Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Forest fires: Indian scenario
1.2. Forest Fire Scenario in Uttarakhand
2. ST
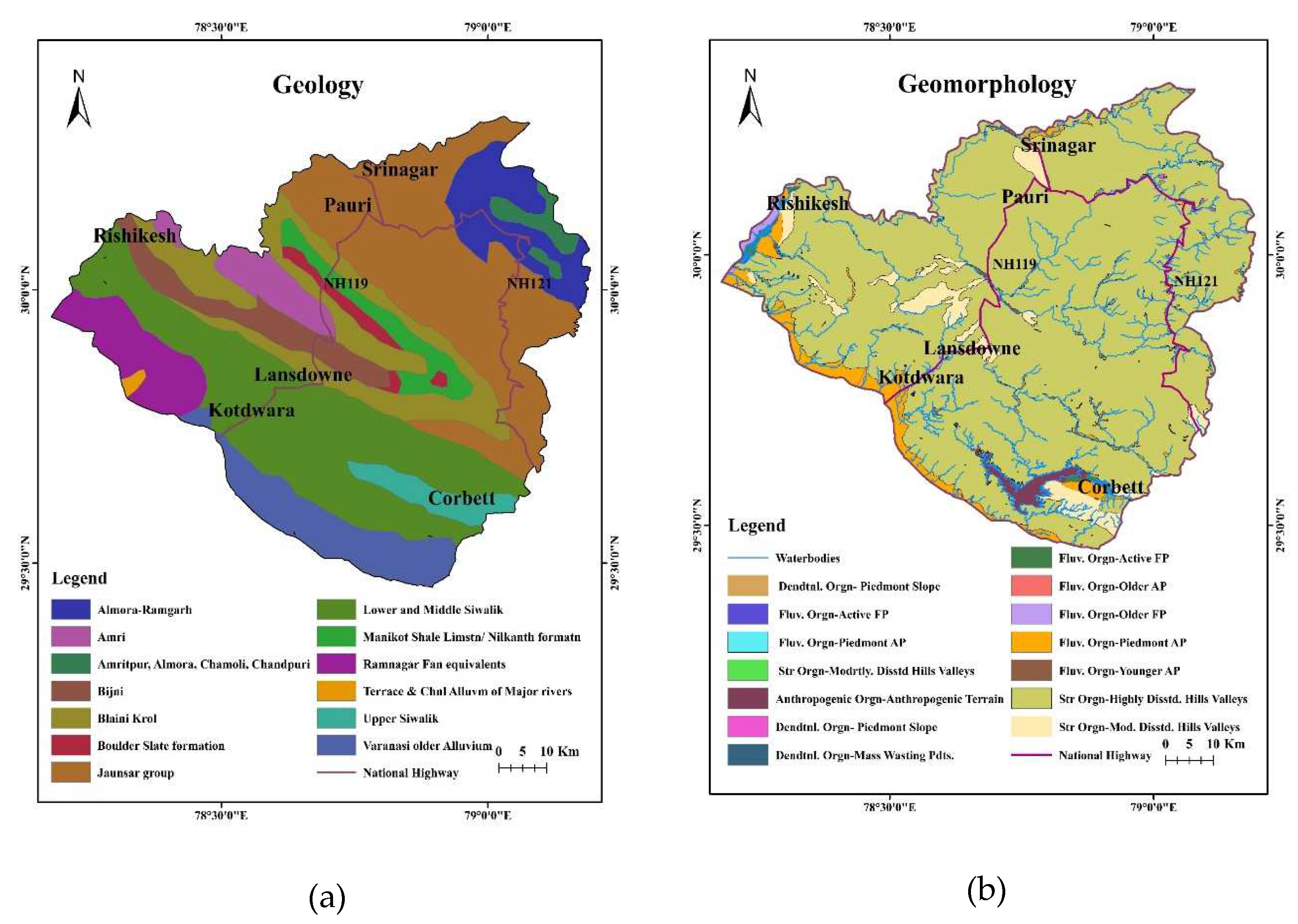
2.1. Geology and Geomorphology
2.2. Tectonic forces
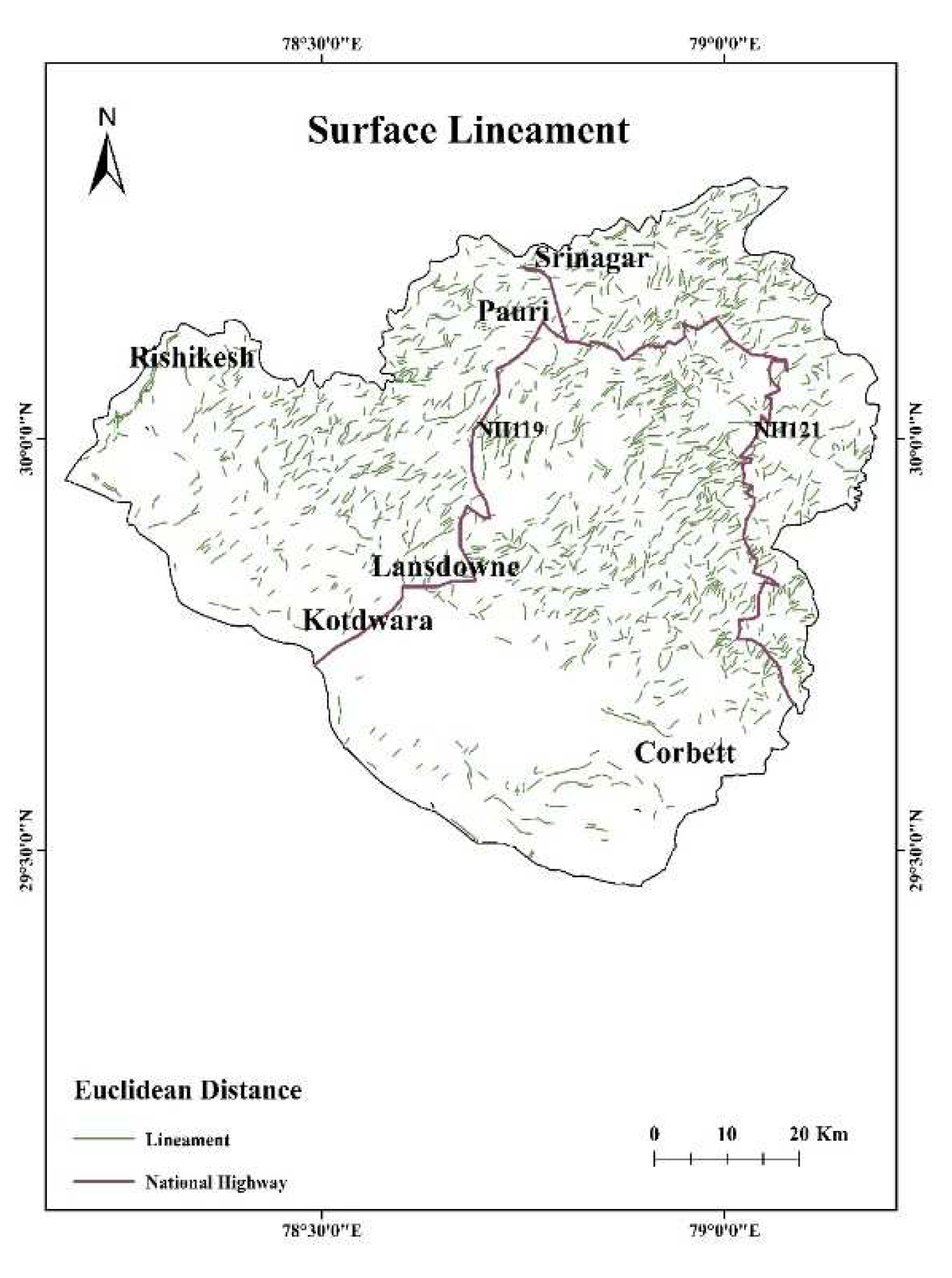
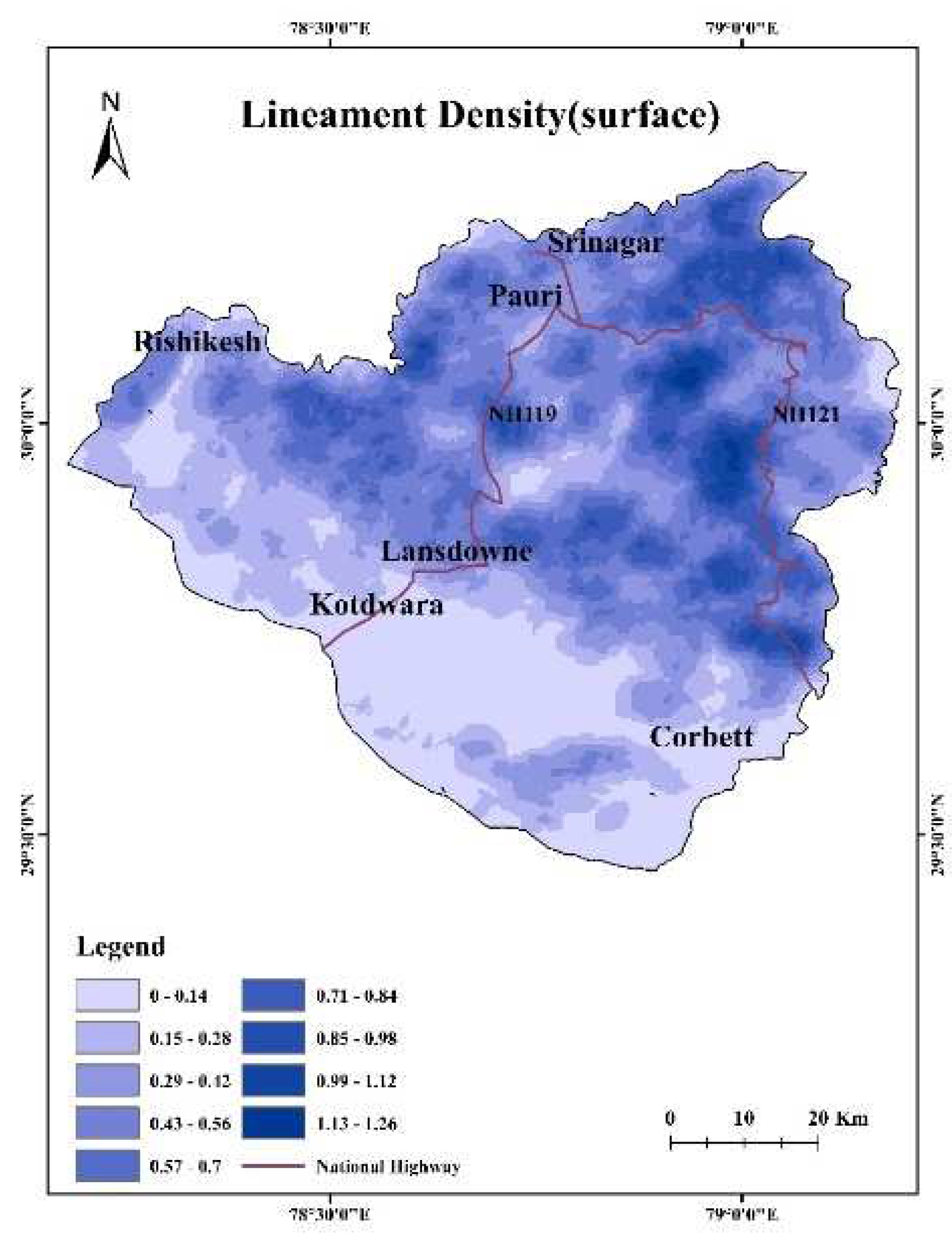
2.3. Lineaments
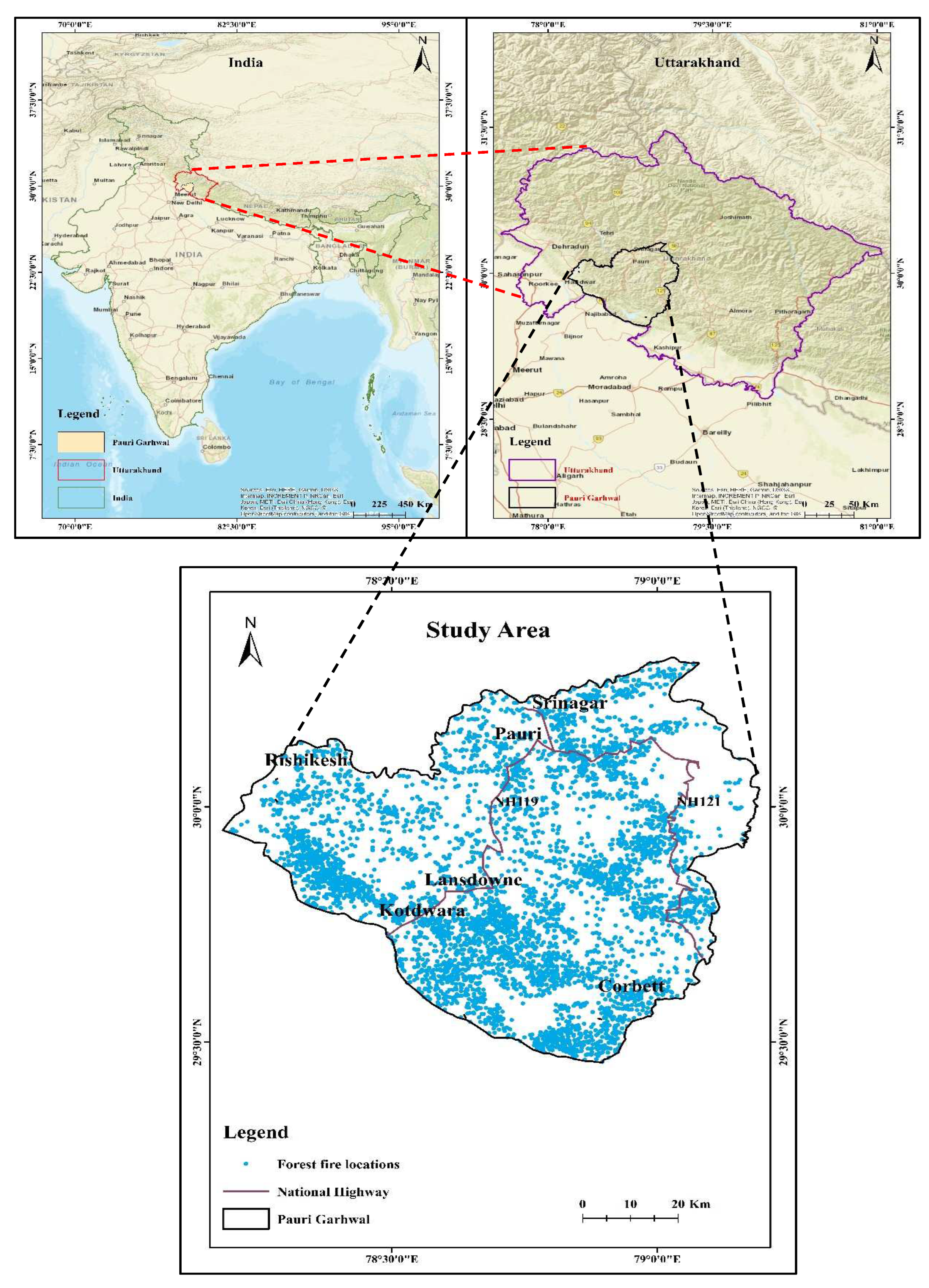
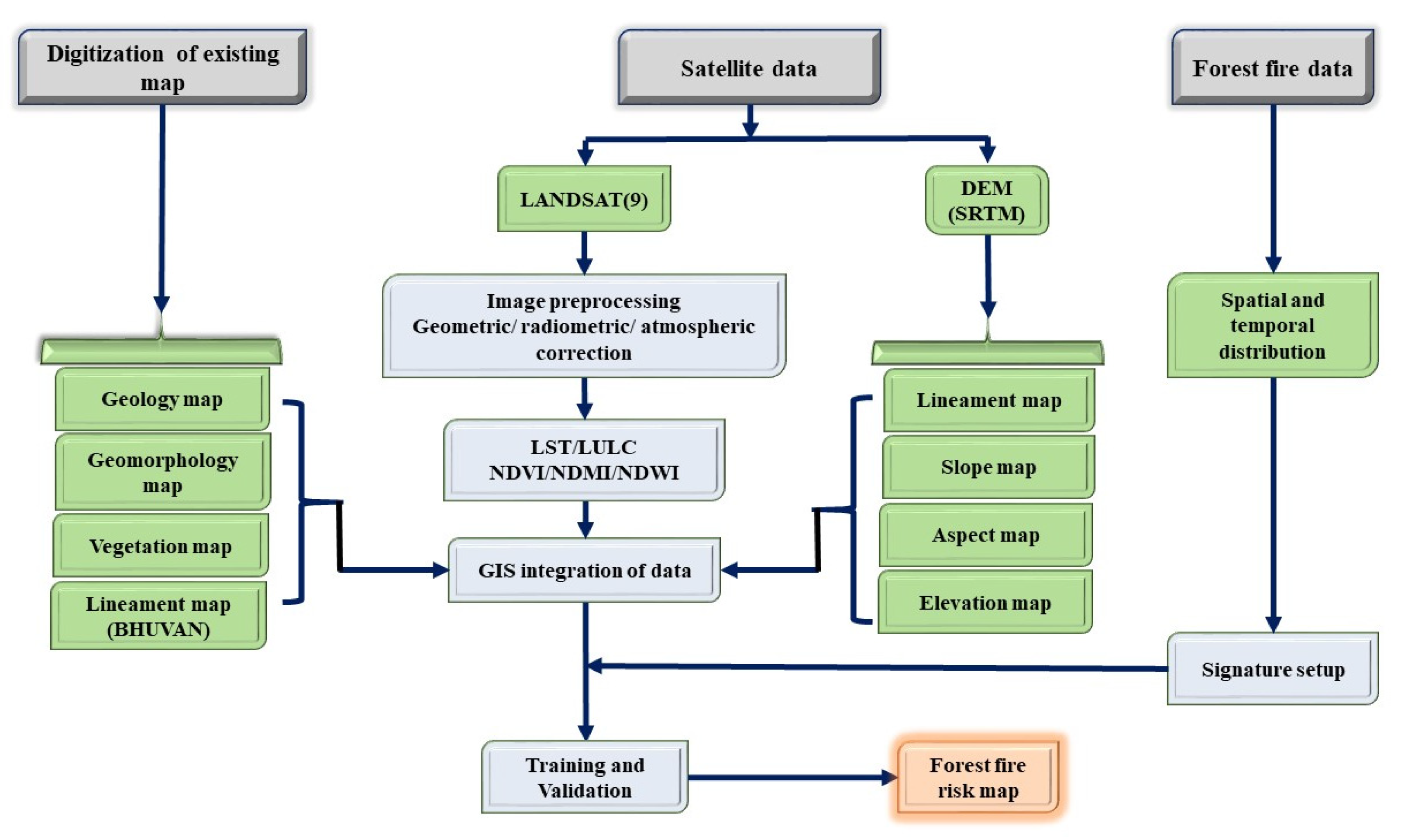
3. Materials and Methods
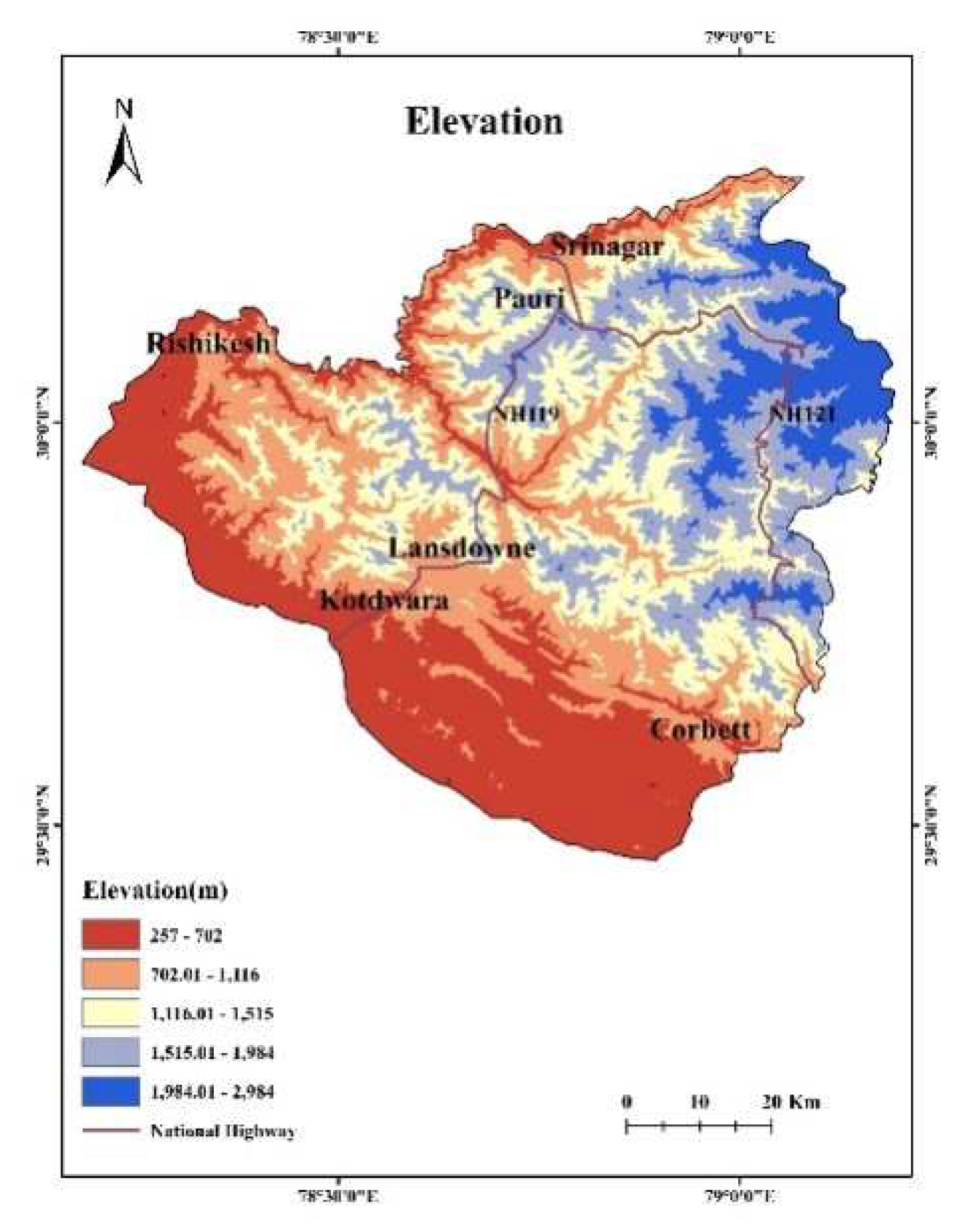
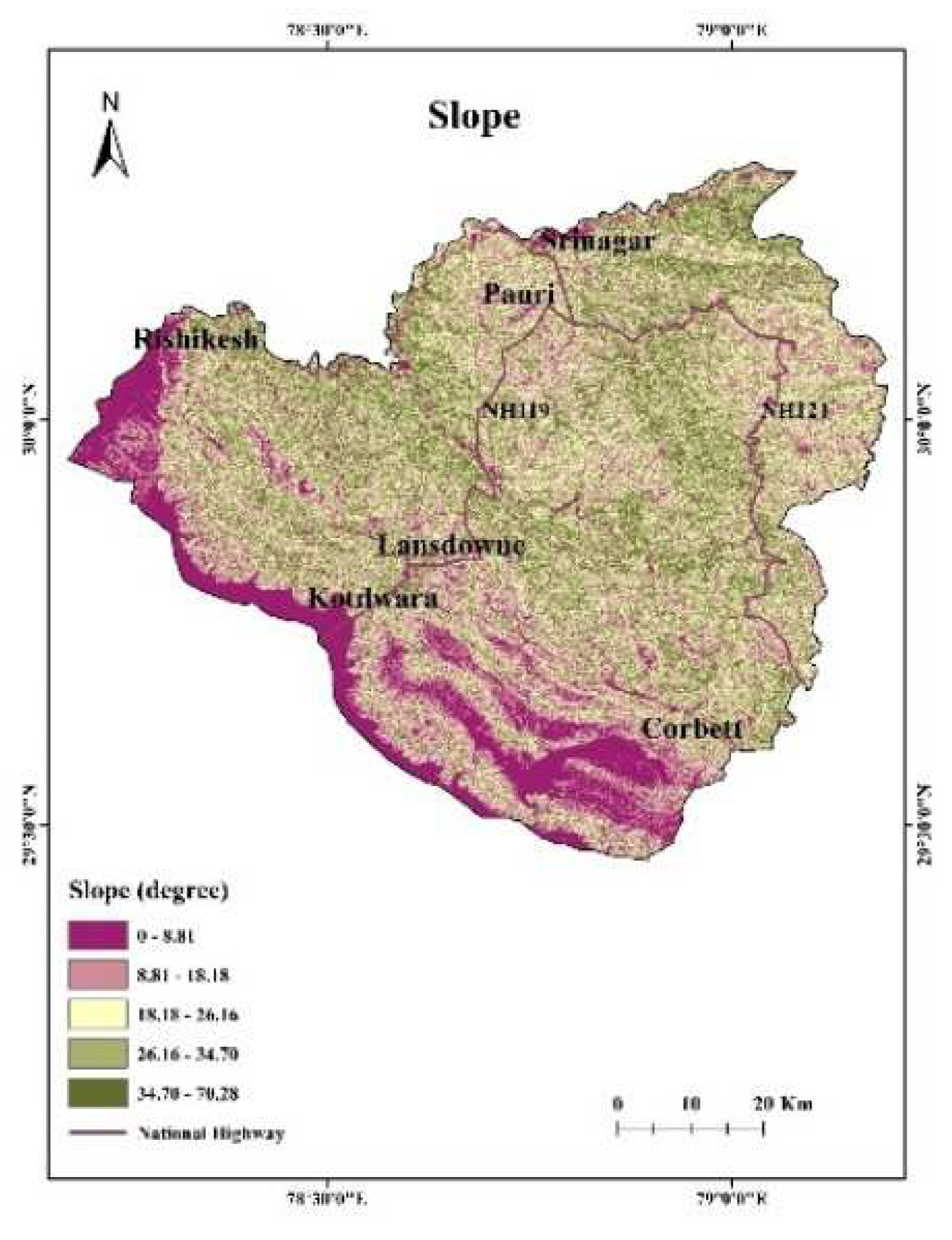
