Submitted:
08 May 2023
Posted:
09 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
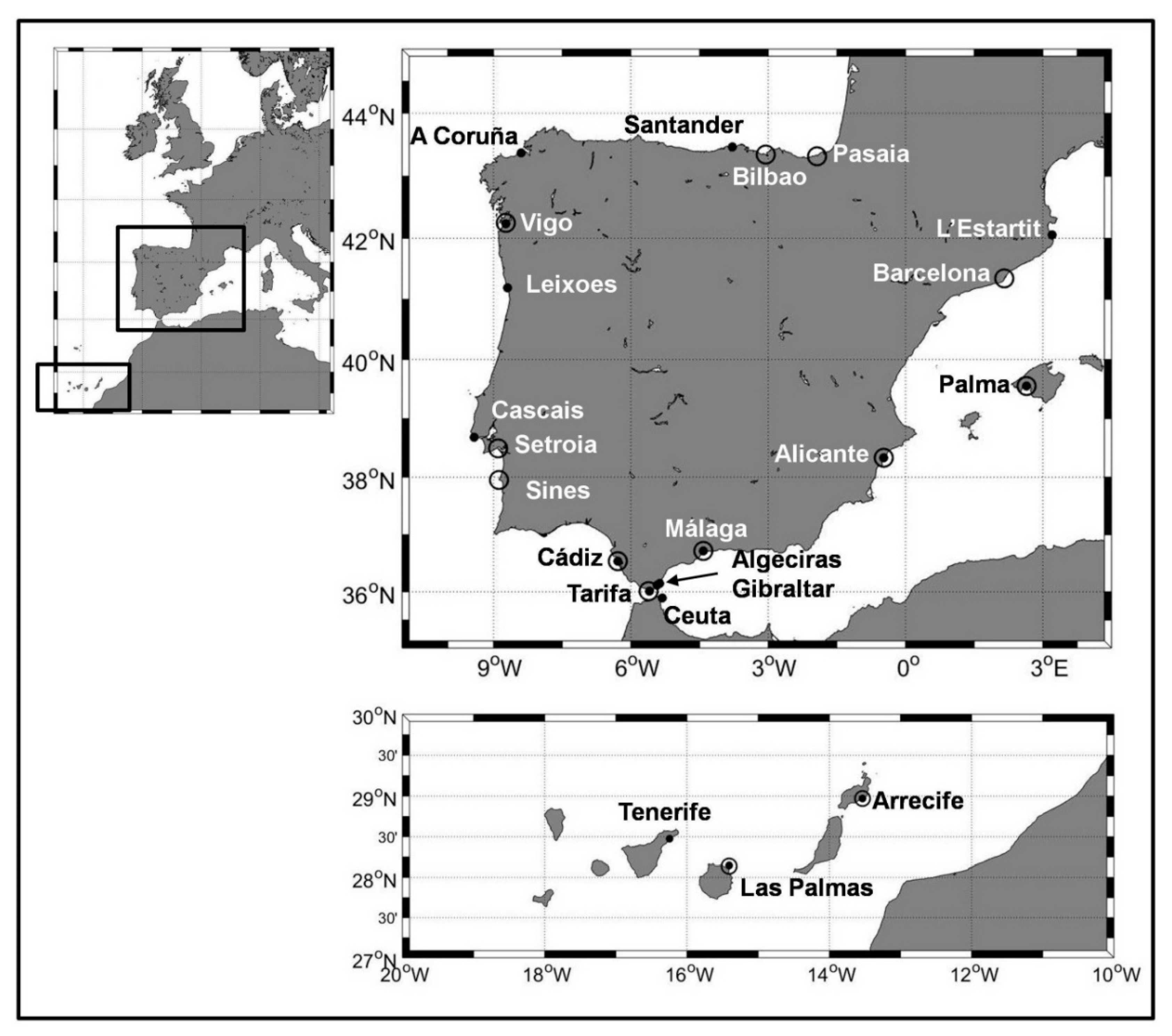
2.1. Sea Level Data
2.2. Altimetry Data
2.3. Temperature and Salinity Data
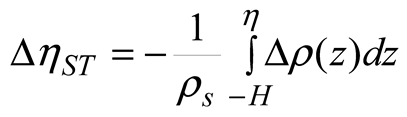
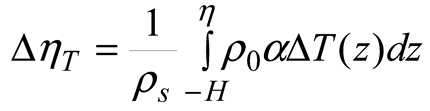
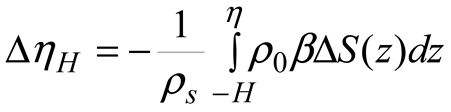
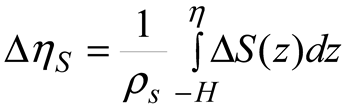
2.4. Atmospheric Variables
2.5. Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Model
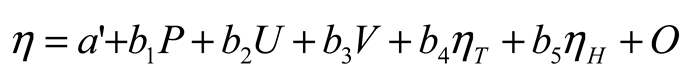
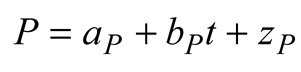
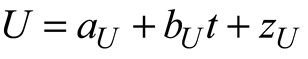
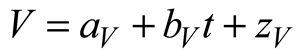
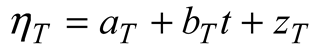
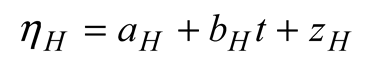
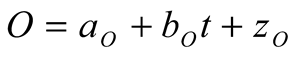
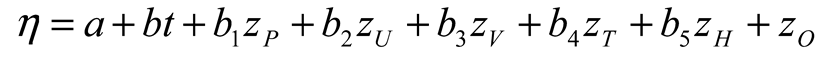
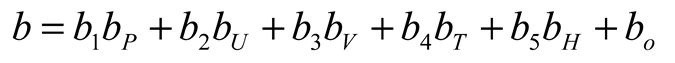
3. Results
3.1. Sea Level Linear Trends
3.2. Linear trends of the atmospheric forcing, and the thermosteric and halosteric sea-level change.
3.3. Linear Model
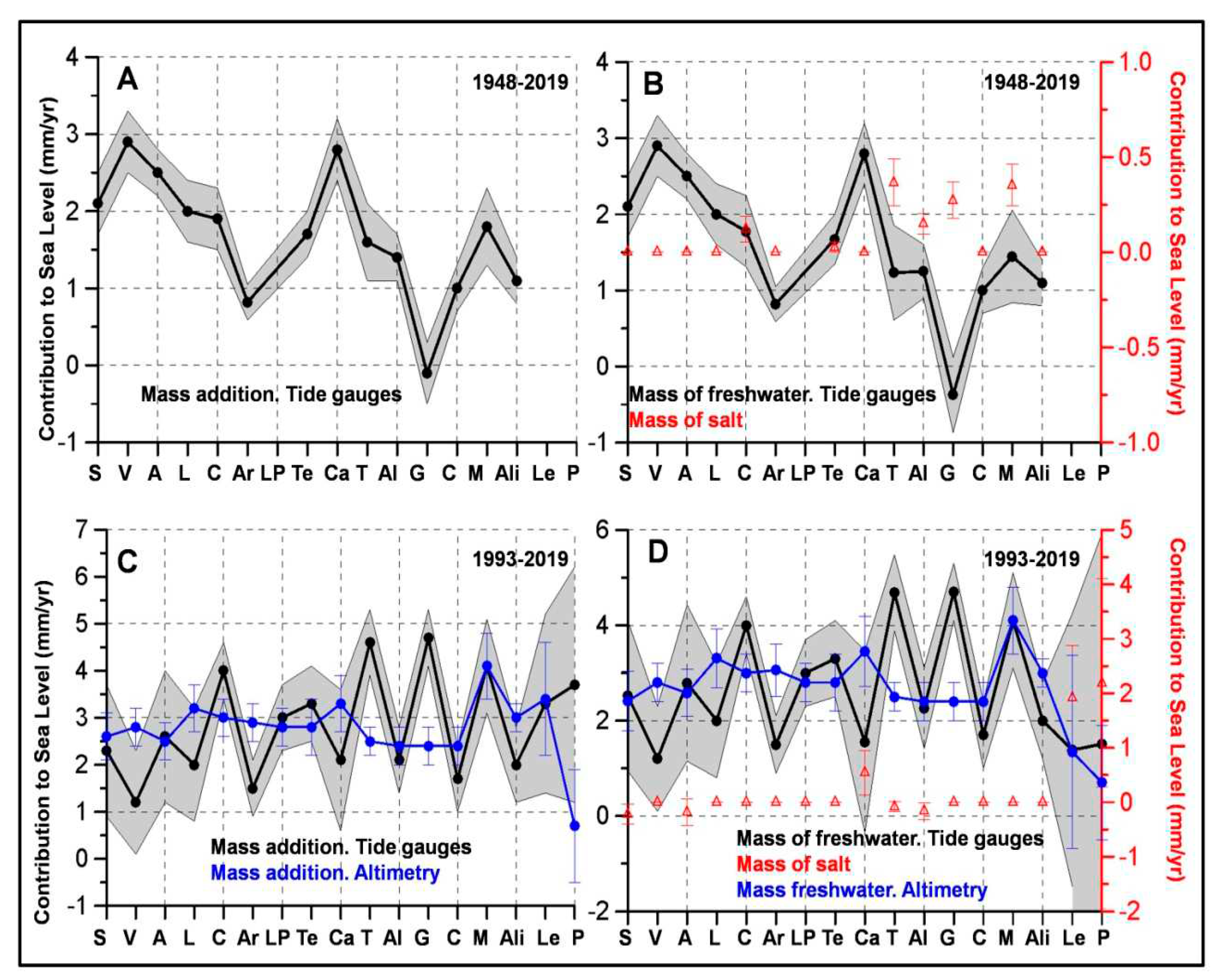
3.4. Mass of Salt and Freshwater Contributions
4. Discussion and Conclusions
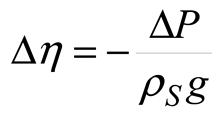
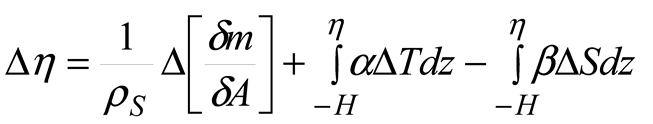
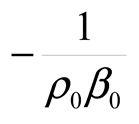
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calafat F. M., Chambers D. P., Tsimplis, M. N. On the ability of global sea level reconstructions to determine trends and variability. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2014. Vol. 119, 1572-1592. [CrossRef]
- Llovel W., Cazenave A., Rogel P., Lombard,M.Bergé-Nguyen A. 2-D reconstruction of past sea level (1950–2003) using tidegauge records and spatial patterns from a general ocean circulation model. Clim. Past Discuss. 2009. Vol. 5, 1109–1132.
- Church J.A., White N. J. A 20th century acceleration in global sea level rise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006. Vol. 33, L01602.
- Church J.A., White N. J. Sea-level rise from late 19th to early 21st century. Surv. Geophys. 2011. Vol. 32, 585–602.
- Church J.A., White N. J., Coleman R., Lambeck K., Mitrovica J. X. Estimates of the Regional Distribution of Sea Level Rise overthe 1950–2000 Period. J. Clim. 2004. Vol. 17, 2609–2625.
- Ramos-Alcántara J., Gomis D., Jordà G. Reconstruction of Mediterranean coastal sea level at different timescales based on tide gauge records. Ocean Sci. 2022. Vol. 18, 1781–1803.
