Submitted:
14 April 2023
Posted:
17 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Clinical assessment and cardiorenal syndromes
4. Biomarkers
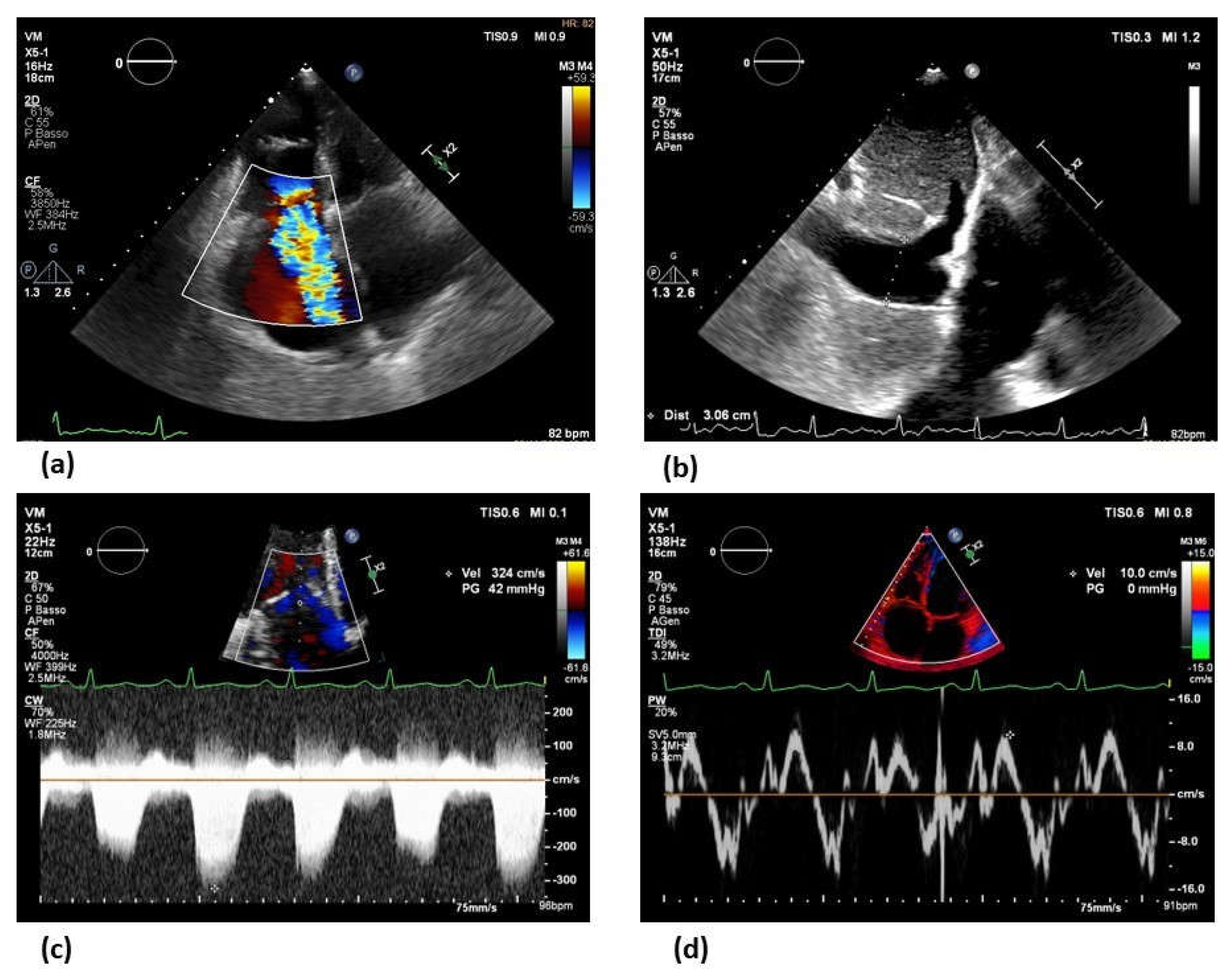
5. Imaging modalities
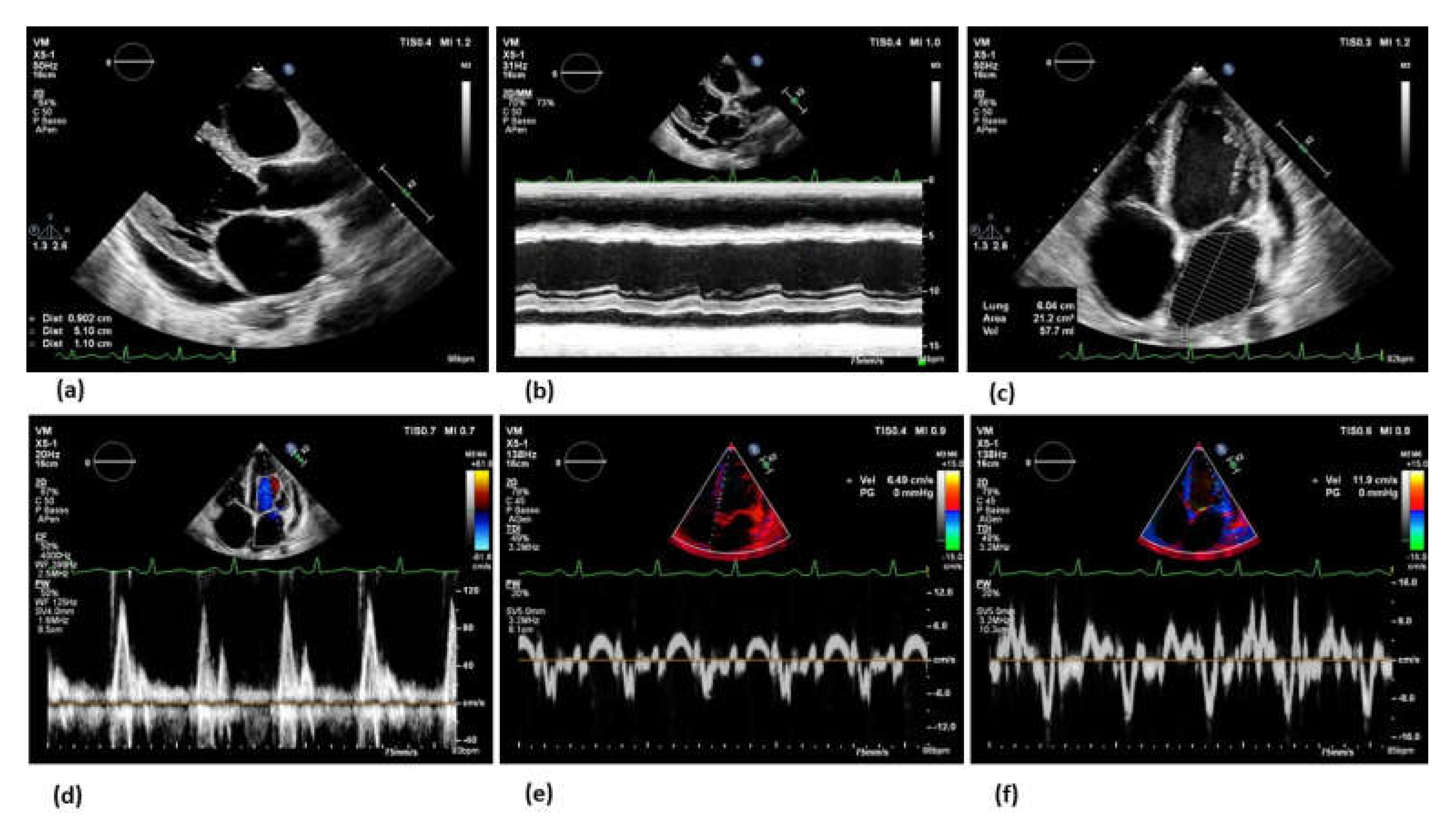
6. Towards personalized treatment
7. Peritoneal dialysis in refractory congestive heart failure
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Triposkiadis, F.; Giamouzis, G.; Parissis, J.; Starling, R.C.; Boudoulas, H.; Skoularigis, J.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G. Reframing the association and significance of co-morbidities in heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2016, 18, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Tang, W.H.; Testani, J.M.; McMurray, J.J. Terminology and definition of changes renal function in heart failure. Eur Heart J 2014, 35, 3413–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Valente, M.A.; Voors, A.A.; O'Connor, C.M.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Renal impairment, worsening renal function, and outcome in patients with heart failure: an updated meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 2014, 35, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottgen, A.; Russell, S.D.; Loehr, L.R.; Crainiceanu, C.M.; Rosamond, W.D.; Chang, P.P.; Chambless, L.E.; Coresh, J. Reduced kidney function as a risk factor for incident heart failure: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007, 18, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, J.T.; Fonarow, G.C.; Costanzo, M.R.; Mathur, V.S.; Wigneswaran, J.R.; Wynne, J.; Committee A.S.A.; Investigators. High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: a report from the ADHERE database. J Card Fail 2007, 13, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.F., Jr.; Fonarow, G.C.; Emerman, C.L.; LeJemtel, T.H.; Costanzo, M.R.; Abraham, W.T.; Berkowitz, R.L.; Galvao, M.; Horton, D.P.; Committee, A.S.A.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for heart failure in the United States: rationale, design, and preliminary observations from the first 100,000 cases in the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE). Am Heart J 2005, 149, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillege, H.L.; Nitsch, D.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Swedberg, K.; McMurray, J.J.; Yusuf, S.; Granger, C.B.; Michelson, E.L.; Ostergren, J.; Cornel, J.H.; et al. Renal function as a predictor of outcome in a broad spectrum of patients with heart failure. Circulation 2006, 113, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damman, K.; Testani, J.M. The kidney in heart failure: an update. Eur Heart J 2015, 36, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, P.; Fonarow, G.C.; Budoff, M.J.; Darabian, S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Cardiorenal syndrome: pathophysiology and potential targets for clinical management. Nat Rev Nephrol 2013, 9, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkeler, S.J.; Damman, K.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.; Navis, G. A re-appraisal of volume status and renal function impairment in chronic heart failure: combined effects of pre-renal failure and venous congestion on renal function. Heart Fail Rev 2012, 17, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edner, M.; Benson, L.; Dahlstrom, U.; Lund, L.H. Association between renin-angiotensin system antagonist use and mortality in heart failure with severe renal insufficiency: a prospective propensity score-matched cohort study. Eur Heart J 2015, 36, 2318–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moertl, D.; Berger, R.; Struck, J.; Gleiss, A.; Hammer, A.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bergmann, A.; Huelsmann, M.; Pacher, R. Comparison of midregional pro-atrial and B-type natriuretic peptides in chronic heart failure: influencing factors, detection of left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and prediction of death. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009, 53, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Pontone, G.; Fusini, L.; De Luca, M.; Cafarelli, F.P.