Submitted:
01 March 2023
Posted:
01 March 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
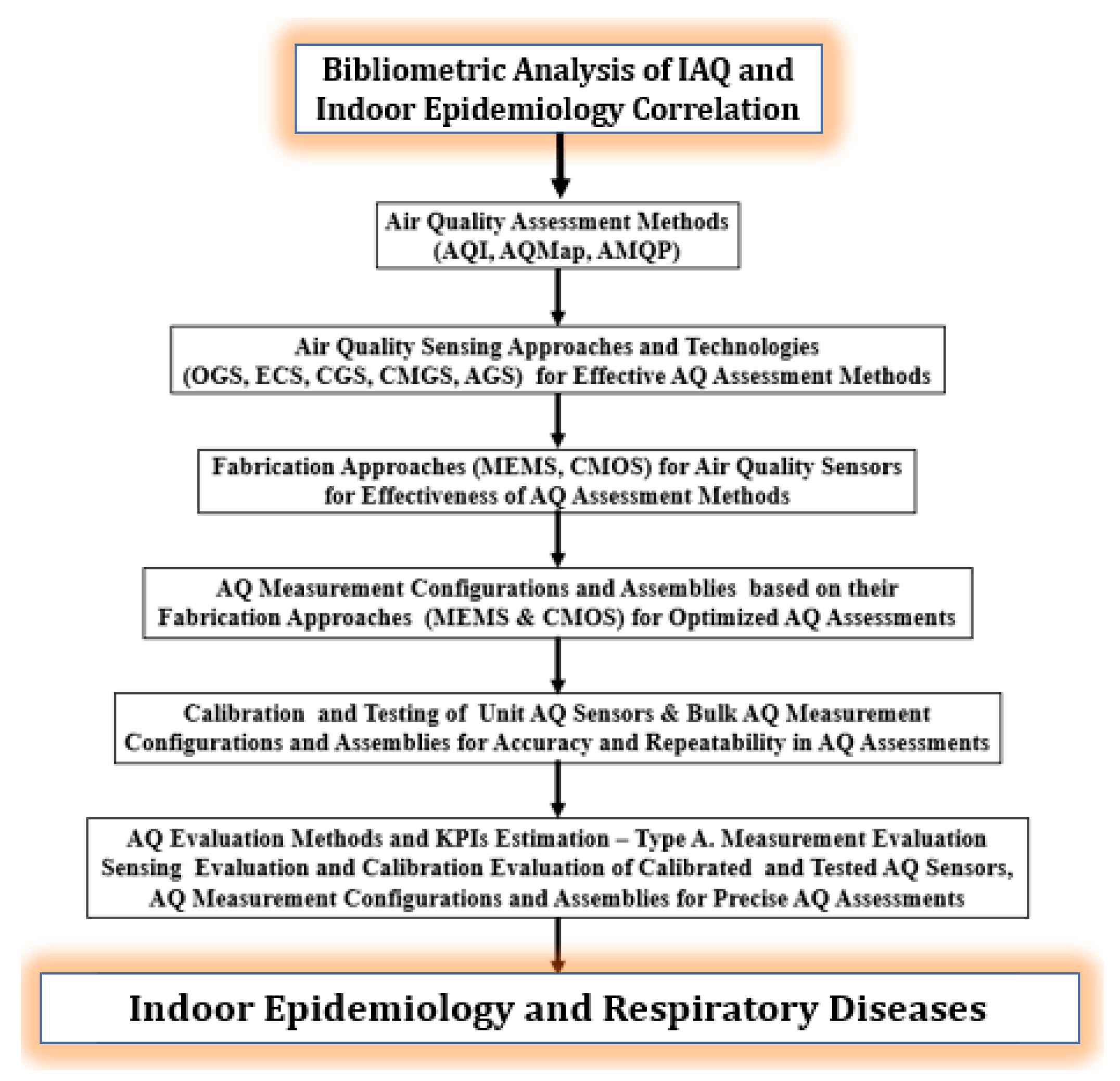
2. Bibliometric Analysis of IAQ and Indoor Epidemiology Correlation
3. Indoor Air Quality Assessment for Indoor Epidemiology
- Indoor Air Pollutants
- Air Quality Index (AQI)
- Air Quality Mapping (AQMap)
- Air Quality Management Plan (AQMP)
3.1. Indoor Air Pollutants
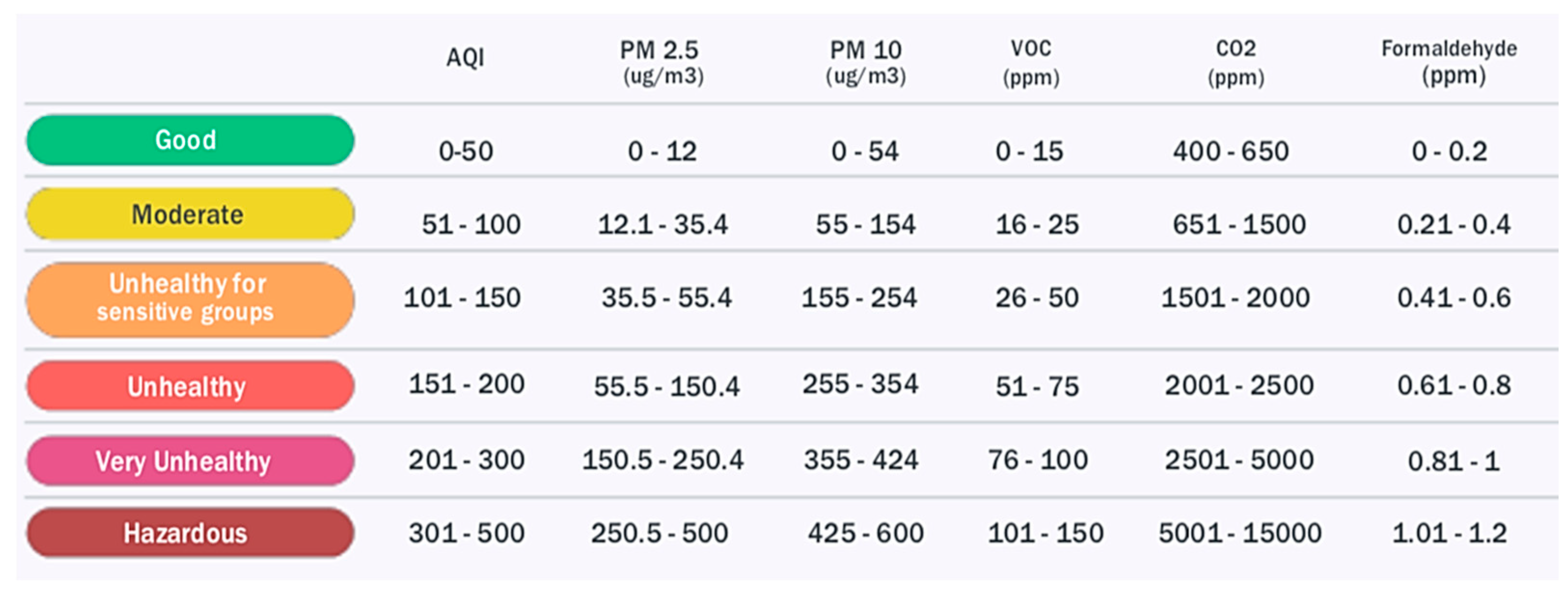
3.2. Air Quality Index (AQI)
3.3. Air Quality Mapping (AQMap)
3.4. Air Quality Management Plan (AMQP)
4. Indoor Epidemiology-focused Air Quality Gas Sensors (AQ-GS) Technologies
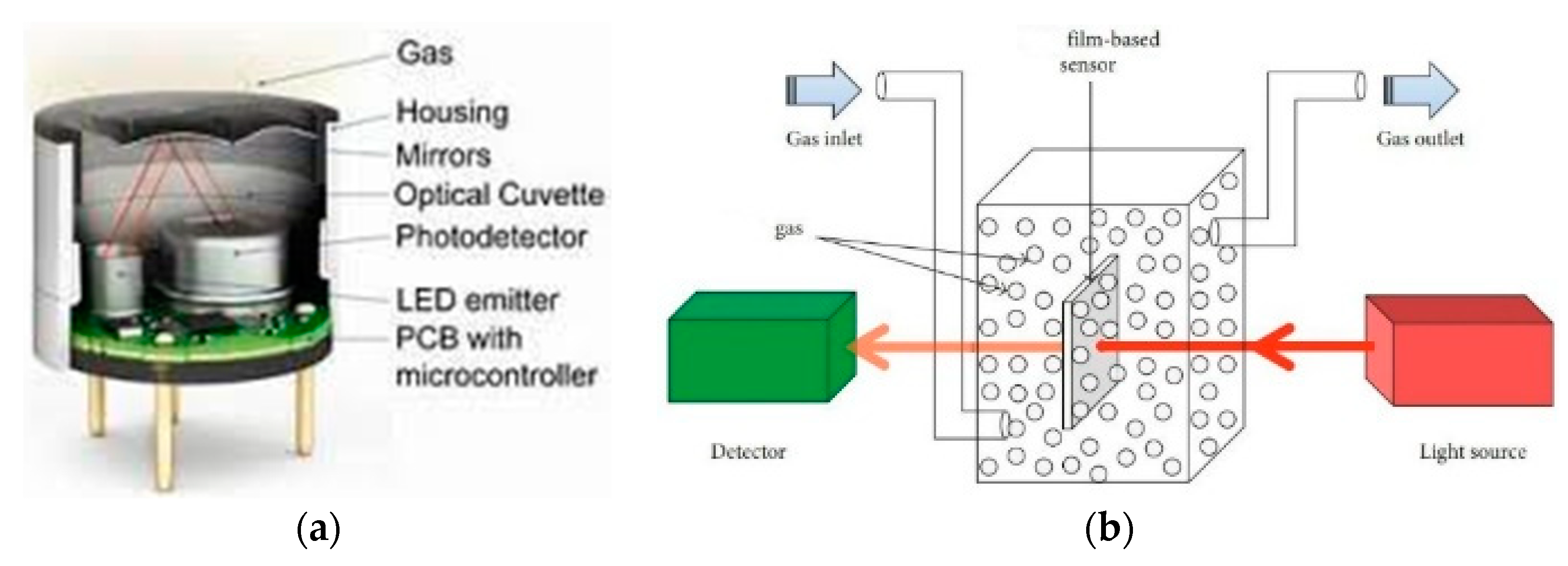
4.1. Optical Gas Sensors (OGS)
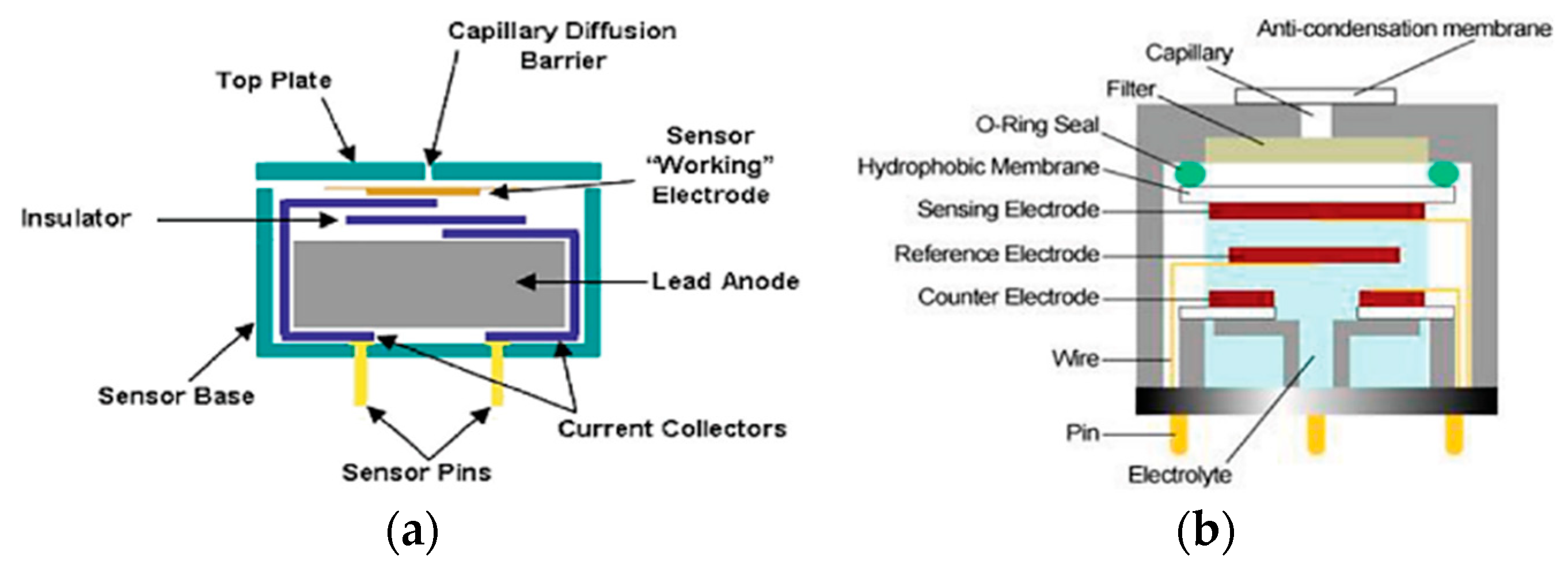
4.2. Electrochemical Gas Sensors (ECS)
4.3. Capacitive Gas Sensors (CGS)
4.4. Low-Cost Calorimetric Gas Sensors (CMGS)
4.5. Low-Cost Acoustic Gas Sensors (AGS)
5. Indoor Epidemiology-Focused Gas Sensors Fabrication Approaches
- Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) Fabrication Approaches
- Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Fabrication Approaches
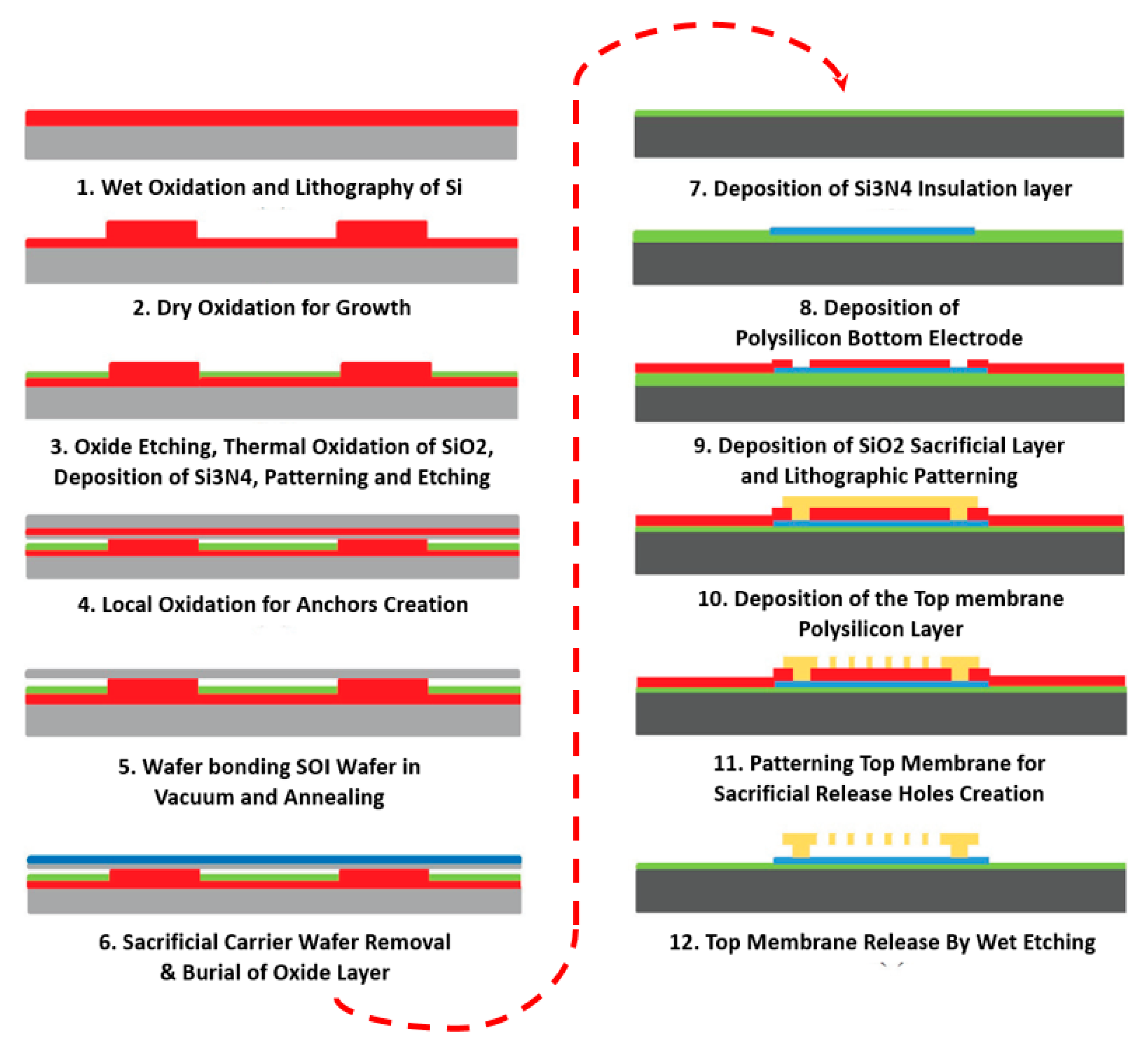
5.1. Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) Fabrication Approaches
5.2. Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Fabrication Approaches
6. Indoor Epidemiology-Focused AQ Measurement Configurations and Assemblies
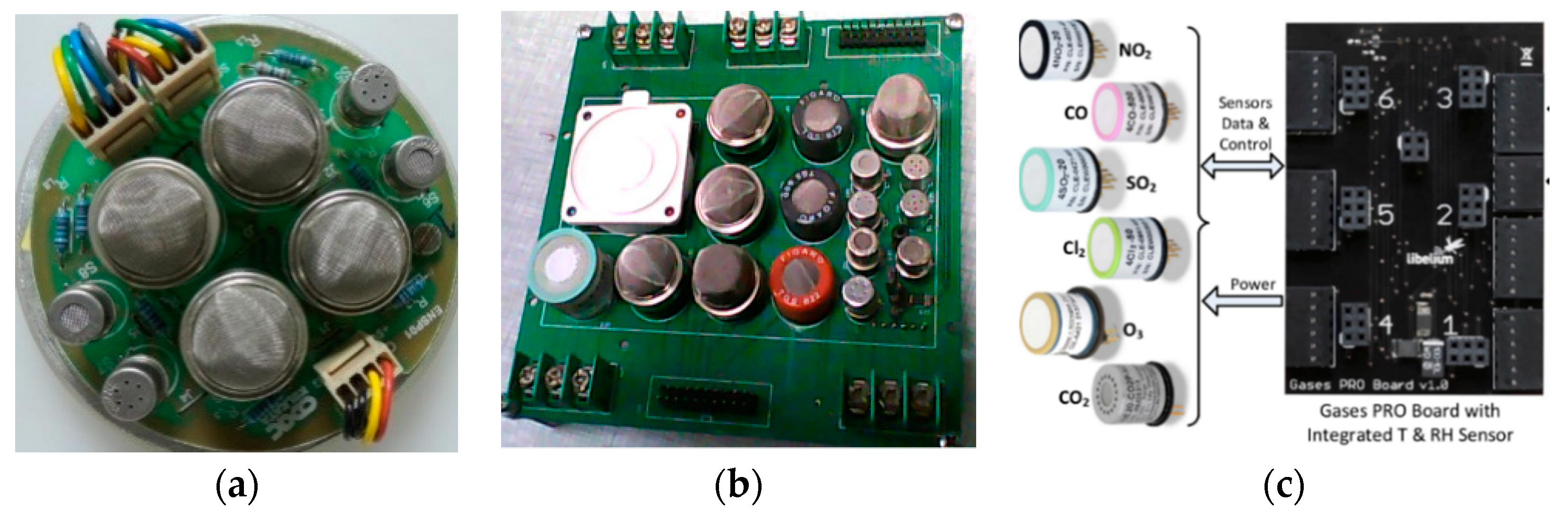
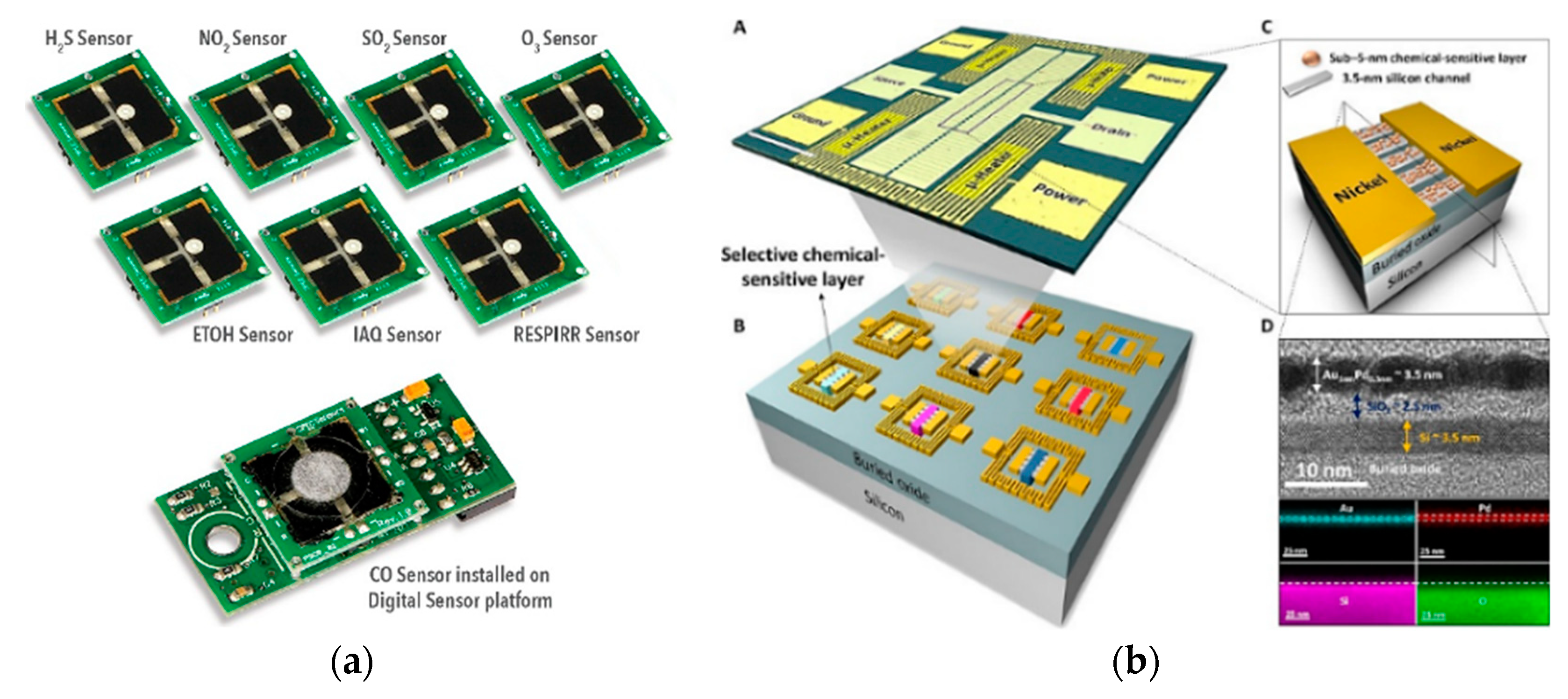
6.1. Gas Sensor Arrays and Grids based on System on Module (SoM) Approach
6.2. Gas Sensors Array on Chip based SOI
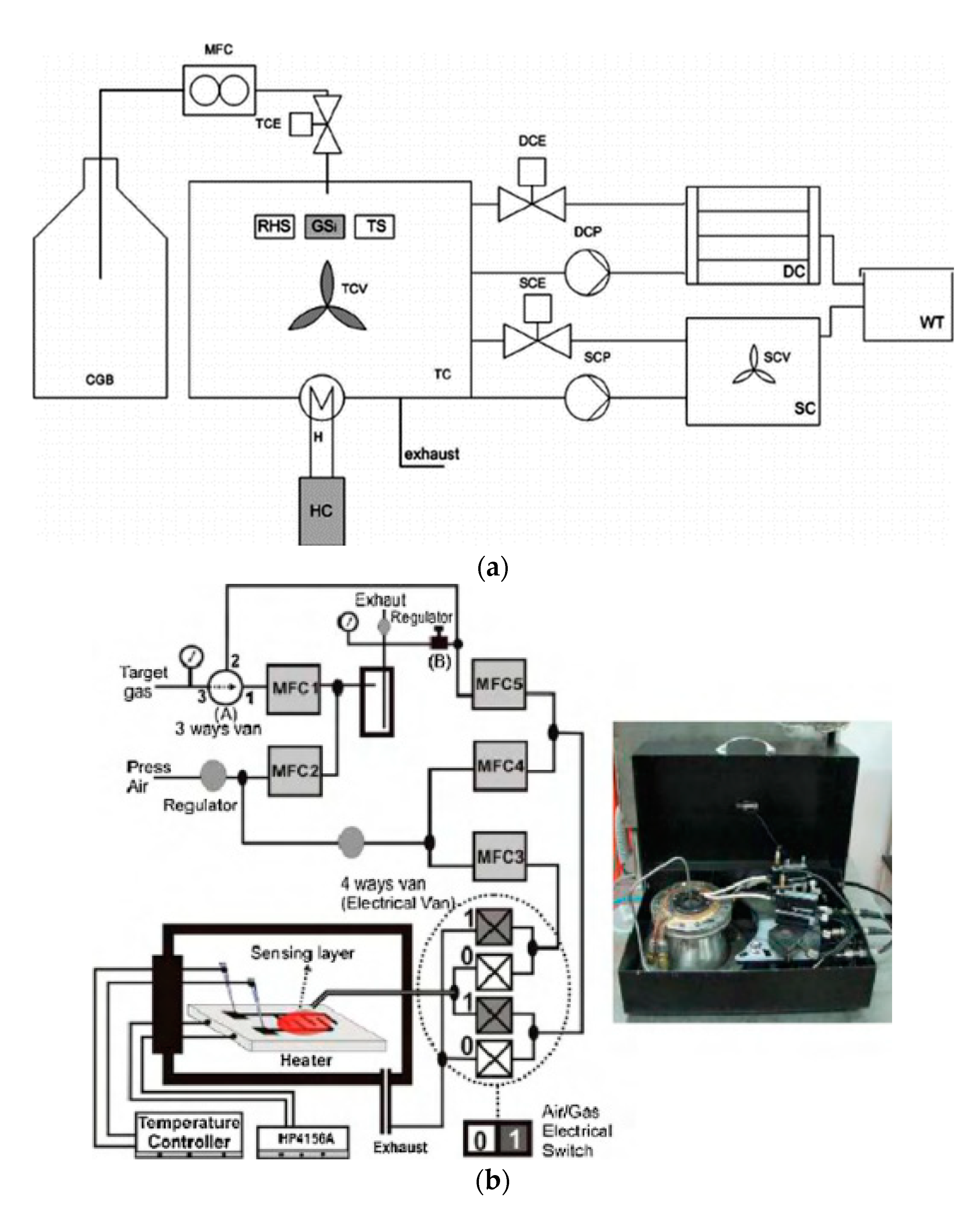
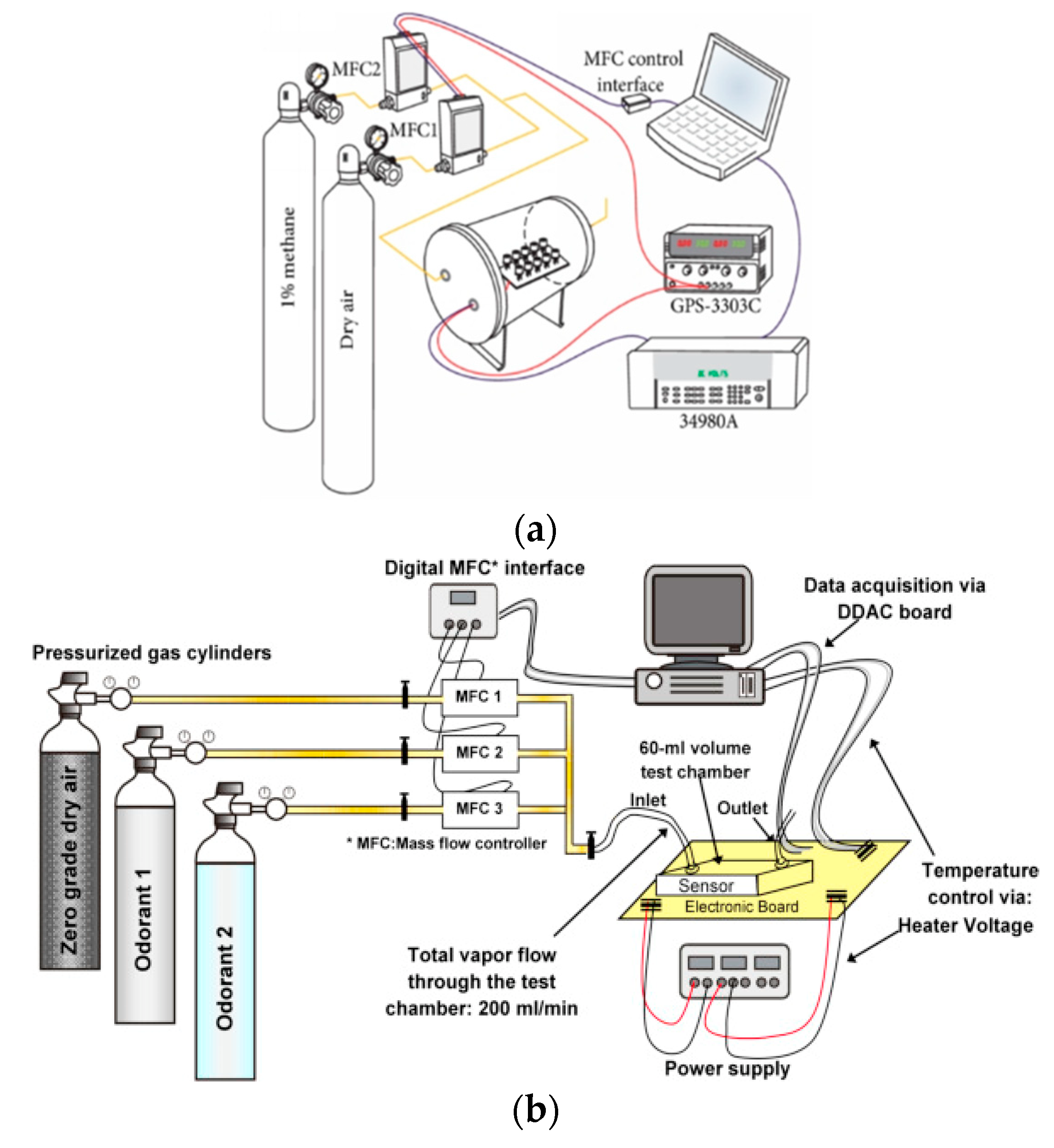
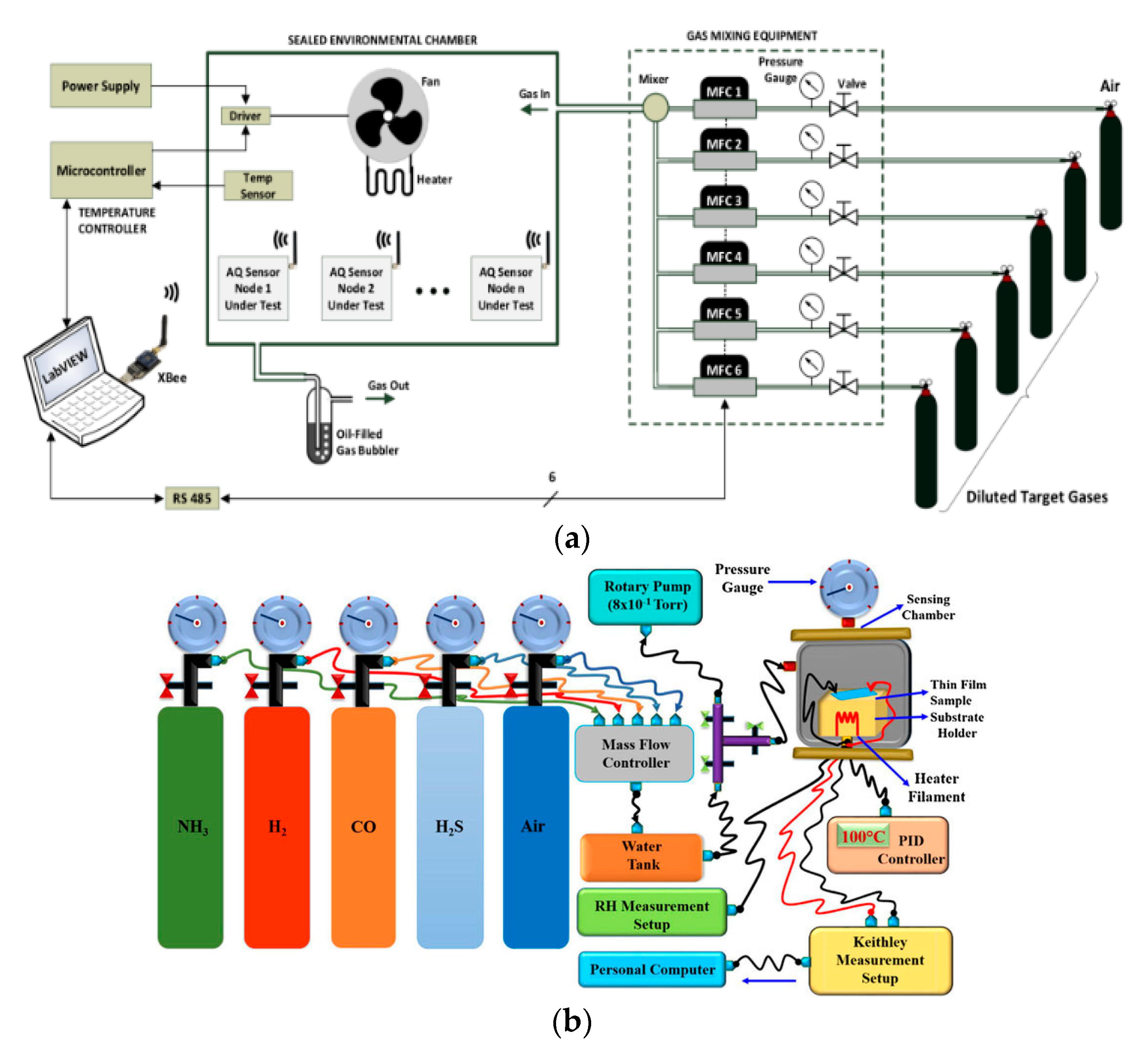
7. Indoor Epidemiology-based Calibration and Testing of AQ Gas Sensors
7.1. Uni-Gas Uni-Sensor Calibration
7.2. Uni-Gas Multi-sensor ENB Calibration
7.3. IoT-based Networked Multi-Gas ENB Calibration
7.4. Climate Smart Heterogeneous ENB Calibration
8. Indoor Epidemiology and Diseases
9. Indoor Epidemiological Merits in Operational and Lifecycle Cost Evaluation of Low-Cost AQ Sensors
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruce, N.; Perez Padilla, R.; and Albalak, R. Indoor air pollution in developing countries: a major environmental and public health challenge. Bulletin of World Health Organization 78 (9), 1078 1092, 2000.
- Taylor, E. The Air Quality Health Index and its Relation to Air Pollutants at Vancouver Airport. B.C. Ministry of Environment, 2018.
- A Guide to Air Quality and Your Health, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Outreach and Information Division, Research Triangle Park, NC. EPA-456/F-14-002, 2014.