- Fox-Kemper B., Hewitt H.T., Xiao C., Aðalgeirsdóttir G., Drijfhout S.S., Edwards T.L., Golledge N.R., Hemer M., Kopp R.E., Krinner G., Mix A., Notz D., Nowicki S., Nurhati I.S., Ruiz L., Sallée J.-B., Slangen A.B.A., Yu Y. Ocean, Cryosphere and Sea Level Change. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. 2021. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1211–1362. [CrossRef]
- Arias P. A. et al. Technical Summary. In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. 2021. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 33−144. [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer M., Glavovic B.C., Hinkel J., van de Wal R., Magnan A.K., Abd-Elgawad A., Cai R., Cifuentes-Jara M., DeConto R.M., Ghosh T., Hay J., Isla F., Marzeion B., Meyssignac B., Sebesvari Z. Sea Level Rise and Implications for Low-Lying Islands, Coasts and Communities. In: IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.)]. 2019. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA, pp. 321-445,. [CrossRef]
- Dangendorf S., Marcos M., Wöppelmann G., Conrad T., Frederikse C. P., Riva R. Reassessment of 20th Century Global Mean Sea Level Rise, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017. Vol. 114,5946–5951. [CrossRef]
- Dangendorf S., Marcos M., Müller A., Zorita E., Riva R., Berk K., Jensen J. Detecting anthropogenic footprints in sea level rise, Nat. Commun. 2015. Vol. 6, 7849. [CrossRef]
- Gomis, D., Tsimplis M., Marcos M., Fenoglio-Marc L., Pérez B., Raicich F., Vilibic I., Wöppelmann G., Monserrat S. Mediterranean Sea-Level Variability and Trends. In The Climate of the Mediterranean Region: From the Past to the Future; Lionello, P.,Ed. 2012. Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
- BongartsLebbe T., Rey-Valette H., Chaumillon É., Camus G., Almar R., Cazenave A., Claudet J., Rocle N., Meur-Férec C., Viard F., Mercier D., Dupuy C., Ménard F., Rossel BA, Mullineaux L., Sicre M-A., Zivian A., Gaill F., Euzen A. Designing Coastal Adaptation Strategies to Tackle Sea Level Rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021. Vol. 8:740602. [CrossRef]
- Gregory J. M., Griffies S. M., Hughes C. W., Lowe J. A., Church J. A., Fukimori I., Gomez N., Kopp R. E., Landerer F., Le Cozannet G., Ponte R. M., Stammer D., Tamisiea M. E., van de Wal R. S. W. Concepts and Terminology for Sea Level: Mean, Variability and Change, Both Local and Global. Surveys in Geophysics. 2019. 40:1251–1289.
