Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Procedure and Data Source & Collection
2.2. Experiment Design
- -
- Order treatments mean accordingly
- -
- The formula uses as follows
- -
- Test criteria
3. Results
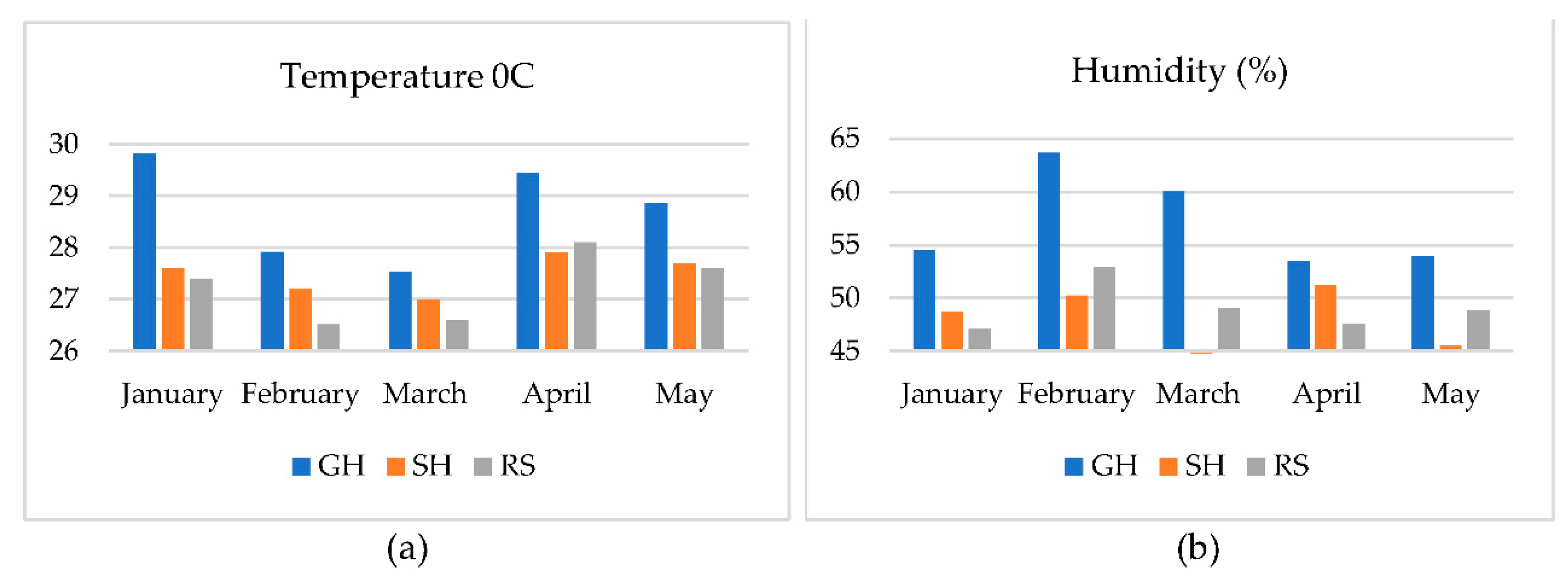
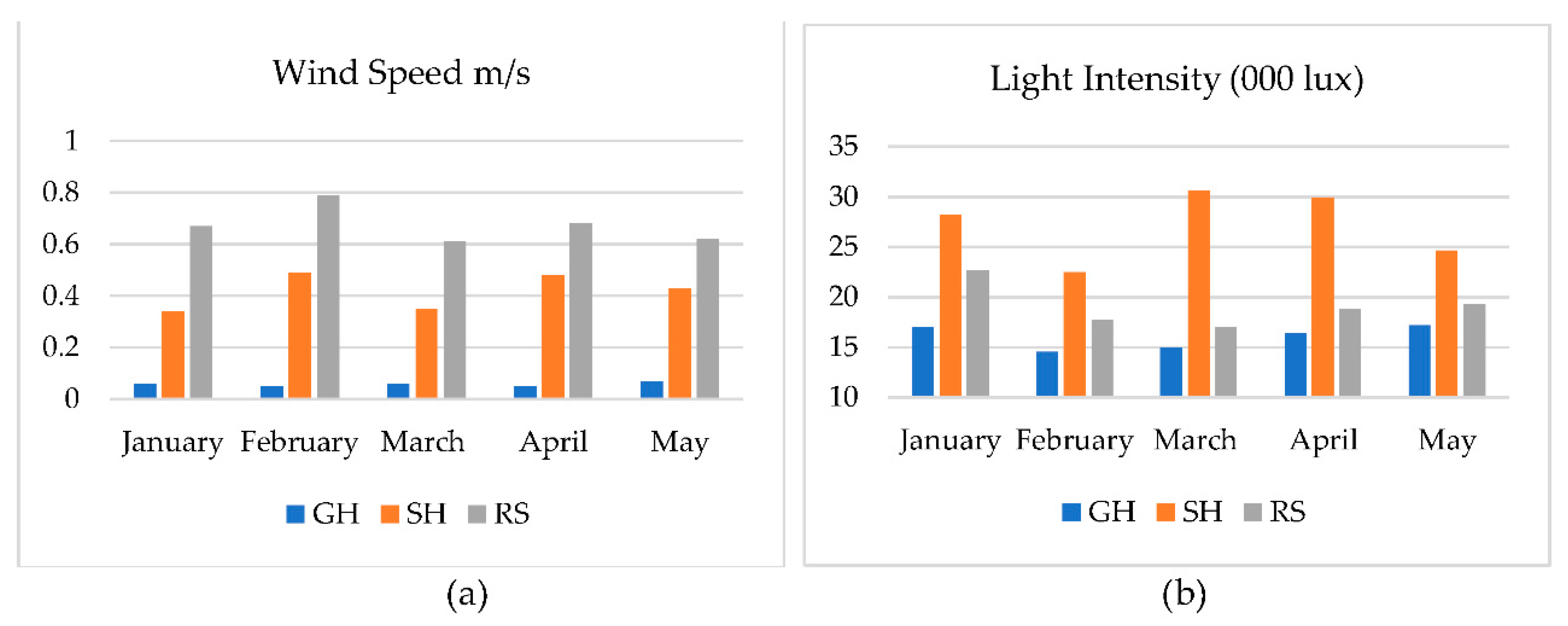
3.1. Observation of Weather within Research
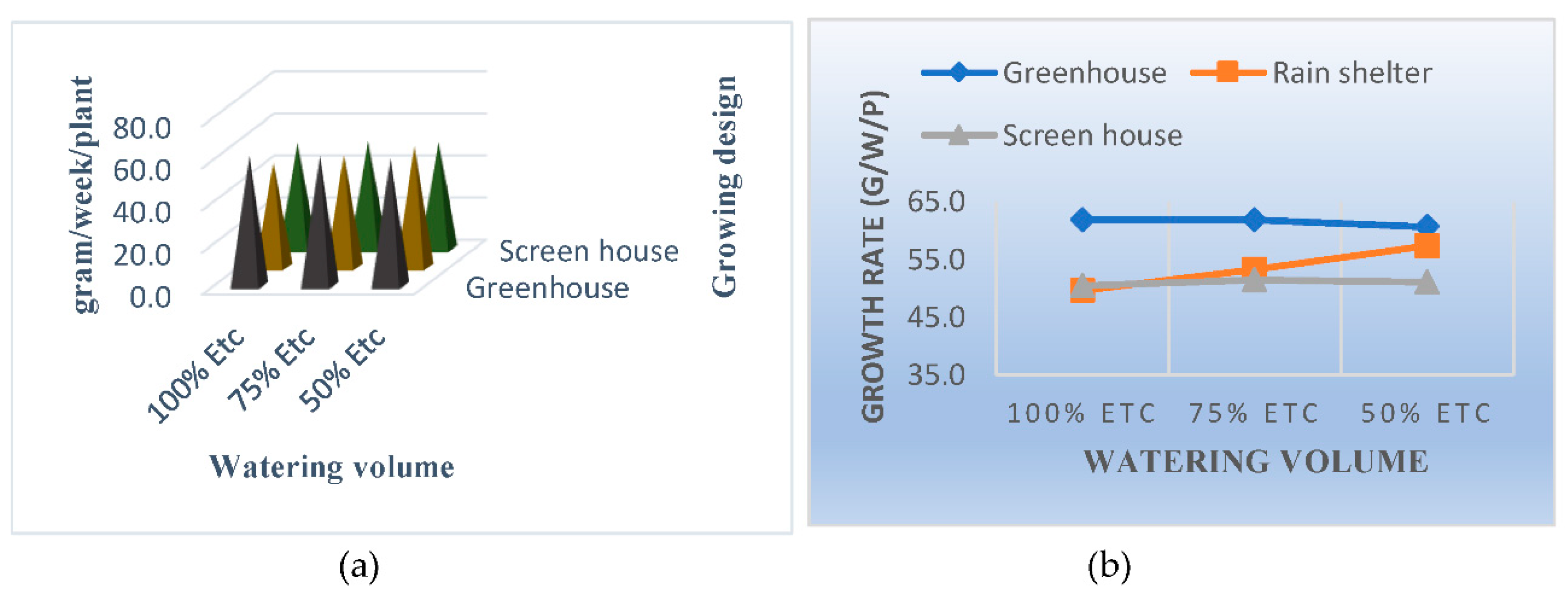
3.2. Grow Rate
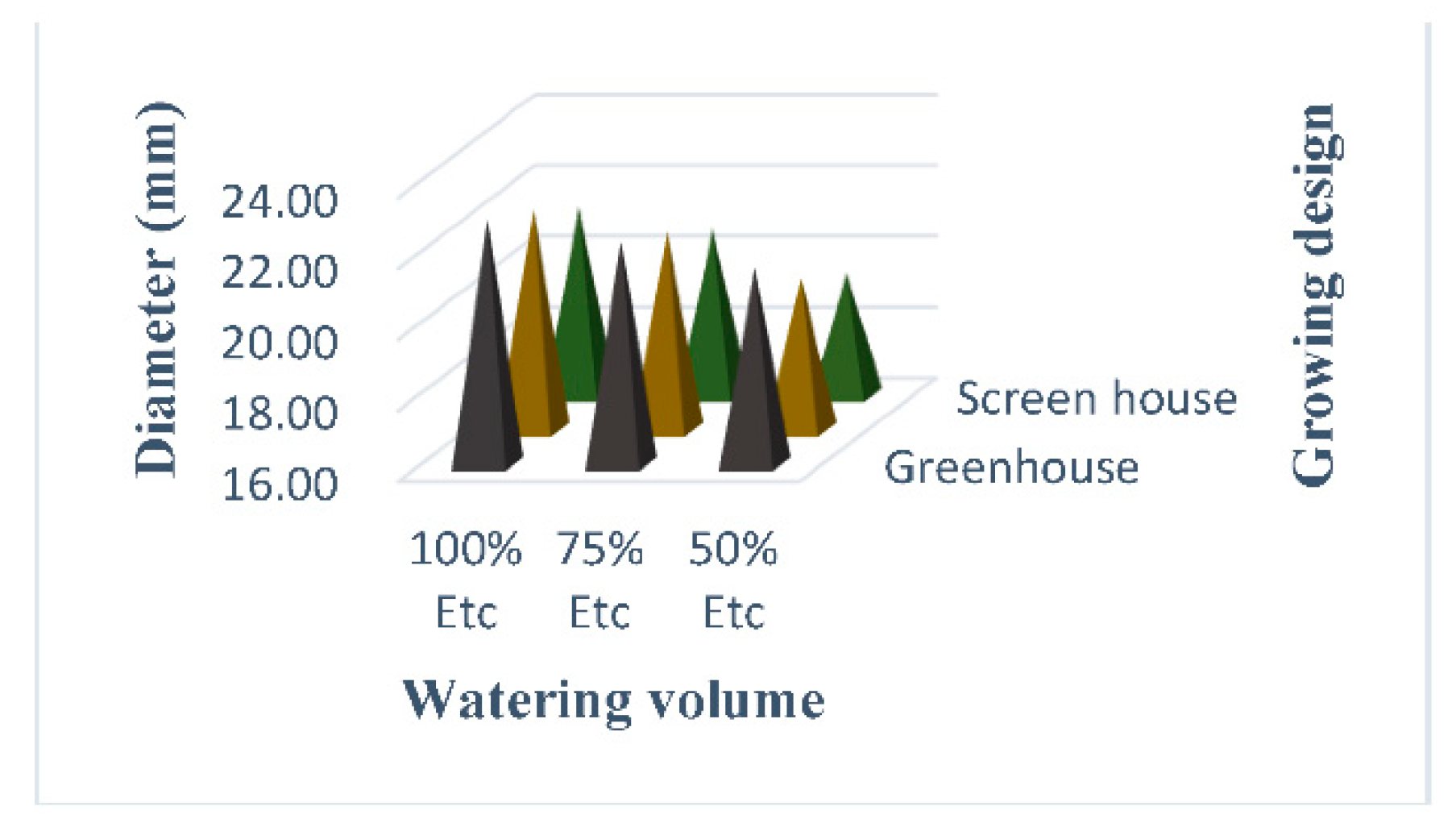