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Beltrama, V.; Muscogiuri, G.; Mushtaq, S.; et al. Additional value of inflammatory biomarkers and carotid artery disease in prediction of significant coronary artery disease as assessed by coronary computed tomography angiography. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2017, 18, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenak, C.; Chavanon, M.L.; Tahirovic, E.; Trippel, T.D.; Tscholl, V.; Stroux, A.; Veskovic, J.; Apostolovic, S.; Obradovic, D.; Zdravkovic, M.; et al. Early NT-proBNP and MR-proANP associated with QoL 1 year after acutely decompensated heart failure: secondary analysis from the MOLITOR trial. Biomark Med 2019, 13, 1493–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, J.A.; Coca, S.G.; Moledina, D.G.; Gentry, M.; Testani, J.M.; Parikh, C.R. Amino-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide for Diagnosis and Prognosis in Patients With Renal Dysfunction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JACC Heart Fail 2015, 3, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horii, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Uemura, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Takitsume, A.; Ueda, T.; Nakagawa, H.; Nishida, T.; Soeda, T.; Okayama, S.; et al. Prognostic value of B-type natriuretic peptide and its amino-terminal proBNP fragment for cardiovascular events with stratification by renal function. J Cardiol 2013, 61, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Anand, I.S.; Vago, T.; Angelici, L.; Barlera, S.; Missov, E.D.; Clerico, A.; Tognoni, G.; Cohn, J.N.; et al. Direct comparison of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in a large population of patients with chronic and symptomatic heart failure: the Valsartan Heart Failure (Val-HeFT) data. Clin Chem 2006, 52, 1528–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, P.A.; Duc, P.; Omland, T.; McCord, J.; Nowak, R.M.; Hollander, J.E.; Herrmann, H.C.; Steg, P.G.; Westheim, A.; Knudsen, C.W.; et al. B-type natriuretic peptide and renal function in the diagnosis of heart failure: an analysis from the Breathing Not Properly Multinational Study. Am J Kidney Dis 2003, 41, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y. Diagnostic and prognostic property of NT-proBNP in patients with renal dysfunction. J Cardiol 2013, 61, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Warner Stevenson, L.; Ahmad, T.; Amin, V.J.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Drazner, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Peterson, P.N.; et al. 2019 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Risk Assessment, Management, and Clinical Trajectory of Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019, 74, 1966–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Van Biesen, W.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Neirynck, N.; Speeckaert, M.; De Bacquer, D.; Verbeke, F. Free p-cresyl sulfate shows the highest association with cardiovascular outcome in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2021, 36, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapa, H.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Shlipak, M.G.; Katz, R.; Ix, J.H.; Sarnak, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Rhee, E.P.; Kimmel, P.L.; Vasan, R.S.; et al. Association of Uremic Solutes With Cardiovascular Death in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis 2022, 80, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Axelsson, J.; Machowska, A.; Heimburger, O.; Barany, P.; Lindholm, B.; Lindstrom, K.; Stenvinkel, P.; Qureshi, A.R. Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality Risk in Patients with Advanced CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2016, 11, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Morita, H.; Daimon, M.; Horio, M.; Kawata, T.; Nakao, T.; Hirokawa, M.; Kitao, R.; Watanabe, D.; Komori, T.; et al. Utility of Cystatin C for Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate in Patients With Muscular Dystrophy. Int Heart J 2016, 57, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, C.A.; Katz, R.; Sarnak, M.J.; Ix, J.; Fried, L.F.; De Boer, I.; Palmas, W.; Siscovick, D.; Levey, A.S.; Shlipak, M.G. Cystatin C identifies chronic kidney disease patients at higher risk for complications. