1. Introduction
The main public health rationale for the worldwide Covid-19 vaccination in 2021 was to reduce the largescale mortality that had been attributed to widespread infection by the novel coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2, beginning in the spring of 2020. The central research question to be answered in this paper is whether the Covid-19 vaccinations are saving more lives from Covid-19 infection, or whether these vaccinations are causing excess deaths due to lethal adverse events following the inoculation. In theory, Covid-19 vaccination should markedly reduce the number of Covid-19-related deaths in comparison to Covid-19-related deaths among the unvaccinated. Indeed, theoretical research published in 2021 estimated that Covid-19 vaccination will reduce the mortality rate [
1]. The public health argument for ongoing vaccinations is based largely on this assertion.
Soon after the vaccination campaign began, however, many medical professionals argued that infection by the coronavirus would provide sufficient natural immunity to afford sufficient protection against subsequent infectious disease in the form of Covid-19. Gazid and colleagues demonstrated that natural infection by SARS-CoV-2 confers antiviral adaptive immunity superior to that afforded by Covid-19 vaccination [
2]. Furthermore, the health care workers expressed a logical, evidence-informed concern that the Covid-19 vaccination, which was being mandated for hospital personnel in many countries, might lead to adverse outcomes for individuals previously infected by SARS-CoV-2. These concerns can be traced back to as early as 2012, when laboratory mice developed severe pulmonary immunopathology after being vaccinated and then exposed to the SARS coronavirus [
3]. A decade later, other mouse data linked the mRNA lipid nanoparticle-based Covid-19 vaccine platform to the phenomena of adaptive immune cell exhaustion and non-responsiveness, both secondary to the chronic stimulation of immune-inflammatory pathways [
4].
Well-designed human studies to address the question of a combined impact of coronavirus infection and subsequent Covid-19 vaccination are lacking. However, a recent study by Otto and colleagues concluded that Covid-19 infection can cause severe disease and death in vaccine recipients, particularly in older adults and those with comorbidities [
5]. Given the fact that SARS-CoV-2 viral variants are highly transmissible and have already infected the majority of the populations in westernized countries, such concerns regarding the combined impact of natural infection and subsequent vaccinations could have serious public health implications, particularly in light of ongoing Covid-19 booster campaigns worldwide.
Analyses of the clinical trial risks of vaccine-associated adverse effects provides additional support for an undesirable impact on mortality. In a secondary analysis of serious adverse events (SAEs) reported in the placebo-controlled, phase III randomized clinical trials of the mRNA Covid-19 vaccines, the authors found a 36% higher risk of SAEs in the Pfizer vaccine group versus the placebo, with 18 additional SAEs per 10,000 vaccinated [
6]
. The SAEs included death and various life-threatening conditions, notably
ischemic stroke, brain hemorrhage, and acute coronary syndrome. Notably, for both the Pfizer and Moderna clinical trials, the excess risk of SAEs was two to four times higher than the risk reduction for Covid-19 hospitalization. Most of these SAEs are relatively common events, such as. Given the short follow-up observation periods for these trials, these risk estimates may be considered conservative.
Given these findings and concerns, it seems imperative that the medical-scientific community devotes more attention to assessing the mortality risks resulting from the impact of Covid-19 vaccination in populations with prior or concurrent SARS-CoV-2 infection based on a positive PCR test result. Estimations of the number of Covid-19 deaths are, from an epidemiological perspective, relatively straightforward and unhampered by the complications of morbidity estimates. With population-wide mortality as an outcome, there are no major confounders or “hidden variables” that could influence the results because, in free-living populations exposed to SARS-CoV-2 and occupying similar geographic regions, vaccinated and unvaccinated persons are living under the same general conditions, with the same sets of risk factors evenly distributed. Vaccinated and non-vaccinated persons in a given region are consuming similar diets and exposed to other similar environmental variables, notably air and water.
Differences in the distribution of SARS-CoV-2 infection between those who have been vaccinated and those who have not been vaccinated are negligible [
7]. Moreover, Covid-19 is spreading at a similar rate between unvaccinated and vaccinated: the apparent impact of vaccination on community transmission of circulating variants of the coronavirus was not significantly different from the impact among unvaccinated people [
8]. For these reasons, population-wide data on vaccination status for individuals of different age groups and living in the same geographic region should be able to provide meaningful data on the mortality-related effects of the vaccines in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These epidemiological considerations enable us to perform a rigorous analysis of the impact of largescale Covid-19 vaccination on the mortality rate of vaccinated versus non-vaccinated groups.
2. Analysis and Results
For the purposes of the analysis, people who are living in a given region (county, state or country) may be designated as “alive”. In this group, we can further delineate “vaccinated” from “unvaccinated” persons. As people are dying within a given timeframe, we can then also estimate total deaths and include subsets based on vaccination status.
Therefore, to assess the impact of vaccination on the mortality rate, we employ the following equation:
We calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated as follows:
The proportional number for a given time period should always be larger than the statistical estimate of dead vaccinated, the product obtained from the calculation. In this case, vaccines are saving lives. If the proportional number is smaller than the statistical number, however, vaccines are increasing the death rate. This calculation should be done for each month of the year 2021 for five age groups: up to 20 years, from ages 20 to 40, from ages 40 to 60, from ages 60 to 80, and above age 80. In this way, the statistical problem known as the Simpson Effect (or Yule-Simpson Paradox, whereby an association between two variables in a population emerges, disappears or reverses when the population is divided into subpopulations) is excluded.
For the rigorous mathematical evaluation of Covid-19 vaccine efficacy, a recent BMJ editorial advocates the use of row data [
9]. We can calculate the exact impact on the entire population in a given country and worldwide by utilizing data on how many deaths occurred in a given four-week period have been at least once vaccinated (referred to by some authors as “ever vaccinated”). This would allow calculating the proportional number of “dead vaccinated” and comparing it with the actual statistical calculation of number of dead vaccinated people.