3.3. Fruit Diameter (mm)
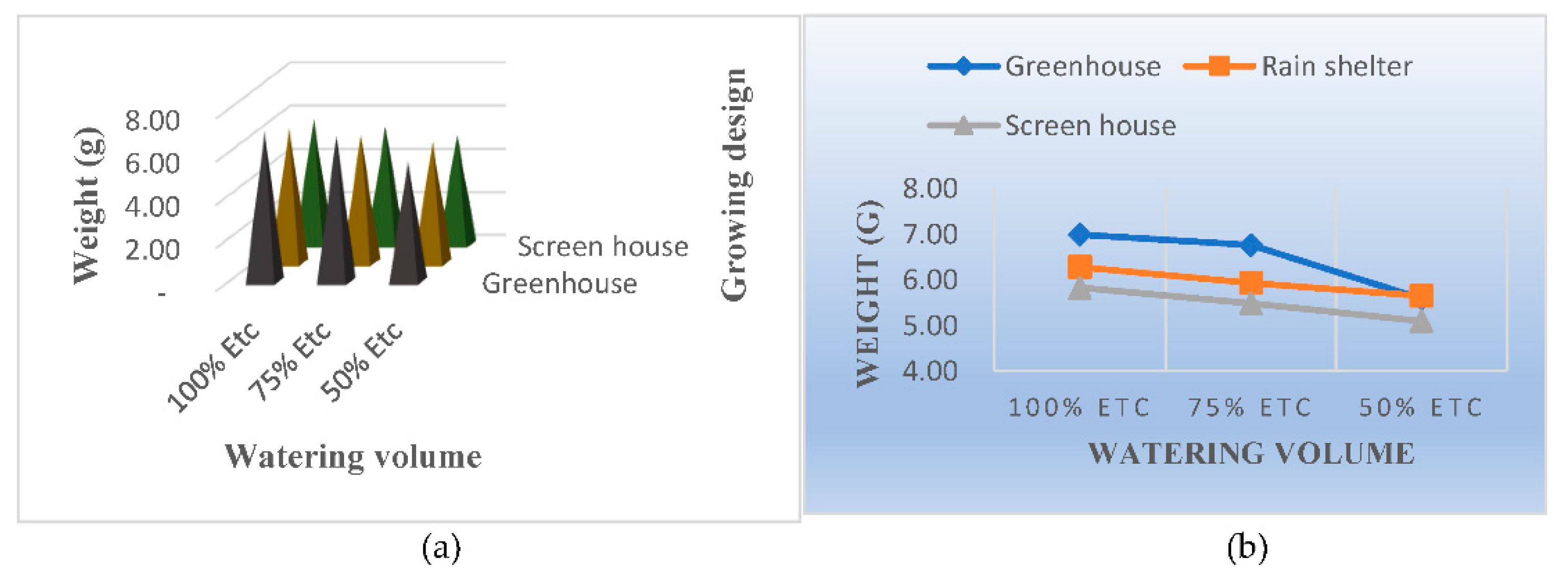
3.4. Single Fruit Weight
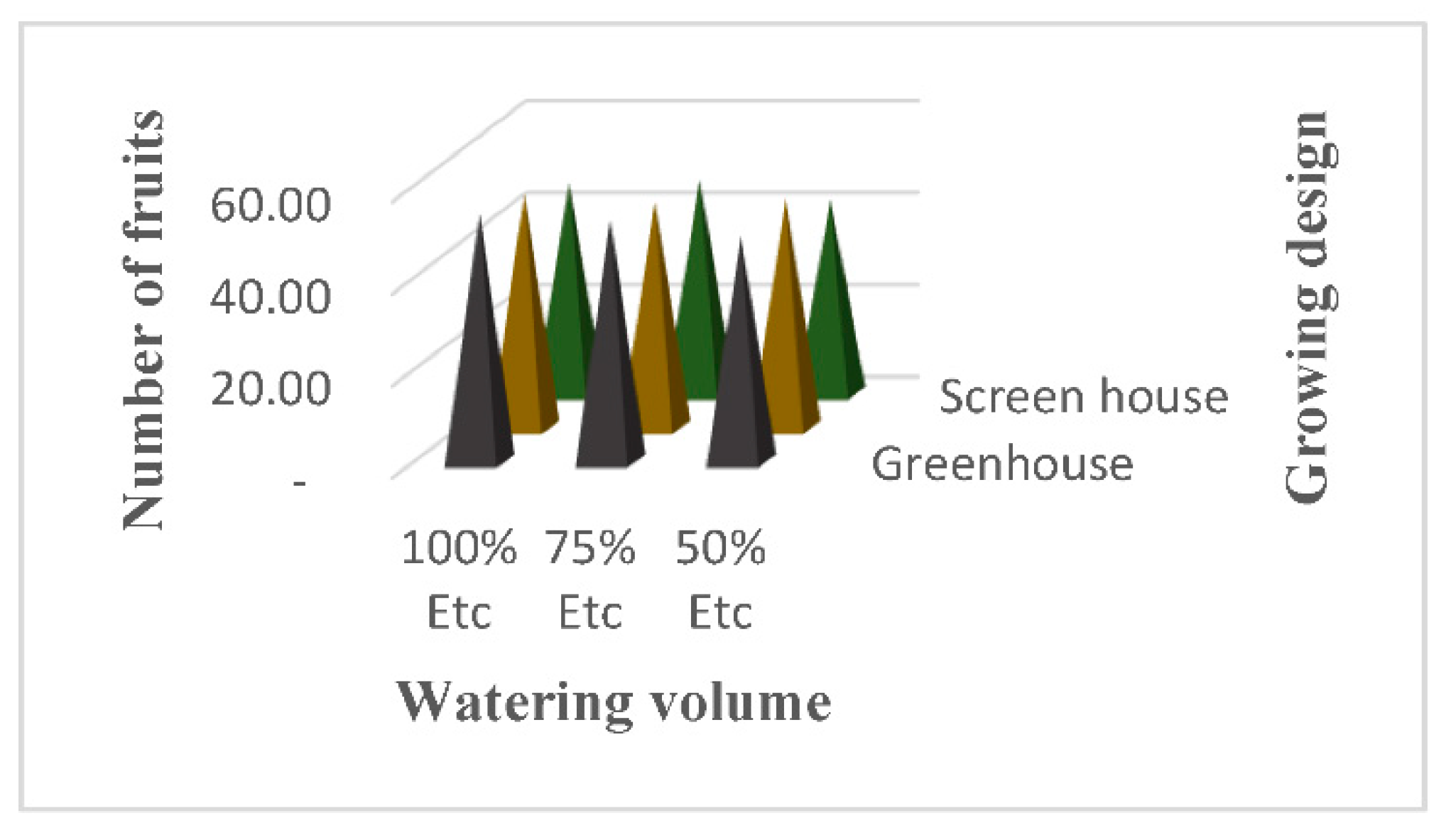
3.5. Fruits per Plant
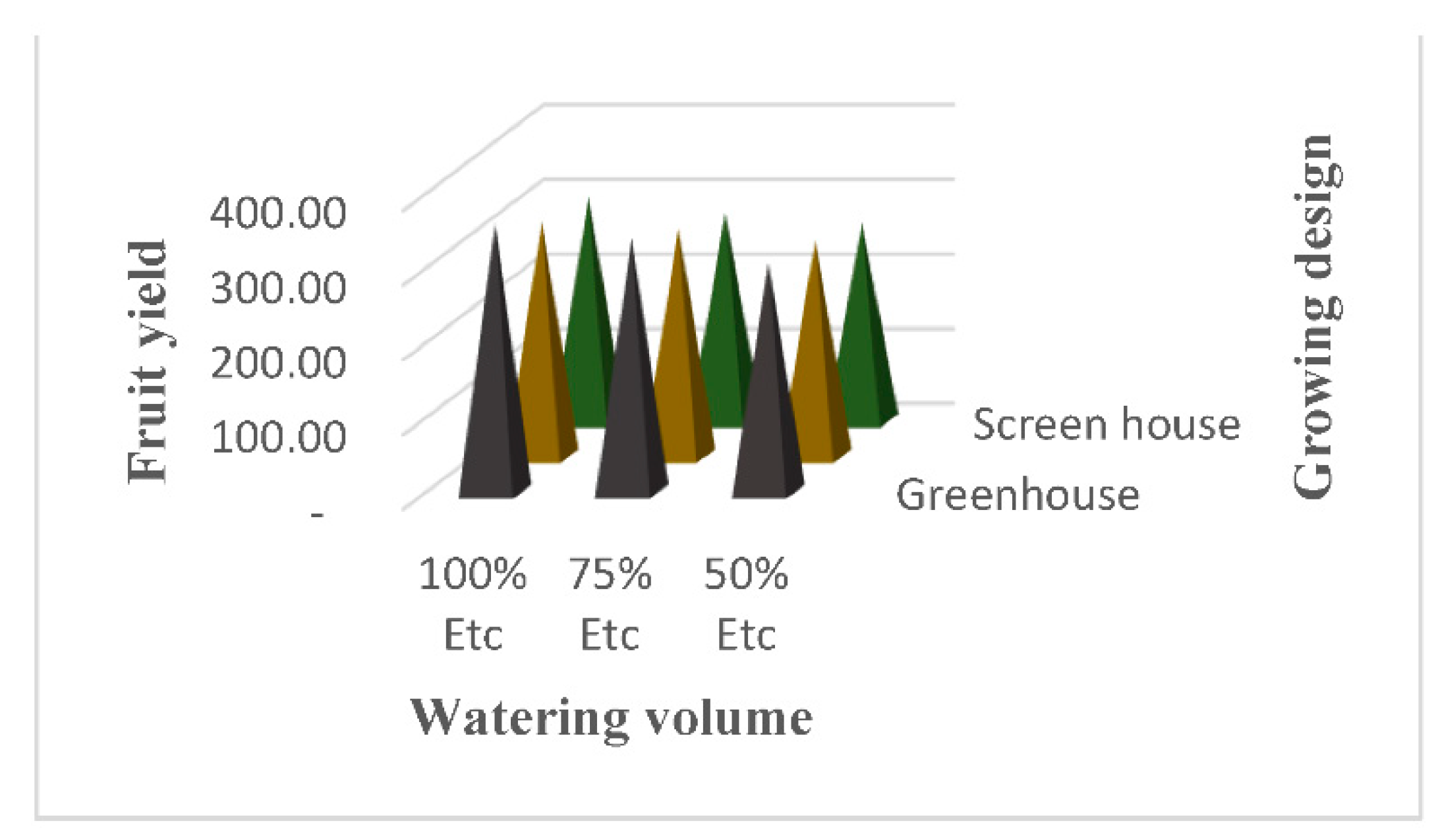
3.6. Fruit Yield per Plant
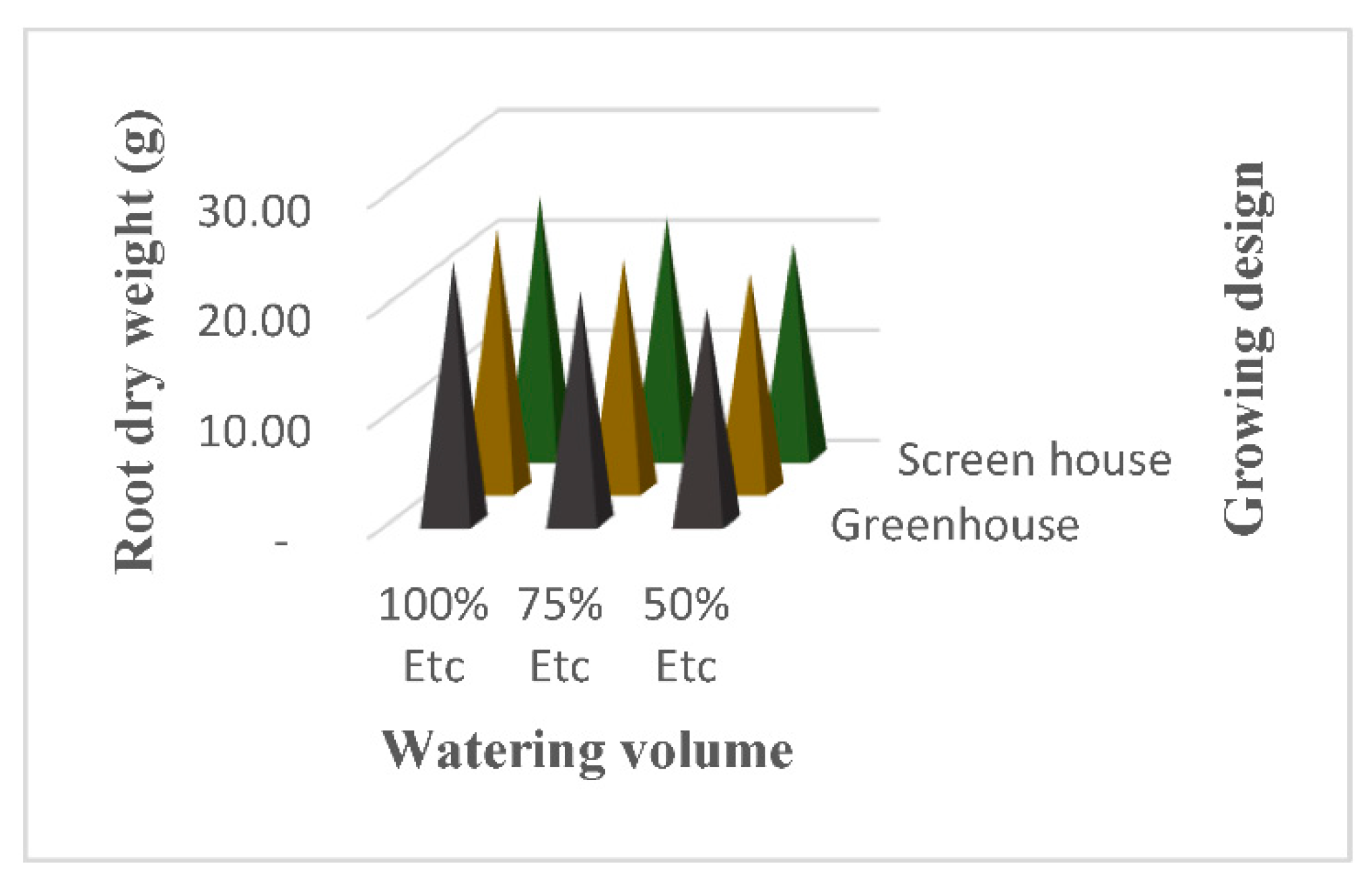
3.7. Root Dry Weight
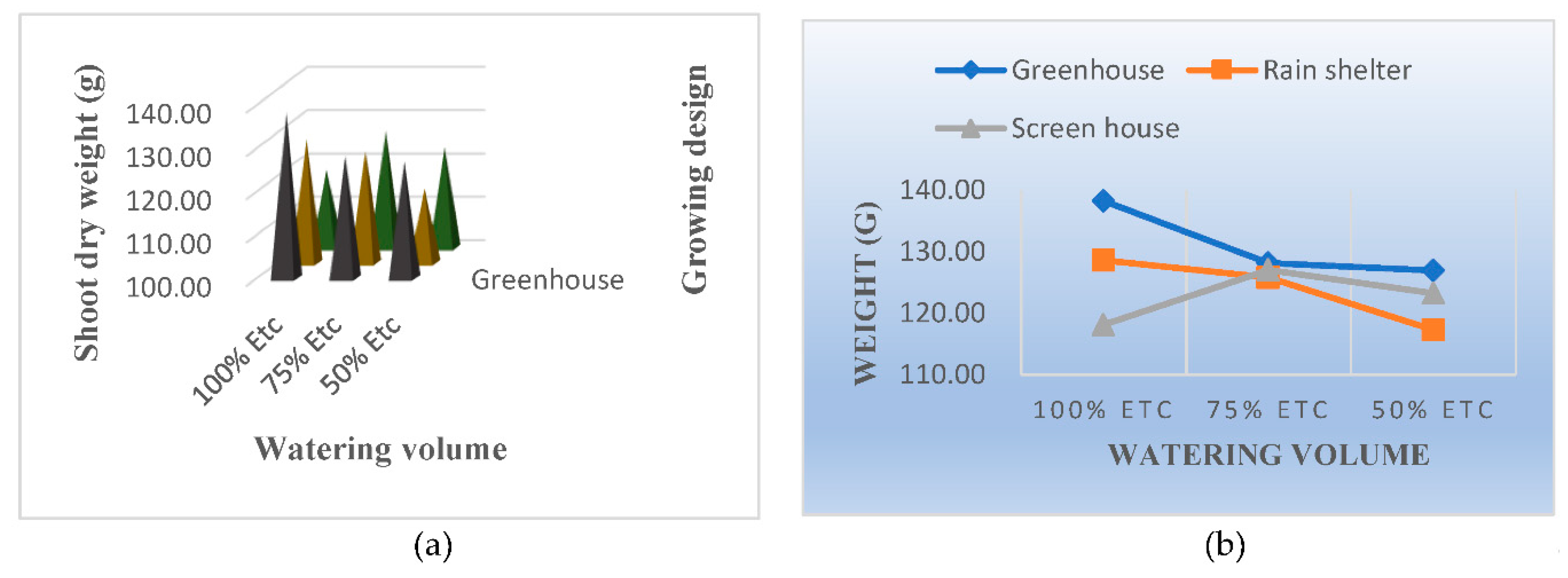
3.8. Shoot Dry Weight
3.9. Root-Shoot Ratio
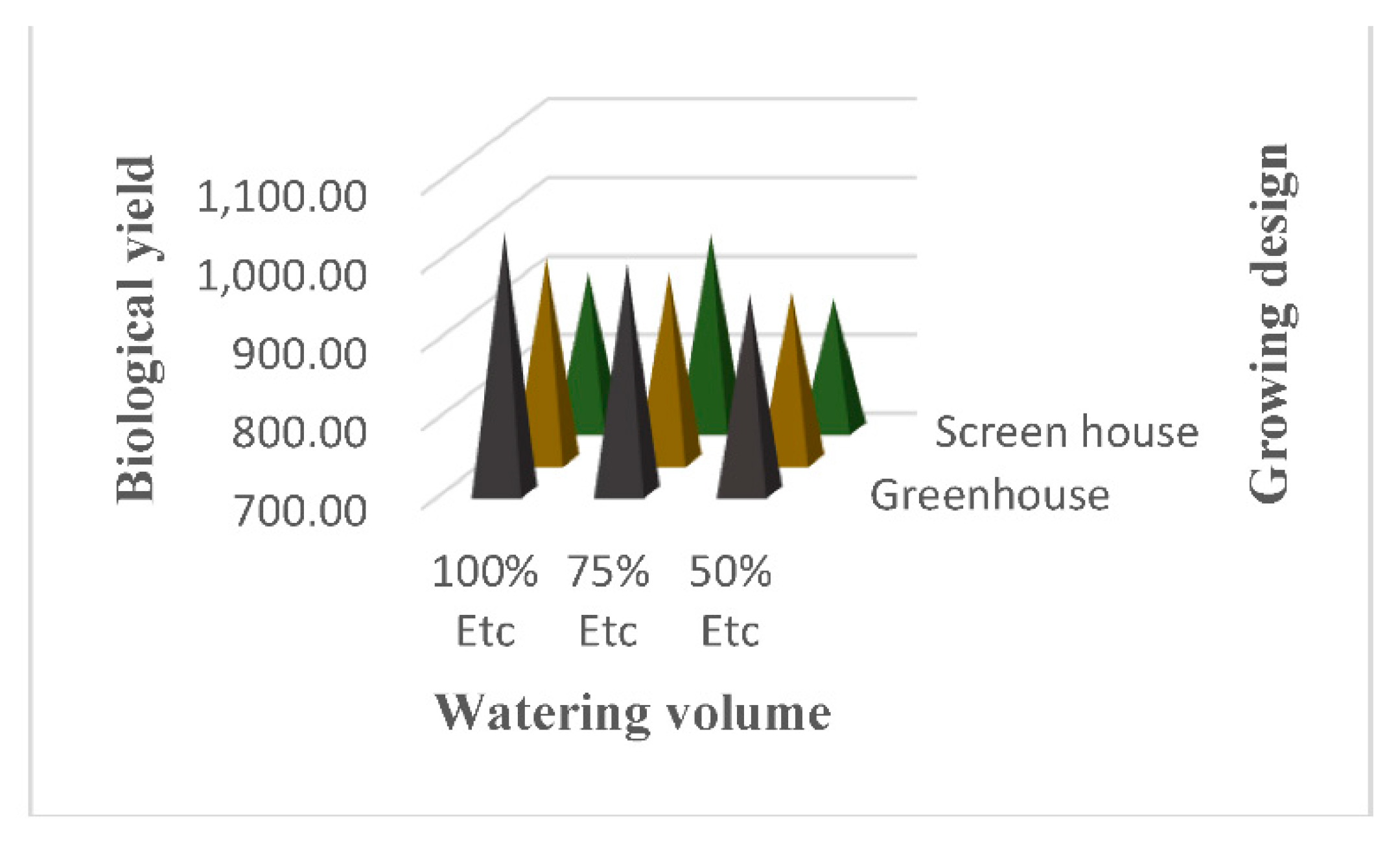
