Submitted:
08 June 2023
Posted:
08 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Determination of ferroptosis in breast related genes
- Transcriptome cohort of breast cancer for patients treated with anthracyclin and taxanes
- Transcriptome dataset testing effect of ferroptosis activators on MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cell line
- Gene expression analyses and association to the breast cancer prognosis
3. Results
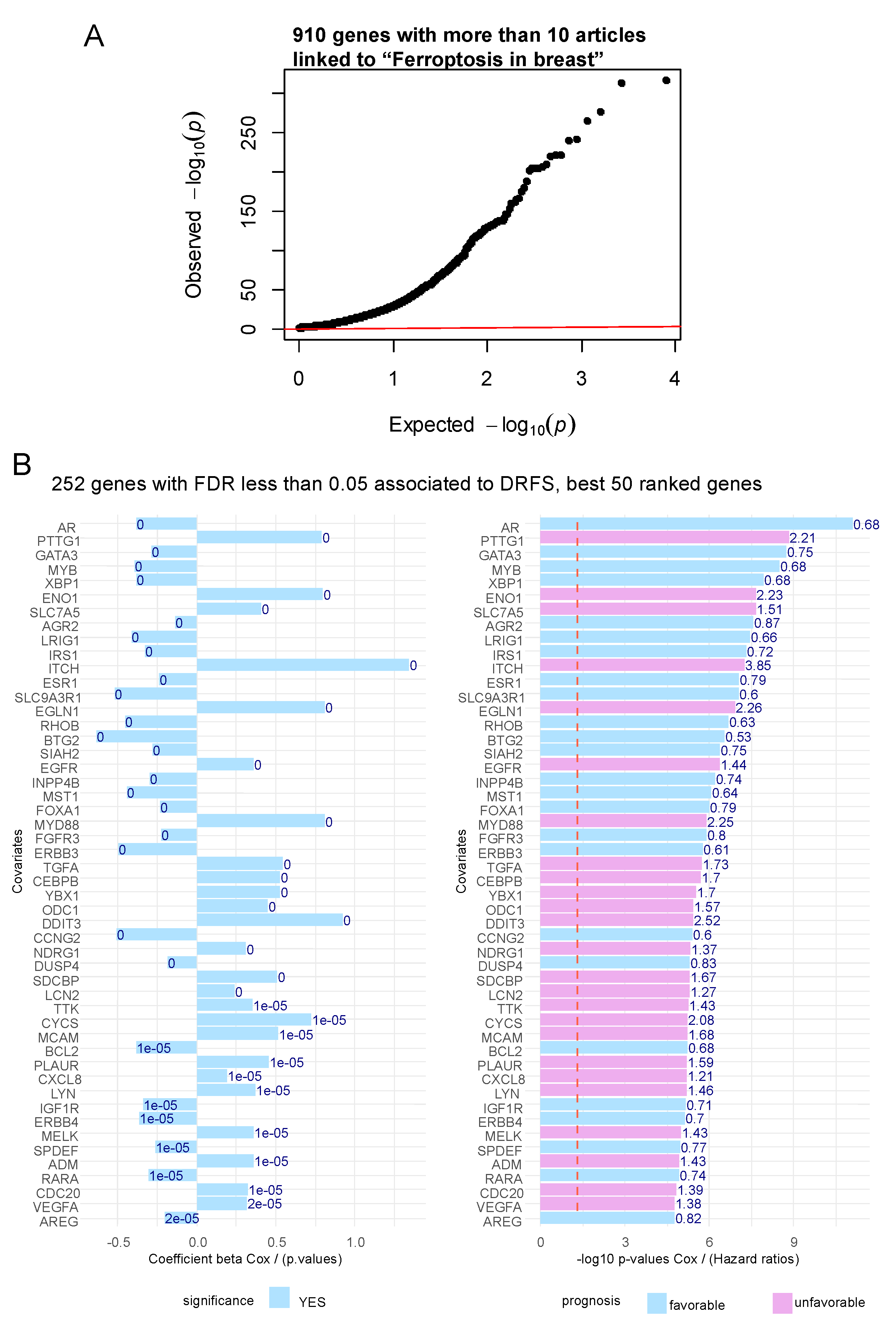
3.1. Ferroptosis gene expression associated to the prognosis of patients with breast cancer
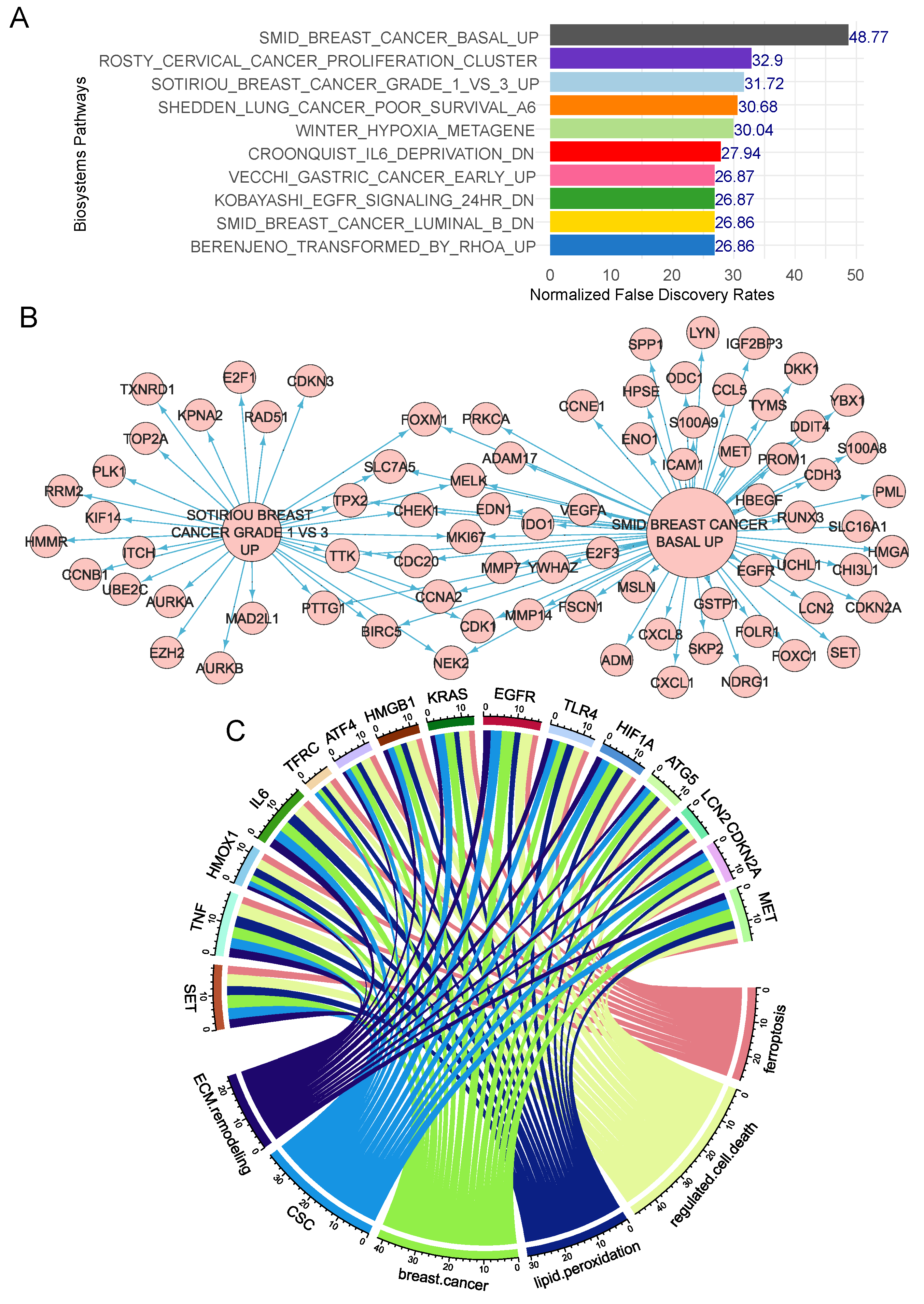
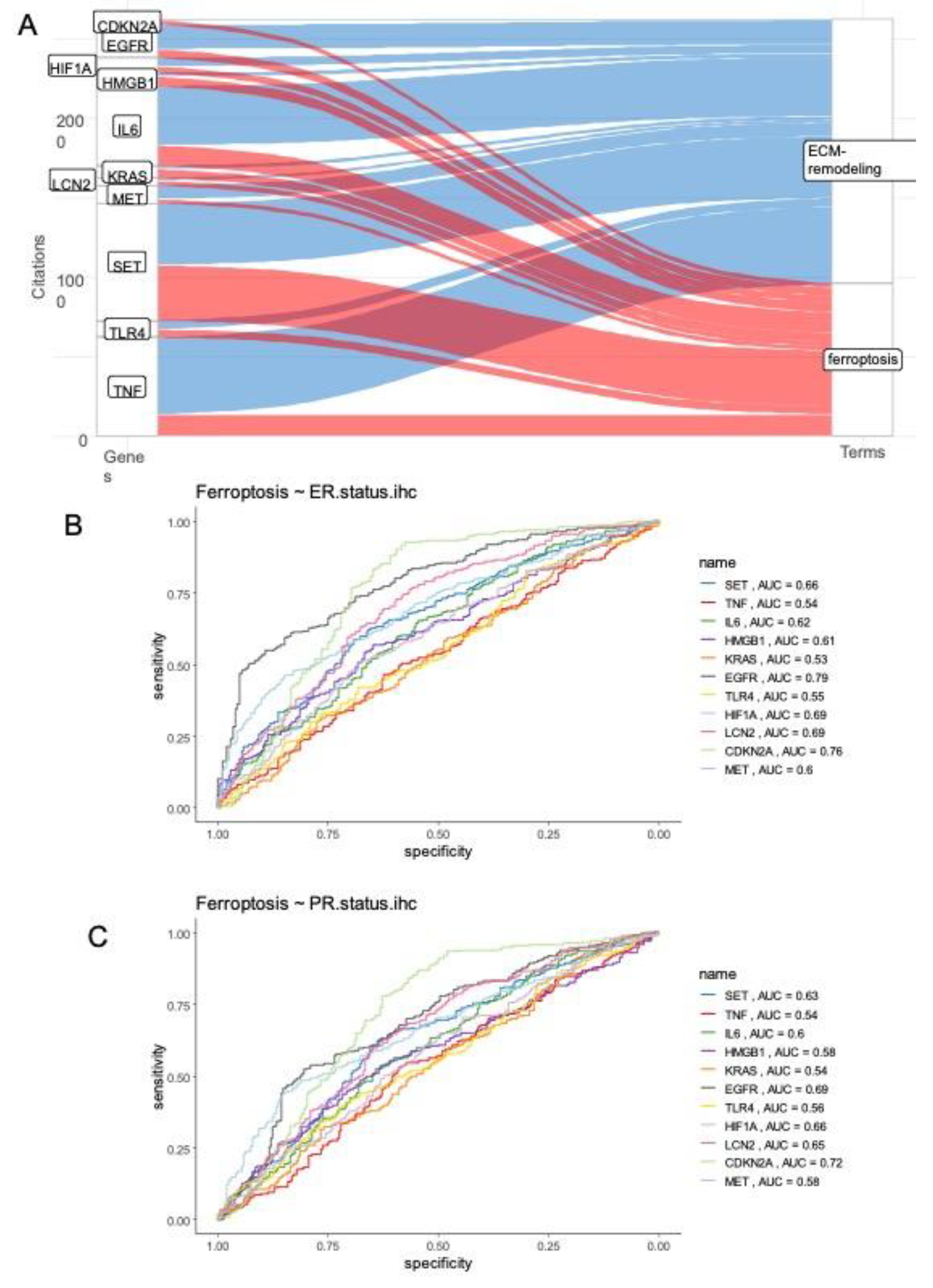
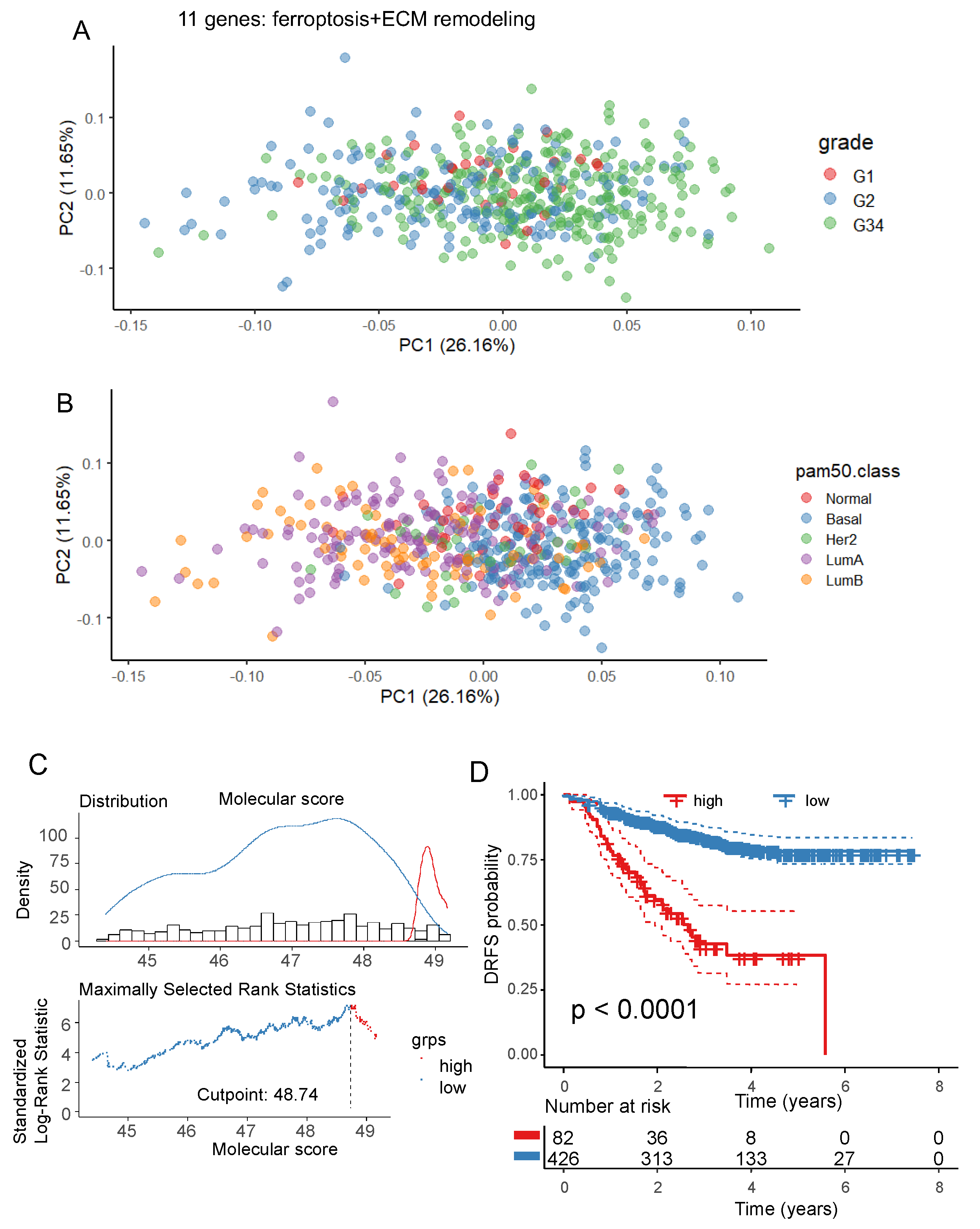
3.2. Ferroptosis/extracellular matrix remodeling expression score and prognosis in breast cancer
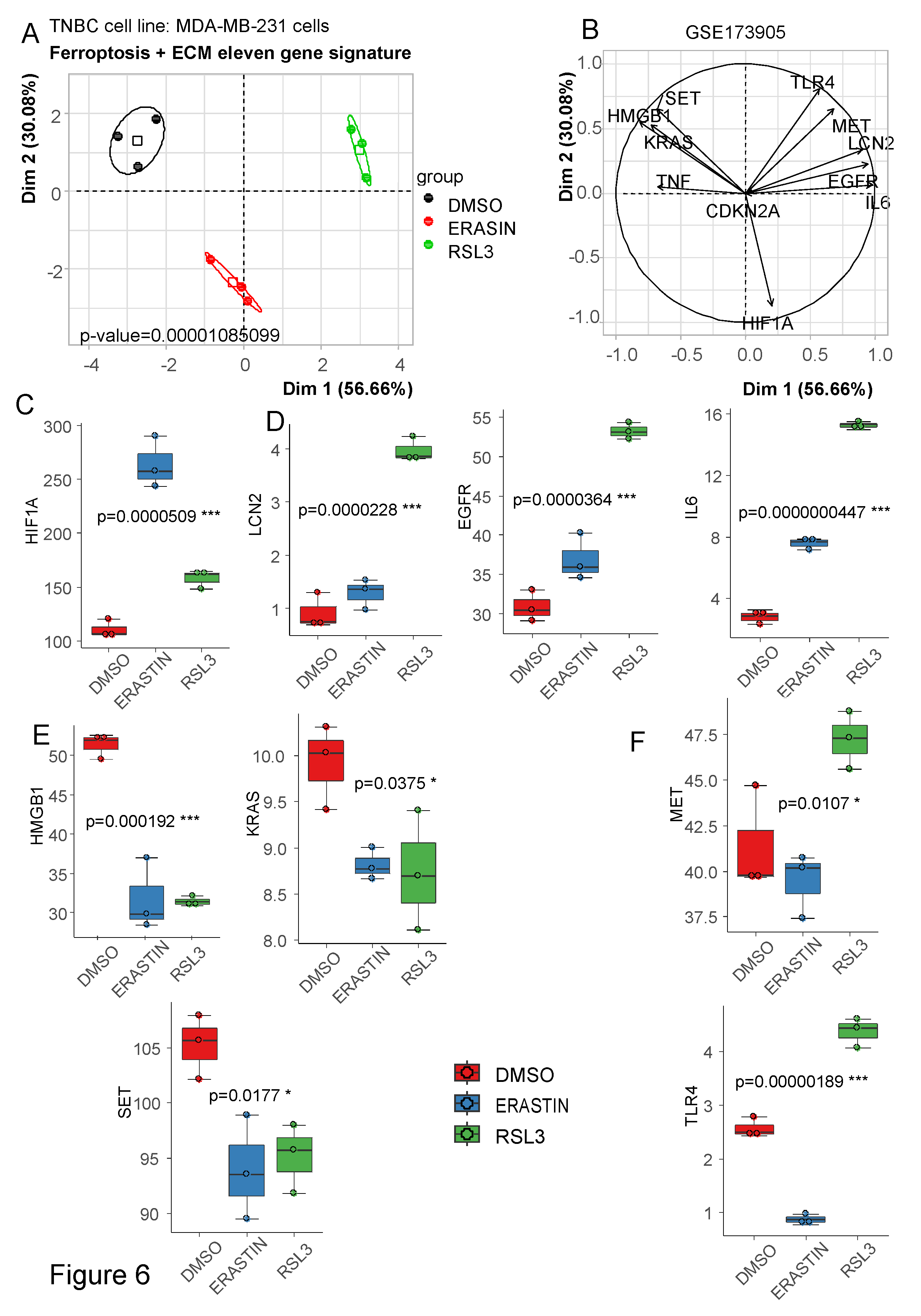
3.3. Ferroptosis/ECM remodeling signature is regulated by ferroptosis activators in triple negative breast cancer cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA A Cancer J Clin 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular Portraits of Human Breast Tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastien, R.R.L.; Rodríguez-Lescure, Á.; Ebbert, M.T.W.; Prat, A.; Munárriz, B.; Rowe, L.; Miller, P.; Ruiz-Borrego, M.; Anderson, D.; Lyons, B.; et al. PAM50 Breast Cancer Subtyping by RT-QPCR and Concordance with Standard Clinical Molecular Markers. BMC Med Genomics 2012, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhan, M.A.; Parveen, F.; Shah, H.; Yalamarty, S.S.K.; Ataide, J.A.; Torchilin, V.P. Recent Advances with Precision Medicine Treatment for Breast Cancer Including Triple-Negative Sub-Type. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Bu, J.; Gu, X. Targeting Ferroptosis, the Achilles’ Heel of Breast Cancer: A Review. