Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
08 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Lipase target selection
2.2. Synthesis, expression, purification and characterization
2.3. Molecular simulations: reasons for improving the lipase “character”
2.4. Molecular simulations: Lid swapping
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Source and Production of WP_075743487.1, WP_075743487.1lid and WP_075743487.1W89M/L60F
4.2. Source of Rhizopus delemar lipase
4.3. Substrate specificity
4.5. Protein and chemical preparation for in silico analysis
4.6. Protein Energy Landscape Exploration (PELE) simulations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yassine Ben, A.; Verger, R.; Abousalham, A. Lipases or esterases: Does it really matter? Toward a new bio-physico-chemical classification. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, N.J.) 2012, 861, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, T.L.; Buchholz, P.C.F.; Pleiss, J. The modular structure of α/β-hydrolases. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1035–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerk, I.K.; Wechselberger, L.; Oberer, M. Adipose triglyceride lipase regulation: An overview. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarda, L.; Desnuelle, P. Action de la lipase pancréatique sur les esters en émulsion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1958, 30, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, R. Interfacial activation of lipases: Facts and artifacts. Trends. Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, L.; Brzozowski, A.M.; Derewenda, Z.S.; Dodson, E.; Dodson, G.; Tolley, S.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Christiansen, L.; Huge-Jensen, B.; Norskov, L.; Thim. , L.; Menge, U. A serine protease triad forms the catalytic centre of a triacylglycerol lipase. Nature 1990, 343, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, F.K.; D’Arcy, A.; Hunziker, W. Structure of human pancreatic lipase. Nature 1990, 343, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Derewenda, U.; Derewenda, Z.S.; Dodson, G.G.; Lawson, D.M.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Bjorkling, F.; Huge-Jensen, B.; Patkar, S.A.; Thim, L. A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature 1991, 351, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Tilbeurgh, H.; Egloff, M.P.; Martinez, C.; Rugani, N.; Verger, R.; Cambillau, C. Interfacial activation of the lipase-procolipase complex by mixed micelles revealed by X-ray crystallography. Nature 1993, 362, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbe, S.; Lafaquière, V.; Guieysse, D.; Monsan, P.; Remaud-Siméon, M.; André, I. Insights into lid movements of Burkholderia cepacia lipase inferred from molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins 2009, 77, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.; Holmberg, K.; Watzke, H.; Leser, M.E.; Miller, R. Lipases at interfaces: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 147–148, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, C.; De Geus, P.; Lauwereys, M.; Matthyssens, G.; Cambillau, C. Fusarium solani cutinase is a lipolytic enzyme with a catalytic serine accessible to solvent. Nature 1992, 356, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, A.; Carrière, F.; Cudrey, C.; Wöldike, H.; Boel, E.; Lawson, D.M.; Ferrato, F.; Cambillau, C.; Dodson, G.G.; Thim, L.; Verger, R. A structural domain (the lid) found in pancreatic lipases is absent in the guinea pig (phospho)lipase. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 4702–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, K.E.; Ransac, S.; Koch, H.B.; Ferrato, F.; Dijkstra, B.W. Topological characterization and modeling of the 3D structure of lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett. 1993, 332, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, M.E.; Cleasby, A.; Johnson, L.N.; Egmond, M.R.; Frenken, L.G. The Crystal structure of triacyl-glycerol lipase from Pseudomonas glumae reveals a partially redundant catalytic aspartate. FEBS Lett. 1993, 331, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppenberg, J.; Hansen, M.T.; Patkar, S.; Jones, T.A. The Sequence, crystal structure determination and refinement of two crystal forms of lipase B from Candida antarctica. Structure 1994, 2, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Rai, R.; Rai, L.C. Proteomics combines morphological, physiological and bio-chemical attributes to unravel the survival strategy of Anabaena sp. PCC7120 under arsenic stress. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Bargiela, R.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Mir, J.; Koch, R.; Golyshina, O.V.; Golyshin, P.N. Biodiversity for biocatalysis: a review of the α/β-hydrolase fold superfamily of esterases-lipases discovered in metagenomes. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2015, 3, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.I.; Lan, D.; Durrani, R.; Huan, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y. The lid domain in lipases: structural and functional determinant of enzymatic properties. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2017, 5, 247303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugi, K.A.; Dichek, H.L.; Santamarina-Fojo, S. Human hepatic and lipoprotein lipase. The loop covering the catalytic site mediates lipase substrate specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 25396–25401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleiss, J.; Fischer, M.; Schmid, R.D. Anatomy of lipase binding sites: The scissile fatty acid binding site. ” Chem. Phys. Lipids 1998, 93, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, S.; Secundo, F.; Ossola, M.; Alberghina, L.; Carrea, G.; Lotti, M. Sequence of the lid affects activity and specificity of Candida rugosa lipase isoenzymes. Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarossa, G.; Lafranconi, P.G.; Alquati, C.; DeGioia, L.; Alberghina, L.; Fantucci, P.; Lotti, M. Mutations in the ‘lid’ region affect chain length specificity and thermostability of a Pseudomonas fragi lipase. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2383–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkhane, A.A.; Yakhchali, B.; Jazii, F.R.; Bambai, B. The effect of substitution of phe181 and phe182 with ala on activity, substrate specificity and stabilization of substrate at the active site of Bacillus thermocatenulatus lipase. J. Mol. Catal., B Enzym. 2009, 61, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourist, R.; Brundiek, H.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Protein engineering and discovery of lipases. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, P.; Cesarini, S.; Diaz, P.; Rodríguez Giordano, S. Saturation mutagenesis in selected amino acids to shift Pseudomonas sp. acidic lipase lip i.3 substrate specificity and activity. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2014, 51, 1330–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, A.; Kademi, A.; Leblanc, D. Lipases and their industrial applications: An overview. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2004, 118, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornscheuer, U.T.; Kazlauskas, R.J. Hydrolases in organic synthesis: Regio- and stereoselective biotransformations, 2nd Edition. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2006, pp. 61-140.