3.10. Biological Yield per Plant
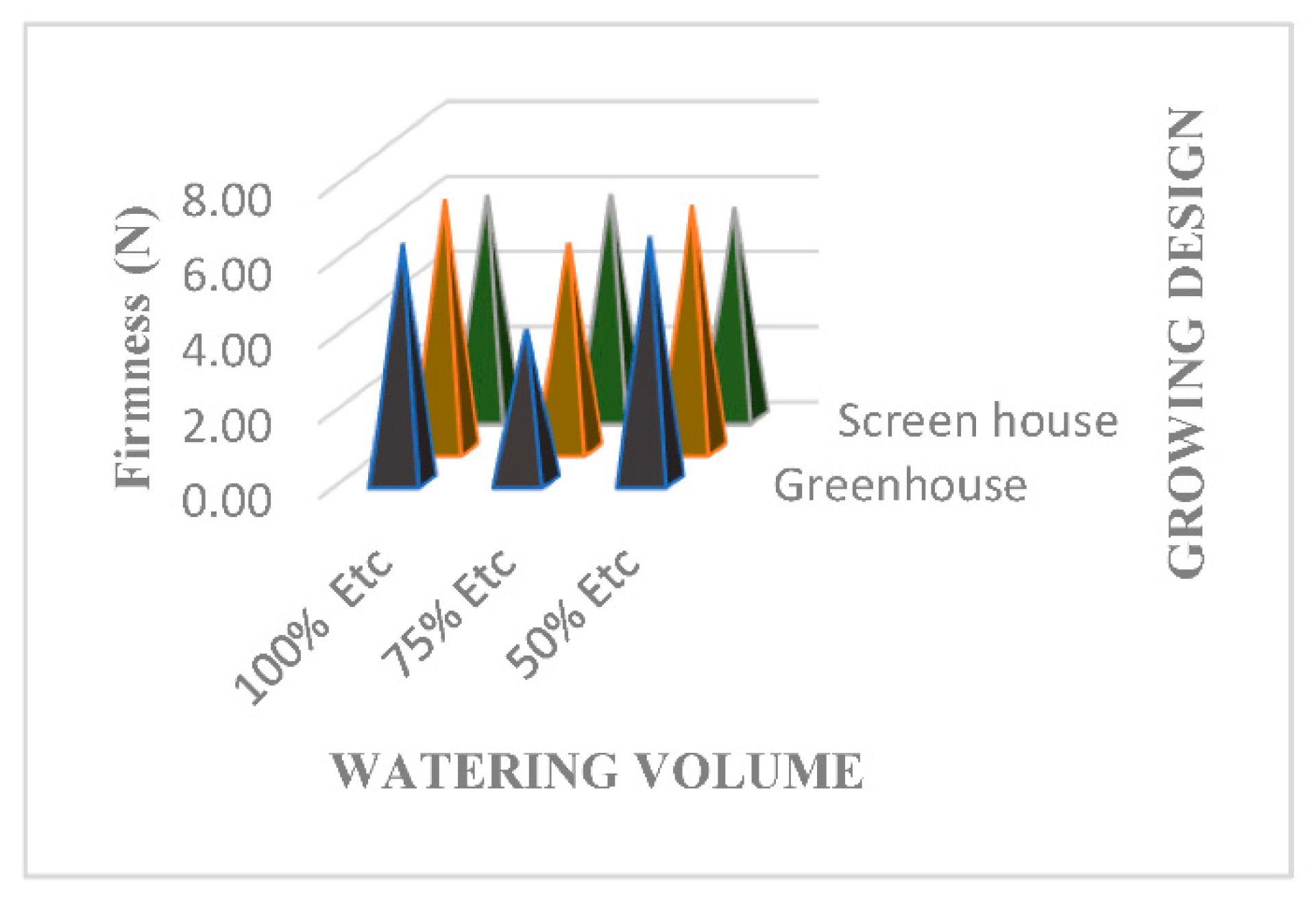
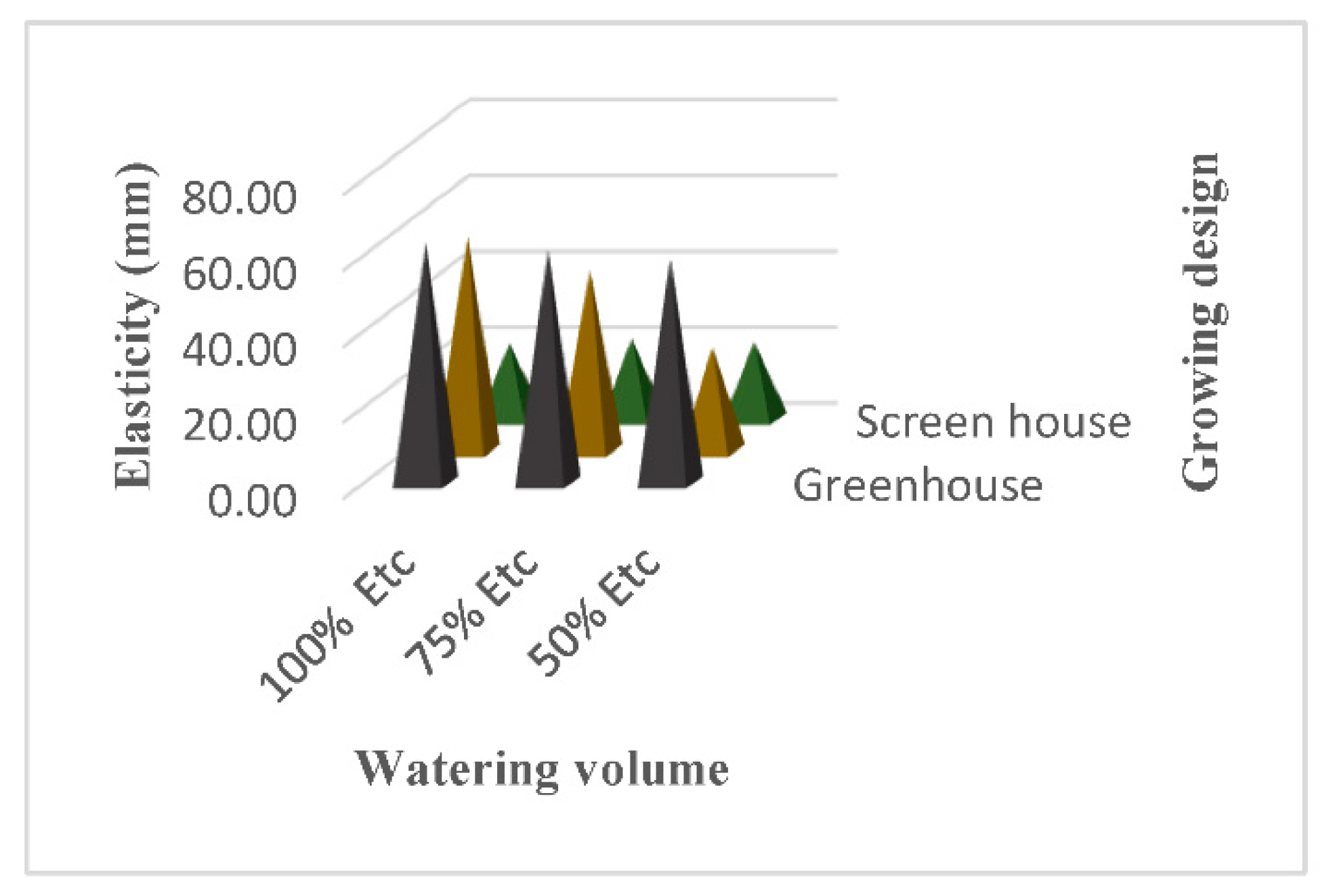
3.12. Fruit Tecture (Firmness and Elsaticity)
4. Discussion
4.1. Growth Rate
4.2. Fruit Diameter
4.3. Single Fruit Weight
4.4. Fruits per Plant
4.5. Fruits Yield per Plant
4.6. Biological Yield per Plant
4.7. Root Dry Weight
4.8. Shoot Dry Weight
4.9. Root Shoot Ratio
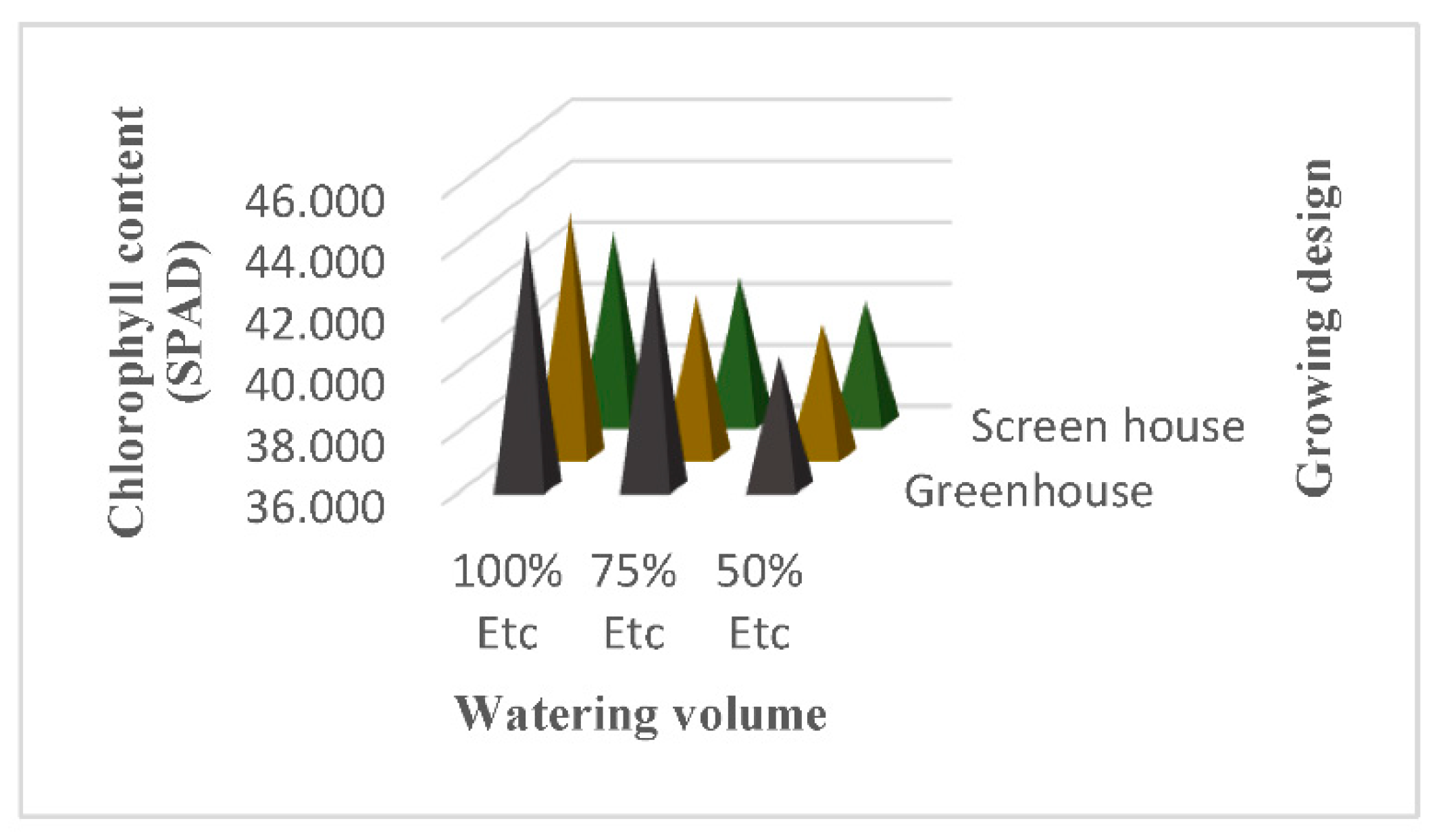
4.10. Chlorophyl Content
4.11. Fruit Texteure (Firmness & Elasticity)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- C. Kittas, N. Katsoulas, N. Rigakis, T. Bartzanas, and E. Kitta, “Effects on microclimate, crop production and quality of a tomato crop grown under shade nets,” J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol., vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 7–12, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Lone, K. Hussain, K. Z. Masoodi, S. Narayan, and S. Mazahir, “Distinctness, uniformity and stability testing of various cherry tomato accessions,” vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 2776–2788, 2021.
- L. D. Melomey, A. Danquah, S. K. Offei, K. Ofori, E. Danquah, and M. Osei, “Review on Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum, L.) Improvement Programmes in Ghana,” United Kingdom: Intechopen, 2019, pp. 49–69. [CrossRef]
- M. Z. Islam, Y. Lee, M. A. Mele, and I. Choi, “Effect of fruit size on fruit quality, shelf life and microbial activity in cherry tomatoes,” vol. 4, no. January, pp. 340–348, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Rahul, M. Rahman, M. Rakibuzzaman, M. N. Islam, and A. F. M. J. Uddin, “Study on growth and yield characteristics of twelve cherry tomato lines,” vol. 17, no. 01, pp. 1403–1409, 2018.