3.1. DEM and its derivatives: The topography data, which includes slope, aspect, and elevation, was acquired using the Digital Elevation Model (DEM) derived from the Shuttle Radar Topographic Mission (SRTM) data of pixel size of 30 m (Figure 4) [7]. The data was assessed through USGS earth explorer website. It was then used to calculate the slope and aspect maps with a spatial resolution of 30m using ArcGIS 10.8 software. Topography is a crucial physiographic component that influences wind behavior, which in turn impacts the area's susceptibility to fire [44].3.2. Landsat Data derivatives: Landsat 9 dataset of 30th March 2023 was downloaded from USGS Earth Explorer website. The dataset was used in preparation of the following maps:
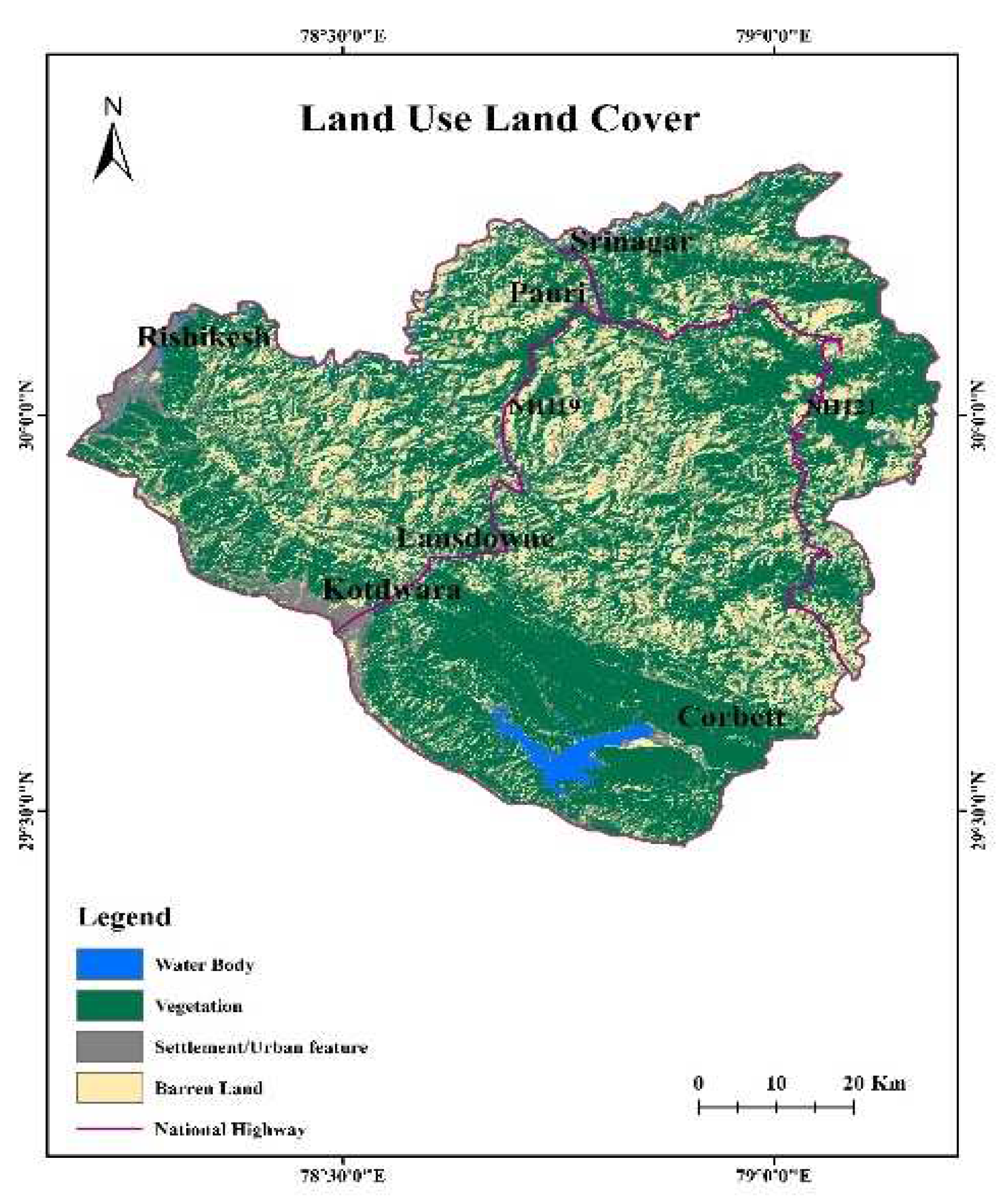
3.2.1. Land Use Land Cover map: The Landsat imagery was used to generate LULC map of the study area. It was done with the help of support vector machine classification. Signatures were fed and the resulting data was classified into 4 classes, namely water, barren, urban/settlement and vegetation.