Corporations and governmental agencies have provided useful data for this purpose. For each company or governmental agency, we can calculate the effectiveness of the Covid-19 vaccination by comparing the days of work with the sick status days in percentage in a given month or year as follows:
For a given company, we can easily see which percentage of sick days is higher. Let’s imagine we have a company with 100 employees, 50% of whom are vaccinated, and 50% of whom are not vaccinated. Vaccinated workers are protected from Covid-19, and should have a much smaller percentage of sick days than nonvaccinated workers. According to the Covid-19 vaccination doctrine percentage of sick days should be much smaller in the vaccinated group of people than in the non-vaccinated group of people.
It should be noted that neonatal mortality has emerged as another factor contributing to changes in population mortality rate. In Slovenia and worldwide, we observe highly increased rates of neonatal mortality in 2022 compared to the previous years. The first check that should be done in this context is the possible influence of Covid-19 vaccination. The number of neonatal deaths
is the sum of the following numbers:
where
is the number of neonatal deaths where both parents are each three times vaccinated, where
is the number of neonatal deaths where one parent is three times vaccinated, and another parent is two times vaccinated (and so on), where
is the number of neonatal deaths where both parents have not been vaccinated. Using this model, we could see possible relations with the Covid-19 vaccination. EMA, VAERS, and the Yellow card reports on high numbers of vaccines’ side effects [
10,
11,
12] are alarming bells for detailed analysis proposed in this article.
The proposed statistical analysis presented in this paper can verify the theoretical study of how many lives were saved by the vaccines in a particular country not only for ages above 60 but for the entire population.
2.1. Calculations of the death rate of the infected vaccinated group and infected non-vaccinated group using official data of the UK HEALTH SECURITY AGENCY
In the calculations, we compare the sample
of the entire population with the sample
in the dead group of persons.
Formula (1) is valid for statistics involving large sample sizes and provides precise results. As medical authorities are hiding the vaccination status of most dead persons
, this is not feasible at this time. We can, however, obtain official data in England about the infected dead group
and write following equation:
The problem is that for non-infected vaccinated dead
, we have no data because medical authorities are not allowing public access to information on vaccination status of dead persons. Let us suppose the group of infected vaccinated people
is dying at a rate similar to that of the group of non-infected vaccinated people
, suggesting that the vaccines are equally protective for both groups (this is reasonable given the claims of 94% and 95% vaccine effectiveness, based on relative risk estimates from Moderna and Pfizer, respectively). We can therefore write the following equation:
Out of (8) follows equation:
In population statistics for England, we obtained data for the number of infected vaccinated dead and data of infected dead . Using equation (9), we calculated the proportional number of infected vaccinated dead and compared it with the statistical number of actual infected vaccinated dead. Thus, we obtained the decreased or increased mortality rate (percentage) associated with or likely attributed to vaccination. The proportional number is the number indicating no impact of vaccination on the death rate. When 10% of the population is vaccinated in the group of SARS-CoV-2-infected dead persons , 10% will be vaccinated. When 20% of the population is vaccinated in the group of SARS-CoV-2 infected dead persons , 20% will be vaccinated, and so on. When 100% of the population is vaccinated in the group of SARS-CoV-2 infected dead persons , 100% will be vaccinated.
Now we will compare the numbers of SARS-CoV-2 infected vaccinated dead persons in official statistics with the SARS-CoV-2 infected vaccinated deaths proportional number
. The statistical number of SARS-CoV-2 infected vaccinated dead persons must be lower than the proportional number
In that case, vaccines would be saving people’s lives. We can then calculate how many SARS-CoV-2 infected persons have been saved from death with vaccination for a given 4-week period, using the following equation:
In this case, the statistical number of SARS-CoV-2 infected vaccinated dead is bigger than the proportional number
, and therefore vaccination has a negative impact on mortality rate. In other words, the vaccination is stealing more lives than it saves, i.e., more people have died prematurely because of getting vaccinated than would have occurred had they chosen not to get vaccinated:
Figure 1.
Comparing proportional number with statistical number.
Figure 1.
Comparing proportional number with statistical number.
The impact of the Covid-19 virus on the death rate in group and in group is the same. The impact of vaccination on the death rate is calculated below.
2.2. The calculation for weeks 35-38 in year 2021
A “vaccinated” person in this calculation is the person that was vaccinated with the first dose or more. Let’s calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated in England between weeks 35 and 38. In this timeframe, there were 3165 Covid-19 deaths in the United Kingdom; 2448 of those persons had been vaccinated [
13]. We see that the percentage of vaccinated UK people with one dose in this period is 65.1%. In 2021 the population of the United Kingdom was 56,191,000 people. 65.1% of the entire population is 36,580,300 people.
Officially declared vaccinated Covid dead persons between 35 and 38 weeks are 2448.
This means that 2448 - 2060 = 388 persons had prematurely passed away due to the vaccination in the period of week 35 - 38.
2.3. The calculation for weeks 39 - 42, 2021
Let’s calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated in England between weeks 39 and 42. In this period there were 2772 covid deaths in the UK. 2270 of them have been vaccinated [
13]. We see that the percentage of vaccinated people in the UK with one dose in this period is 66.1% [
13]. The population of the UK was 56.191.000 people in 2021. 66.1% of the entire population is 37.142.200 people.
Officially declared vaccinated covid dead persons between 39 and 42 weeks are 2270.
This means that 2270 - 1832 = 438 persons had prematurely passed away due to the vaccination in the period weeks 39 - 42:
2.4. The calculation for weeks 43-46, 2021
Let’s calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated in England between weeks 43 and 46. In this four-week period, there were 3726 covid deaths in the UK. 2992 of them have been vaccinated [
13]. We see that the number of vaccinated people in England in this period with the first dose is 67.4% [
13]. The population of the UK was 56.191.000 people in 2021. 67.4% of the entire population is 37.872.700 people. We use equation (7) and we get:
Officially declared vaccinated covid dead persons between 43 and 46 weeks are 2992.
This means that 2992 - 2511 = 481 persons had prematurely passed away due to the vaccination in the period weeks 43 - 46:
2.5. The calculation for weeks 47-50, 2021
Let’s calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated in England between weeks 47 and 50. In this period there were 2956 covid deaths in the UK. 2140 of them have been vaccinated [
13]. By 19 December 2021, the overall vaccine uptake in the UK for dose 1 was 68.2%, see page 3 COVID-19 vaccine surveillance report – week 51[
13]. The population of the UK was 56.191.000 people in 2021. 68.2.% of the entire population is 38.322.200 people. We use equation (7) and we get:
Officially declared vaccinated covid dead persons (one dose or more) between 47 and 50 weeks are 2140.