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 1036140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Kroemer, G. Ferroptosis. Current Biology 2020, 30, R1292–R1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolma, S.; Lessnick, S.L.; Hahn, W.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Identification of Genotype-Selective Antitumor Agents Using Synthetic Lethal Chemical Screening in Engineered Human Tumor Cells. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic Lethal Screening Identifies Compounds Activating Iron-Dependent, Nonapoptotic Cell Death in Oncogenic-RAS-Harboring Cancer Cells. Chemistry & Biology 2008, 15, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, G.; Godfroid, A.; Nishiumi, S.; Cimino, J.; Blacher, S.; Maquoi, E.; Wery, C.; Collignon, A.; Longuespée, R.; Montero-Ruiz, L.; et al. Tumor Resistance to Ferroptosis Driven by Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1) in Cancer Cells and Fatty Acid Biding Protein-4 (FABP4) in Tumor Microenvironment Promote Tumor Recurrence. Redox Biology 2021, 43, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Vanden Berghe, T. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, A.; Battaglia, A.M.; Botta, C.; Aversa, I.; Mancuso, S.; Costanzo, F.; Biamonte, F. Iron Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment—Implications for Anti-Cancer Immune Response. Cells 2021, 10, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, E.; Nandigama, R.; Ergün, S. Extracellular Matrix in the Tumor Microenvironment and Its Impact on Cancer Therapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 6, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, J.-F.; Priller, F.; Barbosa-Silva, A.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. Génie: Literature-Based Gene Prioritization at Multi Genomic Scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D. Turner, S. Qqman: An R Package for Visualizing GWAS Results Using Q-Q and Manhattan Plots. JOSS 2018, 3, 731. [CrossRef]