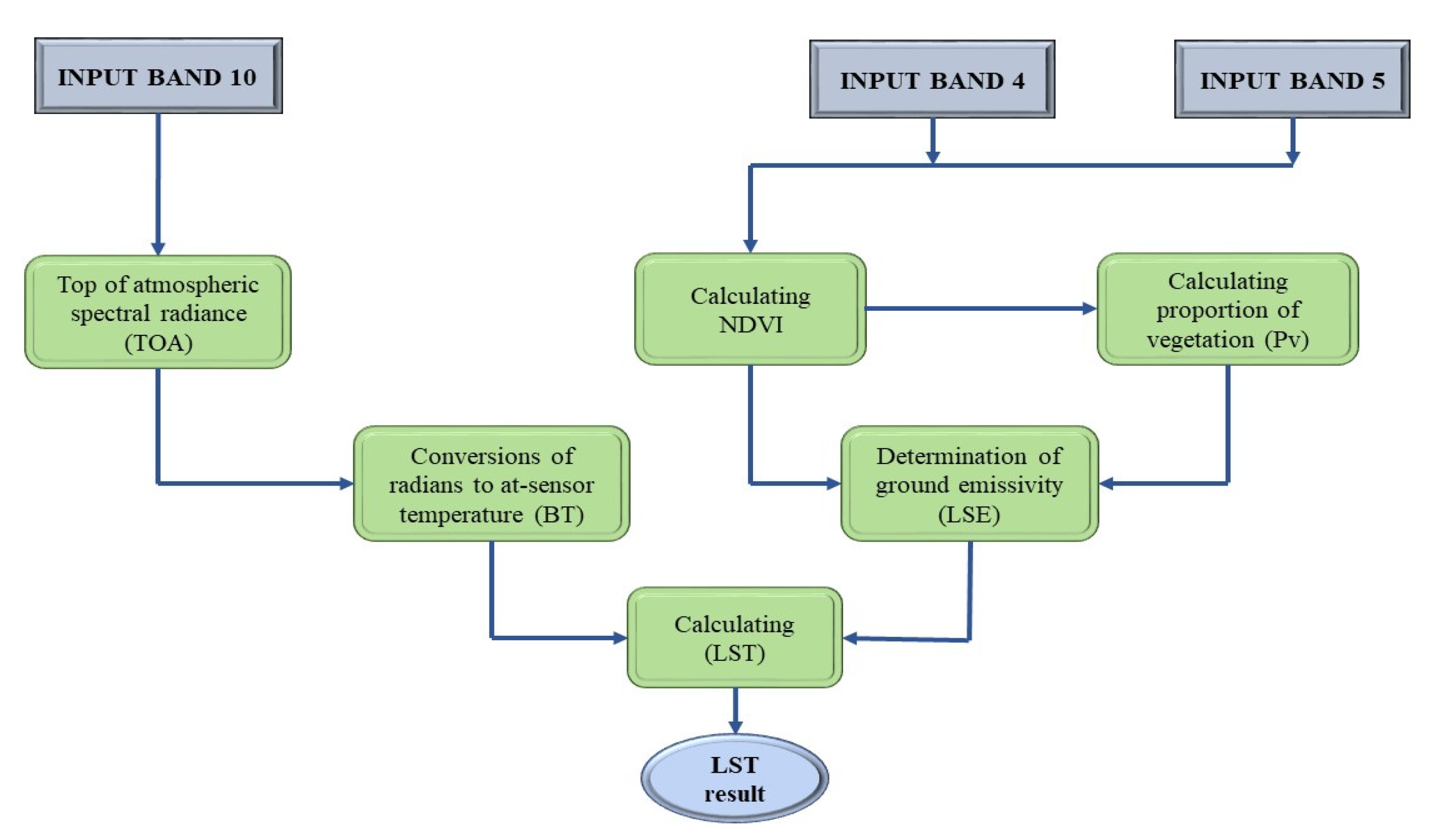
3.2.2. Land Surface Temperature map
3.2.3. Indices used
3.2.4. Forest Fire Data
3.3. Digitization of existing maps
4. Results
4.1. Elevation
4.2. Slope
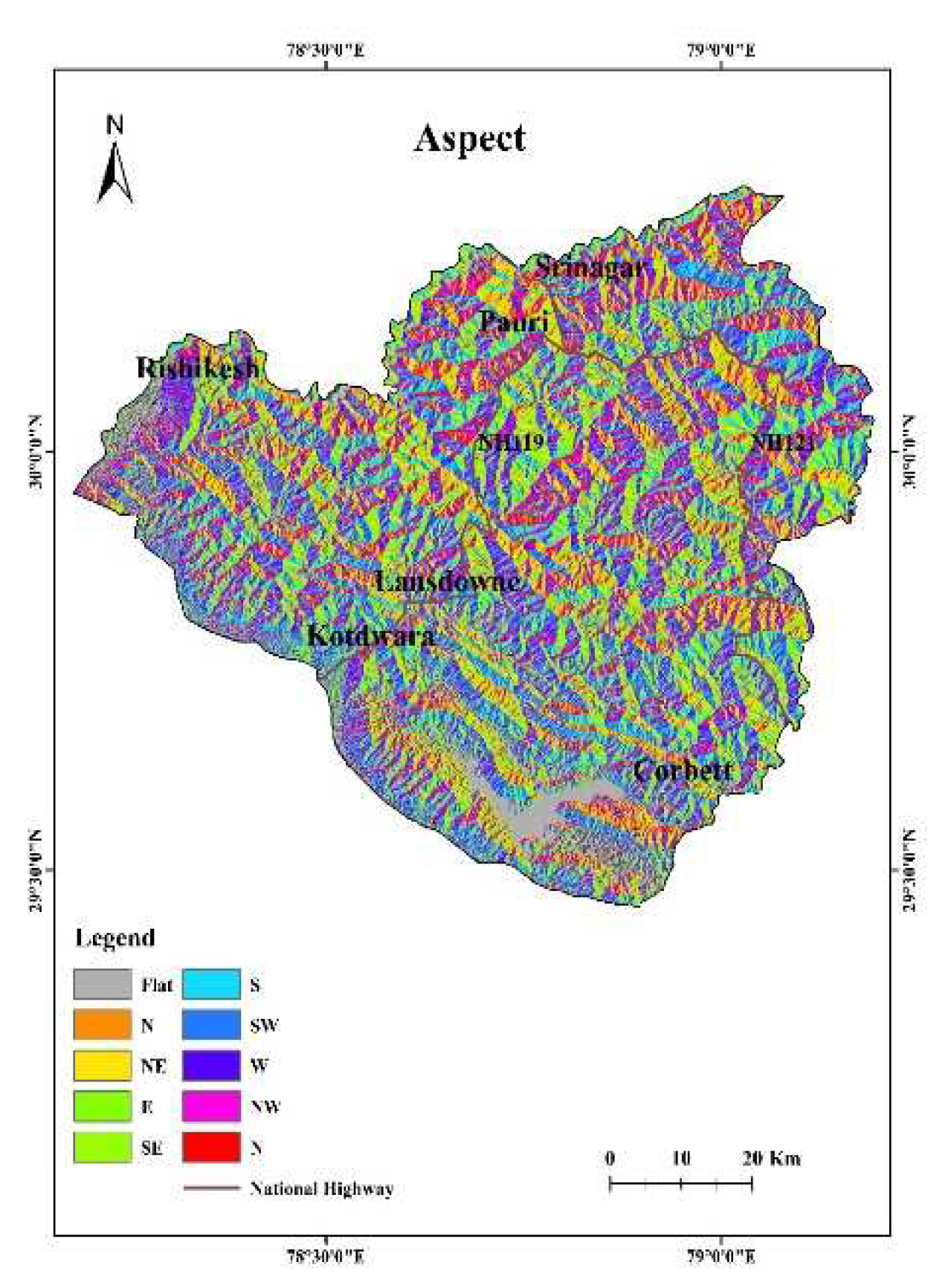
4.3. Aspect
4.4. Land use Land cover
4.5. Lineament Density
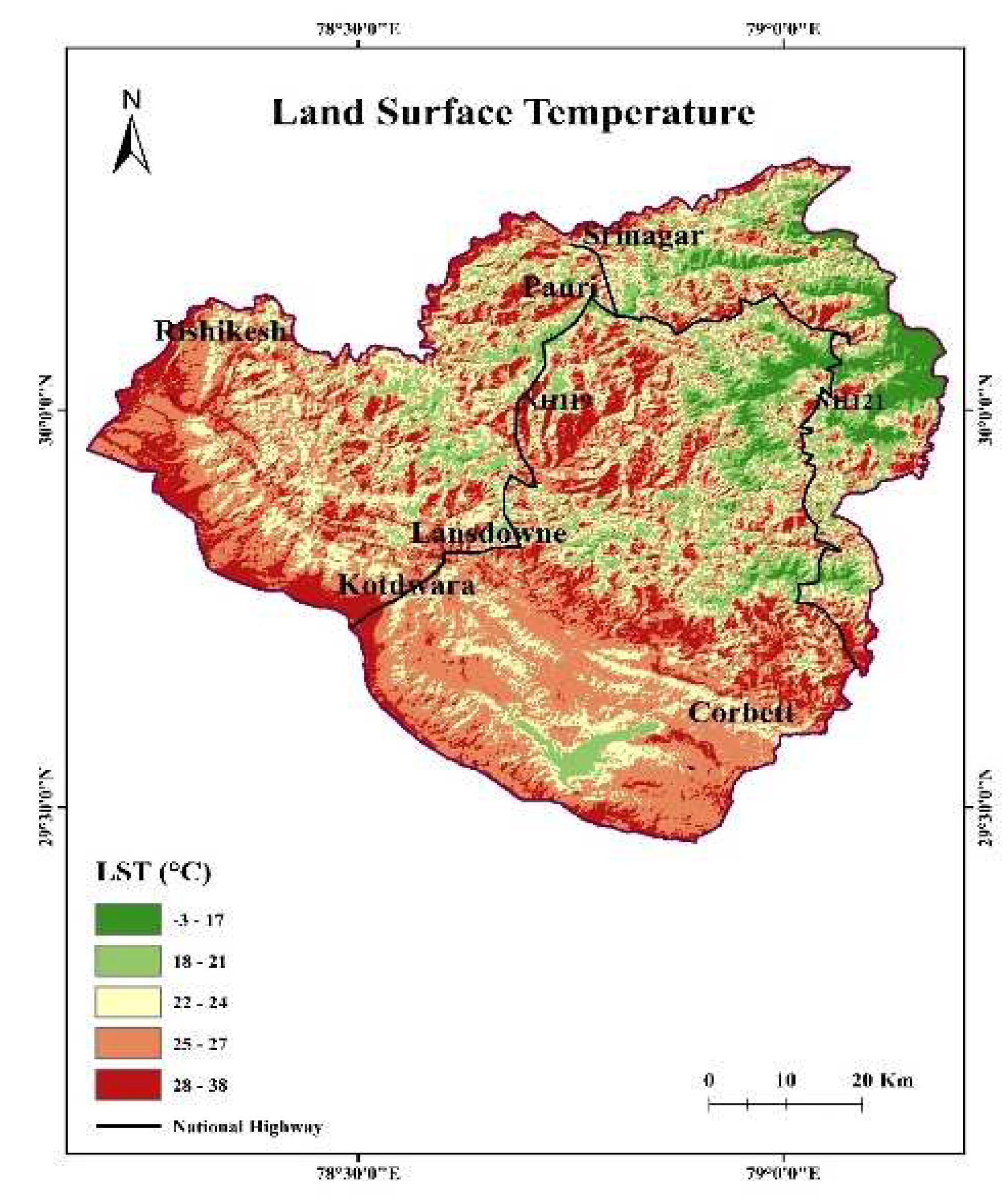
4.6. Land Surface Temperature
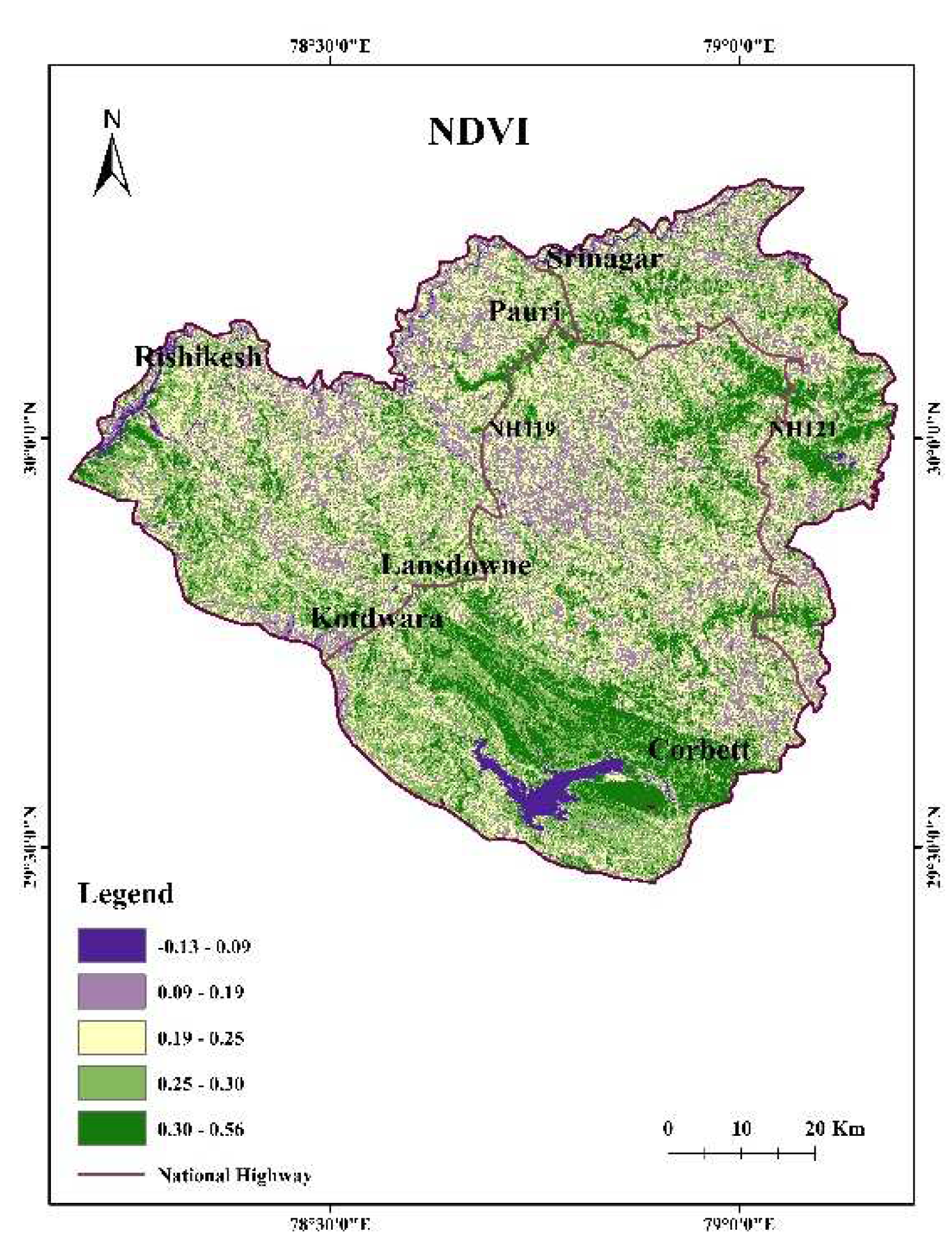
4.7. NDVI
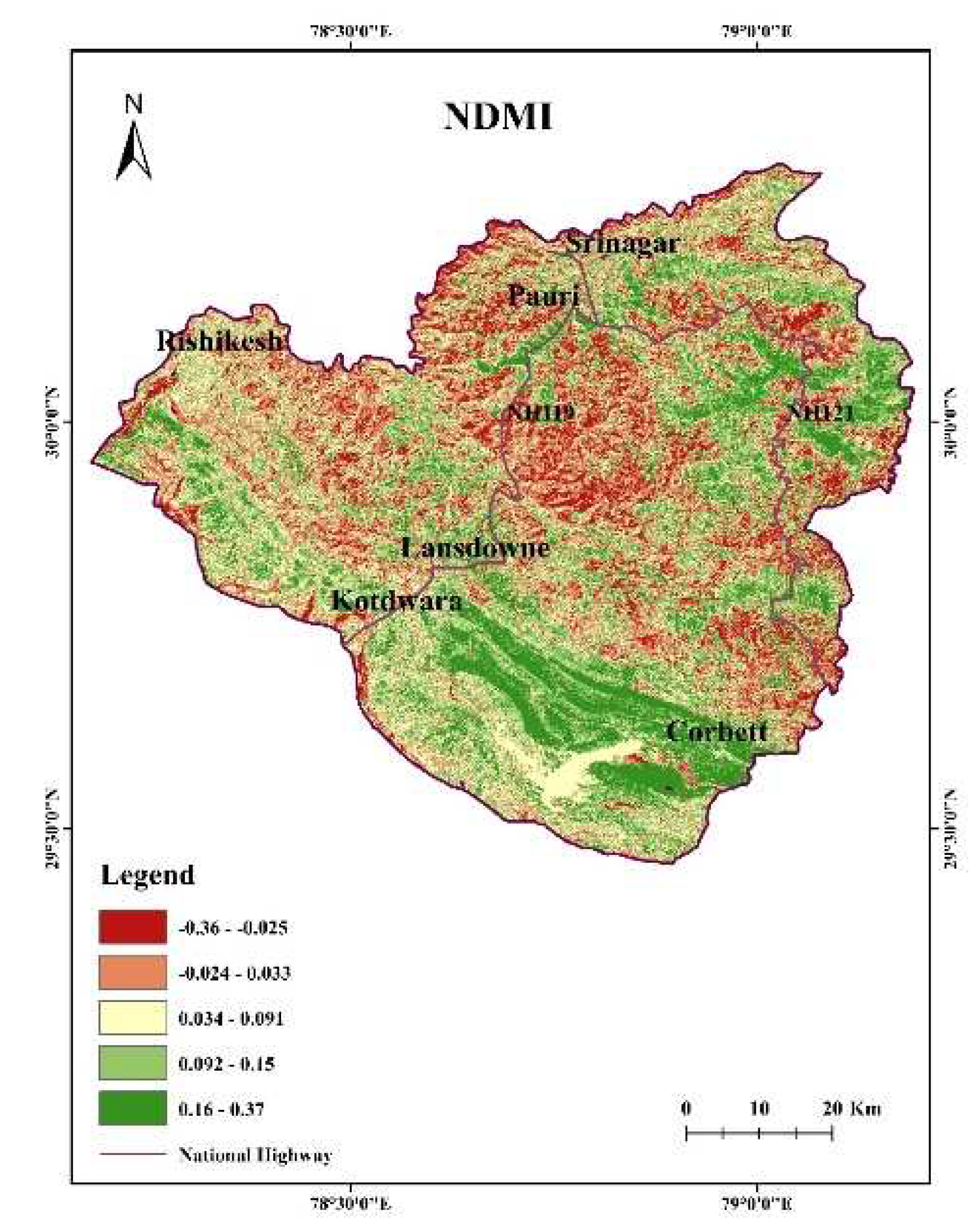
4.8. NDMI
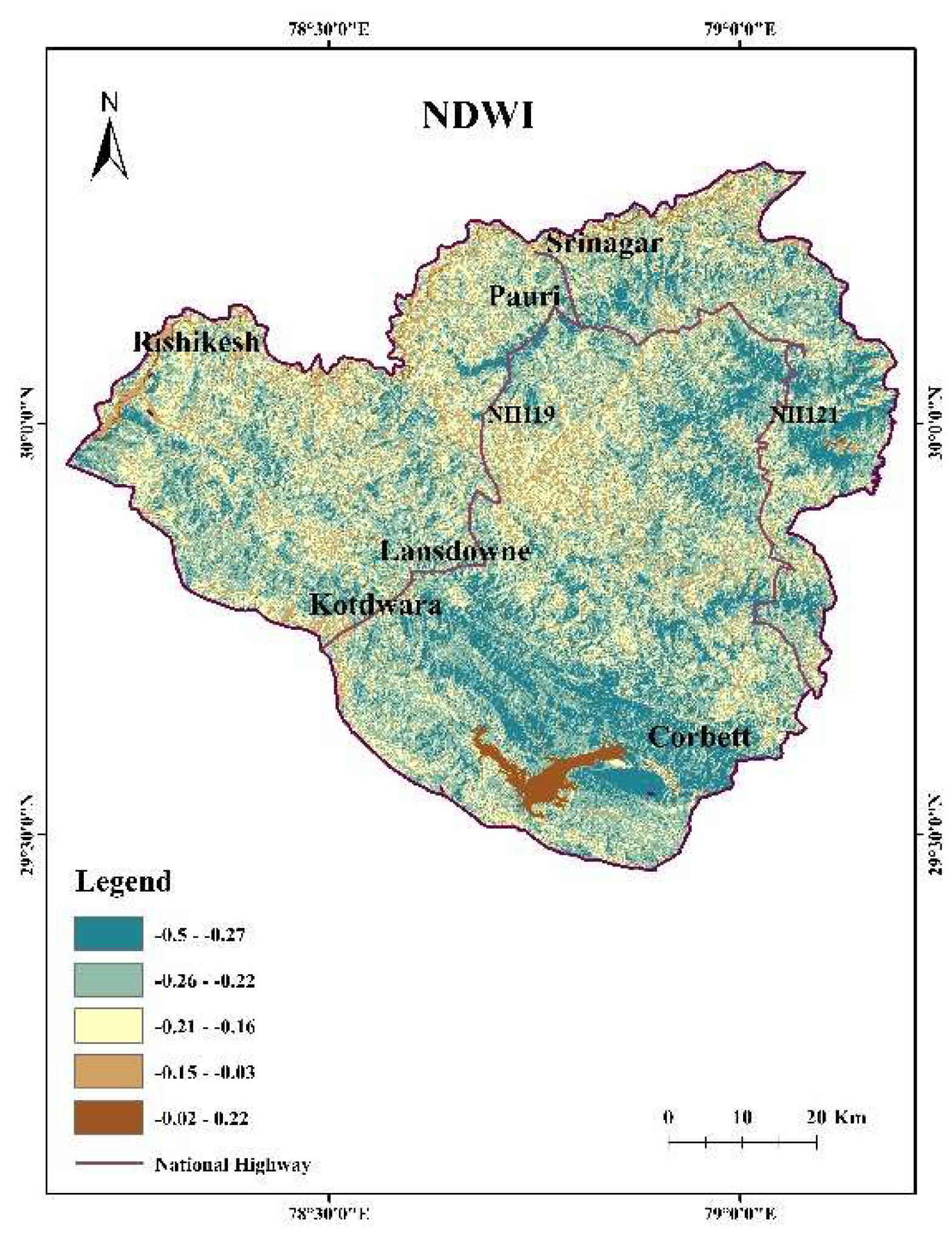
4.9. NDWI
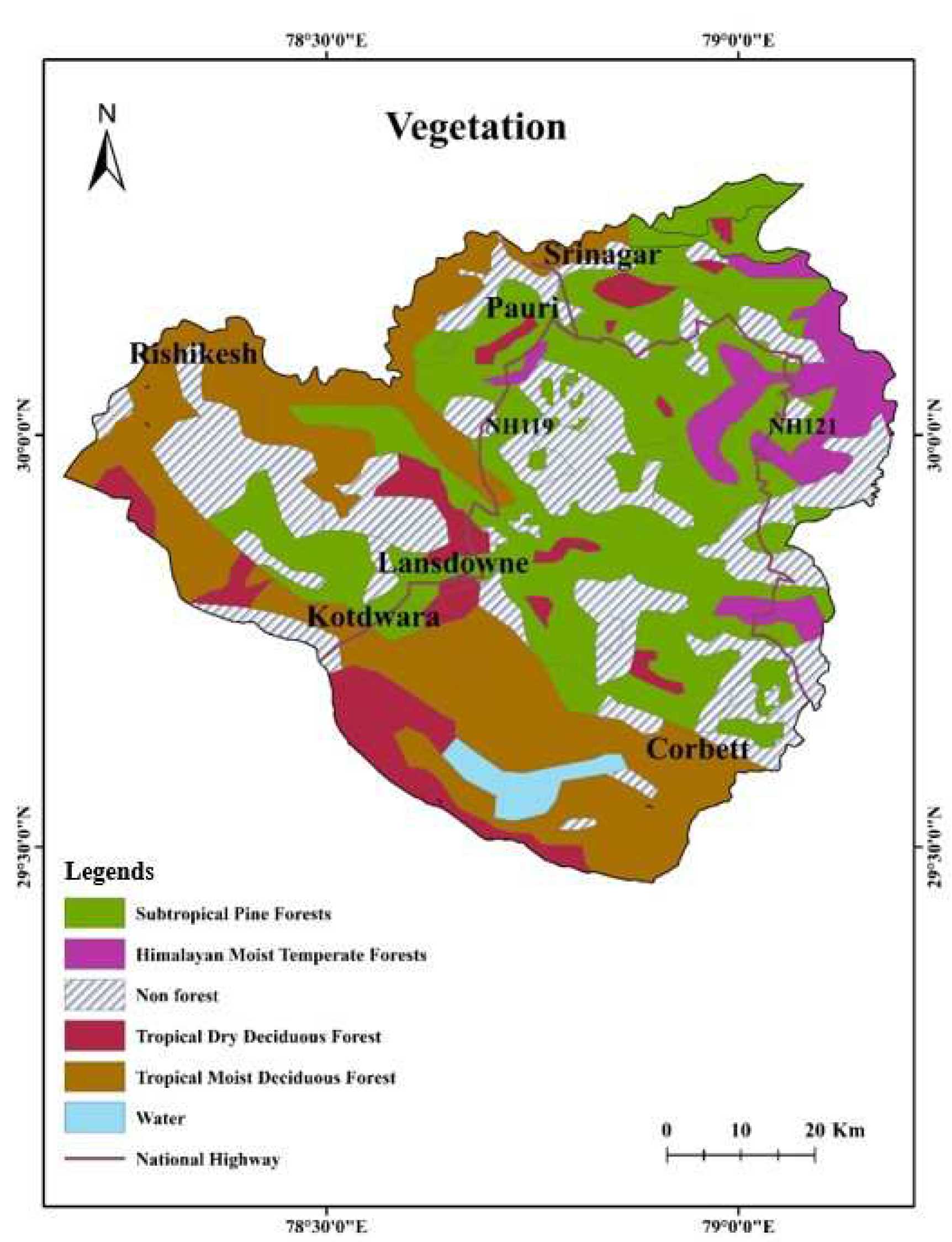
4.10. Vegetation type
