Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
20 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Hypnozoite Biology
1.2. Genetic Engineering of Plasmodium
2. Liver Stage Models for P. vivax
2.1. P. vivax In Vivo Liver Stage Models
2.2. P. vivax In Vitro Liver Stage Platforms
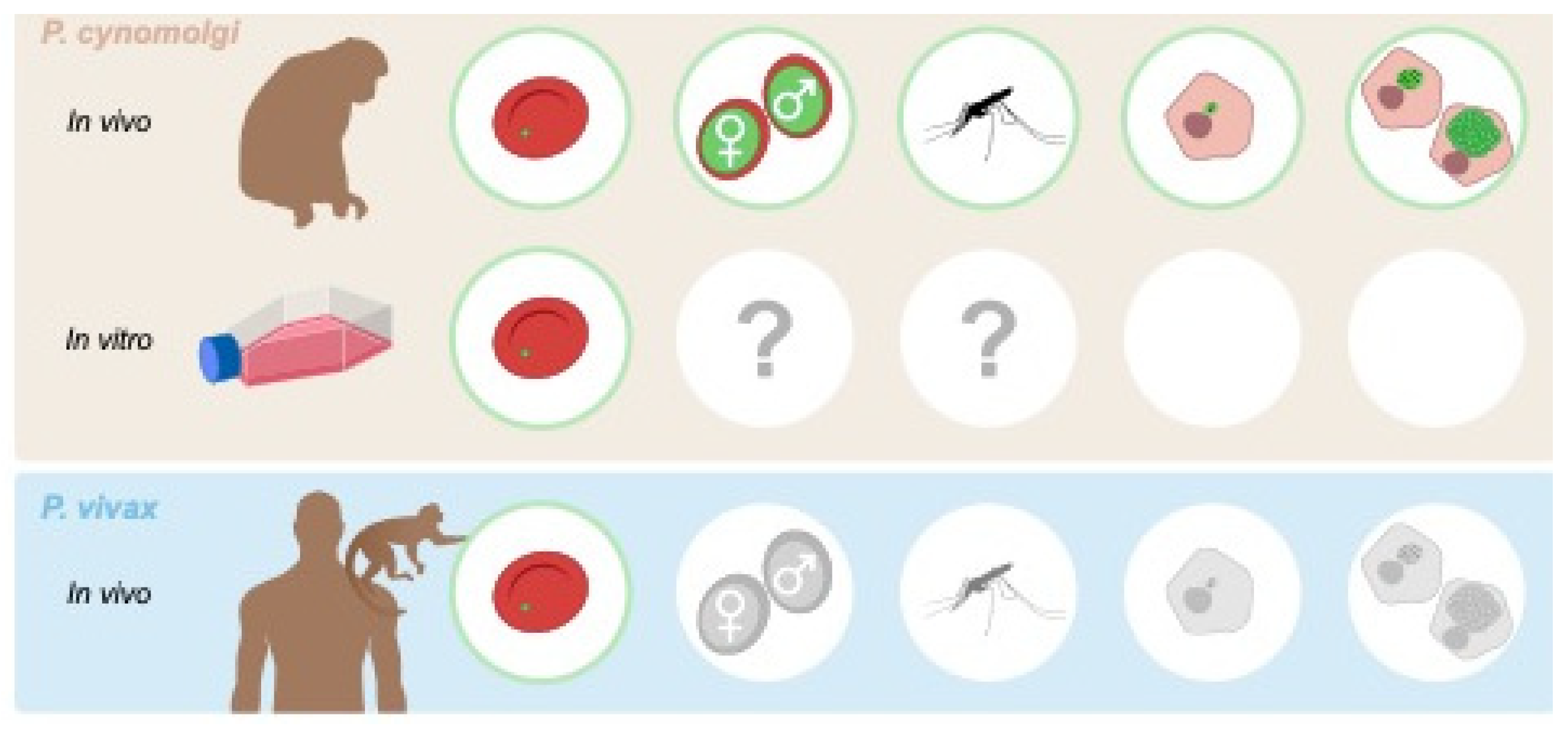
2.3. P. cynomolgi Liver Stage Research Platforms
3. Transfection Technology to Study Hypnozoite Biology
3.1. P. vivax Genetic Engineering Technology
3.2. P. vivax Hypnozoite Research Benefits and Limitations
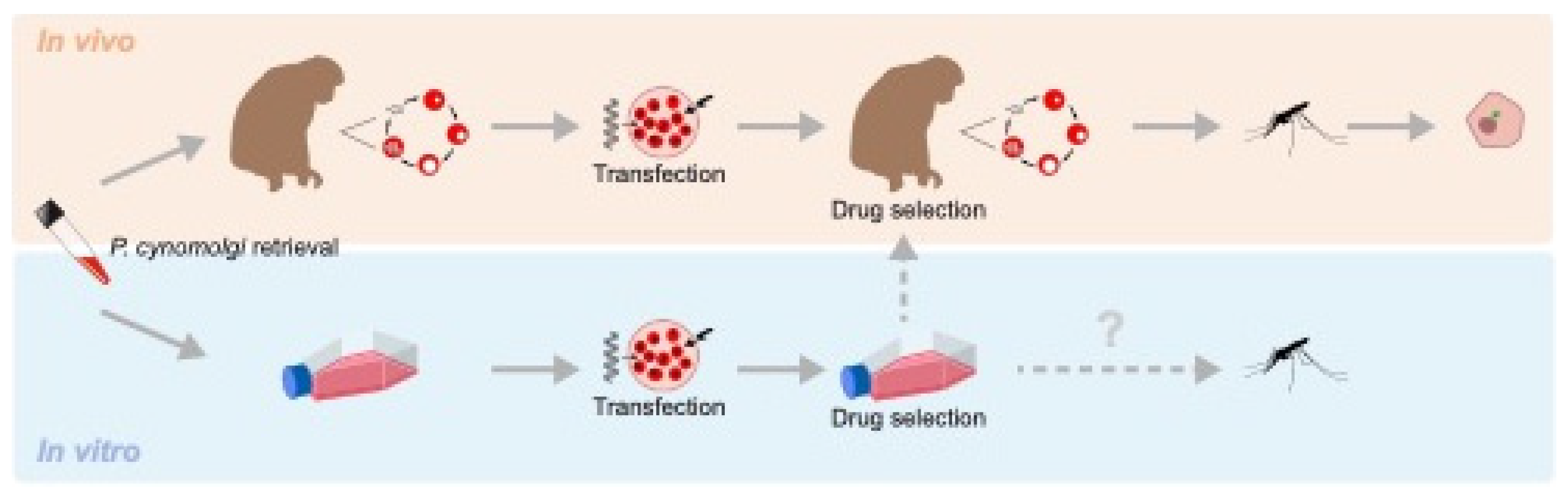
3.3. P. cynomolgi Genetic Engineering Technology
3.3.1. P. cynomolgi In Vivo Genetic Engineering Technology
3.3.2. Application of P. cynomolgi Vivo Derived Transgenic Parasites to the Study of Hypnozoite Biology
3.3.3. P. cynomolgi In Vitro Genetic Engineering Technology
3.4. P. cynomolgi Hypnozoite Research Benefits and Limitations
4. Conclusions and outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- (WHO), W.H.O. World malaria report 2022.
- Battle, K.E.; Lucas, T.C.D.; Nguyen, M.; Howes, R.E.; Nandi, A.K.; Twohig, K.A.; Pfeffer, D.A.; Cameron, E.; Rao, P.C.; Casey, D.; et al. Mapping the global endemicity and clinical burden of Plasmodium vivax, 2000-17: a spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet 2019, 394, 332-343. [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.K. African Plasmodium vivax malaria improbably rare or benign. Trends Parasitol 2022, 38, 683-696. [CrossRef]
- Quaye, I.K.; Aleksenko, L.; Oeuvray, C.; Yewhalaw, D.; Duah, N.; Gyan, B.; Haiyambo, D.H.; Dongho, G.B.D.; Torgby, R.A.; Amoah, L.; et al. The Pan African Vivax and Ovale Network (PAVON): Refocusing on Plasmodium vivax, ovale and asymptomatic malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Parasitol Int 2021, 84, 102415. [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, P.A. Plasmodium vivax Infection in Duffy-Negative People in Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2017, 97, 636-638. [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.K. Evidence and implications of mortality associated with acute Plasmodium vivax malaria. Clin Microbiol Rev 2013, 26, 36-57. [CrossRef]