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011, 22, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lassus, J.; Harjola, V.P.; Sund, R.; Siirila-Waris, K.; Melin, J.; Peuhkurinen, K.; Pulkki, K.; Nieminen, M.S.; group, F.-A.S. Prognostic value of cystatin C in acute heart failure in relation to other markers of renal function and NT-proBNP. Eur Heart J 2007, 28, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivlas, C.; Triposkiadis, F.; Psarras, S.; Giamouzis, G.; Skoularigis, I.; Chryssanthopoulos, S.; Kapelouzou, A.; Ramcharitar, S.; Barnes, E.; Papasteriadis, E.; et al. Left atrial volume index in patients with heart failure and severely impaired left ventricular systolic function: the role of established echocardiographic parameters, circulating cystatin C and galectin-3. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 2017, 11, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortara, A.; Bonadies, M.; Mazzetti, S.; Fracchioni, I.; Delfino, P.; Chioffi, M.; Bersano, C.; Specchia, G. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin predicts worsening of renal function in acute heart failure: methodological and clinical issues. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 2013, 14, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashani, K.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Ardiles, T.; Artigas, A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bell, M.; Bihorac, A.; Birkhahn, R.; Cely, C.M.; Chawla, L.S.; et al. Discovery and validation of cell cycle arrest biomarkers in human acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2013, 17, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestenbaum, B.; Sachs, M.C.; Hoofnagle, A.N.; Siscovick, D.S.; Ix, J.H.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Lima, J.A.; Polak, J.F.; Blondon, M.; Ruzinski, J.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor-23 and cardiovascular disease in the general population: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Circ Heart Fail 2014, 7, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutsey, P.L.; Alonso, A.; Selvin, E.; Pankow, J.S.; Michos, E.D.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Coresh, J. Fibroblast growth factor-23 and incident coronary heart disease, heart failure, and cardiovascular mortality: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. J Am Heart Assoc 2014, 3, e000936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmark, B.A.; Udell, J.A.; Morrow, D.A.; Cannon, C.P.; Steen, D.L.; Jarolim, P.; Budaj, A.; Hamm, C.; Guo, J.; Im, K.; et al. Association of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 With Recurrent Cardiovascular Events in Patients After an Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol 2018, 3, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, C.; Amaral, A.P.; Oskouei, B.; Hu, M.C.; Sloan, A.; Isakova, T.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Aguillon-Prada, R.; Lincoln, J.; Hare, J.M.; et al. FGF23 induces left ventricular hypertrophy. J Clin Invest 2011, 121, 4393–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, O.M.; Januzzi, J.L.; Isakova, T.; Laliberte, K.; Smith, K.; Collerone, G.; Sarwar, A.; Hoffmann, U.; Coglianese, E.; Christenson, R.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and left ventricular hypertrophy in chronic kidney disease. Circulation 2009, 119, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, M.; Ye, R.; Han, X.; Armstrong, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Quarles, L.D. Cardiovascular Interactions between Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 and Angiotensin II. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifheit-Nestler, M.; Kirchhoff, F.; Nespor, J.; Richter, B.; Soetje, B.; Klintschar, M.; Heineke, J.; Haffner, D. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is induced by an activated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cardiac myocytes and promotes the pro-fibrotic crosstalk between cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2018, 33, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlfahrt, P.; Melenovsky, V.; Kotrc, M.; Benes, J.; Jabor, A.; Franekova, J.; Lemaire, S.; Kautzner, J.; Jarolim, P. Association of Fibroblast Growth Factor-23 Levels and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition in Chronic Systolic Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail 2015, 3, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialla, J.J.; Xie, H.; Rahman, M.; Anderson, A.H.; Isakova, T.; Ojo, A.; Zhang, X.; Nessel, L.; Hamano, T.; Grunwald, J.E.