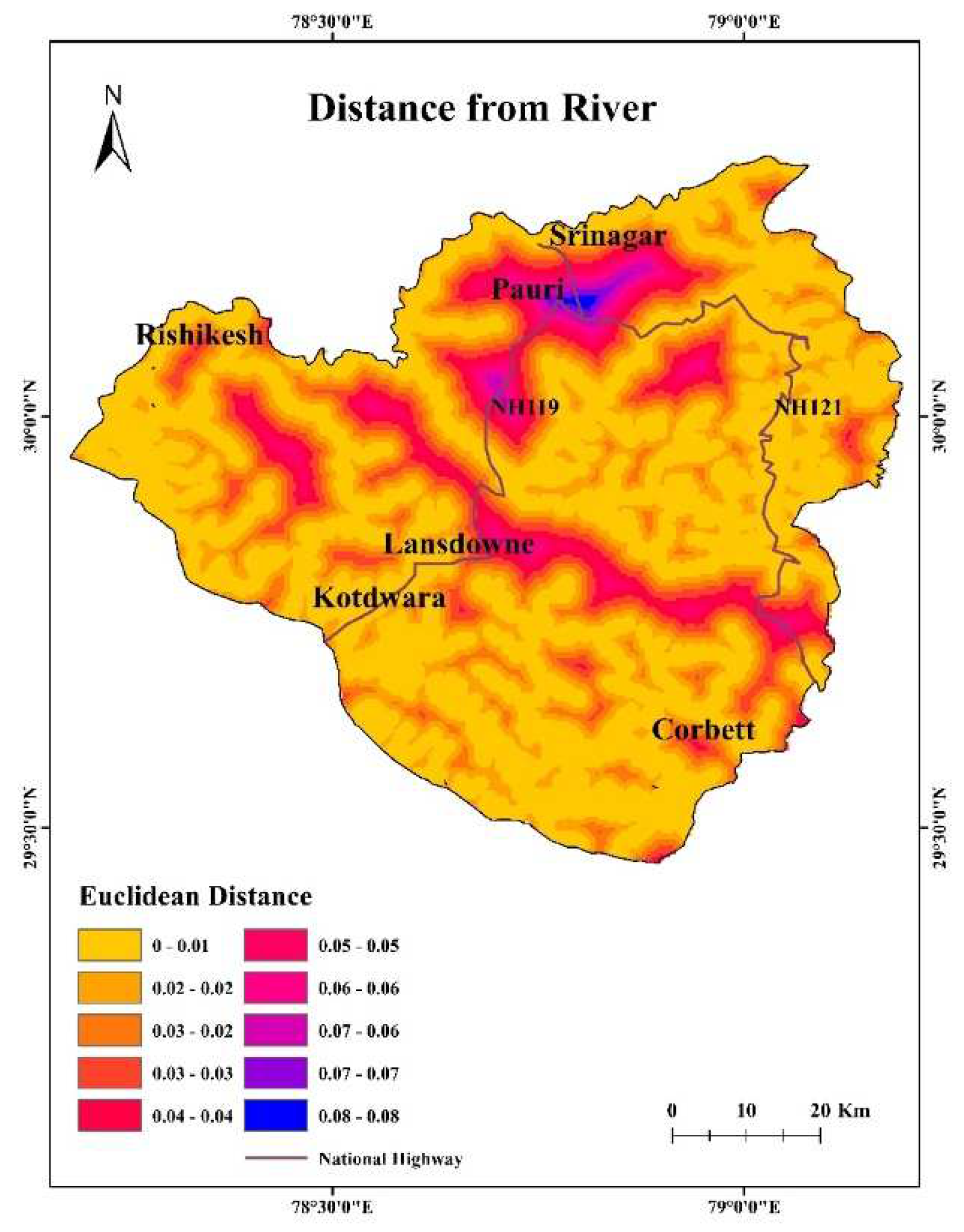
4.11. Distance from Rivers
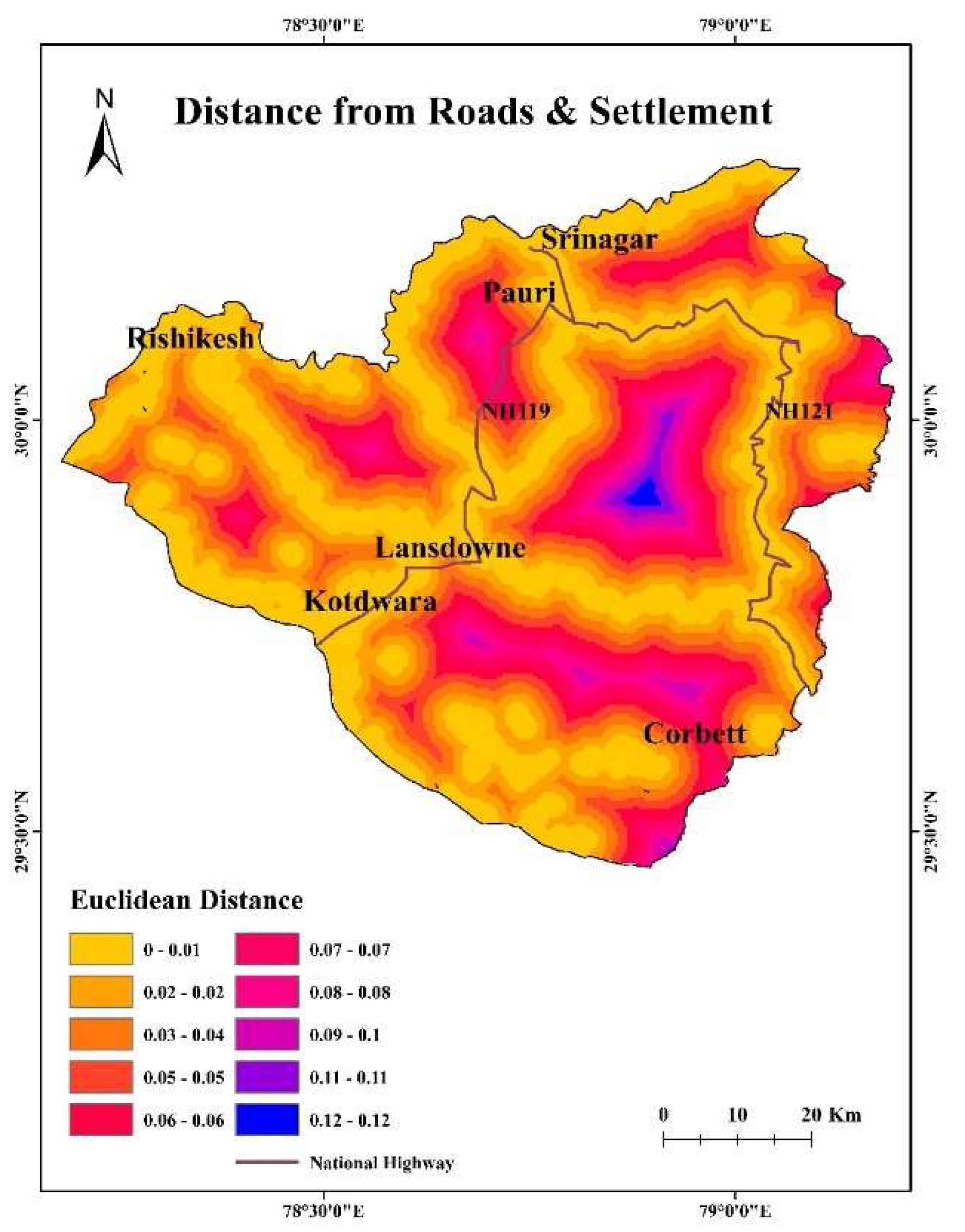
4.12. Distance from roads and settlements
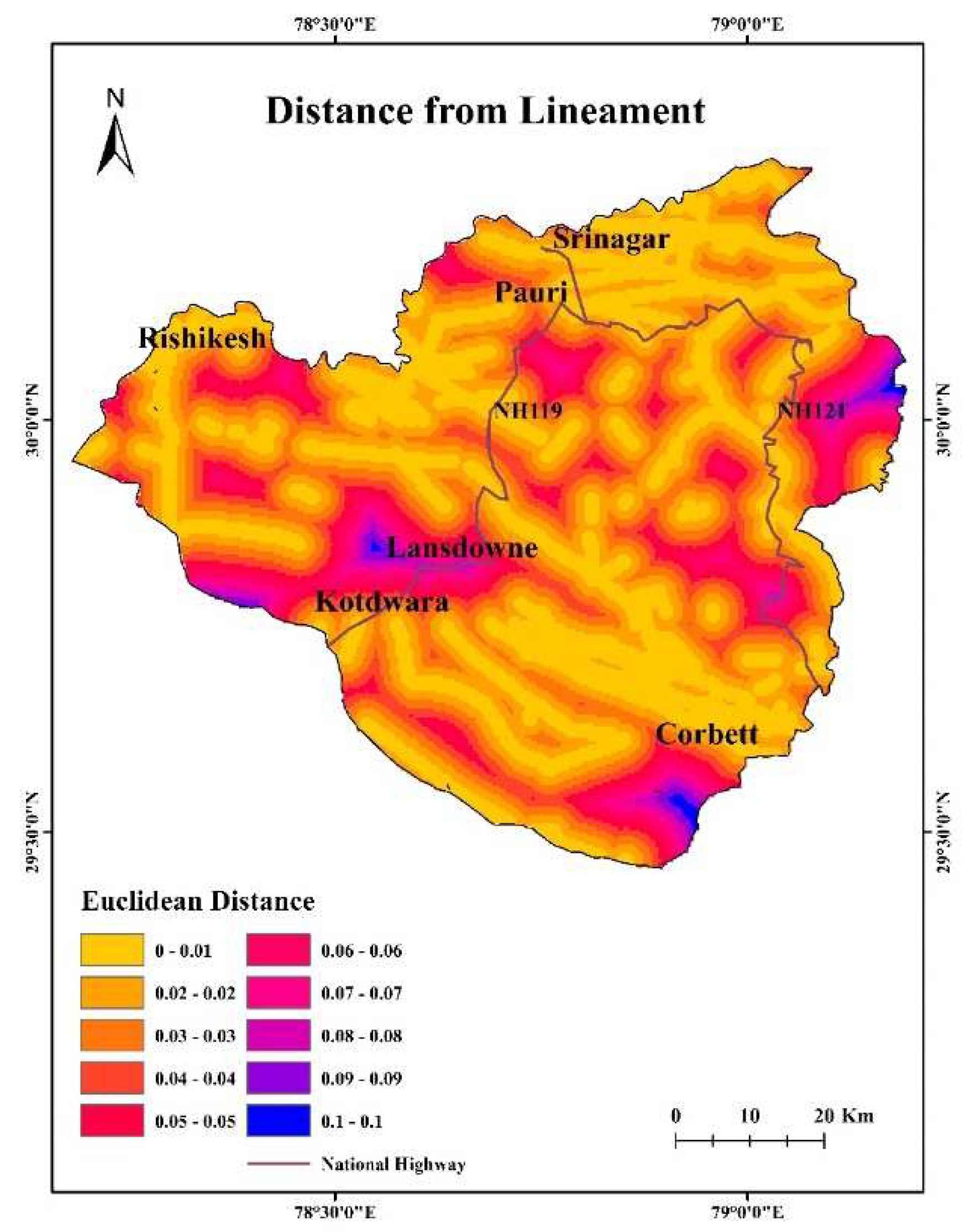
4.13. Distance from deep seated lineaments
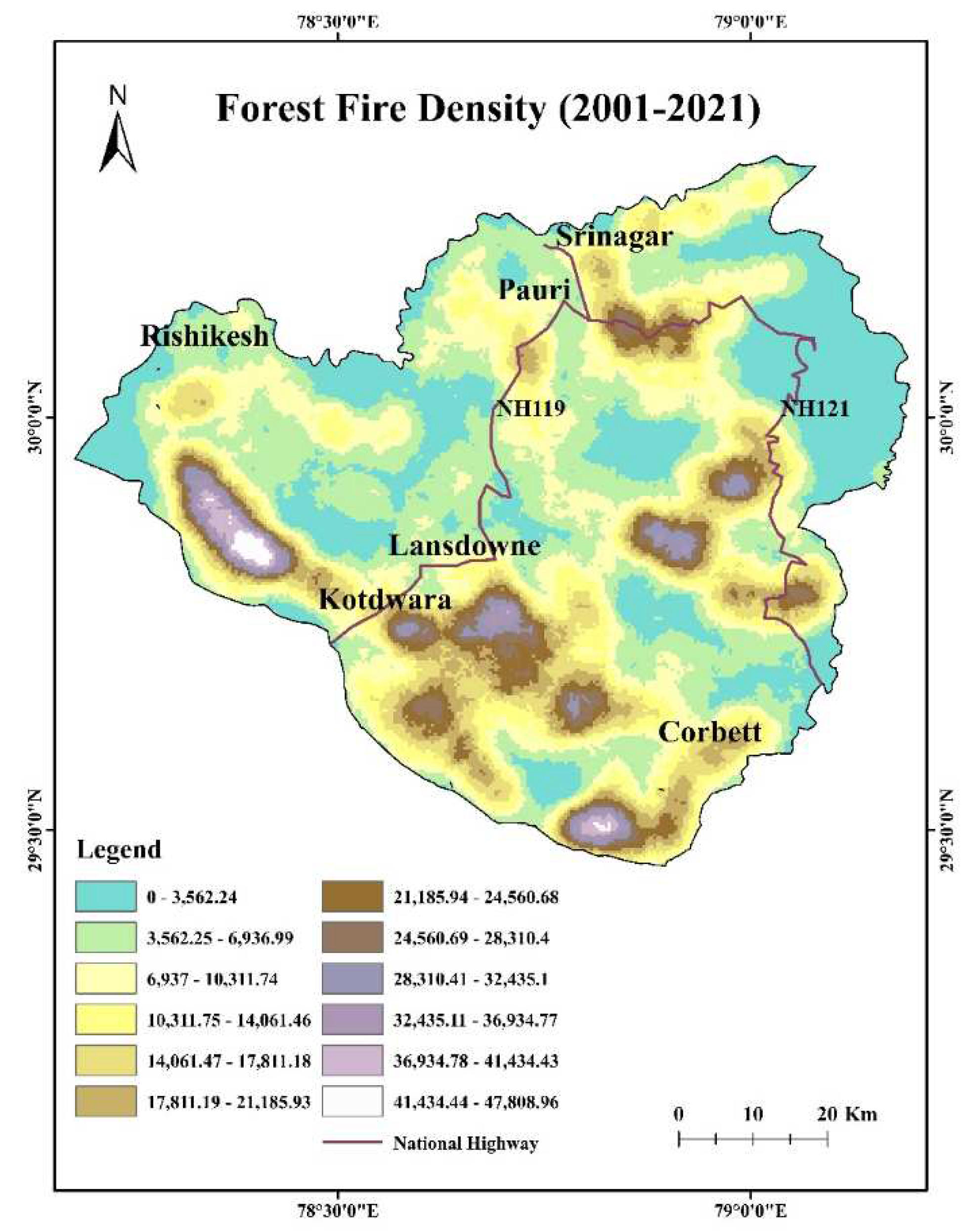
4.14. Forest fire density
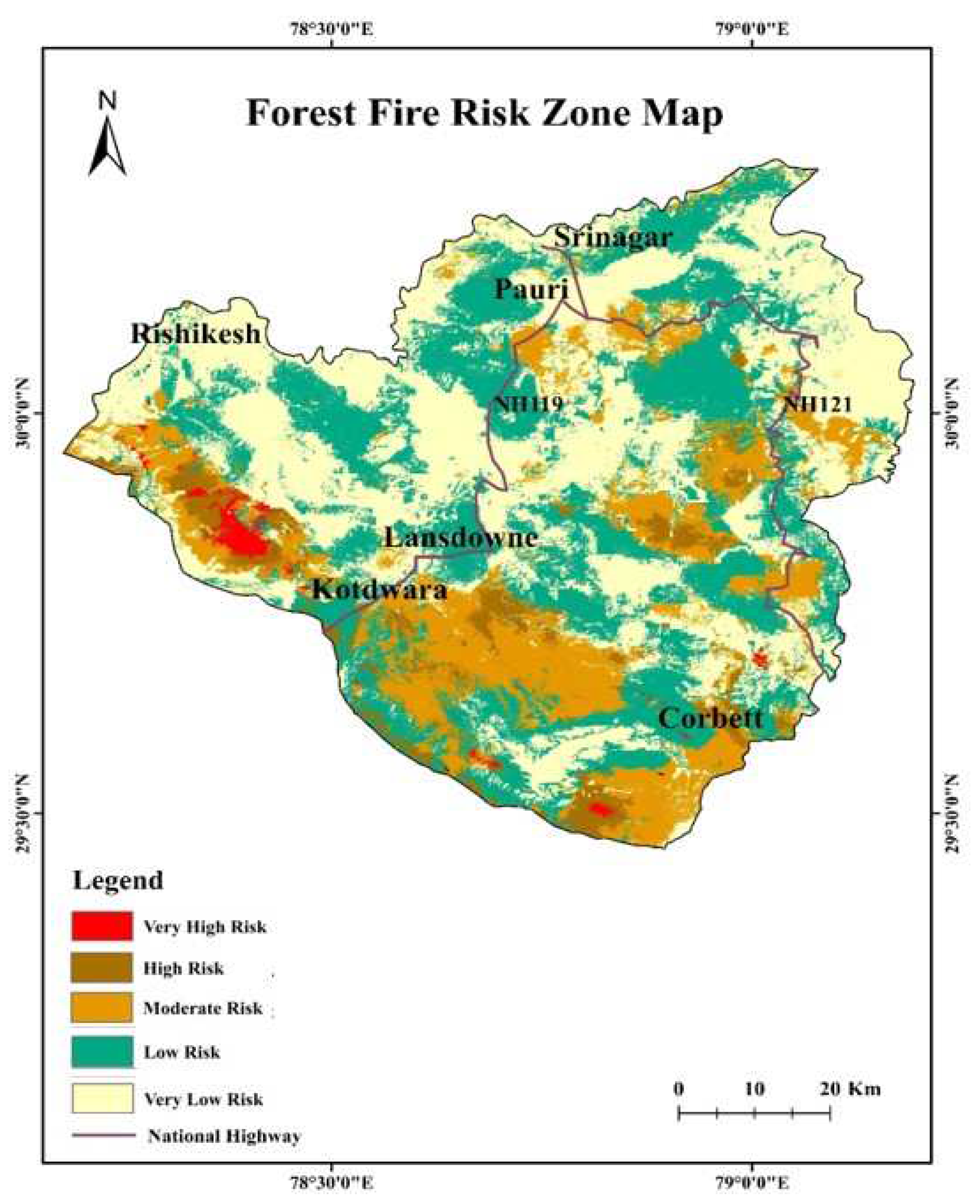
4.15. Forest fire risk map
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiwari, A., Shoab, M., & Dixit, A. GIS-based Forest fire susceptibility modeling in Pauri Garhwal, India: a comparative assessment of frequency ratio, analytic hierarchy process and fuzzy modeling techniques. Natural hazards (2021), 105, 1189-1230. [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, R. K., Mukherjee, S., Raju, K. D., & Saxena, R. Forest fire risk zone mapping from satellite imagery and GIS. International journal of applied earth observation and geoinformation (2002), 4(1), 1-10.
- India State of Forest Report. Ministry of Environment and Forest, Dehradun, India (2011).
- Mukherjee, S., & Raj, K. Analysis of forest fire of Meghalaya using geospatial tools. In 15th ESRI India user conference (2014).
- Chuvieco, E., & Congalton, R. G. Application of remote sensing and geographic information systems to forest fire hazard mapping. Remote sensing of Environment (1989), 29(2), 147-159. [CrossRef]
- Hantson, S., Pueyo, S., & Chuvieco, E. Global fire size distribution: from power law to log-normal. International journal of wildland fire (2016), 25(4), 403-412. [CrossRef]
- Mohajane, M., Essahlaoui, A., Oudija, F., Hafyani, M. E., Hmaidi, A. E., Ouali, A. E., ... & Teodoro, A. C. (2018). Land use/land cover (LULC) using landsat data series (MSS, TM, ETM+ and OLI) in Azrou Forest, in the Central Middle Atlas of Morocco. Environments, 5(12), 131.
