1. Introduction
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a rapidly emerging crisis in Africa [
1]. In 2021, approximately 24 million adults 20‒79 years old worldwide were living with T2D, which is expected to grow to 55 million persons by 2045 [
2]. Approximately 416,000 deaths occurred in Africa in 2021 due to T2D, and it is estimated that 54% of those living with T2D were undiagnosed [
2]. T2D is an established risk factor for dyslipidemia and occurs more frequently in T2D populations than non-T2D populations [
3,
4]. Dyslipidemia is typically characterized according to the imbalance of lipids such as total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides (TG), and low high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C) [
5]. Other risk factors associated with dyslipidemia include increased age, alcohol consumption, decreased vegetable consumption, low physical activity, and high waist circumference [
6]. T2D is known to increase circulating free fatty acids and stimulate very low-density lipoprotein production [
7]. T2D is also associated with elevated TG, increased LDL-C, and low HDL-C, with low HDL-C as the most regularly occurring lipid abnormality [
8,
9]. Statin therapy and aggressive LDL-C control is recommended for persons with T2D [
10,
11].
Lipid abnormalities are the primary link between T2D and cardiovascular disease (CVD) [
3]. Between 1990 and 2013, sub-Saharan west Africa was the only part of the world that experienced increases in CVD-related deaths that were not solely attributable to aging and population growth [
12]. It is estimated that 80% of the world’s burden for CVD occurs in low-and middle-income countries (LMICs), while most of the studies on risk factors for CVD were performed in developed countries [
13,
14]. Sub-Saharan Africa maintains the youngest age demographic associated with CVD deaths [
15]. Unfortunately, in low-income countries, only 3% of rural communities have access to CVD preventive drugs [
16].
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends routine dyslipidemia screening based on age (over 40 years), smoking status, waist circumference, and presence of diabetes or hypertension [
17]. While dyslipidemia is not widely reported in African countries, several recent studies have shown its high prevalence. Several of these studies linked dyslipidemia with age ≥ 40 years, less walking, elevated fasting blood glucose, and higher wealth index [
18].
There are limited studies on dyslipidemia among T2D patients in African settings. In a systematic review of 177 studies at African sites, the prevalence of elevated total cholesterol concentrations, low HDL cholesterol concentrations, and elevated triglyceride concentrations were 34.4%, 39.5% and 3.9%, respectively [
19]. A recent study at public hospitals in Ethiopia among mostly urban T2D participants reported dyslipidemia prevalence of 81.5%, with elevated TG being the most common lipid abnormality [
20]. A study in South Africa among T2D participants showed dyslipidemia rates of 94.0% and 84.0% among males and females, respectively [
21]. At least one study in Africa showed high dyslipidemia prevalence among T2D patients despite the use of lipid-lowering therapy [
22]. High dyslipidemia rates in T2D participants have also been observed in northeastern parts of Africa [
23]. In West Africa, a study in Nigeria reported that dyslipidemia occurred in 60.0% of its non-diabetic population and 89.0% of the diabetic population [
24]. One study in Mali near its urban areas of Bamako, showed that 47.6% of T2D subjects had dyslipidemia [
25].
In rural Mali, screening for dyslipidemia is not routinely performed in healthcare settings. To our knowledge, there are no studies reporting the prevalence of dyslipidemia in T2D populations in rural Mali. Such knowledge would provide a baseline for dyslipidemia occurrence in rural Mali, raise awareness about dyslipidemia in T2D populations, and guide healthcare policy in rural African settings. Given the lack of knowledge on dyslipidemia in rural Mali and recent evidence revealing the crisis of T2D in Africa, the investigators of this study sought to determine and report dyslipidemia prevalence and its associated demographic factors through a field study in Ganadougou, Mali.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
Ganadougou is a rural commune inhabited by the Fulani and Bambara populations. The community lies in the Sikasso Circle along the main freeway to Côte d’Ivoire and consists of 11 municipalities (
Figure 1).
The Ganadougou community spans over 4,000 square kilometers, and its capital city is Niéna. The community’s population is approximately 144,368, and its primary occupations are agriculture and animal husbandry. Ganadougou is approximately 201 miles (323 kilometers) southeast of Mali’s capital city of Bamako. This study was performed in the Ganadougou municipalities of Nièna, Zanièna, Benkadi, and Finkolo-Ganadougou.
2.2. Study Design and Enrollment
Subject recruitment was drawn from an ongoing T2D campaign in the Ganadougou community that began in December 2020. This study was laid out as a cross-sectional design between November 2021 and March 2022. Inclusion criteria were age over 20 years, residency in the Ganadougou community, and confirmed T2D diagnosis. During this campaign, community residents were recruited and received free T2D rapid diagnostic test screening for study participation. A total of 1,417 participants were screened for T2D, and 104 persons with T2D (PWT2D) consented to participate. Cross-sectional surveys were used to collect data for all subjects, including demographic data, co-morbid conditions, and current medications for diabetics and hypertension. All PWT2D were referred for lipid profile assays at the Nièna Community Health Center. During this health center visit, blood pressure was measured using portable monitors, and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) and creatinine levels were measured. The blood sample was taken in a dry tube of sodium fluoride or sodium heparin lithium after 12 hours of fasting. After centrifugation, the appearance was identified and the serum was separated from the packed red cells and then assayed by enzymatic methods. Samples were analyzed using a KENZA 240TX blood chemistry analyzer (Biolabo Diagnostics, France).