- Brancotte, B.; Biton, A.; Bernard-Pierrot, I.; Radvanyi, F.; Reyal, F.; Cohen-Boulakia, S. Gene List Significance At-a-Glance with GeneValorization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Barrett, T.; Benson, D.A.; Bryant, S.H.; Canese, K.; Chetvernin, V.; Church, D.M.; DiCuccio, M.; Edgar, R.; Federhen, S.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzis, C. A Genomic Predictor of Response and Survival Following Taxane-Anthracycline Chemotherapy for Invasive Breast Cancer. JAMA 2011, 305, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lin, Q.; Sun, S.; Yang, N.; Xia, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Q.; Guo, H.; Zhu, M.; et al. Inhibition of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Ferroptosis via Regulating Fatty Acid Metabolism. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. Journal of Statistical Software 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudis, C.A.; Barlow, W.E.; Costantino, J.P.; Gray, R.J.; Pritchard, K.I.; Chapman, J.-A.W.; Sparano, J.A.; Hunsberger, S.; Enos, R.A.; Gelber, R.D.; et al. Proposal for Standardized Definitions for Efficacy End Points in Adjuvant Breast Cancer Trials: The STEEP System. JCO 2007, 25, 2127–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) Hallmark Gene Set Collection. Cell Syst 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Bardes, E.E.; Aronow, B.J.; Jegga, A.G. ToppGene Suite for Gene List Enrichment Analysis and Candidate Gene Prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cline, M.S.