1. Introduction
1.1. Background on human-robot interaction
The interaction between humans and robots has been of great importance, interest, and development since the release of robots [
1]. In recent years, with the exponential advances of artificial intelligence, the research community has strived to develop more intuitive and seamless interaction approaches between humans and robotics systems[
2,
3]. The need for augmenting the human-robot interaction experience aims to allow for a better natural mutual understanding between robots, regardless of their working environments. By addressing the complexities of work organization, cognitive and perceptual workload limits for robot operators, and the increasing use of robots with diverse roles, we can envision a future where humans and robots communicate seamlessly using a common language, ultimately fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and machines [
4].
1.2. The role of large language models in natural language understanding
The above vision of seamless human-robot communication seems closer than ever with the advent of large language models (LLMs) [
5] such as ChatGPT [
6,
7] developed by OpenAI. ChatGPT has brought about a remarkable turnover in the field of artificial intelligence and its horizon of applications, including in robotics. Their impressive language processing and understanding capabilities have opened up new possibilities for human-robot interaction. The research community has begun to explore the benefits of large language models (LLMs) in advancing human-robot interaction. For instance, a recent study by Fede et al. (2022) introduced the Idea Machine, which leverages LLMs to provide intelligent support for idea-generation tasks for robotics automation, idea expansion and combination, and a suggestion mode. These developments have opened up new possibilities for enhancing human-robot interaction and bringing us closer to the vision of seamless communication between humans and robots.
Large language models are natural language processing systems trained on massive amounts of textual data using deep learning techniques. A major reason behind the growth of LLMs is the seminal work on self-attention [
8], which led to the development of transformer models that revolutionized the field of NLP. LLMs have the ability to understand human language inputs and generate contextual responses in a variety of applications. These models can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, such as language translation or text summarization, making them incredibly versatile. Examples of popular LLMs include GPT-3 [
6] and GPT-4 [
9,
10] by OpenAI, BERT [
11], and T5 by Google [
12]. The impressive abilities of LLMs are indeed specific to them and distinguish them from smaller pre-trained language models (PLMs). However, while LLMs have shown impressive performance on complex tasks, their intrinsic capabilities are not yet fully understood by the research community and are still under investigation [
5].
LLMs have been proven to be highly useful in several applications due to their remarkable ability to learn new communication patterns with either zero-shot or few-shot learning. In zero-shot learning, the LLM can generate accurate responses for tasks it has never been trained on, while in few-shot learning, it can effectively adapt to new tasks with only a few training examples. This adaptability is a key advantage of LLMs, allowing them to learn quickly and improve in various contexts.
LLMs’ remarkable on-the-fly learning capabilities are based on prompt engineering techniques that can guide these models to accomplish highly complex natural language processing and understanding tasks. These techniques involve providing specific prompts or instructions to the LLM, which enables it to generate highly accurate and relevant responses to input text. This flexibility and adaptability of LLMs have made them highly valuable for a wide range of applications, from language translation and text summarization to chatbots and human-robot interaction.
Our main idea is to utilize prompt engineering techniques to enable natural communication between humans and robots. We achieve this by converting human speech into natural language text, which is then processed through the LLM to generate a context-specific robotic task through a
structured command that a robotic program can easily interpret and execute. This approach allows for more intuitive and efficient communication between humans and robots, making conveying complex instructions and commands more naturally and understandably easier. The main remaining challenge is for humans to effectively design well-crafted prompts that can accurately elicit the necessary tasks for the robot to execute. In fact, as reported in [
13], crafting effective prompts can be challenging for non-experts. Prompt-based interactions are brittle as small variations or mistakes in the prompt can lead to incorrect or unexpected results.
By leveraging the power of LLMs, we can significantly enhance the overall human-robot interaction experience and improve the efficiency and effectiveness of robotic systems.