- The Plain English Guide to the Clean Air Act, United States Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards, Environmental Protection Agency Research Triangle Park, Publication No. EPA-456/K-07-001, April 2007.
- Xie, X.; et al. A Review of Urban Air Pollution Monitoring and Exposure Assessment Methods. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf., 6, 389, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J., M. Sir Humphry Davy and the coal miners of the world: a commentary on Davy (1816), ‘An account of an invention for giving light in explosive mixtures of fire-damp in coal mines’. Philosophical Transactions A, 2014.
- Setiawan, A.; et al. Catalytic combustion of ventilation air methane (VAM) – long term catalyst stability in the presence of water vapour and mine dust. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Yoo, E.; and Lee, S. Glucose Biosensors: An Overview of Use in Clinical Practice. Sensors, 10(5): 4558–4576 2010. [CrossRef]
- Cowie, C.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes and high risk for diabetes using hemoglobin A1c criteria in the U.S. population in 1988–2006, Diabetes Care. 2010.
- Turner, A. P. Biosensors--sense and sensitivity. Science, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Lee, T., M. Over-the-Counter Biosensors: Past, Present, and Future. Sensors, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Mozaz, S.; et al. Biosensors as Useful Tools for Environmental Analysis and Monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Allsop, T.; et al. Low refractive index gas sensing using a surface plasmon resonance fibre device. Meas. Sci. Technol. 21, 2010. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation: Data and Statistics, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Gillis, D.; et al. How to Monitor Sustainable Mobility in Cities? Literature Review in the Frame of Creating a Set of Sustainable Mobility Indicators. Sustainability, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Kanaroglou, P., S.; et al. Establishing an air pollution monitoring network for intra-urban population exposure assessment: A location-allocation approach. Atmos. Environ, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; et al. Use of a mobile laboratory to evaluate changes in on-road air pollutants during the Beijing 2008 Summer Olympics. Atmos. Chem. Phys, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Amit, K. A review on Air Quality Indexing system. Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment, Vol. 9-2, pp. 101-113, June 2015.
- Bezuglaya, E., Y. Air Pollution Index and Interpretation of Measurements of Toxic Pollutant Concentrations. Atmospheric Environment, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E. The Air Quality Health Index and its Relation to Air Pollutants at Vancouver Airport. B.C. Ministry of Environment, 2008.