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor-23 and cardiovascular events in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.C.; Shi, M.; Gillings, N.; Flores, B.; Takahashi, M.; Kuro, O.M.; Moe, O.W. Recombinant alpha-Klotho may be prophylactic and therapeutic for acute to chronic kidney disease progression and uremic cardiomyopathy. Kidney Int 2017, 91, 1104–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Yoon, J.; An, S.W.; Kuro-o, M.; Huang, C.L. Soluble Klotho Protects against Uremic Cardiomyopathy Independently of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 and Phosphate. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 26, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Ge, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, B. Association between serum Klotho concentration and heart failure in adults, a cross-sectional study from NHANES 2007-2016. Int J Cardiol 2023, 370, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Henry, A.; Roselli, C.; Lin, H.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; Fatemifar, G.; Hedman, A.K.; Wilk, J.B.; Morley, M.P.; Chaffin, M.D.; et al. Genome-wide association and Mendelian randomisation analysis provide insights into the pathogenesis of heart failure. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control, C. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.; Haase, T.; Zeller, T.; Schulte, C. Biomarkers for Heart Failure Prognosis: Proteins, Genetic Scores and Non-coding RNAs. Front Cardiovasc Med 2020, 7, 601364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Muscogiuri, G.; Fusini, L.; Andreini, D.; Mushtaq, S.; Conte, E.; Annoni, A.; Formenti, A.; Mancini, E.M.; et al. Multimodality imaging of left atrium in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2019, 13, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameli, M.; Sciaccaluga, C.; Loiacono, F.; Simova, I.; Miglioranza, M.H.; Nistor, D.; Bandera, F.; Emdin, M.; Giannoni, A.; Ciccone, M.M.; et al. The analysis of left atrial function predicts the severity of functional impairment in chronic heart failure: The FLASH multicenter study. Int J Cardiol 2019, 286, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaibazzi, N.; Porter, T.; Lorenzoni, V.; Pontone, G.; De Santis, D.; De Rosa, A.; Guaricci, A.I. Effect of Coronary Revascularization on the Prognostic Value of Stress Myocardial Contrast Wall Motion and Perfusion Imaging. J Am Heart Assoc 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, M.; Pagura, L.; Porcari, A.; Cameli, M.; Vergaro, G.; Musumeci, B.; Biagini, E.; Canepa, M.; Crotti, L.; Imazio, M.; et al. Unmasking the prevalence of amyloid cardiomyopathy in the real world: results from Phase 2 of the AC-TIVE study, an Italian nationwide survey. Eur J Heart Fail 2022, 24, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Chiarello, G.; Gherbesi, E.; Fusini, L.; Soldato, N.; Siena, P.; Ursi, R.; Ruggieri, R.; Guglielmo, M.; Muscogiuri, G.; et al. Coronary-specific quantification of myocardial deformation by strain echocardiography may disclose the culprit vessel in patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Eur Heart J Open 2022, 2, oeac010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, P.; Guaricci, A.I.; Piazzolla, G.; Volpe, S.; Vozza, A.; Benedetto, M.; Carella, M.C.; Santoro, D.; Monitillo, F.; Baggiano, A.; et al. Improvement of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain after 6-Month Therapy with GLP-1RAs Semaglutide and Dulaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Study. J Clin Med 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, N.; Alkemary, A. Early Detection of Subclinical Uremic Cardiomyopathy Using Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography. Echocardiography 2016, 33, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnasamy, R.; Isbel, N.M.; Hawley, C.M.; Pascoe, E.M.; Leano, R.; Haluska, B.A.; Stanton, T. The association between left ventricular global longitudinal strain, renal impairment and all-cause mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014, 29, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frea, S.; Pidello, S.; Bovolo, V.; Iacovino, C.; Franco, E.; Pinneri, F.; Galluzzo, A.; Volpe, A.; Visconti, M.; Peirone, A.; et al. Prognostic incremental role of right ventricular function in acute decompensation of advanced chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2016, 18, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, M.T.; Holst, D.P.; Kaye, D.M. Tricuspid regurgitation contributes to renal dysfunction in patients with heart failure. J Card Fail 2008, 14, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicori, P.; Carubelli, V.; Zhang, J.; Castiello, T.; Sherwi, N.; Clark, A.L.; Cleland, J.G. IVC diameter in patients with chronic heart failure: relationships and prognostic significance. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2013, 6, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowie, B.; Kluger, R.; Rex, S.; Missant, C. Noninvasive estimation of left atrial pressure with transesophageal echocardiography. Ann Card Anaesth 2015, 18, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Marwick, T.H. Use and Limitations of E/e' to Assess Left Ventricular Filling Pressure by Echocardiography. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2011, 19, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaricci, A.I.; Masci, P.G.; Muscogiuri, G.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Fusini, L.; Lorenzoni, V.; Martini, C.; Andreini, D.; Pavon, A.G.; et al. CarDiac magnEtic Resonance for prophylactic Implantable-cardioVerter defibrillAtor ThErapy in Non-Ischaemic dilated CardioMyopathy: an international Registry. Europace 2021, 23, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al'Aref, S.J.; Altibi, A.M.; Malkawi, A.; Mansour, M.; Baskaran, L.; Masri, A.; Rahmouni, H.; Abete, R.; Andreini, D.; Aquaro, G.; et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance for prophylactic implantable-cardioverter defibrillator therapy international study: prognostic value of cardiac magnetic resonance-derived right ventricular parameters substudy. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Martini, C.; Gatti, M.; Dell'Aversana, S.; Ricci, F.; Guglielmo, M.; Baggiano, A.; Fusini, L.; Bracciani, A.; Scafuri, S.; et al. Feasibility of late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) in ischemic cardiomyopathy using 2D-multisegment LGE combined with artificial intelligence reconstruction deep learning noise reduction algorithm. Int J Cardiol 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faubel, S.; Patel, N.U.; Lockhart, M.E.; Cadnapaphornchai, M.A. Renal relevant radiology: use of ultrasonography in patients with AKI. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 9, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, N.; Seo, Y.; Sai, S.; Machino-Ohtsuka, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Ishizu, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Aonuma, K. Clinical Implications of Intrarenal Hemodynamic Evaluation by Doppler Ultrasonography in Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail 2016, 4, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, G.M.; Lee, K.L.; Bull, D.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Stevenson, L.W.; Goldsmith, S.R.; LeWinter, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Rouleau, J.L.; Ofili, E.O.; et al. Diuretic strategies in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Ueyama, H.; Chopra, N.; Yamaji, T.; Azushima, K.; Kobayashi, R.; Kinguchi, S.; Urate, S.; Suzuki, T.; Abe, E.; et al. Systematic Review of the Association Between Worsening Renal Function and Mortality in Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure. Kidney Int Rep 2020, 5, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testani, J.M.; Brisco, M.A.; Turner, J.M.; Spatz, E.S.; Bellumkonda, L.; Parikh, C.R.; Tang, W.H. Loop diuretic efficiency: a metric of diuretic responsiveness with prognostic importance in acute decompensated heart failure. Circ Heart Fail 2014, 7, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voors, A.A.; Davison, B.A.; Teerlink, J.R.; Felker, G.M.; Cotter, G.; Filippatos, G.; Greenberg, B.H.; Pang, P.S.; Levin, B.; Hua, T.A.; et al. Diuretic response in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: characteristics and