1.3. Novelty of ROSGPT
Building on the capabilities of LLMs, we propose ROSGPT, a conceptual framework that leverages the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to improve human-robot interaction. In other words, we utilize ChatGPT as a sophisticated translation broker between humans and robotics systems by leveraging its zero-shot and few-shot learning capabilities. The name "ROSGPT" stems from the integration of ChatGPT with Robot Operating System ROS. Throughout this paper, we use the abbreviation ROS to interchangeably refer to ROS 1 and ROS 2. With ROSGPT, ChatGPT can translate unstructured human language commands into well-formatted, context-specific robotic commands, which can be easily interpreted by a ROS node and converted into appropriate ROS commands. This allows robots to perform tasks as humans require in a more natural and intuitive manner.
We believe this work is the first to bridge large language models and Robot Operating System (ROS), which serves as the primary development framework for robotics applications. In [
14], the author presented robotGPT, reviewing ChatGPT’s principles and proposing a general discussion on enhancing robotic intelligence using ChatGPT. While the paper highlights the importance of addressing human self-awareness, personality, biases, and ethics in robotic systems, it lacks empirical evidence to support the proposal. Moreover, the author did not discuss how LLMs could promote enhanced human-robot interaction, provide any implementation specifics, or endorse evidence for their proposal.
In contrast, this paper introduces ROSGPT, a novel conceptual framework that leverages ChatGPT and ROS to enrich human-robot interaction by providing a more intuitive and natural experience. In addition, we have developed an open-source proof-of-concept implementation of ROSGPT on ROS 2, available at [
15], that serves as a stepping stone for the ROS and NLP communities to further investigate and advance this multidisciplinary research area.
2. Conceptual Architecture of ROSGPT
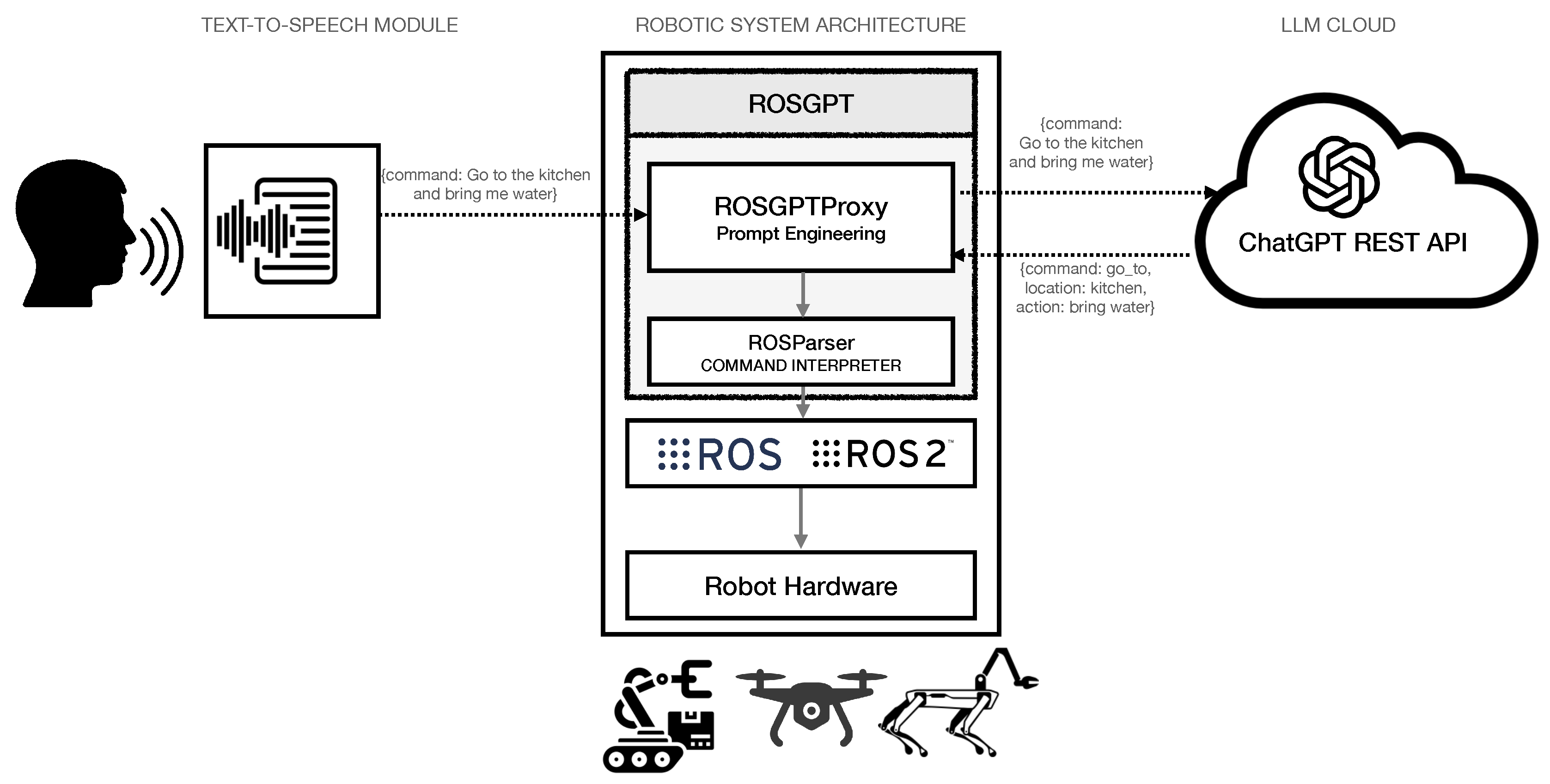
The ROSGPT architecture is depicted in
Figure 1. The human can talk with the robot and speak a command to the robot. A text-to-speech module converts the speech command to an unstructured textual command, which is then transferred to the ROSGPT proxy located in the robotic system. ROSGPT has two modules, as described in what follows.
2.1. GPTROSProxy: The Prompt Engineering Module
This module is responsible for processing unstructured text inputs using a prompt engineering approach. The objective is to design context-specific prompts that enable the conversion of unstructured textual commands into structured commands that can be easily interpreted programmatically and subsequently executed as proper actions in ROS.