2.3. Sample Size
Sample size was calculated based on the prevalence of dyslipidemia in the T2D population. The sample size formula applied the confidence interval for a single proportion as n=(z_(1-α)^2∙p∙q)/e^2, where n is the sample size, z is the normal percentile, α is the type I error rate, p is the estimated prevalence of dyslipidemia among PWT2D, q = 1-p, and e is the margin of error. With p estimated at 63.8%, a type I error rate of 5%, and a 10% margin of error, the minimum required sample size was estimated as n = 89.
2.4. Definitions
The T2D cutoff for positive diagnosis was fasting plasma glucose level of 7.0 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) or higher [
26]. Participants testing positive were invited to take undergo a second rapid diagnostic test. Subjects were also classified as T2D subjects if they self-reported a previous T2D diagnosis on the study questionnaire. For purposes of this study, dyslipidemia was defined as the presence of one or more abnormal serum lipid concentration parameters. Abnormal serum lipid concentrations were defined as follows: serum total cholesterol (TC) level ≥ 5.2 mmol/L (≥ 200 mg/dL, hypercholesterolemia); HDL-C ≤ 1.3 mmol/L (≤50 mg/dL, females) and HDL-C ≤ 1.0 mmol/L (≤ 40 mg/dL, males); LDL-C ≥ 2.6 mmol/L (≥ 100 mg/dL); and serum TG ≥ 1.7 mmol/L (≥ 150 mg/dL, hypertriglyceridemia). Mixed dyslipidemia was considered as the presence of at least two abnormal lipid parameters. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or higher, diastolic blood pressure of at 90 mmHg or higher, or current use of antihypertensive drugs. The atherogenicity index was calculated as the LDL to HDL ratios, and ratios over 3.55 were considered as the presence of atherogenic risk. Blood creatinine levels above 106.1 µmol/L (1.2 mg/dL) were considered as hypercreatinemia. HbA1c values below 7.0% were considered as adequate glycemic control as per the American Diabetes Association guidelines [
27]. Physical activity was classified in terms of occupational activites as: light (limited physical activity, sitting office work, religious leader, and retirement activities), moderate (standing and walking, store work, and teaching activities), and active (walking, lifting, and heavy manual labor).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Data were expressed as frequencies and proportions. Pearson’s chi-square tests were used to test hypotheses comparing proportions between comparison groups. Multiple logistic regression models were applied to perform multivariable analyses. Data were analyzed using the SPSS Statistics for Windows (version 26, IBM, Chicago, IL) and the SAS System (version 9.4, SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC). The type I error threshold was set at 5%.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Dyslipidemia Prevalence and Participant Characteristics
The overall dyslipidemia rate was 87.5% (91/104). The most common lipid parameter abnormality was total cholesterol, where 66.3% (69/104) showed serum total cholesterol levels of 5.2 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) or higher (
Table 1).
Notably, only 9.6% (10/104) of subjects had low HDL-c levels. Approximately 59.6% (62/104) of subjects had multiple lipid abnormalities. Among the 104 T2D participants, 76.9% (80/104) had HbA1c glycemic balance values of 7% or higher. Five of the 13 non-dyslipidemia participants (38.5%) had HbA1c levels of < 7.0%.
Demographic, treatment, and co-morbidity factors known to be associated with T2D are shown by dyslipidemia status in
Table 2.
Factors associated with dyslipidemia were age and hypertension (p = 0.013 and p = 0.036, respectively). Dyslipidemia status did not statistically differ according to sex, age group, T2D treatment, T2D duration, hypercreatinemia status, glycemic balance, or physical activity.
3.2. Lipid Profiles
Study characteristics were classified by lipid parameters (high TC, low HDL-C, high LDL-C, high TG, and mixed dyslipidemia). None of the parameters statistically differed according to sex or age group. High TC and high LDL-c were associated with hypertension status (p = 0.029 and p = 0.006, respectively,
Table 3).
Low HDL-c was significantly associated with HbA1c level (p = 0.003). Elevated atherogenicity index coincident with high TC, low HDL-C, high LDL-C, and mixed dyslipidemia (p = 0.008, < 0.001, 0.020, and 0.003, respectively). Abnormal lipid profiles were not significantly associated with T2D treatment, T2D duration, hypercreatinemia, or physical activity (p ≥ 0.050).