This means that 2140 - 2016 = 124 persons had prematurely passed away due to the vaccination in the period weeks 47 - 50:
2.6. The calculation for weeks 51,2021 – 2,2022
Let’s calculate the proportional number of dead vaccinated in England between weeks 51 2021 and weeks 2 2022. In this period there were 3893 covid deaths in the UK. 2878 of them have been vaccinated. By 16 January 2022, the overall vaccine uptake in England for dose 1 was 68.9%, see page 3 [
13]. The population of the UK was 56.191.000 people in 2021. 68.9.% of the entire population is 38.322.200 people. We use equation (4) and we get:
Officially declared vaccinated covid dead persons (one dose or more) between 52 weeks 2021 and weeks 2 2022 are 2878.
This means that 2878 - 2682 = 196 persons had prematurely passed away due to the vaccination in the period weeks 47 - 50:
Below we have the results of all calculated periods:
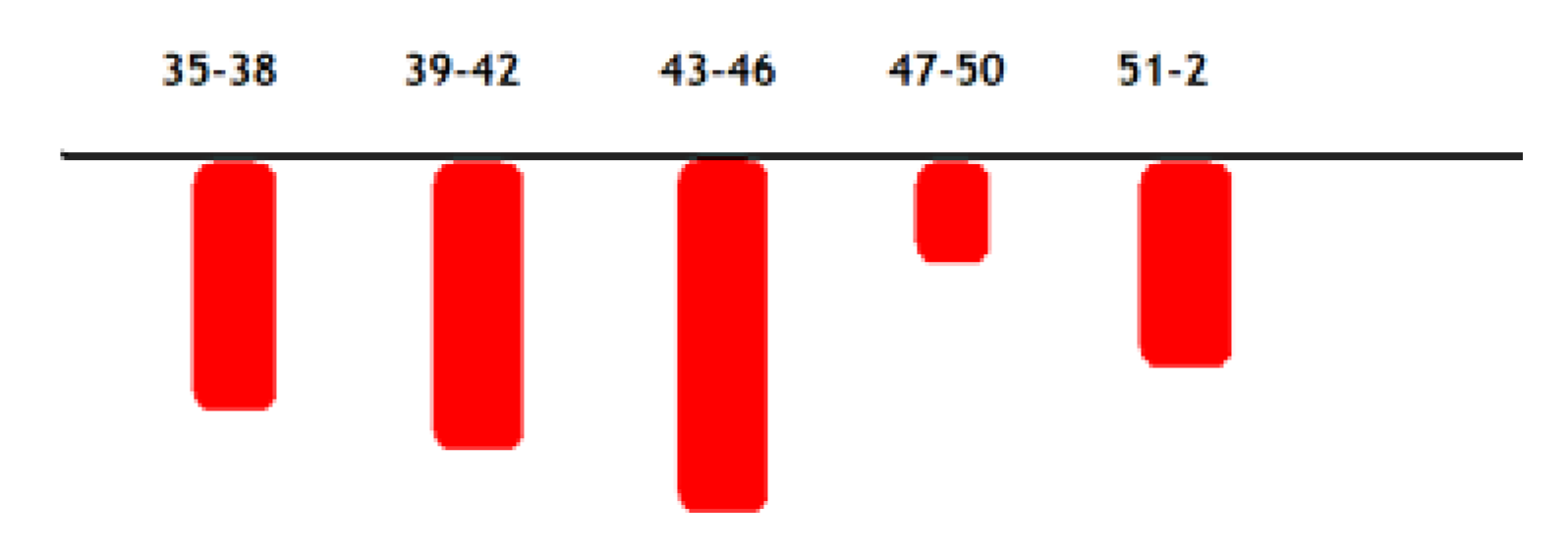
weeks 35-38: total coronavirus-infected deaths are 3165, number of covid infected vaccinated deaths is 2448, number of dead because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 388 which is 15% of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths
weeks 39-42: total coronavirus-infected deaths are 2772, number of covid infected vaccinated deaths is 2270, number of dead because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 438 which is 19% of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths
weeks 43-46: total covid infected deaths are 3726, number of covid infected vaccinated deaths is 2992, number of dead because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 481 which is 16% of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths
weeks 47-50: total coronavirus-infected deaths are 2956, number of covid infected vaccinated deaths is 2140, number of dead because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 124 which is 6% of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths
weeks 51(2021)-2(2022): total coronavirus-infected deaths are 3893, number of covid infected vaccinated deaths is 2878, the number of dead because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 196 which is 7% of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths
In 20 weeks, the total number of deaths among persons who had tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection was 16.505. The total number of the Covid-19 test-positive vaccinated deaths is 12.728. The total number of deaths because of heavy adverse effects caused by vaccination is 1627 persons. This means in the group of Covid-test positive vaccinated deaths which is 12.728 persons, 12.8% have died because of heavy adverse effects. By including all time periods in the calculation, we will have a more comprehensive estimate.
The total number of deaths of the Covid-19 test positive people that died in 20 weeks was 12.728. The total proportional number of vaccinated infected people that died was 11.101. Thus, in the group of test-positive vaccinated deaths, there was a 14.5% higher rate of mortality than in the group of covid positive unvaccinated considering vaccines would not have any influence on the death rate. Our data indicate that infected vaccinated persons have a 14.5% higher probability of dying (ostensibly from prior or concurrent Covid-19 infection, or vaccination, or both) than infected unvaccinated persons.
According to the official narrative, vaccines are saving lives, which means the number of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths statistically recorded should be significantly lower than the proportional calculated number of the coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths. As shown in
Figure 1, our results indicate that the opposite is true. The statistical number of the coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths is significantly higher than the calculated proportional number of coronavirus-infected vaccinated deaths, which means that infected vaccinated people are dying at a higher rate than their infected unvaccinated counterparts, presumably because of adverse effects of the vaccines themselves.