- Price, R.N.; Tjitra, E.; Guerra, C.A.; Yeung, S.; White, N.J.; Anstey, N.M. Vivax malaria: neglected and not benign. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007, 77, 79-87.
- Phyo, A.P.; Dahal, P.; Mayxay, M.; Ashley, E.A. Clinical impact of vivax malaria: A collection review. PLoS Med 2022, 19, e1003890. [CrossRef]
- Bantuchai, S.; Imad, H.; Nguitragool, W. Plasmodium vivax gametocytes and transmission. Parasitol Int 2022, 87, 102497. [CrossRef]
- Krotoski, W.A.; Collins, W.E.; Bray, R.S.; Garnham, P.C.; Cogswell, F.B.; Gwadz, R.W.; Killick-Kendrick, R.; Wolf, R.; Sinden, R.; Koontz, L.C.; et al. Demonstration of hypnozoites in sporozoite-transmitted Plasmodium vivax infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1982, 31, 1291-1293. [CrossRef]
- Hemmer, C.J.; Holst, F.G.; Kern, P.; Chiwakata, C.B.; Dietrich, M.; Reisinger, E.C. Stronger host response per parasitized erythrocyte in Plasmodium vivax or ovale than in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Trop Med Int Health 2006, 11, 817-823. [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Perez, D.A.; Ruiz, J.A.; Patarroyo, M.A. Reticulocytes: Plasmodium vivax target cells. Biol Cell 2013, 105, 251-260. [CrossRef]
- White, N.J. Why Do Some Primate Malarias Relapse? Trends Parasitol 2016, 32, 918-920. [CrossRef]
- White, N.J. Determinants of relapse periodicity in Plasmodium vivax malaria. Malar J 2011, 10, 297. [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.K.; Battle, K.E.; Howes, R.E. Primaquine ineligibility in anti-relapse therapy of Plasmodium vivax malaria: the problem of G6PD deficiency and cytochrome P-450 2D6 polymorphisms. Malar J 2018, 17, 42. [CrossRef]
- Cox, F.E. History of the discovery of the malaria parasites and their vectors. Parasit Vectors 2010, 3, 5. [CrossRef]
- Cogswell, F.B.; Krotoski, W.A.; Hollingdale, M.R.; Gwadz, R.W. Identification of hypnozoites and tissue schizonts of Plasmodium vivax and P. cynomolgi by the immunoperoxidase method. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1983, 32, 1454-1455. [CrossRef]
- Lover, A.A.; Baird, J.K.; Gosling, R.; Price, R.N. Malaria Elimination: Time to Target All Species. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2018, 99, 17-23. [CrossRef]
- Organization, W.H. Global technical strategy for malaria 2016-2030. . 2015.
