Submitted:
12 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
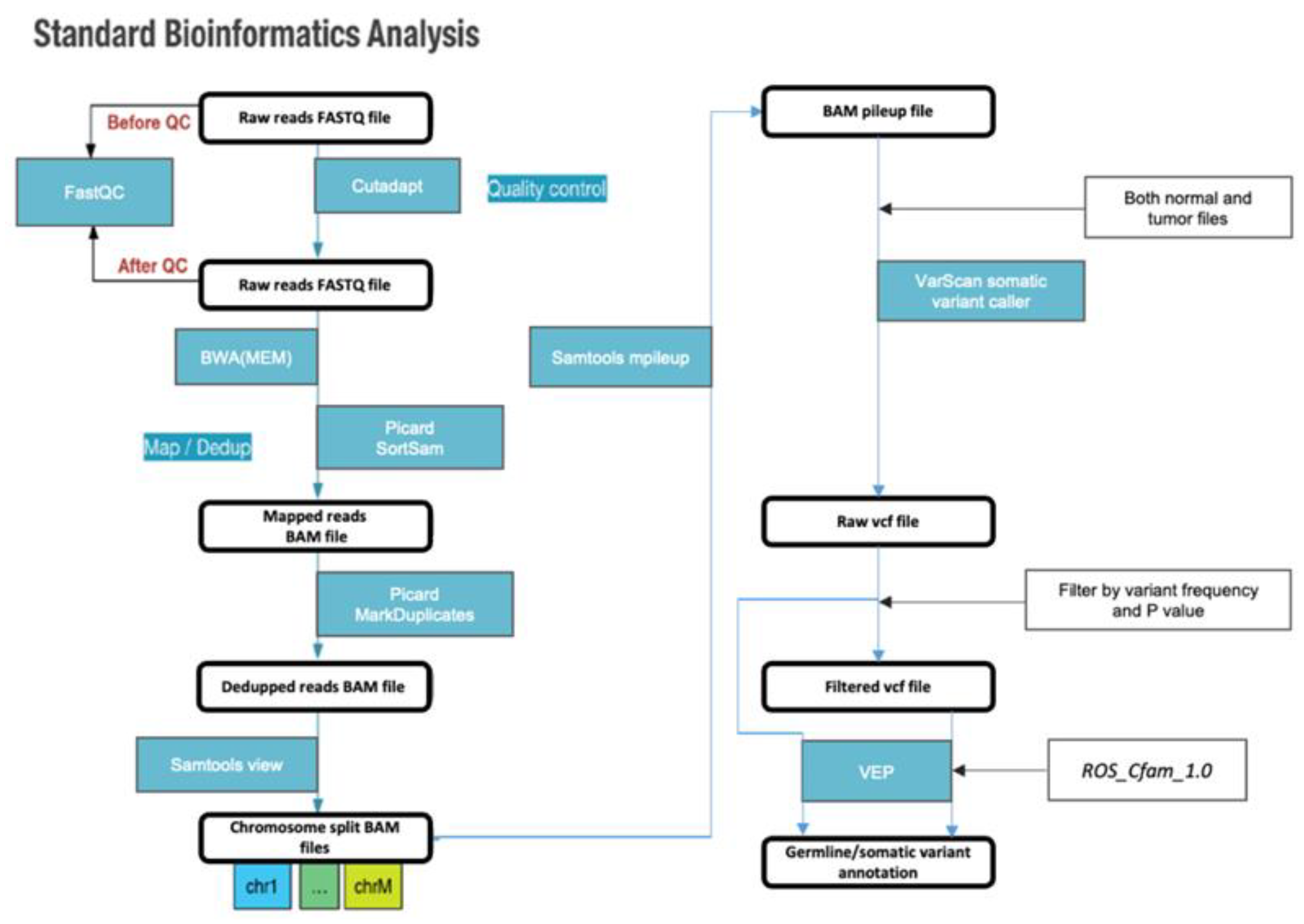
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Immunophenotyping
2.3. DNA extraction and sequencing
2.4. Variant calling
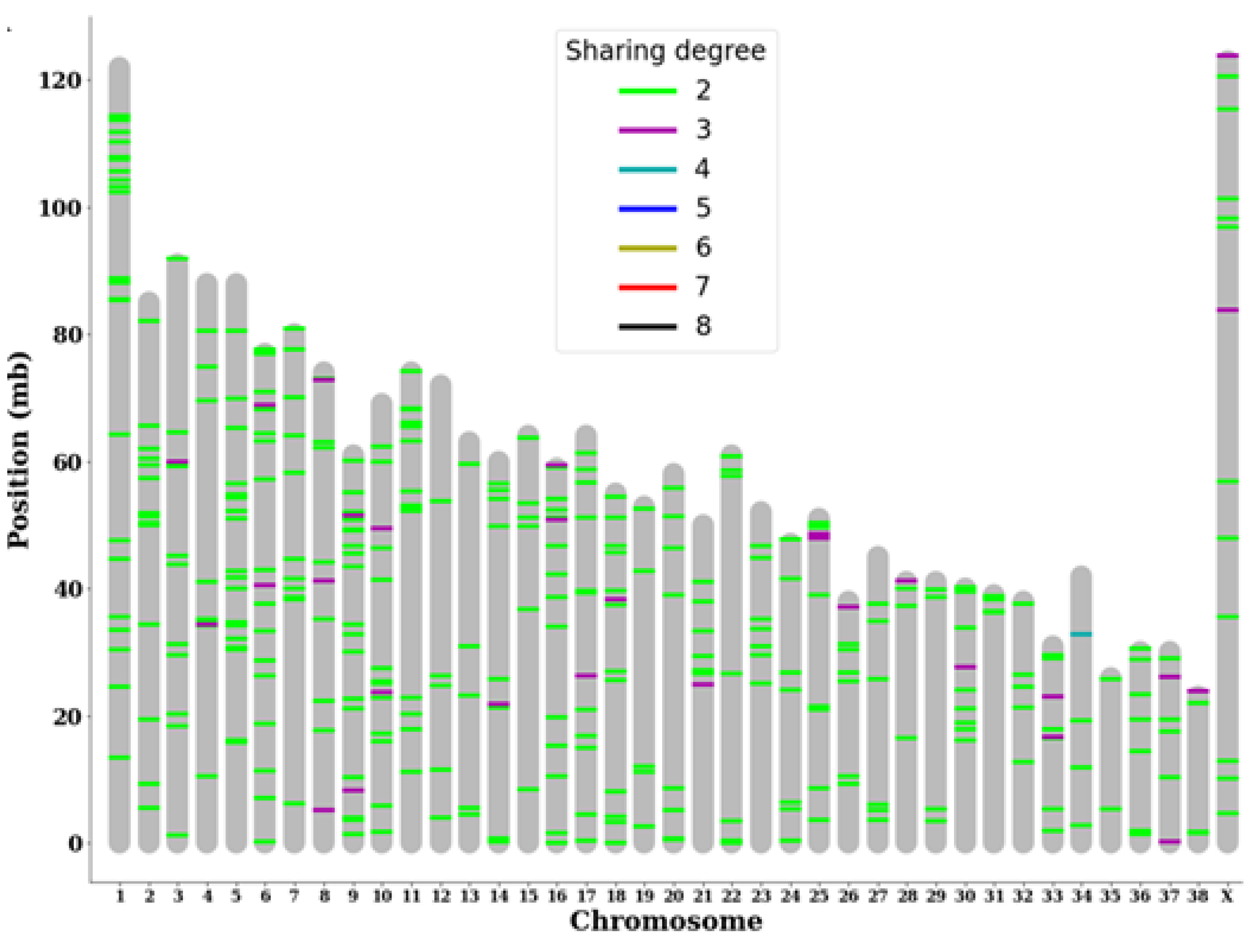
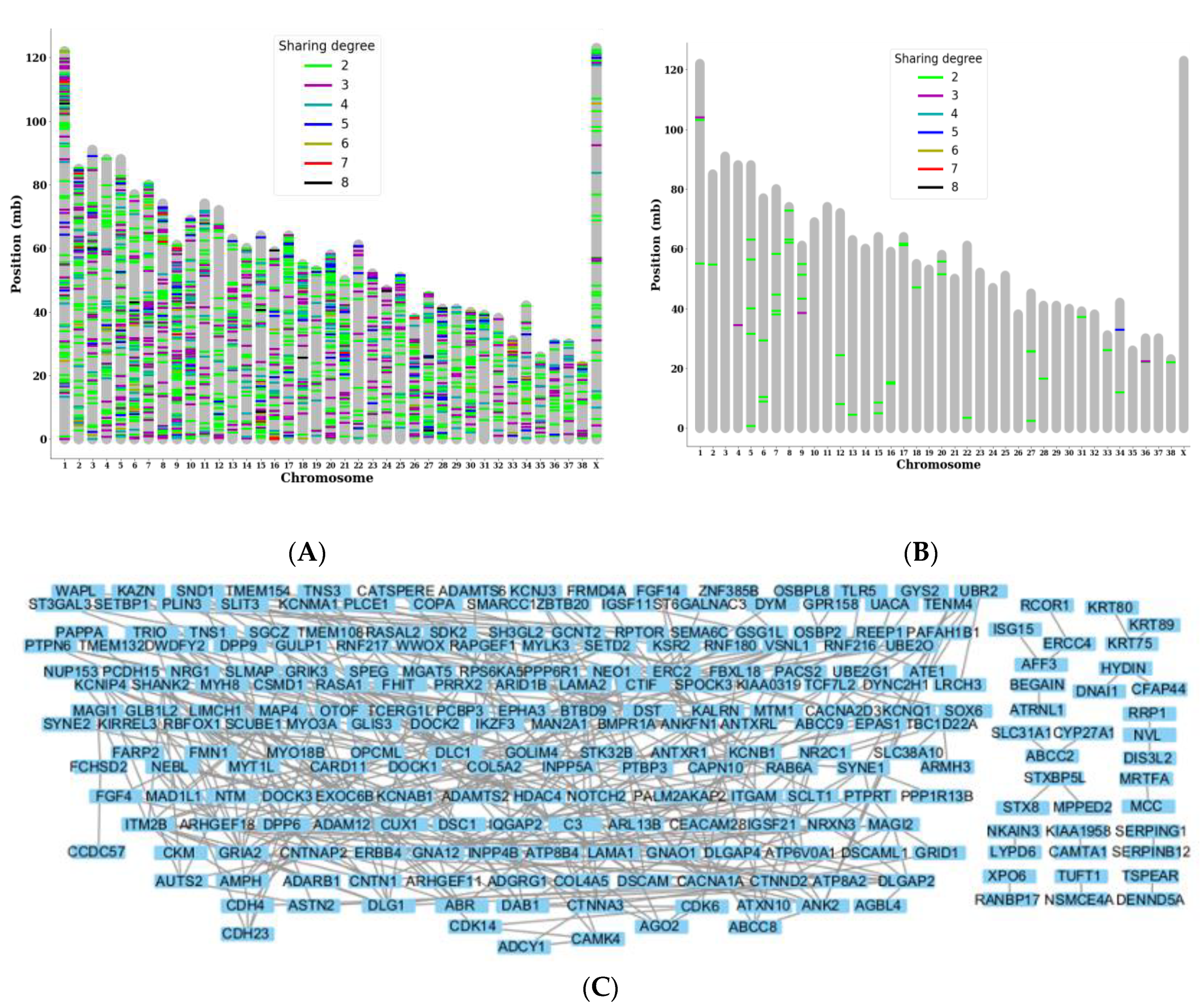
2.5. Sharing analysis
2.6. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction ana analysis of modules
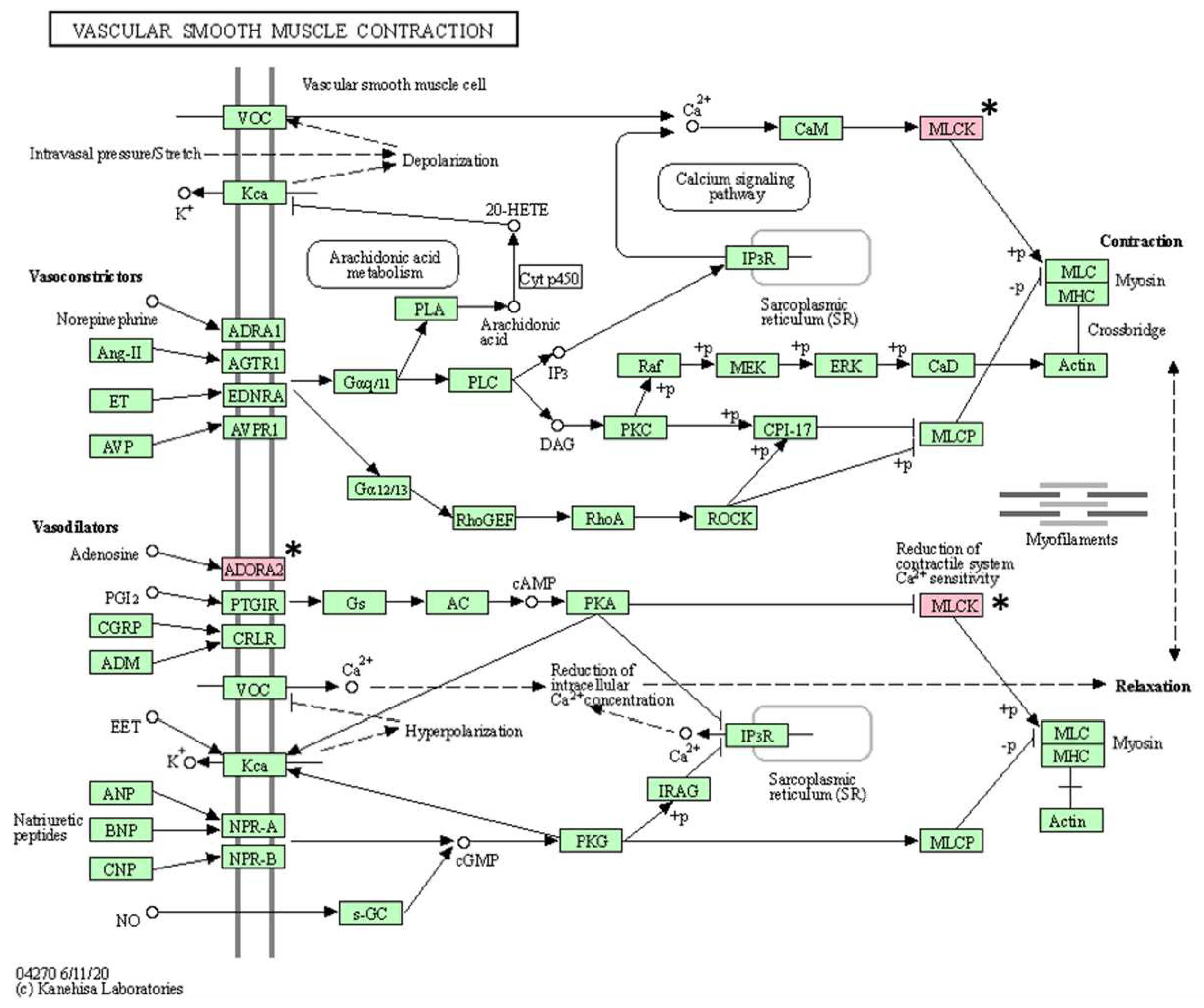
2.7. KEGG pathway analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variant level analysis reveals highly shared GOLIM4 variant
3.2. Gene level sharing analysis shows variant accumulation in a specific PPI network
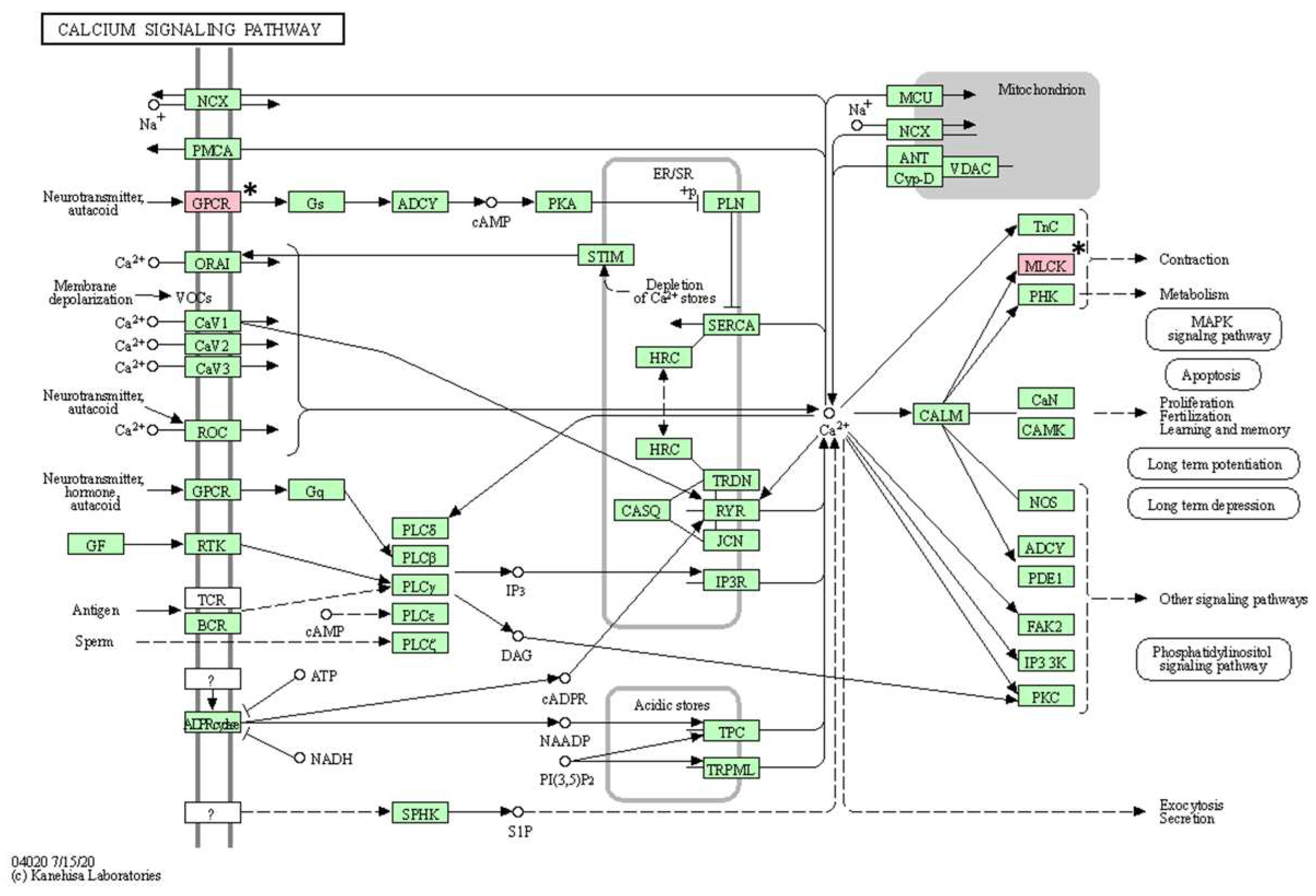
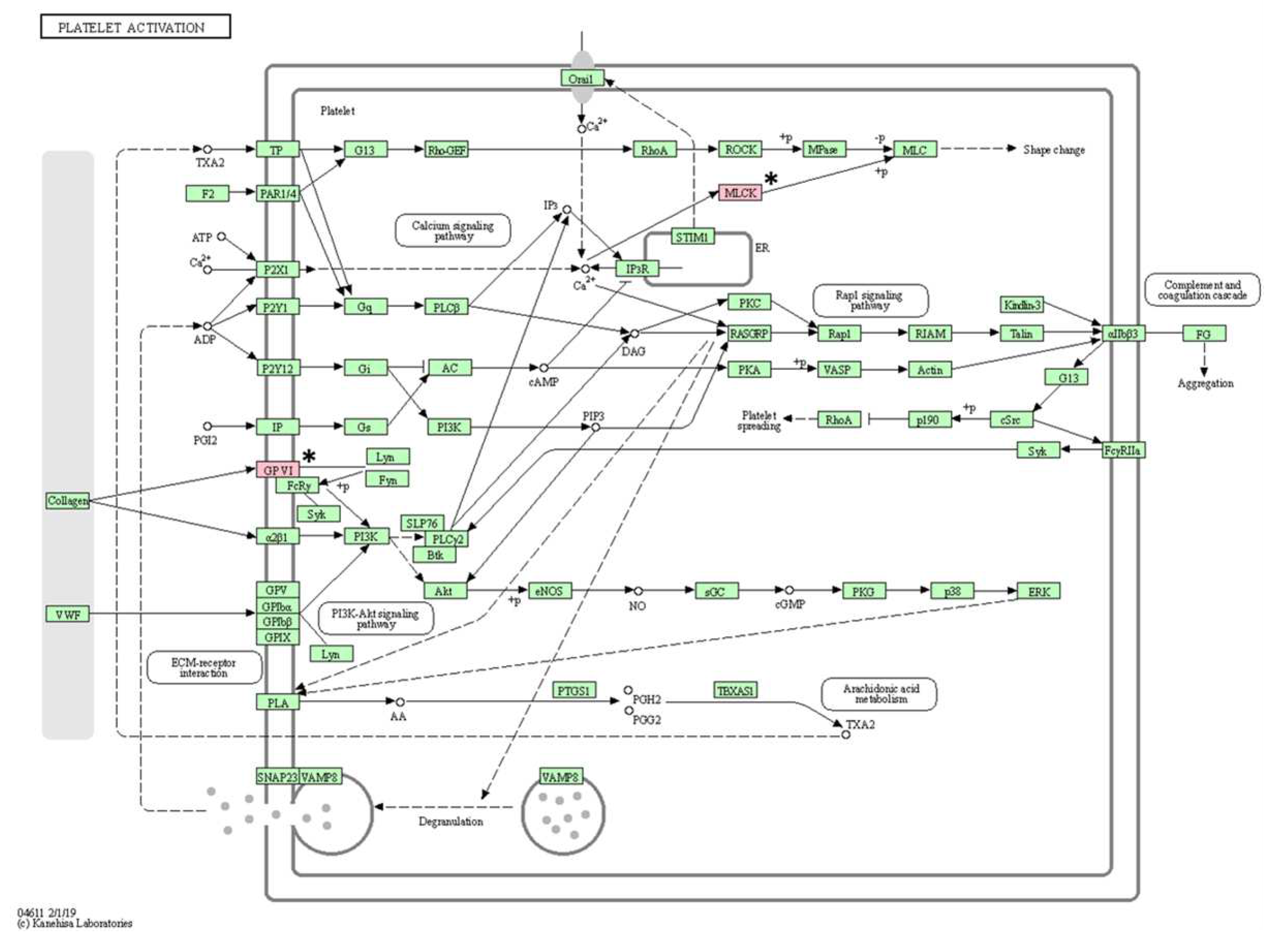
3.3. KEGG pathway analysis results
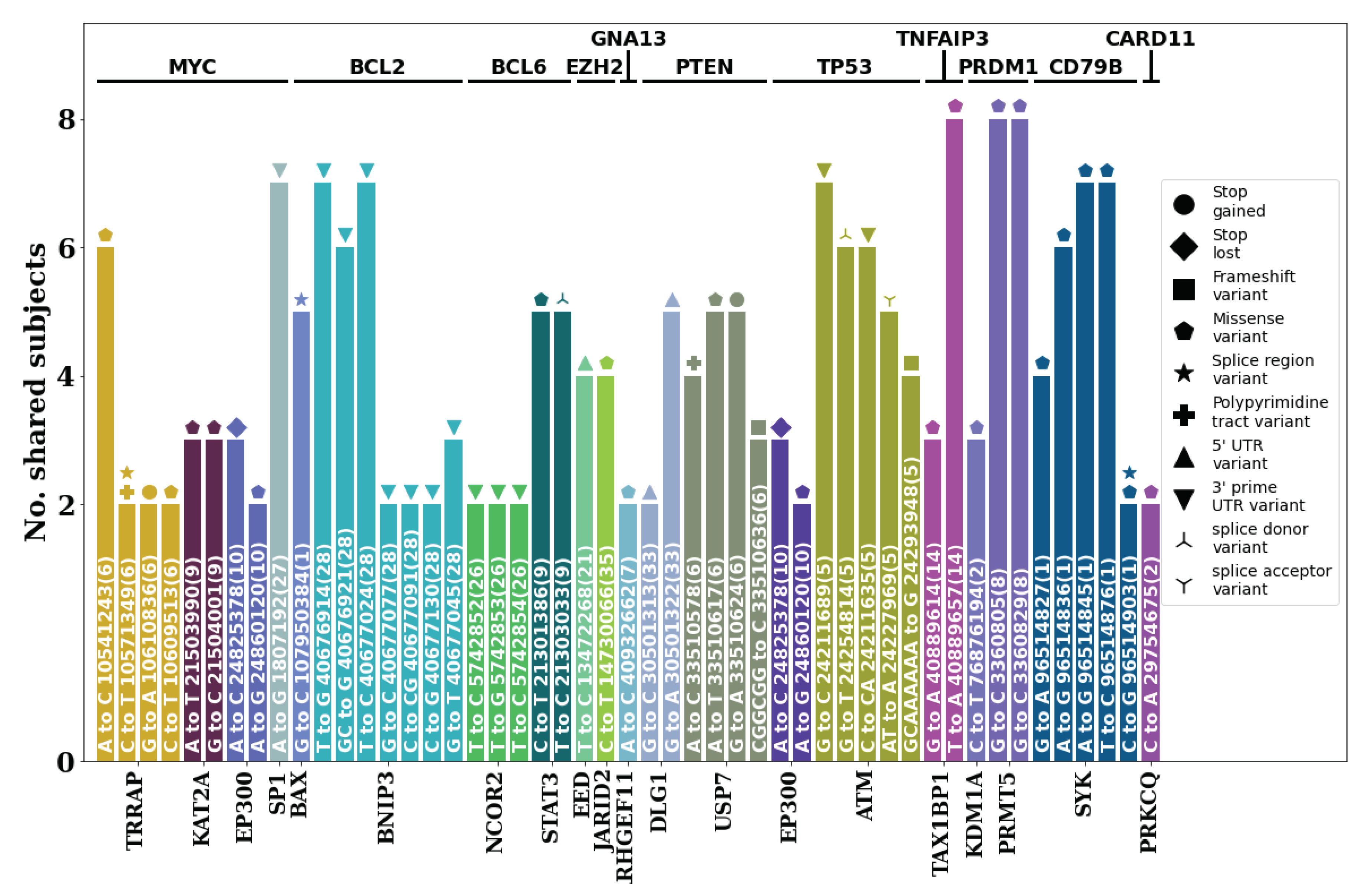
3.4. Highly shared germline mutations in diffuse large BCL (DLBCL)-associated genes and pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bick, D.; Dimmock, D. Whole Exome and Whole Genome Sequencing. Curr Opin Pediatr 2011, 23, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastre, L. Exome Sequencing: What Clinicians Need to Know. Adv Genom Genetics 2014, 4, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teer, J.K; Mullikin, J.C. Exome Seqeuncing: The Sweet Spot before Whole Genomes. Hum Mol Genet 2010, 19, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunstman, J.W.; Juhlin, C.C.; Goh, G.; Brown, T.C.; Stenman, A.; Healy, J.M.; Rubinstein, J.C.; Choi, M.; Kiss, N.; Nelson-Williams, C.; et al. Characterization of the Mutational Landscape of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer via Whole-Exome Sequencing. Hum Mol Genet 2015, 24, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic Active B-Cell-Receptor Signalling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.-H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically Active MYD88 Mutations in Human Lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lam, L.; George, T.C.; Wright, G.W.; Dave, S.S.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Oncogenic CARD11 Mutations in Human Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Science 2008, 319, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, I.; Turner-Maier, J.; Swofford, R.; Koltookian, M.; Johnson, J.; Stewart, C.; Zhang, C.-Z.; Schumacher, S.E.; Beroukhim, R.; Rosenberg, M.; et al. Exome Sequencing of Lymphomas from Three Dog Breeds Reveals Somatic Mutation Patterns Reflecting Genetic Background. Genome Res 2015, 25, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, A.; Woods, J.P.; Bienzle, D.; Wood, G.A.; Coomber, B.L. Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis of High Confidence Variants of B-Cell Lymphoma in Canis Familiaris. Plos One 2020, 15, e0238183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.C.; Vernau, W.; Modiano, J.F.; Olver, C.S.; Moore, P.F.; Avery, A.C. Diagnosis of Canine Lymphoid Neoplasia Using Clonal Rearrangements of Antigen Receptor Genes. Vet Pathol 2003, 40, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnetJ. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows–Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, W.; Pritchard, B.; Rios, D.; Chen, Y.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. Deriving the Consequences of Genomic Variants with the Ensembl API and SNP Effect Predictor. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2069–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C. Best Practices for Variant Calling in Clinical Sequencing. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künstner, A.; Witte, H.M.; Riedl, J.; Bernard, V.; Stölting, S.; Merz, H.; Olschewski, V.; Peter, W.; Ketzer, J.; Busch, Y.; et al. Muta-tional Landscape of High-Grade B-Cell Lymphoma with MYC-, BCL2 and/or BCL6 Rearrangements Characterized by Whole-Exome Sequencing. Haematologica 2021, 107, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, J.G.; Stojanov, P.; Lawrence, M.S.; Auclair, D.; Chapuy, B.; Sougnez, C.; Cruz-Gordillo, P.; Knoechel, B.; Asmann, Y.W.; Slager, S.L.; et al. Discovery and Prioritization of Somatic Mutations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) by Whole-Exome Sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2012, 109, 