Submitted:
18 July 2023
Posted:
18 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Plant Material and Experimental Design
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Vegetative Growth: The Following Parameters Were Undertaken
2.4.1. Average Shoots Length (cm). To Measure Shoot Length (cm) at the End of Spring Cycle, Twenty Shoots per Tree Were Devoted Four Times on Three Different Trees2.4.2. Leaf Area (cm2)
2.4.3. The Volume of Tree Canopy (m3). Tree Size, Expressed as a Canopy Volume Was Measured and Calculated by the Equation of Zekri [28] as Follows: Tree Canopy Volume (m3) = 0.52 × Tree Height × (Diameter2)
2.5. Yield
2.6. Physical Properties of Fruit
2.7. Chemical Properties of Fruit
Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
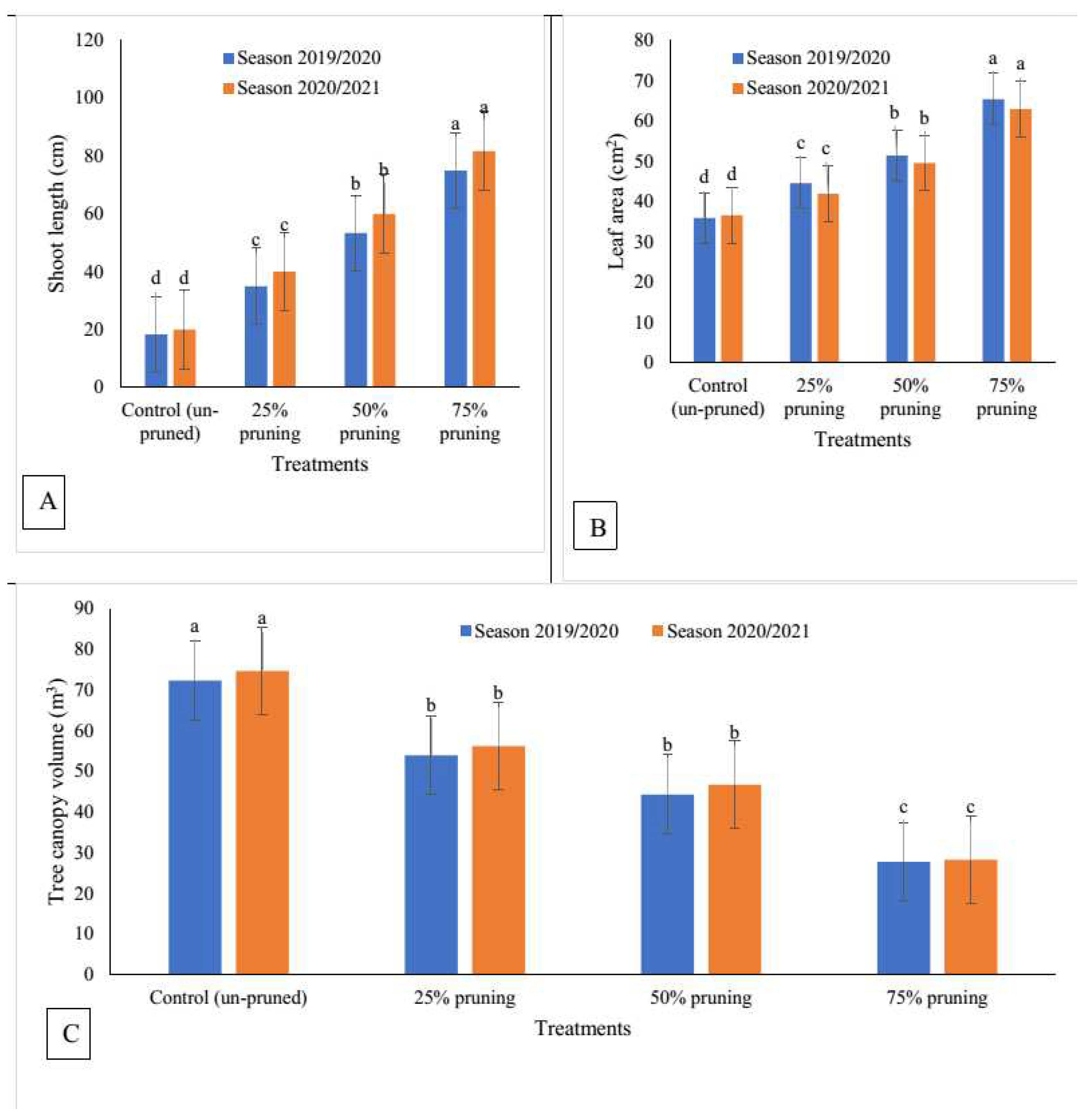
3.1. Effect of Pruning Severity on Vegetative Growth
3.1.1. Shoot Length
3.1.2. Leaf Area
3.1.3. Tree Canopy Volume