- Yerramilli, A.; et al. Air Pollution, Modeling and GIS based Decision Support Systems for Air Quality Risk Assessment. Environmental Science, 2011.
- Bozyazi, E.; et al. Analysis and mapping of air pollution using a GIS approach: A case study of Istanbul, AIR POLLUTION VIII, 2000.
- Kumar, A.; et al. I. Air quality mapping using GIS and economic evaluation of health impact for Mumbai City, India, Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2016.
- IEA, IRENA, UNSD, WB, WHO. Tracking SDG 7: the energy Progress report 2019. Washington: International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, The World Bank, 2019.
- Smith, K., R.; et al. Indoor air pollution in developing countries and acute lower respiratory infections in children, Thorax, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Global health risks: Mortality and burden of diseases attributable to selected major risks. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2014.
- Parajuli, I.; Lee, H.; and Shrestha, K., R. Indoor air quality and ventilation assessment of rural mountainous households of Nepal. Int J Sustain Built Environ, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Wendling, Z., A.; et al. Environmental performance Index, New Haven: Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy, 2018.
- Air quality guidelines for particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide: global update 2005. Summary of risk assessment. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2005.
- A. Lewis, and Edwards, P. Validate personal air-pollution sensors, Nature, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; et al. Air quality trends and potential health effects Development of an aggregate risk index. Atmospheric Environment, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Elen, B.; et al. The Aeroflex: A Bicycle for Mobile Air Quality Measurements. Sensors, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Cannistraro, G.; and Ponterio, L. Analysis of Air Quality in the Outdoor Environment of the City of Messina by an Application of the Pollution Index Method. International Journal of Civil and Environment Engineering, 2009.
- Cincinelli, A.; and Martellini, T. Indoor air quality and health. Int J Environ Res Pu, 2017.
- A Strategic Framework for Air Quality Management in Asia, G. Haq, and D. Schwela, Technical Report, January 2004.
- Foundation Course on Air Quality Management in Asia. Haq, G.; and Schwela, D.; and David, L. SEI, 2008.
- Naess, L. Clean Air Act Advisory Committee Meeting, OAQPS, January 2008.
