Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
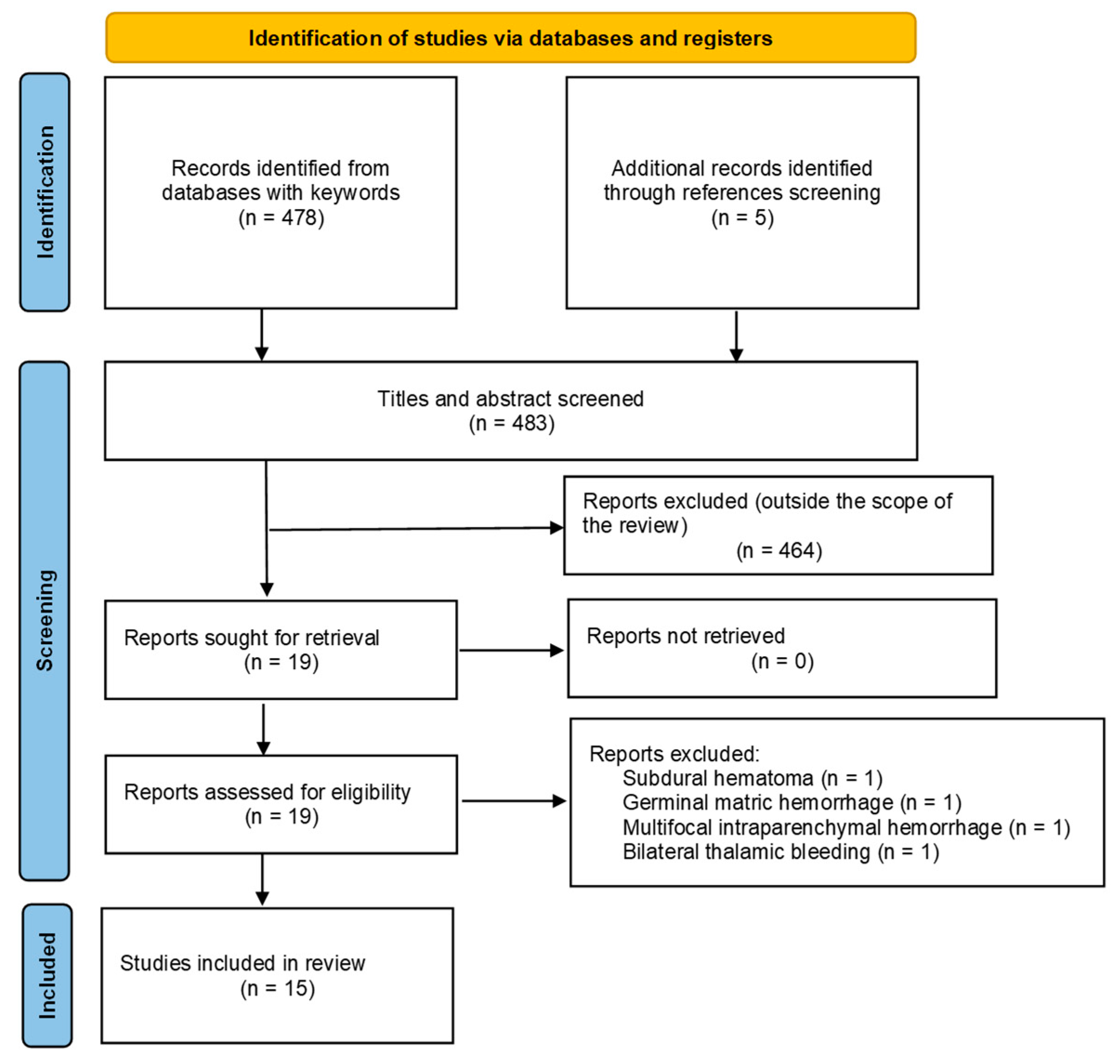
2.2. PRISMA systematic literature review
3. Results
3.1. Clinical series
3.2. Literature review analysis
- 1.
- The median delay between the EVD/VPS procedure and the hemorrhagic complication was 5 days (range from 2 to 15 days).