- Jordà G., Gomis D. On the interpretation of the steric and mass components of sea level variability: The case of the Mediterranean Sea. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans. 2013. Vol. 118, 953-963. [CrossRef]
- Gregory J. M., Lowe J. A. Predictions of global and regionalsea-level rise using AOGCMs with and without flux adjustment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000. Vol. 27, 3069–3072, 2000.
- Wang G., Cheng L., Boyer T., Li C. Halosteric Sea Level Changes during the Argo Era. Water. 2017. Vol. 9, 484; [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis M.N., Baker T. F. Sea level drop in the Mediterranean Sea: An indicator of deep water salinity and temperature changes?Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000. Vol. 27, 1731–1734.
- Jordà G., Gomis D. Reliability of the steric and mass components of Mediterranean sea level as estimated from hydrographic gridded products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013. Vol. 40, 3655–3660. [CrossRef]
- Camargo C. M. L., Riva R. E. M., Hermans T. H. J., Slangen A. B. A. Trends and Uncertainties of Regional Barystatic Sea-level Change in the Satellite Altimetry Era, Earth Syst. Dynam. Discuss. 2021. [preprint]. in review. [CrossRef]
- Tsimplis M.N., Spada G., Marcos M., Fleming N., Multidecadal sea level trends and land movements in the Mediterranean Seawith estimates of factors perturbing tide gauge data and cumulative uncertainties. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011. Vol. 76, 63–76.
- Gomis D., Ruiz S., Sotillo M. G., Álvarez-Fanjul E., Terradas J. Low frequency Mediterranean sea level variability: Thecontribution of atmospheric pressure and wind. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008. Vol. 63, 215–229.
- Marcos M., Tsimplis, M.N. Forcing of coastal sea level rise patterns in the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007. Vol. 34, L18604.
- Carrère L., Lyard F. Modeling the barotropic response of the global ocean to atmospheric wind and pressure forcing - comparisons with observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003. Vol. 30, No. 6, 1275. [CrossRef]
- Storto A., Bonaduce A., Feng X., Yang C. Steric Sea Level Changes from Ocean Reanalyses at Global and Regional Scales. Water. 2019. Vol. 11, 1987. [CrossRef]
- Church J.A., Roemmich D., Domingues C. M., Willis J. K., White N. J., Gilson J. E., Stammer D., Köhl A., Chambers D. P., Landerer F. W., Marotzke J., Gregory J. M., Suzuki T., Cazenave A., Le Traon P.-Y. Ocean Temperature and Salinity Contributions to Global and Regional Sea-Level Change. In Understanding Sea-Level Rise and Variability; Church, J.A., Woodworth, P.L., Aarup, T., Wilson, W.S., Eds.2010. Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 143–176.
- Vargas-Yáñez M., García-Martínez M.C., Moya F., Balbín R., López-Jurado J.L., Serra M., Zunino P., Pascual J., Salat J. Updating temperature and salinity mean values and trends in the Western Mediterranean: The RADMED Project. Prog. in Oceanogr. 2017. Vol. 157, 27–46. [CrossRef]
- Holgate S. J., Matthews A., Woodworth P. L., Rickards L. J., Tamisiea M. E., Bradshaw E., Foden P. R., Gordon K. M., Jevrejeva S., Pugh, J. New Data Systems and Products at the Permanent Service for Mean Sea Level. J. Coast. Res. 2013. Vol. 29, Issue 3: 493 – 504. [CrossRef]
- Marcos M., Puyol B., Wöppelmann G., Herrero C., García-Fernández M. J. The long sea level record at Cádiz (Southern Spain). J. Geophys. Res. 2011. 116, C12003.
- Marcos M., Puyol B., Gómez B. P., Fraile M. A., Talke S. A. Historical tide-gauge sea level observations in Alicante and Santander (Spain) since the 19th century. Geosci. Data J. 2021.
- Marcos M., Puyol B., Calafat F. M., Woppelmann G. Sea level changes at Tenerife Island (NE Tropical Atlantic) since 1927. J. Geophys. Res.: Oceans. 2013. Vol. 118, 4899–4910. [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse P. L. Glacial isostatic adjustment modelling: historical perspectives, recent advances, and future directions. Earth Surf. Dynam. 2018. Vol. 6, 401–429. [CrossRef]
- Peltier W. R. Global Glacial Isostacy and the surface of the ice-age Earth: The ICE-5G (VM2) Model and GRACE. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2004. Vol. 32, 111–149. [CrossRef]
- Peltier W.R. Postglacial Variations in the Level of the Sea: Implications for Climate Dynamics and Solid-Earth Geophysics. Reviews of Geophysics. 1998 Vol. 36(4), 603-689.
- Peltier W.R. On the Hemispheric Origins of Meltwater Pulse 1A. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2005. Vol. 24, 1655-1671.
- Santamaría-Gómez A., Gravelle M., S. Dangendorf, M. Marcos, G. Spada, G. Wöppelmann, 2017. Uncertainty of the 20th century sea-level rise due to vertical land motion errors. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 473, 24–32. [CrossRef]
- Kleinherenbrink M., Riva R., Frederikse T. A comparison of methods to estimate vertical land motion trends from GNSS and altimetry at tide gauge stations. Ocean Sci. 2018. 14, 187–204. [CrossRef]
- Good S.A., Martin M. J., Rayner N. A. Quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013. Vol. 118, 6704–6716.