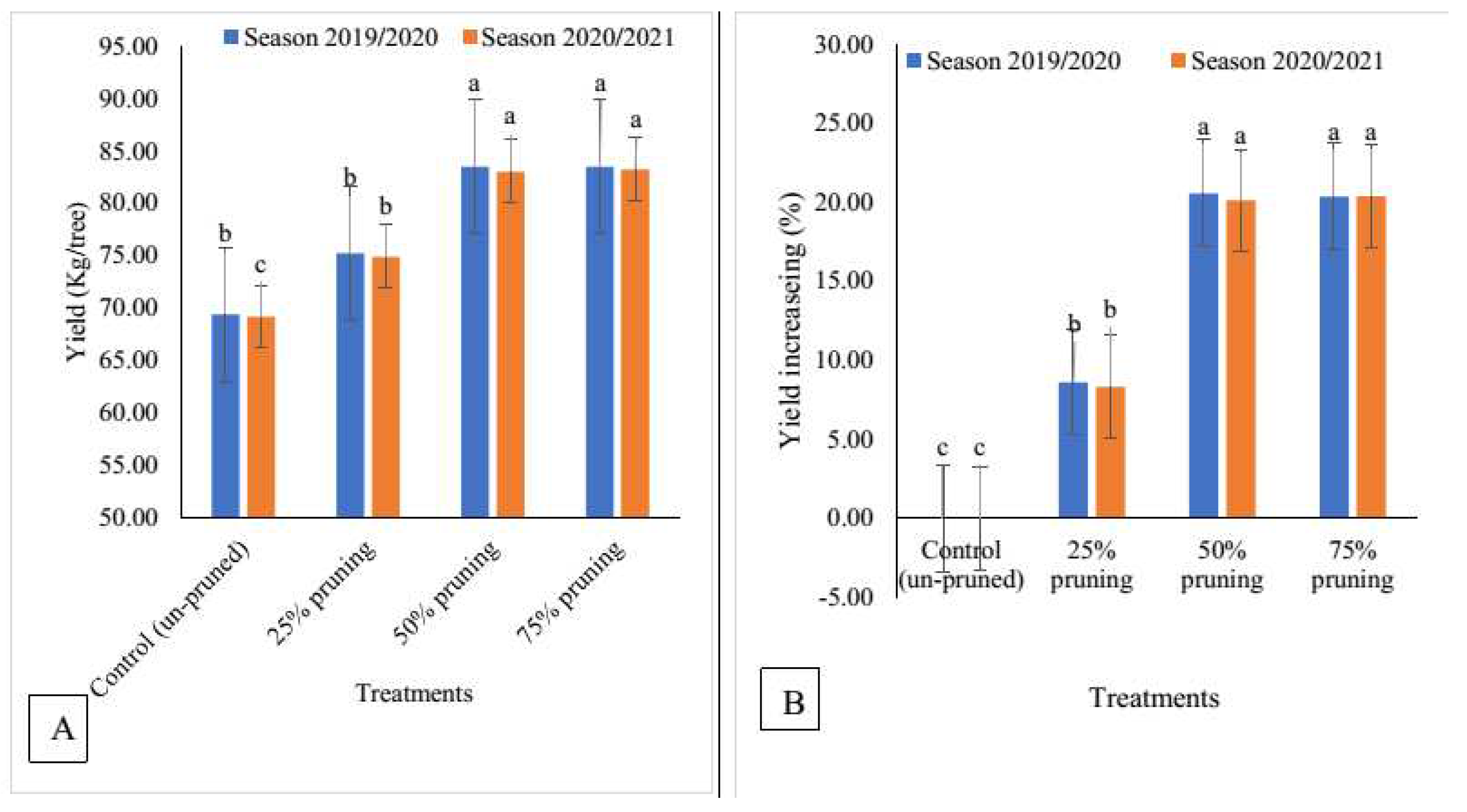
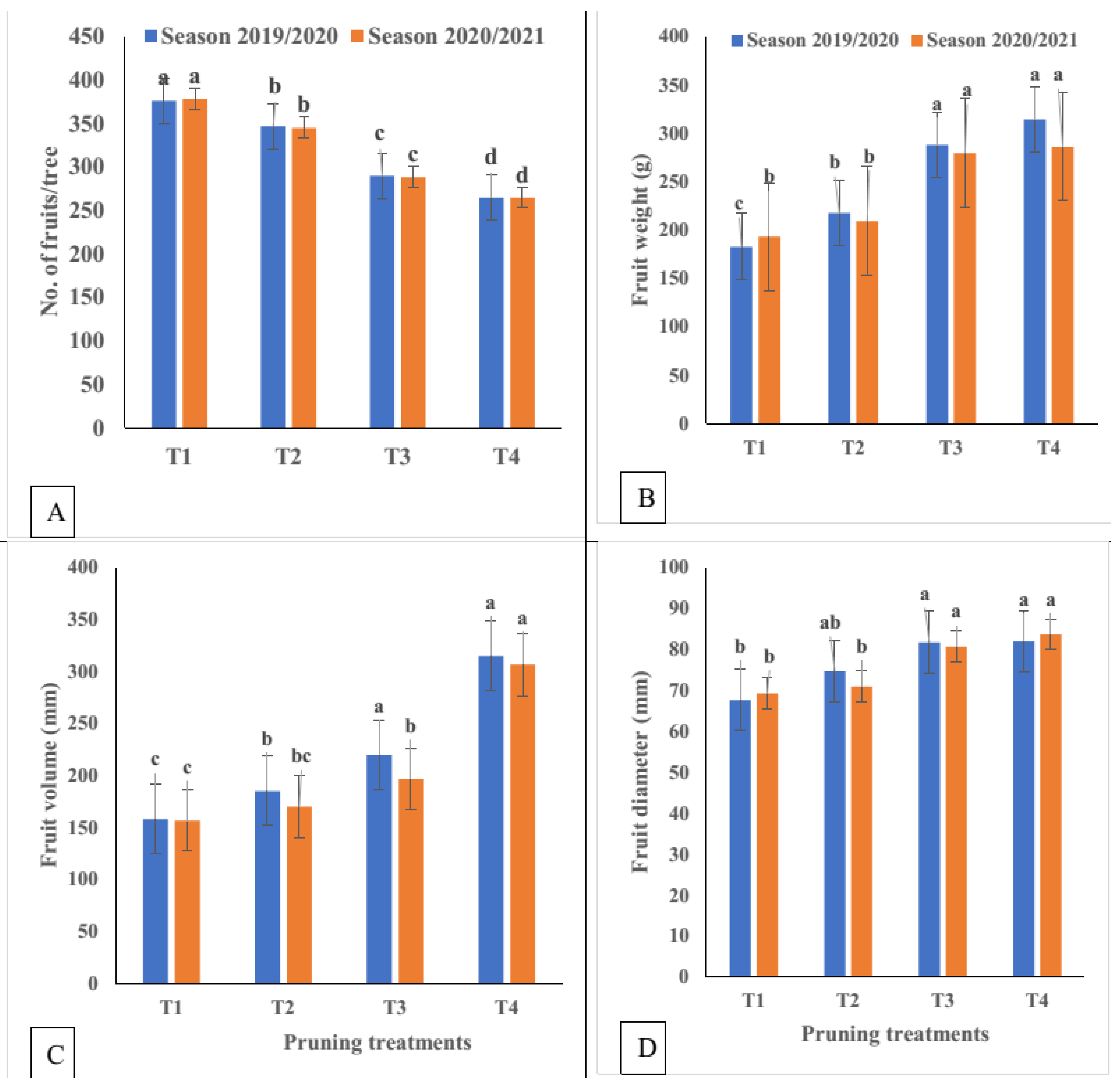
3.2. Effect of Pruning Severity on Yield/Tree
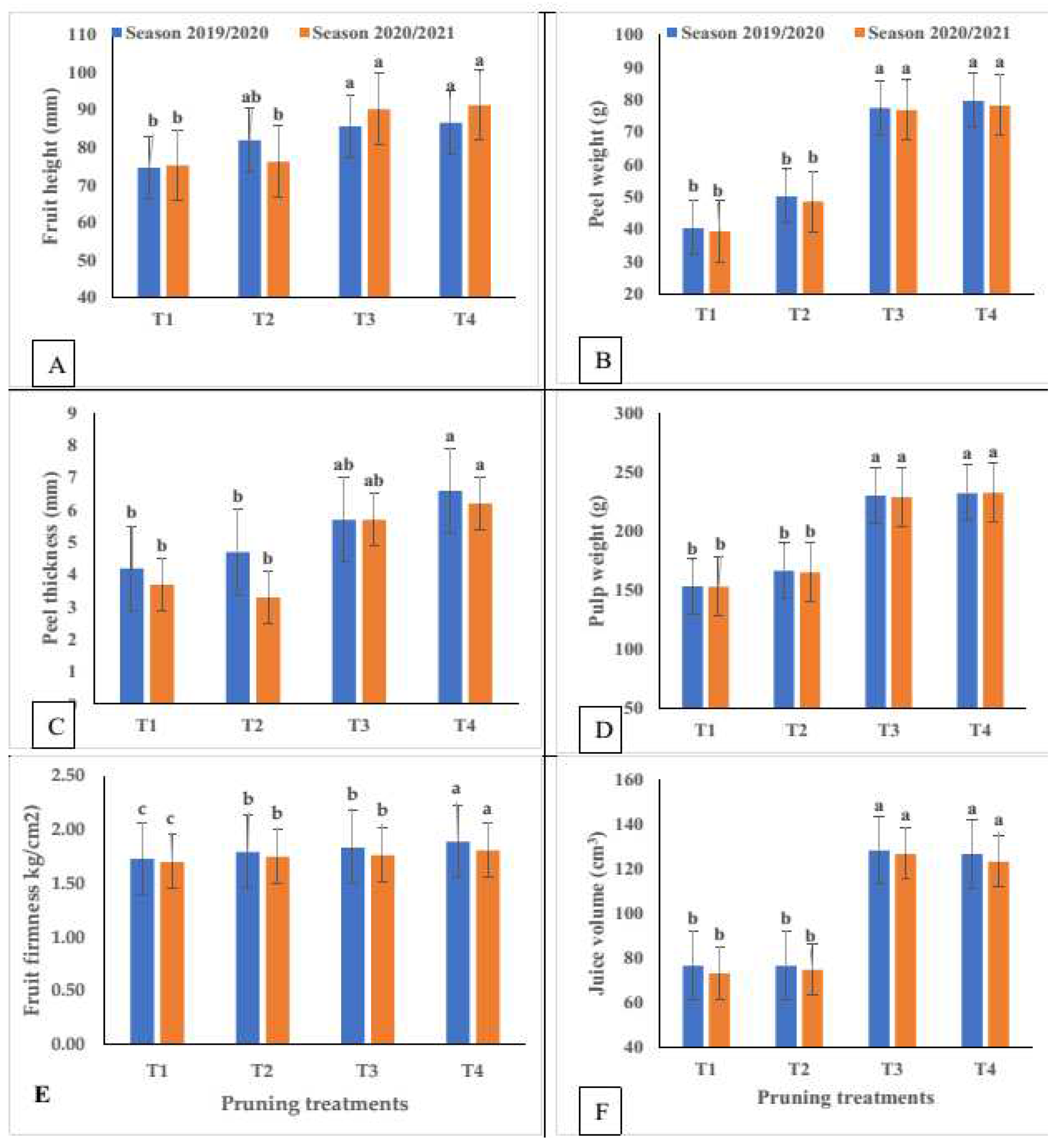
3.3. Physical Characteristics of Fruit
3.3.1. Fruit Weight and Volume
3.3.2. Fruit Firmness
3.3.3. Juice Content of Fruit
3.4. Chemical Characteristics of Fruit
3.4.1. TSS %, TSS/Acid Ratio and Total Acidity
3.4.2. Vitamin C

4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abobatta, W.F. Citrus Varieties in Egypt: An Impression ARTICLE INFORMATION. Int. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Short Commun. 2019, 2663–5585. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, N.A.; KASBIT, D. Citrus Fruit (Kino): Punjab Produced 98% of Production. Exclus. Kino 2017, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, G.H.; Caruso, M.; Gmitter, F.G. Commercial Scion Varieties; Elsevier Inc., 2020. ISBN 9780128122174.