Figure 2.
Obtained results.
Figure 2.
Obtained results.
The proportional numbers
obtained in all five of the 28-day time periods are always smaller than the statistical numbers, see
Figure 2 above. This provides strong proof that vaccines are increasing the death rate. If only in one time period proportional number
would be bigger than statistical number, our analysis would have weak statistical significance. The statistics pertain to a short time span (four weeks, 28 days); therefore the time variables cannot strongly influence the results. In group
and in group
, people could die because of some unknown reasons. Both groups were living under the same living conditions, so some other cause of death would have the same impact on both groups.
3. Discussion
In principle, the gene-based Covid-19 vaccines (mRNA vaccines and adenovirus vector vaccines) were designed to significantly decrease the number of deaths associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection when compared to the number of deaths among infected unvaccinated persons. However, the present analysis points to a net negative benefit in terms of mortality reduction. Based on UK population data at five 28-day intervals in 2021-2022, we found that infected vaccinated persons have a 14.5% higher probability of dying than infected unvaccinated persons.
Our findings are limited in scope but of major statistical relevance. The proposed statistical approach offers a highly reliable estimate of how the Covid-19 vaccination campaign has been impacting the mortality rate for entire populations, apparently adding in a major way to deaths attributed to Covid-19. The relation between the “vaccinated coronavirus-infected deaths” and “non-vaccinated coronavirus-infected deaths” in a short four-week period is a statistically viable measure of the unfavorable impacts of these immunizations on Covid-19 mortality. Based on the rules of statistics, if we were to calculate the relationship between the proportional and real number of vaccinated Covid-19 deaths for all other time periods, we would not expect to see results that contradict the present findings. We are therefore inclined to propose that Covid-19 vaccines are causing lethal adverse effects. It seems reasonable to surmise that such impacts on mortality are not only relevant to England but also to other countries where the vaccines have been adopted on a massive scale.
To widen the scope of this research, we could calculate the mortality impacts on the entire population in England and worldwide. This would require data on how many people who died in a given four-week period have been at least once vaccinated (or ever vaccinated). This would allow calculating the proportional number of “dead vaccinated” and comparing it with the actual statistical number of deaths. Because the proposed calculation might be difficult to understand for medical professionals, here is an example: Let’s imagine that in a given country, in January 2024, we will place a red bracelet on the hands of 30% of the entire population. In every age group, exactly 30% of people will have red bracelet. We follow a number of deaths in the ensuing months and see that exactly 30% dead people in each age group will have a red bracelet. This is how statistics work out when applied to large population sizes. We can imagine that Covid-19 vaccine is a red bracelet and has no impact on the health of the vaccinated person. On this plausible supposition, we calculate a proportional number of deaths. Comparing the proportional number of deaths with the real statistical number of deaths shows us the real impact of vaccination on the population death rate.
Calculation of the impact of Covid-19 vaccination on increased mortality is so straightforward that it could be done by anyone with middle-school mathematics ability who has an interest in assessing and monitoring the mortality impact. Most of the published statistics pertaining to Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness are avoiding this calculation because of immense pressures on the medical profession to hide the disastrous results of the vaccination program; however, it is only a matter of time before the truth is revealed. Human society is evolving rapidly and will not support the unbearable falsehoods concerning how Covid-19 vaccines are impacting human lives.
In this simple effective calculation, the entire population of a given country is divided into five age groups: 0-20 years, 21 to 40 years, 41 to 60 years, 61 to 80 years, and over 80 years. Each age group (total number – TN) consists of two subgroups: vaccinated subgroup (VA) and unvaccinated subgroup (UN):
where
TN stands for all people in a particular group,
VA stands for vaccinated persons and
UN stands for unvaccinated persons. A certain number of people die each month in each age group:
where
D means all dead people in a certain age group,
Dva means dead vaccinated people and
Dun means unvaccinated dead people. Unvaccinated people are not protected from the deadly virus Kovid-19 and therefore should die in greater numbers. The calculation of mortality expressed in percentage in the vaccinated subgroup in a certain age group for each month is calculated as follows:
mortality in percentage of vaccinated subgroup: 100Dva / VA.
The calculation of the mortality in percentage in the unvaccinated subgroup in a certain age group for each month is as follows:
mortality in percentage of unvaccinated subgroup: 100Dun / UN.
For each month, it is possible to accurately calculate the mortality of the vaccinated subgroup in a certain age group and the mortality of the unvaccinated subgroup within a certain age group. Avoiding these calculations is avoiding the fact that Covid-19 vaccination has done major harm to public health worldwide. Carrying out these calculations on a monthly basis and informing the medical community and general public about them is the main obligation of every medical journal. A simple calculation at the end of each monthly report would provide a concise updated analysis of the Covid-19 vaccination impact on the mortality rate for that particular month. Such calculations would reveal the true impact of Covid-19 vaccinations. This must be done immediately in order to preserve the first principle of medicine: “Primum non nocere”.
The results obtained by the present analysis would seem to reinforce the findings of Tojersen and colleagues, who reported that the Covid-19 vaccinations have led to increased death rates among the elderly population [
14,
15]. A report from the insurance company OneAmerica is similarly discouraging, with actuarial data from the latter half of 2021 indicating an unprecedented 40 percent increase in death rates for individuals aged 18 to 64 when compared to the pre-pandemic period [
16]. According to the company’s CEO, this represented the highest mortality rate in the history of insurance records, which entail extensive death data collection annually. Previous largescale catastrophes had increased death rates by no more than 10 percent [
16]. It seems increasingly clear that Covid-19 vaccination programs are not living up to the “safe and effective” terms they had promised to the general public.