- Ishii M., Kimoto, M., Sakamoto, K., Iwasaki, S. Steric sea level changes estimated from historical ocean subsurface temperatureand salinity analyses. J. Oceanogr. 2006. Vol. 62, 155–170.
- Ishii M., Kimoto, M., Sakamoto, K., Iwasaki, S. Subsurface Temperature and Salinity Analyses. Available online: https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds285.3/ (accessed on 19 August 2021).
- López-Jurado J. L., Balbı́n R., Alemany F., Amengual B., Aparicio-González A., Fernández de Puelles M. L., García-Martínez M. C., Gazá M., Jansá J., Morillas-Kieffer A., Moyá F., Santiago R., Serra M., Vargas-Yáñez M., Vicente L. The RADMED Monitoring Programme as a Tool for MSFD Implementation: Towards an Ecosystem-Based Approach. Ocean. Sci. 2015. Vol. 11, 897–908. [CrossRef]
- Gomis D., Tsimplis M. N., Martí-Mínguez B., Ratsimandresy A. W., García-Lafuente J., Josey S. A. Mediterranean Sea level and barotropic flow through the Strait of Gibraltar for the period 1958–2001 and reconstructed since 1659. J. Geophys. Res. 2006. Vol. 111, C11005. [CrossRef]
- Kalnay E., Kanamitsu M., Kistler, R., Collins, W., Deaven, D., Gandin, L., ... & Joseph, D. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bulletin of the American meteorological Society,1996. Vol. 77(3), 437-472.
- Draper N.R., Smith H. 1981. Applied Regression Analysis, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York.
- Vargas-Yáñez M., Moya F., Balbín R., Santiago R., Ballesteros E., Sánchez-Leal R. F., Romero P., García-Martínez Mª Carmen. Seasonal and Long-Term Variability of the Mixed Layer Depth and its Influence on Ocean Productivity in the Spanish Gulf of Cádiz and Mediterranean Sea.Front. Mar. Sci. 2022. Vol. 9:901893. [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Yáñez M., García-Martínez M.C., Moya F., Balbín R., López-Jurado J.L., Serra M., Zunino P., Pascual J., Salat J. Updating temperature and salinity mean values and trends in the Western Mediterranean: The RADMED Project. Prog. in Oceanogr. 2017. Vol. 157, 27–46. [CrossRef]
- Llasses J., Jordà G., Gomis D. Skills of different hydrographic networks in capturing changes in the Mediterranean Sea at climate scales. Clim. Res. 2015. Vol. 63: 1–18, 2015. [CrossRef]
- von Schuckmann K., Cheng L., Palmer M. D., Hansen J., Tassone C., et al. Heat stored in the Earth system: where does the energy go?.Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 2020, 12, 2013–2041. [CrossRef]
- Zemp M., Huss M., Eckert N., Thibert E., Paul F., Nussbaumer S. U., Gärtner-Roer I. Brief communication: Ad hoc estimation of glacier contributions to sea-level rise from the latest glaciological observations. The Cryosphere. 2020. Vol. 14, 1043–1050. [CrossRef]
- Borghini M., Bryden H., Schroeder K., Sparnocchia S., Vetrano A. The Mediterranean is becoming saltier. Ocean Sci. 2014. Vol. 10, 693–700. [CrossRef]
- Coppola L., Raimbault P., Mortier L., Testor P. Monitoring the Environment in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, American, Geophysical Union (AGU). 2019. Vol. 100, hal-03048623. [CrossRef]
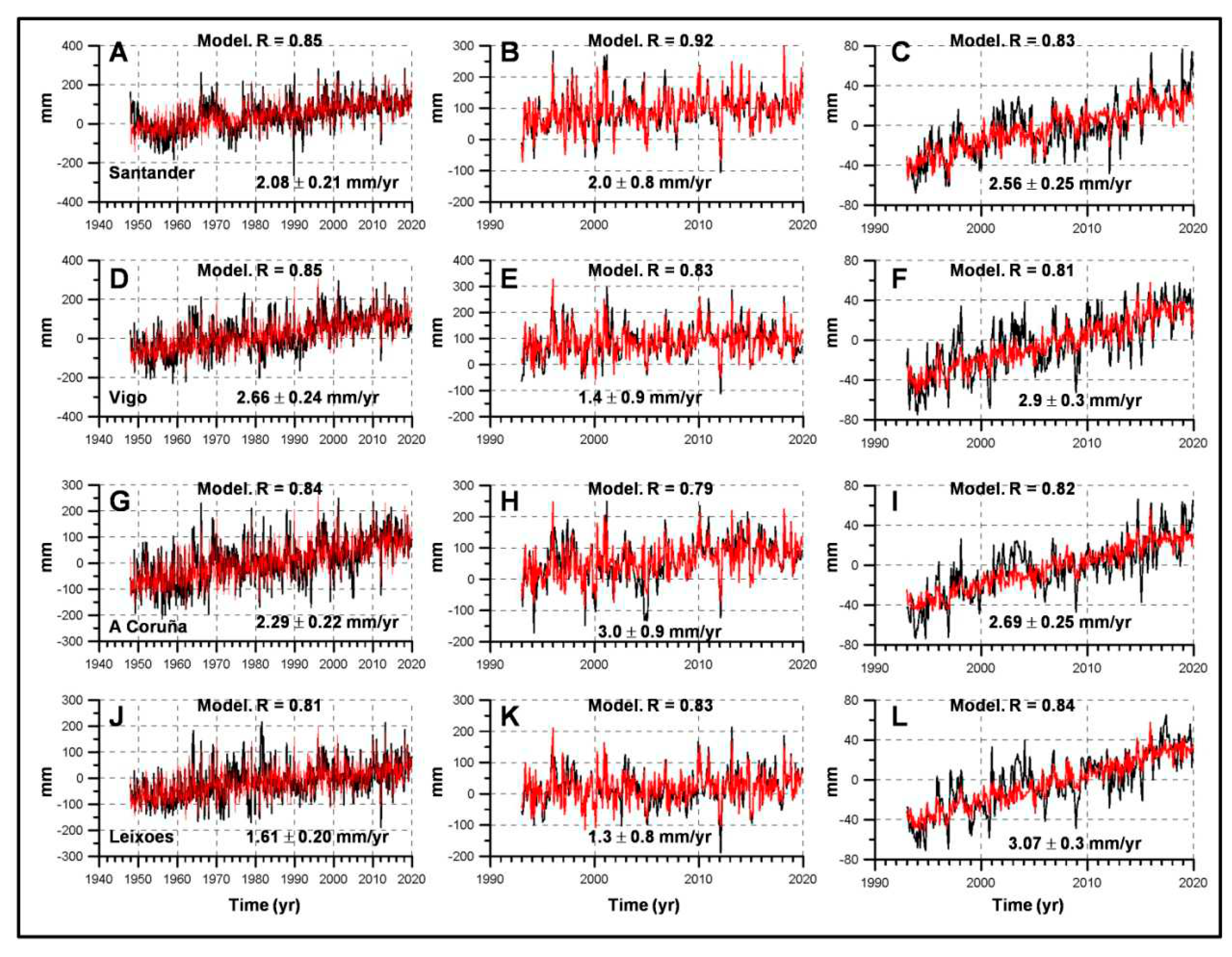
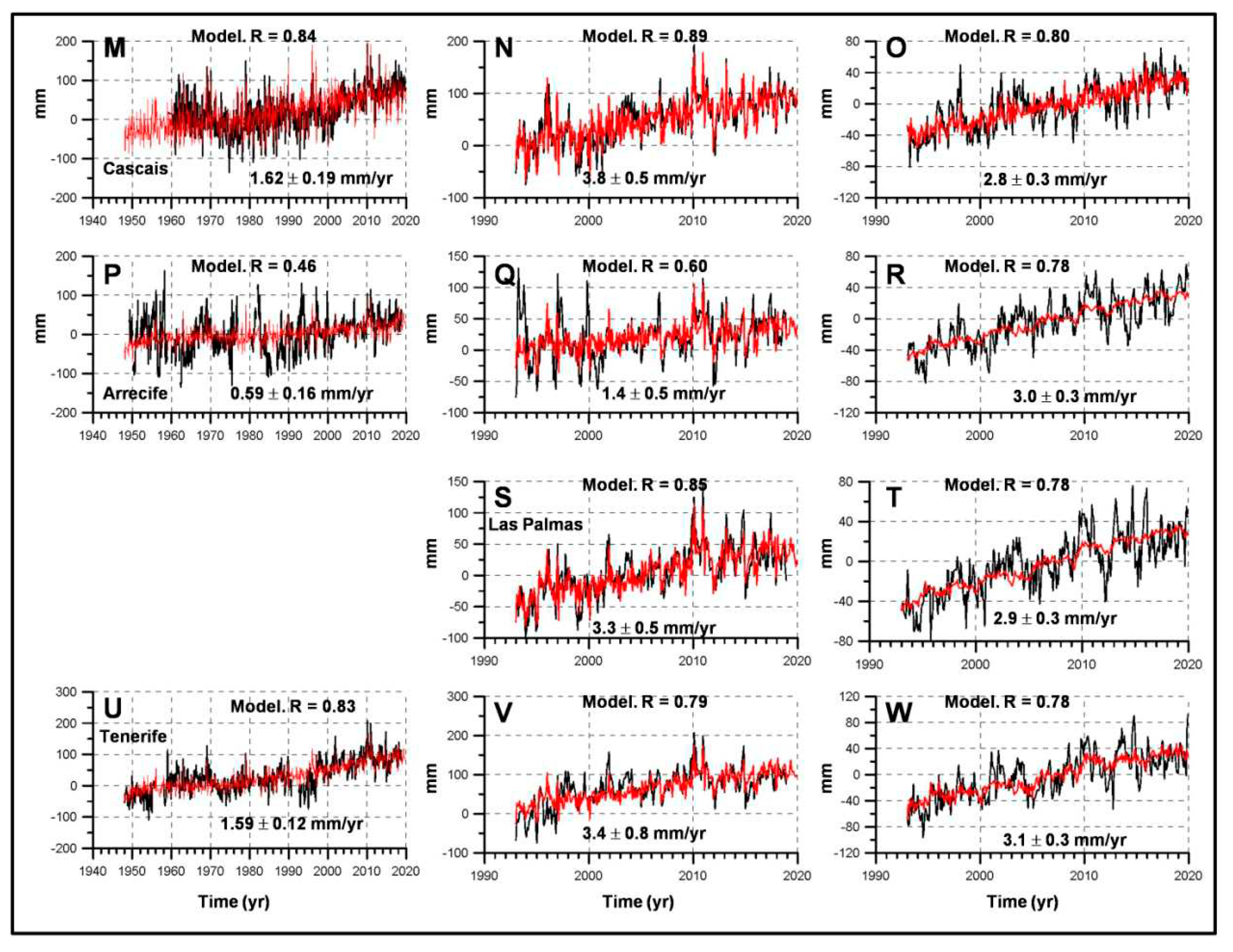
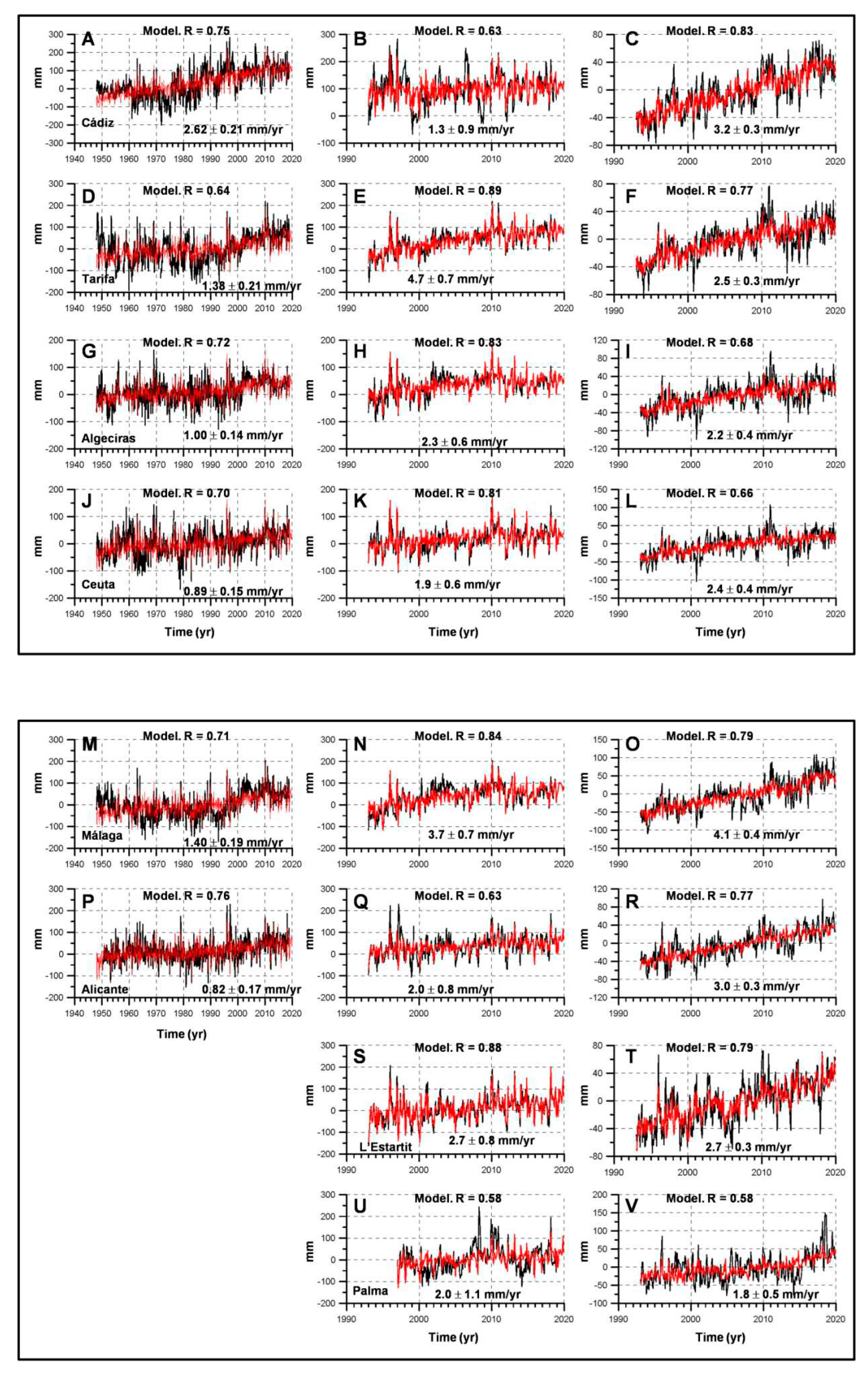