3879–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, J.; Ko, Y. Whole-Exome and Transcriptome Sequencing of Re-fractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 86433–86445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braggio, E.; Wier, S.V.; Ojha, J.; McPhail, E.; Asmann, Y.W.; Egan, J.; Silva, J.A. da; Schiff, D.; Lopes, M.B.; Decker, P.A.; et al. Ge-nome-Wide Analysis Uncovers Novel Recurrent Alterations in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkos, T.M.; Lowe, M. Recognition and Tethering of Transport Vesicles at the Golgi Apparatus. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2017, 47, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cui, X.; Gao, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, W. Golgi Integral Membrane Protein 4 Manipulates Cellular Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Cell Cycle in Human Head and Neck Cancer. Bioscience Rep 2018, 38, BSR20180454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Fluhrer, R.; Reiss, K.; Kremmer, E.; Saftig, P.; Haass, C. Regulated Intramembrane Proteolysis of Bri2 (Itm2b) by ADAM10 and SPPL2a/SPPL2b*. J Biol Chem 2008, 283, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, B.W.; Pytel, P. Expression Pattern of the BCL6 and ITM2B Proteins in Normal Human Brains and in Alzheimer Disease. Appl Immunohisto M M 2017, 25, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Yao, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, R.; Fu, S.; Pan, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, K. G-MDSCs-Derived Exosomal MiRNA-143-3p Promotes Proliferation via Targeting of ITM2B in Lung Cancer. Oncotargets Ther 2020, 13, 9701–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Ackerson, S.M.; Schuck, P.L. Emerging Roles of CST in Maintaining Genome Stability and Human Disease. Frontiers Biosci Landmark Ed 2018, 23, 1564–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Sang, P.B.; Chai, W. CST in Maintaining Genome Stability: Beyond Telomeres. Dna Repair 2021, 102, 103104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Jin, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Fu, J. Lower DSC1 Expression Is Related to the Poor Differentiation and Prognosis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). J Cancer Res Clin 2016, 142, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Mireskandari, M.; Knösel, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kohler, L.H.; Kunze, A.; Presselt, N.; Petersen, I. Diagnostic and Prognostic Impact of Desmocollins in Human Lung Cancer. J Clin Pathol 2012, 65, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knösel, T.; Chen, Y.; Hotovy, S.; Settmacher, U.; Altendorf-Hofmann, A.; Petersen, I. Loss of Desmocollin 1-3 and Homeobox Genes PITX1 and CDX2 Are Associated with Tumor Progression and Survival in Colorectal Carcinoma. Int J Colorectal Dis 2012, 27, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, S.I.; Rimoldi, D.; Iseli, C.; Valsesia, A.; Robyr, D.; Gehrig, C.; Harshman, K.; Guipponi, M.; Bukach, O.; Zoete, V.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies Recurrent Somatic MAP2K1 and MAP2K2 Mutations in Melanoma. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.W.; Marks, R.M.; Sarma, V.; Byers, M.G.; Katz, R.W.; Shows, T.B.; Dixit, V.M. Characterization of a Novel Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Endothelial Primary Response Gene. J Biol Chem 1992, 267, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, C.D.; Taft, A.; Kapulkin, V.; Duke, K.; Kim, S.; Fei, Q.; Wood, D.E.; Sahagan, B.G. Gene Expression Analysis in a Transgenic Caenorhabditis Elegans Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Neurobiol Aging 2003, 24, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Liu, N.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J. CK2 Phosphorylates TNFAIP1 to Affect Its Subcellular Localization and Interaction with PCNA. Mol Biol Rep 2010, 37, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinchuk, O.V.; Motakis, E.; Kuznetsov, V.A. Grinchuk, O.V.; Motakis, E.; Kuznetsov, V.A. Complex Sense-Antisense Architecture of TNFAIP1/POLDIP2 on 17q11.2 Represents a Novel Transcriptional Structural-Functional Gene Module Involved in Breast Cancer Progression. Bmc Genomics 2010, 11, S9–S9.
