Submitted:
06 June 2023
Posted:
07 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Emotional intelligence theoretical models
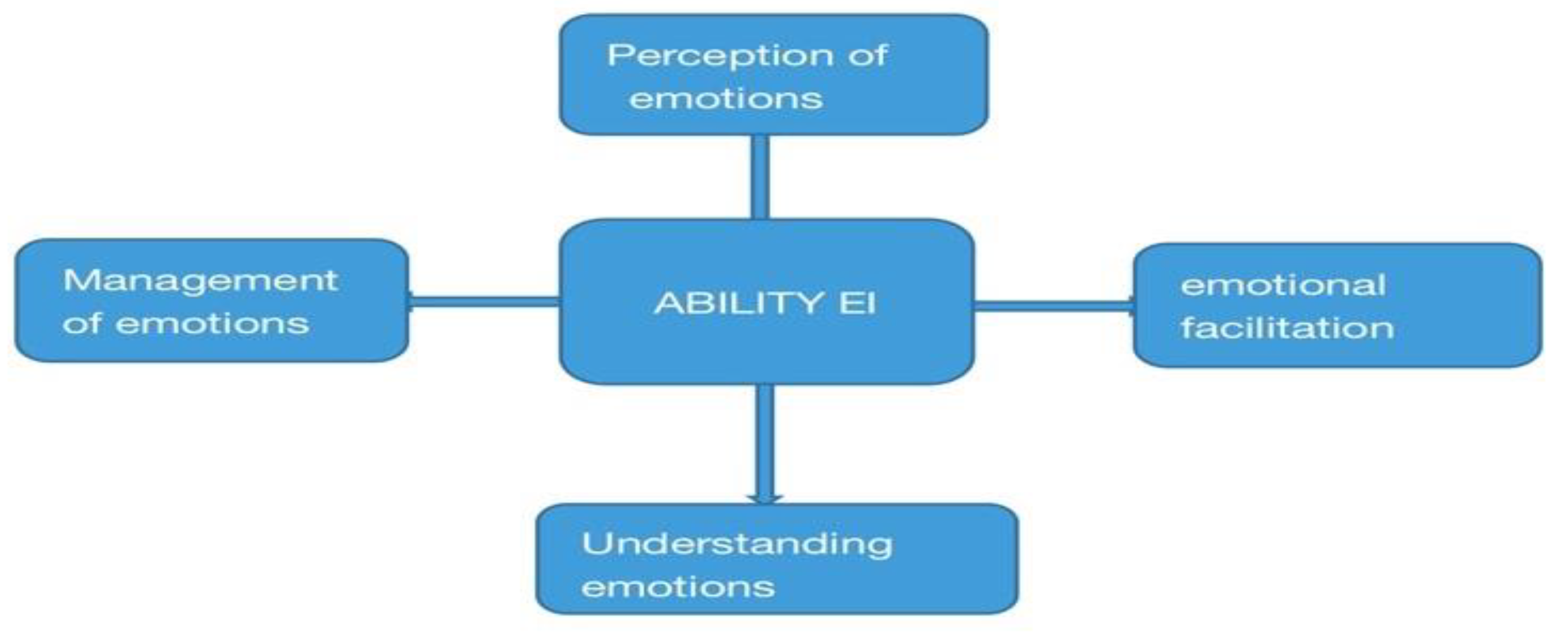
2.1. The ability model of EI.
2.2. The mixed model of EI
2.3. The trait model of EI
3. Method
3.1. Identification of the research question
- What does the literature say about the effects of EI on teachers’ job satisfaction?
- What effects do the different EI models have on teachers' job satisfaction?
- Where are the research gaps in the existing literature?