- Manner, H.I.; Buker, R.S.; Smith, V.E.; Elevitch, C.R. Species Profiles for Pacific Island Agroforestry Citrus ( Citrus ) and Fortunella ( Kumquat ). 2020.
- FAO Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; 2020; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Crops 2020. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC.
- El-Gioushy, S.F.; Sami, R.; Al-Mushhin, A.A.M.; Abou El-Ghit, H.M.; Gawish, M.S.; Ismail, K.A.; Zewail, R.M.Y. Foliar Application of Znso4 and Cuso4 Affects the Growth, Productivity, and Fruit Quality of Washington Navel Orange Trees (Citrus Sinensis l.) Osbeck. Horticulturae 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.M.; Botía, P.; Pérez-Pérez, J.G. Sour Orange Rootstock Increases Water Productivity in Deficit Irrigated ‘Verna’ Lemon Trees Compared with Citrus Macrophylla. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 186, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsal, J.; Johnson, S.; Casadesus, J.; Lopez, G.; Girona, J.; Stöckle, C. Fraction of Canopy Intercepted Radiation Relates Differently with Crop Coefficient Depending on the Season and the Fruit Tree Species. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 184, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deidda, Piero; Filigheddu, Maria Rosu; Canu, Annalisa; Laura, Farro; Benjincasa, F. Light Distribution on Citrus Canopy Affects Physiological Paramaeters and Fruiting Pattern. Ann. Della Fac. Agrar. Dell Univ. Sassari 1992, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski, A.; Schumann, A.; Ebert, T.; Oswalt, C.; Ferrarezi, R.; Waldo, L. Management of Citrus Tree Canopies for Fresh-Fruit Production. Edis 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, H.S.; Banke, A.K.; Sharma, L.K.; Bali, S.K. Journal of Experimental Biology and Agricultural Sciences IMPACT OF PRUNING PRACTICES ON SHOOT GROWTH AND BUD PRODUCTION IN KINNOW ( Citrus Reticulata BLANCO ) PLANTS. J. Exp. Biol. Agrcultural Sci. 2014, 1, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaliwal, H.S.; Banke, A.K.; Kumar, L.; Brar, J.S. Standardization of Pruning Severity for Healthy Bud Production in “Kinnow” (C. Nobilis × C. Deliciosa) Mother Plants. Acta Hortic. 2016, 1130, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, B.; Rajput, M.; Rajan, S.; Rathore, D. Effect of Pruning on Rejuvenation of Old Mango Trees. Indian J. Hortic. 2000, 57, 240–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.R.; Datta, S.C.; Varghese, E. Effect of Surround WP®, a Kaolin-Based Particle Film on Sunburn, Fruit Cracking and Postharvest Quality of ‘Kandhari’ Pomegranates. Crop Prot. 2018, 114, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suklabaidya, Dr.A.; Mehta, K. Rejuvenation of Senile Horticultural Plantations for Improved Productivity and Quality. Int. J. Hortic. Agric. Food Sci. 2019, 3, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Misra, K.K.; Rai, R.; Singh, O. Effect of Shoot Pruning and Paclobutrazol on Vegetative Growth , Flowering and Yield of Lemon ( Citrus Limon Burm .) Cv . Pant Lemon-1 Effect of Shoot Pruning and Paclobutrazol on Vegetative Growth , Flowering and Yield of Lemon ( Citrus Limon Burm .) Cv . 2018.