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-Campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B.; et al. Integration of Biological Networks and Gene Expression Data Using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc 2007, 2, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Yu, J.; Klijn, J.G.M.; Foekens, J.A.; Martens, J.W.M. Subtypes of Breast Cancer Show Preferential Site of Relapse. Cancer Research 2008, 68, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, C.; Neo, S.-Y.; McShane, L.M.; Korn, E.L.; Long, P.M.; Jazaeri, A.; Martiat, P.; Fox, S.B.; Harris, A.L.; Liu, E.T. Breast Cancer Classification and Prognosis Based on Gene Expression Profiles from a Population-Based Study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003, 100, 10393–10398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.-M.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Chen, M.-T.; Zhang, F.-L.; Liu, X.-L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.-Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.-W. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 (HIF-1) Promotes LDL and VLDL Uptake through Inducing VLDLR under Hypoxia. Biochemical Journal 2012, 441, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensaad, K.; Favaro, E.; Lewis, C.A.; Peck, B.; Lord, S.; Collins, J.M.; Pinnick, K.E.; Wigfield, S.; Buffa, F.M.; Li, J.-L.; et al. Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Storage Induced by HIF-1α Contribute to Cell Growth and Survival after Hypoxia-Reoxygenation. Cell Reports 2014, 9, 349–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assidicky, R.; Tokat, U.M.; Tarman, I.O.; Saatci, O.; Ersan, P.G.; Raza, U.; Ogul, H.; Riazalhosseini, Y.; Can, T.; Sahin, O. Targeting HIF1-Alpha/MiR-326/ITGA5 Axis Potentiates Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2022, 193, 331–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebalka, I.A.; Monaco, C.M.F.; Varah, N.E.; Berger, T.; D’souza, D.M.; Zhou, S.; Mak, T.W.; Hawke, T.J. Loss of the Adipokine Lipocalin-2 Impairs