- 2.
- DICH patients were rather young, with a median age of 61 years (range from 17 to 84 years).
- 3.
- A slight male predominance was noted, with a gender ratio of 1.3 M/F.
- 4.
- The most prevalent underlying pathologies in DICH patients were as follows: a) Neurovascular disorders accounted for 47% of the cases, including conditions such as Spontaneous Intracerebral Hematoma and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage resulting from ruptured vascular malformations. b) Traumatic Brain Injuries constituted 23% of the cases. c) Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus was observed in 20% of the cases. d) Other pathologies, such as Brain tumors and Central Nervous System Infectious diseases, were less frequently reported, with respective incidences of 5% and 3% of the patient population.
- 5.
- The majority of cases of DICH were symptomatic, accounting for 66% of patients. This symptomatic presentation correlated with an unfavorable prognosis in 44% of cases, with a Glasgow Outcome Scale (GOS) score of 3 or less indicating poor outcomes. Surgical management was pursued for 22% of all patients, while 3% unfortunately succumbed to their condition before a surgical procedure could be performed. Conservative medical management or therapeutic abstention were the approaches adopted for most patients.
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemorrhagic complications of ventricular shunting procedure
- 1.
- The location of the hematoma was consistently distant from the arteriovenous malformation (AVM) nidus, surrounding the trajectory of the ventricular catheter.
- 2.
- The occurrence of the hemorrhagic complication transpired several weeks after the initial AVM rupture and several days after the placement of the VPS.
- 3.
- Catheter-related DICH manifested in all 10 cases without any evident coagulation disorders or other identifiable risk factors.
- 1.
- Age older than 75 years,
- 2.
- Anticoagulation/antiplatelet therapy,
- 3.
- Other coagulation disorders,
- 4.
- Iterative manipulations during surgery (many drain insertion attempt) surgical difficulties,
- 5.
- Larger diameter of inserted catheter.
4.2. DICH
4.3. Arteriovenous Malformations and physio-pathological mechanisms
4.4. Hydrocephalus management in ruptured bAVM patients