- R. D. Muttappanavar, A. T. Sadashiva, R. C. Vijendrakumar, B. N. Roopa, and P. T. Vasantha, “Combining Ability Analysis of Growth, Yield and Quality Traits in Cherry Tomato ( Solanum lycopersicum var. cersiforme ),” vol. 5, no. 4, p. 2014, 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. K. Singh, Z. Hussain, S. Raman, and N. Patel, “Pusa Golden Cherry Tomato-2 : New promising,” no. February, pp. 2–6, 2022.
- B. Kumar, P. Singh, R. P. Singh, R. N. Kewat, and R. P. Singh, “Evaluation of Quality Parameters at Ripening Stage in New Tomato ( Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) Germplasms,” no. 7, pp. 117–122, 2018.
- P. A. Michailidis and M. K. Krokida, “Drying and Dehydration Processes in Food Preservation and Processing,” in Conventional Food Processing, 1st ed., S. Bhattacharya, Ed. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2015, pp. 1–31.
- H. T. N. Ha and N. M. Thuy, “Application of intermittent vacuum treatment on the osmotic dehydration of black cherry tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum cv. OG),” J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 136–142, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Pratiwi, Elisa Sastra, and Inggita Utami, “Growth Response of Oval Red Cherry Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum Var. Cerasiforme) to Different Frequency of Watering,” Bioeduscience, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 183–187, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Rm, E. Mbega, and P. Ndakidemi, “Drought Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants : Physiological Responses Associated with Water Deficit Stress in Solanum lycopersicum Advances in Crop Science and Technology Drought Tolerance Mechanisms in Plants : Physiological Responses Associated with Water De,” no. July, 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. Liu, X. Shi, S. Zhang, Y. Shi, and Y. Long, “Saccharinity test on cherry tomatoes based on hyperspectral imaging,” Int. J. Des. Nat. Ecodynamics, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 103–111, 2020. [CrossRef]
- V. Alfeo, D. Planeta, S. Velotto, R. Palmeri, and A. Todaro, “Cherry tomato drying: Sun versus convective oven,” Horticulturae, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 1–12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- B. Valliyodan, H. Ye, L. Song, M. Murphy, J. G. Shannon, and H. T. Nguyen, “Genetic diversity and genomic strategies for improving drought and waterlogging tolerance in soybeans,” vol. 68, no. 8, pp. 1835–1849, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. Sun et al., “Systematic analysis of the sugar accumulation mechanism in sucrose- and hexose- accumulating cherry tomato fruits,” BMC Plant Biol., vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. I. E. Song et al., “The role of the seed coat in adaptation of dimorphic seeds of the euhalophyte Suaeda salsa to salinity,” 2016. [CrossRef]
- Sun, K., Bei, Y. Liu, and Z. Pan, “Humic Acid Improves Greenhouse Tomato Quality and Bacterial Richness in Rhizosphere Soil,” ACS Omega, 2022. [CrossRef]
- D. Dannehl, C. Huber, T. Rocksch, S. Huyskens-Keil, and U. Schmidt, “Interactions between changing climate conditions in a semi-closed greenhouse and plant development, fruit yield, and health-promoting plant compounds of tomatoes,” Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam)., vol. 138, pp. 235–243, 2012. [CrossRef]
- C., D. Singh, S. Akhtar, and S. K. Dutta, “Effect of Microclimate on Yield and Quality Attributes of Cherry Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. var. cerasiforme) under Open Field and Polyhouse Conditions,” Int. J. Environ. Clim. Chang., vol. 11, no. June, pp. 24–30, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Devgan, P. Kaur, N. Kumar, and A. Kaur, “Active modified atmosphere packaging of yellow bell pepper for retention of physico-chemical quality attributes,” J. Food Sci. Technol., vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 878–888, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Liu et al., “Optimizing irrigation frequency and amount to balance yield, fruit quality and water use efficiency of greenhouse tomato,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 226, no. April, p. 105787, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wu et al., “Responses of growth, fruit yield, quality and water productivity of greenhouse tomato to deficit drip irrigation,” Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam)., vol. 275, no. July 2020, p. 109710, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. I. Montero, “Evaporative cooling in greenhouses: Effect on microclimate, water use efficiency and plant respons,” Acta Hortic., vol. 719, pp. 373–383, 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. Dannehl, M. Josuttis, C. Ulrichs, and U. Schmidt, “The potential of a confined closed greenhouse in terms of sustainable production, crop growth, yield and valuable plant compounds of tomatoes,” J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual., vol. 87, pp. 210–219, 2014. [CrossRef]
- I. Romacho et al., “The growth and yield of cherry tomatoes in net covered greenhouses,” Acta Hortic., vol. 719, pp. 529–534, 2006. [CrossRef]
- H. A. Ahemd, A. A. Al-Faraj, and A. M. Abdel-Ghany, “Shading greenhouses to improve the microclimate, energy and water saving in hot regions: A review,” Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam)., vol. 201, pp. 36–45, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Abhivyakti and, P. Kumari, “Impact of microclimatic modification on tomato quality through mulching inside and outside the polyhouse,” Agric. Sci. Dig. - A Res. J., vol. 35, no. 3, p. 178, 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Molina-Aiz, D. L. Valera, A. López, A. J. Álvarez, and C. Escamirosa, “Effects of insect-proof screens used in greenhouse on microclimate and fruit yield of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) in a mediterranean climate,” Acta Hortic., vol. 927, pp. 707–714, 2012. [CrossRef]
- E. Coyago-Cruz et al., “Yield response to regulated deficit irrigation of greenhouse cherry tomatoes,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 213, no. June 2018, pp. 212–221, 2019. [CrossRef]
- E. Holcman, P. C. Sentelhas, and S. da C. Mello, “Microclimatic changes caused by different plastic coverings in greenhouses cultivated with cherry tomato in southern Brazil,” Rev. Bras. Meteorol., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 125–133, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Hemming, F. de Zwart, A. Elings, A. Petropoulou, and I. Righini, “Cherry tomato production in intelligent greenhouses-sensors and ai for control of climate, irrigation, crop yield, and quality,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 20, no. 22, pp. 1–30, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Hussain et al., “Genetic variability studies in cherry tomato for growth, yield, and quality traits in open field conditions,” Int. J. Agric. Appl. Sci., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 60–64, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Kaur and N. S. Dhillon, “Estimation of yield and quality traits of cherry tomato under the influence of micronutrients in protected condition Estimation of yield and quality traits of cherry tomato under the influence of micronutrients in protected condition,” no. March, pp. 3–7, 2022.
