Enterprise resources include human resources, financial resources, information resources, technical resources, and market resources. Talent is the foundation of all resources, so talent resources are the most critical part of this indicator, which mainly reflects the technological strength and development potential. Financial resources are fundamental to the economy, and without financial support, optimal allocation of financial resources cannot be achieved. The allocation effect is the actual result of the development of science and technology, and it is also the most intuitive reflection of the level of development of science and technology.
3.1. Current Situation of Resource Management and Allocation
(1) Enterprise Human Resource Management Allocation
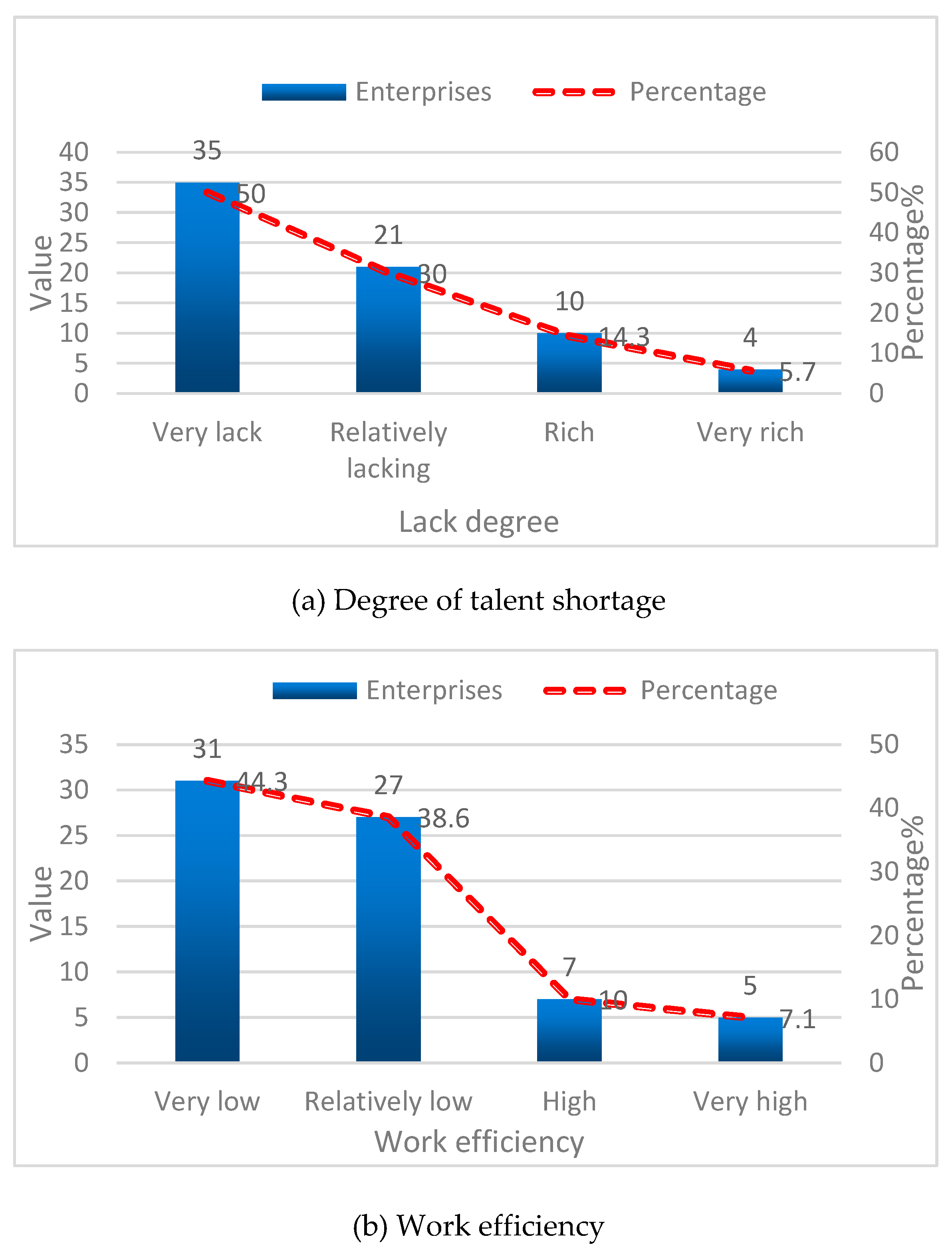
Judging from the proportion of talent in the total population, there is still a certain gap between China and developed countries [
11]. According to relevant surveys, China’s total human resources are relatively small, which is a significant gap from economically developed countries, as well as from some developing countries and emerging industrialized countries. Therefore, the current shortage of frontline personnel in China has not been resolved. Both in terms of quantity and quality, talent needs to be improved.
