Submitted:
12 June 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
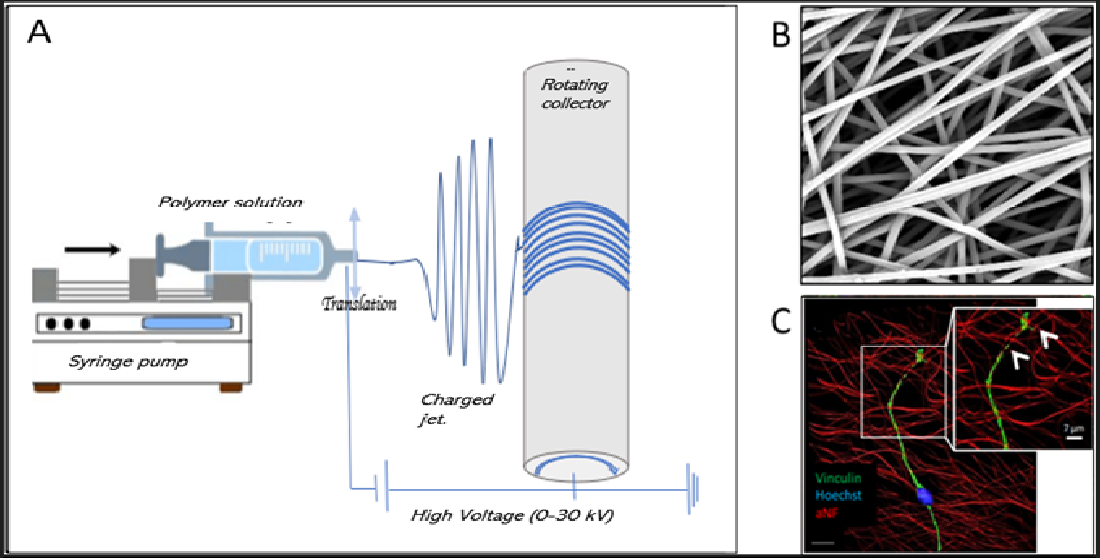
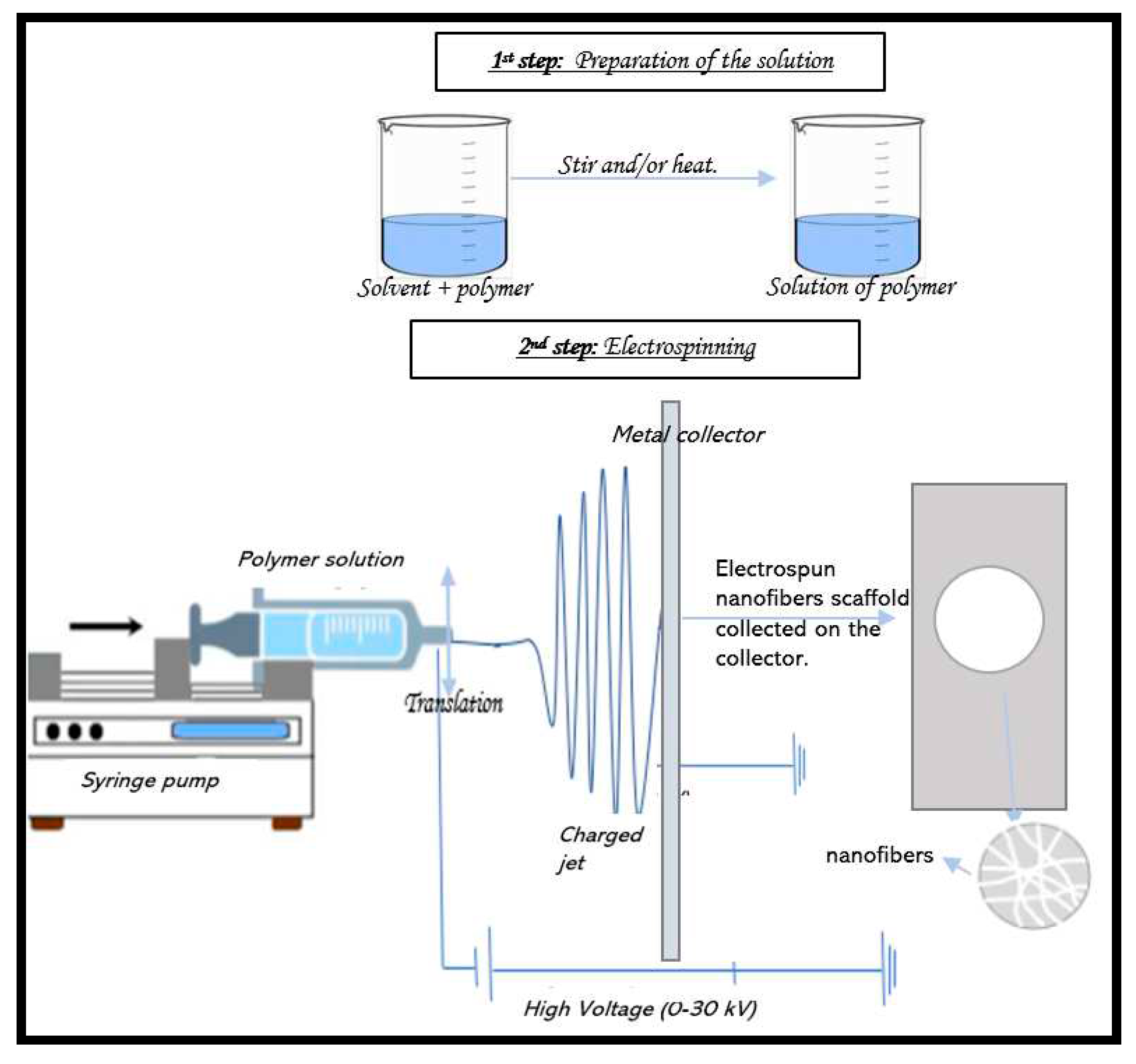
2. Electrospinning Process
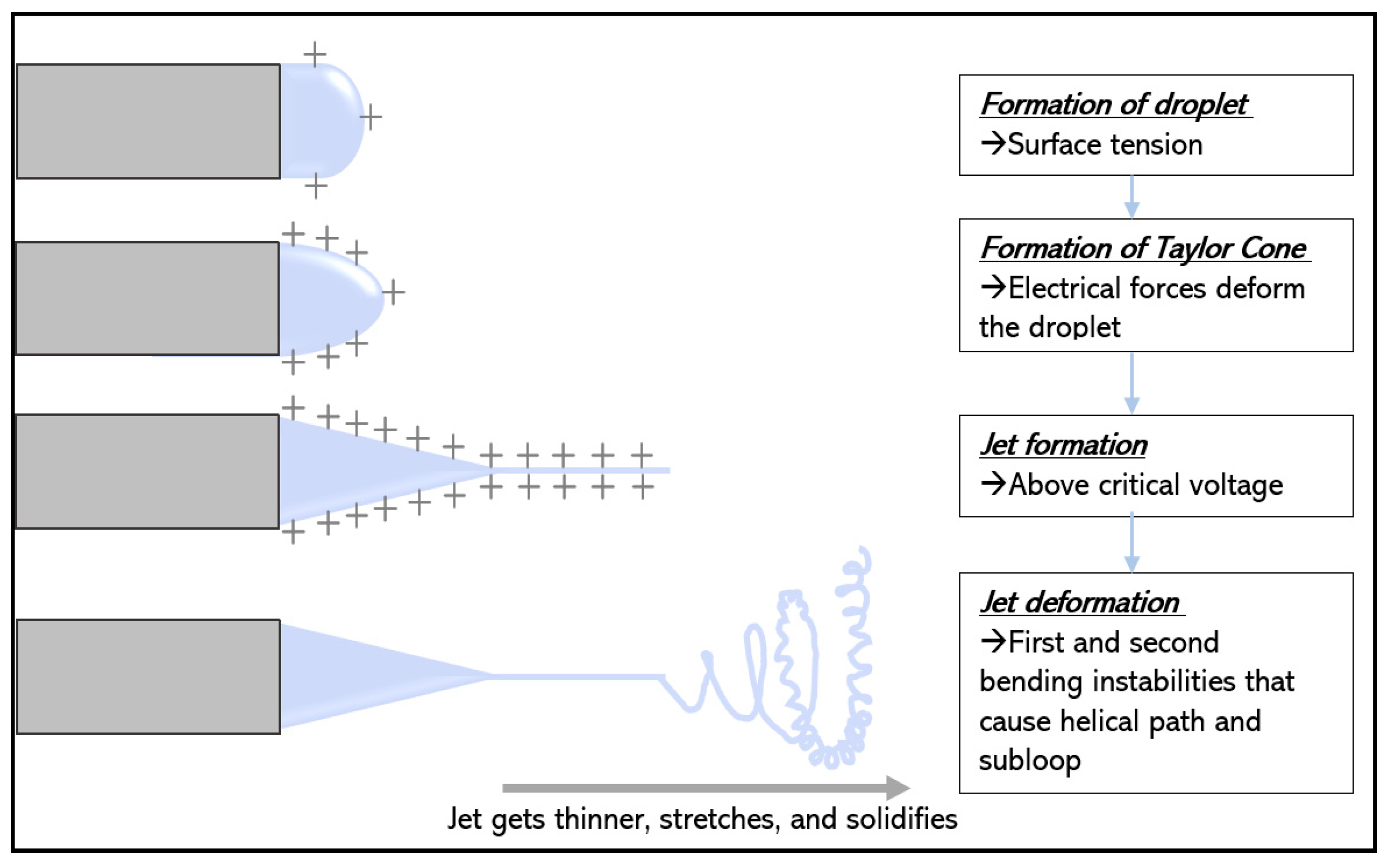
2.1. Principle
2.2. Formation of Taylor Cone upon charging a liquid droplet
2.3. Stretching and thinning of the charged jet
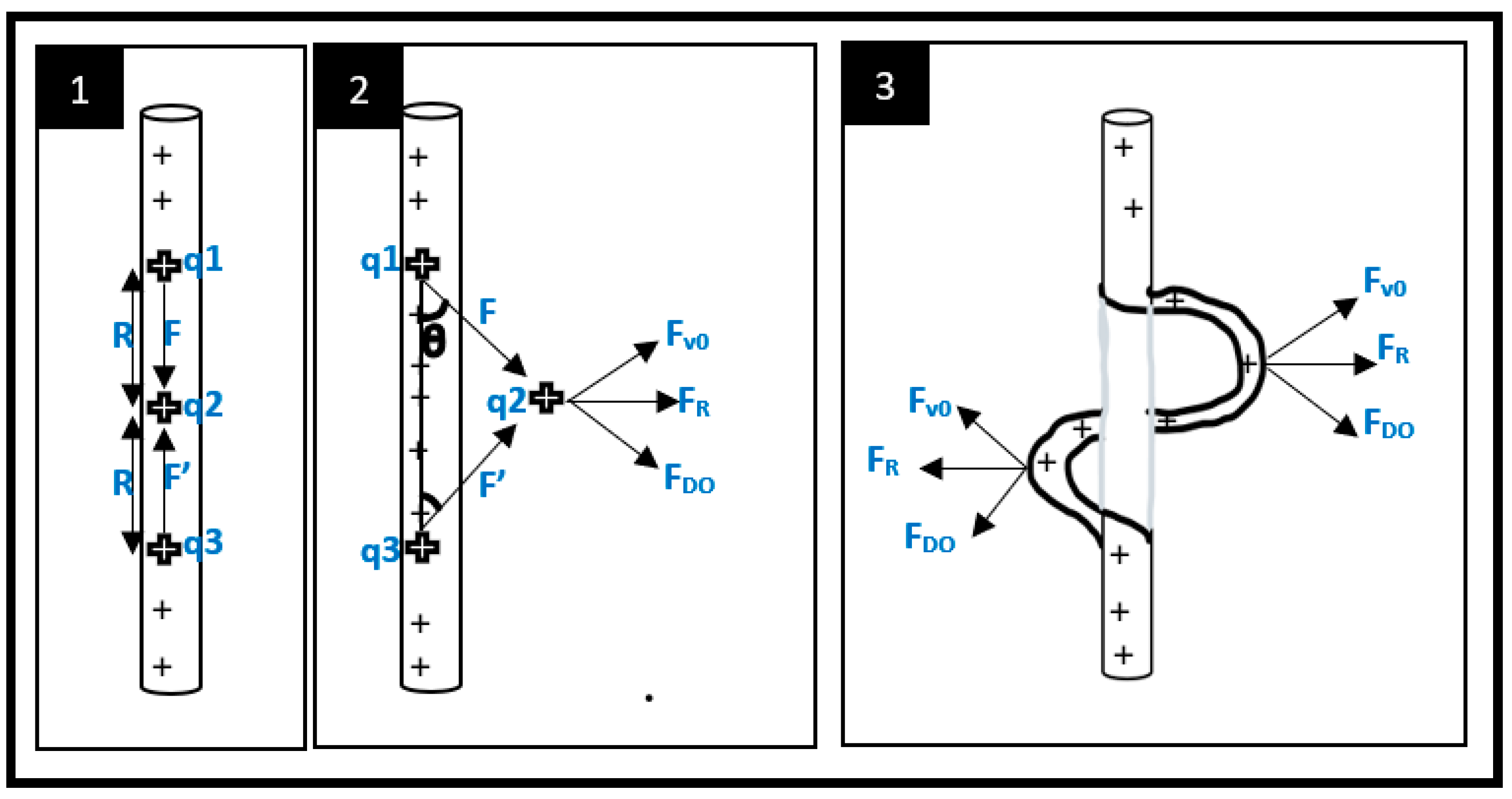
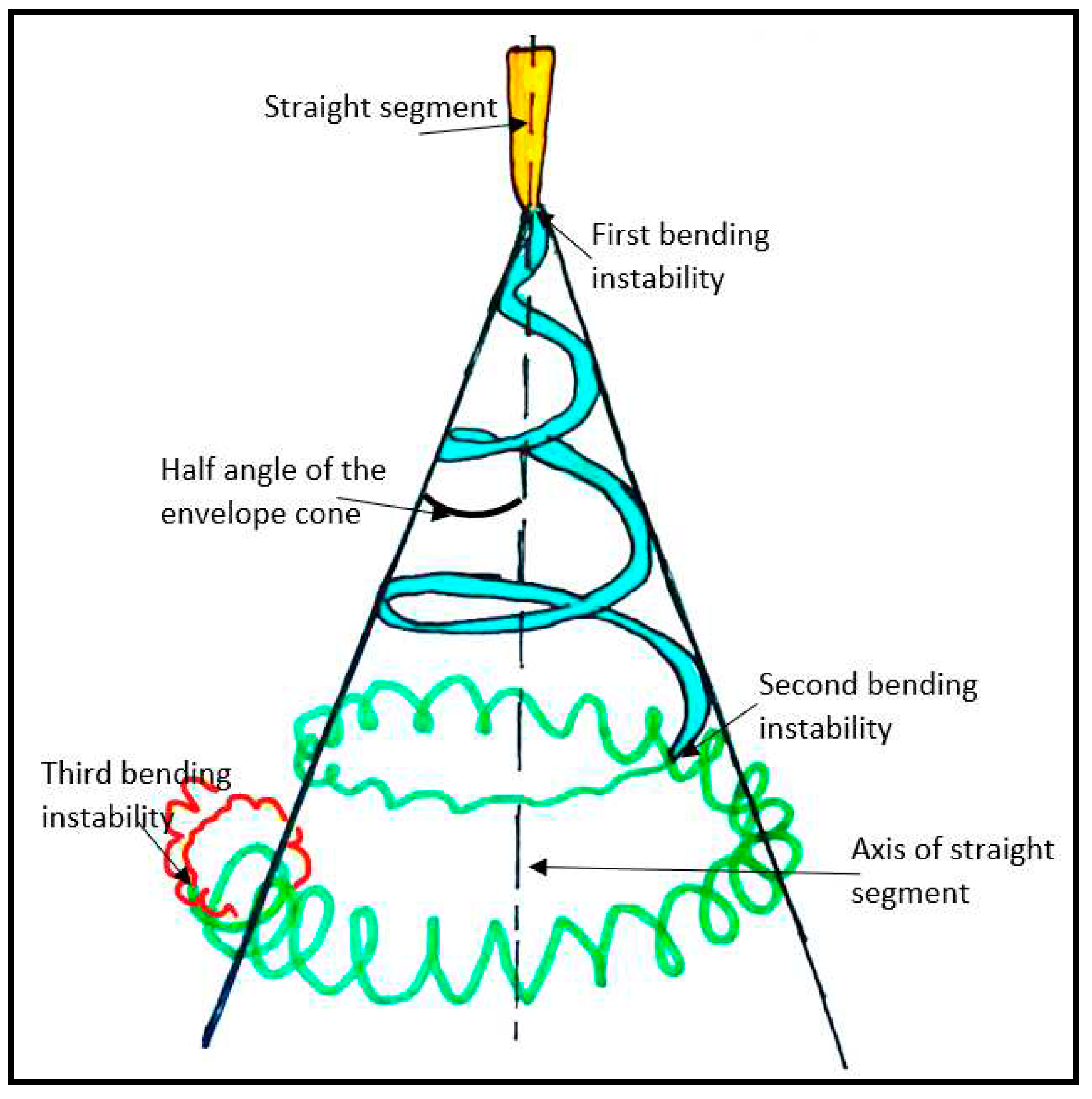
2.4. Deposition of solid fibers
2.5. Control of the electrospinning process
2.5.1. Effects of the voltage:
2.5.2. Effects on the flowrate:
2.5.3. Effect on the distance between metallic collector and needle:
2.5.4. Effects of needle diameter:
2.5.5. Effects of polymer concentration in solution:
2.5.6. Effect of solution conductivity:
2.5.7. Solvent effects:
2.5.8. Effect of the targeted drum size and its speed of rotation:
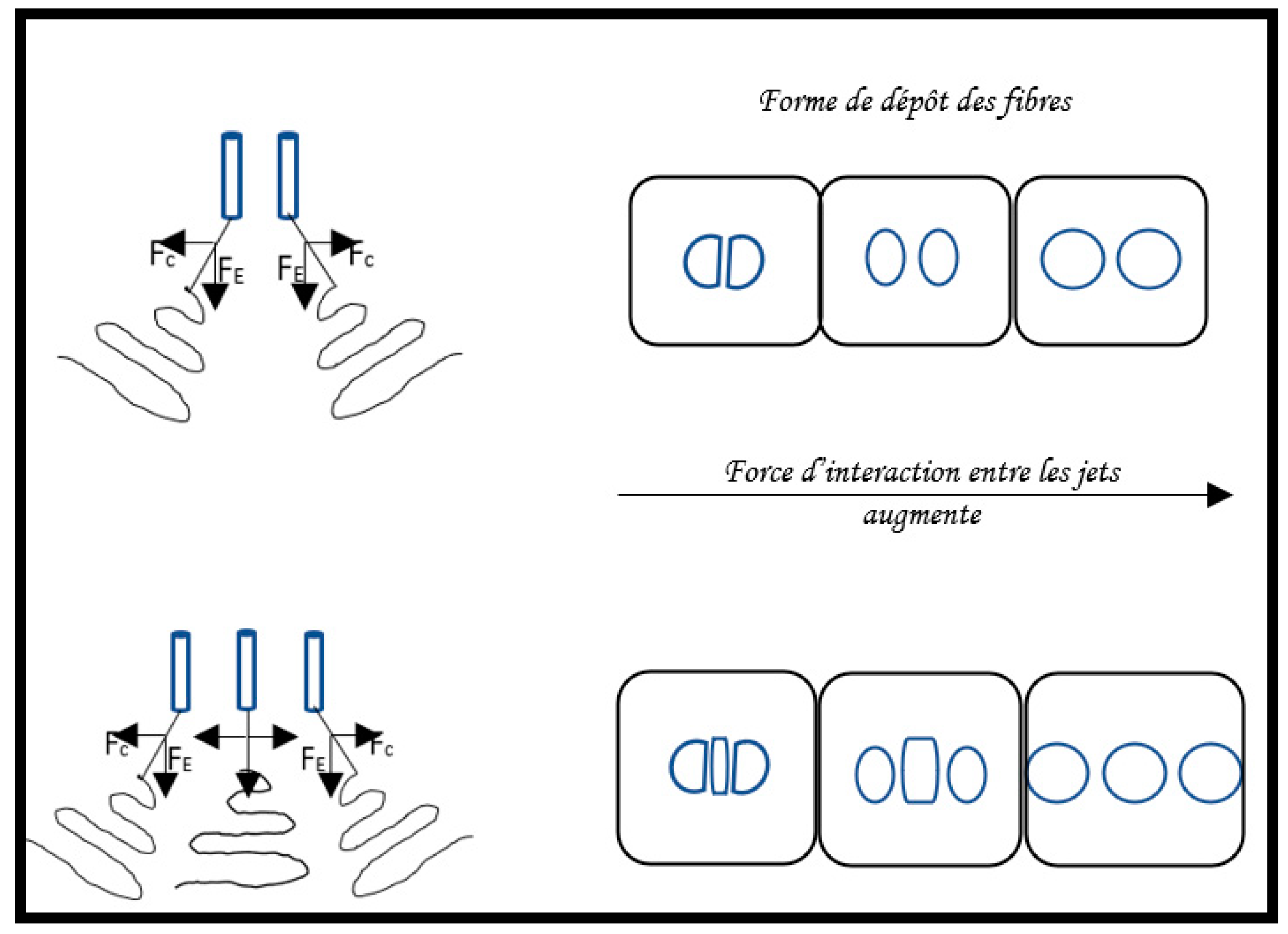
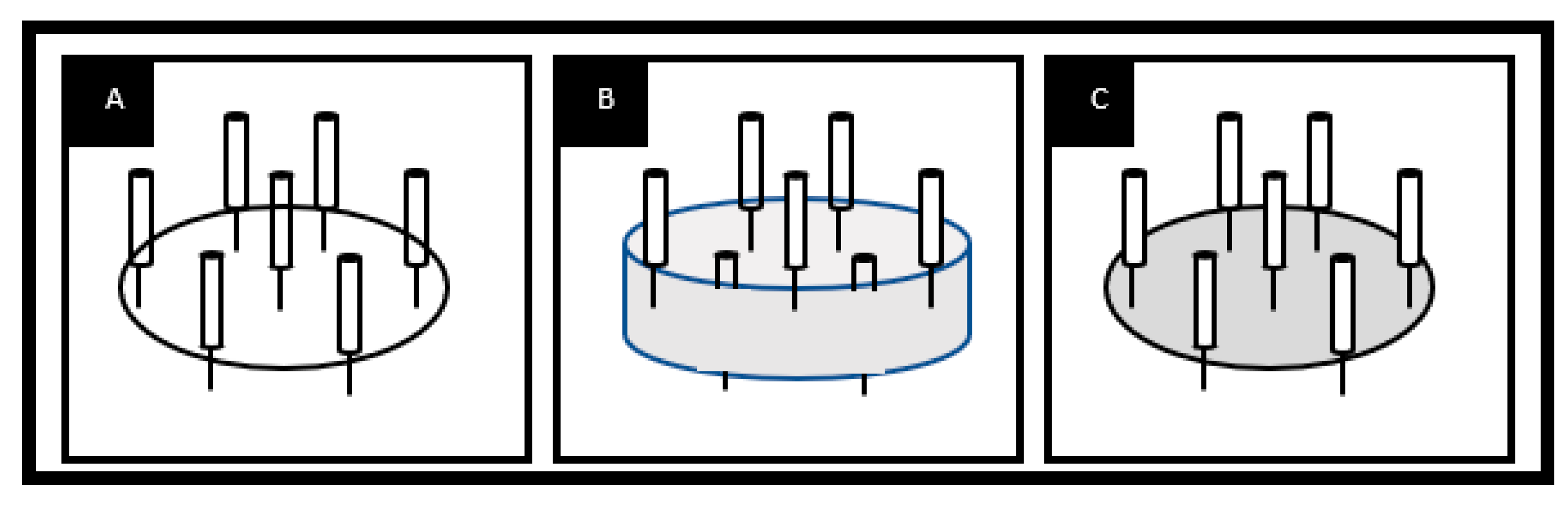
2.6. Multineedle for large scale production
2.6.1. Multi-needle electrospinning process:
- Principle and properties
- Control of fiber formation in multi-needle electrospinning setup.