- van Dijk, M.R.; Waters, A.P.; Janse, C.J. Stable transfection of malaria parasite blood stages. Science 1995, 268, 1358-1362. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sifri, C.D.; Lei, H.H.; Su, X.Z.; Wellems, T.E. Transfection of Plasmodium falciparum within human red blood cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1995, 92, 973-977. [CrossRef]
- Kafsack, B.F.; Rovira-Graells, N.; Clark, T.G.; Bancells, C.; Crowley, V.M.; Campino, S.G.; Williams, A.E.; Drought, L.G.; Kwiatkowski, D.P.; Baker, D.A.; et al. A transcriptional switch underlies commitment to sexual development in malaria parasites. Nature 2014, 507, 248-252. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Hughes, K.R.; Modrzynska, K.K.; Otto, T.D.; Pfander, C.; Dickens, N.J.; Religa, A.A.; Bushell, E.; Graham, A.L.; Cameron, R.; et al. A cascade of DNA-binding proteins for sexual commitment and development in Plasmodium. Nature 2014, 507, 253-257. [CrossRef]
- Cowman, A.F.; Baldi, D.L.; Healer, J.; Mills, K.E.; O'Donnell, R.A.; Reed, M.B.; Triglia, T.; Wickham, M.E.; Crabb, B.S. Functional analysis of proteins involved in Plasmodium falciparum merozoite invasion of red blood cells. FEBS Lett 2000, 476, 84-88. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.C.; Vaughan, A.M.; Kublin, J.G.; Fishbauger, M.; Seilie, A.M.; Cruz, K.P.; Mankowski, T.; Firat, M.; Magee, S.; Betz, W.; et al. A genetically engineered Plasmodium falciparum parasite vaccine provides protection from controlled human malaria infection. Sci Transl Med 2022, 14, eabn9709. [CrossRef]
- Roestenberg, M.; Walk, J.; van der Boor, S.C.; Langenberg, M.C.C.; Hoogerwerf, M.A.; Janse, J.J.; Manurung, M.; Yap, X.Z.; Garcia, A.F.; Koopman, J.P.R.; et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2a trial of the genetically attenuated malaria vaccine PfSPZ-GA1. Sci Transl Med 2020, 12. [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.; Corey, V.; Scherer, C.A.; Kato, N.; Comer, E.; Maetani, M.; Antonova-Koch, Y.; Reimer, C.; Gagaring, K.; Ibanez, M.; et al. High-Throughput Luciferase-Based Assay for the Discovery of Therapeutics That Prevent Malaria. ACS Infect Dis 2016, 2, 281-293. [CrossRef]
- Jongco, A.M.; Ting, L.M.; Thathy, V.; Mota, M.M.; Kim, K. Improved transfection and new selectable markers for the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium yoelii. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2006, 146, 242-250. [CrossRef]
- Kocken, C.H.; van der Wel, A.; Thomas, A.W. Plasmodium cynomolgi: transfection of blood-stage parasites using heterologous DNA constructs. Exp Parasitol 1999, 93, 58-60. [CrossRef]
- Reece, S.E.; Thompson, J. Transformation of the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium chabaudi and generation of a stable fluorescent line PcGFPCON. Malar J 2008, 7, 183. [CrossRef]
- van der Wel, A.M.; Tomas, A.M.; Kocken, C.H.; Malhotra, P.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P.; Thomas, A.W. Transfection of the primate malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi using entirely heterologous constructs. J Exp Med 1997, 185, 1499-1503. [CrossRef]
- Moraes Barros, R.R.; Straimer, J.; Sa, J.M.; Salzman, R.E.; Melendez-Muniz, V.A.; Mu, J.; Fidock, D.A.; Wellems, T.E. Editing the Plasmodium vivax genome, using zinc-finger nucleases. J Infect Dis 2015, 211, 125-129. [CrossRef]
- Pfahler, J.M.; Galinski, M.R.; Barnwell, J.W.; Lanzer, M. Transient transfection of Plasmodium vivax blood stage parasites. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2006, 149, 99-101. [CrossRef]
- Kocken, C.H.; Ozwara, H.; van der Wel, A.; Beetsma, A.L.; Mwenda, J.M.; Thomas, A.W. Plasmodium knowlesi provides a rapid in vitro and in vivo transfection system that enables double-crossover gene knockout studies. Infect Immun 2002, 70, 655-660. [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.E.; Christensen, P.; Racklyeft, A.; Dhingra, S.K.; Chua, A.C.Y.; Remmert, C.; Suwanarusk, R.; Matheson, J.; Blackman, M.J.; Kaneko, O.; et al. Integrative genetic manipulation of Plasmodium cynomolgi reveals MultiDrug Resistance-1 Y976F associated with increased in vitro susceptibility to mefloquine. J Infect Dis 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ngotho, P.; Soares, A.B.; Hentzschel, F.; Achcar, F.; Bertuccini, L.; Marti, M. Revisiting gametocyte biology in malaria parasites. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2019, 43, 401-414. [CrossRef]
- Bertschi, N.L.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Zeeman, A.M.; Schuierer, S.; Nigsch, F.; Carbone, W.; Knehr, J.; Gupta, D.K.; Hofman, S.O.; van der Werff, N.; et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals reduced transcriptional activity in the malaria parasite Plasmodium cynomolgi during progression into dormancy. Elife 2018, 7. [CrossRef]
