Submitted:
03 April 2023
Posted:
05 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatic analysis
2.2. Molecular docking
2.3. QSAR model development
2.4. Cell lines and culture conditions
2.5. Electrophysiological Measurements
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results
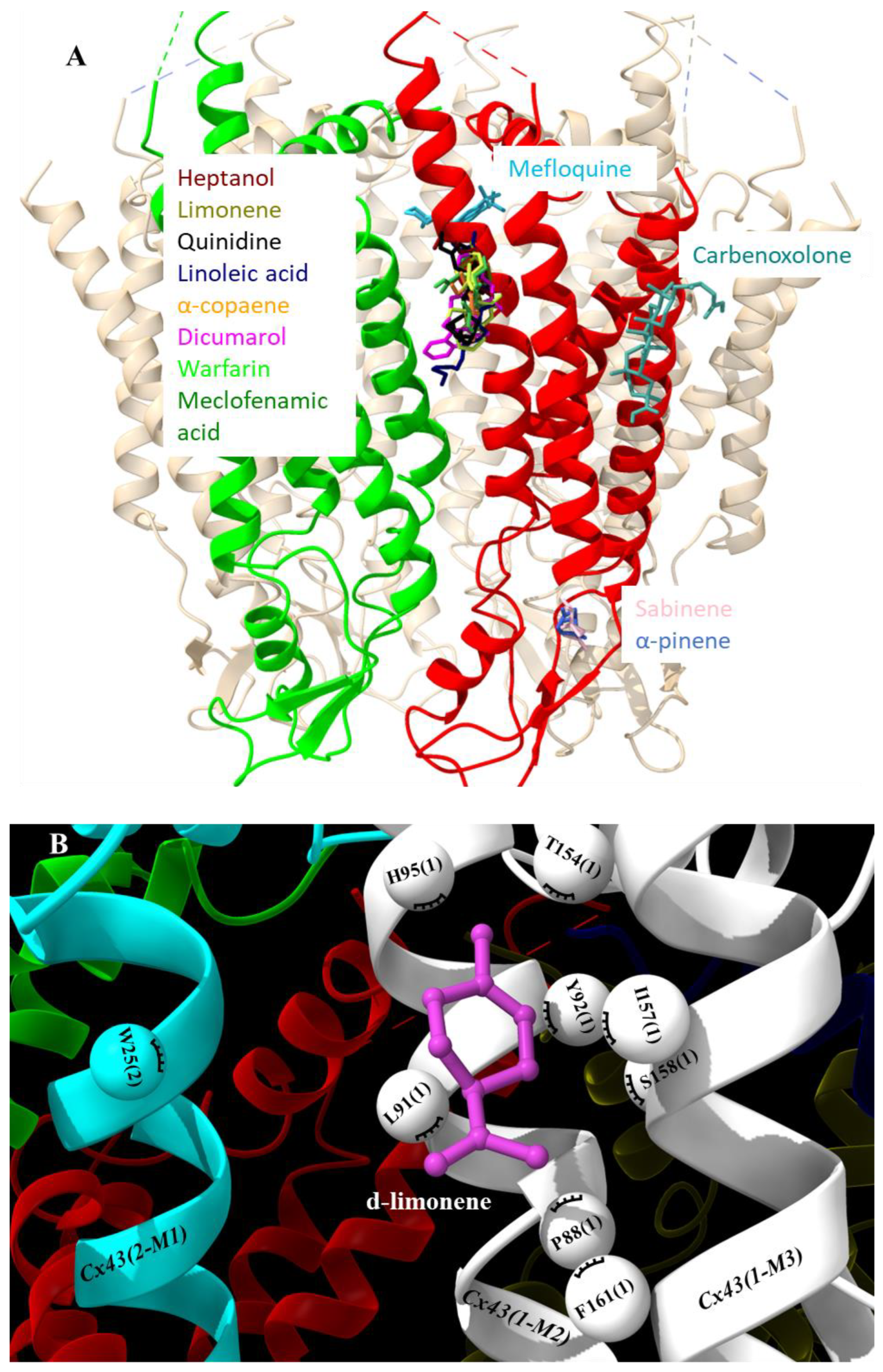
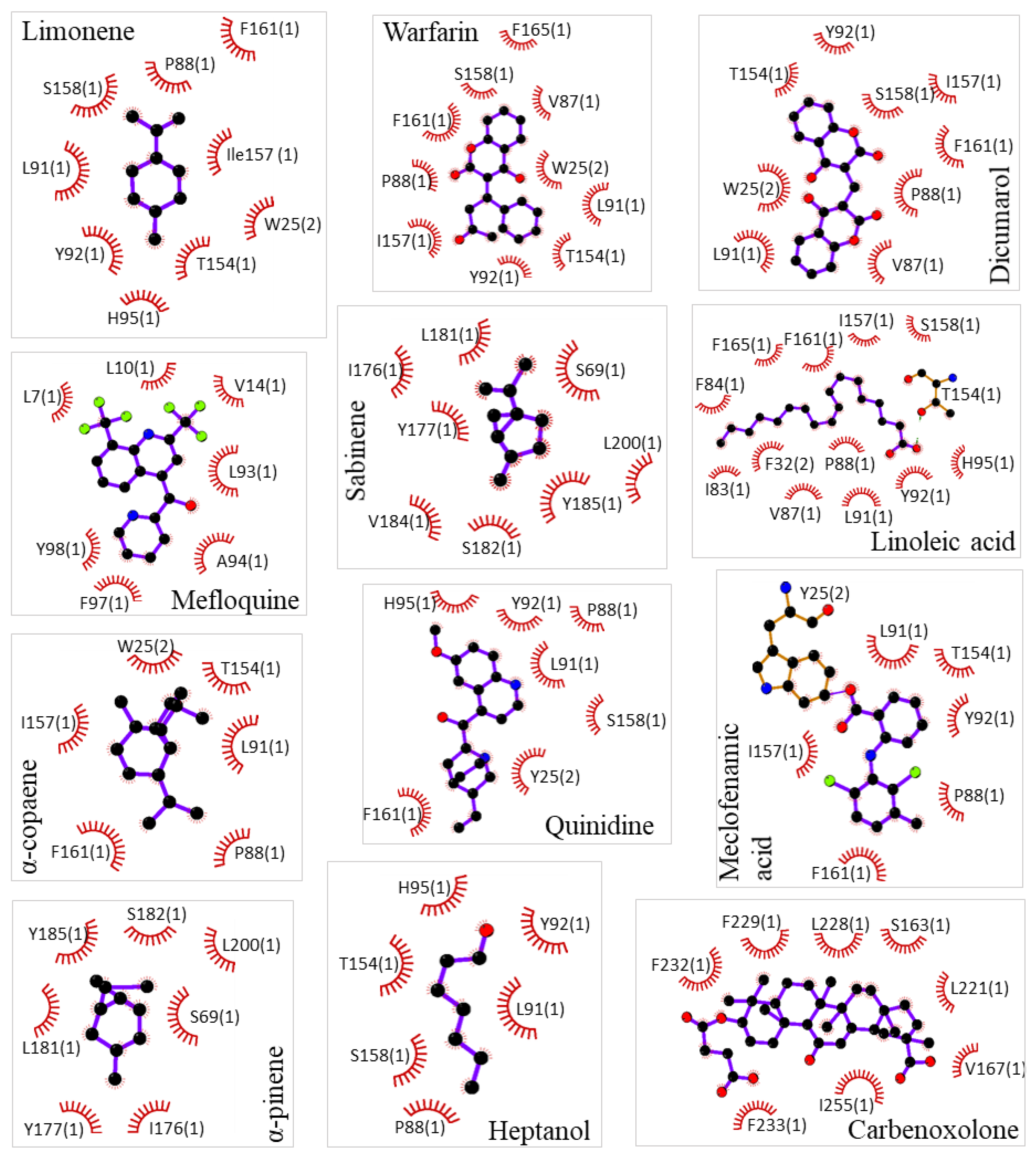
3.1. Molecular docking of Cx43 inhibitors
3.2. QSAR modeling of Cx43 inhibitors
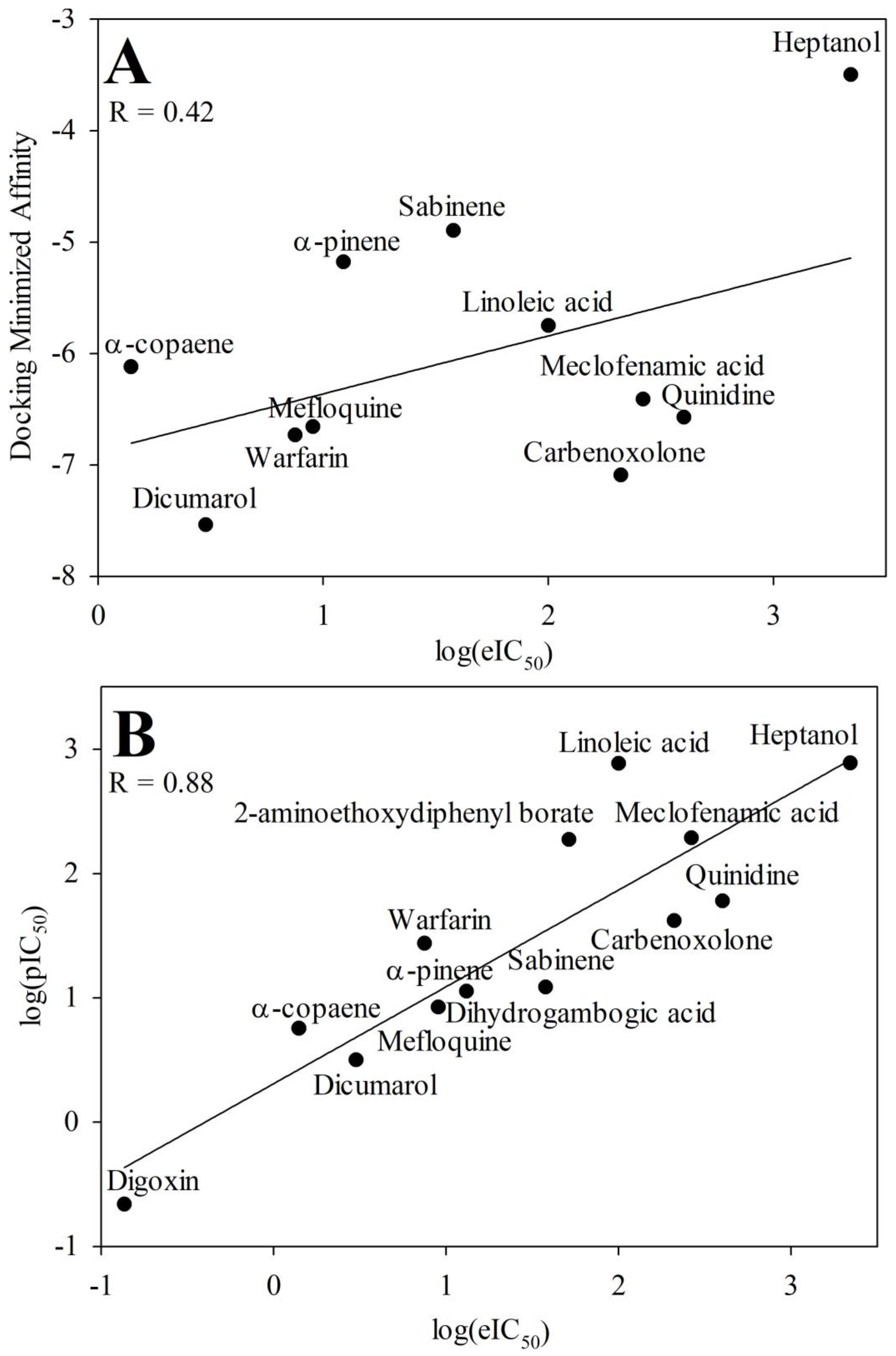
| PubChem CID | Name | Log(eIC50) | BCUTp-1l | SM1_Dzs | Log(pIC50) | Docking minimized affinity | Log(pIC50) from docking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11240513 | α-Pinene [19] | 1.08 | 6.26 | -0.33 | 0.92 | -5.18 | 1.96 |
| 12303902 | α-Copaene [19] | 0.14 | 6.49 | -0.49 | 0.75 | -6.12 | 1.59 |
| 18818 | Sabinene [19] | 1.57 | 6.23 | -0.64 | 1.08 | -4.90 | 2.07 |
| 4037 | Meclofenamic acid [18] | 2.42 | 4.44 | 0.85 | 2.28 | -6.41 | 1.47 |
| 4046 | Mefloquine [17] | 0.95 | 3.73 | 5.91 | 0.92 | -6.66 | 1.38 |
| 441074 | Quinidine [17] | 2.60 | 4.91 | 0.92 | 1.77 | -6.57 | 1.41 |
| 5280450 | Linoleic acid [21] | 2.00 | 3.72 | 1.19 | 2.88 | -5.75 | 1.73 |
| 54676038 | Dicumarol [14] | 0.47 | 5.05 | 3.67 | 0.50 | -7.54 | 1.03 |
| 54678486 | Warfarin [14] | 0.87 | 4.66 | 2.38 | 1.43 | -6.73 | 1.35 |