- Vitolo, C.; et al. Modeling Air Pollution, Climate, and Health Data Using Bayesian Networks: A Case Study of the English Regions. Earth and Space Science, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, B.; and Bartonov, A. Air Quality Management Planning (AMQP). Chemical Industry & Chemical Engineering Quarterly, 2012.
- Larssen, S.; Gram, F.; and Haugsbakk, I. URBAIR. Urban air quality management strategy in Asia. Kathmandu Valley city specific report, NILU Kjeller, 1995.
- Dimitroulopoulou, C.; et al NDAIR: A probabilistic model of indoor air pollution in UK homes. Atmospheric Environment, 2006.
- Arungu-Olende, S. Rural energy, Nat Resour Forum, 1984.
- Karagulian, F.; et al. Review of sensors for air quality monitoring. Joint Research Centre (JRC) Technical Reports, 2019.
- Alexandre, M.; and Gerboles, M. Review of small commercial sensors for indicative monitoring of ambient gas. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 2012.
- Castell, N.; et al, Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environment International, 2017.
- Jiang, D. L. Environmental Gas Sensors 2020-2030. Technologies, Manufacturers, Forecasts, 2020.
- Yoo, K. S. Gas Sensors for Monitoring Air Pollution. Monitoring, Control and Effects of Air Pollution, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. M.; et al. A multi-gas sensing system for air quality monitoring. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Applied System Invention, 2018.
- Aakash, C.; and Kumar, P. iSCAPE - Improving the Smart Control of Air Pollution in Europe. Summary of air quality sensors and recommendations for application, 2017.
- Kawasaki, H.; Ueda, T.; Suda, Y.; and Ohshima, T. Optical Emission Spectroscopy of Low-Discharge-Power Magnetron Sputtering Plasmas Using Pure Tungsten Target. Sensors and Actuators B, 2004. [CrossRef]
- West, D. L.; Montgomery, F. C.; and Armstrong, T. R. Development of NOx Sensors for Heavy Vehicle Applications. Sensors and Actuators B, 2005.
- Hodgkinson, J.; and Tatam, R. P. Optical gas sensing: a review. Meas. Sci. Technol, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; and Telting-Diaz, M. Electrochemical Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2004.
- Cretescu, I.; et al. Electrochemical Sensors for Monitoring of Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution. IntechOpen, 2017.
- Tierney, M. J.; and Kim, H. O. L. Electrochemical gas sensor with extremely fast response times. Analytical Chemistry, 1993. [CrossRef]
- Park, C. O.; Fergus, J.W.; Miura, M.; Park, J.; and Choi, A. Solid-state electrochemical gas sensors. Ionics, 2009.
- Ishihara, T.; and Matsubara, S. Capacitive Type Gas Sensors. Journal of Electroceramics, 1998. [CrossRef]
- Schoeneberg, U.; et al. A novel readout technique for capacitive gas sensors. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Brianda, D.; et al. Integration of MOX gas sensors on polyimide hotplates. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Amirola, J.; et al. Design fabrication and test of micromachined-silicon capacitive gas sensors with integrated readout. Proceedings Smart Sensors, Actuators, and MEMS, 2003.
- Oberländer, J.; et al. Detection of hydrogen peroxide vapor by use of manganese (IV) oxide as catalyst for calorimetric gas sensors. Physica Status Solidi (A) Applications and Materials, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Riegel, J.; and Härdt, K. H. Analysis of combustible gases in air with calorimetric gas sensors based on semiconducting BaTiO3 ceramics. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 1990. [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, P.; et al. Realization of a calorimetric gas sensor on polyimide foil for applications in aseptic food industry. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Serry, M.; Voiculcscu, I.; and Kobtan, A. Catalytic Hafnium Oxide Calorimetric MEMS Gas and Chemical Sensor. IEEE Sensors, 2018.
- Wang, Y. W.; et al. Film bulk acoustic resonator based gas sensor: a sensitive detector for gas chromatography. Transducers, 2017.
- Reichl, W.; et al. Novel Gas Sensors Based on Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators. IEEE Sensors, 2004.
- Barié, N.; et al. Work place monitoring using a high sensitive surface acoustic wave based sensor system. Transducers, 2007.
- Liu, X.; et al. Enhanced Sensitivity of a Hydrogen Sulfide Sensor Based on Surface Acoustic Waves at Room Temperature. Sensors, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Spannhake, J.; et al. Micro-Fabrication of Gas Sensors. Solid State Gas Sensing, 2008.
- Nazemi, H.; et al. Advanced Micro- and Nano-Gas Sensor Technology: A Review. Sensors, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Kakoty, P.; and Bhuyan, M. Fabrication of Micromachined SnO2 Based MOS Gas Sensor with Inbuilt Microheater for Detection of Methanol. Sens. Transducers, 2016.
- Liu, T.; Burger, C.; and Chu, B. Nanofabrication in polymer matrices. Prog. Polym. Sci, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Park, K. K.; et al. Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers via local oxidation and direct wafer bonding. J. Microelectromech. Syst, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Hung, V. N.; et al. High-frequency one-chip multichannel quartz crystal microbalance fabricated by deep RIE. Sensors Actuators A Phys, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Bochenkov, V.; and Sergeev, G. Preparation and chemiresistive properties of nanostructured materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Ghoorchian, A.; and Alizadeh, N. Chemiresistor gas sensor based on sulfonated dye-doped modified conducting polypyrole film for high sensitive detection of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene in air. Sens. Actuators B Chem, 2018.
- Hsueh, Y. T.; Smith, R. L.; and Northrup, M. A. Microfabricated, Electrochemi-iluminescence Cell for the Detection of Amplified DNA. Transducers, 1995.
- Lakin, K. M.; Kline, G. R.; and McCarron, K. T. High-Q microwave acoustic resonators and filters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech, 1993. [CrossRef]
- Erguri, A. et al. Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers: Fabrication technology. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. J.; et al. Functionalization layers for CO2 sensing using capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers. Sens. Actuators B Chem, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Ergun, A. S.; Yaralioglu, G. G.; and Khuri-Yakub, B. T. Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers: Theory and technology. J. Aerosp. Eng, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, C. D.; Cretu, E.; and Rohling, R. Fabrication and testing of polymer-based capacitive micromachined ultrasound transducers for medical imaging. Microsyst. Nanoeng, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; et al. Highly Sensitive Detection of DMMP Using a CMUT-Based Chemical Sensor. Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, 2010.
- Emadi, A.; and Buchanan, D. Capacitive Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducer with Multiple Deflectable Membranes. U.S. Patent 9,925,561, 27 March 2018.
- Park, K.K.; et al. Fabrication of capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers via local oxidation and direct wafer bonding. J. Microelectromech. Syst, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Haotian, L.; et al. Microhotplates for Metal Oxide Semiconductor Gas Sensor Applications—Towards the CMOS-MEMS Monolithic Approach.
- Graf, M.; et al. Microfabricated gas sensor systems with sensitive nanocrystalline metal-oxide films. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Afridi, M. Y.; et al. A monolithic CMOS microhotplate-based gas sensor system. IEEE Sens. J., 2002. [CrossRef]
- Graf, M.; et al. Micro-fabricated gas sensor systems with sensitive nanocrystalline metal-oxide films. J. Nanoparticle Res., 2006.
- Jiang, Y.; et al. Chemiresistive Sensor Array from Conductive Polymer Nanowires Fabricated by Nanoscale Soft Lithography. Nanoscale, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Zhao W. H.; and Wu, W. Gas Sensors Based on Chemi-Resistive Hybrid Functional Nanomaterials. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; et al. Chemoresistive materials for electronic nose: Progress, perspectives, and challenges. InfoMat, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; and Duan, X. Recent advances in micro detectors for micro gas chromatography. Science China Materials, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; et al. Biomolecules Detection Using Microstrip Sensor with Highly-ordered Nanowires Array. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019.
- Hwang, S.; et al. A near single crystalline TiO2 nanohelix array: enhanced gas sensing performance and its application as a monolithically integrated electronic nose. The Analyst, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; et al. Smart gas sensor arrays powered by artificial intelligence. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019.
- Guz, L.; et al. Application of Gas Sensor Arrays in Assessment of Wastewater Purification Effects. Sensors, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Lipatov, A.; et al. Highly selective gas sensor arrays based on thermally reduced graphene oxide. NanoScale, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Macías, M. M.; et al. A Compact and Low Cost Electronic Nose for Aroma Detection. Sensors, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; et al. Least Squares Neural Network-Based Wireless E-Nose System Using an SnO2 Sensor Array. Sensors, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, H.; et al. Room temperature multiplexed gas sensing using chemical-sensitive 3.5-nm-thin silicon transistors. Science Advances, 2017.
- https://pib.gov.in/NEWSITE/erelcontent.aspx?relid=123091 (Visited on Oct 6, 2020).
- Yan, J.; Tian, F.; and Shen, Y. A PSO-SVM Method for Parameters and Sensor Array Optimization in Wound Infection Detection based on Electronic Nose. Journal of Computational Physics, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Hung, C. M.; et al. On-chip growth of semiconductor metal oxide nanowires for gas sensors: A review. Journal of Science: Advanced Materials and Devices 2, 2017. [CrossRef]
- https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2016/08/18/985749/0/en/SPEC-Sensors-Releases-Open-Source-Digital-Gas-Sensor-Developer-Kit-for-the-Internet-of-Things.html (Visited on Oct 6, 2020).
- Shekhar, C.; et al. Single Chip Gas Sensor Array for Air Quality Monitoring. IEEE Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2017.
- Gang, Z. Y.; et al. An Innovative Gas Sensor with On-Chip Reference Using Monolithic Twin Laser. Chinese Physics Letters, 2017.
- Zhang, G.; et al. La2O3-sensitized SnO2 nanocrystalline porous film gas sensors and sensing mechanism toward formaldehyde. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Postolache, O. A. et al. Smart Sensors Network for Air Quality Monitoring Applications. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; et al. A Survey on Gas Sensing Technology. Sensors, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Casey, J. G.; et al. Testing the performance of field calibration techniques for low-cost gas sensors in new deployment locations: across a county line and across Colorado. Atmos. Meas. Tech., 2018. [CrossRef]
- Leidinger, M.; et al. Characterization and calibration of gas sensor systems at ppb level—a versatile test gas generation system. Measurement Science and Technology, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Thong, L.V.; et al. Comparative study of gas sensor performance of SnO2 nanowires and their hierarchical nanostructures. Sensors and Actuators B, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; et al. A Method for Selecting Optimal Number of Sensors to Improve the Credibility. Journal of Sensors, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Fonollosa, F.; et al. Chemical gas sensor array dataset. Data in Brief, Volume 3, 2015.
- Kumar, A.; et al. Fabrication of porous silicon filled Pd/SiC nanocauliflower thin films for high performance H2 gas sensor. Sensors and Actuators B, 2018.
- Benammar, M. A..; et al. A Smart Rig for Calibration of Gas Sensor Nodes. Sensors, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Maag, B.; et al. A Survey on Sensor Calibration in Air Pollution Monitoring Deployments. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; et al. Field calibration of a cluster of low-cost available sensors for air quality monitoring. Part A: Ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; et al. Field calibration of electrochemical NO2 sensors in a citizen science context. Atmos. Meas. Technol, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Hagan, D. H.; et al. Calibration and assessment of electrochemical air quality sensors by co-location with regulatory-grade instruments. J. Atmos. Meas. Technol, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Hasenfratz, D.; et al. On-the-fly calibration of low-cost gas sensors. 9th European Conference on Wireless Sensor Networks, pp. 228–244, 2012.
- Yang, F.; et al. Dynamic calibration of electrochemical sensor for accelerated analytic quantification. IEEE Sens. J., 2012. [CrossRef]
- Tian B.; et al. Environment-Adaptive Calibration System for Outdoor Low-Cost Electrochemical Gas Sensors. IEEE Access, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Asghar, U.; et al. Development of Highly Efficient Multi-variable Wireless Sensor System Design for Energy Harvesting. arXiv:1802.05755, 2018.
- Luo, H.; et al. Design of indoor air quality monitoring system based on wireless sensor network. International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, A.R.; et al. A Mobile GPRS-Sensors Array for Air Pollution Monitoring. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Penza, M.; et al. Urban Air Quality Monitoring with Networked Low-Cost Sensor-Systems. Eurosensors, 2017.
- Touati, F.; et al. Environmentally Powered Multiparametric Wireless Sensor Node for Air Quality Diagnostic. Sensors and Materials, 2015.
- Kang, J. et al. A Comprehensive Real-Time Indoor Air-Quality Level Indicator. Sustainability, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Abdaoui, A.; et al. A Smart Rig for Calibration of Gas Sensor Nodes: Test and Deployment. IWCMC, 2020.
- Tariq, H. et al. An Autonomous Multi-Variable Outdoor Air Quality Mapping Wireless Sensors IoT Node for Qatar. IWCMC, 2020.
- Tariq, H.; et al. A Real-time Gradient Aware Multi-Variable Hand-held Urban Scale Air Quality Mapping IoT System. DTS, 2020.
- Abdaoui, A.; et al; Energy Efficient Real-time Out Door Air Quality Monitoring. IWCMC, 2020.
- Allen, G. The Role of PM and Ozone Sensor Testing/Certification Programs, Retrieved from: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production /files/session_07_b_allen.pdf, 2018.
- Smith, K.R.; et al., Clustering approaches to improve the performance of low cost air pollution sensors. Faraday Discuss, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Hvidtfeldt, K.R.; et al. Evaluation of the Danish AirGIS air pollution modeling system against measured concentrations of PM2.5, PM10, and black carbon, Environ. Epidemiol, 2018.