- Toenhake, C.G.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Wu, H.; Kanyal, A.; Nieuwenhuis, I.G.; van der Werff, N.M.; Hofman, S.O.; Zeeman, A.M.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Bartfai, R. Epigenetically regulated RNA-binding proteins signify malaria hypnozoite dormancy. Cell Rep 2023, 42, 112727. [CrossRef]
- Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Roma, G.; Gupta, D.K.; Schuierer, S.; Nigsch, F.; Carbone, W.; Zeeman, A.M.; Lee, B.H.; Hofman, S.O.; Faber, B.W.; et al. A comparative transcriptomic analysis of replicating and dormant liver stages of the relapsing malaria parasite Plasmodium cynomolgi. Elife 2017, 6. [CrossRef]
- Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Zeeman, A.M.; van Amsterdam, S.M.; van den Berg, A.; Klooster, E.J.; Iwanaga, S.; Janse, C.J.; van Gemert, G.J.; Sauerwein, R.; Beenhakker, N.; et al. Transgenic fluorescent Plasmodium cynomolgi liver stages enable live imaging and purification of Malaria hypnozoite-forms. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54888. [CrossRef]
- Voorberg-van der Wel, A.M.; Zeeman, A.M.; Nieuwenhuis, I.G.; van der Werff, N.M.; Klooster, E.J.; Klop, O.; Vermaat, L.C.; Kumar Gupta, D.; Dembele, L.; Diagana, T.T.; et al. A dual fluorescent Plasmodium cynomolgi reporter line reveals in vitro malaria hypnozoite reactivation. Commun Biol 2020, 3, 7. [CrossRef]
- Voorberg-van der Wel, A.M.; Zeeman, A.M.; Nieuwenhuis, I.G.; van der Werff, N.M.; Kocken, C.H.M. Dual-Luciferase-Based Fast and Sensitive Detection of Malaria Hypnozoites for the Discovery of Anti-relapse Compounds. Methods Mol Biol 2022, 2524, 397-408. [CrossRef]
- Coatney G.R., C.W.E., Warren M., and Contacos P. G. . The primate malarias [original book published 1971].
- Joyner, C.; Barnwell, J.W.; Galinski, M.R. No more monkeying around: primate malaria model systems are key to understanding Plasmodium vivax liver-stage biology, hypnozoites, and relapses. Front Microbiol 2015, 6, 145. [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczak, S.A.; Vaughan, A.M.; Kangwanrangsan, N.; Roobsoong, W.; Fishbaugher, M.; Yimamnuaychok, N.; Rezakhani, N.; Lakshmanan, V.; Singh, N.; Kaushansky, A.; et al. Plasmodium vivax liver stage development and hypnozoite persistence in human liver-chimeric mice. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 526-535. [CrossRef]
- Schafer, C.; Dambrauskas, N.; Reynolds, L.M.; Trakhimets, O.; Raappana, A.; Flannery, E.L.; Roobsoong, W.; Sattabongkot, J.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; Kappe, S.H.I.; et al. Partial protection against P. vivax infection diminishes hypnozoite burden and blood-stage relapses. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 752-756 e754. [CrossRef]
- Flannery, E.L.; Kangwanrangsan, N.; Chuenchob, V.; Roobsoong, W.; Fishbaugher, M.; Zhou, K.; Billman, Z.P.; Martinson, T.; Olsen, T.M.; Schafer, C.; et al. Plasmodium vivax latent liver infection is characterized by persistent hypnozoites, hypnozoite-derived schizonts, and time-dependent efficacy of primaquine. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev 2022, 26, 427-440. [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Moreno-Perez, D.A.; Arevalo-Pinzon, G.; Curtidor, H.; Patarroyo, M.A. Plasmodium vivax in vitro continuous culture: the spoke in the wheel. Malar J 2018, 17, 301. [CrossRef]
- Thomson-Luque, R.; Adams, J.H.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Pasini, E.M. From marginal to essential: the golden thread between nutrient sensing, medium composition and Plasmodium vivax maturation in in vitro culture. Malar J 2019, 18, 344. [CrossRef]
- Valenciano, A.L.; Gomez-Lorenzo, M.G.; Vega-Rodriguez, J.; Adams, J.H.; Roth, A. In vitro models for human malaria: targeting the liver stage. Trends Parasitol 2022, 38, 758-774. [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, R.; Velmurugan, S.; Chakiath, C.; Andrews Donkor, L.; Milhous, W.; Barnwell, J.W.; Collins, W.E.; Hoffman, S.L. Establishment of an in vitro assay for assessing the effects of drugs on the liver stages of Plasmodium vivax malaria. PLoS One 2010, 5, e14275. [CrossRef]
- Hollingdale, M.R.; Collins, W.E.; Campbell, C.C.; Schwartz, A.L. In vitro culture of two populations (dividing and nondividing) of exoerythrocytic parasites of Plasmodium vivax. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1985, 34, 216-222. [CrossRef]
- Sattabongkot, J.; Yimamnuaychoke, N.; Leelaudomlipi, S.; Rasameesoraj, M.; Jenwithisuk, R.; Coleman, R.E.; Udomsangpetch, R.; Cui, L.; Brewer, T.G. Establishment of a human hepatocyte line that supports in vitro development of the exo-erythrocytic stages of the malaria parasites Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2006, 74, 708-715.