clinical outcome--an analysis from RELAX-AHF. Eur J Heart Fail 2014, 16, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed) 2022, 75, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, C.B.; Sanders, P.W.; Allman, R.M.; Rogers, W.J.; Patel, K.; Aban, I.B.; Rich, M.W.; Pitt, B.; White, M.; Bakris, G.C.; et al. Effects of enalapril in systolic heart failure patients with and without chronic kidney disease: insights from the SOLVD Treatment trial. Int J Cardiol 2013, 167, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, W.; Tighiouart, H.; Ku, E.; Salem, D.; Sarnak, M.J. Acute declines in estimated glomerular filtration rate on enalapril and mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Kidney Int 2019, 96, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Bushinsky, D.A.; Kitzman, D.W.; Ruschitzka, F.; Metra, M.; Filippatos, G.; Rossignol, P.; Du Mond, C.; Garza, D.; Berman, L.; et al. Evaluation of an individualized dose titration regimen of patiromer to prevent hyperkalaemia in patients with heart failure and chronic kidney disease. ESC Heart Fail 2018, 5, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Anker, S.D.; Bushinsky, D.A.; Kitzman, D.W.; Zannad, F.; Huang, I.Z.; Investigators, P.-H. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of RLY5016, a polymeric potassium binder, in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with chronic heart failure (the PEARL-HF) trial. Eur Heart J 2011, 32, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Tamargo, J. Renin-angiotensin system blockade: Finerenone. Nephrol Ther 2017, 13 Suppl 1, S47–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, J. Eplerenone (Inspra), a new aldosterone antagonist for the treatment of systemic hypertension and heart failure. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2004, 17, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauben, M.; Reich, L.; Gerrits, C.M.; Madigan, D. Detection of spironolactone-associated hyperkalaemia following the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES). Drug Saf 2007, 30, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannad, F.; McMurray, J.J.; Drexler, H.; Krum, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Swedberg, K.; Shi, H.; Vincent, J.; Pitt, B. Rationale and design of the Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalization And SurvIval Study in Heart Failure (EMPHASIS-HF). Eur J Heart Fail 2010, 12, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zannad, F.; McMurray, J.J.; Krum, H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Swedberg, K.; Shi, H.; Vincent, J.; Pocock, S.J.; Pitt, B.; Group, E.-H.S. Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N Engl J Med 2011, 364, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; Lefkowitz, M.P.; Rizkala, A.R.; Rouleau, J.; Shi, V.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; et al. Dual angiotensin receptor and neprilysin inhibition as an alternative to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in patients with chronic systolic heart failure: rationale for and design of the Prospective comparison of ARNI with ACEI to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and morbidity in Heart Failure trial (PARADIGM-HF). Eur J Heart Fail 2013, 15, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.S.; Vardeny, O.; Claggett, B.; McMurray, J.J.; Packer, M.; Swedberg, K.; Rouleau, J.L.; Zile, M.R.; Lefkowitz, M.; Shi, V.; et al. Reduced Risk of Hyperkalemia During Treatment of Heart Failure With Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists by Use of Sacubitril/Valsartan Compared With Enalapril: A Secondary Analysis of the PARADIGM-HF Trial. JAMA Cardiol 2017, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, J.K.; Wikstrand, J.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Goldstein, S.; Hjalmarson, A.; Johansson, P.; Kjekshus, J.; Ohlsson, L.; Samuelsson, O.; et al. The influence of renal function on clinical outcome and response to beta-blockade in systolic heart failure: insights from Metoprolol CR/XL Randomized Intervention Trial in Chronic HF (MERIT-HF). J Card Fail 2009, 15, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cice, G.; Ferrara, L.; D'Andrea, A.; D'Isa, S.; Di Benedetto, A.; Cittadini, A.; Russo, P.E.; Golino, P.; Calabro, R. Carvedilol increases two-year survivalin dialysis patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: a prospective, placebo-controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 41, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voors, A.