- He, L.; Schupp, J. Sensing and Automation in Pruning of Apple Trees: A Review. Agronomy 2018, 8, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronje, R.; Human, C.; Ratlapane, I. Pruning Strategies for Young ‘Nadorcott’ Mandarin Trees Planted in High Density Orchards in South Africa. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2021, 21, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrigliolo, F.; Roccuzzo, G. Modern Trends of Citrus Pruning in Italy. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 2011, 25, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashora, L.K.; Bhatnagar, P.; Singh, B. Impact of Pruning on Rejuvenation of Declining Nagpur Mandarin Orchard Impact of Pruning on Rejuvenation of Declining Nagpur Mandarin ( Citrus Reticulata Blanco .) Orchard Jitendra Singh *, L . K . Dashora , P . Bhatnagar and Bhim Singh. 2016.
- Salama, B.; Abou-Hadid, A.; Abdelhamid, N.; El-Shinawy, M. Effect of Prunning Pattern and Soil Mulching on Yield and Quality of Keitt Mango in New Reclaimed Lands. Arab Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 26, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisth, T.; Zekri, M.; Alferez, F. 2022–2023 Florida Citrus Production Guide: Canopy Management. 4.
- Tang, Y.; Hou, C.J.; Luo, S.M.; Lin, J.T.; Yang, Z.; Huang, W.F. Effects of Operation Height and Tree Shape on Droplet Deposition in Citrus Trees Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongal, A.; Amatya, S.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q.; Lewis, K. Sensors and Systems for Fruit Detection and Localization: A Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 116, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladaniya, M.S.; Marathe, R.A.; Das, A.K.; Rao, C.N.; Huchche, A.D.; Shirgure, P.S.; Murkute, A.A. High Density Planting Studies in Acid Lime (Citrus Aurantifolia Swingle). Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekri, M. Factors Affecting Citrus Production and Quality. 4.
- Ahmed, F.F. (Minia Univ. (Egypt). F. of A.; Morsy, M.H. A New Method for Measuring Leaf Area in Different Fruit Species. Minia J. Agric. Res. Dev. Egypt v. 19.
- Zekri, M. Original Article Citrus Rootstocks Affect Scion Nutrition, Fruit Quality, Growth, Yiel d and Economical Retur n. Fruits 2000, 55, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Farag, K.M.; Elsabagh, A.S.; Nagy, N.M.N.; Mekkawy, O.M. Field Applications for Color Enhancement of “Valencia” Oranges While Reducing Leaf Abscission. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2019, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Naby, S.K.M.; Ahmed Mohamed, A.A.; El-Naggar, Y.I.M. Effect of Melatonin, GA3 and Naa on Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of ‘Canino’ Apricot Fruits. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2019, 18, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC Association of Official Analytical Chemist. Official Methods of Analysis 18th Edition Washington DC, USA. Off. Methods Anal. 2016, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Dashora, L.K.; Bhatnagar, P.; Singh, B. Impact of Pruning on Rejuvenation of Declining Nagpur Mandarin Orchard Impact of Pruning on Rejuvenation of Declining Nagpur Mandarin ( Citrus Reticulata Blanco .) Orchard Jitendra Singh *, L . K . Dashora , P . Bhatnagar and Bhim Singh. 2016.