- Pewkliang, Y.; Rungin, S.; Lerdpanyangam, K.; Duangmanee, A.; Kanjanasirirat, P.; Suthivanich, P.; Sa-Ngiamsuntorn, K.; Borwornpinyo, S.; Sattabongkot, J.; Patrapuvich, R.; et al. A novel immortalized hepatocyte-like cell line (imHC) supports in vitro liver stage development of the human malarial parasite Plasmodium vivax. Malar J 2018, 17, 50. [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.; Schwartz, R.E.; March, S.; Galstian, A.; Gural, N.; Shan, J.; Prabhu, M.; Mota, M.M.; Bhatia, S.N. Human iPSC-derived hepatocyte-like cells support Plasmodium liver-stage infection in vitro. Stem Cell Reports 2015, 4, 348-359. [CrossRef]
- Gural, N.; Mancio-Silva, L.; Miller, A.B.; Galstian, A.; Butty, V.L.; Levine, S.S.; Patrapuvich, R.; Desai, S.P.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; Kappe, S.H.I.; et al. In Vitro Culture, Drug Sensitivity, and Transcriptome of Plasmodium Vivax Hypnozoites. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 395-406 e394. [CrossRef]
- March, S.; Ng, S.; Velmurugan, S.; Galstian, A.; Shan, J.; Logan, D.J.; Carpenter, A.E.; Thomas, D.; Sim, B.K.; Mota, M.M.; et al. A microscale human liver platform that supports the hepatic stages of Plasmodium falciparum and vivax. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 104-115. [CrossRef]
- Chua, A.C.Y.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Ong, J.J.Y.; Wong, J.Y.; Yip, A.; Singh, N.H.; Qu, Y.; Dembele, L.; McMillian, M.; Ubalee, R.; et al. Hepatic spheroids used as an in vitro model to study malaria relapse. Biomaterials 2019, 216, 119221. [CrossRef]
- Mazier, D.; Landau, I.; Druilhe, P.; Miltgen, F.; Guguen-Guillouzo, C.; Baccam, D.; Baxter, J.; Chigot, J.P.; Gentilini, M. Cultivation of the liver forms of Plasmodium vivax in human hepatocytes. Nature 1984, 307, 367-369. [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Maher, S.P.; Conway, A.J.; Ubalee, R.; Chaumeau, V.; Andolina, C.; Kaba, S.A.; Vantaux, A.; Bakowski, M.A.; Thomson-Luque, R.; et al. A comprehensive model for assessment of liver stage therapies targeting Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium falciparum. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1837. [CrossRef]
- Carlton, J.M.; Adams, J.H.; Silva, J.C.; Bidwell, S.L.; Lorenzi, H.; Caler, E.; Crabtree, J.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Merino, E.F.; Amedeo, P.; et al. Comparative genomics of the neglected human malaria parasite Plasmodium vivax. Nature 2008, 455, 757-763. [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44-53. [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, A.M.; Lakshminarayana, S.B.; van der Werff, N.; Klooster, E.J.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Kondreddi, R.R.; Bodenreider, C.; Simon, O.; Sauerwein, R.; Yeung, B.K.; et al. PI4 Kinase Is a Prophylactic but Not Radical Curative Target in Plasmodium vivax-Type Malaria Parasites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2016, 60, 2858-2863. [CrossRef]
- Mancio-Silva, L.; Gural, N.; Real, E.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Butty, V.L.; March, S.; Nerurkar, N.; Hughes, T.K.; Roobsoong, W.; Fleming, H.E.; et al. A single-cell liver atlas of Plasmodium vivax infection. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 1048-1060 e1045. [CrossRef]
- Ruberto, A.A.; Maher, S.P.; Vantaux, A.; Joyner, C.J.; Bourke, C.; Balan, B.; Jex, A.; Mueller, I.; Witkowski, B.; Kyle, D.E. Single-cell RNA profiling of Plasmodium vivax-infected hepatocytes reveals parasite- and host- specific transcriptomic signatures and therapeutic targets. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12, 986314. [CrossRef]
- Krotoski, W.A.; Bray, R.S.; Garnham, P.C.; Gwadz, R.W.; Killick-Kendrick, R.; Draper, C.C.; Targett, G.A.; Krotoski, D.M.; Guy, M.W.; Koontz, L.C.; et al. Observations on early and late post-sporozoite tissue stages in primate malaria. II. The hypnozoite of Plasmodium cynomolgi bastianellii from 3 to 105 days after infection, and detection of 36- to 40-hour pre-erythrocytic forms. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1982, 31, 211-225.