- Zema, D. A., Nunes, J. P., & Lucas-Borja, M. E. Improvement of seasonal runoff and soil loss predictions by the MMF (Morgan-Morgan-Finney) model after wildfire and soil treatment in Mediterranean forest ecosystems. Catena (2020), 188, 104415. [CrossRef]
- Pyne, S. J., Andrews, P. L., & Laven, R. D. (1996). Introduction to Wildland Fire, John Wiley and Sons. New York.
- Saha, S., & Howe, H. F. Species composition and fire in a dry deciduous forest. Ecology (2003), 84(12), 3118-3123. [CrossRef]
- Negi, G. C. S. Forest fire in Uttarakhand: causes, consequences and remedial measures. International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences (2019), 45(1), 31-37.
- Hoffmann, A. A., Siegert, F., & Hinrichs, A. Fire damage in East Kalimantan in 1997/98 related to land use and vegetation classes: satellite radar inventory results and proposals for further actions (1999) (p. 26). IFFM/SFMP.
- Potter, L., & Lee, J. Oil palm in Indonesia: its role in forest conversion and the fires of 1997/1998. Report to the WWF, Indonesia Programme, Jakarta (1998).
- Dennis, R. A., Mayer, J., Applegate, G., Chokkalingam, U., Colfer, C. J. P., Kurniawan, I., & Tomich, T. P. Fire, people and pixels: linking social science and remote sensing to understand underlying causes and impacts of fires in Indonesia. Human Ecology (2005), 33, 465-504. [CrossRef]
- Alkhatib, A. A. A review on forest fire detection techniques. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks (2014), 10(3), 597368.
- Giglio, L., Van der Werf, G. R., Randerson, J. T., Collatz, G. J., & Kasibhatla, P.. Global estimation of burned area using MODIS active fire observations. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics (2006), 6(4), 957-974. [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, A., Gautam, A. P., Sharma, S. P., Bhujel, K. B., Sharma, G., Thapa, P. B., ... & Poudel, S. Forest fire risk mapping using GIS and remote sensing in two major landscapes of Nepal. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk (2020), 11(1), 2569-2586. [CrossRef]
- Randerson, J. T., Liu, H., Flanner, M. G., Chambers, S. D., Jin, Y., Hess, P. G., ... & Zender, C. S. The impact of boreal forest fire on climate warming. science (2006), 314(5802), 1130-1132. [CrossRef]
- Negi, M. S., & Kumar, A. Assessment of increasing threat of forest fires in Uttarakhand, using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Global Journal of Advanced Research (2016), 3(6), 457-468.
- Goldammer, J. G. (Ed.). Fire in the tropical biota: Ecosystem processes and global challenges (2012), (Vol. 84). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Cochrane, M. A., & Laurance, W. F. Fire as a large-scale edge effect in Amazonian forests. Journal of Tropical Ecology (2002), 18(3), 311-325. [CrossRef]
- Renard, Q., Pélissier, R., Ramesh, B. R., & Kodandapani, N. Environmental susceptibility model for predicting forest fire occurrence in the Western Ghats of India. International Journal of Wildland Fire (2012), 21(4), 368-379. [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, S. V., & Somashekar, R. K. Application of remote sensing and geographical information system in mapping forest fire risk zone at Bhadra wildlife sanctuary, India. Journal of Environmental Biology (2010), 31(6), 969.
- Kandya, A. K., Kimothi, M. M., Jadhav, R. N., & Agarwal, J. P. Application of Geographic Information System in Identification of'Fire-Prone'Areas: A Feasibility Study in Parts of Junagadh (Gujarat). Indian Forester (1998), 124(7), 531-536.
- India State of Forest Report (ISFR). Forest Survey of India, https://fsi.nic.in/forest-report-2019, (2021).
- Champion, H. G., & Seth, S. K. A revised survey of the forest types of India. Manager of publications (1968).
- Babu KV, S., Roy, A., & Prasad, P. R. Forest fire risk modeling in Uttarakhand Himalaya using TERRA satellite datasets. European Journal of Remote Sensing (2016), 49(1), 381-395.
- Pandey, K., & Ghosh, S. K. Modeling of parameters for forest fire risk zone mapping. The International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences (2018), 42, 299-304. [CrossRef]
- Pham, B. T., Khosravi, K., & Prakash, I. Application and comparison of decision tree-based machine learning methods in landside susceptibility assessment at Pauri Garhwal Area, Uttarakhand, India. Environmental Processes (2017), 4(3), 711-730. [CrossRef]
- Gaur, R. D., & Bartwal, B. S. DIFFERENT TYPES OF FOREST COMMUNITIES IN PAURI DISTRICT. Garhwal Himalaya: ecology and environment (1993), 131.
- Dobhal, G. L. Development of the hill areas: a case study of pauri garhwal district. Concept Publishing Company (2005).
- Sharma, C. M., Baduni, N. P., Gairola, S., Ghildiyal, S. K., & Suyal, S. (2010). Tree diversity and carbon stocks of some major forest types of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Forest Ecology and Management, 260(12), 2170-2179. [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A., Banerjee, S., Sundriyal, Y., & Rana, V. An integrated assessment of the geomorphic evolution of the Garhwal synform: Implications for the relative tectonic activity in the southern part of the Garhwal Himalaya. Journal of Earth System Science (2022), 131(1), 56. [CrossRef]
- Valdiya, K. S. Geology of kumaun lesser Himalaya (Vol. 291). Dehradun: Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology (1980).
- Auden, J. B. Structure of the Himalaya in Garhwal. Records Geological Survey of India (1937), 71, 407-433.
- Gupta, L. N. Abnormal tectonics of the allochthonous Lansdowne granite and the tectonic history of Garhwal nappe. Indian Mineral (1976), 17, 73-85.
- Kumar, U., Kumar, B., & Mallick, N. Groundwater prospects zonation based on RS and GIS using fuzzy algebra in Khoh River watershed, Pauri-Garhwal District, Uttarakhand, India. Global Perspectives on Geography (GPG) (2013), 1(3), 37-45.
- Krishnamurthy, J., & Srinivas, G. Role of geological and geomorphological factors in ground water exploration: a study using IRS LISS data. International Journal of Remote Sensing (1995), 16(14), 2595-2618. [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, C. P., Sanwal, J., John, B., Anandasabari, K., Rajendran, K., Kumar, P., ... & Chopra, S. Footprints of an elusive mid-14th century earthquake in the central Himalaya: Consilience of evidence from Nepal and India. Geological Journal (2019), 54(5), 2829-2846. [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, C. P., Singh, T. E. J. P. A. L., Mukul, M. A. L. A. Y., Thakkar, M. A. H. E. S. H., Kothyari, G. C., John, B., & Rajendran, K. Paleoseismological studies in India (2016-2020): status and prospects. In Proc Indian Natn Sci Acad (2020, March), (Vol. 86, No. 1, pp. 585-607). [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M., Singh, G., & Malik, J. N. Geological and geomorphic evidences of neotectonic activity along the Himalayan Frontal Thrust, Nahan Salient, NW Himalaya, India. Quaternary International (2021), 575, 5-20. [CrossRef]
- O'leary, D. W., Friedman, J. D., & Pohn, H. A. Lineament, linear, lineation: some proposed new standards for old terms. Geological Society of America Bulletin (1976), 87(10), 1463-1469.
- Moore, G. K., & Waltz, F. A. Objective procedures for lineament enhancement and extraction. Photogrammetric Engineering and remote sensing (1983), 49(5), 641-647.
- Erten, E., Kurgun, V., & Musaoglu, N. Forest fire risk zone mapping from satellite imagery and GIS: a case study. In XXth Congress of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Istanbul, Turkey (2004, July), (pp. 222-230).
- Avdan, U., & Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for automated mapping of land surface temperature using LANDSAT 8 satellite data. Journal of sensors (2016), 2016, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S. K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. International journal of remote sensing (1996), 17(7), 1425-1432. [CrossRef]
- Buechling, A., & Baker, W. L. A fire history from tree rings in a high-elevation forest of Rocky Mountain National Park. Canadian Journal of Forest Research (2004), 34(6), 1259-1273. [CrossRef]
- Chuvieco, E., & Congalton, R. G. Mapping and inventory of forest fires from digital processing of TM data. Geocarto International (1988), 3(4), 41-53. [CrossRef]
- Gaither, C. J., Poudyal, N. C., Goodrick, S., Bowker, J. M., Malone, S., & Gan, J. Wildland fire risk and social vulnerability in the Southeastern United States: An exploratory spatial data analysis approach. Forest policy and economics (2011), 13(1), 24-36. [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, M. J., Gessler, P. E., Morgan, P., Hudak, A. T., & Smith, A. M. Characterizing and mapping forest fire fuels using ASTER imagery and gradient modeling. Forest ecology and management (2005), 217(2-3), 129-146. [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D. X. Slope and wind effects on fire propagation. International Journal of Wildland Fire (2004), 13(2), 143-156.
- Mermoz, M., Kitzberger, T., & Veblen, T. T. Landscape influences on occurrence and spread of wildfires in Patagonian forests and shrublands. Ecology (2005), 86(10), 2705-2715. [CrossRef]
- Minnich, R. A. THE GEOGRAPHY OF FIRE AND CONIFER FORESTS IN THE EASTERN TRANSVERSE RANGES, CALIFORNIA. University of California, Los Angeles (1978).
- Van Wagner, C. E. Effect of slope on fires spreading downhill. Canadian journal of forest research (1988) (Print), 18(6), 818-820.
- Pourtaghi, Z. S., Pourghasemi, H. R., & Rossi, M. (2015). Forest fire susceptibility mapping in the Minudasht forests, Golestan province, Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(4), 1515-1533. [CrossRef]
- Iwan, R., Limberg, G., Moeliono, M., Sudana, M., & Wollenberg, E. Mobilizing community conservation: a community initiative to protect its forest against logging in Indonesia. In Xth Meeting of the International Association for the Study of Common Property (2004, August) (pp. 9-13).
- Hayes, G. L. Influence of altitude and aspect on daily variations in factors of forest-fire danger (No. 591). US Department of Agriculture (1941).
- Beaty, R. M., & Taylor, A. H. Spatial and temporal variation of fire regimes in a mixed conifer forest landscape, Southern Cascades, California, USA. Journal of Biogeography (2001), 28(8), 955-966. [CrossRef]
- Tien Bui, D., Le, K. T. T., Nguyen, V. C., Le, H. D., & Revhaug, I. Tropical Forest fire susceptibility mapping at the Cat Ba National Park Area, Hai Phong City, Vietnam, using GIS-based kernel logistic regression. Remote Sensing (2016), 8(4), 347.
- Mukherjee, S. Role of satellite sensors in groundwater exploration. Sensors (2008), 8(3), 2006-2016. [CrossRef]
- Flannigan, M. D., Wotton, B. M., Marshall, G. A., De Groot, W. J., Johnston, J., Jurko, N., & Cantin, A. S. Fuel moisture sensitivity to temperature and precipitation: climate change implications. Climatic Change (2016), 134, 59-71. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Hunt Jr, E. R., Qu, J. J., Hao, X., & Daughtry, C. S. Remote sensing of fuel moisture content from ratios of narrow-band vegetation water and dry-matter indices. Remote Sensing of Environment (2013), 129, 103-110.
| Class | Area (km2) |
Geographic area (%) |
| Very Dense Forest | 5,046.76 | 9.44 |
| Moderately Dense Forest | 12,805.24 | 23.94 |
| Open Forest | 6,451.04 | 12.06 |
| Total | 24,303.04 | 45.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