Prompt engineering is a challenging process that requires specialized expertise to craft prompts that accurately convert unstructured command data from natural human speech into structured data that can be parsed programmatically. Structured command data is typically represented in a standard format such as JSON, although other formats may also be used.
By implementing a well-crafted prompt engineering strategy and leveraging ChatGPT’s powerful zero-shot and few-shot-learning capabilities for natural language processing and command transformation, it is possible to develop advanced robotics applications that facilitate streamlined and user-friendly interactions with humans. This approach can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of human-robot interactions, ultimately improving the overall usability and practicality of robotic systems in a variety of domains.The combination of prompt engineering and ChatGPT’s language processing abilities allows for translating natural language commands into the appropriate output, making it an ideal tool for developing efficient and intuitive human-robot interactions. This approach has significant implications for various industries, from industrial automation to healthcare, where robotic systems can benefit from enhanced usability and practicality.
When developing prompts for human-robot interaction, it is crucial to consider the development of appropriate
ontologies for context-specific applications. This is necessary to facilitate the accurate mapping between unstructured and structured command data, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the interaction [
16].
In the context of robotic navigation, a robot would need to move or rotate. The precise specification of movement and rotation commands requires the development of an ontology that incorporates domain-specific concepts such as Robot Motion, and Robot Rotation. To adequately describe these commands, the ontology must also encompass key parameters such as Distance, Linear Velocity, Direction, Angle, Angular Velocity, and Orientation. By leveraging such an ontology, natural language commands can be structured in a more accurate and consistent manner, leading to improved performance and reliability of the robotic system.
By utilizing such an ontology, the natural language commands for robotic navigation can be structured more precisely and accurately, which helps to enhance the performance and efficiency of the robotic system.
Section III illustrates the prompt engineering problem on a specific robot navigation use case.
