -88 at 102 Hz |
~10−13 | 2022 | [144] |
| SiO2 microrod resonator | 11.4 GHz | -107 at 103 Hz -133 at 104 Hz |
‒ | 2022 | [146] |
| Functions | CS (GHz) | No. of WC | Operation bandwidth or processing speed |
RMSE | Year | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Integral-order Hilbert transform | ~200 | 20 | 0.3 − 16.9 GHz | ‒ | 2015 | [34] |
| Integral-order differentiation |
~200 | 8 | ~8.5 GHz | ~7.24% | 2017 | [224] |
| Square root differentiation | ~200 | 7 | ~8.5 GHz | ~4.02% | 2018 | [83] |
| Fractional-order Hilbert transform | ~49 | 17 | 0.48 − 16.45 GHz | ~2.92% | 2019 | [35] |
| Fractional-order differentiation | ~49 | 27 | ~15.49 GHz | ‒ | 2020 | [37] |
| Integration | ~49 | 81 | ~11.9 GHz | ‒ | 2020 | [38] |
| Phase-encoding | ~49 | 60 | ~6 Gbit/s d) | ‒ | 2020 | [40] |
| Arbitrary waveform generation | ~49 | 81 | ~5.6 GHz | ‒ | 2020 | [39] |
| Arbitrary waveform generation | ~100 a) | 21 b) | < 4 GHz c) | ‒ | 2022 | [225] |
| No. of WCs | Microcomb characteristic |
MF | Maximum data rate |
Maximum SE | TD | BER | Year | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | A low-noise comb |
16-QAM | 1.44 Tbit/s |
6 bits/s/Hz |
300 km |
7.5×10-4 | 2014 | [41] |
| 179 | Two single soliton combs |
16-QAM | 55.0 Tbit/s |
5.2 bits/s/Hz |
75 km |
6.7×10-5 | 2017 | [42] |
| 20 | A mode-locked dark-pulse comb |
64-QAM | 4.4 Tbit/s |
‒ | 80 km |
2.5×10-3 | 2018 | [43] |
| 80 | A soliton crystal comb |
64-QAM | 44.2 Tbit/s |
10.4 bits/s/Hz | 76.6 km | 2.6×10-2 | 2020 | [44] |
| 52 | A single soliton comb |
256-QAM | 12 Tbit/s |
10.4 bits/s/Hz |
82 km |
~10-2 | 2021 | [251] |
| 52 | A single soliton comb |
16-QAM | 8 Tbit/s |
6.7 bits/s/Hz |
2100 km |
~10-2 | 2021 | [251] |
| 20 | Two single soliton combs | 16-QAM | 1.68 Tbit/s |
‒ | 50 km |
~10-4 | 2022 | [252] |
| 145 | A single soliton comb |
NRZ | 1.45 Tbit/s |
1 bits/s/Hz |
40 km |
< 10-9 | 2022 | [45] |
| 20 | A dark soliton microcomb | PAM4 | 2 Tbit/s |
‒ | 2 km |
~10-2 | 2022 | [33] |
| Dual-comb spectroscopy | Microresonators | CS (GHz) |
Wavelengths range (nm) |
Spectral resolution (GHz) | Acquisition time (µs) |
Year | Refs. | |
| Two silica microdisk resonators | ~22 | 1538 – 1562 | ~22 | ~20 | 2016 | [60] | ||
| Two Si3N4 MRRs | ~450 | near 1561 | ~450 | ~20 | 2018 | [260] | ||
| Two silicon MRRs | ~127 | 2900 – 3100 | ~127 | ~2 | 2018 | [148] | ||
| A silica wedge resonator | ~22 | Near 3300 | ~1.4 | ‒ | 2020 | [261] | ||
| A silica wedge resonator | ~22 | Near 3300 | ~1.4 | ~2 × 105 | 2021 | [265] | ||
| Ranging | Microresonators | CS (GHz) |
Wavelength range (nm) | Spatial resolution (µm) |
Acquisition time (µs) |
Year | Refs. | |
| Two Si3N4 MRRs | ~100 | 1529 – 1620 | ~2 | ~0.01 | 2018 | [46] | ||