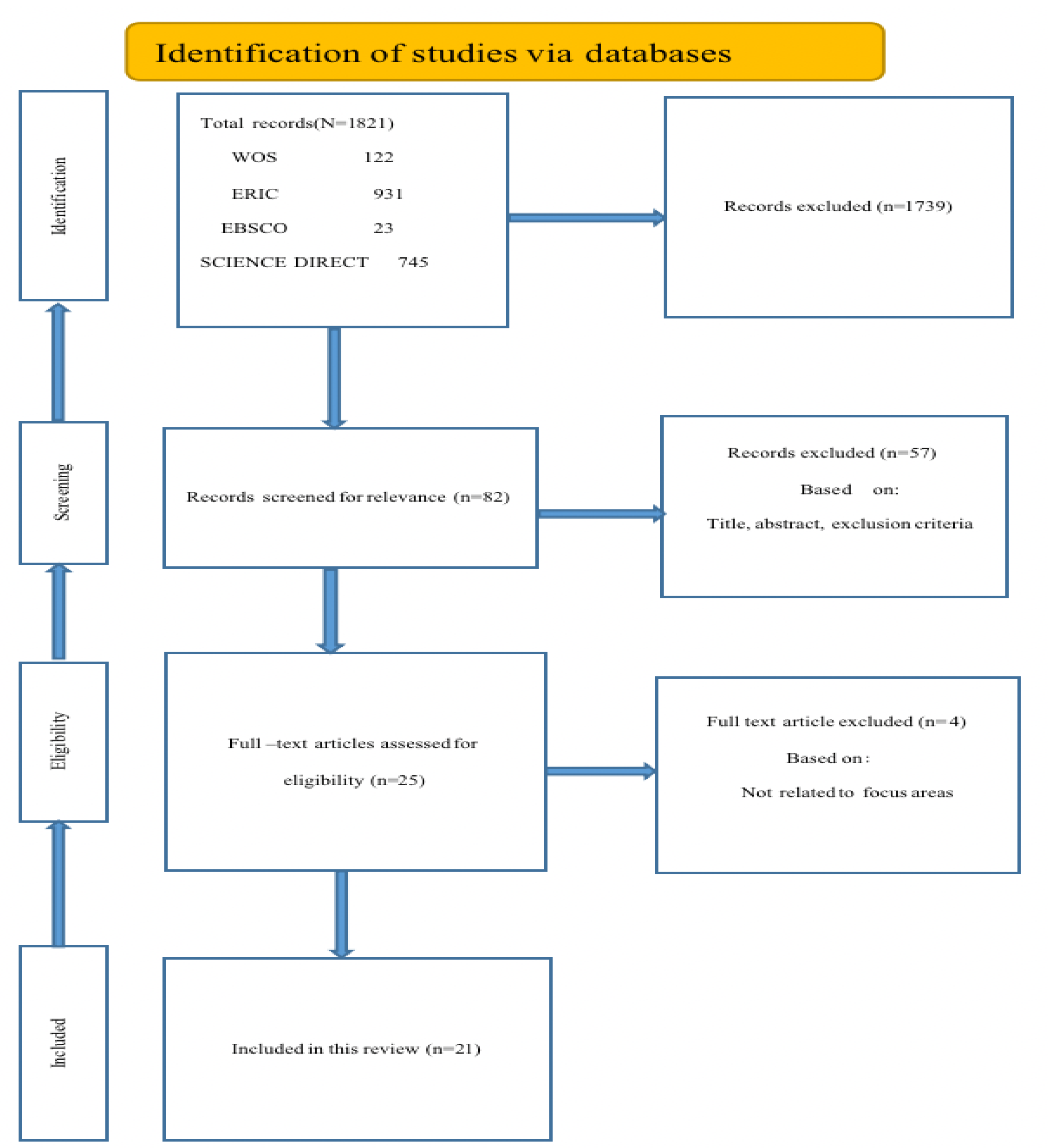
3.2. Identifying relevant studies
3.3. Study selection
3.4. Charting the data.
3.5. Summarizing, and reporting the results.
4. Results
4.1. Studies ‘characteristics
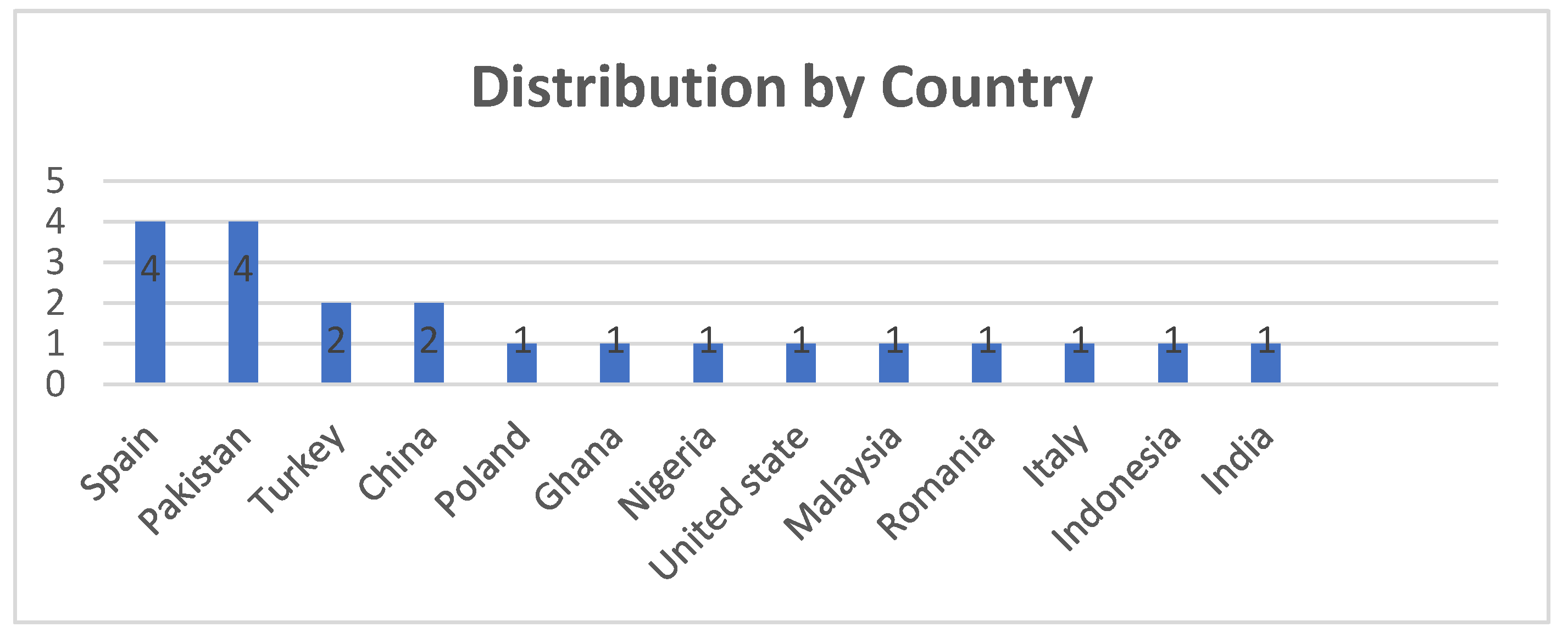
4.1.1. Studies distribution by country
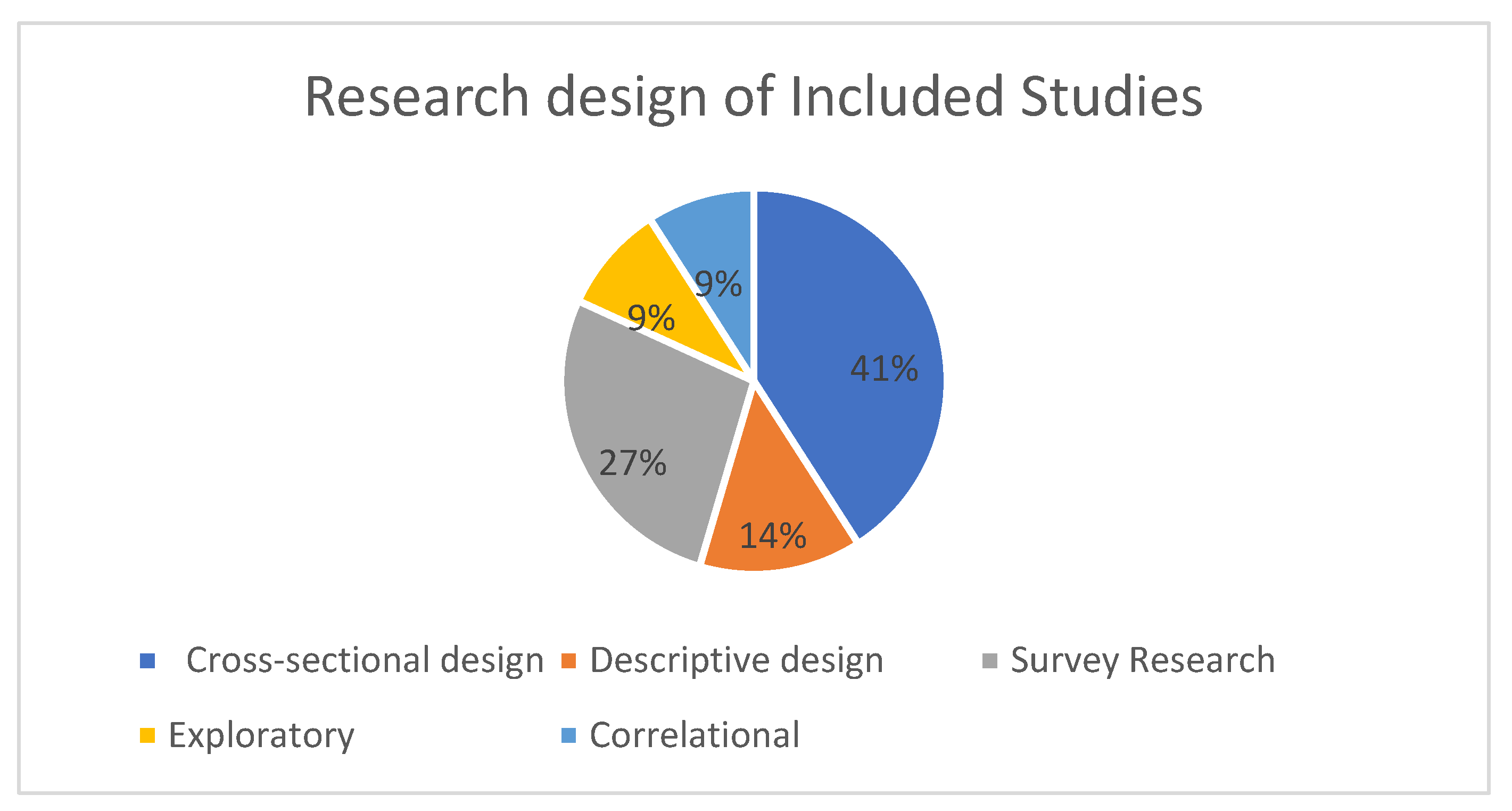
4.1.2. Research Methods of Included Studies
4.1.3. Participants Involved in the Research.
4.2. Measures and instruments
4.3. Summary of studies in relation to the effects of emotional intelligence on teachers’ job satisfaction
4.3.1. Direct effect of EI on teachers’ job satisfaction
4.3.2. Indirect effect of EI on teachers ‘job satisfaction
4.4. The effects of various EI models on teachers' job satisfaction
4.5. Research gaps in the existing literature
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thorndike E. L.Intelligence and its uses. Harper’s magazine, 1920.
- Salovey P. and Mayer J. D. Emotional Intelligence. Imagin Cogn Pers, 1990, 185–211. doi: 10.2190/DUGG-P24E-52WK-6CDG. [CrossRef]
- Mayer J. D. and Salovey P.What is emotional intelligence? In P. Salovey & D. J. Sluyter (Eds.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Educational implications ,Basic Books, 1997.