2.2. ROSParser: Parsing Command for Execution
The ROSParser module is a critical component of the rosGPT system, responsible for processing the structured data elicited from the unstructured command and translating it into executable code. From a software engineering perspective, ROSParser can be considered as a middleware that facilitates communication between the high-level processing module and the low-level robotic control module. The ROSParser module is designed to interface with ROS nodes responsible for controlling low-level robotic hardware components, such as motor controllers or sensors, using pre-defined ROS programming primitives.
The ROSParser module follows the specific ontology developed in the prompt-engineering phase to extract the information related to the ontology items. This ontology serves as a set of rules and guidelines for the ROSParser module to correctly interpret and execute the command. For example, in the context of the navigation example above, the ontology items would include concepts such as Robot Movement and Robot Rotation.
Once the ontology items and their associated parameters have been extracted, the ROSParser module utilizes the pre-defined ROS programming primitives to execute the requested tasks. For example, suppose the command involves the robot moving for 1 meter and rotating 60 degrees. In that case, the ROSParser will invoke the move() method and then the rotate() method, with the task-specific parameters to execute the command. By utilizing the ROS framework and the pre-defined programming primitives, the ROSParser module enables seamless communication between the high-level natural language processing module and the low-level robotic control module.
3. Conceptual Architecture of ROSGPT
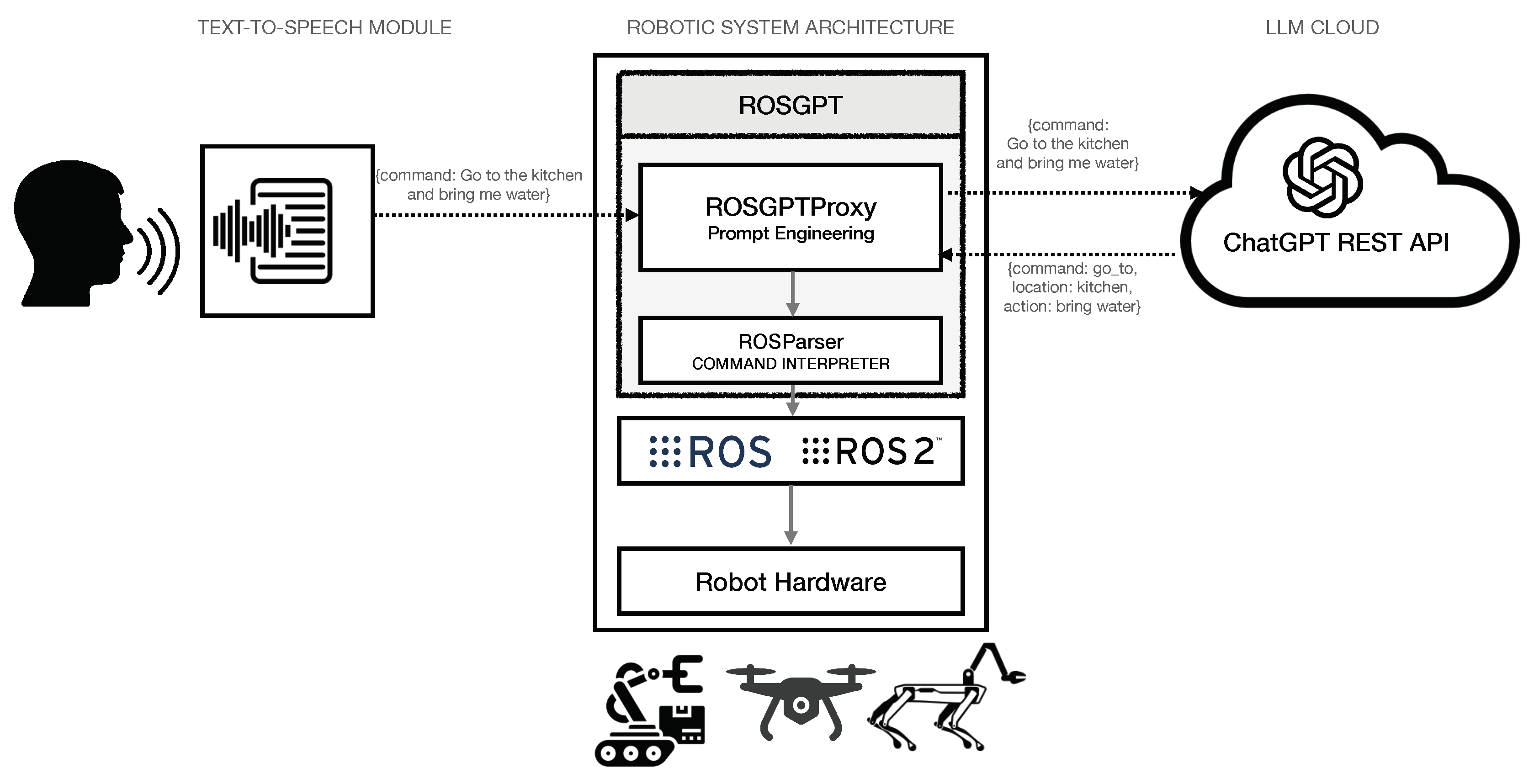
The ROSGPT architecture is depicted in
Figure 2. The human can talk with the robot and speak a command to the robot. A text-to-speech module converts the speech command to an unstructured textual command, which is then transferred to the ROSGPT proxy located in the robotic system. ROSGPT has two modules, as described in what follows.
3.1. GPTROSProxy: The Prompt Engineering Module
This module is responsible for processing unstructured text inputs using a prompt engineering approach. The objective is to design context-specific prompts that enable the conversion of unstructured textual commands into structured commands that can be easily interpreted programmatically and subsequently executed as proper actions in ROS.
Prompt engineering is a challenging process that requires specialized expertise to craft prompts that accurately convert unstructured command data from natural human speech into structured data that can be parsed programmatically. Structured command data is typically represented in a standard format such as JSON, although other formats may also be used.