2.6.2. Other approaches
2.6.3. New directions for future development
3. Electrospinning of Scaffold for biological studies
3.1. Why electrospun 3D scaffold cultures?
3.1.1. 3D cultures versus 2D culture
3.1.2. 3D scaffolds
3.1.3. Production of 3D scaffolds
3.2. Choice of materials
3.2.1. Polymers
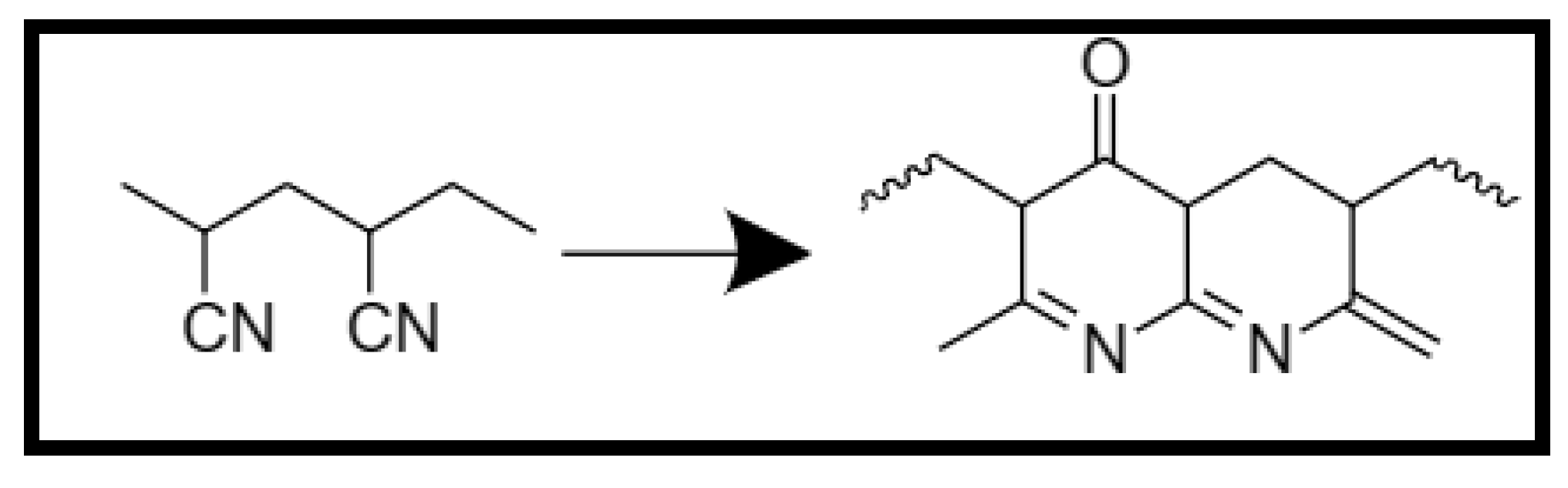
3.2.2. Specific case of PAN
- Electrospinning of PAN
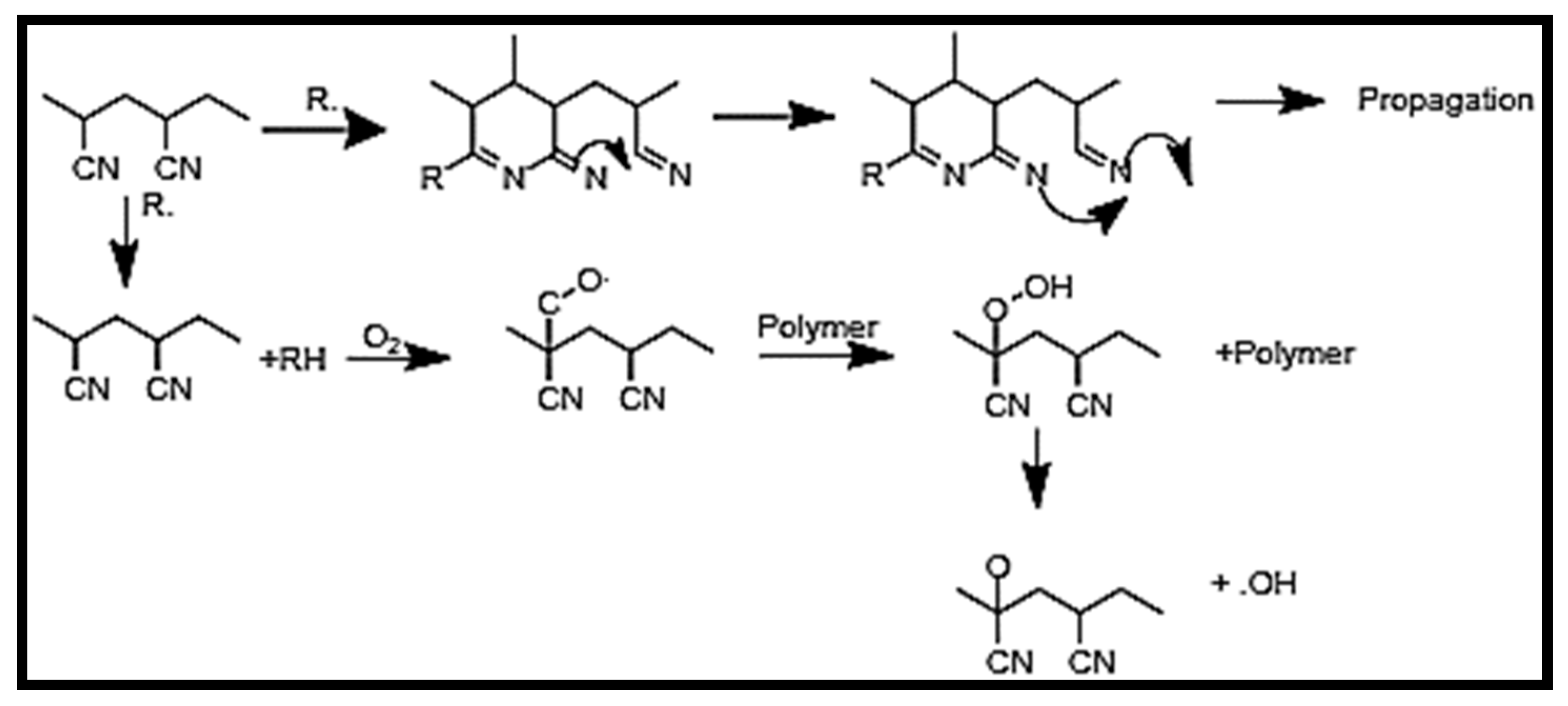
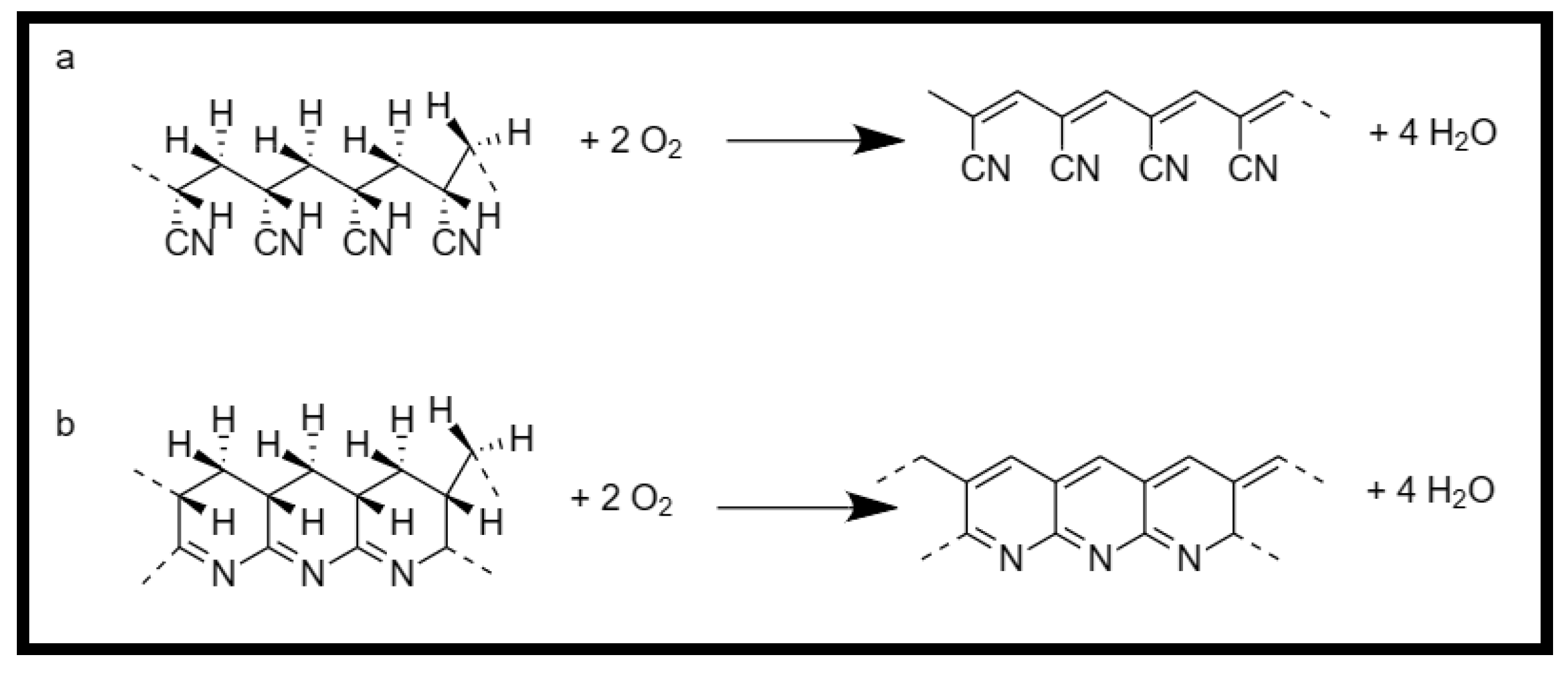
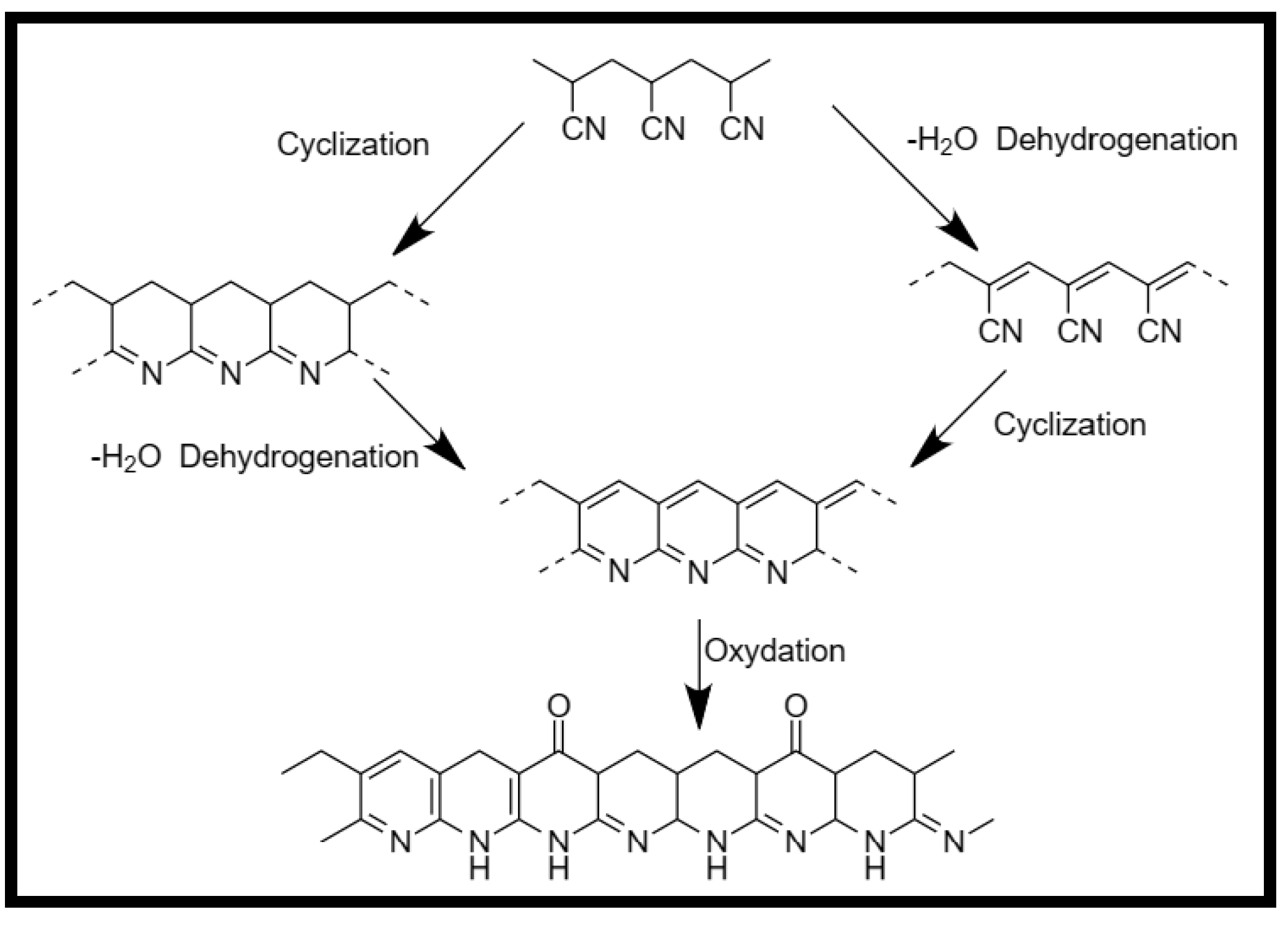
- Thermal treatment of Polyacrylonitrile.
- Functionalization of PAN fibers
3.2.3. Peptides and proteins
3.3. Control of scaffold architecture
3.3.1. Modification of the surface
- Biochemical modification
- Surface morphology and potential modification
3.3.2. Modification of the structure
- Alignment
- Diameter
- Porosity
3.4. Application in biological field
3.4.1. Studying migration.
3.4.2. Cancer research
3.4.3. Biosensors
3.4.4. Stem cells differentiation and cell therapy
3.4.5. Tissue engineering
- Bone tissue engineering
- Neural tissue engineering
- Vascular tissue engineering [60]
- Cartilage tissue engineering
- Tendon/ligament tissue engineering
- Cardiac tissue engineering
- Other tissue engineering
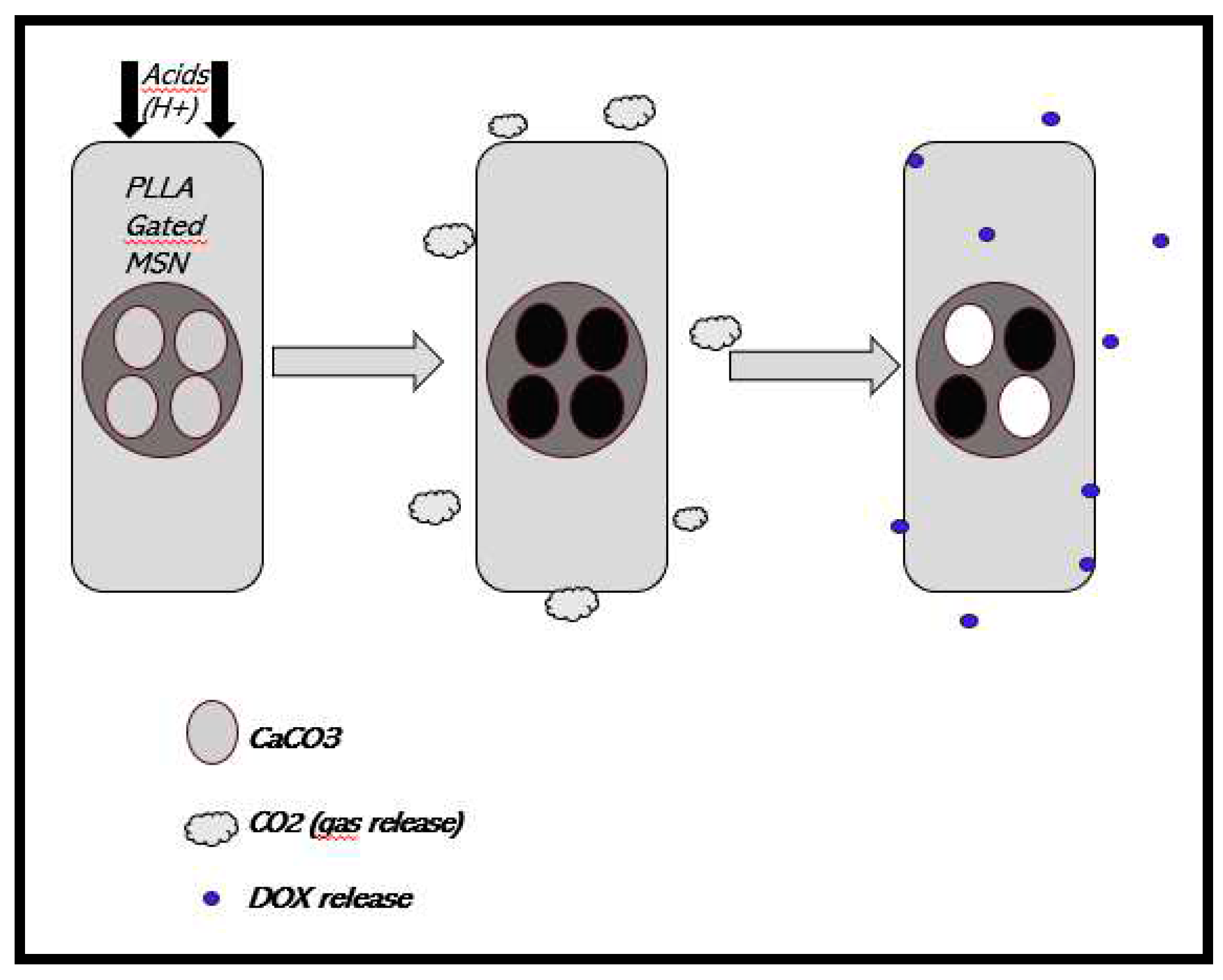
3.4.6. Drug delivery
3.4.7. Wound healing
3.4.8. Implant coating
3.5. Combining microfluidic and electrospun fibers scaffold
4. Conclusion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cherry, R.H. History of Sericulture. Bulletin of the Entomological Society of America 1987, 33, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollrath, F.; Knight, D.P. Liquid Crystalline Spinning of Spider Silk. Nature 2001, 410, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, M.; Keerl, D.; Scheibel, T. Spider Silk: From Soluble Protein to Extraordinary Fiber. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3584–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y.G.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Natural Fibers as Sustainable and Renewable Resource for Development of Eco-Friendly Composites: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenmozhi, S.; Dharmaraj, N.; Kadirvelu, K.; Kim, H.Y. Electrospun Nanofibers: New Generation Materials for Advanced Applications. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2017, 217, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.-E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun Nanofibers: Solving Global Issues. Materials Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, Y. Recent Advances in Energy Materials by Electrospinning. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2018, 81, 1825–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of Polymeric Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. Journal of Controlled Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus Fibre Production Methods: From Specifics to Technological Convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, J.F. Apparatus for Electrically Dispersing Fluids 1902.