- Abiodullah M. and Aslam M. Emotional Intelligence as a Predictor of Teacher Engagement in Classroom.Bulletin of Education and Research, 2020,127-140., 2020.
- Anari N. N. Teachers: emotional intelligence, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment. Journal of workplace Learning,2012, vol. pp. 256–269.
- Yin H. B., J. C. K., and Zhang Z. H. Exploring the relationship among teachers’ emotional intelligence, emotional labor strategies and teaching satisfaction. Teach Teach Educ,2013, pp. 137-145.
- Ghanizadeh A. and Moafian F. The role of EFL teachers’ emotional intelligence in their success. ELT journal, 2010,424-435. [CrossRef]
- Iordanoglou D. The teacher as leader: The relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness, commitment, and satisfaction. Journal of Leadership Studies, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Singh B. and Kumar A. Effect of emotional intelligence and gender on job satisfaction of primary school teachers.European Journal of Educational Research,2016,1-9. [CrossRef]
- Hongying S. Literature Review of Teacher Job Satisfaction. Chinese Education & Society,2007 ,11–16. doi: 10.2753/CED1061-1932400502. [CrossRef]
- Pepe A, Addimando L. and Veronese G. Measuring teacher job satisfaction: Assessing invariance in the Teacher Job Satisfaction Scale (TJSS) across six countries. Eur J Psychol, 2017,396–416. doi: 10.5964/ejop.v13i3.1389. [CrossRef]
- Cooper H. M., “Organizing knowledge syntheses: A taxonomy of literature reviews,” Knowledge in society, vol. 1, pp. 1–104, 1988. [CrossRef]
- Arksey H. and O’Malley L.Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework.Int J Soc Res Methodol, 2005,19–32. doi: 10.1080/1364557032000119616. [CrossRef]
- Mayer J. D., Caruso D. R., and Salovey P. Selecting a measure of emotional intelligence: The case for ability scales. 2000.
- Bar-On R.The emotional quotient inventory (EQ-i): A test of emotional intelligence. Toronto: Multi-Health Systems, 1997.
- Goleman.Working with Emotional Intelligence. J Pers Soc Psychol, 1998,947-959.
- Petrides K. V and Furnham A. Trait emotional intelligence: psychometric investigation with reference to established trait taxonomies. Eur J Pers, 2001,425–448. doi: 10.1002/per.416. [CrossRef]
- Grant M. J and Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J,2009 ,91-108. [CrossRef]
- Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., and Altman D. G.Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med,2009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [CrossRef]
- Wong C. S. and Law K. S.The effects of leader and follower emotional intelligence on performance and attitude: An exploratory study. Leadersh Q,2002,243–274. doi: 10.1016/S1048-9843(02)00099-1. [CrossRef]
- Hancer M. and George R. T. Job Satisfaction Of Restaurant Employees: An Empirical Investigation Using The Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research,2003, 85–100. doi: 10.1177/1096348002238882. [CrossRef]
- Weiss D. J. ,Dawis R. V., and. England G. W.Manual for the Minnesota satisfaction questionnaire. Minnesota studies in vocational rehabilitation.1967.
- WARR P., COOK J., and WALL T. Scales for the measurement of some work attitudes and aspects of psychological well-being. Journal of Occupational Psychology,1979, pp. 129–148. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8325.1979.tb00448.x. [CrossRef]
- Judge T. A., Locke E. A., Durham C. C., and Kluger A. N. Dispositional effects on job and life satisfaction: The role of core evaluations. Journal of Applied Psychology,1998,17–34. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.83.1.17. [CrossRef]
- Zhi-yong X. and Zhi-hong Z. An empirical study of job satisfaction of Beijing primary school teachers. Teach. Educ. Res., 2012.