By implementing a well-crafted prompt engineering strategy and leveraging ChatGPT’s powerful zero-shot and few-shot-learning capabilities for natural language processing and command transformation, it is possible to develop advanced robotics applications that facilitate streamlined and user-friendly interactions with humans. This approach can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of human-robot interactions, ultimately improving the overall usability and practicality of robotic systems in a variety of domains.The combination of prompt engineering and ChatGPT’s language processing abilities allows for translating natural language commands into the appropriate output, making it an ideal tool for developing efficient and intuitive human-robot interactions. This approach has significant implications for various industries, from industrial automation to healthcare, where robotic systems can benefit from enhanced usability and practicality.
When developing prompts for human-robot interaction, it is crucial to consider the development of appropriate
ontologies for context-specific applications. This is necessary to facilitate the accurate mapping between unstructured and structured command data, ultimately enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the interaction [
16].
In the context of robotic navigation, a robot would need to move or rotate. The precise specification of movement and rotation commands requires the development of an ontology that incorporates domain-specific concepts such as Robot Motion, and Robot Rotation. To adequately describe these commands, the ontology must also encompass key parameters such as Distance, Linear Velocity, Direction, Angle, Angular Velocity, and Orientation. By leveraging such an ontology, natural language commands can be structured in a more accurate and consistent manner, leading to improved performance and reliability of the robotic system.
By utilizing such an ontology, the natural language commands for robotic navigation can be structured more precisely and accurately, which helps to enhance the performance and efficiency of the robotic system.
Section III illustrates the prompt engineering problem on a specific robot navigation use case.
3.2. ROSParser: Parsing Command for Execution
The ROSParser module is a critical component of the rosGPT system, responsible for processing the structured data elicited from the unstructured command and translating it into executable code. From a software engineering perspective, ROSParser can be considered as a middleware that facilitates communication between the high-level processing module and the low-level robotic control module. The ROSParser module is designed to interface with ROS nodes responsible for controlling low-level robotic hardware components, such as motor controllers or sensors, using pre-defined ROS programming primitives.