| 636403 | Carbenoxolone [18] | 2.32 | 3.75 | 4.18 | 1.62 | -7.09 | 1.21 |
| 8129 | Heptanol [18] | 3.34 | 3.93 | 0.66 | 2.89 | -3.50 | 2.62 |
| 1598 | 2-APB [20] | 1.71 | 4.64 | 0.41 | 2.27 | - | - |
| 2724385 | Digoxin [18] | -0.86 | 4.26 | 8.45 | -0.66 | - | - |
| 6857793 | DGBA [16] | 1.11 | 4.30 | 4.20 | 1.05 | - | - |
| 22311 | d-Limonene | 1.41 | 6.18 | -0.50 | 1.07 | -5.12 | 1.98 |
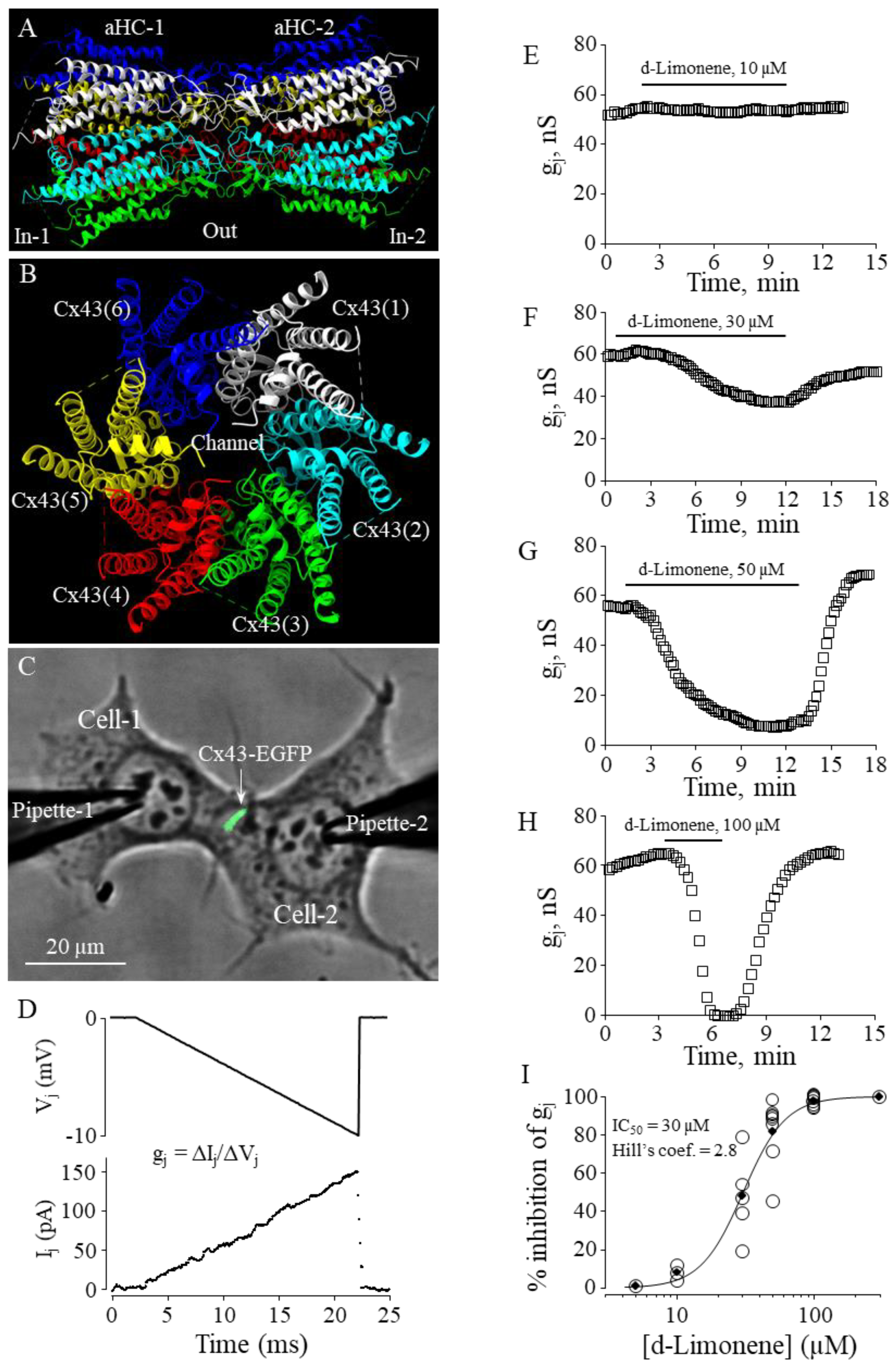
3.3. D-limonene dose-dependently inhibits Cx43 GJ conductance
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Del Ry, S.; Moscato, S.; Bianchi, F.; Morales, M.A.; Dolfi, A.; Burchielli, S.; Cabiati, M.; Mattii, L. Altered expression of connexin 43 and related molecular partners in a pig model of left ventricular dysfunction with and without dipyrydamole therapy. Pharmacological Research 2015, 95, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Račkauskas, M.; Neverauskas, V.; Skeberdis, V.A. Diversity and properties of connexin gap junction channels. Medicina 2010, 46, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, C.M.; Andrade, D.C.; Toledo, C.; Díaz, H.S.; Pereyra, K.V.; Diaz-Jara, E.; Schwarz, K.G.; Marcus, N.J.; Retamal, M.A.; Quintanilla, R.A. Cardiac remodeling and arrhythmogenesis are ameliorated by administration of Cx43 mimetic peptide Gap27 in heart failure rats. Scientific