| Period | Linear trends (b ± 95 % CI). Tide gauges. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948-2019 | Sea Level b |
Pressure bP |
U-wind bU |
V-wind bV |
Thermost. bT |
Halost. bH |
| Location (GIA) | mm/yr | dbar/yr | ms-1/yr | ms-1/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr |
| Santander (-0.11) |
2.08 ± 0.21 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0.62 ± 0.10 | 0.36 ± 0.15 |
| Vigo (-0.12) |
2.66 ± 0.24 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.72 ± 0.16 | -1.41 ± 0.18 | ||
| A Coruña (0.0) |
2.29 ± 0.22 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.14 | -0.78 ± 0.17 | ||
| Leixoes (-0.2) |
1.61 ± 0.20 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.78 ± 0.17 | -1.41 ± 0.19 | ||
| Cascais (-0.07) |
1.62 ± 0.19 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.98 ± 0.20 | -1.26 ± 0.24 | ||
| Arrecife (0.01) |
0.59 ± 0.16 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.96 ± 0.15 | ||
| Las Palmas (0.05) |
||||||
| Tenerife (0.09) |
1.59 ± 0.12 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 1.19 ± 0.12 | -0.32 ± 0.13 | |
| Cádiz (-0.18) |
2.62 ± 0.21 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | -0.01 ± 0.01 | 1.43 ± 0.12 | -1.16 ± 0.25 | |
| Tarifa (-0.18) |
1.38 ± 0.21 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 1.13 | -1.21 ± 0.25 | ||
| Algeciras (-0.19) |
1.00 ± 0.14 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.13 | -1.21 ± 0.25 | ||
| Gibraltar (-0.19) |
-0.18 ± 0.16 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.13 | -1.21 ± 0.25 | ||
| Ceuta (-0.18) |
0.89 ± 0.15 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 1.48 ± 0.13 | -1.21 ± 0.25 | ||
| Málaga (-0.23) |
1.40 ± 0.19 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | -0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.53 ± 0.13 | -1.51 ± 0.24 | |
| Alicante (-0.05) |
0.82 ± 0.17 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | -0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.44 ± 0.09 | -1.91 ± 0.15 | |
| L’Estartit (0.06) |
||||||
| Palma (0.25) |
||||||
| Period | Linear trends (b ± 95% CI) Tide gauges and altimetry. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993-2019 | Sea level b | PressurebP | U-wind bU | V-wind bV | Thermost. bT | Halost. bH |
| Location | mm/yr | dbar/yr | ms-1/yr | ms-1/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr |
| Santander Tide Gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 0.8 2.56± 0.25 |
-0.02 ± 0.02 |
-0.02 ± 0.02 |
1.5 ± 0.7 |
||
| Vigo Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.4 ± 0.9 2.9± 0.3 |
0.9 ± 0.8 |
||||
| A Coruña Tide Gauge Altimetry |
3.0 ± 0.9 2.69 ± 0.25 |
1.1 ± 0.6 |
0.7 ± 0.7 |
|||
| Leixoes Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.3 ± 0.8 3.07± 0.25 |
0.02 ± 0.02 |
-0.03 ± 0.02 |
1.0 ± 0.9 |
||
| Cascais Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.8 ± 0.5 2.8± 0.3 |
-0.05 ± 0.03 |
||||
| Arrecife Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.4 ± 0.5 3.0 ± 0.3 |
-0.03 ± 0.02 |
-0.03 ± 0.02 |
1.0 ± 0.6 |
||
| Las Palmas Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.3 ± 0.5 2.9 ± 0.3 |
-0.02 ± 0.02 |
0.02 ± 0.02 |
0.8 ± 0.5 |