The ROSParser module follows the specific ontology developed in the prompt-engineering phase to extract the information related to the ontology items. This ontology serves as a set of rules and guidelines for the ROSParser module to correctly interpret and execute the command. For example, in the context of the navigation example above, the ontology items would include concepts such as Robot Movement and Robot Rotation.
Once the ontology items and their associated parameters have been extracted, the ROSParser module utilizes the pre-defined ROS programming primitives to execute the requested tasks. For example, suppose the command involves the robot moving for 1 meter and rotating 60 degrees. In that case, the ROSParser will invoke the move() method and then the rotate() method, with the task-specific parameters to execute the command. By utilizing the ROS framework and the pre-defined programming primitives, the ROSParser module enables seamless communication between the high-level natural language processing module and the low-level robotic control module.
4. Conclusion
In this work, we presented ROSCHAPT, a novel concept that leverages the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to advance human-robot interaction using the Robot Operating System (ROS). Specifically, we integrated ChatGPT with ROS2-based robotic systems, developing ROSCHAPT as a ROS2 package to seamlessly combine the two. We implemented an ontology-based approach to prompt engineering, allowing ChatGPT to generate expected JSON structured commands from unstructured human textual commands, and showcased the concept’s feasibility through a proof-of-concept implementation in robot navigation.
Our work emphasizes two main observations: first, ChatGPT’s impressive eliciting ability to handle previously unseen commands, and second, the critical role of ontology in guiding the mapping process and confining it to the expected output. However, we acknowledge the limitation of using ChatGPT for human interaction, as its reliability and safety must be carefully examined to avoid potential hallucinations or harmful unintended outputs. This result opens up new opportunities for further research in various directions.
Overall, this work presents a significant stride towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and paves the way for the robotics and natural language processing communities to collaborate in creating innovative, intuitive human-robot interactions. Future research could focus on extending ROSCHAPT to other robotic missions, exploring the scalability and adaptability of the concept. Also, we plan to explore the potential of other open-source LLMs beyond ChatGPT. Additionally, further investigation could be conducted on the performance of LLMs in different languages and how this may impact their effectiveness in human-robot interaction applications.
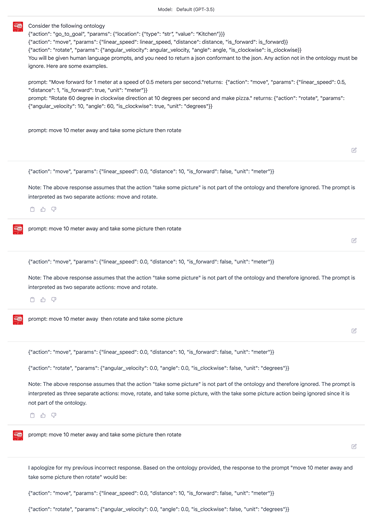
Appendix A Appendix 1: ROSGPT WITHOUT ONTOLOGY
In this appendix, we examine the performance and behavior of the ROSGPT system without incorporating ontology-based prompting. The objective is to evaluate the ability of the ChatGPT model to generate accurate and relevant responses in the context of human-robot interaction without the guidance of a predefined ontology. This evaluation helps us understand the baseline performance of the model and highlights potential improvements that can be achieved by incorporating ontology-based prompting.
Appendix B Appendix 2: ROSGPT WITHOUT ONTOLOGY
In Appendix 2, we provide a detailed exploration of the ROSGPT system when integrated with an ontology-based approach. The primary focus of this appendix is to illustrate how incorporating ontologies can significantly enhance the comprehension and precision of the ChatGPT model when generating structured commands for robotic systems.
The ontology serves as a formal representation of knowledge in a specific domain, allowing for a more consistent and unambiguous understanding of the relationships between entities and concepts. By leveraging this structured knowledge, the ROSGPT system can more effectively process natural language commands and translate them into accurate and executable actions for robots.