- Krotoski, W.A.; Garnham, P.C.; Bray, R.S.; Krotoski, D.M.; Killick-Kendrick, R.; Draper, C.C.; Targett, G.A.; Guy, M.W. Observations on early and late post-sporozoite tissue stages in primate malaria. I. Discovery of a new latent form of Plasmodium cynomolgi (the hypnozoite), and failure to detect hepatic forms within the first 24 hours after infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1982, 31, 24-35.
- Hawking, F.; Worms, M.J.; Gammage, K. 24- and 48-hour cycles of malaria parasites in the blood; their purpose, production and control. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1968, 62, 731-765. [CrossRef]
- Krotoski, W.A.; Krotoski, D.M.; Garnham, P.C.; Bray, R.S.; Killick-Kendrick, R.; Draper, C.C.; Targett, G.A.; Guy, M.W. Relapses in primate malaria: discovery of two populations of exoerythrocytic stages. Preliminary note. Br Med J 1980, 280, 153-154. [CrossRef]
- G.R., C. Reminiscences: My Forty-Year Romance with Malaria. Transactions of the Nebraska Academy of Sciences and Affiliated Societies 1985, 222.
- Corcoran, K.D.; Hansukjariya, P.; Sattabongkot, J.; Ngampochjana, M.; Edstein, M.D.; Smith, C.D.; Shanks, G.D.; Milhous, W.K. Causal prophylactic and radical curative activity of WR182393 (a guanylhydrazone) against Plasmodium cynomolgi in Macaca mulatta. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1993, 49, 473-477. [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.E., Jr.; Ager, A.L.; Brown, J.L.; Chapple, F.E.; Whitmire, R.E.; Rossan, R.N. New tissue schizontocidal antimalarial drugs. Bull World Health Organ 1981, 59, 463-479.
- Deye, G.A.; Gettayacamin, M.; Hansukjariya, P.; Im-erbsin, R.; Sattabongkot, J.; Rothstein, Y.; Macareo, L.; Fracisco, S.; Bennett, K.; Magill, A.J.; et al. Use of a rhesus Plasmodium cynomolgi model to screen for anti-hypnozoite activity of pharmaceutical substances. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2012, 86, 931-935. [CrossRef]
- Dow, G.S.; Gettayacamin, M.; Hansukjariya, P.; Imerbsin, R.; Komcharoen, S.; Sattabongkot, J.; Kyle, D.; Milhous, W.; Cozens, S.; Kenworthy, D.; et al. Radical curative efficacy of tafenoquine combination regimens in Plasmodium cynomolgi-infected Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Malar J 2011, 10, 212. [CrossRef]
- Dutta, G.P.; Puri, S.K.; Bhaduri, A.P.; Seth, M. Radical curative activity of a new 8-aminoquinoline derivative (CDRI 80/53) against Plasmodium cynomolgi B in monkeys. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1989, 41, 635-637. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H. Appraisals of compounds of diverse chemical classes for capacities to cure infections with sporozoites of Plasmodium cynomolgi. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1983, 32, 231-257. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, L.H.; Fradkin, R.; Genther, C.S.; Rossan, R.N.; Squires, W. Responses of Sporozoite-Induced and Trophozoite-Induced Infections to Standard Antimalarial Drugs. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1982, 31, 646-665.
- Sodeman, T.M.; Contacos, P.G.; Collins, W.E.; Smith, C.S.; Jumper, J.R. Studies on the prophylactic and radical curative activity of RC-12 against Plasmodium cynomolgi in Macaca mulatta. Bull World Health Organ 1972, 47, 425-428.