Satellite Cell Activation and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2018, 315, C714–C721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valashedi, M.R.; Roushandeh, A.M.; Tomita, K.; Kuwahara, Y.; Pourmohammadi-Bejarpasi, Z.; Kozani, P.S.; Sato, T.; Roudkenar, M.H. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of Lcn2 in Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 Ameliorates Erastin-Mediated Ferroptosis and Increases Cisplatin Vulnerability. Life Sci 2022, 304, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Adipocytes Can Induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer Cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2015, 153, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirat, B.; Bochet, L.; Dabek, M.; Daviaud, D.; Dauvillier, S.; Majed, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meulle, A.; Salles, B.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Cancer-Associated Adipocytes Exhibit an Activated Phenotype and Contribute to Breast Cancer Invasion. Cancer Res 2011, 71, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, M.; Zeng, N.; Xiong, M.; Hu, W.; Lv, W.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y. Cancer-Associated Adipocytes: Emerging Supporters in Breast Cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2020, 39, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyamfi, J.; Eom, M.; Koo, J.-S.; Choi, J. Multifaceted Roles of Interleukin-6 in Adipocyte-Breast Cancer Cell Interaction. Transl Oncol 2018, 11, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Adorno-Cruz, V.; Chang, Y.-F.; Jia, Y.; Kawaguchi, M.; Dashzeveg, N.K.; Taftaf, R.; Ramos, E.K.; Schuster, E.J.; El-Shennawy, L.; et al. EGFR Inhibition Blocks Cancer Stem Cell Clustering and Lung Metastasis of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6632–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sheng, H.