- Electrostatic Spraying of Liquids. Von A. G. Bailey, Research Studies Press LTD Taunton, Somerset/John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York 1988, 197 Seiten, 24,75 $. Phys. Unserer Zeit 1989, 20, 160–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, N.; LaJeunesse, D.; Kelkar, A.D.; Zhang, L. Antifungal Activity of Amidoxime Surface Functionalized Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Materials Letters 2015, 141, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Mamun, A.; Kutzli, I.; Diestelhorst, E.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A.; 1 Faculty of Engineering and Mathematics, Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences, Bielefeld, Germany; et al. Cell Growth on Electrospun Nanofiber Mats from Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Blends. AIMS Bioengineering 2020, 7, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Kinzel, F.; Hauser, T.; Többer, A.; Klöcker, M.; Döpke, C.; Böttjer, R.; Wehlage, D.; Rattenholl, A.; Ehrmann, A. Comparative Study of Pleurotus Ostreatus Mushroom Grown on Modified PAN Nanofiber Mats. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.-F.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Huang, D.-W. Multi-Jet Electrospinning via Auxiliary Electrode. Materials Letters 2015, 141, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Tian, L.; Pan, Z. Structures and Mechanical Properties of Plied and Twisted Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Yarns Fabricated by a Multi-Needle Electrospinning Device. Fibers Polym 2016, 17, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SalehHudin, H.S.; Mohamad, E.N.; Mahadi, W.N.L.; Muhammad Afifi, A. Multiple-Jet Electrospinning Methods for Nanofiber Processing: A Review. Materials and Manufacturing Processes 2018, 33, 479–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Akampumuza, O.; Hou, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X. A Low Filtration Resistance Three-Dimensional Composite Membrane Fabricated via Free Surface Electrospinning for Effective PM 2.5 Capture. Environ. Sci.: Nano 2017, 4, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda, E.; Fabre, C.; Zhang, C.; Martin-Fernandez, M.; Iskratsch, T.; Saleh, A.; Bauchet, L.; Cambedouzou, J.; Hugnot, J.-P.; Duffau, H.; et al. Glioma Stem Cells Invasive Phenotype at Optimal Stiffness Is Driven by MGAT5 Dependent Mechanosensing. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Ismail, A.F. Post Spinning and Pyrolysis Processes of Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-Based Carbon Fiber and Activated Carbon Fiber: A Review. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis 2012, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, N.; Sharp, J.; Nunna, S.; Creighton, C.; Magniez, K.; Jyotishkumar, P.; Salim, N.V.; Fox, B. Structural Transformation of Polyacrylonitrile Fibers during Stabilization and Low Temperature Carbonization. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2016, 128, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Z.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of Oxygen on the Structural Evolution of Polyacrylonitrile Fibers during Rapid Thermal Treatment. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 6356–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.U.; Han, N.K.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, W.H.; Jeong, Y.G. Spectroscopic Analyses on Chain Structure and Thermal Stabilization Behavior of Acrylonitrile/Methyl Acrylate/Itaconic Acid-Based Copolymers Synthesized by Aqueous Suspension Polymerization. Fibers Polym 2018, 19, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, K.; Zhang, A.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Liang, J. Structural Transformation of Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Fibers during Rapid Thermal Pretreatment in Nitrogen Atmosphere. Polymers 2020, 12, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.-K. A Comprehensive Review Summarizing the Effect of Electrospinning Parameters and Potential Applications of Nanofibers in Biomedical and Biotechnology. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.-L.; Gong, R.-H.; Porat, I. Mass Production of Nanofibre Assemblies by Electrostatic Spinning. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.P.; Hem, R.P.; Cheol, S.K. Novel Robot-Assisted Angled Multi-Nozzle Electrospinning Set-up: Computer Simulation with Experimental Observation of Electric Field and Fiber Morphology - Chan Hee Park, Hem Raj Pant, Cheol Sang Kim, 2014. Available online: https://journals-sagepub-com.inc.bib.cnrs.fr/doi/10.1177/0040517513517961 (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning Jets and Polymer Nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-H.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, W.-W. Critical Length of Straight Jet in Electrospinning. Polymer 2005, 46, 12637–12640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.; Federici, J.; Imura, Y.; Catalani, L.H. Charge Generation, Charge Transport, and Residual Charge in the Electrospinning of Polymers: A Review of Issues and Complications. Journal of Applied Physics 2012, 111, 044701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Chiang, S.W.; Chu, X.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Gan, L.; Xu, C.; Yao, Y.; He, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Effects of Solvent on Structures and Properties of Electrospun Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Nanofibers: ARTICLE. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. The Effects of Solution Properties and Polyelectrolyte on Electrospinning of Ultrafine Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Fibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmati, A.H.; Rashidi, A.; Ghazisaeidi, R.; Drean, J.-Y. Effect of Needle Length, Electrospinning Distance, and Solution Concentration on Morphological Properties of Polyamide-6 Electrospun Nanowebs. Textile Research Journal 2013, 83, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Shen, M.; Ma, H.; Guo, R.; Zhu, M.; Wang, S.; Shi, X. Fabrication of Water-Stable Electrospun Polyacrylic Acid-Based Nanofibrous Mats for Removal of Copper (II) Ions in Aqueous Solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, NA–NA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Wu, L.; Han, Y.; Sheng, J. Study on Morphology of Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Mats. European Polymer Journal 2005, 41, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, V.; Anandjiwala, R.D.; Maaza, M. The Influence of Electrospinning Parameters on the Structural Morphology and Diameter of Electrospun Nanofibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Xu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, W.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; et al. Optimization of Electric Field Uniformity of Multi-Needle Electrospinning Nozzle. AIP Advances 2019, 9, 105104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, W. ; Szadkowski Investigation of Electrospinning with the Use of a Multi-Jet Electrospinning Head. 2005.
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Guan, Z. Electrospun Uniform Fibres with a Special Regular Hexagon Distributed Multi-Needles System. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2008, 142, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theron, S.A.; Yarin, A.L.; Zussman, E.; Kroll, E. Multiple Jets in Electrospinning: Experiment and Modeling. Polymer 2005, 46, 2889–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z.; Zahn, M. A Shield Ring Enhanced Equilateral Hexagon Distributed Multi-Needle Electrospinning Spinneret. IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gong, R.H.; Zeng, Y. Multijet Motion and Deviation in Electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48533–48540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, S.; Forgách, L.; Zelkó, R.; Sebe, I. Scale-up of Electrospinning: Market Overview of Products and Devices for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Purposes. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapałczyńska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyła, W.; Zajączkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Bliźniak, R.; Łuczewski, Ł.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D Cell Cultures – a Comparison of Different Types of Cancer Cell Cultures. Arch Med Sci 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sośniak, J.; Opiela, J. 3D Cell Culture Technology – A New Insight Into in Vitro Research – A Review. Annals of Animal Science 2021, 21, 1257–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Marhuenda, E.; Fabre, C.; Hassani, Z.; Weille, J. de; Boukhaddaoui, H.; Guelfi, S.; Maldonado, I.L.; Hugnot, J.-P.; Duffau, H.; et al. A Novel 3D Nanofibre Scaffold Conserves the Plasticity of Glioblastoma Stem Cell Invasion by Regulating Galectin-3 and Integrin-Β1 Expression. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 14612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basic Concepts on 3D Cell Culture; Kasper, C. , Egger, D., Lavrentieva, A., Eds.; Learning Materials in Biosciences; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; ISBN 978-3-030-66748-1. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, T.C.; Amanah, A.Y.; Gluck, J.M. Electrospun Scaffolds and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.-H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture 2017, 266–277. [Google Scholar]
- Shologu, N.; Szegezdi, E.; Lowery, A.; Kerin, M.; Pandit, A.; Zeugolis, D.I. Recreating Complex Pathophysiologies in Vitro with Extracellular Matrix Surrogates for Anticancer Therapeutics Screening. Drug Discovery Today 2016, 21, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habanjar, O.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Delort, L. 3D Cell Culture Systems: Tumor Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages. IJMS 2021, 22, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M.P.; Chavali, M.S. Recent Advances in Biomaterials for 3D Scaffolds: A Review. Bioactive Materials 2019, 4, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Fu, H.; Han, Z.; Sun, Y. Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: A Review. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 26252–26262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, X. Electrospinning and Emerging Healthcare and Medicine Possibilities. APL Bioengineering 2020, 4, 030901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, X.; Gohil, S.V.; Laurencin, C.T. Biomaterials for Bone Regenerative Engineering. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2015, 4, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, A.; Gelain, F. Synthetic Scaffolds for 3D Cell Cultures and Organoids: Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevers, H. Modeling Development and Disease with Organoids 2016.
- Nemati, S.; Kim, S.; Shin, Y.M.; Shin, H. Current Progress in Application of Polymeric Nanofibers to Tissue Engineering. Nano Convergence 2019, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavo, M.; Serio, F.; Kale, N.R.; D’Amone, E.; Gigli, G.; del Mercato, L.L. Electrospun Nanofibers in Cancer Research: From Engineering of in Vitro 3D Cancer Models to Therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4887–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abazari, M.F.; Zare Karizi, S.; Hajati-Birgani, N.; Kohandani, M.; Torabinejad, S.; Nejati, F.; Nasiri, N.; Maleki, M.H.; Mohajerani, H.; Mansouri, V. Curcumin-loaded PHB / PLLA Nanofibrous Scaffold Supports Osteogenesis in Adipose-derived Stem Cells in Vitro. Polym Adv Technol 2021, 32, 3563–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrondo, L.; St. John Manley, R. Electrostatic Fiber Spinning from Polymer Melts. I. Experimental Observations on Fiber Formation and Properties. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. Ed. 1981, 19, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Pramanik, K. Chitosan-Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibers by Free Surface Electrospinning for Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2016, 13, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, W.; Formo, E.; Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Ceramic Nanofibers Fabricated by Electrospinning and Their Applications in Catalysis, Environmental Science, and Energy Technology: CERAMIC NANOFIBERS FABRICATED BY ELECTROSPINNING AND THEIR APPLICATIONS. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Hu, B.; Yao, Q.-F.; Wang, K.; Yu, S.-H. Large-Scale Synthesis of Flexible Free-Standing SERS Substrates with High Sensitivity: Electrospun PVA Nanofibers Embedded with Controlled Alignment of Silver Nanoparticles. Available online: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/nn900812f (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Rahaman, M.S.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Mustafa, A. A Review of Heat Treatment on Polyacrylonitrile Fiber. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2007, 92, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, O.; Ucar, N.; Onen, A.; Karacan, I.; Kizildag, N.; Demirsoy, N.; Vurur, O.F.; Borazan, I. Effect of Differently Functionalized Carbon Nanotubes on the Properties of Composite Nanofibres. Indian J. Fibre Text. Tes. 2016, 41, 138–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, A.; Vega, E.; Katiyar, R.; Valentin, R. Functionalized Nanowires from Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers.; Briones, F., Ed.; Maspalomas, Gran Canaria, Spain, 18 May 2007; p. 659106.