- Millet, P.; Fisk, T.L.; Collins, W.E.; Broderson, J.R.; Nguyen-Dinh, P. Cultivation of exoerythrocytic stages of Plasmodium cynomolgi, P. knowlesi, P. coatneyi, and P. inui in Macaca mulatta hepatocytes. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1988, 39, 529-534. [CrossRef]
- Dembele, L.; Gego, A.; Zeeman, A.M.; Franetich, J.F.; Silvie, O.; Rametti, A.; Le Grand, R.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; Sauerwein, R.; van Gemert, G.J.; et al. Towards an in vitro model of Plasmodium hypnozoites suitable for drug discovery. PLoS One 2011, 6, e18162. [CrossRef]
- Zeeman, A.M.; van Amsterdam, S.M.; McNamara, C.W.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Klooster, E.J.; van den Berg, A.; Remarque, E.J.; Plouffe, D.M.; van Gemert, G.J.; Luty, A.; et al. KAI407, a potent non-8-aminoquinoline compound that kills Plasmodium cynomolgi early dormant liver stage parasites in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 1586-1595. [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, K.; Tajeri, S.; Arnold, C.S.; Amanzougaghene, N.; Franetich, J.F.; Vantaux, A.; Soulard, V.; Bordessoulles, M.; Cazals, G.; Bousema, T.; et al. Artemisinin-independent inhibitory activity of Artemisia sp. infusions against different Plasmodium stages including relapse-causing hypnozoites. Life Sci Alliance 2022, 5. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Dembele, L.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Roma, G.; Yip, A.; Chuenchob, V.; Kangwanrangsan, N.; Ishino, T.; Vaughan, A.M.; Kappe, S.H.; et al. The Plasmodium liver-specific protein 2 (LISP2) is an early marker of liver stage development. Elife 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, P.L.; Luo, Z.; Divis, P.C.S.; Friedrich, V.K.; Conway, D.J.; Singh, B.; Barnwell, J.W.; Carlton, J.M.; Sullivan, S.A. Characterizing the genetic diversity of the monkey malaria parasite Plasmodium cynomolgi. Infect Genet Evol 2016, 40, 243-252. [CrossRef]
- Dembele, L.; Franetich, J.F.; Lorthiois, A.; Gego, A.; Zeeman, A.M.; Kocken, C.H.; Le Grand, R.; Dereuddre-Bosquet, N.; van Gemert, G.J.; Sauerwein, R.; et al. Persistence and activation of malaria hypnozoites in long-term primary hepatocyte cultures. Nat Med 2014, 20, 307-312. [CrossRef]
- Cubi, R.; Vembar, S.S.; Biton, A.; Franetich, J.F.; Bordessoulles, M.; Sossau, D.; Zanghi, G.; Bosson-Vanga, H.; Benard, M.; Moreno, A.; et al. Laser capture microdissection enables transcriptomic analysis of dividing and quiescent liver stages of Plasmodium relapsing species. Cell Microbiol 2017, 19. [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, S.; Kawai, S.; Katakai, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Nakade, T.; Yasutomi, Y.; Horii, T.; Tanabe, K. Contrasting infection susceptibility of the Japanese macaques and cynomolgus macaques to closely related malaria parasites, Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium cynomolgi. Parasitol Int 2015, 64, 274-281. [CrossRef]
- Pasini, E.M.; Bohme, U.; Rutledge, G.G.; Voorberg-Van der Wel, A.; Sanders, M.; Berriman, M.; Kocken, C.H.; Otto, T.D. An improved Plasmodium cynomolgi genome assembly reveals an unexpected methyltransferase gene expansion. Wellcome Open Res 2017, 2, 42. [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, S.; Sullivan, S.A.; Kawai, S.; Nakamura, S.; Kim, H.R.; Goto, N.; Arisue, N.; Palacpac, N.M.; Honma, H.; Yagi, M.; et al. Plasmodium cynomolgi genome sequences provide insight into Plasmodium vivax and the monkey malaria clade. Nat Genet 2012, 44, 1051-1055. [CrossRef]
- Akinyi, S.; Hanssen, E.; Meyer, E.V.; Jiang, J.; Korir, C.C.; Singh, B.; Lapp, S.; Barnwell, J.W.; Tilley, L.; Galinski, M.R. A 95 kDa protein of Plasmodium vivax and P. cynomolgi visualized by three-dimensional tomography in the caveola-vesicle complexes (Schuffner's dots) of infected erythrocytes is a member of the PHIST family. Mol Microbiol 2012, 84, 816-831. [CrossRef]
- Barale, J.C.; Menard, R. Centromeric plasmids and artificial chromosomes: new kids on the Plasmodium transfection block. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 181-183. [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, G.; Briquet, S.; Risco-Castillo, V.; Gaultier, C.; Topcu, S.; Ivanescu, M.L.; Franetich, J.F.; Hoareau-Coudert, B.; Mazier, D.; Silvie, O. A rapid and robust selection procedure for generating drug-selectable marker-free recombinant malaria parasites. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 4760. [CrossRef]
- van Schaijk, B.C.; van Dijk, M.R.; van de Vegte-Bolmer, M.; van Gemert, G.J.; van Dooren, M.W.; Eksi, S.; Roeffen, W.F.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P.; Sauerwein, R.W. Pfs47, paralog of the male fertility factor Pfs48/45, is a female specific surface protein in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2006, 149, 216-222. [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, S.; Kato, T.; Kaneko, I.; Yuda, M. Centromere plasmid: a new genetic tool for the study of Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33326. [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, S.; Khan, S.M.; Kaneko, I.; Christodoulou, Z.; Newbold, C.; Yuda, M.; Janse, C.J.; Waters, A.P. Functional identification of the Plasmodium centromere and generation of a Plasmodium artificial chromosome. Cell Host Microbe 2010, 7, 245-255. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, G.; Roma, G.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Beibel, M.; Zeeman, A.M.; Schuierer, S.; Torres, L.; Flannery, E.L.; Kocken, C.H.M.; Mikolajczak, S.A.