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, M.; Lou, H.; Miao, Y.; Cheng, N.; Zhang, W.; Ding, D.; Li, W. Co-Loaded Lapatinib/PAB by Ferritin Nanoparticles Eliminated ECM-Detached Cluster Cells via Modulating EGFR in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, G.E.; Hockings, H.; Hilton, D.M.; Kermorgant, S. The Role of MET in Chemotherapy Resistance. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1927–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. Roles of HGF as a Pleiotropic Factor in Organ Regeneration. EXS 1993, 65, 225–249. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar, E.A.; Graveel, C.R. MET in Human Cancer: Germline and Somatic Mutations. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 205–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Song, L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Gong, A.; Liao, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D. Activated Stellate Cell Paracrine HGF Exacerbated Pancreatic Cancer Cell Ferroptosis Resistance. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022, 2985249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zou, J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The Redox Protein High-Mobility Group Box 1 in Cell Death and Cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, H.-Z.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, Y. HMGB1 Regulates Ferroptosis through Nrf2 Pathway in Mesangial Cells in Response to High Glucose. Biosci Rep 2021, 41, BSR20202924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Chu, P.-Y.; Chen, J.-L.; Huang, C.-T.; Lee, C.-H.; Lau, K.-Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Lien, P.-J.; Tseng, L.