Reports 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, M. Pharmacology of connexin channels. In Connexins: a guide, Harris, A.L., Locke, D., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, 2009; pp. 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Mickus, R.; Jančiukė, G.; Raškevičius, V.; Mikalayeva, V.; Matulytė, I.; Marksa, M.; Maciūnas, K.; Bernatonienė, J.; Skeberdis, V.A. The effect of nutmeg essential oil constituents on Novikoff hepatoma cell viability and communication through Cx43 gap junctions. Biomed Pharmacother 2021, 135, 111229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; You, T.; Yuan, D.; Han, X.; Hong, X.; He, B.; Wang, L.; Tong, X.; Tao, L.; Harris, A.L. Cisplatin and oxaliplatin inhibit gap junctional communication by direct action and by reduction of connexin expression, thereby counteracting cytotoxic efficacy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010, 333, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.-m.; Xia, C.-k.; Zhao, N.; Dong, Q.; Lei, M.; Xia, J.-h. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid preferentially blocks late Na current generated by ΔKPQ Nav1.5 channels. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2012, 33, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Su, G.-h.; Wang, Y.-h.; Lu, Y.-x.; Zhao, H.-l.; Shuai, X.-x. 18β-Glycyrrhetinic Acid Improves Cardiac Diastolic Function by Attenuating Intracellular Calcium Overload. Current Medical Science 2020, 40, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meves, H. Arachidonic acid and ion channels: an update. British journal of pharmacology 2008, 155, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. Pharmacologic Analysis of Drug-Receptor Interaction, 2 ed.; Raven Press, Ltd.: New York, NY 10036, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Bae, H.; Jo, J.; Yoon, S. Comprehensive ensemble in QSAR prediction for drug discovery. BMC bioinformatics 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.n.; Qin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Liang, G. Comprehensive interactions of ACE inhibitors with their receptor by a Support Vector Machine model and molecular docking. Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 2017, 64, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, R.D. Topomer CoMFA: a design methodology for rapid lead optimization. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2003, 46, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, A.; Dhein, S. Pharmacology of gap junctions. New pharmacological targets for treatment of arrhythmia, seizure and cancer? Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2005, 1719, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, S.R.; Williams, Z.J.; Pridham, K.J.; Gourdie, R.G. Peptidic connexin43 therapeutics in cardiac reparative medicine. Journal of cardiovascular development and disease 2021, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.J.; Yeo, J.H.; Yoon, S.M.; Lee, J. Gambogic acid and its analogs inhibit gap junctional intercellular communication. Frontiers in pharmacology 2018, 9, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picoli, C.; Nouvel, V.; Aubry, F.; Reboul, M.; Duchêne, A.; Jeanson, T.; Thomasson, J.; Mouthon, F.; Charvériat, M. Human connexin channel specificity of classical and new gap junction inhibitors. Journal of biomolecular screening 2012, 17, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, M.; Sharpe, P.; Garner, C.; Hughes, R.; Pollard, C.; Bowes, J. Investigation of connexin 43 uncoupling and prolongation of the cardiac QRS complex in preclinical and marketed drugs. British Journal of Pharmacology 2014, 171, 4808–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickus, R.; Jančiukė, G.; Raškevičius, V.; Mikalayeva, V.; Matulytė, I.; Marksa, M.; Maciūnas, K.; Bernatonienė, J.; Skeberdis, V.A. The effect of nutmeg essential oil constituents on Novikoff hepatoma cell viability and communication through Cx43 gap junctions. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2021, 135, 111229. [Google Scholar]
- D'hondt, C.; Ponsaerts, R.; De Smedt, H.; Bultynck, G.; Himpens, B. Pannexins, distant relatives of the connexin family with specific cellular functions? Bioessays 2009, 31, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willebrords, J.; Maes, M.; Yanguas, S.C.; Vinken, M. Inhibitors of connexin and pannexin channels as potential therapeutics. Pharmacology & therapeutics 2017, 180, 144–160. [Google Scholar]
- Karr, L.L.; Coats, J.R. Insecticidal properties of d-limonene. Journal of Pesticide Science 1988, 13, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, M.J.; Chung, B.Y.; Bang, D.Y.; Lim, S.K.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.S.; Cho, M.C.; Yoon, K.; Kim, H.S. Safety evaluation and risk assessment of d-limonene. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health, Part B 2013, 16, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J. D-Limonene: safety and clinical applications. Alternative medicine review 2007, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nature protocols 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Cha, H.J.; Jeong, H.; Lee, S.-N.; Lee, C.-W.; Kim, M.; Yoo, J. Structural insights into the gating mechanism of human Cx43/GJA1 gap junction channel. 2021.