- The EPA Village Green, https://www.epa.gov/air-research/village-green-project. (Visited on Oct 6, 2020).
- Jiao, W.; et al., Field assessment of the village green project: an autonomous community air quality monitoring system. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015. [CrossRef]
- EC WG, Guide to the Demonstration of Equivalence of Ambient Air Monitoring Methods, Report by EC Working Group on Guidance: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/air/quality/legislation/pdf/equivalence.pdf, 2010. (Visited on Oct 6, 2020).
- Amico, A. D’.; et al. A contribution on some basic definitions of sensors properties. IEEE Sensors J., 2001. [CrossRef]
- Heimann, I.; et al. Source attribution of air pollution by spatial scale separation using high spatial density networks of low cost air quality sensors. Atmos. Environ, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Spinelle, L.; et al. Protocol of Evaluation and Calibration of Low-cost Gas Sensors for the Monitoring of Air Pollution. Publications Office of the European Union. EUR 26112EN, 2013.
- Viana, M.; et al. Field comparison of portable and stationary instruments for outdoor urban air exposure assessments. Atmos. Environ, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Air Quality in Europe 2013 Report. EEA Report. No. 9/2013, Copenhagen, 112 pages, 2013.
- Air Quality in Europe 2014 Report. EEA Report. No. 5/2014, Copenhagen, 80 pages, 2014.
- Zhu, W.; et al. Short-term effects of air pollution on lower respiratory diseases and forecasting by the group method of data handling. Atmos. Environ., 2012. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wargocki, P.; Lian, Z.; Thyregod, C. Effects of exposure to carbon dioxide and bioeffluents on perceived air quality, self-assessed acute health symptoms and cognitive performance. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 47–64. [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.L.; et al. Spatiotemporal modeling of PM2.5 data with missing values. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2003.
- Persily, A.; de Jonge, L. Carbon dioxide generation rates for building occupants. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 868–879. [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, O.; Wyart, G.; Mandin, C.; Blondeau, P.; Cabanes, P.-A.; Leclerc, N.; Mullot, J.-U.; Boulanger, G.; Redaelli, M. Association of carbon dioxide with indoor air pollutants andexceedance of health guideline values. Build. Environ. 2015, 93, 115–124.
- ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2013. Ventilation for Acceptable Indoor Air Quality; American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc.: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Azuma, K.; Kagi, N.; Yanagi, U.; Osawa, H. Effects of low-level inhalation exposure to carbon dioxide in indoor environments: A short review on human health and psychomotor performance. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 51–56. [CrossRef]
- Ritter, M.; et al. Air pollution modeling over very complex terrain: An evaluation of WRF-Chem over Switzerland for two 1-year periods. Atmos. Res, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, A. Application of CFD Methods for Modelling in Air Pollution Problems: Possibilities and Gaps. Environ. Monit. Assess, 2000. [CrossRef]
- Chen. J.; et al. Forecasting smog-related health hazard based on social media and physical sensor. Inf. Syst., 2017.
- Shimadera, H.; et al. Evaluation of Air Quality Model Performance for Simulating Long-Range Transport and Local Pollution of PM2.5 in Japan. Adv. Meteorol., 2016. [CrossRef]
- International Programme on Chemical Safety. Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Nhung, N. T. T.; et al. Short-term association between ambient air pollution and pneumonia in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of time-series and case-crossover studies. Environ. Pollut., 2017. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-España, R.; et al. Air-pollution prediction in smart cities through machine learning methods: A case of study in Murcia, Spain. J. Univ. Comput. Sci., 2018.