The reason for China’s talent shortage is that more than half of China’s human resources are trained by the informal education system. Compared with the talents cultivated through formal education, their professional and technical level is still far from satisfactory, which is the main reason for the low overall quality and level of China’s human resources. In recent years, a large proportion of China’s talent has been flowing overseas. As Western developed countries have conducted more in-depth development of human resources, the demand for related talent has also become greater. Stimulated by the rich lives and wages of other countries, China’s human resources have begun to flood into Western countries, resulting in a significant loss of China’s human resources. In accordance with this development trend, China is still unable to maintain a balance between the outflow and inflow of human resources in a short period of time.
(2) Information resource management allocation
Although the country has spent enormous resources on research to obtain information resource data, these data are scattered among different departments and have not been published, leading to the fact that relevant institutions and enterprises in China cannot share them. This has resulted in a very serious waste of resources. Under such circumstances, the development of some enterprises has stagnated due to the lack of corresponding information resource support. Although financial and human resources are the foundation of enterprise survival, they cannot be separated from the support of information resources [
12,
13].
The deficiencies in the allocation of information resources include a lack of overall planning, high investment, high risks, and a lack of unified standards and norms [
14]. However, due to the barriers existing in China’s scientific and technological information resources, this has greatly affected the resource management allocation of Chinese enterprises, and the cost is also increasingly high. Finally, enterprises have been unable to improve their comprehensive competitiveness, and over time, the optimization of their efficiency has become slow. Enterprises in the eastern region not only receive strong support from the government, but also have a sense of technological upgrading. Enterprises in the western region receive relatively little capital and weak awareness, which results in lower productivity in the western region than in the eastern region.
(3) Financial resources
From the perspective of funding sources, the state invests much less in corporate funding than institutions such as research institutions and universities. From the perspective of enterprise size, funds are more invested in large and medium-sized enterprises, while investment in small and medium-sized enterprises is relatively small, so there is less interaction between small and medium-sized enterprises and the government [
15]. Due to the influence of natural conditions and other factors, the economic development of the eastern region is better than that of the western region. Therefore, the country’s economic investment in the east is much higher than that in the west. This has resulted in enterprises in the western region only relying on their own investment to summarize their experience. However, due to their own reasons, companies often encounter financing difficulties, unreasonable compensation and benefits, and other issues.
Compared with small and medium-sized enterprises in the eastern region, small and medium-sized enterprises in the western region would develop slowly due to external reasons such as geography, policy environment, and internal reasons. This naturally leads to the instability of their own capital chain, which affects the overall allocation of resources by enterprises. In short, from the perspective of financial resources, the irrational structure of government investment and enterprise investment can lead to an uneven distribution of resources in the entire distribution system, thereby affecting the optimization of enterprise benefits [
16,
17].
3.2. Benefit Optimization Resource Management Allocation Algorithm Based on Macroeconomic Prediction Model
Whether it is national macroeconomic management or individual investment, it is necessary to predict the development trend of the economy. When forecasting and analyzing China’s macro economy, it is generally based on mathematical models, using regression analysis and other means to analyze and predict relevant economic indicators. The artificial neural network is an intelligent bionic model based on physiology. It simulates the thinking abilities of the human brain, utilizing continuous learning, recollection, induction, and organization of a large number of individual cases to find something with certain regularity among them. This algorithm can achieve large-scale parallel computing.
Macroeconomic forecasting models play an important role in economic decision-making. At the government level, macroeconomic forecasting is an important basis for the country to formulate macroeconomic policies, formulate economic development plans, and conduct macroeconomic regulation. At the enterprise level, the judgment of macroeconomic trends is the primary prerequisite for enterprises to make operational decisions such as production, sales, and investment.