3.3. Glycemic Balance by Treatment Type
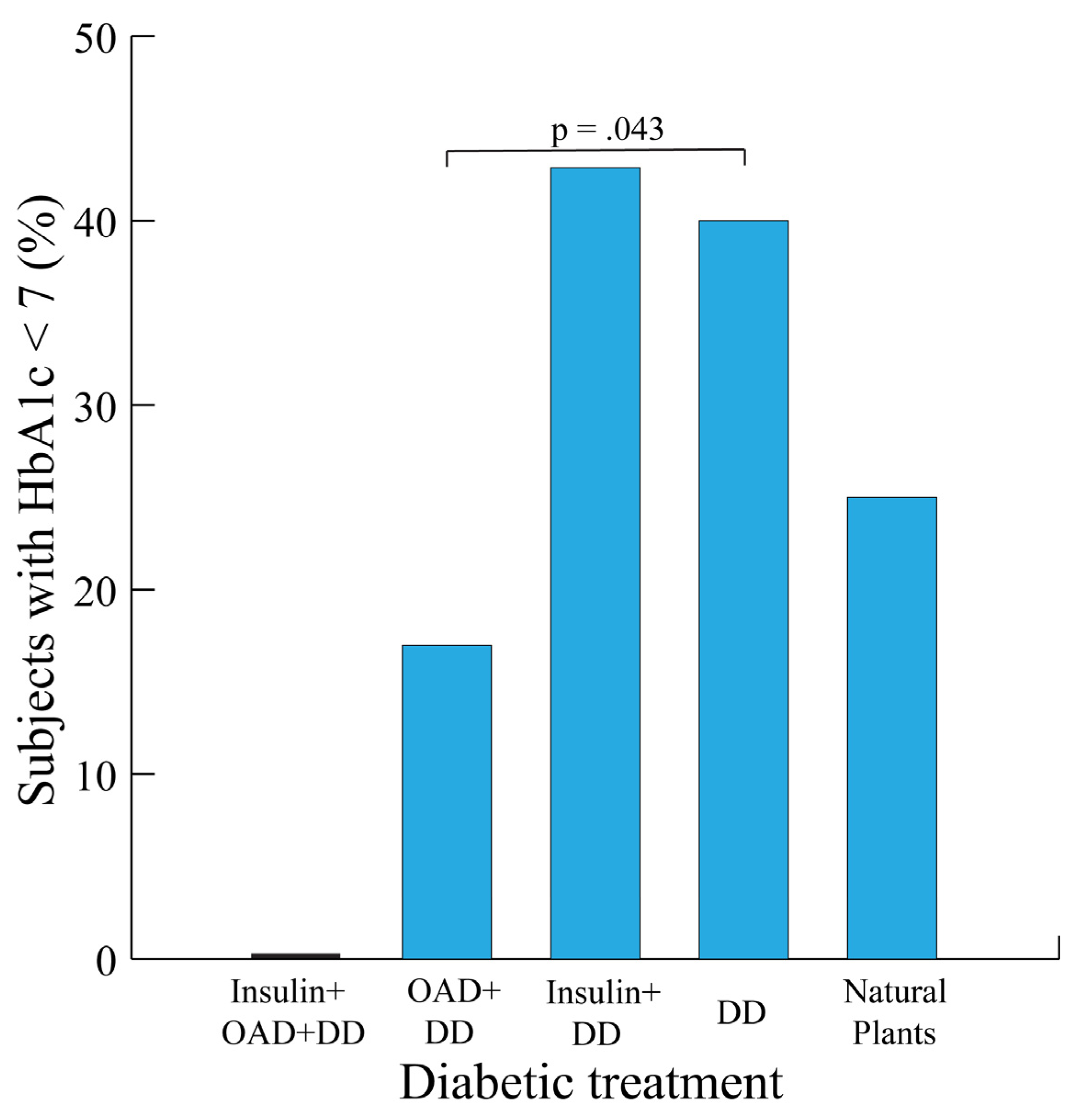
Participants receiving insulin and DD were the most likely to have ideal T2D HbA1c levels (42.9% with HbA1c < 7). Those receiving DD alone were more likely than those with OAD+DD to have an HbA1c of less than seven (p = 0.043,
Figure 2).
None of the 8 subjects receiving insulin + OAD + DD had HbA1c values of less than seven. The lowest HbA1c values were observed for participants receiving OAD (0.0% and 17.0% for insulin plus OAD plus DD and OAD plus DD, respectively).