- Deters, K.; et al. Modeling PM2.5 Urban Pollution Using Machine Learning and Selected Meteorological Parameters. J. Electr. Comput. Eng., 2017.
- Carnevale, C.; et al. Lazy Learning based surrogate models for air quality planning. Environ. Model. Softw., 2016. [CrossRef]
- Gacquer, D.; et al. Comparative study of supervised classification algorithms for the detection of atmospheric pollution. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., 2011. [CrossRef]
- Raub, J.A.; Mathieu-Nolf, M.; Hampson, N.B.; Thom, S.R. Carbon monoxide poisoning–A public health perspective. Toxicology 2000, 145, 1–14.
- Rybarczyk, Y.; et al. Machine Learning Approaches for Outdoor Air Quality Modelling: A Systematic Review. Applied Sciences, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W. Z.; et al. Potential assessment of the ‘support vector’ machine method in forecasting ambient air pollution trends. Chemosphere, 2015.
- Luecken, D. J.; et al. Development and analysis of air quality modeling simulations for hazardous air pollutants. Atmospheric Environment, 2006. [CrossRef]
- Emmerich, S.J.; Persily, A.K. State-of-the-Art Review of CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation Technology and Application; Diane Publishing: Darby, PA, USA, 2003; p. 43.
- Nguyen, D.; et al. A brief review of air quality models and their applications. Open Journal of Atmospheric and Climate Change, 2014.
- Nordiska, M. Interaction between climate change, air pollution and related impacts. Nordic Council of Ministers’ publishing house, 2014.
- R Development Core: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, 2001.
- Roadknight, C. M.; et al. Modeling complex environmental data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1997.
- Walter, A.; et al. Simulation of global and hemispheric temperature variations and signal detection studies using neural networks. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 1998.
- Wang, W.; et al. Three improved neural network models for air quality forecasting. Engineering Computations, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G. D.; et al. A quantitative assessment of source contributions to inhalable particulate matter pollution in metropolitan Boston. Atmos Environ, 1985. [CrossRef]
- Lary, D.; et al. Using machine learning to estimate global PM2.5 for environmental health studies. Environ Health Insights, 2015.
- Jiang, W.; et al. Using social media to detect outdoor air pollution and monitor air quality index (AQI): a geo-targeted spatiotemporal analysis framework with Sina Weibo (Chinese twitter). PloS ONE, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Bonne, U.; et al. Microanemometer-based flow sensing. Proc. 5th IGT Symp. Natural Gas Quality Measurement, Chicago, IL, USA, 1990.
- Bonne, U.; et al. Method and apparatus for measuring selected properties of a fluid of interest using a single heater element. US Pat. 6 079 253, 2000.
- Ye, Y.; et al. Online sequential extreme learning machine in nonstationary environments. Neurocomputing, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J. R.; et al. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Advances in adaptive data analysis, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C. J.; et al. A refined index of model performance. International Journal of Climatology, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C. J.; et al. On The Validation of Models. Physical Geography, 1981.
- Witten, I. H.; et al. Data Mining - Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques. United States: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 2011.
- Willmott, C. J.; et al. Some Comments on the Evaluation of Model Performance. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1982.