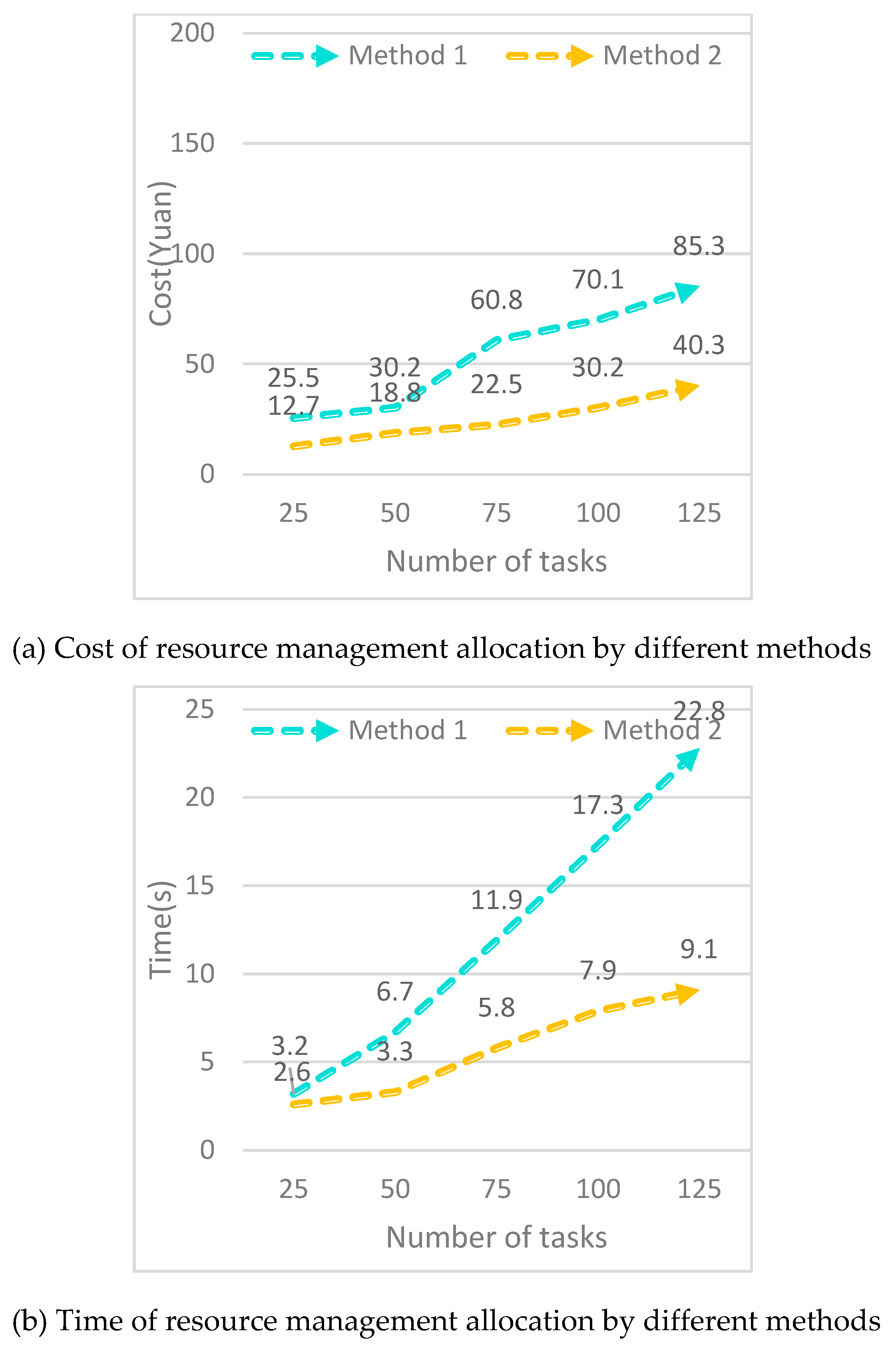
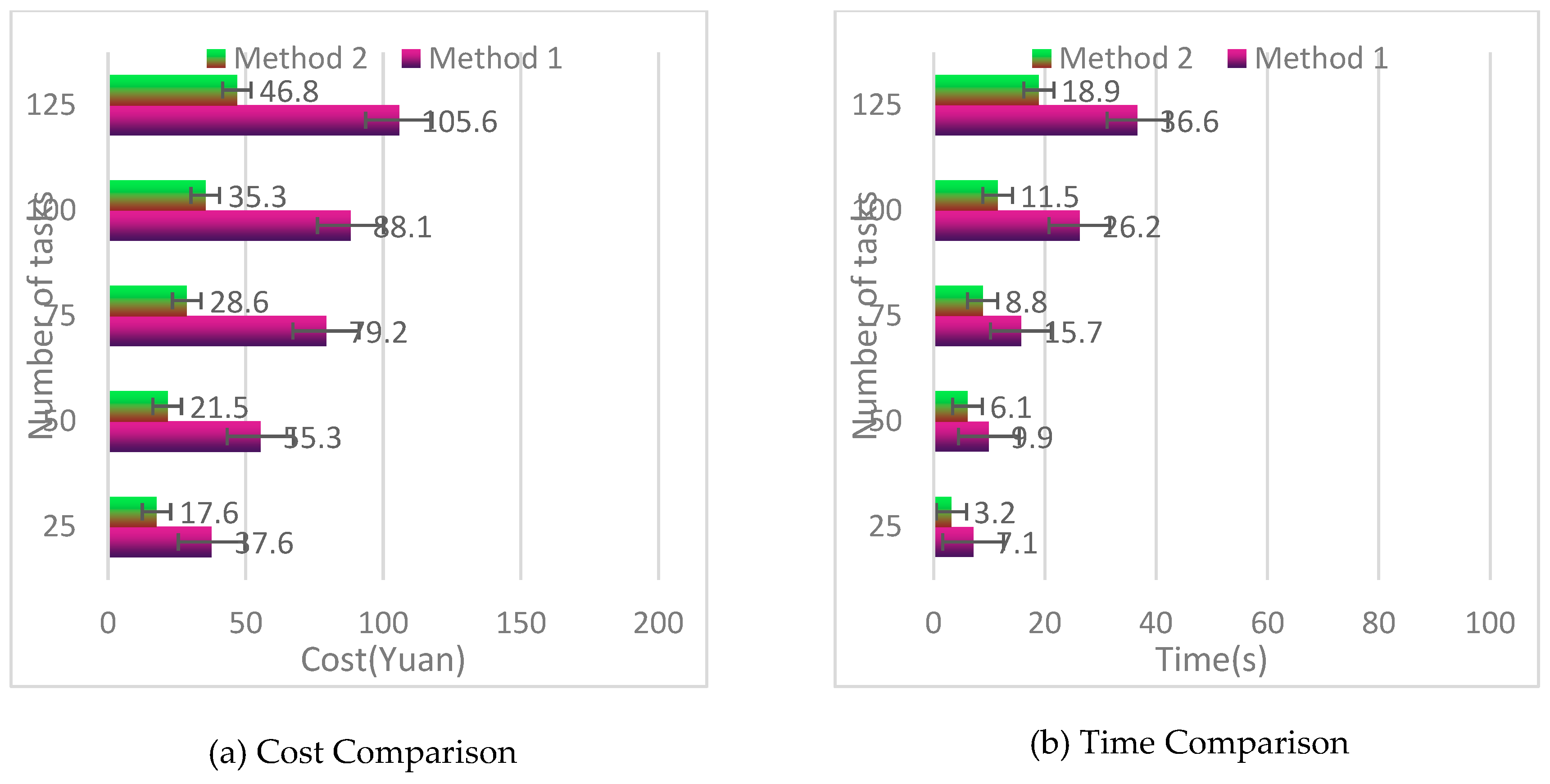
Grid resource scheduling is a very important method, which constructs a revenue function based on time, cost constraints, and user service quality to achieve effective scheduling of grid resources and meet different user needs. Based on the development needs of grid technology, this paper proposes two different scheduling algorithms.