- Pandey, S.N. Mango Cultivars. Mango Cultivation; International Book Distributing Company, Lucknow, India: India, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Awasthi, Y.C.; Mitra, C.R. Madhuca Butyracea. Constituents of the Fruit-Pulp and the Bark. Phytochemistry 1968, 7, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Bichuke, S.M.; Sonkamble, A.M. Effect of Severity and Time of Pruning on Growth, Flowering and Fruit Set of Hasta Bahar in Acid Lime. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 6, 968–974. [Google Scholar]
- Adhikari, S.; Kandel, T.P. Effect of Time and Level of Pruning on Vegetative Growth, Flowering, Yield, and Quality of Guava. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2015, 15, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueca, P.; Mateu, G.; Garcerá, C.; Fonte, A.; Ortiz, C.; Torregrosa, A. Yield and Economic Results of Different Mechanical Pruning Strategies on “Navel Foyos” Oranges in the Mediterranean Area. Agric. Switz. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.P.; Singh, N. Effect of Rejuvenation Pruning on the Growth, Productivity and Disease Incidence in Declining Trees of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum L.) Cv. Kandhari Kabuli. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2018, 10, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Ahmad, S.; Haider, S.T.-A.; Naz, S. Effect of Pruning to Improve Yield and Fruit Quality of ‘Kinnow’ Mandarin Plants under High Density Plantation. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2019, 2, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Salem; G. M. Hasseb; H. M. Kamel Effect of Pruning Severity on Vegetative Growth, Flowering and Fruit Setting of Balady Mandarin Trees (Citrus Reticulata Blanco.). 2009. [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.E. Effect of Pruning Severity on Yield and Fruit Quality of Two Mandarin Cultivars. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1216, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milind Ladaniya Cultivars and Producing Countries. Commercial fresh citrus cultivars and producing countries; Elsevier: San Diego, 2008; pp. 13–65. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, J. , Y., & Eshel, G. Effects of 2, 4-D, Ethephon, and NAA on Fruit Size and Yield of Star Rubi Red Grapefruit. In Proceedings of the In Proceedings of the International Society of Citriculture; pp. 1992520–523.
- Din, A.; Asghar, M.; Parveen, S. Evaluation of Kinnow Mandarin As Influenced By Pre-Harvest Management Practices. 2014, 50, 381–392.
- Yildirim, B.; Yeşiloǧlu, T.; Incesu, M.; Kamiloǧlu, M.U.; Çimen, B.; Tamer, Ş. Effects of 2,4-DP (2,4-Dichlorophenoxypropionic Acid) Plant Growth Regulator on Fruit Size and Yield of Valencia Oranges (Citrus Sinensis Osb.). N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2012, 40, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Davies, F.S.; Littell, R.C. Pruning and Skirting Affect Canopy Microclimate, Yields, and Fruit Quality of “Orlando” Tangelo. HortScience 2000, 35, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.; Khan, A.S.; Basra, S.M.A.; Malik, A.U. Foliar Application of Moringa Leaf Extract, Potassium and Zinc Influence Yield and Fruit Quality of ‘Kinnow’ Mandarin. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 210, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joubert, F. J. , Du Plessis, M. H., & Stassen, P.J.C. Pruning Strategies to Alleviate Overcrowding in Higher Density Citrus Orchards. J. Appl. Hortic. 2000, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bowman, K.D.; Joubert, J. Citrus Rootstocks; Elsevier Inc., 2020. ISBN 9780128122174.
- Umar, M.; Ahmad, S.; Haider, S.T.-A.; Naz, S. Effect of Pruning to Improve Yield and Fruit Quality of ‘Kinnow’ Mandarin Plants under High Density Plantation. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2019, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansavini, S.; Musacchi, S. Canopy Architecture, Training and Pruning in the Modern European Pear Orchards: An Overview. Acta Hortic. 1994, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.A.; Tariq, M.A.; Asi, A.A. Effect of Micronutrients Application on the Yield and Quality of Kinnow Mandarin ( Citrus Reticulata Blanco. ). 2006, 38, 169–172. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Gorriz, B.; Porras Castillo, I.; Torregrosa, A. Effect of Mechanical Pruning on the Yield and Quality of ‘Fortune’ Mandarins. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghdady G., A. Effect of Pruning on Yield and Fruit Quality of Balady Mandarin. Ann. Agric Sc Moshtohor 1993, 31, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthi, S. Comparative Efficacy of Sulphate of Potash and Muriate of Potash on Yield and Quality of Chilli (Capsicum Annuum L.), Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore), 2002.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