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, B.A.; Rosalind Lai, P.M.; Du, R. Hydrocephalus after Arteriovenous Malformation Rupture. FOC 2013, 34, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilard, V.; Metayer, T.; Gakuba, C.; Langlois, O.; Proust, F.; Emery, E.; Gaberel, T. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Related to AVM Rupture: Description, Outcomes and Impact of Intraventricular Fibrinolysis. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery 2018, 164, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirmani, A.; Sarmast, A.; Bhat, A. Role of External Ventricular Drainage in the Management of Intraventricular Hemorrhage; Its Complications and Management. Surg Neurol Int 2015, 6, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukamachi, A.; Koizumi, H.; Nukui, H. Postoperative Intracerebral Hemorrhages: A Survey of Computed Tomographic Findings after 1074 Intracranial Operations. Surgical Neurology 1985, 23, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, E.S.; Kellner, C.P.; Nelson, E.; McDowell, M.M.; Bruce, S.S.; Bruce, R.A.; Zhuang, Z.; Connolly, E.S. Hemorrhagic Complications of Ventriculostomy: Incidence and Predictors in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Clinical Article. JNS 2014, 120, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniker, A.H.; Vaynman, A.Y.; Karimi, R.J.; Sabit, A.O.; Holland, B. Hemorrhagic Complications Of External Ventricular Drainage. Operative Neurosurgery 2006, 59, ONS-419–ONS-425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Xu, L.; Yang, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J. Characteristics of Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 42693–42699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, X.; Yu, B.; Shen, L.; Zhang, X. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: A Retrospective Study. World Neurosurgery 2017, 107, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yang, S.-X.; Wang, Y.-R. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine 2015, 94, e2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liu, Q.; Ying, G.; Zhu, X. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt: Two Case Reports and a Literature Review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Suo, S.; Gao, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Symptomatic Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in Adults without Bleeding Tendency. World Neurosurgery 2017, 106, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savitz, M.H.; Bobroff, L.M. Low Incidence of Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. Journal of Neurosurgery 1999, 91, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-T.