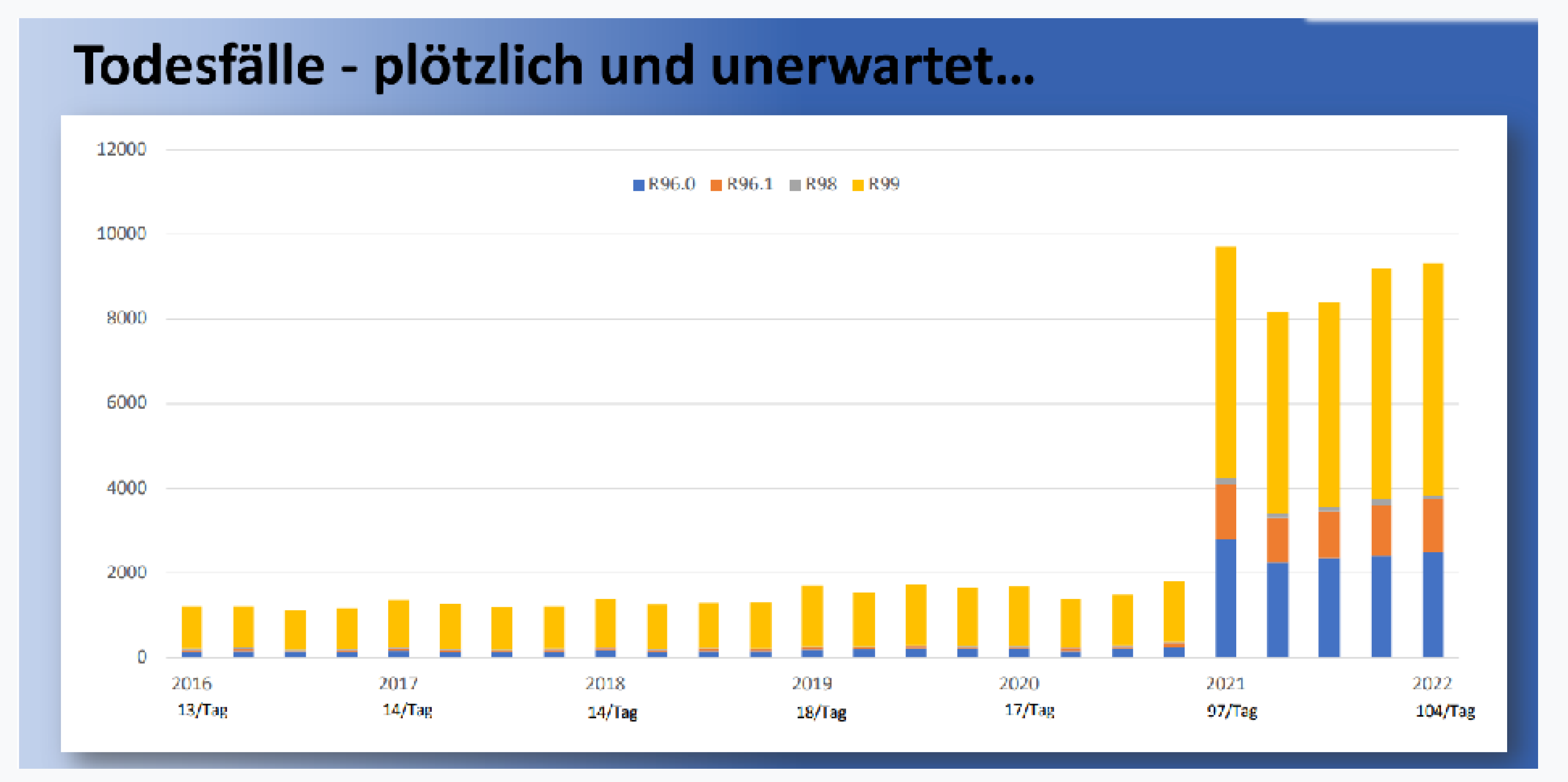
Other concerning data come from German public health authorities showing that “sudden death of unknown cause” increased dramatically in the past two years. In 2021 and 2022, according to official German statistics, approximately 14,800 people died, compared to an annual average of only 1,600 people in the previous five years [
17]. According to analyses from the Paul Ehrlich Institute, these “sudden death of unknown cause” increased by about 560% in 2021 and 2022 over previous years [
18]. These data are sounding off alarms that something went terribly wrong with the public health response to Covid-19.
Figure 3.
Increase of sudden death cause unknown in Germany in 2021 and 2022.
Figure 3.
Increase of sudden death cause unknown in Germany in 2021 and 2022.
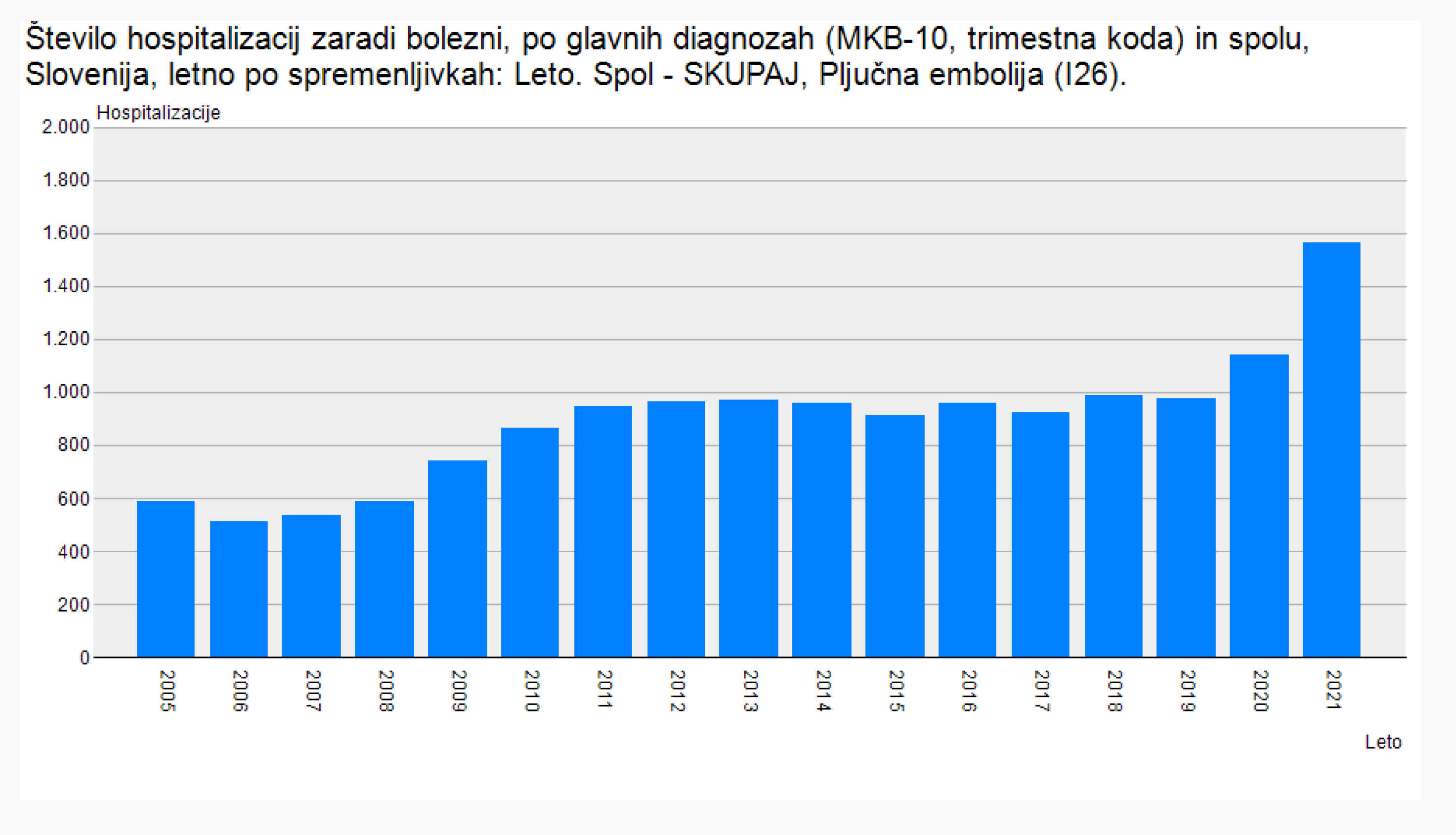
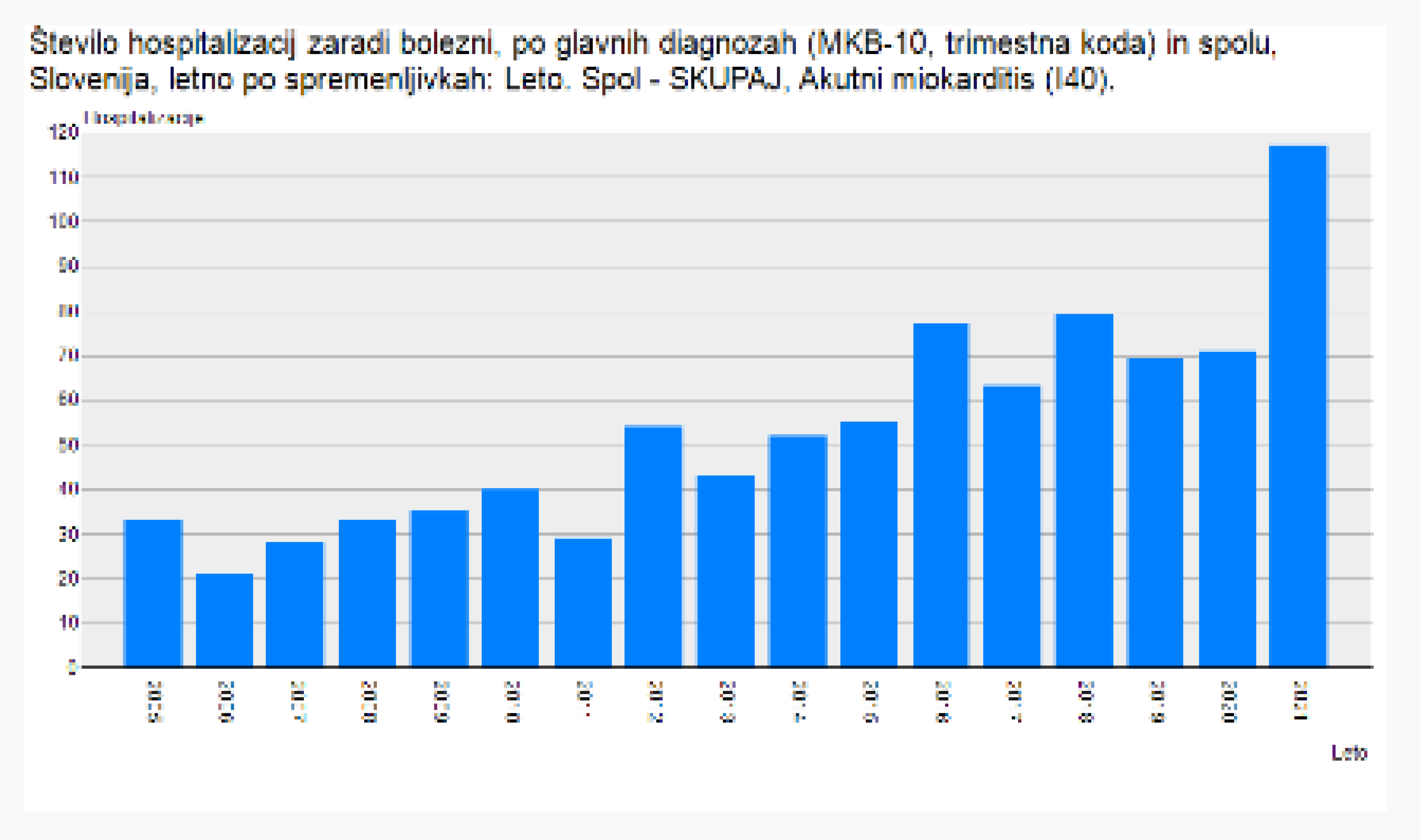
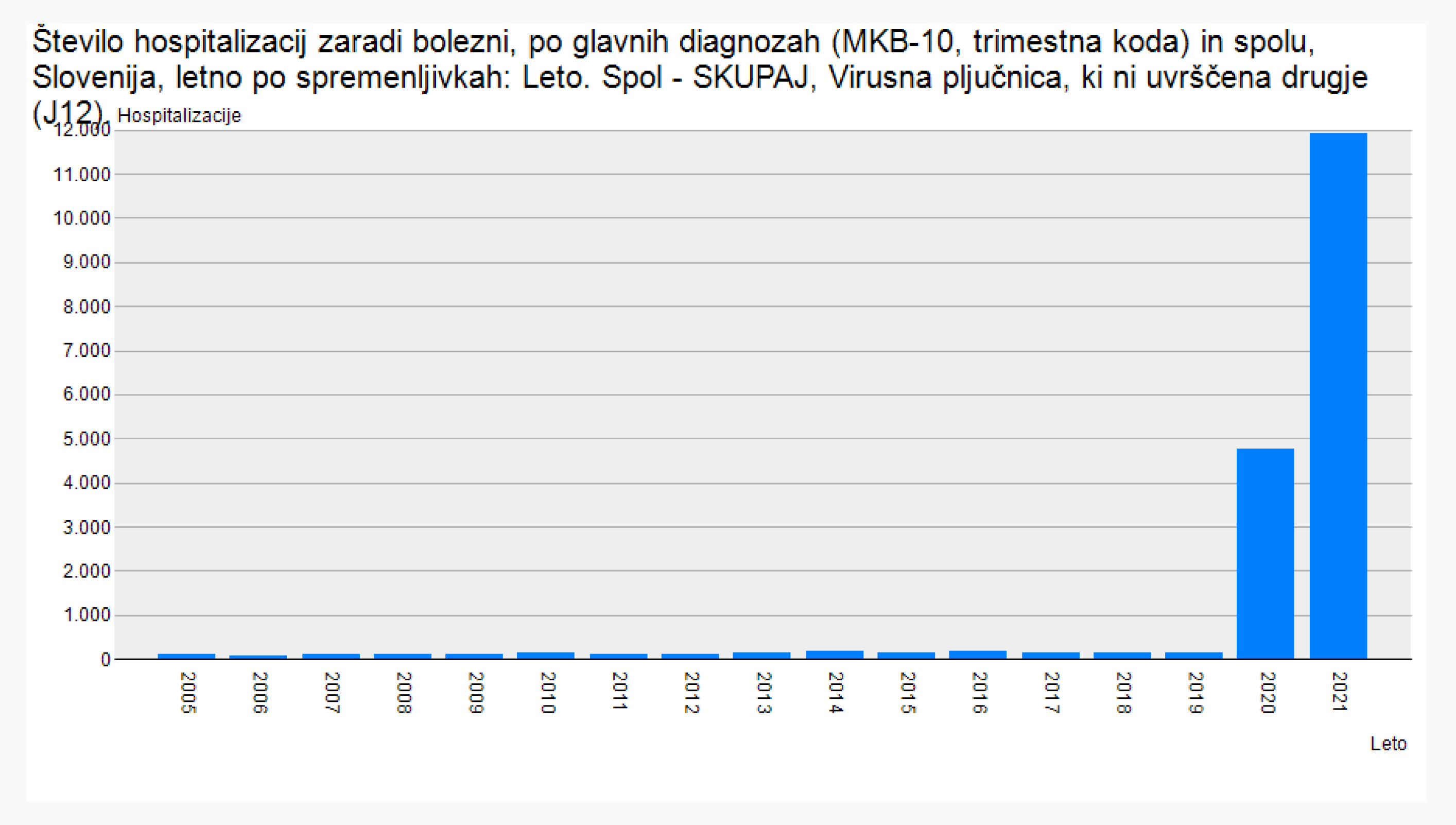
Data from Slovenia’s National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ) are also ringing alarm bell. Pulmonary embolism increased by about 36% from 2021 to 2022. In that same two-year period, chronic myocarditis increased by about 65%, while viral pneumonia increased by about 149% [
19].
Figure 4.
Increase of pulmonary embiolism in 2021.
Figure 4.
Increase of pulmonary embiolism in 2021.