- Both Engel, A.; Bechelany, M.; Fontaine, O.; Cherifi, A.; Cornu, D.; Tingry, S. One-Pot Route to Gold Nanoparticles Embedded in Electrospun Carbon Fibers as an Efficient Catalyst Material for Hybrid Alkaline Glucose Biofuel Cells. ChemElectroChem 2016, 3, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, J.A.; Mamun, S.A. Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Mats Containing Titania/AgNP Composite Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Applications. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Konar, M.; Sahoo, H.; Hota, G. Surface Functionalization of Electrospun PAN Nanofibers with ZnO–Ag Heterostructure Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Antibacterial Study. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 205704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, J.; Menkhaus, T.J.; Varadaraju, H.; Sun, Y.; Fong, H. Antimicrobial Nano-Fibrous Membranes Developed from Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers. Journal of Membrane Science 2011, 369, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grothe, T.; Storck, J.L.; Dotter, M.; Ehrmann, A. Impact of Solid Content in the Electrospinning Solution on the Physical and Chemical Properties of Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Nanofibrous Mats. TEKSTILEC 2020, 63, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.Y.; Ren, J.; Vancso, G.J. Process Optimization and Empirical Modeling for Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Nanofiber Precursor of Carbon Nanofibers. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H. Study on the Thermal Oxidative Stabilization Reactions and the Formed Structures in Polyacrylonitrile during Thermal Treatment. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2017, 140, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyam, H.; Jazar, R.N.; Nunna, S.; Golkarnarenji, G.; Badii, K.; Fakhrhoseini, S.M.; Kumar, S.; Naebe, M. PAN Precursor Fabrication, Applications and Thermal Stabilization Process in Carbon Fiber Production: Experimental and Mathematical Modelling. Progress in Materials Science 2020, 107, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlant, W.J.; Parsons, J.L. Pyrolysis of Polyacrylonitrile. J. Polym. Sci. 1956, 22, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruixue, Z.; Xudong, Z.; Zhongmin, G.; Xiaoyang, L.; Xiaolei, C. Influence of Thermal Temperature on the Structure and Sealed Micropores of Stabilized Polyacrylonitrile Fibers. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2017, 33, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergin, İ.; Ismar, E.; Sarac, A.S. Oxidative Stabilization of Polyacrylonitrile Nanofibers and Carbon Nanofibers Containing Graphene Oxide (GO): A Spectroscopic and Electrochemical Study. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1616–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Ku, B.-C.; Kim, J.; Joh, H.-I. Structural Evolution of Polyacrylonitrile Fibers in Stabilization and Carbonization. ACES 2012, 02, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanderi, J.; Schneider, J.J. Polyacrylonitrile-Derived 1D Carbon Structures via Template Wetting and Electrospinning. Z. anorg. allg. Chem. 2009, 635, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.C.; Ahn, W.; Kim, C.Y. Reaction Mechanisms of Polyacrylonitrile on Thermal Treatment. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1993, 33, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzer, E.; Müller, D.J. The Influence of Oxygen on the Chemical Reactions during Stabilization of Pan as Carbon Fiber Precursor. Carbon 1975, 13, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.Xue; Michael, A.McKinney; Charles, A. Wilkie The Thermal Degradation of Polyacrylonitrile - ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www-sciencedirect-com.inc.bib.cnrs.fr/science/article/pii/S0141391097000487?via%3Dihub (accessed on 14 September 2021).
- Alarifi, I.M.; Khan, W.S.; Asmatulu, R. Synthesis of Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile- Derived Carbon Fibers and Comparison of Properties with Bulk Form. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-J.; Wang, C.-G.; Bai, Y.-J.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, B. Effect of Oxygen Uptake and Aromatization on the Skin–Core Morphology during the Oxidative Stabilization of Polyacrylonitrile Fibers - Yu - 2008 - Journal of Applied Polymer Science - Wiley Online Library. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2008, 107, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, Y.B.; Glattauer, V.; Briggs, K.L.; Zappe, S.; Ramshaw, J.A.M. Collagen-Based Layer-by-Layer Coating on Electrospun Polymer Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9198–9204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.; Kara, A.A.; Acartürk, F. Peptide-Protein Based Nanofibers in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 148, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, K.; Tian, H.; Yin, L. The Potential of Electrospinning/Electrospraying Technology in the Rational Design of Hydrogel Structures. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, S.; Wehlage, D.; Juhász Junger, I.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning a Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell. Catalysts 2019, 9, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Is the Organization and Function of the Genome Regulated? | MBInfo. Available online: https://www.mechanobio.info/avada_faq/what-is-genome-regulation-2/ (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Cho, A.-N.; Jin, Y.; Kim, S.; Kumar, S.; Shin, H.; Kang, H.-C.; Cho, S.-W. Aligned Brain Extracellular Matrix Promotes Differentiation and Myelination of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Oligodendrocytes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2019, 11, 15344–15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park Suk-Hee Creation of a Hybrid Scaffold with Dual Configuration of Aligned and Random Electrospun Fibers. ACS applied materials 2016, v. 8, 2826–2832. [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Fu, S.-J. Osteogenesis of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Poly(Dopamine)-Coated Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) Fiber Mats. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 58, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedjari, S.; Hébraud, A.; Eap, S.; Siegwald, S.; Mélart, C.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Schlatter, G. Electrostatic Template-Assisted Deposition of Microparticles on Electrospun Nanofibers: Towards Microstructured Functional Biochips for Screening Applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 83600–83607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kador, K.E.; Alsehli, H.S.; Zindell, A.N.; Lau, L.W.; Andreopoulos, F.M.; Watson, B.D.; Goldberg, J.L. Retinal Ganglion Cell Polarization Using Immobilized Guidance Cues on a Tissue-Engineered Scaffold. Acta Biomaterialia 2014, 10, 4939–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwally, S.; Ferraris, S.; Spriano, S.; Krysiak, Z.J.; Kaniuk, Ł.; Marzec, M.M.; Kim, S.K.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Gruszczyński, A.; Wytrwal-Sarna, M.; et al. Surface Potential and Roughness Controlled Cell Adhesion and Collagen Formation in Electrospun PCL Fibers for Bone Regeneration. Materials & Design 2020, 194, 108915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, Z.; Xu, H.; Ke, Q. An Aligned Porous Electrospun Fibrous Membrane with Controlled Drug Delivery – An Efficient Strategy to Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing with Improved Angiogenesis. Acta Biomaterialia 2018, 70, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Klingner, A. A Review on Electrospun Polymeric Nanofibers: Production Parameters and Potential Applications. Polymer Testing 2020, 90, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; et al. The Effects of Alignment and Diameter of Electrospun Fibers on the Cellular Behaviors and Osteogenesis of BMSCs 2021.
- Han, D.G.; Ahn, C.B.; Lee, J.-H.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Son, K.H. Optimization of Electrospun Poly(Caprolactone) Fiber Diameter for Vascular Scaffolds to Maximize Smooth Muscle Cell Infiltration and Phenotype Modulation. Polymers 2019, 11, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling Surface Morphology of Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers: Effect of Humidity and Molecular Weight in the Electrospinning Process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro- and Nanostructured Surface Morphology on Electrospun Polymer Fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, J.T. Highly Porous Fibers by Electrospinning into a Cryogenic Liquid - PDF Free Download. Available online: https://docecity.com/highly-porous-fibers-by-electrospinning-into-a-cryogenic-liq-5f101e4ba5206.html (accessed on 27 January 2022).
- Nayani, K.; Katepalli, H.; Sharma, C.S.; Sharma, A.; Patil, S.; Venkataraghavan, R. Electrospinning Combined with Nonsolvent-Induced Phase Separation To Fabricate Highly Porous and Hollow Submicrometer Polymer Fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hong, Y. Enhancing Cell Infiltration of Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds in Tissue Regeneration. Bioactive Materials 2016, 1, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Direct Fabrication of Composite and Ceramic Hollow Nanofibers by Electrospinning. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi-avalshahr, A.R.; Nokhasteh, S.; Molavi, A.M.; Mohammad-pour, N.; Sadeghi, M. Tailored PCL Scaffolds as Skin Substitutes Using Sacrificial PVP Fibers and Collagen/Chitosan Blends. IJMS 2020, 21, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, J.; Huang, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Lannutti, J. Improved Cellular Infiltration in Electrospun Fiber via Engineered Porosity. Tissue Engineering 2007, 13, 2249–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Macroporous and Nanofibrous Hyaluronic Acid/Collagen Hybrid Scaffold Fabricated by Concurrent Electrospinning and Deposition/Leaching of Salt Particles. Acta Biomaterialia 2008, 4, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, M.F.; Chan, W.Y.; Chian, K.S.; Rasheed, M.Z.; Anderson, J.M. Fabrication and in Vitro and in Vivo Cell Infiltration Study of a Bilayered Cryogenic Electrospun Poly(D,L-Lactide) Scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2010, 9999A, NA. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, M.F.; Rasheed, M.Z.; Lim, T.C.; Chian, K.S. In Vitro Cell Infiltration and in Vivo Cell Infiltration and Vascularization in a Fibrous, Highly Porous Poly(D,L-Lactide) Scaffold Fabricated by Cryogenic Electrospinning Technique. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 91A, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopherson, G.T.; Song, H.; Mao, H.-Q. The Influence of Fiber Diameter of Electrospun Substrates on Neural Stem Cell Differentiation and Proliferation. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, Q.P.; Sharma, U.; Mikos, A.G. Electrospun Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Microfiber and Multilayer Nanofiber/Microfiber Scaffolds: Characterization of Scaffolds and Measurement of Cellular Infiltration. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.B.; Jeong, S.I.; Bae, M.S.; Yang, D.H.; Heo, D.N.; Kim, C.H.; Alsberg, E.; Kwon, I.K. Highly Porous Electrospun Nanofibers Enhanced by Ultrasonication for Improved Cellular Infiltration. Tissue Engineering Part A 2011, 17, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, C.-H. Gelatin Blending and Sonication of Chitosan Nanofiber Mats Produce Synergistic Effects on Hemostatic Functions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2016, 82, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Both, S.K.; Jansen, J.A. In Vivo Bone Generation via the Endochondral Pathway on Three-Dimensional Electrospun Fibers. Acta Biomaterialia 2013, 9, 4505–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Di, N.; Song, L.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Fabrication of Electrospun Poly(L-Lactide-Co-ɛ-Caprolactone)/Collagen Nanoyarn Network as a Novel, Three-Dimensional, Macroporous, Aligned Scaffold for Tendon Tissue Engineering. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods 2013, 19, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hashaikeh, R.; Arafat, H.A. Development of Eco-Efficient Micro-Porous Membranes via Electrospinning and Annealing of Poly (Lactic Acid). Journal of Membrane Science 2013, 436, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Wise, S.G.; Li, Z.; Maitz, P.K.M.; Young, C.J.; Wang, Y.; Weiss, A.S. Tailoring the Porosity and Pore Size of Electrospun Synthetic Human Elastin Scaffolds for Dermal Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6729–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeney, B.A.; Tambralli, A.; Anderson, J.M.; Andukuri, A.; Lim, D.-J.; Dean, D.R.; Jun, H.-W. Cell Infiltration and Growth in a Low Density, Uncompressed Three-Dimensional Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
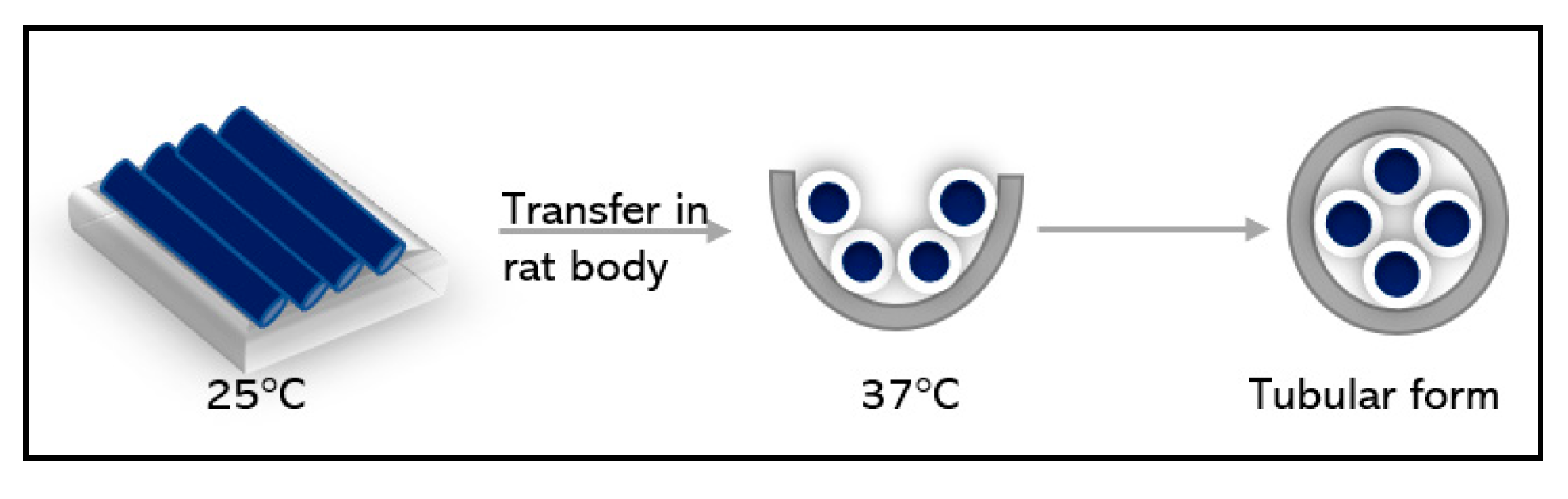
- Chen, L.; AL-Shawk, A.; Rea, C.; Mazeh, H.; Wu, X.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Song, W.; Markel, D.C.; Ren, W. Preparation of Electrospun Nanofibers with Desired Microstructures Using a Programmed Three-Dimensional (3D) Nanofiber Collector. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2020, 106, 110188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, W.; Marhuenda, E.; Reynolds, P.; O’Neill, C.; Pandey, P.; Samuel Wilson, D.G.; Freeley, M.; Huang, D.; Hu, J.; Gondarenko, S.; et al. Regulation of Cardiomyocyte Adhesion and Mechanosignalling through Distinct Nanoscale Behaviour of Integrin Ligands Mimicking Healthy or Fibrotic Extracellular Matrix. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2022, 377, 20220021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhuenda, E. Mécanotransduction des cellules souches de glioblastome dans un nouveau modèle de culture tridimensionnel: implication de la MGAT5 dans la perception de l’environnement mécanique. 280.