-M.; et al. SET Overexpression Is Associated with Worse Recurrence-Free Survival in Patients with Primary Breast Cancer Receiving Adjuvant Tamoxifen Treatment. J Clin Med 2018, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Muñoz, A.; Gallego, E.; de Luque, V.; Pérez-Rivas, L.G.; Vicioso, L.; Ribelles, N.; Lozano, J.; Alba, E. Lack of Evidence for KRAS Oncogenic Mutations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.-K.; Suh, Y.; Yoo, K.-C.; Cui, Y.-H.; Kim, H.; Kim, M.-J.; Gyu Kim, I.; Lee, S.-J. Activation of KRAS Promotes the Mesenchymal Features of Basal-Type Breast Cancer. Exp Mol Med 2015, 47, e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, S.; Volk-Draper, L.D.; Ran, S. TLR4 Is a Novel Determinant of the Response to Paclitaxel in Breast Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2013, 12, 1676–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
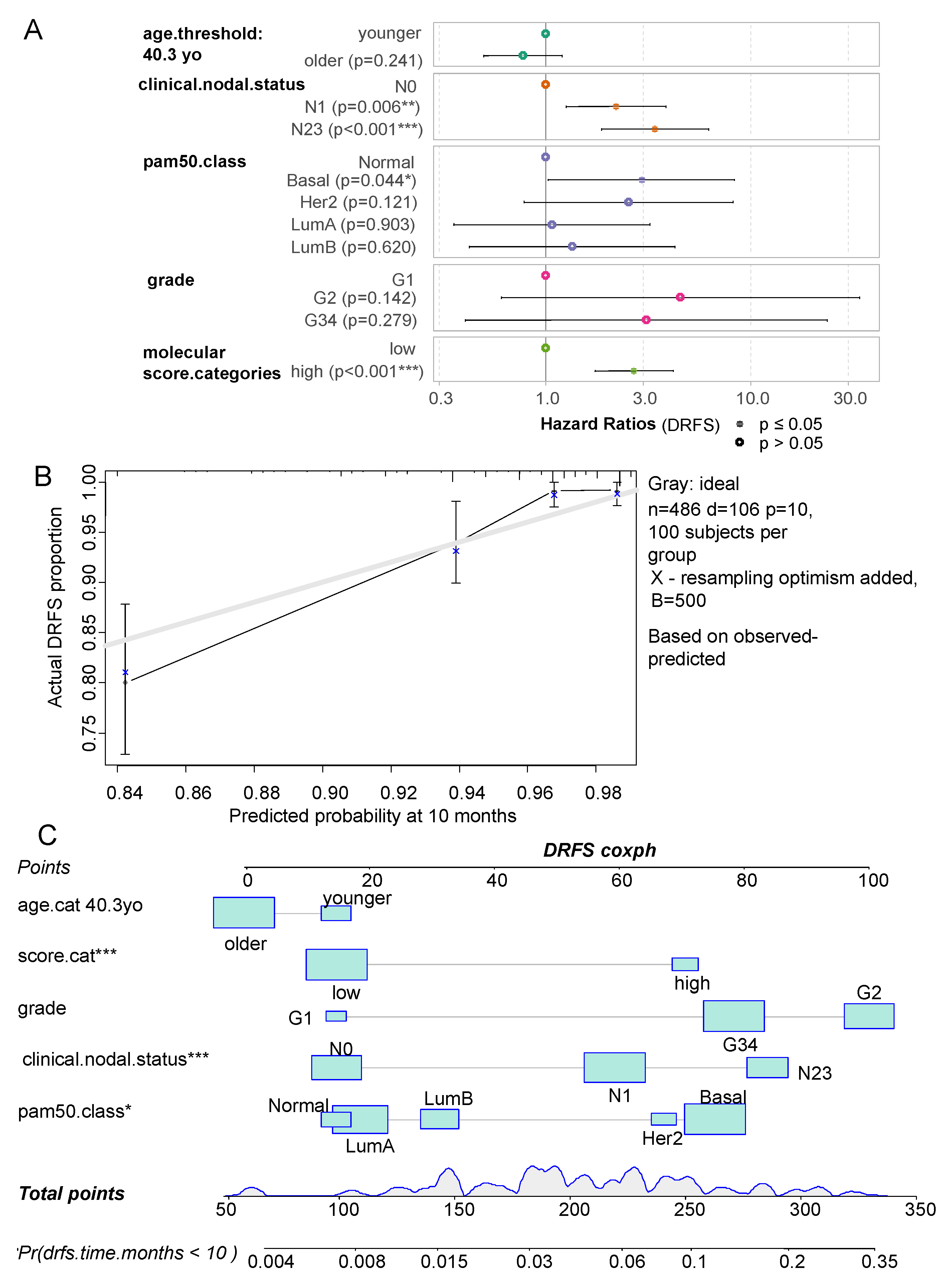
| Variable | Level | low (n=426) | high (n= 82) | Total (n=508) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age.years | mean (sd) | 49.7 (10.4) | 50.5 (10.8) | 49.8 (10.5) | 0.524161 |
| age.categories (40.3 yo) | younger | 79 (18.5) | 20 (24.4) | 99 (19.5) | |
| older | 347 (81.5) | 62 (75.6) | 409 (80.5) | 0.283927 | |
| er.status.ihc | Negative | 144 (34.1) | 61 (76.2) | 205 (40.8) | |
| Positive | 278 (65.9) | 19 (23.8) | 297 (59.2) | < 1e-04 | |
| missing | 4 | 2 | 6 | ||
| pr.status.ihc | Negative | 192 (45.6) | 66 (82.5) | 258 (51.5) | |
| Positive | 229 (54.4) | 14 (17.5) | 243 (48.5) | < 1e-04 | |
| missing | 5 | 2 | 7 | ||
| pam50.class | Normal | 42 (9.9) | 2 (2.4) | 44 (8.7) | |
| Basal | 123 (28.9) | 66 (80.5) | 189 (37.2) | ||
| Her2 | 33 (7.7) | 4 (4.9) | 37 (7.3) | ||
| LumA | 152 (35.7) | 8 (9.8) | 160 (31.5) | ||
| LumB | 76 (17.8) | 2 (2.4) | 78 (15.4) | < 1e-04 | |
| clinical.tumor.stage | T-0,1,2 | 247 (58.0) | 41 (50.0) | 288 (56.7) | |
| T-3 | 119 (27.9) | 26 (31.7) | 145 (28.5) | ||