Figure 5.
Increase of chronic myocarditis in 2021.
Figure 5.
Increase of chronic myocarditis in 2021.
Figure 6.
Increase of viral pneumonia in 2021.
Figure 6.
Increase of viral pneumonia in 2021.
The status of the vaccination of these patients is not publicly known, which makes it impossible to calculate the exact impact of Covid-19 vaccination on the increase of these diseases. Despite several calls of researchers from different fields, NIJZ is keeping these data confidential. It is unprecedented that a scientific organization of public health is hiding data that could prove the danger of a given medical treatment. In the lives of people in Slovenia, the only big change of life in 2021 was massive Covid-19 vaccination, so the vaccines represent the most logical candidate for the increased morbidity and mortality. Only when the data become publicly available will we be able to carry out calculations of exact percent of patients that were vaccinated.
4. Conclusion
Covid-19 vaccination policies have been widely adopted on the supposition that Covid-19 vaccination was “safe and effective”, a slogan that was widely circulated, even in the medical literature. This present calculations suggest that, rather than “safe and effective”, Covid-19 vaccination has done irreparable harm to the health and lifespans of billions of people worldwide. Based on calculations performed for each of five 28-day intervals in 2021 and 2022, our results indicate that the mortality of the vaccinated coronavirus-infected groups was 14.5% higher on average than the mortality of non-vaccinated coronavirus-infected groups.
The findings of this analysis warrant an extensive reassessment of UK Health Security Agency data on Covid-19-related mortality and vaccination status for different age groups in England. Every UK county has accurate data on vaccination status, including information on who was vaccinated, how many times they were vaccinated, and who was not vaccinated. As long as the person is alive, vaccination status can be verified. After death, however, vaccination status is usually lost or disregarded, and yet death rate comparisons between the vaccinated and non-vaccinated groups offer us the most reliable evidence for the vaccination's relative impact on mortality. Similarly, it is common practice to hide the vaccination status of sick people, whether the diagnosis is Covid-19 or other illnesses. When a person gets sick and visits his or her doctor, the physician typically will not ask about Covid-19 vaccination status. In this way, the potentially catastrophic impact of Covid-19 vaccination, now and in the future, continues to remain obscure.