- Price J. L. and Mueller C. W. A Causal Model of Turnover for Nurses. Academy of Management Journal, 1981, 543–565. doi: 10.2307/255574. [CrossRef]
- Brayfield A. H. and Rothe H. F. An index of job satisfaction. journal of applied psychology, 1951, p. 307.
- Elo S. and Kyngäs H.The qualitative content analysis process. J Adv Nurs, 2008,107-115. [CrossRef]
- Rogowska A. M. and Meres H. The Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction in the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Life Satisfaction among Teachers during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ, 2022, 666–676.doi: 10.3390/ejihpe12070050. [CrossRef]
- Peláez-Fernández M. A., Mérida-López S., Sánchez-Álvarez N., and Extremera N.Managing Teachers’ Job Attitudes: The Potential Benefits of Being a Happy and Emotional Intelligent Teacher.Front Psychol, 2021. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.661151. [CrossRef]
- Latif H. ,Majoka M. I., and Khan M. I.Emotional intelligence and job performance of high school female teachers. Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research.2017.
- Sökmen Y. and Sarikaya İ.The mediating role of self-efficacy between emotional intelligence and job satisfaction of primary school teachers. European Review of Applied Psychology, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Waruwu B.The Correlation between Teachers’ Perceptions about Principal’s Emotional Intelligence and Organizational Climate and Job Satisfaction of Teachers of State Senior High School in Gunungsitoli Nias, Indonesia. Journal of Education and Practice,2015, 142-147.
- Wijayati D. T., Kautsar A., and Karwanto K. Emotional Intelligence, Work Family Conflict, and Job Satisfaction on Junior High School Teacher’s Performance. International Journal of Higher Education, 2020, 179-188.
- Colomeischi A. A. and Colomeischi T. Teachers’ Attitudes towards Work in Relation with Emotional Intelligence and Self-efficacy. Procedia Soc Behav Sci, 2014,615–619. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.12.435. [CrossRef]
- Li M., Pérez-Díaz P. A., Mao Y., and Petrides K. V.A Multilevel Model of Teachers’ Job Performance: Understanding the Effects of Trait Emotional Intelligence, Job Satisfaction, and Organizational Trust.Front Psychol, 2018.doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02420. [CrossRef]
- Toprak M. and Savaş A. C.School headmasters’ emotional intelligence and teachers’ job satisfaction: Moderation effect of emotional labor. New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development, 2020,4–18. doi: 10.1002/nha3.20282. [CrossRef]
- Mérida-López S. and Extremera N.The Interplay of Emotional Intelligence Abilities and Work Engagement on Job and Life Satisfaction: Which Emotional Abilities Matter Most for Secondary-School Teachers?. Front Psychol, 2020. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.563634. [CrossRef]
- Miao C. ,Humphrey R. H., and Qian S. A meta-analysis of emotional intelligence effects on job satisfaction mediated by job resources, and a test of moderators. Pers Individ Dif, 2017,281–288. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.04.031. [CrossRef]
- Mérida-López S., Quintana-Orts C., Hintsa T. and Extremera N. Emotional intelligence and social support of teachers: Exploring how personal and social resources are associated with job satisfaction and intentions to quit job.Revista de Psicodidáctica, 2022, 168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.psicoe.2022.02.001. [CrossRef]
- Karim J., Bibi Z., Ur Rehman, and Khan M. S. Emotional Intelligence and Perceived Work-related Outcomes: Mediating Role of Workplace Incivility Victimization.Pakistan Journal of Psychological Research, 2015.
- Sun P., Chen J. J., and Jiang H. Coping humor as a mediator between emotional intelligence and job satisfaction : A study on Chinese primary school teachers. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 2017.