3.4. Hypertension by Sex
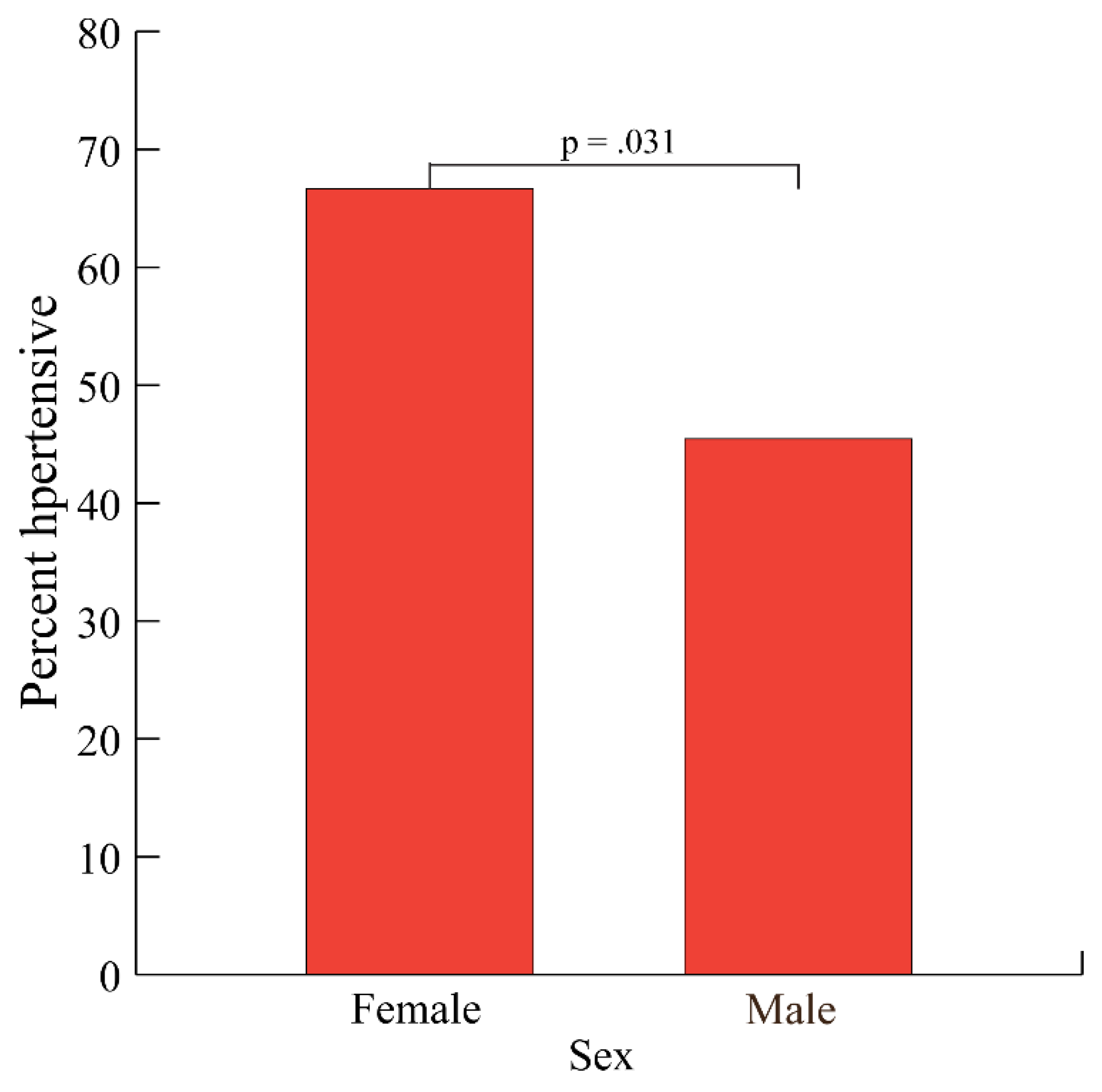
The overall percentage of T2D subjects with hypertension was 57.7% (60/104). Hypertension rates were significantly higher among females than males (66.7% versus 45.5%, respectively, p = 0.031,
Figure 3).
Level of physical activity also differed between sex groups (p = 0.004,
Table S1). Sex group did not differ by age group, treatment type, T2D duration, glycemic balance, or atherogenicity index (p = 0.732, 0.204, 0.938, 0.220, 0.464, and 0.522, respectively,
Table S1).
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this study is the first recent of its kind investigating dyslipidemia in rural Mali. Dyslipidemia prevalence was estimated here as 87.5% among T2D subjects in the rural Malian community of Ganadougou. The high prevalence rates observed occurred across all age and sex groups. Glycemic balance was generally high among study subjects suggesting that this group of T2D subjects was largely uncontrolled through treatment. While it is likely that uncontrolled diabetes in this rural community was impacted by the challenges for providing statin therapy in rural locations, other studies have shown that high dyslipidemia prevalence may persist among T2D populations receiving therapy [
28]. The results in our study may provide a baseline pattern for lipid-lowering interventions such as statin therapy. The general lipid profiles here were similar to other studies, save for the unexpectedly normal HDL-c levels. It is possible that this finding is an artifact of the study’s sample size, and insufficient data were available for subgroup analyses as only four subjects reported low HDL-c. Some studies have described TC/HDL-cholesterol ratio as the single most predictive lipid factor [
29]. In this study, HDL-c was normal for most subjects, which directly impacted these ratios.