||
| Tenerife Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.4± 0.8 3.1± 0.3 |
-0.02 ± 0.02 |
0.02 ± 0.02 |
1.5 ± 0.5 |
||
| Cádiz Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.3 ± 0.9 3.2± 0.3 |
-0.03 ± 0.02 |
0.7 ± 0.6 |
2.8 ± 1.1 |
||
| Tarifa Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.7 ± 0.7 2.5± 0.3 |
2.4 ± 0.7 |
1.5 ± 1.2 |
|||
| Algeciras Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.3 ± 0.6 2.4± 0.4 |
2.4 ± 0.7 |
1.5 ± 1.2 |
|||
| Gibraltar Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.7 ± 0.6 2.4± 0.4 |
2.4 ± 0.7 |
1.5 ± 1.2 |
|||
| Ceuta Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.9 ± 0.6 2.4± 0.4 |
2.4 ± 0.7 |
1.5 ± 1.2 |
|||
| Málaga Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.7 ± 0.7 4.1± 0.4 |
0.03 ± 0.03 |
2.4 ± 0.7 |
|||
| Alicante Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 0.8 3.0± 0.3 |
2.9 ± 0.4 |
-4.2 ± 0.6 |
|||
| L’Estartit Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.7 ± 0.8 2.7 ± 0.3 |
2.9 ± 0.3 |
-6.2 ± 0.4 |
|||
| Palma* Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 1.1 1.8 ± 0.5 |
3.7 ± 0.5 |
-5.9 ± 0.5 |
|||
| Period | Coefficients of the linear model for sea level from Tide gauges | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948-2019 | Time b | Pressure b1 | U-wind b2 | V-wind b3 | Thermost. b4 | Halost. b5 | R |
| Location | mm/yr | mm/mbar | mm/ms-1 | mm/ms-1 | |||
| Santander |
2.08 ± 0.21 | -9.4 ± 0.9 | 8.2 ± 2.1 | 14.9± 2.3 | 0.85 | ||
| Vigo |
2.66 ± 0.24 | -11.6 ± 1.1 | -11.31 ± 2.3 | 20.2 ± 2.4 | 0.85 | ||
| A Coruña |
2.29 ± 0.22 | -9.9 ± 1.0 | -5.4 ± 2.2 | 18.1 ± 2.3 | 0.84 | ||
| Leixoes |
1.61 ± 0.20 | -8.2± 1.0 | 21.1± 2.1 | -0.10± 0.05 | 0.81 | ||
| Cascais |
1.62 ± 0.19 | -11.3±1.0 | -5.1 ± 1.4 | 4.0 ± 1.2 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.84 | |
| Arrecife |
0.59 ± 0.16 | -9.6 ± 1.8 | 0.11 ± 0.07 | 0.46 | |||
| Las Palmas |
|||||||
| Tenerife |
1.59 ± 0.12 | -12.1 ± 1.3 | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 0.07 ± 0.06 | 0.83 | ||
| Cádiz |
2.62 ± 0.21 | -12.1 ± 1.8 | -10.0 ± 2.5 | 6± 3 | 0.75 | ||
| Tarifa |
1.38 ± 0.21 | -12.7 ±2.0 | -7.9± 2.1 | 15 ±7 | 0.22 ± 0.11 | 0.22 ± 0.05 | 0.64 |
| Algeciras |
1.00 ± 0.14 | -11.8± 1.2 | -6.9 ± 1.3 | 13 ± 4 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.72 | |
| Gibraltar |
-0.18 ± 0.16 | -10.7± 1.5 | -6.2 ± 1.7 | 18± 5 | 0.22 ± 0.08 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | 0.62 |
| Ceuta |
0.89 ± 0.15 | -12.7± 1.3 | 13±5 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.70 | ||
| Málaga |
1.40 ± 0.19 | -14.1± 1.3 | -11.7± 1.8 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | 0.71 | |
| Alicante |
0.82 ± 0.17 | -13.6 ± 1.0 | -6.2 ± 1.8 | 7±3 | 0.76 | ||
| L’Estartit |
|||||||
| Palma |
|||||||
| Period | Coefficients ± 95% CI of the linear model for sea level from Tide gauges and altimetry | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993-2019 | Time b | Pressure b1 | U-wind b2 | V-wind b3 | Thermost. b4 | Halost. b5 | R |
| Location | mm/yr | mm/mbar | mm/ms-1 | mm/ms-1 | |||
| Santander Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 0.8 2.56 ± 0.25 |
-10.0 ± 0.9 1.3 ± 0.6 |
10.2 ± 2.0 2.4 ± 1.3 |