- Simpson, R.; et al. A statistical analysis of particulate data sets in Brisbane, Australia. Atmospheric Environment: Part B. Urban Atmosphere, 1992. [CrossRef]
- Penza, M.; Suriano, D.; Villani, M.G.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M. Towards Air Quality Indices in Smart Cities by Calibrated Low-Cost Sensors Applied to Networks; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 2014.
- Castell, N.; Dauge, F.R.; Schneider, P.; Vogt, M.; Lerner, U.; Fishbain, B.; Broday, D.; Bartonova, A. Can commercial low-cost sensor platforms contribute to air quality monitoring and exposure estimates? Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 293–302.
- Han, P.; Mei, H.; Liu, D.; Zeng, N.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Calibrations of Low-Cost Air Pollution Monitoring Sensors for CO, NO2, O3, and SO2. Sensors 2021, 21, 256. [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Burch, M.; Diehl, S.; Weiskopf, D. A taxonomy and survey of dynamic graph visualization. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 36, pp. 133–159.
- Tariq, H., and Shafaq, S. Real-time Contactless Bio-Sensors and Systems for Smart Healthcare using IoT and E-Health Applications. WSEAS Transactions on Biology and Biomedicine. Volume 19, Pages 91-106.
- Petra, B., et al. Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tušimice Observatory. Atmosphere, 2020.
- Tariq, H., et al. A Real-time Gradient Aware Multi-Variable Handheld Urban Scale Air Quality Mapping IoT System. IEEE International Conference on Design & Test of Integrated Micro & Nano-Systems, 2020.
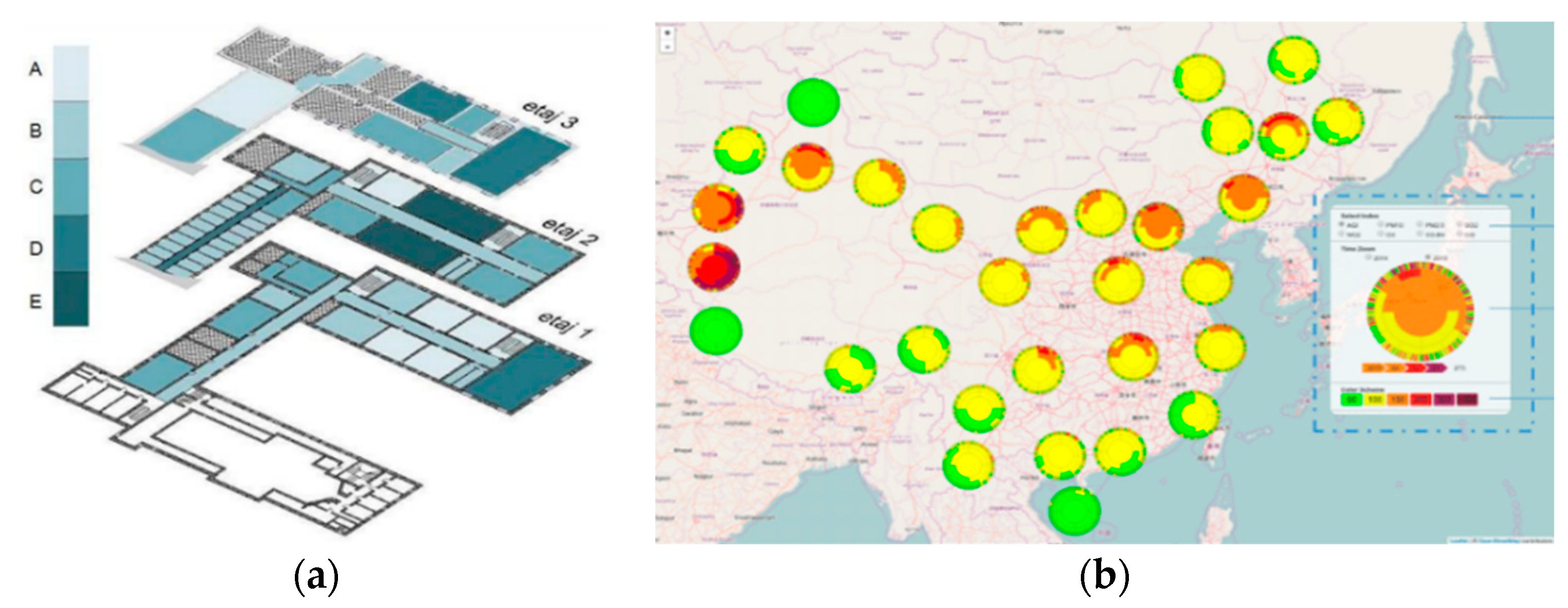
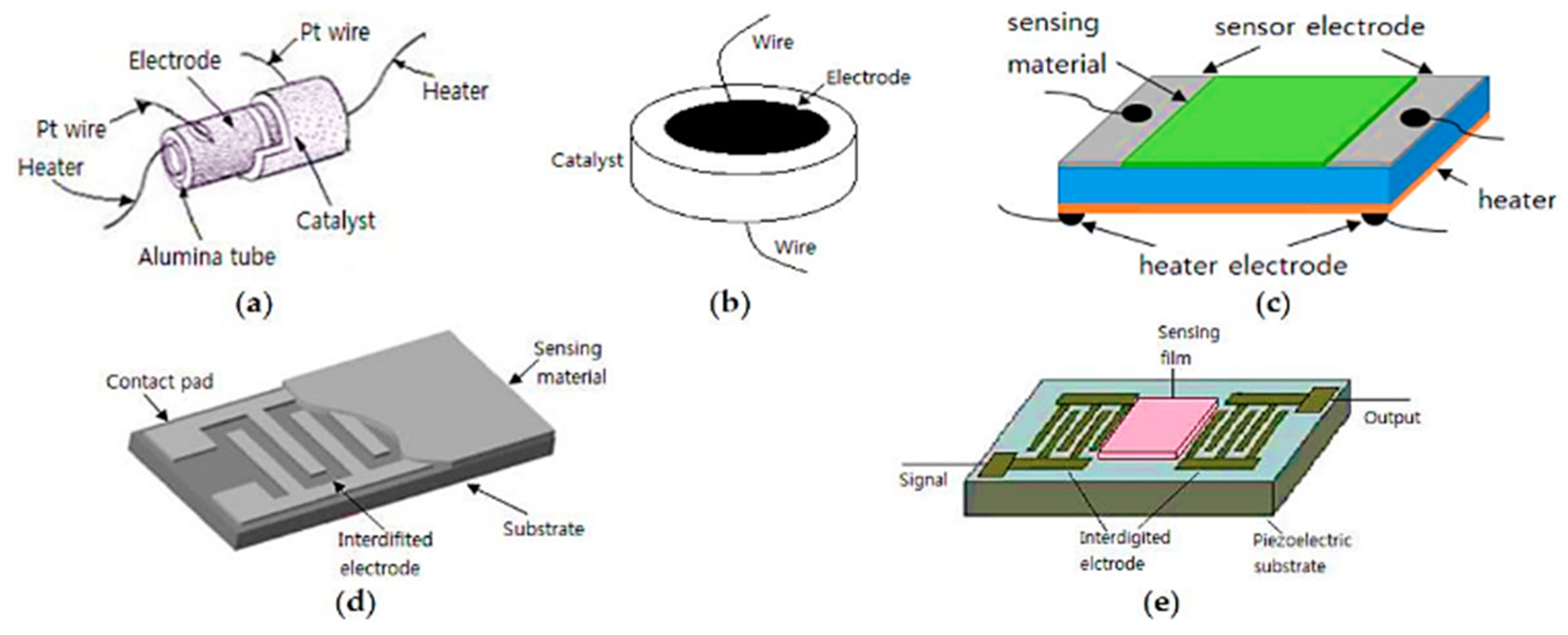
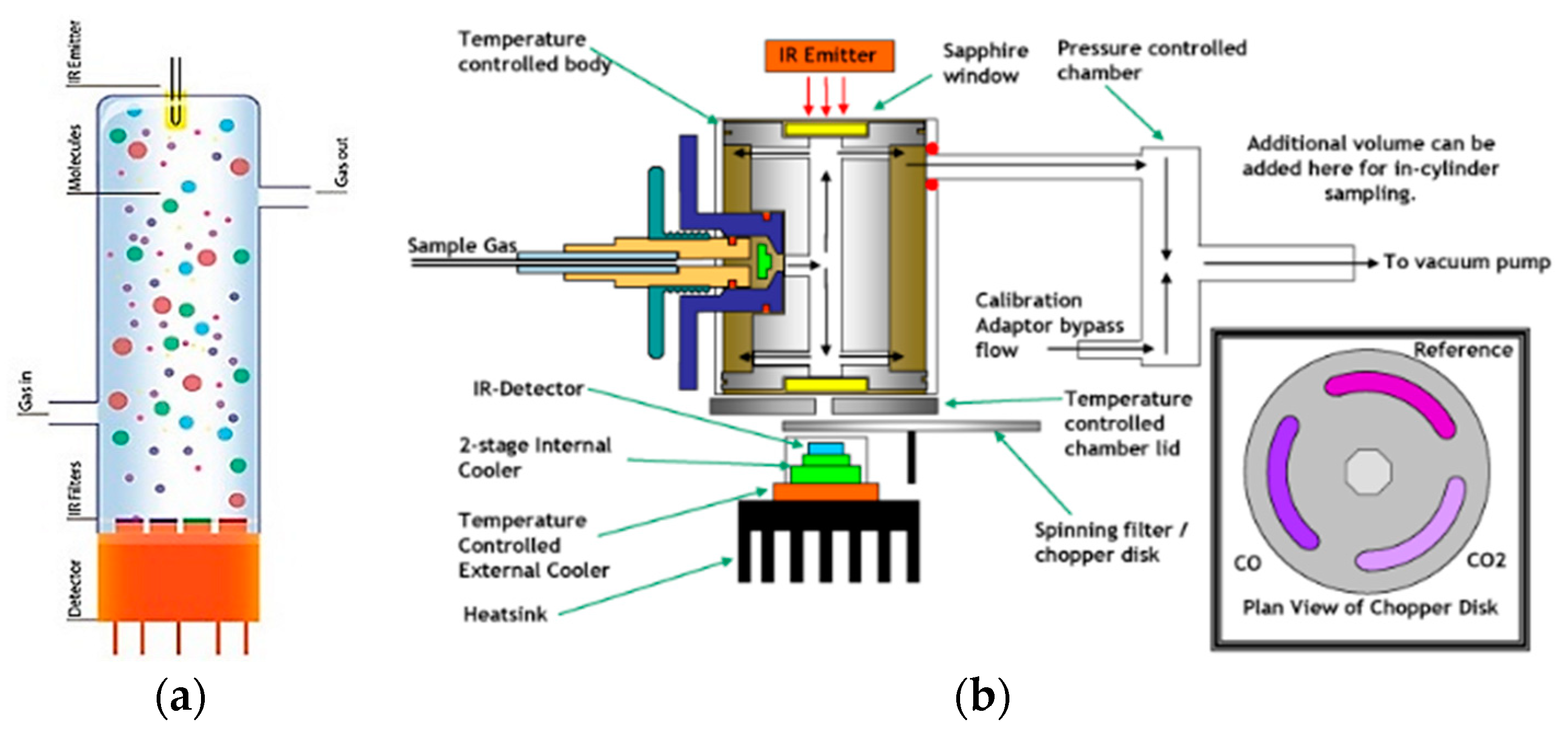
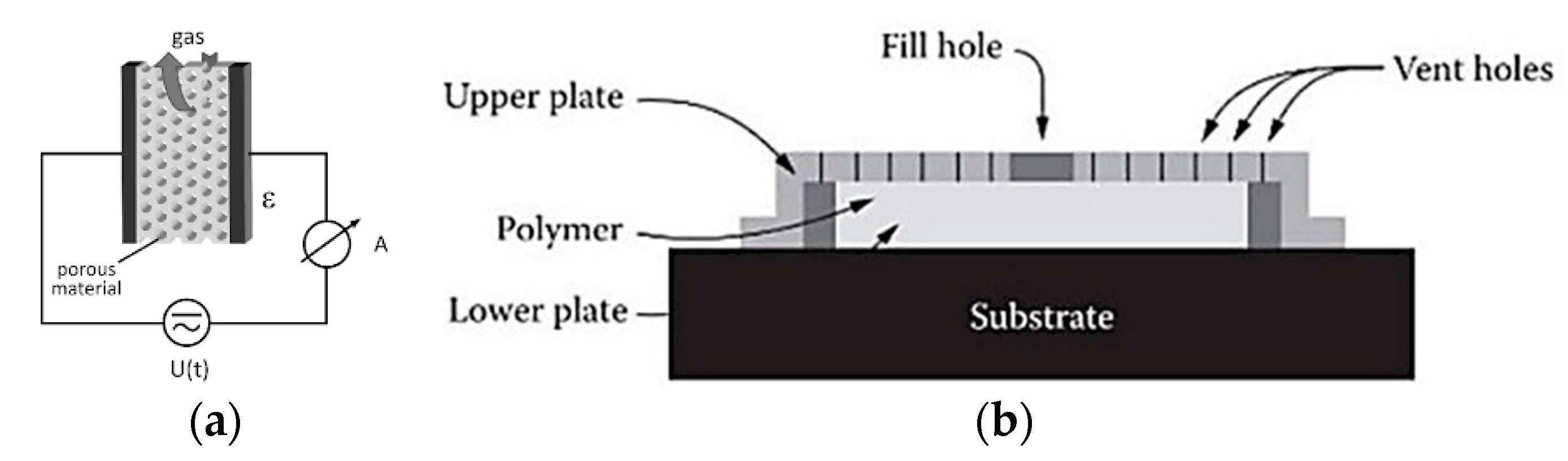
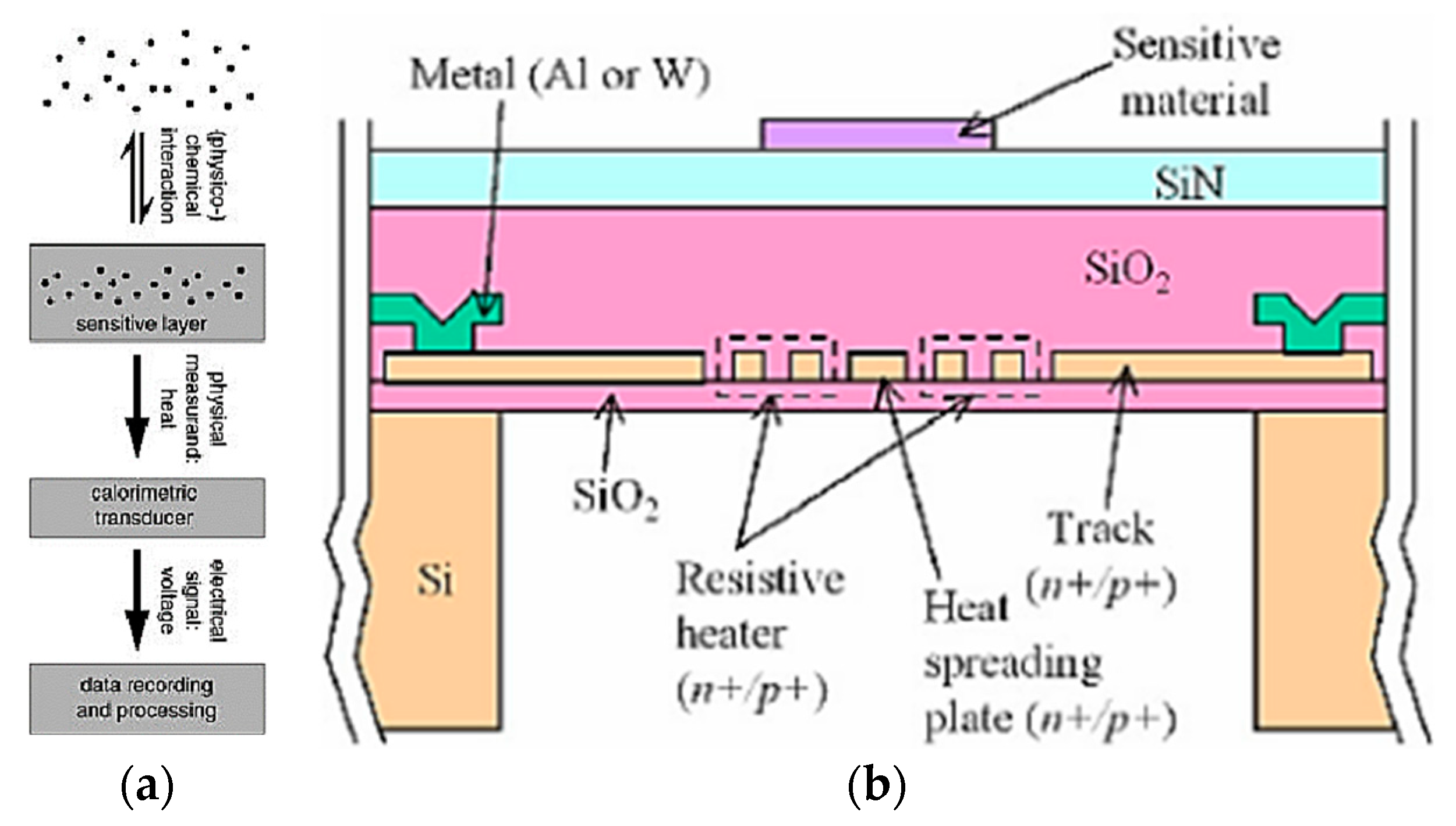
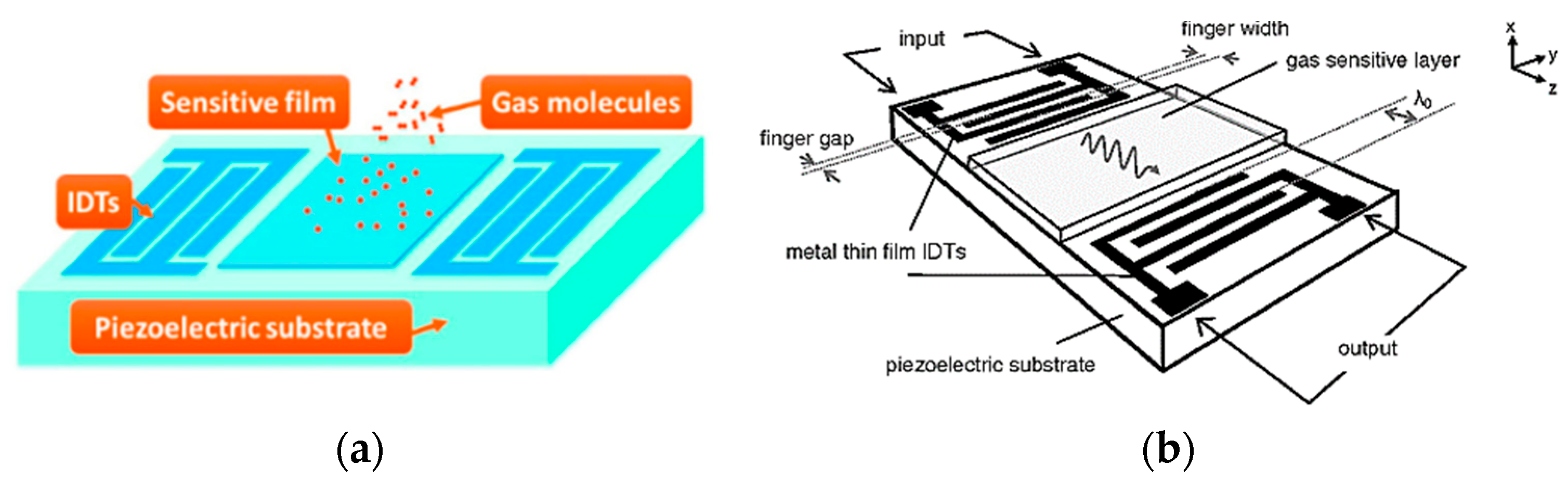
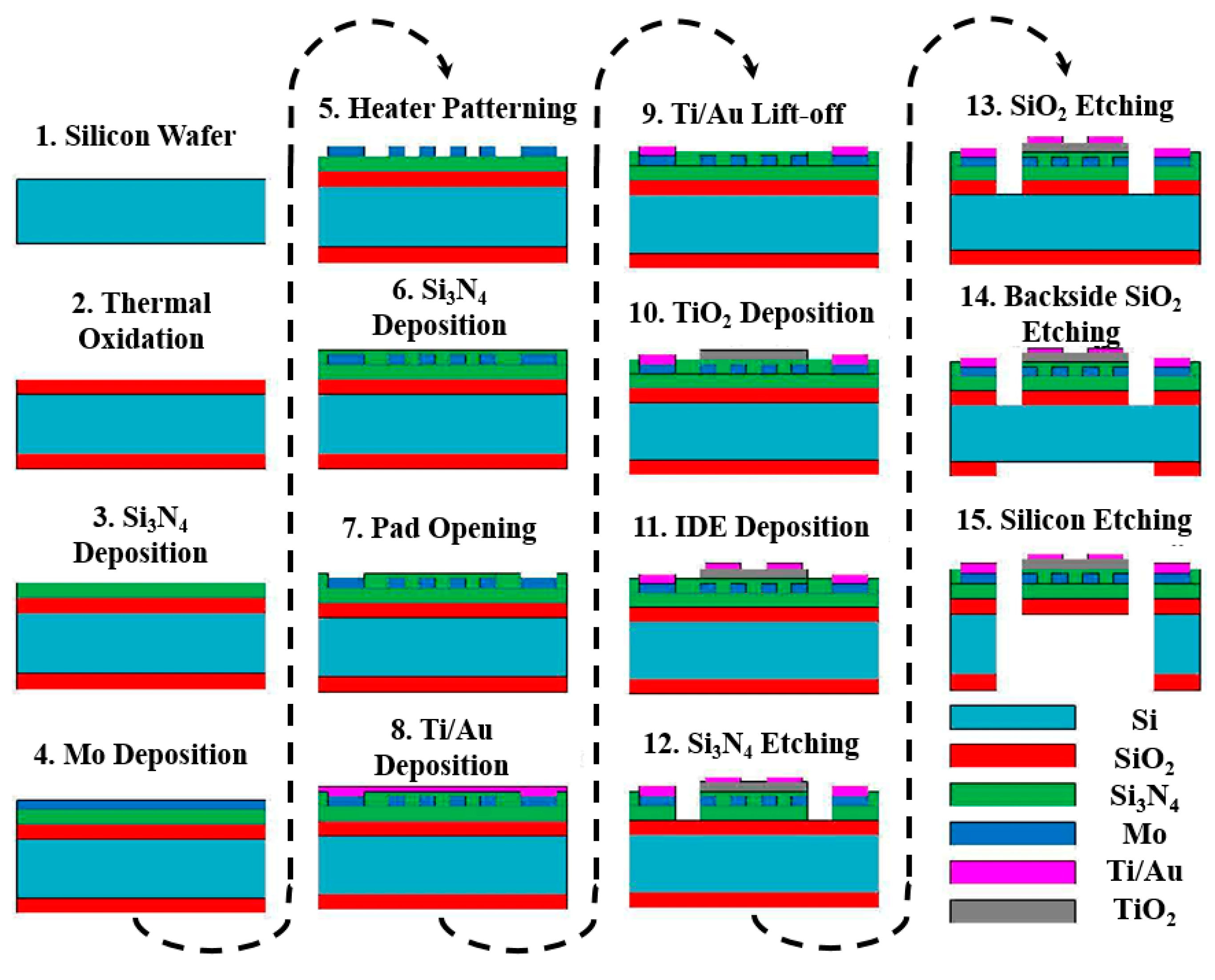
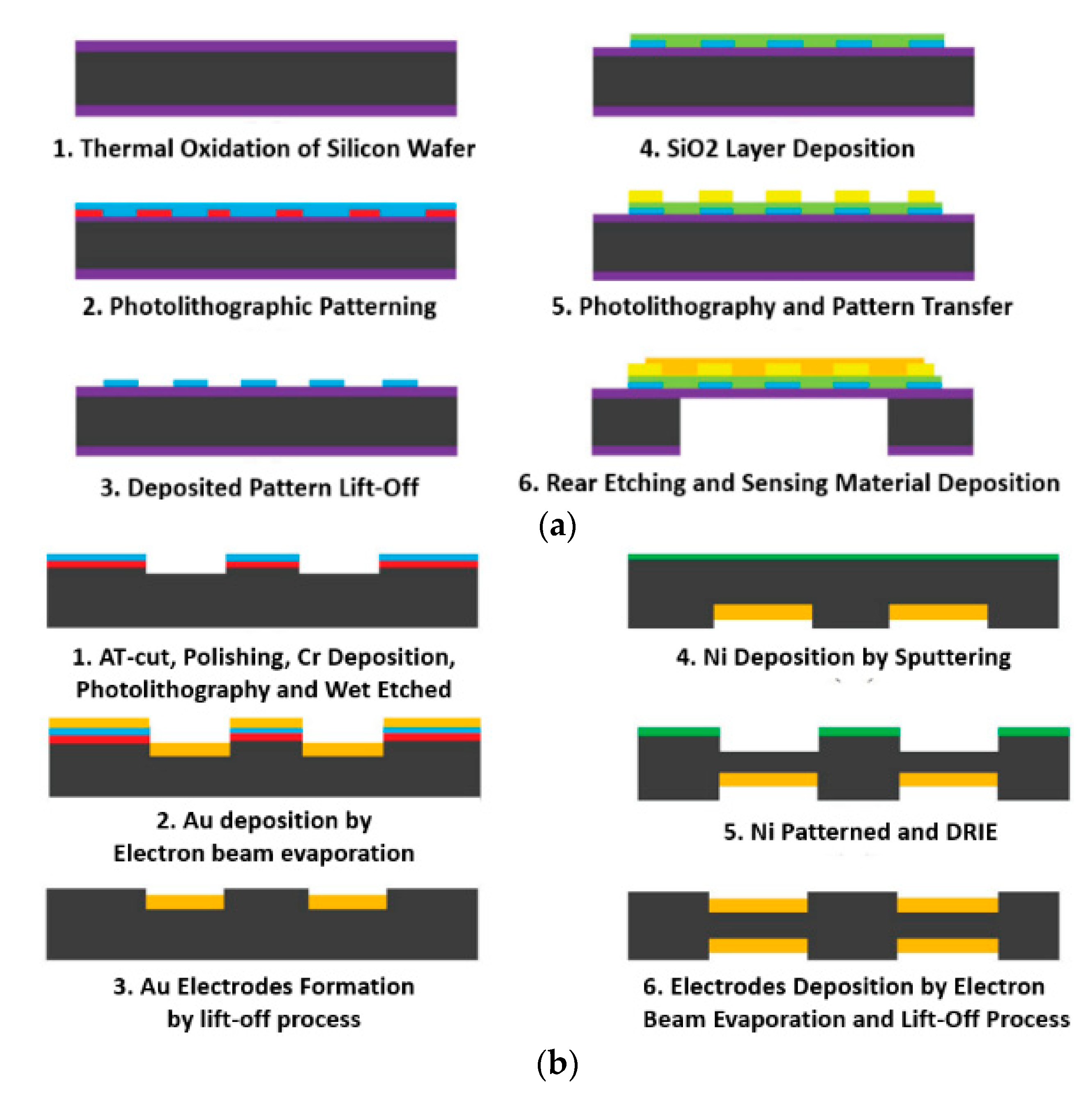
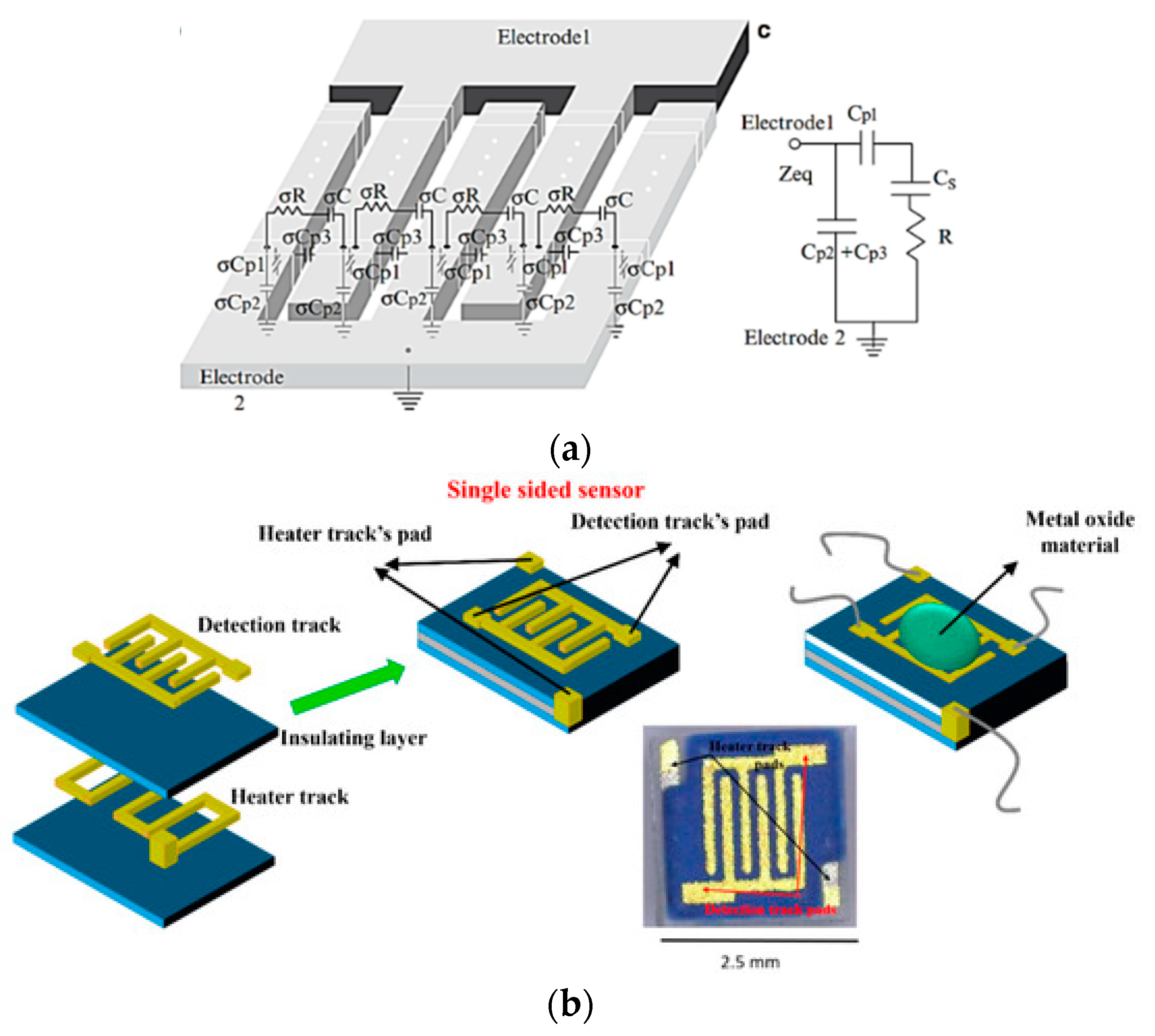
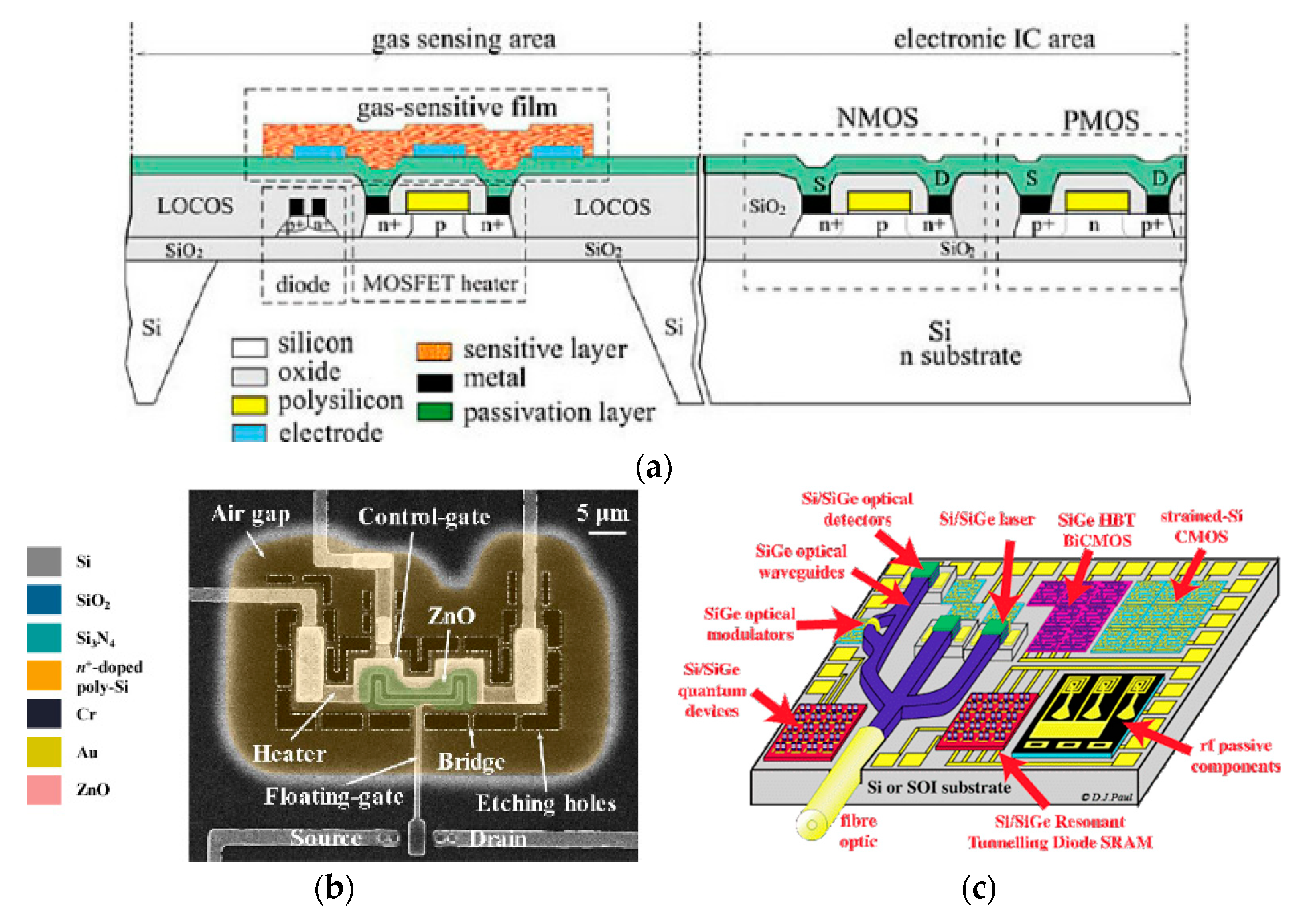
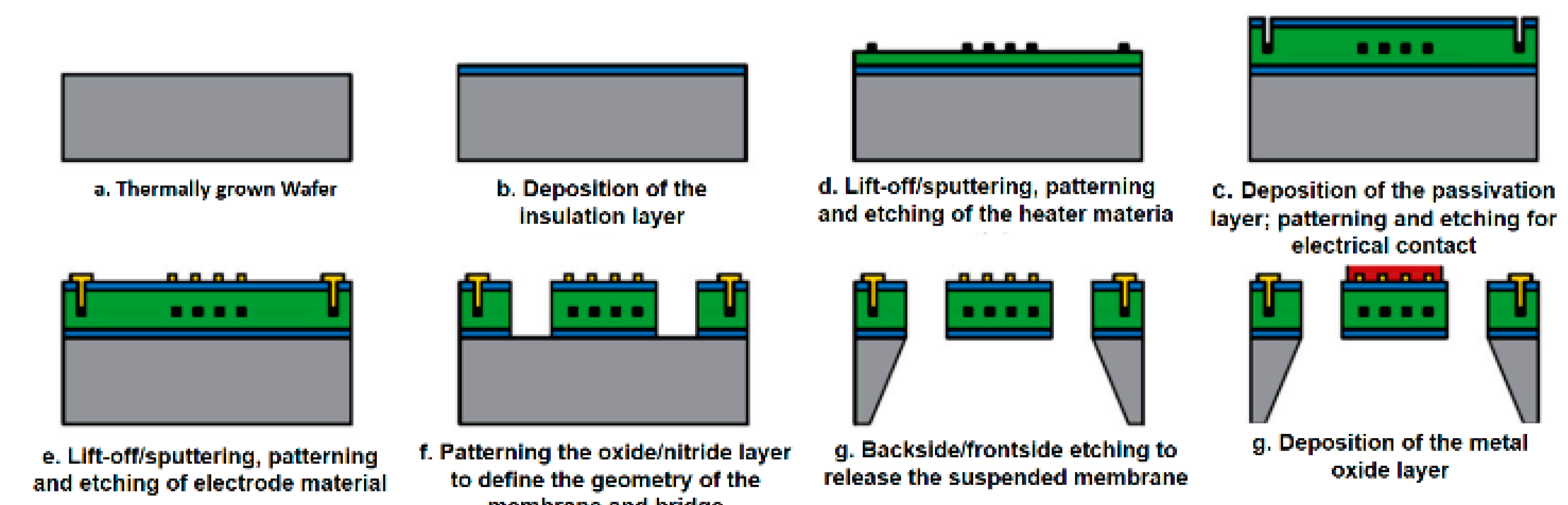
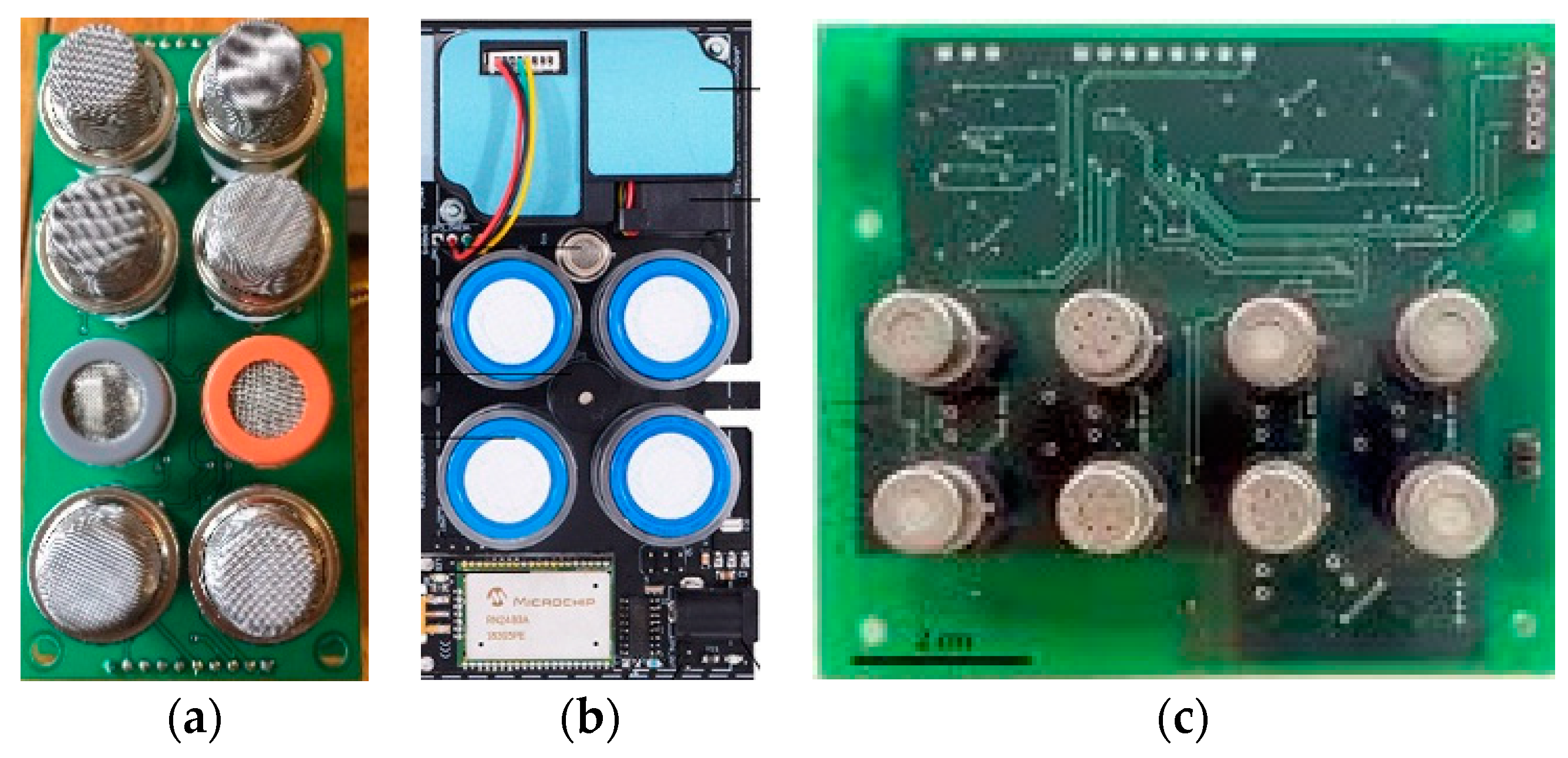
| # | Description | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keywords | Indoor air quality, indoor respiratory diseases, indoor pollutants, indoor epidemiolgy, epidemiology-focused sensors, epidemiology-focused air quality methods, epidemiology-focused systems. |
| 2 | Citations (50-5000) | [5000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1200 1000 800 500 300 250 200 150 100 50] |
| 3 | Years (50) | 170 + [10 20 30 40 50 2] |
| 4 | Authors per paper (1-20) | [1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 20] |
| 5 | Operators | WHO, NIH, CDC, US EPA, Methods, Policies, Rules, Approaches, Cases, Reports |
| Pollutants | Concentration Levels (mg/m3) | Exposure Time | Organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 60 |
15 min 30 min |
WHO | |
| CO | 30 10 |
1 h 8 h |
|
| 29 10 |
1 h 8 h |
USEPA | |
| CO2 | 1800 | 1 h | WHO |
| 0.4 | 1 h | WHO | |
| NO2 | 0.15 | 24 h | |
| 0.1 | 1 year | USEPA | |
| PM | 0.15 0.05 |
24 h 1 year |
USEPA |
| 0.5 | 10 min | WHO | |
| SO2 | 0.35 | 1 h | |
| 0.365 0.08 |
24 h 1 year |
USEPA |
| Indoor Epidemiological Merits | Uni-Gas Uni-Sensor Calibration | Uni-Gas Multi-Sensor ENB Calibration | IoT-based Networked Multi-Gas ENB Calibration | Climate Smart Heterogeneous ENB Calibration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Scale (per 24 hours) | 1-24 | 10-120 | 10-1840 | 10-144 |
| System Setup Cost (per 10 sensors) | $2~5.1M | $0.4~2M | $1~1.8M | $4~7M |
| Types of Sensors Supported | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| IoT Support and Remote Calibration | No | No | Yes | No |
| Calibration Cost (per 10 sensors) | $3-10 | $12-19 | $2-8 | $35-120 |
| Real-time AQI based Climate Focused Calibration | No | No | No | Yes |
| ML/DL Model-in-Loop Support | No | No | Yes | No |
| # | Indoor Pollutants | Indoor Diseases and Health Problems |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | PM2.5 and PM10 [131,132,133,134,135] |