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Robertson, M.; Ford, I.; Borer, J.S.; Bohm, M.; Komajda, M.; Swedberg, K.; Tavazzi, L.; investigators, S. The effect of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on renal function in patients with chronic heart failure: an analysis from SHIFT. Eur J Heart Fail 2014, 16, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefansson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S.J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarafidis, P.; Ortiz, A.; Ferro, C.J.; Halimi, J.M.; Kreutz, R.; Mallamaci, F.; Mancia, G.; Wanner, C.; Hypertension; the Kidney' working group of the European Society of, H. Sodium--glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for patients with diabetic and nondiabetic chronic kidney disease: a new era has already begun. J Hypertens 2021, 39, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, E.-K.C.G.; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.S.; Wells, G.A.; Talajic, M.; Arnold, M.O.; Sheldon, R.; Connolly, S.; Hohnloser, S.H.; Nichol, G.; Birnie, D.H.; Sapp, J.L.; et al. Cardiac-resynchronization therapy for mild-to-moderate heart failure. N Engl J Med 2010, 363, 2385–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turakhia, M.P.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Carrero, J.J.; Clase, C.M.; Deo, R.; Herzog, C.A.; Kasner, S.E.; Passman, R.S.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Reinecke, H.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias: conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Eur Heart J 2018, 39, 2314–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amici, G.; Bergia, R.; Cancarini, G.; Corciulo, R.; Feriani, M.; Iadarola, G.M.; La Milia, V.; Manili, L.; Neri, L.; Russo, R.; et al. Prescription in peritoneal dialysis. J Nephrol 2013, 26 Suppl 21, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovich, R.P.; Moncrief, J.W.; Nolph, K.D.; Ghods, A.J.; Twardowski, Z.J.; Pyle, W.K. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Ann Intern Med 1978, 88, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, C.D.; Gokal, R.; Peers, E. A randomized multicenter clinical trial comparing isosmolar icodextrin with hyperosmolar glucose solutions in CAPD. MIDAS Study Group. Multicenter Investigation of Icodextrin in Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. Kidney Int 1994, 46, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossekettler, L.; Schmack, B.; Meyer, K.; Brockmann, C.; Wanninger, R.; Kreusser, M.M.; Frankenstein, L.; Kihm, L.P.; Zeier, M.; Katus, H.A.; et al. Peritoneal dialysis as therapeutic option in heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail 2019, 6, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Haastert, B.; Kohnle, M.; Rump, L.C.; Kelm, M.; Trapp, R.; Aker, S. Peritoneal dialysis relieves clinical symptoms and is well tolerated in patients with refractory heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Eur J Heart Fail 2012, 14, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtaszek, E.; Grzejszczak, A.; Niemczyk, S.; Malyszko, J.; Matuszkiewicz-Rowinska, J. Peritoneal Ultrafiltration in the Long-Term Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure Refractory to Pharmacological Therapy. Front Physiol 2019, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cnossen, T.T.; Kooman, J.P.; Krepel, H.P.; Konings, C.J.; Uszko-Lencer, N.H.; Leunissen, K.M.; van der Sande, F.M. Prospective study on clinical effects of renal replacement therapy in treatment-resistant congestive heart failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012, 27, 2794–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.; Gonzalez, M.; Minana, G.; Garcia-Ramon, R.; Sanchis, J.; Bodi, V.; Nunez, E.; Puchades, M.J.; Palau, P.; Merlos, P.; et al. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis as a therapeutic alternative in patients with advanced congestive heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 2012, 14, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Abrahams, Z.; Francis, G.S.; Sokos, G.