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B. PubChem 2019 update: improved access to chemical data. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, D1102–D1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNutt, A.T.; Francoeur, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Masuda, T.; Meli, R.; Ragoza, M.; Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. GNINA 1.0: molecular docking with deep learning. Journal of cheminformatics 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Science 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-descriptor: An open source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. Journal of computational chemistry 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, N.R.; Smith, H. Applied regression analysis; John Wiley & Sons, 1998; Volume 326. [Google Scholar]
- Eberly, L.E. Multiple linear regression. Topics in Biostatistics 2007, 165–187. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzi, M.; Dejaegher, B.; Heyden, Y.V. Feature selection methods in QSAR studies. Journal of AOAC International 2012, 95, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scior, T.; Medina-Franco, J.; Do, Q.-T.; Martínez-Mayorga, K.; Yunes Rojas, J.; Bernard, P. How to recognize and workaround pitfalls in QSAR studies: a critical review. Current medicinal chemistry 2009, 16, 4297–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukauskas, F.F.; Jordan, K.; Bukauskiene, A.; Bennett, M.V.; Lampe, P.D.; Laird, D.W.; Verselis, V.K. Clustering of connexin 43–enhanced green fluorescent protein gap junction channels and functional coupling in living cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 2556–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeberdis, V.A.; Rimkute, L.; Skeberdyte, A.; Paulauskas, N.; Bukauskas, F.F. pH-dependent modulation of connexin-based gap junctional uncouplers. The Journal of Physiology 2011, 589, 3495–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R. Molecular Descriptors for Chemoinformatics: Volume I: Alphabetical Listing/Volume II: Appendices, References; John Wiley & Sons, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Randic, M. On molecular identification numbers. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences 1984, 24, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.S.; van Veen, T.A.; de Bakker, J.M.; van Rijen, H.V. Functional consequences of abnormal Cx43 expression in the heart. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2012, 1818, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaume, A.G.; de Sousa, P.A.; Kulkarni, S.; Langille, B.L.; Zhu, D.; Davies, T.C.; Juneja, S.C.; Kidder, G.M.; Rossant, J. Cardiac malformation in neonatal mice lacking connexin43. Science 1995, 267, 1831–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, M.S.C.; van Veen, T.A.B.; de Bakker, J.M.T.; van Rijen, H.V.M. Functional consequences of abnormal Cx43 expression in the heart. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Biomembranes 2012, 1818, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-Marques, T.; Anjo, S.I.; Pereira, P.; Manadas, B.; Girão, H. Interacting Network of the Gap Junction (GJ) Protein Connexin43 (Cx43) is Modulated by Ischemia and Reperfusion in the Heart*[S]. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2015, 14, 3040–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.W.; Lampe, P.D. Therapeutic strategies targeting connexins. Nature reviews Drug discovery 2018, 17, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picoli, C.; Soleilhac, E.; Journet, A.; Barette, C.; Comte, M.; Giaume, C.; Mouthon, F.; Fauvarque, M.-O.; Charvériat, M. High-content screening identifies new inhibitors of connexin 43 gap junctions. ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2019, 17, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, A. Drugs for atrial fibrillation. Digoxin comes from Digitalis lanata. BMJ: British Medical Journal 1996, 312, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticherling, C.; Oral, H.; Horrocks, J.; Chough, S.P.; Baker, R.L.; Kim, M.H.; Wasmer, K.; Pelosi, F.; Knight, B.P.; Michaud, G.F. Effects of Digoxin on acute, atrial fibrillation–induced changes in atrial refractoriness. Circulation 2000, 102, 2503–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscovitz, T.; Aldrighi, J.M.; Abrahanshon, P.A.; Zorn, T.M.; Logullo, A.F.; Gebara, O.C.; Rosano, G.G.; Ramires, J.F. Repercussions of digoxin, digitoxin and estradiol on the endometrial histomorphometry of oophorectomized mice. Gynecol Endocrinol 2005, 20, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, A.A.; Camm, A.J. Quinidine. New England Journal of Medicine 1998, 338, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojodjojo, P.; Kanagaratnam, P.; Segal Oliver, R.; Hussain, W.; Peters Nicholas, S. The Effects of Carbenoxolone on Human Myocardial Conduction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2006, 48, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladipo, G.O.A.; Essien, E.E.; Andy, J.J. Complete heart block in chronic chloroquine poisoning. International journal of cardiology 1983, 4, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevin, R.L. Mefloquine blockade of connexin 36 and connexin 43 gap junctions and risk of suicide. Biological Psychiatry 2012, 71, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, E.; Boengler, K.; Antoons, G.; Sipido, K.R.; Schulz, R.; Leybaert, L. Pharmacological modulation of connexin-formed channels in cardiac pathophysiology. Br J Pharmacol 2011, 163, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, C. Overcoming the shortcomings of peptide-based therapeutics. Future Drug Discovery 2022, 4, FDD75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Locke, D. Connexins. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, W.H.; Boitano, S. Connexin mimetic peptides: specific inhibitors of gap-junctional intercellular communication. Biochemical Society Transactions 2001, 29, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgert, C.J.; Baker, S.P.; Matthews, J.C. Potency matters: thresholds govern endocrine activity. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology 2013, 67, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