How this horrible stain on public health and the medical system has been allowed to persist is a complex question. By the end of 2020, all of the established security measures and scientific standards for public health responsiveness to a pandemic had been subverted. Early treatment protocols using low-cost, effective off-label drugs were banned, thanks to an intensive misinformation campaign orchestrated by the vaccine establishment. Nutritional and lifestyle measures for bolstering antiviral immunity were ignored by the mainstream medical community. In clinical practice, the new rules for treatment and management of Covid-19-related disease were not evidence-based but instead were driven primarily by political and financial interests that have their roots in the medical-pharmaceutical industrial complex. The modern medical system of many westernized countries has forsaken its ethical center, which is best summarized by the ancient Latin dictum of Primum Non Nocere, “First, Do No Harm”. The only way for medical doctors to reclaim the ethos of their once noble profession, and to do so with grace and respect, is to stop acquiescing to corrupt federal agencies and pharmaceutical influence, to take medicine back into their own hands.
Perhaps we can learn from the example set by India, the second largest country in the world. Despite enormous media pressure worldwide declaring that vaccination was the only way to prevent Covid-19 infection, many clinics and hospitals in India endorsed the use of the low-cost anti-parasitic drug Ivermectin, and with excellent results [
20]. This shows that Indian doctors are maintaining a high level of medical ethics, and this has likely saved many lives while preserving the original spirit of “good medicine”. The primary aim of medical care should be to increase health and well-being, not to increase illness so that more drugs can be sold. For the last two decades, the use of pharmaceuticals has increased drastically all over the world. This is not a coincidence; it is the Big Pharma business plan. Because healthy human beings with competent immune systems are not customers for this gargantuan industry, they represent an obstacle to the industry’s progress. This is where medicine must fight to reclaim its independence, by asserting that its purpose is (1) to promote health, (2) to prevent disease, and (3) to cure of disease, in that order. In India, this original purpose of medicine is still alive and well.
References
- Meslé MM, Brown J, Mook P, Hagan J, Pastore R, Bundle N, Spiteri G, et al. Estimated number of deaths directly averted in people 60 years and older as a result of COVID-19 vaccination in the WHO European Region, December 2020 to November 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021 Nov;26(47):2101021. [CrossRef]
- Gazid S, Shlezinger R, Perez G, Lotan R, Peretz A, Ben-Tov A, Cohen D, et al. Comparing SARS-CoV-2 natural immunity to vaccine-induced immunity: reinfections versus breakthrough infections, August 25, 2021. Medvix Preprint. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.08.24.21262415v1.full.pdf.
- Tseng CT, Sbrana E, Iwata-Yoshikawa N, Newman PC, Garron T, Atmar RL, Peters CJ, Couch RB. Immunization with SARS coronavirus vaccines leads to pulmonary immunopathology on challenge with the SARS virus. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35421. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Erratum in: PLoS One. 2012;7(8). doi:10.1371/annotation/2965cfae-b77d-4014-8b7b-236e01a35492. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3335060/. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin Z, Bouteau A, Herbst C, Igyártó BZ. Pre-exposure to mRNA-LNP inhibits adaptive immune responses and alters innate immune fitness in an inheritable fashion. PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 2;18(9):e1010830. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9477420/. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto M, Burrell AJC, Neto AS, Alliegro PV, Trapani T, Cheng A, Udy AA; SPRINT-SARI Australia Investigators. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of critically ill patients with one, two and three doses of vaccination against COVID-19 in Australia. Intern Med J. 2022 Jul 16:10.1111/imj.15884. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35841294. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9349669/. [CrossRef]
- Fraiman J, Erviti J, Jones M, Greenland S, Whelan P, Kaplan RM, Doshi P. Serious adverse events of special interest following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in randomized trials in adults. Vaccine. 2022 Sep 22;40(40):5798-5805. Epub 2022 Aug 31. PMID: 36055877. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9428332/. [CrossRef]
- Lei Y, Zhang J, Schiavon CR, He M, Chen L, Shen H, Zhang Y, Yin Q, Cho Y, Andrade L, Shadel GS, Hepokoski M, Lei T, Wang H, Zhang J, Yuan JX, Malhotra A, Manor U, Wang S, Yuan ZY, Shyy JY. SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Impairs Endothelial Function via Downregulation of ACE 2. Circ Res. 2021 Apr 30;128(9):1323-1326. Epub 2021 Mar 31. PMID: 33784827 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8091897/. [CrossRef]
- Mallapaty S. COVID vaccines cut the risk of transmitting Delta - but not for long. Nature. 2021 Oct 5. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34611341 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34611341/. [CrossRef]
- Doshi P. Godlee F. Editorial: Covid-19 vaccines and treatments: we must have raw data, now. BMJ 2022; 376. (Published 19 January 2022) Cite this as: BMJ 2022;376:o102. [CrossRef]
- Yellow cart reports. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/coronavirus-covid-19-vaccine-adverse-reactions.
- VAERS. https://vaers.hhs.gov/.
- EMA. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en.
- UK HEALTH SECURITY AGENCY. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/covid-19-vaccine-weekly-surveillance-reports.
- Tojersen I. Covid-19: Norway investigates 23 deaths in frail elderly patients after vaccination. BMJ 2021;372:n149 (Published 15 January 2021). https://www.bmj.com/content/372/bmj.n149.
- Tojersen I. Covid-19: Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine is “likely” responsible for deaths of some elderly patients, Norwegian review finds. BMJ 2021;373:n1372 (Published 27 May 2021). https://www.bmj.com/content/373/bmj.n1372.
- Blaylock RL. COVID UPDATE: What is the truth? Surg Neurol Int. 2022;13:167. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9062939/. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KBV DATEN. https://afdbundestag.de/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Daten-Impffolgen.pdf.
- Paul-Ehrlich-Institute, Unclear deaths https://www.pei.de/DE/home/home-node.html, Langen, Germany 2022, Conference held 12.12.2022 in Berlin. https://afdbundestag.de/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Daten-Impffolgen.pdf Hi.
- National Institute of Public Health (NIJZ). https://nijz.si/en/.
- Behera P, Patro BK, Singh AK, Chandanshive PD, S R R, Pradhan SK, Pentapati SSK, Batmanabane G, Mohapatra PR, Padhy BM, Bal SK, Singh SR, Mohanty RR. Role of ivermectin in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers in India: A matched case-control study. PLoS One. 2021 Feb 16;16(2). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).