Dyslipidemia has received little attention in West Africa. The majority of dyslipidemia studies are based on populations of European decent with limited studies based on African populations [
30]. Among these African population-based studies, the majority are Northern African populations and Southern African populations. A PubMed key word search yielded only 20 hits through the key words “Mali” “dyslipidemia”, and only one of these hits corresponded to an article published since 2016. There are considerable challenges in dyslipidemia reporting in rural parts of Africa. First, screening is not typically incorporated into standard care. Incorporating information regarding dyslipidemia into lifestyle programs adapted for low- and middle-income countries such as Lifestyle Africa may offer a promising solution [
31]. Dyslipidemia treatment sometimes only involves modest changes in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats (good fats) fat consumption coupled with weight loss. For this reason, telehealth and education campaigns may provide viable solutions. An integral treatment and education component would benefit from expressing quantitative lipid profiles in terms of their cardiovascular risk factors.
The importance of field studies in remote areas in Africa cannot be understated. For instance, it is estimated that 59.7% of T2D cases are undiagnosed. Previous studies have shown that 79–100% of participants of T2D subjects were initially diagnosed during cross-sectional surveys [
32]. In one of our earlier studies (data not shown), a majority (62.5%) of subjects diagnosed with T2D were unaware of their diabetic status. These results suggest that carrying out field studies are beneficial beyond the research implications. While diagnostics for dyslipidemia are not widely available at many African field sites, potential reporting and monitoring solutions may consider the occurrence of related illnesses. For instance, many comorbidities related to dyslipidemia and T2D are bidirectional. Tsimihodimos et al. 2018 note that the pathogenic relationship between T2D and hypertension is bidirectional [
33].
Temporal trends for cardiovascular disease and T2D have outpaced much of the developed world over the past three decades (8.3% to 13.1% and 1.0 to 2.0 between 1990 and 2020 for CVD and T2D, respectively,
Figure S1). Because diabetes is one of its primary causes of dyslipidemia, it is likely that dyslipidemia occurrence has also increased. This study was performed in a rural area, but urbanization is spreading in Africa and cardiovascular risk profiles are reportedly worse in urban areas [
34] which could suggest that this trend may increase in the absence of interventions. An initial first step toward raising awareness about dyslipidemia in PWT2D lies in raising awareness about T2D. It has been established that the nutritional transition is occurring in Africa [
35]. A meta-analysis has shown a link between plant diets and lipid profiles [
36]. Angassa et al. (2022) noted vegetable intake as a significant contributing factor for dyslipidemia in Ethiopia [
6]. Longitudinal studies are needed to determine whether vegetable intake patterns are changing in Africa.
Studies have suggested that potentially all diabetics have abnormal lipid profiles [
11], and thus should be considered simultaneously with diabetic therapy. While point of care is a plausible approach, to our knowledge, none of the subjects in this study received adequate statin therapy. Previous researchers have suggested the use of fixed-dose combination therapy approaches to increase adherence [
37]. This solution could perhaps partially address both cost for multiple treatments and adherence and distribution challenges. Others have suggested increased m-health programs [
14]. Regardless of the approach, routine reporting and improving data systems in rural areas is needed. A better understanding health seeking behaviors related to dyslipidemia is also needed as good first steps.
Studies focusing on epigenetics are needed to complement and build on efforts from epidemiological studies. The LDL receptor protein and ATP-binding cassettes play key roles in lipid function [
38]. There are few studies that focus on these characteristics in Africa, studies are needed to complement those studies in developed countries. Within Africa, genetic associations differ by geographic location [
30]. A natural progression for epidemiological studies for diabetic dyslipidemia lies in epigenetics. One example is a study which combined genetic and epigenetic analysis to understand the mechanism associating hepatic insulin resistance and non-alcoholic disease in (T2D) patients [
39]. Epigenetics studies have shown that environmental factors also have a crucial role in the development of T2D [
40], which suggests that epidemiological studies may not necessarily generalize over geographic regions. It is worth mentioning that lipid imbalances in T2D subjects may be due to genetically determined disorders unrelated to glycemic balance or insulin resistance [
41]. Genetic etiology of dyslipidemia is complicated, including both rare monogenic and complex polygenic disorders [
42]. For example, mutations in LDLR (LDL receptor) and APOB (apolipoprotein B-100) genes may cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia (a defect with severe life-long elevations in low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol) [
43]; mutations in the LDLR adaptor protein 1 (LDLRAP1) gene cause autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia [
44]. Sex-specific genetic architecture has also been described previously [
45]. For complex disorders, variants in genes with clear biological and clinical importance such as LDLRAP1, SCARB1, and NPC1L1 have been identified, corresponding to approximately 25─30% of the genetic variance for various dyslipidemia traits [
46]. It is likely that dyslipidemia among our subjects are a mixture of monogenic and polygenic disorders, which should be investigated in future works.