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Lv, H.-T.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.-H. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt Procedure: Two Case Reports and a Review of Literature. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2021, 25, 6093–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennett, B. Assessment of Outcome after Severe Brain Damage: A Practical Scale. The Lancet 1975, 305, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. The Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Tacconi, L. Safety of Deep Venous Thrombosis Prophylaxis with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin in Brain Surgery. Prospective Study on 746 Patients. Surgical Neurology 2008, 70, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chibbaro, S.; Cebula, H.; Todeschi, J.; Fricia, M.; Vigouroux, D.; Abid, H.; Kourbanhoussen, H.; Pop, R.; Nannavecchia, B.; Gubian, A.; et al. Evolution of Prophylaxis Protocols for Venous Thromboembolism in Neurosurgery: Results from a Prospective Comparative Study on Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin, Elastic Stockings, and Intermittent Pneumatic Compression Devices. World Neurosurgery 2018, 109, e510–e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganau, M.; Prisco, L.; Cebula, H.; Todeschi, J.; Abid, H.; Ligarotti, G.; Pop, R.; Proust, F.; Chibbaro, S. Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis in Neurosurgery: State of the Art on Prophylaxis Protocols and Best Clinical Practices. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2017, 45, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganau, M.; Ligarotti, G.K.I.; Meloni, M.; Chibbaro, S. Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Mechanical and Pharmacological Thromboprophylaxis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, S224–S224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, A.; Shinohara, A.; Munekata, K.; Maki, Y. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt. Surgical Neurology 1985, 24, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, R.B.; Zimmerman, R.D.; Devinsky, O. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting. Neurosurgery 1986, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derdeyn, C.P.; Delashaw, J.B.; Broaddus, W.C.; Jane, J.A. Detection of Shunt-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage by Postoperative Skull Films: A Report of Two Cases. Neurosurgery 1988, 22, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascalchi, M. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after CSF Shunt for Communicating “Normal-Pressure” Hydrocephalus. Case Report. Ital J Neuro Sci 1991, 12, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcázar, L.; Alfaro, R.; Tamarit, M.; Gómez-Angulo, J.C.; Ortega, J.M.; Aragonés, P.; Jerez, P.; Salazar, F.; Del Pozo, J.M. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion. Case Report and Literature Review. Neurocirugía 2007, 18, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaki, K.; Uchiyama, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Hamada, J. Intracerebral Hemorrhage Secondary to Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Insertion -Four Case Reports-: —Four Case Reports—. Neurol. Med. Chir.(Tokyo) 2010, 50, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musali, S.R.; Manne, S.; Beniwal, H.K.; Butkuri, N.; Gollapudi, P.R.; Nandigama, P.K. Delayed Intracerebral Hemorrhage after Placement of a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in a Case of Hydrocephalus: A Rare Case Report and Review of Literature. Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice 2019, 10, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.K.; Cha, S.H.; Choi, B.K.; Lee, J.I.; Yun, E.Y.; Choi, C.H. Hemorrhage Rates Associated with Two Methods of Ventriculostomy: External Ventricular Drainage vs. Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Procedure. Neurol. Med. Chir.(Tokyo) 2014, 54, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.; Tummala, R.P. Risk Factors for Hemorrhage Associated with External Ventricular Drain Placement and Removal. JNS 2017, 126, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, P. A New Inflammatory Parameter Can Predict Delayed Intracranial Hemorrhage Following Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 13763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Mesa-Tejada, R.; Quick, C.M.; Bollen, A.W.; Joshi, S.