heart or lung illness, nonfatal heart attacks, irregular heartbeats, worsened asthma, impaired lung function, and a rise in respiratory symptoms including coughing or trouble breathing. |
| 2 | NO2 [136,137,138,139] | At high quantities, it shortens breath and irritates the mucous membranes of the nose, throat, and eyes. Long-term inhalation of nitrogen dioxide can cause lung damage. It could result in persistent bronchitis. Those who have asthma and chronic obstructive lung disease may experience worsening symptoms from exposure to low levels (COPD). Also, it could make other respiratory illnesses worse. |
| 3 | CO [137,138,139,140,141] | Chronic headaches, nauseousness, stomach discomfort, vomiting, weakness, dizziness, fainting, confused mental neural response, exhaustion, loss of consciousness, seizure, and irreversible brain damage are some of the symptoms. In the worst scenarios, death is also conceivable. |
| 4 | CO2 [140,141,142,143] | respiratory tract infections, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and rhinosinusitis. |
| 5 | VoCs [144,145,146,147] | Some VOCs are known or suspected carcinogens. inflammation, including irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat; headaches and lack of coordination; nausea; liver, renal, or central nervous system damage. |
| % | Indoor Pollutants | Indoor Diseases and Health Problems |
|---|---|---|
| 32% | Ischemic heart disease [147,148,149,150,151] | Affects 32% of people. Exposure to home air pollution is responsible for 12% of all fatalities from ischemic heart disease, or more than a million premature deaths yearly. |
| 23% | Stroke [152,153,154,155,156] | Accounts for 23% of deaths, with usage of solid fuels and kerosene in the home contributing to household air pollution on a regular basis, accounting for around 12% of all stroke deaths. |
| 21% | Pneumonia and Low Respiratory Infections (LRI) [157,158,159,160,161,162,163,164] | LRIs account for 21% of fatalities, and exposure to indoor air pollution nearly doubles the risk of childhood LRI and accounts for 44% of all pneumonia-related deaths in children under the age of five. Adults who have acute LRIs are at danger from household air pollution, which also causes 22% of all adult fatalities from pneumonia. |
| 19% | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [164,165,166,167,168] | Accounts for 19% of cases. In low- and middle-income nations, exposure to home air pollution is to be reason for 23% of all fatalities from COPD in adults. |
| 6% | Lungs Cancer [147,148,149,150,151] |
6% of lung cancer-related fatalities in adults are linked to exposure to carcinogens from home air pollution brought on by the use of kerosene or solid fuels like wood, charcoal, or coal. This exposure accounts for around 11% of lung cancer deaths in adults. |
| USD ($) | Rooms Monitored (>100) | GSA/GSG Assemblies (>10X) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Elements | OGS | ECS | CGS | MOS | OGS ENB | ECS ENB |
CGS ENB |
MOS ENB |
| Lifeline Cost (K) [172,173,174,175] | 10 | 1.5 | 17.1 | 3.7 | 3.5 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.4 |
| Manufacturing Setup Cost (M) [69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,176] |
23~40 | 18~29 | 7~13 | 33~80 | 13~17 | 8~11 | 9~10 | 3~5 |
| Calibration Cost (K) [177,178,179,180] |
17 | 12 | 19 | 4 | 29 | 15 | 9.5 | 1.4 |
| Adaptation Cost (K) [19,181,182,183,184] |
30 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 12 | 3 | 1.1 | 0.3 |
| Sampling Rate Upgrade Cost (K) [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,185,186,187,188] |
3 | 11 | 9 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.12 |
| Networked Sensing Cost (K) [189,193] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Real-time AQI Mapping Cost (K) [184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193] |
0.7 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 0.5 | 1.6 | 9.5 | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).