The primary limitations of this study were the convenience sampling strategy and the sample size. While the overall sample size provided adequate statistical power for general comparisons, the study was not powered for subgroup or multiple comparisons. Also, insulin storage was not always ideal which likely impacted the treatment results reported here.
5. Conclusions
Diabetic dyslipidemia was highly common in the rural T2D population studied here. This project was performed in a low-resource environment, where data systems were weak and screening for dyslipidemia was either infrequent or did not previously occur. Multi-tiered strategies are needed for managing T2D that consider lipid status. Routine screening of lipid profiles into the public health care system is needed.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Temporal trends in cardiovascular disease and T2D in sub-Saharan Africa, 1990‒2020; Table S1: Study characteristics by sex.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: AD, SOD, JGS, M Diakite, TYA, CC, MW, KT, DS, IAN; Data collection: AD, DMC, KK, M Diarra, DK, MAT, DSB, OK, OD; Investigation: AD, DMC, KK, M Diarra, DK, MAT, DSB, OK, FGF, OD, MS; Data curation and analysis: AD, JGS; Validation and verification: TYA, M Diakite; Writing – original draft preparation: AD, JGS; Writing – review and editing: AD, JGS, CZ, KT, JL, MW, SF, SOD; Visualization: AD, JGS; Supervision: M Diakite, JGS, SOD, TYA, SF; Project administration: JGS, JL, SOD; Funding acquisition: JGS, JL, SOD. All of the authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Fogarty International Center and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases sections of the National Institutes of Health under award number U2RTW010673 for the West African Center of Excellence for Global Health Bioinformatics Research Training. AD is supported by a fellowship through the African Center for Excellence in Bioinformatics of Bamako. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee at the University of Sciences, Techniques and Technologies of Bamako (USTTB, reference number: 2021/164/CE/USTTB).
Informed Consent Statement
Each study participant was at least 20 years of age and provided verbal informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
Data supporting the results for this study are provided as tables within the article and as
Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support for our training programs by the Fogarty International Center of the National Institutes of Health to make this study possible. We also thank the African Centers of Excellence in Bioinformatics (ACE) for developing the teaching computer laboratories at the University of Sciences, Techniques and Technologies of Bamako for carrying out our training programs. We are particularly grateful to the study participants in the Ganadougou community and sincerely hope this work serves as a building block toward increased awareness and mitigation of diabetes and dyslipidemia in West Africa.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Jaffar, S., and G. Gill. "The Crisis of Diabetes in Sub-Saharan Africa." Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 5, no. 8 (2017): 574-75. [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. "Diabetes in Africa." https://www.idf.org/our-network/regions-members/africa/diabetes-in-africa.html (accessed May 6, 2022).
- Wu, L., and K. G. Parhofer. "Diabetic Dyslipidemia." Metabolism 63, no. 12 (2014): 1469-79. [CrossRef]
- Mooradian, Arshag D. "Dyslipidemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus." Nature Reviews Endocrinology 5, no. 3 (2009): 150-59. [CrossRef]
- Pappan, N., and A. Rehman. "Dyslipidemia." In Statpearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
- Angassa, D., S. Solomon, and A. Seid. "Factors Associated with Dyslipidemia and Its Prevalence among Awash Wine Factory Employees, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A Cross-Sectional Study." BMC Cardiovasc Disord 22, no. 1 (2022): 22. [CrossRef]
- Davidson, MH & Pulipati, VP,. "Merck Manual, Professional Version: Dyslipidemia." Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/endocrine-and-metabolic-disorders/lipid-disorders/dyslipidemia (accessed April 27, 2022).