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Lawton, M.T.; Young, W.L. Evidence of Increased Endothelial Cell Turnover in Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moftakhar, P.; Hauptman, J.S.; Malkasian, D.; Martin, N.A. Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations. Part 1: Cellular and Molecular Biology. FOC 2009, 26, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Choi, E.-J.; McDougall, C.M.; Su, H. Brain Arteriovenous Malformation Modeling, Pathogenesis, and Novel Therapeutic Targets. Transl. Stroke Res. 2014, 5, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlikowska, L.; Tran, M.N.; Achrol, A.S.; McCulloch, C.E.; Ha, C.; Lind, D.L.; Hashimoto, T.; Zaroff, J.; Lawton, M.T.; Marchuk, D.A.; et al. Polymorphisms in Genes Involved in Inflammatory and Angiogenic Pathways and the Risk of Hemorrhagic Presentation of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Stroke 2004, 35, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Sugita, Y.; Nakashima, S.; Okada, Y.; Yoshitomi, M.; Kimura, Y.; Miyoshi, H.; Morioka, M.; Ohshima, K. Alternatively Activated Macrophages Play an Important Role in Vascular Remodeling and Hemorrhaging in Patients with Brain Arteriovenous Malformation. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2016, 25, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
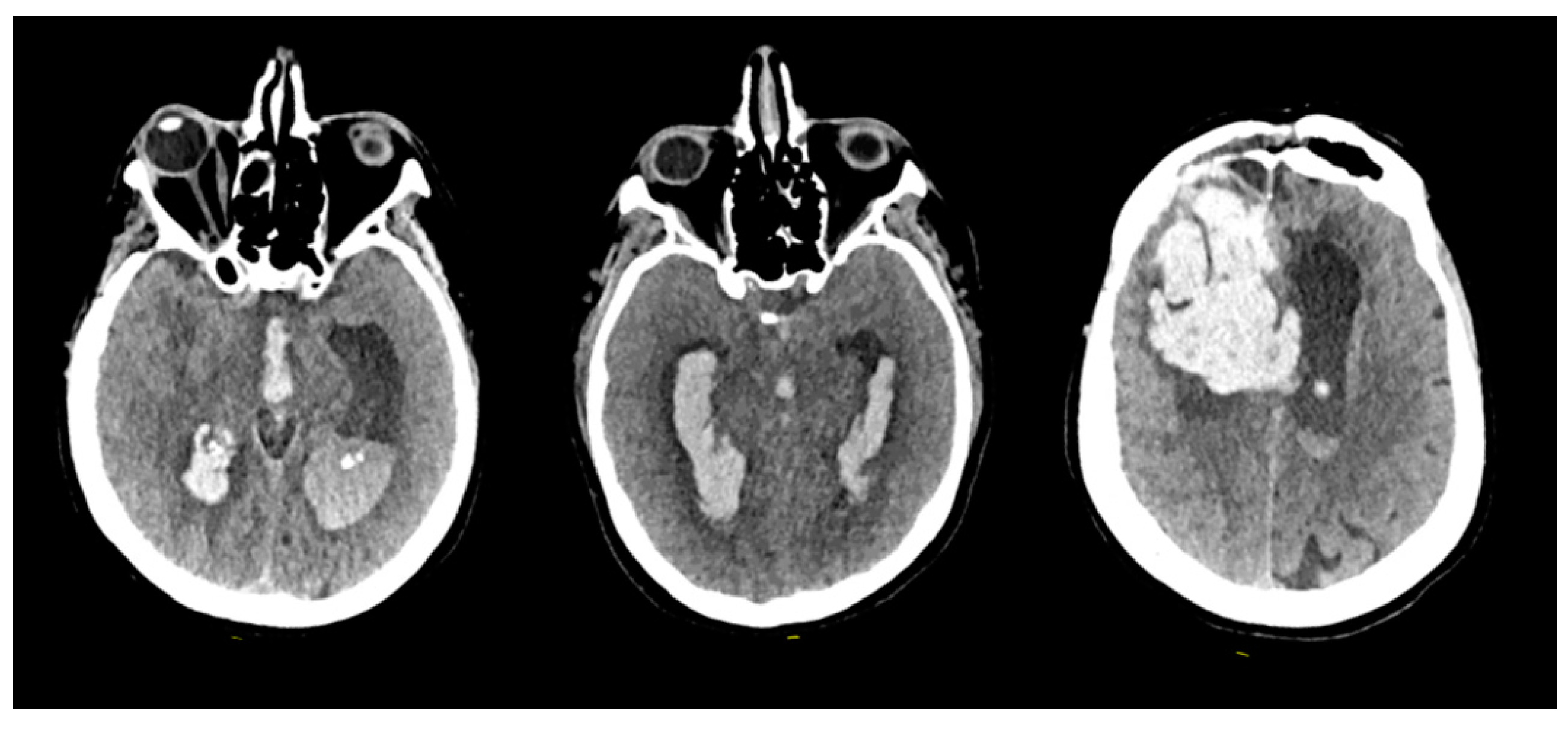
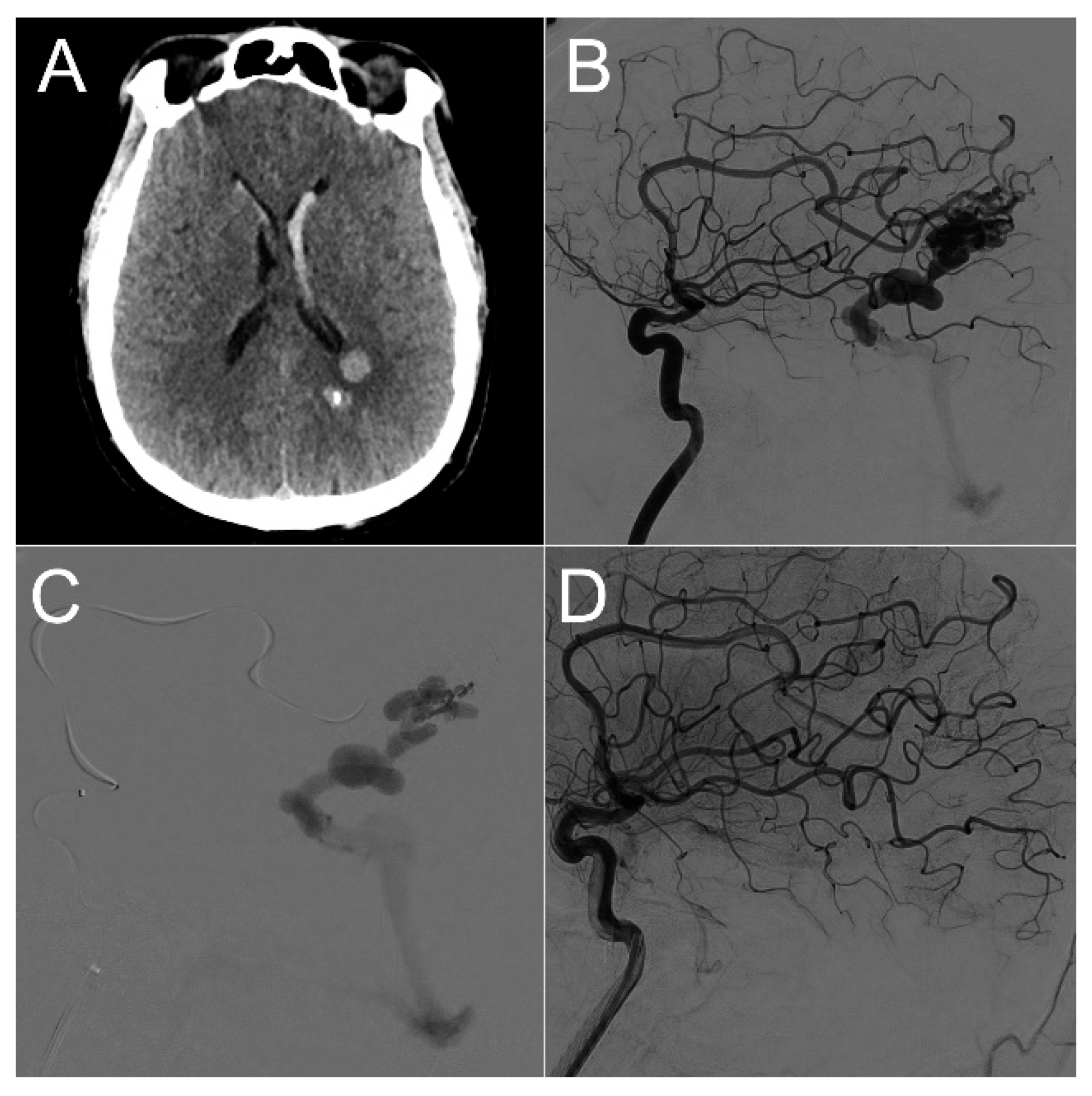
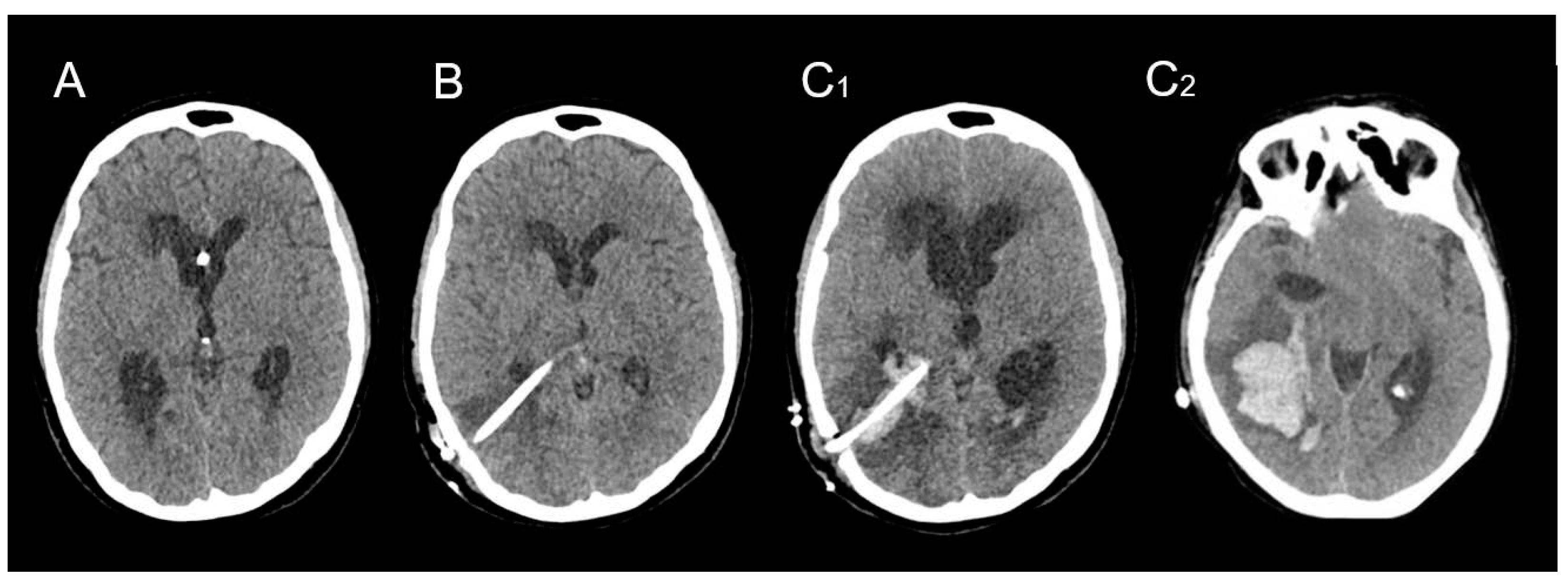
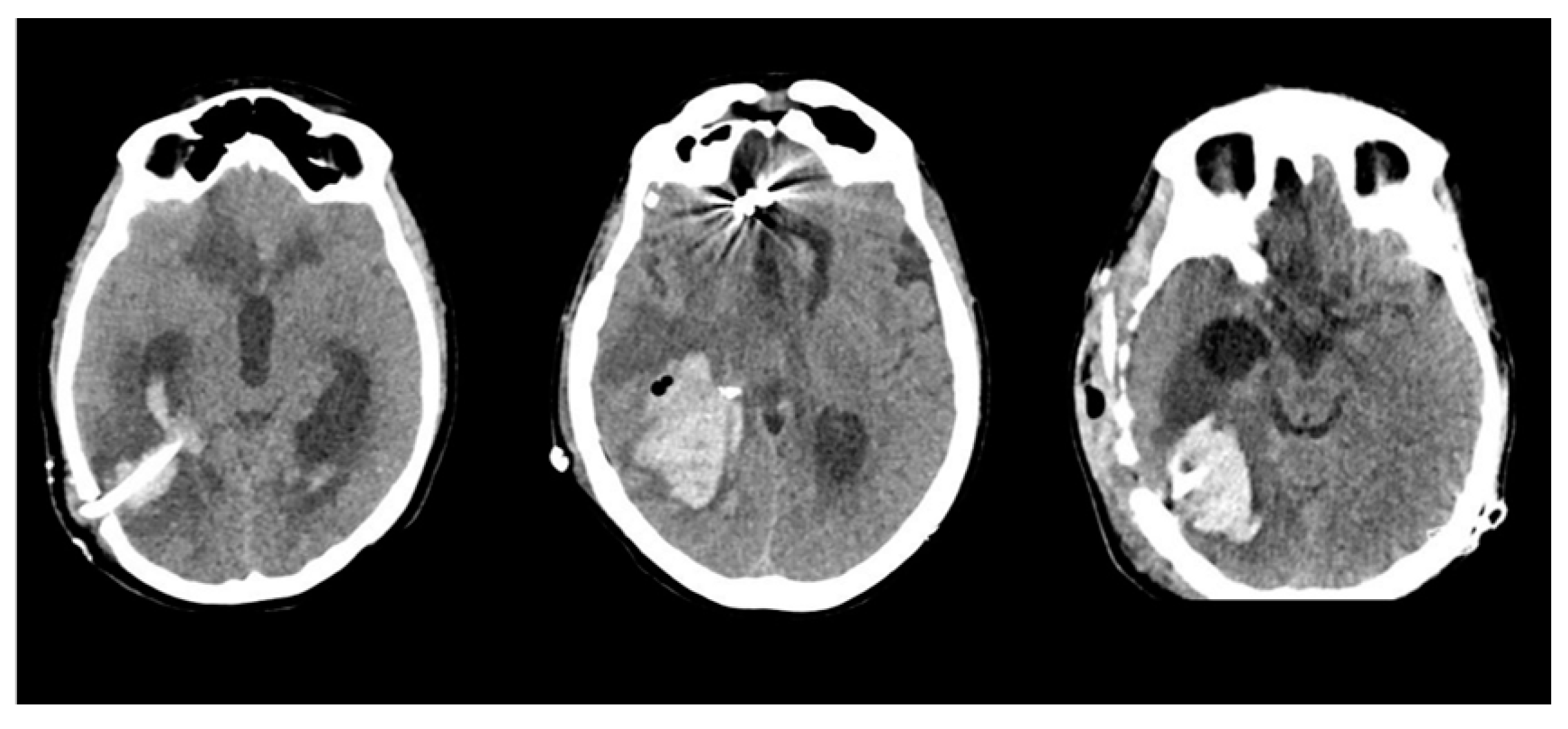
| Sex | Age | AVM Location | Spetzler-Martin Grade | Draining Vein(s) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 21 | Left parieto-occipital | 3 | Lateral sinus | Embolization |
| M | 40 | Left parietal | 3 | Straight sinus | Embolization |
| F | 37 | Left cerebellar | 3 | Left sigmoid sinus | Embolization |
| F | 58 | Right cerebellar | 3 | Vein of Galen, inferior petrous sinus | Embolization |
| F | 29 | Right parietal | 3 | Superior Sagittal Sinus | Surgery |
| M | 30 | Right parietal | 2 | Superior Sagittal Sinus | Surgery |
| F | 57 | Right frontal | 3 | Vein of Galen | Embolization |
| M | 61 | Left basifrontal | 3 | Vein of Galen | Embolization |
| F | 48 | Left temporo-parietal | 2 | Superior Sagittal Sinus | Embolization + Surgery |
| F | 34 | Left temporal | 3 | Superior Sagittal Sinus, lateral sinus | Embolization + Surgery |