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of hepatocytes infected with the replicative form of the malaria parasite Plasmodium cynomolgi. Malar J 2022, 21, 393. [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B.F.; Valley, M.P.; Butler, B.L.; Wood, M.G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; et al. Engineered luciferase reporter from a deep sea shrimp utilizing a novel imidazopyrazinone substrate. ACS Chem Biol 2012, 7, 1848-1857. [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.R.; Das, S.; Wong, E.H.; Andenmatten, N.; Stallmach, R.; Hackett, F.; Herman, J.P.; Muller, S.; Meissner, M.; Blackman, M.J. Robust inducible Cre recombinase activity in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum enables efficient gene deletion within a single asexual erythrocytic growth cycle. Mol Microbiol 2013, 88, 687-701. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.; Briquet, S.; Patarot, D.; Loubens, M.; Hoareau-Coudert, B.; Silvie, O. The dimerisable Cre recombinase allows conditional genome editing in the mosquito stages of Plasmodium berghei. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0236616. [CrossRef]
- Knuepfer, E.; Napiorkowska, M.; van Ooij, C.; Holder, A.A. Generating conditional gene knockouts in Plasmodium - a toolkit to produce stable DiCre recombinase-expressing parasite lines using CRISPR/Cas9. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 3881. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.; Racklyeft, A.; Ward, K.E.; Matheson, J.; Suwanarusk, R.; Chua, A.C.Y.; Kaneko, O.; Aung, H.L.; Renia, L.; Amanzougaghene, N.; et al. Improving in vitro continuous cultivation of Plasmodium cynomolgi, a model for P. vivax. Parasitol Int 2022, 89, 102589. [CrossRef]
- Chua, A.C.Y.; Ong, J.J.Y.; Malleret, B.; Suwanarusk, R.; Kosaisavee, V.; Zeeman, A.M.; Cooper, C.A.; Tan, K.S.W.; Zhang, R.; Tan, B.H.; et al. Robust continuous in vitro culture of the Plasmodium cynomolgi erythrocytic stages. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3635. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbal, M.; Gorman, M.; Macpherson, C.R.; Martins, R.M.; Scherf, A.; Lopez-Rubio, J.J. Genome editing in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat Biotechnol 2014, 32, 819-821. [CrossRef]
- Carrasquilla, M.; Adjalley, S.; Sanderson, T.; Marin-Menendez, A.; Coyle, R.; Montandon, R.; Rayner, J.C.; Pance, A.; Lee, M.C.S. Defining multiplicity of vector uptake in transfected Plasmodium parasites. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 10894. [CrossRef]
- Knuepfer, E.; Wright, K.E.; Kumar Prajapati, S.; Rawlinson, T.A.; Mohring, F.; Koch, M.; Lyth, O.R.; Howell, S.A.; Villasis, E.; Snijders, A.P.; et al. Divergent roles for the RH5 complex components, CyRPA and RIPR in human-infective malaria parasites. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15, e1007809. [CrossRef]
- Kocken, C.H.; Zeeman, A.M.; Voorberg-van der Wel, A.; Thomas, A.W. Transgenic Plasmodium knowlesi: relieving a bottleneck in malaria research? Trends Parasitol 2009, 25, 370-374. [CrossRef]
- Mohring, F.; Hart, M.N.; Patel, A.; Baker, D.A.; Moon, R.W. CRISPR-Cas9 Genome Editing of Plasmodium knowlesi. Bio Protoc 2020, 10, e3522. [CrossRef]
- Mohring, F.; Hart, M.N.; Rawlinson, T.A.; Henrici, R.; Charleston, J.A.; Diez Benavente, E.; Patel, A.; Hall, J.; Almond, N.; Campino, S.; et al. Rapid and iterative genome editing in the malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi provides new tools for P. vivax research. Elife 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.W.; Hall, J.; Rangkuti, F.; Ho, Y.S.; Almond, N.; Mitchell, G.H.; Pain, A.; Holder, A.A.; Blackman, M.J. Adaptation of the genetically tractable malaria pathogen Plasmodium knowlesi to continuous culture in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 531-536. [CrossRef]
- Moraes Barros, R.R.; Gibson, T.J.; Kite, W.A.; Sa, J.M.; Wellems, T.E. Comparison of two methods for transformation of Plasmodium knowlesi: Direct schizont electroporation and spontaneous plasmid uptake from plasmid-loaded red blood cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2017, 218, 16-22. [CrossRef]
- Moraes Barros, R.R.; Thawnashom, K.; Gibson, T.J.; Armistead, J.S.; Caleon, R.L.; Kaneko, M.; Kite, W.A.; Mershon, J.P.; Brockhurst, J.K.; Engels, T.; et al. Activity of Plasmodium vivax promoter elements in Plasmodium knowlesi, and a centromere-containing plasmid that expresses NanoLuc throughout the parasite life cycle. Malar J 2021, 20, 247. [CrossRef]
- Verzier, L.H.; Coyle, R.; Singh, S.; Sanderson, T.; Rayner, J.C. Plasmodium knowlesi as a model system for characterising Plasmodium vivax drug resistance candidate genes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2019, 13, e0007470. [CrossRef]
| Material Used for Transfection | Transfection Tools Available | Used to Investigate |
Refs |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
P. vivax vivo |
in vivo derived blood stages | Transient transfection, Zinc-finger mediated recombination | blood stages in vivo |
[32,33] |
|
P. cynomolgi vivo |
in vivo derived blood stages |
Homology directed recombination, episomal, centromere |
blood stages (in vivo); liver stage schizonts and hypnozoites (in vitro) |
[29,37,38,39,40,41,42,90] |
|
P. cynomolgi vitro |
in vitro derived blood stages |
Episomal, Crispr/Cas9 |
blood stages in vitro |
[35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