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Tan, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-372 Maintains Oncogene Characteristics by Targeting TNFAIP1 and Affects NFκB Signaling in Human Gastric Carcinoma Cells. Int J Oncol 2013, 42, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, R.; Meng, W.; Sun, H.-L.; Kim, T.; Ye, Z.; Fassan, M.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Li, B.; Vicentini, C.; Peng, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-224 Promotes Tumor Progression in Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Proc National Acad Sci 2015, 112, E4288–E4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, A.; Wutz, G.; Huet, S.; Jaritz, M.; Wuensche, A.; Schirghuber, E.; Davidson, I.F.; Tang, W.; Cisneros, D.A.; Bhaskara, V.; et al. Wapl Is an Essential Regulator of Chromatin Structure and Chromosome Segregation. Nature 2013, 501, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.Q.; Maresca, M.; Brand, T. van den; Braccioli, L.; Schijns, M.M.G.A.; Teunissen, H.; Bruneau, B.G.; Nora, E.P.; Wit, E. de WAPL Maintains a Cohesin Loading Cycle to Preserve Cell-Type Specific Distal Gene Regulation. Nat Genet 2021, 53, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, H.; Duan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, R.; Li, M.; Wang, B. AKT-dependent Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes in Familial Hidradenitis Suppurativa with a NCSTN Mutation: A Potential Role of Defective MiR-100-5p. Brit J Dermatol 2020, 182, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Tymen, S.D.; Chen, D.; Fang, Z.J.; Zhao, Y.; Dragas, D.; Dai, Y.; Marucha, P.T.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-99 Family Targets AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway in Dermal Wound Healing. Plos One 2013, 8, e64434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yi, Y.; Shi, G.; Li, S.; Chen, S.; Lin, Y.; Li, Z.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Zhong, S. Role of Brf1 Interaction with ER α, and Significance of Its Overexpression, in Human Breast Cancer. Mol Oncol 2017, 11, 1752–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Xi, S.; Liang, J.; Shi, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Levy, D.; Zhong, S. The Significance of Brf1 Overexpression in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 6243–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.; Huang, C.; Ren, W.; Chen, J.; Xia, N.; Zhong, S. Mitogen- and Stress-Activated Protein Kinase 1 Mediates Alcohol-Upregulated Transcription of Brf1 and TRNA Genes to Cause Phenotypic Alteration. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020, 2067959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loveridge, C.J.; Slater, S.; Campbell, K.J.; Nam, N.A.; Knight, J.; Ahmad, I.; Hedley, A.; Lilla, S.; Repiscak, P.; Patel, R.; et al. Correction: BRF1 Accelerates Prostate Tumourigenesis and Perturbs Immune Infiltration. Oncogene 2020, 39, 2450–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yan, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Gan, W.; Lv, S.; Zeng, Z.; Hou, Y.; Yang, M. SEMA6B Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis and Correlates With the Tumor Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer. Frontiers Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 687319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Műzes, G.; Sipos, F. Relation of Immune Semaphorin/Plexin Signaling to Carcinogenesis. Eur J Cancer Prev 2014, 23, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neufeld, G.; Mumblat, Y.; Smolkin, T.; Toledano, S.; Nir-Zvi, I.; Ziv, K.; Kessler, O. The Role of the Semaphorins in Cancer. Cell Adhes Migr 2016, 10, 652–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Meng, Z. Expression and Gene Regulation Network of Adenosine Receptor A2B in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker. Frontiers Mol Biosci 2021, 8, 663011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchio, E.A.; Tan, C.Y.R.; Gregory, K.J.; Christopoulos, A.; White, P.J.; May, L.T. Ligand-Independent Adenosine A2B Receptor Constitutive Activity as a Promoter of Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2016, 357, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasama, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Kasamatsu, A.; Okamoto, A.; Koyama, T.; Minakawa, Y.; Ogawara, K.; Yokoe, H.; Shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; et al. Adenosine A2b Receptor Promotes Progression of Human Oral Cancer. Bmc Cancer 2015, 15, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, C.; Wittevrongel, C.; Thys, C.; Smethurst, P.A.; Geet, C.V.; Freson, K. A Compound Heterozygous Mutation in Glycoprotein VI in a Patient with a Bleeding Disorder. J Thromb Haemost 2009, 7, 1356–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Induruwa, I.; Moroi, M.; Bonna, A.; Malcor, J. -D.; Howes, J. -M.; Warburton, E.A.; Farndale, R.W.; Jung, S.M. Platelet Collagen Receptor Glycoprotein VI-dimer Recognizes Fibrinogen and Fibrin through Their D-domains, Contributing to Platelet Adhesion and Activation during Thrombus Formation. J Thromb Haemost 2018, 16, 389–404.
- Mammadova-Bach, E.; Gil-Pulido, J.; Sarukhanyan, E.; Burkard, P.; Shityakov, S.; Schonhart, C.; Stegner, D.; Remer, K.; Nurden, P.; Nurden, A.T.; et al. Platelet Glycoprotein VI Promotes Metastasis through Interaction with Cancer Cell-Derived Galectin-3. Blood 2020, 135, 1146–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, S.; Shao, Y.; Wu, J.; Jin, G.; Lin, W.; Peng, X.; Xu, X. A Novel Mechanism for A-to-I RNA-Edited AZIN1 in Promoting Tumor Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, C.H.; Chan, T.H.M.; Chow, R.K.K.; Song, Y.; Liu, M.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Fu, L.; Kong, K.L.; et al. Recoding RNA Editing of AZIN1 Predisposes to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat Med 2013, 19, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, H.C.; Wulf, M.; Weidling, C.; Rasmussen, L.P.; Pless, S.A. The NALCN Channel Complex Is Voltage Sensitive and Directly Modulated by Extracellular Calcium. Sci Adv 2020, 6, eaaz3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, R.F.; Guan, W.; Zhorov, B.S.; Spafford, J.D. Selectivity Filters and Cysteine-Rich Extracellular Loops in Voltage-Gated Sodium, Calcium, and NALCN Channels. Front Physiol 2015, 6, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Kamynina, E.; Morley, S.; Chung, S.; Muakkassa, N.; Wang, H.; Brathwaite, S.; Sharma, G.; Manor, D. Plekhg4 Is a Novel Dbl Family Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Protein for Rho Family GTPases*. J Biol Chem 2013, 288, 14522–14530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, T.; Nomura, S.; Morita, H.; Ko, T.; Fujita, T.; Toko, H.; Uto, K.; Hagiwara, N.; Aburatani, H.; Komuro, I. Identification of MYLK3 Mutations in Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Sci Rep-uk 2017, 7, 17495.
- Bateman, A.; Sandford, R. The PLAT Domain: A New Piece in the PKD1 Puzzle. Curr Biol 1999, 9, R588–S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillet, N.; Schwander, M.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Sczaniecka, A.; Kolatkar, A.; Velasco, J.; Webster, J.A.; Kahrizi, K.; Najmabadi, H.; Kimberling, W.J.; et al. Mutations in LOXHD1, an Evolutionarily Conserved Stereociliary Protein, Disrupt Hair Cell Function in Mice and Cause Progressive Hearing Loss in Humans. Am J Hum Genetics 2009, 85, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J.; Bootman, M.D.; Roderick, H.L. Calcium Signalling: Dynamics, Homeostasis and Remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 2003, 4, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.A.; Yapa, K.T.D.S.; Monteith, G.R. Altered Calcium Signaling in Cancer Cells. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta Bba - Biomembr 2015, 1848, 2502–2511.