| Series | Number of patients | Onset day of hemorrhage | Age | Gender | Localisation of the ventricular catheter | Primary disease leading to hydrocephalus | Symptomatic | Management | Glasgow outcome scale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsumura et al (1985) | 1 | 7 | 17 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 5 |
| Snow et al (1986) | 1 | 7 | 43 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | - | - |
| Derdeyn et al (1988) | 2 | 2 | 56 | M | PH | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 4 |
| 2 | 73 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Mascalchi et al (1991) | 1 | 15 | 68 | M | AH | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 1 |
| Savitz et al (1999) | 2 | 2 | - | - | PH | - | No | Conservative | - |
| 2 | - | - | PH | - | No | Conservative | - | ||
| Alcazar et al (2007) | 1 | 6 | 64 | F | PH | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 1 |
| Misaki et al (2010) | 2 | 5 | 55 | M | PH | SAH | No | Conservative | - |
| 3 | 64 | M | PH | SAH | No | Conservative | - | ||
| Zhou et al (2012) | 2 | 5 | 32 | F | AH | NPH | Yes | Death before surgery | 1 |
| 3 | 58 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Ma et al (2015) | 1 | 8 | 67 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Palliative care | - |
| Guo et al (2017) | 20 | 3 | 58 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
| 3 | 54 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 3 | 61 | M | - | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 4 | 61 | M | - | Tumoral | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 4 | 75 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 5 | 84 | F | - | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 6 | 48 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 1 | ||
| 6 | 61 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Surgery | 1 | ||
| 6 | 62 | M | - | TBI | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 6 | 78 | M | - | NPH | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 7 | 64 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 7 | 65 | F | - | Tumoral | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 7 | 76 | F | - | ICH | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 8 | 66 | M | - | TBI | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 8 | 69 | M | - | NPH | No | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 57 | F | - | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 69 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 9 | 72 | M | - | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 10 | 33 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 10 | 30 | M | - | ICH | Yes | Conservative | 4 | ||