- Tanes, M.L.; Xue, J.; Xia, Y. A General Strategy for Generating Gradients of Bioactive Proteins on Electrospun Nanofiber Mats by Masking with Bovine Serum Albumin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5580–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.C.; Rubiano, A.; Dyson, K.; Simmons, C.S. Mechanical Characterization of Human Brain Tumors from Patients and Comparison to Potential Surgical Phantoms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangasser, B.L.; Shamsan, G.A.; Chan, C.E.; Opoku, K.N.; Tüzel, E.; Schlichtmann, B.W.; Kasim, J.A.; Fuller, B.J.; McCullough, B.R.; Rosenfeld, S.S.; et al. Shifting the Optimal Stiffness for Cell Migration. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 15313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handorf, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Halanski, M.A.; Li, W.-J. Tissue Stiffness Dictates Development, Homeostasis, and Disease Progression. Organogenesis 2015, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Ma, J.; Ni, G.; Zhou, S. From Nano to Micro to Macro: Electrospun Hierarchically Structured Polymeric Fibers for Biomedical Applications. Progress in Polymer Science 2018, 81, 80–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavo, M.; Fato, M.; Peñuela, L.; Beltrame, F.; Raiteri, R.; Scaglione, S. Microenvironment Complexity and Matrix Stiffness Regulate Breast Cancer Cell Activity in a 3D in Vitro Model. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 35367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, N.F.; Li, Q.; Melnichouk, O.; Huszti, E.; Martin, L.J.; Gunasekara, A.; Mawdsley, G.; Yaffe, M.J.; Minkin, S. Evidence That Breast Tissue Stiffness Is Associated with Risk of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levental, K.R.; Yu, H.; Kass, L.; Lakins, J.N.; Egeblad, M.; Erler, J.T.; Fong, S.F.T.; Csiszar, K.; Giaccia, A.; Weninger, W.; et al. Matrix Crosslinking Forces Tumor Progression by Enhancing Integrin Signaling. Cell 2009, 139, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, A.M.I.; Ali, A.S.M.; Al-Zeer, M.A.; Barhoum, A.; EL-Hallouty, S.; Shousha, W.G.; Berg, J.; Kurreck, J.; Khalil, A.S.G. Spontaneous Formation of 3D Breast Cancer Tissues on Electrospun Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Nanofibrous Scaffolds. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 2114–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Duan, X.; Wu, L.; Lo, P.-K.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds Promote Breast Cancer Cell Alignment and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Langmuir 2012, 28, 2028–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, C.; Mota, C.; Moscato, S.; D’Alessandro, D.; Ugel, S.; Sartoris, S.; Bronte, V.; Boggi, U.; Campani, D.; Funel, N.; et al. Interfacing Polymeric Scaffolds with Primary Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells to Develop 3D Cancer Models. Biomatter 2014, 4, e955386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.-Y.; Kim, T.-E.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, J.S.; Jin, S.; Yoon, S.; Bae, H.-R.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, Y.H. Three-Dimensional Culture and Interaction of Cancer Cells and Dendritic Cells in an Electrospun Nano-Submicron Hybrid Fibrous Scaffold. IJN 2016, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Betancur, M.; Patel, G.D.; Valmikinathan, C.M.; Mukhatyar, V.J.; Vakharia, A.; Pai, S.B.; Brahma, B.; MacDonald, T.J.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Guiding Intracortical Brain Tumour Cells to an Extracortical Cytotoxic Hydrogel Using Aligned Polymeric Nanofibres. Nature Mater 2014, 13, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Md.A.; Mondal, K.; Singh, C.; Dhar Malhotra, B.; Sharma, A. Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Conjugated Mesoporous Zinc Oxide Nanofibers for Breast Cancer Diagnostics. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7234–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.B.; Singh, V.; Vanjari, S.R.K.; Singh, S.G. One Step Biofunctionalized Electrospun Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Embedded Zinc Oxide Nanowire Interface for Highly Sensitive Detection of Carcinoma Antigen-125. Biosensors and Bioelectronics 2017, 88, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Behera, P.; Viapiano, M.S.; Lannutti, J.J. Rapid Response Oxygen-Sensing Nanofibers. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, 3450–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Tan, Y.; Xu, T.; Yin, D.; Wang, M.; Shen, M.; Chen, X.; Shi, X.; Zhu, X. Hyaluronic Acid-Functionalized Electrospun PLGA Nanofibers Embedded in a Microfluidic Chip for Cancer Cell Capture and Culture. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Mercato, L.L.; Moffa, M.; Rinaldi, R.; Pisignano, D. Ratiometric Organic Fibers for Localized and Reversible Ion Sensing with Micrometer-Scale Spatial Resolution. Small 2015, 11, 6417–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Ye, Z.; Roy, K.; Chinnappan, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Liu, W.; Ghosh, R. A Review on Electrospun Nanofibers Based Advanced Applications: From Health Care to Energy Devices. Polymers 2021, 13, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Tan, H.L.; Ideris, N.; Mohd Zain, Z.; Idris, S.S.; Radacsi, N. Ultra-Sensitive Electrosprayed AuNPs-Decorated PAA/PAN Electrospun Nanofibers as Glucose Sensor. Journal of Materials Research 2021, 36, 4317–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooraninejad, S.; Hoveizi, E.; Hushmandi, K.; Gooraninejad, S.; Tabatabaei, S.R.F. Small Molecule Differentiate PDX1-Expressing Cells Derived from Human Endometrial Stem Cells on PAN Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold: Applications for the Treatment of Diabetes in Rat. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhou, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; He, L.; Ye, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zuo, B.; Zhang, H. Optimization of Electrospun TSF Nanofiber Alignment and Diameter to Promote Growth and Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Applied Surface Science 2012, 261, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabra, S.; Ragab, D.M.; Agwa, M.M.; Rohani, S. Recent Advances in Electrospun Nanofibers for Some Biomedical Applications. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 144, 105224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Zhu, J.P.; Childs, H.R.; Lu, H.H. Nanofiber-Based Transforming Growth Factor-Β3 Release Induces Fibrochondrogenic Differentiation of Stem Cells. Acta Biomaterialia 2019, 93, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Davoodi, P.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Shape Memory Polymer Micro-/Nanofibers and Tailoring Their Roles for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blachowicz, T.; Ehrmann, A. Most Recent Developments in Electrospun Magnetic Nanofibers: A Review. Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics 2020, 15, 155892501990084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieringa, P.; Girao, A.; Ahmed, M.; TruckenmÜller, R.; Welle, A.; Micera, S.; Wezel, R.; Moroni, L. A One-Step Biofunctionalization Strategy of Electrospun Scaffolds Enables Spatially Selective Presentation of Biological Cues. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Shao, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Sun, Q.; Ruan, S. Fibers by Electrospinning and Their Emerging Applications in Bone Tissue Engineering. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, H.; Shen, Y.; Tang, H.; Yi, B.; Qin, C.; Zhang, Y. Shape Memory and Osteogenesis Capabilities of the Electrospun Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate- Co -3-Hydroxyvalerate) Modified Poly( l -Lactide) Fibrous Mats. Tissue Engineering Part A 2021, 27, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, Md.K.; Sun, L.; Ullah, A.; Ullah, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Park, S.; Kato, Y.; Tamada, Y.; Kim, I.S. Polyacrylonitrile/Carbon Black Nanoparticle/Nano-Hydroxyapatite (PAN/NCB/HA) Composite Nanofibrous Matrix as a Potential Biomaterial Scaffold for Bone Regenerative Applications. Materials Today Communications 2021, 27, 102259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, H.S.; Rashid, R.; Amna, T.; Hamid, R.; Sheikh, F.A. Recent Advances in Formulating Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes: Delivering Active Phytoconstituents. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2020, 60, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadian, H. Electro-Conductive Carbon Nanofibers as the Promising Interfacial Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering 2020, 112021.