- R. Leyva et al., “Effects of climatic control on tomato yield and nutritional quality in Mediterranean screenhouse,” J. Sci. Food Agric., vol. 94, no. 1, pp. 63–70, 2014. [CrossRef]
- J. Zheng et al., “Responses of drip irrigated tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) yield, quality and water productivity to various soil matric potential thresholds in an arid region of Northwest China,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 129, pp. 181–193, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Z. Pék, P. Szuvandzsiev, H. Daood, A. Neményi, and L. Helyes, “Effect of irrigation on yield parameters and antioxidant profiles of processing cherry tomato,” Cent. Eur. J. Biol., vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 383–395, 2014. [CrossRef]
- R. N. Barbagallo, I. Di Silvestro, and C. Patanè, “Yield, physicochemical traits, antioxidant pattern, polyphenol oxidase activity and total visual quality of field-grown processing tomato cv. Brigade as affected by water stress in Mediterranean climate,” J. Sci. Food Agric., vol. 93, no. 6, pp. 1449–1457, 2013. [CrossRef]
- L. Helyes, A. Lugasi, and Z. Pék, “Effect of irrigation on processing tomato yield and antioxidant components,” Turkish J. Agric. For., vol. 36, no. 6, pp. 702–709, 2012. [CrossRef]
- D. D. Nangare, Y. Singh, P. S. Kumar, and P. S. Minhas, “Growth, fruit yield and quality of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) as affected by deficit irrigation regulated on phenological basis,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 171, pp. 73–79, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Liu, A. wang Duan, F. sheng Li, J. sheng Sun, Y. cong Wang, and C. tao Sun, “Drip Irrigation Scheduling for Tomato Grown in Solar Greenhouse Based on Pan Evaporation in North China Plain,” J. Integr. Agric., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 520–531, 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. E. d. S. Oliveira, T. Zoz, A. Jalal, C. de C. Seron, R. A. da Silva, and M. C. M. T. Filho, “Tolerance of tomato seedling cultivars to different values of irrigation water salinity1,” Rev. Bras. Eng. Agric. e Ambient., vol. 26, no. 10, pp. 697–705, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Jarquín-Enríquez, E. M. Mercado-Silva, J. L. Maldonado, and J. Lopez-Baltazar, “Lycopene content and color index of tomatoes are affected by the greenhouse cover,” Sci. Hortic. (Amsterdam)., vol. 155, pp. 43–48, 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Dorais, D. L. Ehret, and A. P. Papadopoulos, “Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) health components: From the seed to the consumer,” Phytochem. Rev., vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 231–250, 2008. [CrossRef]
- V. Cantore et al., “Combined effect of deficit irrigation and strobilurin application on yield, fruit quality and water use efficiency of ‘cherry’ tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.),” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 167, pp. 53–61, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Harmanto, V. M. Salokhe, M. S. Babel, and H. J. Tantau, “Water requirement of drip irrigated tomatoes grown in greenhouse in tropical environment,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 71, no. 3, pp. 225–242, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Qasim, I. Ahmad, and T. Ahmad, “Optimizing fertigation frequency for Rosa hybrida L.,” Pakistan J. Bot., vol. 40, no. 2, pp. 533–545, 2008.
- V. Valenzano, A. Parente, F. Serio, and P. Santamaria, “Effect of growing system and cultivar on yield and water-use efficiency of greenhouse-grown tomato,” J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol., vol. 83, no. 1, pp. 71–75, 2008. [CrossRef]
- E. Coyago-Cruz et al., Study of commercial quality parameters, sugars, phenolics, carotenoids and plastids in different tomato varieties, vol. 277. Elsevier Ltd, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. P. N. Gent, “Effect of degree and duration of shade on quality of greenhouse tomato,” HortScience, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 514–520, 2007. [CrossRef]
- D. Harel, H. Fadida, A. Slepoy, S. Gantz, and K. Shilo, “The effect of mean daily temperature and relative humidity on pollen, fruit set and yield of tomato grown in commercial protected cultivation,” Agronomy, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 167–177, 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. Ozbahce and A. F. Tari, “Effects of different emitter space and water stress on yield and quality of processing tomato under semi-arid climate conditions,” Agric. Water Manag., vol. 97, no. 9, pp. 1405–1410, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhai, Q. Yang, and M. Hou, “The effects of saline water drip irrigation on tomato yield, quality, and blossom-end rot incidence—a 3a case study in the South of China,” PLoS One, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 1–17, 2015. [CrossRef]
- H. Abdel-Razz, A. Ibrahim, M. Wahb-Allah, and A. Alsadon, “Response of Cherry Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme) to Pruning Systems and Irrigation Rates under Greenhouse Conditions,” Asian J. Crop Sci., vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 275–285, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Walter, H. Heuberger, and W. H. Schnitzler, “Sensibility of different vegetables to oxygen deficiency and aeration with H2O2 in the rhizosphere,” Acta Hortic., vol. 659, pp. 499–508, 2004. [CrossRef]
- D. Kapoor, S. Bhardwaj, M. Landi, A. Sharma, M. Ramakrishnan, and A. Sharma, “The impact of drought in plant metabolism: How to exploit tolerance mechanisms to increase crop production,” Appl. Sci., vol. 10, no. 16, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Asadi, M. H. Lebaschy, A. Khourgami, A. Hosein, and S. Rad, “Effect of drought stress on the morphology of three Salvia sclarea populations,” Ann. Biol. Res., vol. 3, no. 9, pp. 4503–4507, 2012.
- M. Maleki, H. Ebrahimzade, M. Gholami, and V. Niknam, “The effect of drought stress and exogenous abscisic acid on growth, protein content and antioxidative enzyme activity in saffron (Crocus sativus L.),” African J. Biotechnol., vol. 10, no. 45, pp. 9068–9075, 2011. [CrossRef]
- C. Salazar, C. Hernández, and M. T. Pino, “Plant water stress: Associations between ethylene and abscisic acid response,” Chil. J. Agric. Res., vol. 75, no. August, pp. 71–79, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. Hidayat, B. Frasetya, and I. N. Syamsudin, “Adjustment of phosphorus concentration to increase growth and yield of cherry tomato using hydroponic drip system,” J. Agro, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 140–147, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Razmjoo, P. Heydarizadeh, and M. R. Sabzalian, “Effect of salinity and drought stresses on growth parameters and essential oil content of Matricaria chamomila,” Int. J. Agric. Biol., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 451–454, 2008.
- M. Farooq, S. M. A. Basra, A. Wahid, Z. A. Cheema, M. A. Cheema, and A. Khaliq, “Physiological role of exogenously applied glycinebetaine to improve drought tolerance in fine grain aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.),” J. Agron. Crop Sci., vol. 194, no. 5, pp. 325–333, 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. Gheidary, D. Akhzari, and M. Pessarakli, “Effects of salinity, drought, and priming treatments on seed germination and growth parameters of Lathyrus sativus L.,” J. Plant Nutr., vol. 40, no. 10, pp. 1507–1514, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Teitel, “The effect of screened openings on greenhouse microclimate,” Agric. For. Meteorol., vol. 143, no. 3–4, pp. 159–175, 2007. [CrossRef]
- N. Katsoulas and C. Kittas, “Impact of Greenhouse Microclimate on Plant Growth and Development with Special Reference to the Solanaceae,” Eur. J. Plant Sci. Biotechnol., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 31–44, 2008.
- A. Rostami Ajirloo and E. Amiri, “Responses of Tomato Cultivars to Water-Deficit Conditions (Case Study: Moghan Plain, Iran),” Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., vol. 49, no. 18, pp. 2267–2283, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Al Hassan, M. Martínez Fuertes, F. J. Ramos Sánchez, O. Vicente, and M. Boscaiu, “Effects of salt and water stress on plant growth and on accumulation of osmolytes and antioxidant compounds in cherry tomato,” Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 1–11, 2015. [CrossRef]
- V. Ezin, R. De La Pena, and A. Ahanchede, “Flooding tolerance of tomato genotypes during vegetative and reproductive stages,” Brazilian J. Plant Physiol., vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 131–142, 2010. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Soleh, M. Ariyanti, I. R. Dewi, and M. Kadapi, “Chlorophyll fluorescence and stomatal conductance of ten sugarcane varieties under waterlogging and fluctuation light intensity,” Emirates J. Food Agric., vol. 30, no. 11, pp. 935–940, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Ploeg and, E. Heuvelink, “Influence of sub-optimal temperature on tomato growth and yield: A review,” J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol., vol. 80, no. 6, pp. 652–659, 2005. [CrossRef]
- M. Joung and Y. Shin, “Physicochemical quality, antioxidant compounds, and activity of ‘Beta Tiny’ and ‘TY Nonari’ cherry tomatoes during storage,” Korean J. Food Sci. Technol., vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 63–71, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Tsouvaltzis, S. Gkountina, and A. S. Siomos, “Quality Traits and Nutritional Components of Cherry Tomato in Relation to the Harvesting Period, Storage Duration and Fruit Position in the Truss,” Plants, vol. 12, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. D. Melomey, A. Danquah, S. K. Offei, K. Ofori, E. Danquah, and M. Osei, “Review on Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum, L.) Improvement Programmes in Ghana,” Recent Adv. Tomato Breed. Prod., no. January, 2019. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