- Lee Y. H., Kwon H. H., and Richards K. A.Emotional Intelligence, Unpleasant Emotions, Emotional Exhaustion, and Job Satisfaction in Physical Education Teaching. Journal of Teaching in Physical Education.2019, 1–31. doi: 10.1123/jtpe.2018-0177. [CrossRef]
- Luque-Reca O., García-Martínez, I., Pulido-Martos, M., Burguera, J. L., & Augusto-Landa, J. M., Teachers’ life satisfaction: A structural equation model analyzing the role of trait emotion regulation, intrinsic job satisfaction and affect. Teaching and Teacher Education,2022 [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0742051X22000397.
- Tett R. P., Freund K. A., Christiansen N. D., Fox K. E., and Coaster J.Faking on self-report emotional intelligence and personality tests: Effects of faking opportunity, cognitive ability, and job type. Pers Individ Dif,2012 ,195–201. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2011.10.017. [CrossRef]
- Butakor P. K., Guo Q., and Adebanji A. O. Using structural equation modeling to examine the relationship between Ghanaian teachers’ emotional intelligence, job satisfaction, professional identity, and work engagement. Psychology in the Schools,2021,534-552.
| Search terms | |
|---|---|
| AND | Emotional intelligence OR self-awareness OR self-motivation OR empathy OR Emotion regulation |
| Job satisfaction | |
| Teacher OR instructor OR educator. | |
| line | Authors(year) | Sample size | Population | Measures | Context | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Rogowska, A. M., & Meres, H. (2022) |
N=322 |
primary, high,technical secondary school -Trade school teachers |
-Multivariate Emotional Intelligence Scale (MEIS) -Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ)—short form |
Poland | Emotional intelligence is a significant positive predictor of job satisfaction. |
| 2 | Peláez-Fernández, M. A., et al (2021) | N= 685 | -childhood - primary -secondary school teachers |
-Wong and Law EI Scale -Overall job satisfaction scale |
Spain | Emotional intelligence was positively related to happiness and job satisfaction |
| 3 | Latif, H., Majoka, M. I., & Khan, M. I. (2017) | N=210 | Secondary school Female teachers | -Self-Report Emotional Intelligence Test (SREIT) -Job Satisfaction Scale |
Pakistan | EI had significant direct effect on job satisfaction |
| 4 | Mérida-López, S., & Extremera, N. (2020) | N=190 | Secondary-school teachers | -Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT v.2.0) Spanish version -Job satisfaction was measured with a 5-item scale Spanish version scale |
Southern Spain | -ERA did not show a significant main effect for predicting levels of teachers’job satisfaction -However, the interaction between work engagement and ERA significantly augmented the prediction of both job and life satisfaction. |
| 5 | Sökmen, Y., & Sarikaya, İ. (2022). | N=252 | primary school teachers | -Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire–Short Form (TEQue-SF) -Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire MSQ Scale |
Turkey | Self-efficacy and emotional intelligence levels of primary school teachers predict their job satisfaction levels in a meaningful and positive way. |
| 6 | Toprak, M., & Savaş, A. C. (2020). | N=27 school Headmasters and 469 Teachers. |
primary and secondary school |
-Bar-on Emotional Quotent Inventory (EQ-i) -Short-Form Minnesota Satisfaction Questionnaire (MSQ) |
Turkey | -Headmasters' EI competencies and teachers' EL competencies significantly predict teachers ' job satisfaction |
| 7 | Butakor, P. K., Guo, Q., & Adebanji, A. O. (2021) | N=197 | Senior High School and basic schools | Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale |
Ghana | EI positively affected teachers’job satisfaction |
| 8 | Sun, P., Chen, J. J., & Jiang, H. (2017). | N=398 | Primary school teachers | -Wong Law Emotional Intelligence Scale -Overall Job Satisfaction Scale. |
China | -Coping humor was a significant mediator between EI and job satisfaction -coping humor only mediated two sub-dimensions of EI (use of emotion and regulation of emotion) and job satisfaction. |