| A silica wedge resonator | ~9.36 | 1530 – 1570 | ~0.2 | ~176 | 2018 | [47] | ||
| A Si3N4 MRR | ~99 | 1550 – 1630 | ~1 × 104 | ‒ | 2020 | [48] | ||
| A Hydex MRR | ~48.97 | 1530 – 1595 | ~0.028 | ~28 | 2020 | [49] | ||
| A tapered Si3N4 MRR | ~88.5 | 1575 – 1615 | ~0.003 | ‒ | 2021 | [266] | ||
| Astrocombs | Microresonators | CS (GHz) |
Wavelength range (nm) | Calibration precision (m/s) | Instability (mHz) |
Year | Refs. | |
| A silica disk resonator | ~20 | 1530 – 1580 | ~3.4 | ~10 at 103 s |
2019 | [51] | ||
| A Si3N4 MRR | ~23.7 | 1486 – 1685 | ~0.25 | ~1000 at 1 s |
2019 | [50] | ||
| Frequency measurements | Microresonators | CS (GHz) |
Wavelength range (nm) | Parameters and values |
Precision (GHz) |
Year | Refs. | |
| A silica disk resonator | ~15 | 700 – 2100 | Freq. drift 180 mHz/s |
‒ | 2018 | [267] | ||
| A silica wedge resonator | ~22 | 1545 – 1560 | Optical freq. ~192.79 THz |
~0.0025 | 2019 | [143] | ||
| Two Si3N4 MRRs | ~197 ~216 |
1430 – 1660 | Microwave freq. ~197 GHz |
~0.995 | 2020 | [268] | ||
| A Hydex MRR | ~49 | 1500 – 1620 | freq. spectrum 200 – 2400 GHz |
0.075 | 2021 | [269] | ||
| Spectrum channelizers | Microresonators | CS (GHz) |
Wavelength range (nm) | Slice resolution (GHz) |
Channel numbers | Year | Refs. | |
| Two Hydex MRRs | ~200 | 1535 – 1565 | ~1.04 | 20 | 2018 | [270] | ||
| Two Hydex MRRs | ~49 | 1535 – 1570 | ~0.12 | 92 | 2020 | [271] | ||
| Photonic hardware |
Input data dimension | Computing speed (OPS a)) | Scalability & reconfigurability b) | Integrated components | Year | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle-sensitive pixels | 2.3 × 106 | ‒ | Level 1 | ASP image sensor | 2016 | [304] |
| Mach-Zenhder interferometer arrays | 4 | CW c) | Level 2 | Weight & sum circuits | 2017 | [299] |
| Diffractive optical surfaces | 784 | CW | Level 2 | None | 2018 | [305] |
| Digital micromirrors | 2 × 106 | 1000 d) | Level 2 | None | 2020 | [306] |
| Spatial light modulators | 65536 | CW | Level 2 | None | 2021 | [307] |
| Optical microcombs | 16 | ~4 trillions | Level 2 | Light source, and weight & sum circuits | 2021 | [55] |
| Optical microcombs | 2.5 × 105 | ~11.3 trillions | Level 3 | Light source | 2021 | [56] |
| Microresonator | Pump power (mW) | Measured NR (dB) |
Squeezing after loss correction(dB) |
Year | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si3N4 MRR | 90 | 1.7 | 5 | 2015 | [326] |
| LiNbO3 WGMR | 0.3 | 1.4 | − | 2019 | [327] |
| Si3N4 MRRs | 48 at ~1543 nm 54 at ~1559 nm |
1.34 | 3.09 | 2020 | [325] |
| Si3N4 MRR | 104.9 | 1.0 a) 1.5 b) |
4 c) 7 d) |
2020 | [328] |
| Si3N4 MRRs | 70 | 1.65 | 8 | 2021 | [329] |
| SiO2 wedge resonator | 120 | 1.6 | 3.1 | 2021 | [330] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