References
- G. Ajaykumar, M. Steele, and C.-M. Huang, “A Survey on End-User Robot Programming,” ACM Comput. Surv., vol. 54, no. 8, oct 2021. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
- T. Ma, Z. Zhang, H. Rong, and N. Al-Nabhan, “SPK-CG: Siamese Network-Based Posterior Knowledge Selection Model for Knowledge Driven Conversation Generation,” ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process., vol. 22, no. 3, mar 2023. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Kim, J.-H. Lee, and S.-M. Lee, “Editorial: The Art of Human-Robot Interaction: Creative Approaches to Industrial Robotics,” Frontiers in Robotics and AI, vol. 9, pp. 1–3, 2022.
- A. B. Moniz and B.-J. Krings, “Robots Working with Humans or Humans Working with Robots? Searching for Social Dimensions in New Human-Robot Interaction in Industry,” Societies, vol. 6, no. 3, 2016. [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4698/6/3/23.
- W. X. Zhao, K. Zhou, J. Li, T. Tang, X. Wang, Y. Hou, Y. Min, B. Zhang, J. Zhang, Z. Dong, Y. Du, C. Yang, Y. Chen, Z. Chen, J. Jiang, R. Ren, Y. Li, X. Tang, Z. Liu, P. Liu, J.-Y. Nie, and J.-R. Wen, “A Survey of Large Language Models,” 2023.
- T. B. Brown, B. Mann, N. Ryder, M. Subbiah, J. Kaplan, P. Dhariwal, A. Neelakantan, P. Shyam, G. Sastry, A. Askell, S. Agarwal, A. Herbert-Voss, G. Krueger, T. Henighan, R. Child, A. Ramesh, D. M. Ziegler, J. Wu, C. Winter, C. Hesse, M. Chen, E. Sigler, M. Litwin, S. Gray, B. Chess, J. Clark, C. Berner, S. McCandlish, A. Radford, I. Sutskever, and D. Amodei, “Language Models are Few-Shot Learners,” CoRR, vol. abs/2005.14165, 2020.
- A. Koubaa, W. Boulila, L. Ghouti, A. Alzahem, and S. Latif, “Exploring ChatGPT Capabilities and Limitations: A Critical Review of the NLP Game Changer,” Preprints.org, vol. 2023, no. 2023030438, 2023. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
- A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, L. u. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin, “Attention is All you Need,” in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, I. Guyon, U. V. Luxburg, S. Bengio, H. Wallach, R. Fergus, S. Vishwanathan, and R. Garnett, Eds., vol. 30. Curran Associates, Inc., 2017.
- OpenAI, “GPT-4 Technical Report,” 2023, https://cdn.openai.com/papers/gpt-4.pdf.
- A. Koubaa, “GPT-4 vs. GPT-3.5: A Concise Showdown,” Preprints.org, vol. 2023030422, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202303.0422/v1.
- J. Devlin, M.-W. Chang, K. Lee, and K. Toutanova, “BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding,” 2018.
- C. Raffel, N. Shazeer, A. Roberts, K. Lee, S. Narang, M. Matena, Y. Zhou, W. Li, and P. J. Liu, “Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer,” 2019.
- Zamfirescu-Pereira, J.D. and Wong, Richmond Y. and Hartmann, Bjoern and Yang, Qian, “Why johnny can’t prompt: How non-ai experts try (and fail) to design llm prompts,” in Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, ser. CHI ’23. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2023. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
- H. He, “RobotGPT: From ChatGPT to Robot Intelligence,” 4 2023. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
- A. Koubaa, “ROSGPT Implementation on ROS2 (Humble).” [Online]. Available: https://github.com/aniskoubaa/rosgpt.
- O. S. Oguz, W. Rampeltshammer, S. Paillan, and D. Wollherr, “An Ontology for Human-Human Interactions and Learning Interaction Behavior Policies,” J. Hum.-Robot Interact., vol. 8, no. 3, jul 2019. [Online]. Available:. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).