| T-4 | 60 (14.1) | 15 (18.3) | 75 (14.8) | 0.379010 | |
| clinical.nodal.status | N-0 | 140 (32.9) | 17 (20.7) | 157 (30.9) | |
| N-1 | 205 (48.1) | 39 (47.6) | 244 (48.0) | ||
| N-2,3 | 81 (19.0) | 26 (31.7) | 107 (21.1) | 0.013986 | |
| clinical.ajcc.stage | IIB | 131 (30.8) | 20 (24.4) | 151 (29.7) | |
| IIIA | 99 (23.2) | 22 (26.8) | 121 (23.8) | ||
| IIIB | 63 (14.8) | 17 (20.7) | 80 (15.7) | ||
| IIA | 109 (25.6) | 12 (14.6) | 121 (23.8) | ||
| IIIC | 16 (3.8) | 7 (8.5) | 23 (4.5) | ||
| Inflammatory | 2 (0.5) | 2 (2.4) | 4 (0.8) | ||
| I | 6 (1.4) | 2 (2.4) | 8 (1.6) | 0.033976 | |
| grade | G-1 | 32 (7.8) | 0 (0.0) | 32 (6.6) | |
| G-2 | 167 (40.8) | 13 (16.9) | 180 (37.0) | ||
| G-3,4 | 210 (51.3) | 64 (83.1) | 274 (56.4) | < 1e-04 | |
| missing | 17 | 5 | 22 | ||
| drfs.status | 1 | 70 (16.4) | 41 (50.0) | 111 (21.9) | |
| 0 | 356 (83.6) | 41 (50.0) | 397 (78.1) | < 1e-04 | |
| drfs.time.years | mean (sd) | 3.2 (1.6) | 2 (1.2) | 3 (1.6) | < 1e-04 |
| type.taxane | Taxotere | 78 (45.6) | 14 (51.9) | 92 (46.5) | |
| Taxol | 93 (54.4) | 13 (48.1) | 106 (53.5) | 0.691854 | |
| missing | 255 | 55 | 310 |
| variables | Hazard ratios | Confidence-low | Confidence-high | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| age.cat older | 0.770 | 0.498 | 1.192 | 2.41E-01 |
| clinical.nodal.statusN1 | 2.202 | 1.255 | 3.862 | 5.91E-03 |
| clinical.nodal.statusN23 | 3.395 | 1.857 | 6.205 | 7.15E-05 |
| pam50.classBasal | 2.924 | 1.027 | 8.327 | 4.45E-02 |
| pam50.classHer2 | 2.530 | 0.783 | 8.177 | 1.21E-01 |
| pam50.classLumA | 1.071 | 0.356 | 3.221 | 9.03E-01 |
| pam50.classLumB | 1.339 | 0.422 | 4.252 | 6.20E-01 |
| Grade.G2 | 4.526 | 0.603 | 33.950 | 1.42E-01 |
| Grade.G34 | 3.085 | 0.402 | 23.693 | 2.79E-01 |
| score.high | 2.689 | 1.728 | 4.185 | 1.17E-05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