- Warraich, H. J., and J. S. Rana. "Dyslipidemia in Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease." Cardiovasc Endocrinol 6, no. 1 (2017): 27-32. [CrossRef]
- Masilela, Charity, Oladele Vincent Adeniyi, and Mongi Benjeddou. "Prevalence, Patterns and Determinants of Dyslipidaemia among South African Adults with Comorbidities." Sci Rep 12, no. 1 (2022): 337. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Liya, and Klaus G. Parhofer. "Diabetic Dyslipidemia." Metabolism 63, no. 12 (2014): 1469-79. [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, Krishnaswami. "Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes." Lipids in Health and Disease 9, no. 1 (2010): 144. [CrossRef]
- Roth, G. A., M. H. Forouzanfar, A. E. Moran, R. Barber, G. Nguyen, V. L. Feigin, M. Naghavi, G. A. Mensah, and C. J. Murray. "Demographic and Epidemiologic Drivers of Global Cardiovascular Mortality." N Engl J Med 372, no. 14 (2015): 1333-41. [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S., S. Hawken, S. Ounpuu, T. Dans, A. Avezum, F. Lanas, M. McQueen, A. Budaj, P. Pais, J. Varigos, and L. Lisheng. "Effect of Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors Associated with Myocardial Infarction in 52 Countries (the Interheart Study): Case-Control Study." Lancet 364, no. 9438 (2004): 937-52. [CrossRef]
- Bowry, A. D., J. Lewey, S. B. Dugani, and N. K. Choudhry. "The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Epidemiology and Management." Can J Cardiol 31, no. 9 (2015): 1151-9. [CrossRef]
- Moran, A., M. Forouzanfar, U. Sampson, S. Chugh, V. Feigin, and G. Mensah. "The Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Diseases in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries and Risk Factors 2010 Study." Prog Cardiovasc Dis 56, no. 3 (2013): 234-9. [CrossRef]
- Leong, D. P., P. G. Joseph, M. McKee, S. S. Anand, K. K. Teo, J. D. Schwalm, and S. Yusuf. "Reducing the Global Burden of Cardiovascular Disease, Part 2: Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease." Circ Res 121, no. 6 (2017): 695-710. [CrossRef]
- Marcus, M. E., C. Ebert, P. Geldsetzer, M. Theilmann, B. W. Bicaba, G. Andall-Brereton, P. Bovet, F. Farzadfar, M. Singh Gurung, C. Houehanou, M. R. Malekpour, J. S. Martins, S. S. Moghaddam, E. Mohammadi, B. Norov, S. Quesnel-Crooks, R. Wong-McClure, J. I. Davies, M. A. Hlatky, R. Atun, T. W. Bärnighausen, L. M. Jaacks, J. Manne-Goehler, and S. Vollmer. "Unmet Need for Hypercholesterolemia Care in 35 Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Cross-Sectional Study of Nationally Representative Surveys." PLoS Med 18, no. 10 (2021): e1003841. [CrossRef]
- Gebreegziabiher, Gebremedhin, Tefera Belachew, Kibrti Mehari, and Dessalegn Tamiru. "Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Associated Risk Factors among Adult Residents of Mekelle City, Northern Ethiopia." PLoS One 16, no. 2 (2021): e0243103. [CrossRef]
- Noubiap, J. J., J. J. Bigna, J. R. Nansseu, U. F. Nyaga, E. V. Balti, J. B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, and A. P. Kengne. "Prevalence of Dyslipidaemia among Adults in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis." Lancet Glob Health 6, no. 9 (2018): e998-e1007. [CrossRef]
- Abdissa, D., and D. Hirpa. "Dyslipidemia and Its Associated Factors among Adult Diabetes Outpatients in West Shewa Zone Public Hospitals, Ethiopia." BMC Cardiovasc Disord 22, no. 1 (2022): 39. [CrossRef]
- Omodanisi, E. I., Y. Tomose, B. I. Okeleye, S. K. O. Ntwampe, and Y. G. Aboua. "Prevalence of Dyslipidaemia among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in the Western Cape, South Africa." Int J Environ Res Public Health 17, no. 23 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Pitso, Lebohang, Thabiso Rafaki Petrus Mofokeng, and Riette Nel. "Dyslipidaemia Pattern and Prevalence among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Lipid-Lowering Therapy at a Tertiary Hospital in Central South Africa." BMC Endocrine Disorders 21, no. 1 (2021): 159. [CrossRef]
- Achila, Oliver Okoth, Millen Ghebretinsae, Abraham Kidane, Michael Simon, Shewit Makonen, and Yohannes Rezene. "Factors Associated with Poor Glycemic and Lipid Levels in Ambulatory Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Patients in Asmara, Eritrea: A Cross-Sectional Study." Journal of Diabetes Research 2020 (2020): 5901569. [CrossRef]
- Oguejiofor, O. C., C. H. Onwukwe, and C. U. Odenigbo. "Dyslipidemia in Nigeria: Prevalence and Pattern." Ann Afr Med 11, no. 4 (2012): 197-202. [CrossRef]
- Maiga, Youssoufa, Salimata Diallo, Fatoumata dite Nènè Konipo, Oumar Sangho, Modibo Sangaré, Seybou H. Diallo, Saliou Mahamadou, Yann Péréon, Bernard Giumelli, Awa Coulibaly, Mariam Daou, Zoumana Traoré, Djeneba Sow Sylla, Mohamed Albakaye, Cheick Oumar Guinto, Madani Ouologem, Adama S. Sissoko, Hamar A. Traoré, Souleymane Papa Coulibaly, Philippe Damier, Nadine Attal, and Julien Nizard. "Diabetic Polyneuropathy with/out Neuropathic Pain in Mali: A Cross-Sectional Study in Two Reference Diabetes Treatment Centers in Bamako (Mali), Western Africa." PLoS One 15, no. 11 (2020): e0241387. [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation. "Idf Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition." https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK581934/#:~:text=In%202021%2C%20it%20is%20estimated,impaired%20glucose%20tolerance%20in%202021. (accessed December 13, 2022).
- American Diabetes, Association. "6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021." Diabetes Care 44, no. Supplement_1 (2020): S73-S84.