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Young, J.B.; Tang, W.H.W. Importance of venous congestion for worsening of renal function in advanced decompensated heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009, 53, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadarola, G.M.; Lusardi, P.; La Milia, V.; Amici, G.; Santarelli, S.; Virga, G.; Basile, C.; Bertoli, S.; Bonofiglio, R.; Del Rosso, G.; et al. Peritoneal ultrafiltration in patients with advanced decompensated heart failure. J Nephrol 2013, 26 Suppl 21, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, R.O.; Barbosa, F.; Farre, N. Peritoneal dialysis in heart failure: focus on kidney and ventricular dysfunction. Rev Cardiovasc Med 2021, 22, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Biomarker | HF type | Prognosis | Cut-off | Cut-off adjusted according to eGFR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT-ProBNP | AHF/CHF | Short and long- term cardiovascular events and all-cause death | AHF:300 pg/ml CHF: 125 pg/ml |
As diagnostic value: -AHF and CKD stage 3-5: 1200-6000 pg/ml. As prognostic value: Only two studies have tried to give a cut-off: -Horii et al, reported 259.7 pg/ml (eGFR >30 ml/min/1.73 m2) and 5111 pg/ml (eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2) [17]. -Masson et al, reported 769 (eGFR >60 ml/min/1.73 m2) and 2023 pg/ml (eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2) [18]. |
| BNP | AHF/CHF | Short and long- term cardiovascular events, all-cause death, and quality of life. |
Diagnostic threshold: AHF>400 pg/ml CHF: >150 pg/ml |
As diagnostic value: CHF: Only one study has tried to give a cut-off: -McCullough et all reported for patient with CKD stage 3-5 (eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73m2) >200 pg/ml [19]. As prognostic value: CHF: Only one study has tried to give a cut-off: -Horii et al, reported 90.8 pg/ml (eGFR >30 ml/min/1.73 m2) and 157 pg/ml (eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73 m2) [17]. |
| Biomarker | Prognosis | Prediction | Cut-off adjusted according to eGFR |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsTnT | Short- and long- term mortality | HF occurrence and death in CKD without cardiac symptoms | As prognostic value: -13 ng/L CKD stage 1 -15 ng/L CKD stage 2 -22 ng/L CKD stage 3 -40 ng/L CKD stage 4-5 As prediction value in patient without HF: <5 ng/L lower risk of HF within 12 years |
| Serum creatinine criteria | Urine output | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKI Stage | KDIGO | RIFLE | AKIN | |
| 1 (Risk) | Increase ≥ 0.3 mg/dl within 48 h or ≥ 1.5 or 2-fold from baseline | Increase x 1.5 baseline or eGFR decrease > 25% | Increase 1.5- 1.9 times from baseline or ≥ 0.3 mg/dl increase within 48 h | < 0.5 ml/Kg/h for 6-12 h |
| 2 (Injury) | 2.0 - 2.9 times from baseline | Increase x 2 from baseline or eGFR decrease > 50% | Increase > 2- to 3-fold from baseline | < 0.5 ml/Kg/h for 2 h |
| 3 (Failure) | 3.0 times from baseline or increase to ≥ 4 mg/dl or initiation of renal replacement therapy or, in patient < 18 years decrease in eGFR to < 35 ml/min per 1.73 m2 | Increase x 3 from baseline or eGFR decrease > 75%, or serum creatinine > 4 mg/dl with an acute rise > 0.5 mg/dl | Increase > 300% (> 3-fold) from baseline, or ≥ 4 mg/dl with an acute rise ≥ 0.5 mg/dl or on renal replacement therapy | < 0.3 ml/Kg/h for 24 h or anuria for 12 h. |
| DRUG AVAILABLE | Recommended CREATININE or eGFR |
|---|---|
| Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) | <2.5 mg/dl or > 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 |
| Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) | <3 mg/dl |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) | <2.5 mg/dl or > 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 |
| B-blockers -Carvedilol -Metoprolol -Bisoprolol |
<2.8 mg/dl or > 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 >45 ml/min/1.73 m2 <3.5 mg/dl |
| Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) | > 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 |
| Ivabradine | <2.5 mg/dl |
| SGLT2 inhibitor -Dapagliflozin -Empagliflozin |
> 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 > 20 ml/min/1.73 m2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