(1) Optimal scheduling algorithm for benefit under auction mechanism
Auction mechanism is currently the most commonly used market based grid resource management and allocation model. The advantage of this model is that when buyers are uncertain about their bids, using this method has high flexibility and high bargaining efficiency. Auction is a good way to allocate resources when resource providers do not know how to value their resources. The efficiency optimization scheduling algorithm under the auction mechanism is relatively mature in theory and has a wide range of applications, and retains some basic characteristics of economic models, consistent with rational pricing in the market.
Since time and cost are the two most important factors that affect benefits, the benefit functions proposed in this paper include cost based benefit functions and time based benefit functions.
In a real economic environment, the optimization of enterprise performance is usually profit oriented. Profit margin is a relative measure that can be used to measure the profitability of an enterprise within a specific period of time. Profit margin can not only evaluate the profit objectives of an enterprise, but also compare the internal and various stages of operation and management of the enterprise. A higher profit margin indicates that the cost of obtaining revenue is lower and the profitability of the enterprise is higher.
The introduction of profit margins in grid scheduling allows for maximum efficiency when executing tasks:
represents the revenue generated by resource i executing n jobs of user j, represents the unit price determined by auction between resource i and user j, and represents the time taken by resource i to complete job k.
Since resources themselves need to pay a certain price when completing tasks submitted by users, the calculation function for resource loss is as follows:
represents the loss incurred by resource i in executing n jobs of user j, and
represents the loss per unit time of resource i. The benefits obtained by the resource after completing the job are as follows:
represents the benefit value obtained by resource i in completing the job submitted by user j. The higher the value, the stronger the ability of resource to obtain benefits, and the greater the benefits obtained by resource. To sum up, the cost based benefit function is:
When a resource cannot meet the time and budget constraints proposed by the user, the benefit function is 0, which means that the job of user j cannot be executed on the resource. When the is larger, the user pays more, and the completion time is shorter, the resource efficiency is greater.
In the initial stage of grid applications, if more resource owners want to invest their resources in the grid, it is necessary to allow resource owners to obtain greater benefits while providing resources. When scheduling, using the benefit function, it can calculate the value of the benefit, and give priority to the users with the greatest benefit, so that users can obtain this resource. In this way, resource providers can obtain the maximum benefits and promote resource providers to provide more grid resources.
(2) Grid resource scheduling algorithm based on benefit function driven
The current grid resource scheduling algorithm is just a simple assumption, that is, users want to complete a task in the shortest time or at the lowest cost, but it does not consider that each user has their own needs. For example, users do not want to complete a task in the shortest time because it may cost a higher cost to obtain a high-performance resource, but users do not want to spend the least cost to complete a task because it may take a longer time to obtain a low-performing resource.
On this basis, an optimization algorithm based on time and cost constraints is proposed. By constructing a benefit function to achieve constraints on time and cost, users can achieve different choices of time and cost through customized constraints, thereby comprehensively reflecting different user needs and improving user satisfaction with resources.
When the user’s preference for time or cost is not very clear, for example, the user does not want to spend the shortest time to complete the task. Because this may lead to greater expenditures, he wants to find a balance between time and cost, which means that he would prioritize the resources that spend the shortest time when the costs are the same. The benefit function relative to time is as follows:
is the predicted time spent by resource i executing user j’s job, and
is the user-defined maximum time limit for completing the job. The smaller the
, the smaller the
value, and the shorter the time the user spends completing the job. The benefit function relative to cost is as follows:
When the price is lower or the completion time is shorter, the
value is smaller, and the user can spend less money to complete the task, better meeting the user’s demand for service quality, and the user’s benefit value is greater. To sum up, the benefit function is defined as follows:
represents the user’s constraint factor on time, and represents the user’s constraint factor on cost.
Realizing resource scheduling through dynamic optimization of time or cost alone cannot accurately reflect users’ needs for time and cost. In resource scheduling, a dynamic user-defined scheduling algorithm based on time and cost is adopted to address users’ requirements for constraints such as time and cost. Based on this, a benefit function is used to allocate the most valuable resources to users. This benefit function reflects the differences in time and cost among different users, and dynamically adjusts different scheduling algorithms based on user needs. This allows it to adapt to the needs of users, consistent with the principles of resource allocation in the actual economic market.