- Xu, T.; Yang, H.; Yang, D.; Yu, Z.-Z. Polylactic Acid Nanofiber Scaffold Decorated with Chitosan Islandlike Topography for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 21094–21104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Malheiro, A. de B.F.B.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Mota, C.; Wieringa, P.A.; Moroni, L. Direct Writing Electrospinning of Scaffolds with Multidimensional Fiber Architecture for Hierarchical Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 38187–38200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Universitat Politècnica de València, E. Universitat Politècnica de València. ing.agua 2014, 18, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, M.P.; Venugopal, J.R.; Chyan, T.T.; Hai, L.B.; Chan, C.K.; Lim, A.Y.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun Biocomposite Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Neural Tissue Engineering. Tissue Engineering Part A 2008, 14, 1787–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenab, A.; Roghanian, R.; Ghorbani, N.; Ghaedi, K.; Emtiazi, G. The Efficacy of Electrospun PAN/Kefiran Nanofiber and Kefir in Mammalian Cell Culture: Promotion of PC12 Cell Growth, Anti-MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells Activities, and Cytokine Production of PBMC. IJN 2020, Volume 15, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi, A.; Zebarjad, S.M.; Salehi, H.; Katoueizadeh, E.; Alizadeh, A. Assessing Physicochemical, Mechanical, and in Vitro Biological Properties of Polycaprolactone/Poly(Glycerol Sebacate)/Hydroxyapatite Composite Scaffold for Nerve Tissue Engineering. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2022, 275, 125224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Yang, J.; O’Connor, D.M.; Zhu, C.; Huo, D.; Boulis, N.M.; Xia, Y. Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stem Cells into Schwann Cells for the Promotion of Neurite Outgrowth on Electrospun Fibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12299–12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffa, A.; Vocetkova, K.; Sovkova, V.; Rampichova, M.; Filova, E.; Amler, E. Polycaprolactone Nanofiber Mesh with Adhered Liposomes as a Simple Delivery System for Bioactive Growth Factors. Transl Med Rep 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; Qi, Z.; Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Fu, C.; Zheng, S.; Kong, W.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X. Graphene Oxide-PLGA Hybrid Nanofibres for the Local Delivery of IGF-1 and BDNF in Spinal Cord Repair. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 2019, 47, 650–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Tremblay, P.-L.; Zhang, T. Optimizing the Electrical Conductivity of Polyacrylonitrile/Polyaniline with Nickel Nanoparticles for the Enhanced Electrostimulation of Schwann Cells Proliferation. Bioelectrochemistry 2021, 140, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golafshan, N.; Kharaziha, M.; Fathi, M. Tough and Conductive Hybrid Graphene-PVA: Alginate Fibrous Scaffolds for Engineering Neural Construct. Carbon 2017, 111, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Thomopoulos, S.; Xia, Y. Electrospun Nanofibers for Regenerative Medicine. Advanced Healthcare Materials 2012, 1, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, K.; Sun, B.; Fang, J.; Zhang, K.; EI-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X. The Aligned Core–Sheath Nanofibers with Electrical Conductivity for Neural Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7945–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Fan, C.; Zhao, X.; Lu, W.W. Bioinspired Multichannel Nerve Guidance Conduit Based on Shape Memory Nanofibers for Potential Application in Peripheral Nerve Repair. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 12579–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Yu, H.-S.; Lee, H.-H. Nanofibrous Matrices of Poly(Lactic Acid) and Gelatin Polymeric Blends for the Improvement of Cellular Responses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2008, 87A, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhurakkat Perikamana, S.K.; Lee, J.; Ahmad, T.; Kim, E.M.; Byun, H.; Lee, S.; Shin, H. Harnessing Biochemical and Structural Cues for Tenogenic Differentiation of Adipose Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Development of an in Vitro Tissue Interface Mimicking Tendon-Bone Insertion Graft. Biomaterials 2018, 165, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, S.B.; Chainani, A.; Hippensteel, K.J.; Kishan, A.; Gilchrist, C.; Garrigues, N.W.; Ruch, D.S.; Guilak, F.; Little, D. Aligned Multilayered Electrospun Scaffolds for Rotator Cuff Tendon Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomaterialia 2015, 24, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.D.; Nair, L.S.; Nukavarapu, S.P.; McLaughlin, S.; Laurencin, C.T. Novel Nanostructured Scaffolds as Therapeutic Replacement Options for Rotator Cuff Disease. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 2010, 92, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, E.; Yang, L.; Yuan, H.; Tu, W.; Zhang, H.; Yin, Z.; Shen, W.; Chen, X.; et al. An Epigenetic Bioactive Composite Scaffold with Well-Aligned Nanofibers for Functional Tendon Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomaterialia 2018, 66, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Tallawi, M.; Frati, C.; Falco, A.; Gervasi, A.; Quaini, F.; Roether, J.A.; Hochburger, T.; Schubert, D.W.; Seik, L.; et al. Bioactive Electrospun Fibers of Poly(Glycerol Sebacate) and Poly(ε-Caprolactone) for Cardiac Patch Application. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2015, 4, 2012–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, C.; Hendrickson, T.; Whitney, L.V.; Paradiso, F.; Abasi, S.; Tasciotti, E.; Taraballi, F.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Electrospun Electroconductive Constructs of Aligned Fibers for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 2022, 44, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lee, A.-R.; Lin, W.-H.; Lin, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-K.; Tsai, W.-B. Electrospun PLGA Fibers Incorporated with Functionalized Biomolecules for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Tissue Engineering Part A 2014, 20, 1896–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, Y. Induction and Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells into Functional Cardiomyocytes on a Compartmented Monolayer of Gelatin Nanofibers. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 14530–14540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi Amirabad, L.; Massumi, M.; Shamsara, M.; Shabani, I.; Amari, A.; Mossahebi Mohammadi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Vakilian, S.; Steinbach, S.K.; Khorramizadeh, M.R.; et al. Enhanced Cardiac Differentiation of Human Cardiovascular Disease Patient-Specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells by Applying Unidirectional Electrical Pulses Using Aligned Electroactive Nanofibrous Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6849–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, S.; Shevach, M.; Feiner, R.; Dvir, T. Coiled Fiber Scaffolds Embedded with Gold Nanoparticles Improve the Performance of Engineered Cardiac Tissues. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 9410–9414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischer, S.; Shapira, A.; Feiner, R.; Dvir, T. Modular Assembly of Thick Multifunctional Cardiac Patches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2017, 114, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Castell, O.; Ontoria-Oviedo, I.; Badia, J.D.; Amaro-Prellezo, E.; Sepúlveda, P.; Ribes-Greus, A. Conductive Polycaprolactone/Gelatin/Polyaniline Nanofibres as Functional Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Regeneration. Reactive and Functional Polymers 2022, 170, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Huang, C.; Sun, B.; Aqeel, B.M.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Mo, X.; Wan, X. Fabrication and Characterization of Metal Stent Coating with Drug-Loaded Nanofiber Film for Gallstone Dissolution. J Biomater Appl 2016, 31, 784–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shan, H.; Wang, J.; Hou, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, Q.; Guan, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Characterization of Nanostructured Ureteral Stent with Gradient Degradation in a Porcine Model. IJN 2015, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Morsi, Y.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Chen, C.; Mo, X. Application of a Bilayer Tubular Scaffold Based on Electrospun Poly( l -Lactide-Co-Caprolactone)/Collagen Fibers and Yarns for Tracheal Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Cui, Y.; Zheng, L.; Kah-Hoe Chow, P.; Wang, C.-H. Development of a Gene/Drug Dual Delivery System for Brain Tumor Therapy: Potent Inhibition via RNA Interference and Synergistic Effects. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7483–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, J.A.; Liu, R.; Freedman, J.D.; Padera, R.; Schwartz, J.; Colson, Y.L.; Grinstaff, M.W. Prevention of Lung Cancer Recurrence Using Cisplatin-Loaded Superhydrophobic Nanofiber Meshes. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaweera, I.; Levesque-Bishop, D.; Shi, Y.; Di Pasqua, A.J.; Balkus, K.J. Radiotherapeutic Bandage Based on Electrospun Polyacrylonitrile Containing Holmium-166 Iron Garnet Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Skin Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22250–22256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.; Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Ye, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Quan, L.; Pan, C. Design Redox-Sensitive Drug-Loaded Nanofibers for Bone Reconstruction. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Ebara, M.; Aoyagi, T. Temperature-Responsive Electrospun Nanofibers for ‘on–off’ Switchable Release of Dextran. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 2012, 13, 064203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhu, C.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Xia, Y. Integration of Phase-Change Materials with Electrospun Fibers for Promoting Neurite Outgrowth under Controlled Release. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yildirimer, L.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Z.Y.W.; Cao, Z.; Pan, G.; Cui, W. Tumor-Triggered Controlled Drug Release from Electrospun Fibers Using Inorganic Caps for Inhibiting Cancer Relapse. Small 2015, 11, 4284–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achille, C.; Sundaresh, S.; Chu, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M. Cdk2 Silencing via a DNA/PCL Electrospun Scaffold Suppresses Proliferation and Increases Death of Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Orue, I.; Gainza, G.; Gutierrez, F.B.; Aguirre, J.J.; Evora, C.; Pedraz, J.L.; Hernandez, R.M.; Delgado, A.; Igartua, M. Novel Nanofibrous Dressings Containing RhEGF and Aloe Vera for Wound Healing Applications. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2017, 523, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Us 10253328 | PDF | Nucleic Acid Sequence | Gene Expression. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/414235424/Us-10253328 (accessed on 31 January 2022).
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Reda, M.M.; Klingner, A. Preparation and Characterization of Green Carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS) – Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Electrospun Nanofibers Containing Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) and Its Potential Use as Biomaterials. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 151, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-L.; Lai, R.-Y.; Zhuang, C.-H.; Chiu, W.-H.; Lee, K.-M. Microstructure and Biological Properties of Electrospun In Situ Polymerization of Polycaprolactone-Graft-Polyacrylic Acid Nanofibers and Its Composite Nanofiber Dressings. Polymers 2021, 13, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, J.; Ran, B.; Yang, X.; Zheng, W.; Long, Y.; Jiang, X. Small Molecular TGF-Β1-Inhibitor-Loaded Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Preventing Hypertrophic Scars. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32545–32553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.; Pan, G.; Li, B.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W. Surface Biofunctional Drug-Loaded Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Comprehensive Repairing Hypertrophic Scars. Biomaterials 2016, 83, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Cellular and Molecular Basis of Wound Healing in Diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2007, 117, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Galusková, D.; Kaňková, H.; Zheng, K.; Michálek, M.; Liverani, L.; Galusek, D.; Boccaccini, A.R. Electrospun PCL Fiber Mats Incorporating Multi-Targeted B and Co Co-Doped Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles for Angiogenesis. Materials 2020, 13, 4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lv, F.; Li, T.; Han, Y.; Yi, Z.; Liu, M.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Electrospun Micropatterned Nanocomposites Incorporated with Cu 2 S Nanoflowers for Skin Tumor Therapy and Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11337–11349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; An, Q.; Li, D.; Wu, T.; Chen, W.; Sun, B.; Ei-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Zhu, W.; Mo, X. Heparin and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Loaded Poly(L-Lactide-Co-Caprolactone) Nanofiber Covered Stent-Graft for Aneurysm Treatment. j biomed nanotechnol 2015, 11, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Delaney, M.; Frey, M. Anti-Escherichia Coli Functionalized Silver-Doped Carbon Nanofibers for Capture of E. Coli in Microfluidic Systems. Polymers 2020, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufay, M.; Jimenez, M.; Casetta, M.; Chai, F.; Blanchemain, N.; Stoclet, G.; Cazaux, F.; Bellayer, S.; Degoutin, S. PCL Covered PP Meshes Plasma-Grafted by Sulfonated Monomer for the Prevention of Postoperative Abdominal Adhesions. Materials Today Communications 2021, 26, 101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrell, J.A.; Jones, C.G.; Kabandana, G.K.M.; Chen, C. From Cells-on-a-Chip to Organs-on-a-Chip: Scaffolding Materials for 3D Cell Culture in Microfluidics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6667–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, P.; Piscitelli, E.; Marrese, M.; Martino, V.; Cirillo, V.; Guarino, V.; Angeli, E.; Cocola, C.; Pelucchi, P.; Repetto, L.; et al. Integrating Microstructured Electrospun Scaffolds in an Open Microfluidic System for in Vitro Studies of Human Patient-Derived Primary Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3649–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