- Raal, F. J., D. J. Blom, S. Naidoo, P. Bramlage, and P. Brudi. "Prevalence of Dyslipidaemia in Statin-Treated Patients in South Africa: Results of the Dyslipidaemia International Study (Dysis)." Cardiovasc J Afr 24, no. 8 (2013): 330-8. [CrossRef]
- Criqui, M. H., and B. A. Golomb. "Epidemiologic Aspects of Lipid Abnormalities." Am J Med 105, no. 1a (1998): 48s-57s. [CrossRef]
- Noubiap, Jean Jacques, Edith Pascale M. Mato, Magellan Guewo-Fokeng, Arnaud D. Kaze, Houssam Boulenouar, and Ambroise Wonkam. "Genetic Determinants of Dyslipidemia in African-Based Populations: A Systematic Review." Omics 22, no. 12 (2018): 749-58. [CrossRef]
- Catley, D., T. Puoane, L. Tsolekile, K. Resnicow, K. K. Fleming, E. A. Hurley, J. M. Smyth, F. T. Materia, E. V. Lambert, M. Z. Vitolins, N. S. Levitt, and K. Goggin. "Evaluation of an Adapted Version of the Diabetes Prevention Program for Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Cluster Randomized Trial to Evaluate "Lifestyle Africa" in South Africa." PLoS Med 19, no. 4 (2022): e1003964. [CrossRef]
- Mbanya, J. C., A. A. Motala, E. Sobngwi, F. K. Assah, and S. T. Enoru. "Diabetes in Sub-Saharan Africa." Lancet 375, no. 9733 (2010): 2254-66. [CrossRef]
- Tsimihodimos, Vasilis, Clicerio Gonzalez-Villalpando, James B. Meigs, and Ele Ferrannini. "Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus." Hypertension 71, no. 3 (2018): 422-28. [CrossRef]
- Kodaman, N., M. C. Aldrich, R. Sobota, F. W. Asselbergs, K. A. Poku, N. J. Brown, J. H. Moore, and S. M. Williams. "Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Ghana During the Rural-to-Urban Transition: A Cross-Sectional Study." PLoS One 11, no. 10 (2016): e0162753. [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B. M., L. S. Adair, and S. W. Ng. "Global Nutrition Transition and the Pandemic of Obesity in Developing Countries." Nutr Rev 70, no. 1 (2012): 3-21. [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T., A. E. Zemlin, R. T. Erasmus, S. S. Madlala, M. Faber, and A. P. Kengne. "Assessment of the Association between Plant-Based Dietary Exposures and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Profile in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review." BMC Public Health 22, no. 1 (2022): 361. [CrossRef]
- Noubiap, J. J. "Clustering of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Sub-Saharan Africans." Pan Afr Med J 38 (2021): 112. [CrossRef]
- Obsa, M. S., G. Ataro, N. Awoke, B. Jemal, T. Tilahun, N. Ayalew, B. Z. Woldegeorgis, G. A. Azeze, and Y. Haji. "Determinants of Dyslipidemia in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis." Front Cardiovasc Med 8 (2021): 778891. [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, R., and D. Iannelli. "Role of Epigenetics in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity." Biomedicines 9, no. 8 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S. H., and K. S. Park. "Recent Progress in Genetic and Epigenetic Research on Type 2 Diabetes." Exp Mol Med 48, no. 3 (2016): e220. [CrossRef]
- Lazarte, J., and R. A. Hegele. "Dyslipidemia Management in Adults with Diabetes." Can J Diabetes 44, no. 1 (2020): 53-60. [CrossRef]
- Berberich, Amanda J, and Robert A Hegele. "The Complex Molecular Genetics of Familial Hypercholesterolaemia." Nature Reviews Cardiology 16, no. 1 (2019): 9-20. [CrossRef]
- Rader, Daniel J, Jonathan Cohen, and Helen H Hobbs. "Monogenic Hypercholesterolemia: New Insights in Pathogenesis and Treatment." J Clin Invest 111, no. 12 (2003): 1795-803. [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, Livia, Claudio Priore Oliva, Giovanni Mario Pes, Lilla Di Scala, Antonella Bellocchio, Raffaele Fresa, Alfredo Cantafora, Marcello Arca, Sebastiano Calandra, and Stefano Bertolini. "Autosomal Recessive Hypercholesterolemia (Arh) and Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (Fh): A Phenotypic Comparison." Atherosclerosis 188 (2006): 398-405. [CrossRef]
- Ober, Carole, Dagan A. Loisel, and Yoav Gilad. "Sex-Specific Genetic Architecture of Human Disease." Nature Reviews Genetics 9 (2008): 911-22. [CrossRef]
- Teslovich, Tanya M., Kiran Musunuru, Albert V. Smith, Andrew C. Edmondson, and etc. "Biological, Clinical, and Population Relevance of 95 Loci for Blood Lipids." Nature 466, no. 7307 (2010): 707-13. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).