| Gong et al (2017) | 12 | 3 | 62 | M | AH | ICH | Yes | Death before surgery | 1 |
| 3 | 64 | F | PH | TBI | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 7 | 76 | M | AH | SAH | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 3 | 50 | M | AH | SAH | Yes | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 4 | 61 | F | AH | TBI | - | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 5 | 67 | M | AH | Infectious | - | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 7 | 65 | M | AH | NPH | No | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 4 | 61 | M | AH | NPH | - | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 3 | 60 | M | AH | TBI | - | Conservative | 4 | ||
| 4 | 53 | F | PH | SAH | - | Surgery | 2 | ||
| 5 | 68 | F | AH | NPH | - | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 5 | 61 | M | AH | SAH | - | Surgery | 3 | ||
| Hou et al (2017) | 4 | 9 | 56 | F | AH | Tumoral | Yes | Surgery | 1 |
| 2 | 48 | M | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 3 | 65 | M | PH | NPH | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| 4 | 51 | F | AH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| Musali et al (2019) | 1 | 7 | 56 | F | PH | Infectious | Yes | Conservative | 1 |
| Wang et al (2021) | 2 | 9 | 49 | F | PH | SAH | Yes | Conservative | 5 |
| 6 | 76 | F | PH | TBI | Yes | Conservative | 5 | ||
| Present study | 10 | 2 | 21 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
| 2 | 44 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 3 | 37 | F | PH | AVM | No | Surgery | 4 | ||
| 4 | 58 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Surgery | 3 | ||
| 5 | 29 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 3 | ||
| 5 | 30 | M | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 5 | 57 | F | PH | AVM | No | Surgery | 3 | ||
| 6 | 61 | M | PH | AVM | No | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 6 | 48 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 1 | ||
| 6 | 34 | F | PH | AVM | Yes | Conservative | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