| 9 | D’Amico, A., Geraci, A., & Tarantino, C. (2020). | N=238 | -infantry -primary -secondary school teachers |
-Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS) -Organizational Satisfaction Scale |
Italy | There is a positive correlation between PEI (perceived EI) and job satisfaction |
| 10 | Mérida-López, S., Quintana-Orts, C., Hintsa, T., & Extremera, N. (2022) | N=1,079 | -preschool, primary, and secondary schools |
-The Spanish version of the Wong and Law EI Scale -Spanish version of the Job Satisfaction Scale |
Spain | -EI was positively related to job satisfaction only via support from supervisors, which, in turn, was negatively related to intentions to quit. |
| 11 | Lee, Y. H., Kwon, H. H., & Richards, K. A. R. (2019). | N=271 | High school physical educators | -Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT SCALE) |
United States | The direct effect of EI on teacher job satisfaction was not significant, but there was a positive and significant indirect effect as mediated through unpleasant emotions and emotional exhaustion |
| 12 | Li, M., Pérez-Díaz, P. A., Mao, Y., & Petrides, K. V. (2018) | N=881 teachers and N=37 principals |
Primary schools Teachers |
Trait Emotional Intelligence Questionnaire-Short Form(TEIQue-SF) -Job satisfaction scale. |
Mainland China (hubei province) | Teachers with higher trait EI perform better than those with lower trait EI, partially because they are more satisfied with their jobs, which, in turn, leads to better performance. |
| 13 | Waruwu, B. (2015). | N=170 | Senior High School Teachers |
Used Goleman mixed EI Model Scale | Indonesia. | There is a significant positive relationship between teachers' perceptions of the principal's emotional intelligence and job satisfaction of teachers. |
| 14 | Singh, B., & Kumar, A. (2016). | N=300 | Primary school teachers | -Emotional Intelligence Scale (EIS) -Teachers’Job Satisfaction Scale (TJSS) |
India | The five dimensions of EI predict teachers’ job satisfaction. |
| 15 | Wijayati, D. T., Kautsar, A., & Karwanto, K. (2020). | N=200 | Junior high schools teachers |
-Goleman mixed EI model |
Pakistan | Emotional Intelligence has a significant positive effect on Job Satisfaction |
| 16 | Kassim, S. I., Bambale, A. J., & Jakada, B. A. (2016). | N=98 | University lecturers | -Wong and Law -Generic job satisfaction scale |
Nigeria | There is positive relationship between regulation of emotion and job satisfaction. |
| 17 | Ahmed, H. (2015). | N=100 | University Teachers |
-EI questionnaire based on Goleman model was used for the measurement -Wysocky and Kromm’s Job Description Index contains 41 questions measuring job satisfaction. |
Pakistan |
There is a significant positive correlation between Job satisfaction and emotional intelligence. |
| 18 | Colomeischi, A. A., & Colomeischi, T. (2014). | N=575 | Urban and rural area teachers |
-The Schutte et al. (1998) EI scale. -The Work Satisfaction Questionnaire |
Romania |
The more emotional intelligent they are the more satisfied with their teaching job they are and also, they have a more positive attitude towards work. |
| 19 | Luque-Reca, O., García-Martínez, I., Pulido-Martos, M., Burguera, J. L., & Augusto-Landa, J. M. (2022). | N=423 |
Primary school teachers |
-Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS; Spanish version) |
southern Spain. |
Trait ER was shown to be capable of indirectly influencing intrinsic job satisfaction through both PA and NA (negatively in this case) |
| 20 | Karim, J., Bibi, Z., Ur Rehman, S., & Khan, M. S. (2015). | N= 150 | University teachers | -Wong and Law Emotional Intelligence Scale (WLEIS). -Job Satisfaction Survey. |
Pakistan | Workplace incivility mediates the relationship between EI and work-related outcomes including job satisfaction. |
| 21 | Mustafa, M. Z., Buntat, Y., Razzaq, A. R. A., Daud, N., & Ahad, R. (2014) | N=138 |
Teachers from various vocational colleges |
-Used Goleman mixed EI Model Scale |
Malaysia southern zone | There was a positive relationship between emotional intelligence and job satisfaction |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