11.7 ± 2.5 6.4 ± 1.6 |
0.19 ± 0.11 0.19 ± 0.07 |
0.10 ± 0.07 0.09 ± 0.05 |
0.92 0.83 |
| Vigo Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.4 ± 0.9 2.9 ± 0.3 |
-11.6 ± 1.4 |
-9 ± 3 -4.8 ± 1.4 |
18 ± 3 6.1 ± 1.4 |
0.27 ± 0.15 0.13 ± 0.07 |
0.19 ± 0.13 0.10 ± 0.06 |
0.83 0.81 |
| A Coruña Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.0 ± 0.9 2.69 ± 0.25 |
-9.3 ± 1.6 0.8 ± 0.6 |
-4 ± 3 -1.4 ± 1.3 |
18 ± 4 5.2 ± 1.4 |
0.27 ± 0.19 0.12 ± 0.07 |
0.18 ± 0.17 0.08 ± 0.06 |
0.79 0.82 |
| Leixoes Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.3 ± 0.8 3.07 ± 0.25 |
-8.3 ± 1.4 1.2 ± 0.7 |
21 ± 3 5.7 ± 1.4 |
0.12 ± 0.06 |
0.08 ± 0.05 |
0.83 0.84 |
|
| Cascais Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.8 ± 0.5 2.8 ± 0.3 |
-8.7 ± 1.0 |
-5.8 ± 1.4 -3.1 ± 1.1 |
4.6 ± 1.3 4.6 ± 1.0 |
0.89 0.80 |
||
| Arrecife Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.4 ± 0.5 3.0 ± 0.3 |
-7.7 ± 2.1 |
3.8 ± 2.4 |
0.19 ± 0.08 |
0.13 ± 0.08 |
0.60 0.78 |
|
| Las Palmas Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.3 ± 0.5 2.9 ± 0.3 |
-9.7 ± 1.8 | 4.2 ± 2.2 |
0.26 ± 0.09 0.18 ± 0.08 |
0.13 ± 0.08 0.11 ± 0.07 |
0.85 0.78 |
|
| Tenerife Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.7 ± 0.5 3.1 ± 0.3 |
-12 ± 2 -3.6 ± 1.8 |
-3.5 ± 2.2 |
0.21 ± 0.12 0.25 ± 0.09 |
0.10 ± 0.10 0.15 ± 0.08 |
0.79 0.78 |
|
| Cádiz Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.3 ± 0.9 3.2 ± 0.3 |
-9.9 ± 2.5 |
-8 ± 3 -3.4 ± 1.2 |
11 ± 5 7.0 ± 1.5 |
0.09 ± 0.06 |
-0.13 ± 0.08 0.04 ± 0.03 |
0.63 0.83 |
| Tarifa Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.7 ± 0.7 2.5 ± 0.3 |
-12.2 ± 1.7 |
-7.3 ± 1.7 -2.6 ± 1.1 |
25 ± 6 18 ± 3 |
0.04 ± 0.04 |
0.89 0.77 |
|
| Algeciras Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.3 ± 0.6 2.4 ± 0.4 |
-10.5 ± 1.6 -1.5 ± 1.5 |
-5.5 ± 1.6 -3.4 ± 1.5 |
22 ± 6 16 ± 5 |
0.08 ± 0.03 |
0.83 0.68 |
|
| Gibraltar Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.7 ± 0.6 2.4 ± 0.4 |
-10.8 ± 2.0 -1.5 ± 1.5 |
-7.2 ± 2.0 -3.4 ± 1.5 |
23 ± 7 16 ± 5 |
0.84 0.68 |
||
| Ceuta Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.9 ± 0.6 2.4 ± 0.4 |
-12.1 ± 1.6 |
-1.9 ± 1.5 |
18 ± 6 20 ± 5 |
0.08 ± 0.06 |
0.81 0.66 |
|
| Málaga Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.7 ± 0.7 4.1 ± 0.4 |
-12.1 ± 1.8 |
12.3 ± 2.1 -4.4 ± 1.6 |
8 ± 5 13 ± 4 |
0.06 ± 0.06 |
0.15 ± 0.04 |
0.84 0.79 |
| Alicante Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 0.8 3.0 ± 0.3 |
-10.3 ± 1.6 -3.0 ± 1.1 |
-3.1 ± 1.8 |
5.4 ± 3.0 |
0.63 0.77 |
||
| L’Estartit Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.7 ± 0.8 2.7 ± 0.3 |
-13.5 ± 1.0 -2.9 ± 0.7 |
-8 ± 3 |
4.2 ± 2.1 3.3 ± 1.3 |
0.27 ± 0.14 0.3 ± 0.1 |
0.22 ± 0.12 0.25 ± 0.09 |
0.88 0.79 |
| Palma Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 1.1 2.0 ± 1.1 |
-9.7 ± 2.0 -2.3 ± 1.1 |
6 ± 3 |
0.34 ± 0.14 |
0.28 ± 0.23 |
0.58 0.58 |
|
| Period | Contributions to Sea Level trends from tide gauges. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1948-2019 | Mass add. | Pressure | U-wind | V-wind | Thermost. | Halost. |
| Location | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr |
| Santander |
2.1 ± 0.4 | -0.20 ± 0.10 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | ||