- Borsig, L. The Role of Platelet Activation in Tumor Metastasis. Expert Rev Anticanc 2008, 8, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpatkin, S.; Pearlstein, E. Role of Platelets in Tumor Cell Metastases. Ann Intern Med 1981, 95, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeksma, O.C.; Miranda, N.F. de; Veelken, H. Germline Mutations Predisposing to Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J 2017, 7, e541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample No. | Breed | Age (years) | Sex | Cytological results | PARR results (monoclonal) | Lymphoma WHO stage | Survival time (days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maltese | 5 | SF | Diffuse, large | IgH major | stage IV, substage a | Euthanasia |
| 2 | Welsh corgi | 8 | IF | Diffuse, large | IgH major | stage IV, substage b | 30, loss |
| 3 | Cocker spaniel | 11 | IF | Diffuse, intermediate | IgH major | stage IV, substage b | Loss |
| 4 | Shih tzu | 10 | CM | Diffuse, intermediate | IgH major | stage V, substage b | 406 |
| 5 | Maltese | 6 | SF | Diffuse, intermediate | IgH minor | stage IV, substage b | 407 |
| 6 | White terrier | 6 | IF | Diffuse, large | IgH minor | stage IV, substage a | 435, loss |
| 7 | Mixed breed | 7 | IM | Diffuse, large | IgH major | stage IV, substage a | - |
| 8 | Welsh corgi | 9 | CM | Diffuse, intermediate | IgH major | stage IV, substage a | 232 |
| Reaction No. | Product | Primer names | Primer specificity | Primer sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cµ | Sigmf1 | Cµ | TTC CCC CTC ATC ACC TGT GA |
| Srµ3 | Cµ | GGT TGT TGA TTG CAC TGA GG | ||
| 2 | IgH major | CB1 | VH | CAG CCT GAG AGC CGA GGA CAC |
| CB2 | JH | TGA GGA GAC GGT GAC CAG GGT | ||
| 3 | IgH minor | CB1 | VJ | CAG CCT GAG AGC CGA GGA CAC |
| CB3 | JH | TGA GGA CAC AAA GAG TGA GG | ||
| 4 | TCRγ | TCRγ1 | JH | ACC CTG AGA ATT GTG CCA GG |
| TCRγ2 | JH | GTT ACT ATA AAC CTG GTA AC | ||
| TCRγ3 | VH | TCT GGG RTG TAY TAC TGT GCT GTC TGG |
| Reaction No. | Product | Initial denaturation | 40 cycles | Final extension | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Denaturation | Annealing | Extension | ||||
| 1 | Cµ | 94°C, 15 s | 94°C, 15 s | 57°C, 15 s | 72°C, 15 s | 72°C, 15 s |
| 2 | IgH major | 94°C, 15 min | 94°C, 15 s | 63°C, 15 s | 72°C, 15 s | - |
| 3 | IgH minor | 94°C, 15 min | 94°C, 15 s | 57°C, 15 s | 72°C, 15 s | 72°C, 1 min |
| 4 | TCRγ | 94°C, 15 min | 94°C, 15 s | 52°C, 15 s | 72°C, 15 s | - |
| Gene name | Chromosome | Variant type(Position reference base variant impact) | Degree of sharing |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOLIM4 | 34 | 32880086_C_T_3_prime_UTR_variant | 4 |
| ITM2B | 22 | 3396316_CTGGGGGCGGGTGGG_C_5_prime_UTR_variant | 2 |
| STN1 | 28 | 16517367_CA_C_splice_polypyrimidine_tract_variant&intron_variant | 2 |
| PLEKHG4B | 34 | 11903730_G_C_missense_variant&splice_region_variant | 2 |
| PLEKHG4B | 34 | 11903747_G_T_splice_polypyrimidine_tract_variant&intron_variant | 2 |
| UNC79 | 8 | 63061314_A_G_splice_polypyrimidine_tract_variant&intron_variant | 2 |
| UNC79 | 8 | 63061318_G_A_splice_polypyrimidine_tract_variant&intron_variant | 2 |
| BRF1 | 8 | 72881347_G_A_missense_variant | 2 |
| ENSCAFG 00845007156 | 16 | 15352766_C_G_missense_variant | 2 |
| SEMA6B | 20 | 55831203_G_A_3_prime_UTR_variant | 2 |
| DSC1 | 7 | 58326567_CT_C_frameshift_variant | 2 |
| TNFAIP1 | 9 | 43411403_T_G_missense_variant | 2 |
| MYLK3 | 15 | 8510405_G_A_splice_donor_5th_base_variant&intron_variant | 2 |
| WAPL | 4 | 34552139_TTC_T_3_prime_UTR_variant | 2 |
| ADORA2B | 5 | 40018212_CA_C_frameshift_variant&start_lost | 2 |
| LOXHD1 | 7 | 44757742_GAA_G_frameshift_variant | 2 |
| GP6 | 1 | 103278325_A_AG_frameshift_variant | 2 |
| AZIN1 | 13 | 4527111_A_G_stop_lost | 2 |
| NCSTN | 38 | 21997405_T_G_missense_variant | 2 |
| pathway ID | Name of pathways | No. of genes involved | Name of genes involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| hsa04270 | vascular smooth muscle contraction | 2 | ADORA2B, MYLK3 |
| hsa04020 | calcium signaling pathway | 2 | ADORA2B, MYLK3 |
| hsa04611 | platelet activation | 2 | GP6, MYLK3 |
| hsa04512 | ECM-receptor interaction | 1 | GP6 |
| hsa04921 | oxytocin signaling pathway | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa04810 | regulation of actin cytoskeleton | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa04360 | axon guidance | 1 | SEMA6B |
| hsa04371 | apelin signaling pathway | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa05034 | alcoholism | 1 | ADORA2B |
| hsa04022 | cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa04971 | gastric acid secretion | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa05010 | Alzheimer disease | 1 | NCSTN |
| hsa04510 | focal adhesion | 1 | MYLK3 |
| hsa04330 | notch signaling pathway | 1 | NCSTN |
| hsa04080 | neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 1 | ADORA2B |
| hsa04015 | Rap1 signaling pathway | 1 | ADORA2B |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