| Vigo |
2.9 ± 0.4 |
-0.22 ± 0.13 | ||||
| A Coruña |
2.5 ± 0.3 | -0.18 ± 0.11 | ||||
| Leixoes |
2.0 ± 0.4 | -0.18 ± 0.08 | -0.18 ± 0.10 | |||
| Cascais |
1.9 ± 0.4 | -0.22 ± 0.11 | 0.08 ± 0.09 | -0.09 ± 0.05 | ||
| Arrecife |
0.82 ± 0.23 | -0.22 ± 0.07 | ||||
| Las Palmas |
||||||
| Tenerife |
1.7 ± 0.3 | -0.20 ± 0.07 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | -0.02 ± 0.02 | ||
| Cádiz |
2.8 ± 0.4 | -0.23 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | |||
| Tarifa |
1.6 ± 0.5 | -0.27 ± 0.10 | 0.33 ± 0.16 | -0.27 ± 0.09 | ||
| Algeciras |
1.4 ± 0.3 | -0.25 ± 0.08 | -0.11 ± 0.04 | |||
| Gibraltar |
-0.1 ± 0.4 | -0.22 ± 0.08 | 0.32 ± 0.12 | -0.20 ± 0.07 | ||
| Ceuta |
1.0 ± 0.3 | -0.26 ± 0.09 | 0.19 ± 0.09 | |||
| Málaga |
1.8 ± 0.5 | -0.29 ± 0.12 | 0.16 ± 0.13 | -0.26 ± 0.08 | ||
| Alicante |
1.1 ± 0.3 | -0.25 ± 0.13 | -0.04 ± 0.03 | |||
| L’Estartit |
||||||
| Palma |
||||||
| Period | Contributions to Sea Level trends from tide gauges and altimetry. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1993-2019 | Mass add. | Pressure | U-wind | V-wind | Thermost. | Halost. |
| Location | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr | mm/yr |
| Santander Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.3 ± 1.4 2.6 ± 0.5 |
-0.22 ±.0.22 -0.05 ± 0.06 |
-0.24 ± 0.21 -0.13 ± 0.12 |
0.16 ± 0.13 -0.14 ± 0.09 |
||
| Vigo Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.2 ± 1.1 2.8 ± 0.4 |
0.24 ± 0.24 0.12 ± 0.12 |
||||
| A Coruña Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.6 ± 1.4 2.5 ± 0.4 |
0.3 ± 0.3 0.14 ± 0.11 |
0.14 ± 0.18 0.06 ± 0.07 |
|||
| Leixoes Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 1.2 3.2 ± 0.5 |
-0.7 ± 0.4 -0.19 ± 0.12 |
0.08 ± 0.09 |
|||
| Cascais Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.0 ± 0.6 3.0 ± 0.4 |
-0.21 ± 0.15 -0.21 ± 0.14 |
||||
| Arrecife Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.5 ± 0.6 2.9 ± 0.4 |
-0.10 ± 0.11 |
0.12 ± 0.11 |
|||
| Las Palmas Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.0 ± 0.7 2.8 ± 0.4 |
0.09 ± 0.09 |
0.21 ± 0.16 0.14 ± 0.11 |
|||
| Tenerife Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.3 ± 0.8 2.8 ± 0.6 |
-0.07 ± 0.08 |
0.32 ± 0.21 0.38 ± 0.18 |
|||
| Cádiz Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.1 ± 1.5 3.3 ± 0.6 |
-0.4 ± 0.3 -0.24 ± 0.14 |
-0.10 ± 0.14 0.06 ± 0.07 |
-0.4 ± 0.3 0.11 ± 0.10 |
||
| Tarifa Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.6 ± 0.7 2.5 ± 0.3 |
0.06 ± 0.07 |
||||
| Algeciras Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.1 ± 0.7 2.4 ± 0.4 |
0.12 ± 0.11 |
||||
| Gibraltar Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.7 ± 0.6 2.4 ± 0.4 |
|||||
| Ceuta Tide gauge Altimetry |
1.7 ± 0.7 2.4 ± 0.4 |
0.19 ± 0.15 |
||||
| Málaga Tide gauge Altimetry |
4.1 ± 1.0 4.1 ± 0.7 |
-0.4 ± 0.3 -0.13 ± 0.12 |
0.14 ± 0.15 |
|||
| Alicante Tide gauge Altimetry |
2.0 ± 0.8 3.0 ± 0.3 |
|||||
| L’Estartit Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.3 ± 1.9 3.4 ± 1.2 |
0.8 ± 0.4 0.8 ± 0.3 |
-1.4 ± 0.7 -1.5 ± 0.6 |
|||
| Palma Tide gauge Altimetry |
3.7 ± 2.5 0.7 ± 1.2 |
1.3 ± 0.6 |
-1.6 ± 1.4 |
|||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