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemetsen, T.; Raknes, I.A.; Fu, J.; Agafonov, A.; Balasundaram, S.V.; Tartari, G.; Robertsen, E.; Willassen, N.P. The MAR databases: development and implementation of databases specific for marine metagenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D692–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, M.; Funatsu, J.; Mikami, B.; Kugimiya, W.; Matsuo, T.; Morita, Y. The crystal structure of lipase II from Rhizopus niveus at 2.2 A resolution. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, H.D.; McCarthy, J.E.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Schmid, R.D. Cloning, expression, characterization and role of the leader sequence of a lipase from Rhizopus oryzae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1399, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouioui, I.; Rückert, C.; Willemse, J.; van Wezel, G.P.; Klenk, H.P.; Busche, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Bredholt, H.; Zotchev, S.B. Acti-noalloteichus fjordicus sp. nov. isolated from marine sponges: phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and genomic charac-terisation. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1705–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda, S.; Fernandez-Lopez, L.; Benedens, M.; Bollinger, A.; Thies, S.; Schumacher, J.; Coscolín, C.; Kazemi, M.; Santiago, G.; Gertzen, C.G.W.; Gonzalez-Alfonso, J.L.; Plou, F.J.; Jaeger, K.E.; Smits, S.H.J.; Ferrer, M.; Guallar, V. A Plurizyme with transaminase and hydrolase activity catalyzes cascade reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202207344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.R.; King, G.; Moreau, R.A.; Haas, M.J. Altered acyl chain length specificity of Rhizopus delemar lipase through mutagenesis and molecular modeling. Lipids 1997, 32, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, K.W.; Vitalis, A.; Alcantara, R.; Guallar, V. PELE: Protein Energy Landscape Exploration. A novel Monte Carlo based technique.” J Chem Theory Comput 2005, 1, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Municoy, M.; Roda, S.; Soler, D.; Soutullo, A.; Guallar. V. AquaPELE: A Monte Carlo-based Algorithm to sample the effects of buried water molecules in proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2020, 16, 7655–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecina, D.; Gilabert, J.F.; Guallar, V. Adaptive simulations, towards interactive protein-ligand modeling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; Shaw, D.E.; Francis, P.; Shenkin, P.S. Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derewenda, U.; Swenson, L.; Wei, Y.; Green, R.; Kobos, P.M.; Joerger, R.; Haas, M.J.; Derewenda, Z.S. Conformational lability of lipases observed in the absence of an oil-water interface: crystallographic studies of enzymes from the fungi Humicola lanuginosa and Rhizopus delemar. J. Lipid Res. 1994, 35, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; Mandrich, L.; Menchise, V.; Giordano, V.; Febbraio, F.; Rossi, M.; Pedone, C.; Manco, G. A substrate-induced switch in the reaction mechanism of a thermophilic esterase: kinetic evidences and structural basis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 6815–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; Galdiero, S.; Manco, G.; Lang, D.; Rossi, M.; Pedone, C. A snapshot of a transition state analogue of a novel thermophilic esterase belonging to the subfamily of mammalian hormone-sensitive lipase. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 303, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrich, L.; Menchise, V.; Alterio, V.; De Simone, G.; Pedone, C.; Rossi, M.; Manco, G. Functional and structural features of the oxyanion hole in a thermophilic esterase from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius. Proteins 2008, 71, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höppner, A.; Bollinger, A.; Kobus, S.; Thies, S.; Coscolín, C.; Ferrer, M.; Jaeger, K.E.; Smits, S.H.J. Crystal structures of a novel family IV esterase in free and substrate-bound form. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 3570–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distaso, M.; Cea-Rama, I.; Coscolín, C.; Chernikova, T.N.; Tran, H; Ferrer, M. ; Sanz-Aparicio, J.; Golyshin, P.N. The mobility of the cap domain is essential for the substrate promiscuity of a family iv esterase from Sorghum rhizosphere microbiome. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0180722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; Bridgland, A.; Meyer, C.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Ballard, A.J.; Cowie, A.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Jain, R.; Adler, J.; Back, T.; Petersen, S.; Reiman, D.; Clancy, E.; Zielinski, M.; Steinegger, M.; Pacholska, M.; Berghammer, T.; Bodenstein, S.; Silver, D.; Vinyals, O.; Senior, A.W.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kohli, P.; Hassabis, D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, J.L.; Beard, H.S.; Cao, Y.; Cho, A.E.; Damm, W.; Farid, R.; Felts, A.K.; Halgren, T.A.; Mainz, D.T.; Maple, J.R.; Murphy, R.; Philipp, D.M.; Repasky, M.P.; Zhang, L.Y.; Berne, B.J.; Friesner, R.A.; Gallicchio, E.; Levy, R.M. Integrated modeling program, Applied Chemical Theory (IMPACT). J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1752–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilatovskiy, A.V.; Abagyan, R.; Kufareva, I. Quantum mechanics approaches to drug research in the era of structural chemogenomics. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2013, 113, 2110–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atilgan, A.R.; Durell, S.R.; Jernigan, R.L.; Demirel, M.C.; Keskin, O.; Bahar, I. Anisotropy of fluctuation dynamics of proteins with an elastic network model. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashford, D.; Case, D.A. Generalized born models of macromolecular solvation effects. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2000, 51, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.W.; Zhu, S.S.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Y. Conversion of a Rhizopus chinensis lipase into an esterase by lid swapping. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
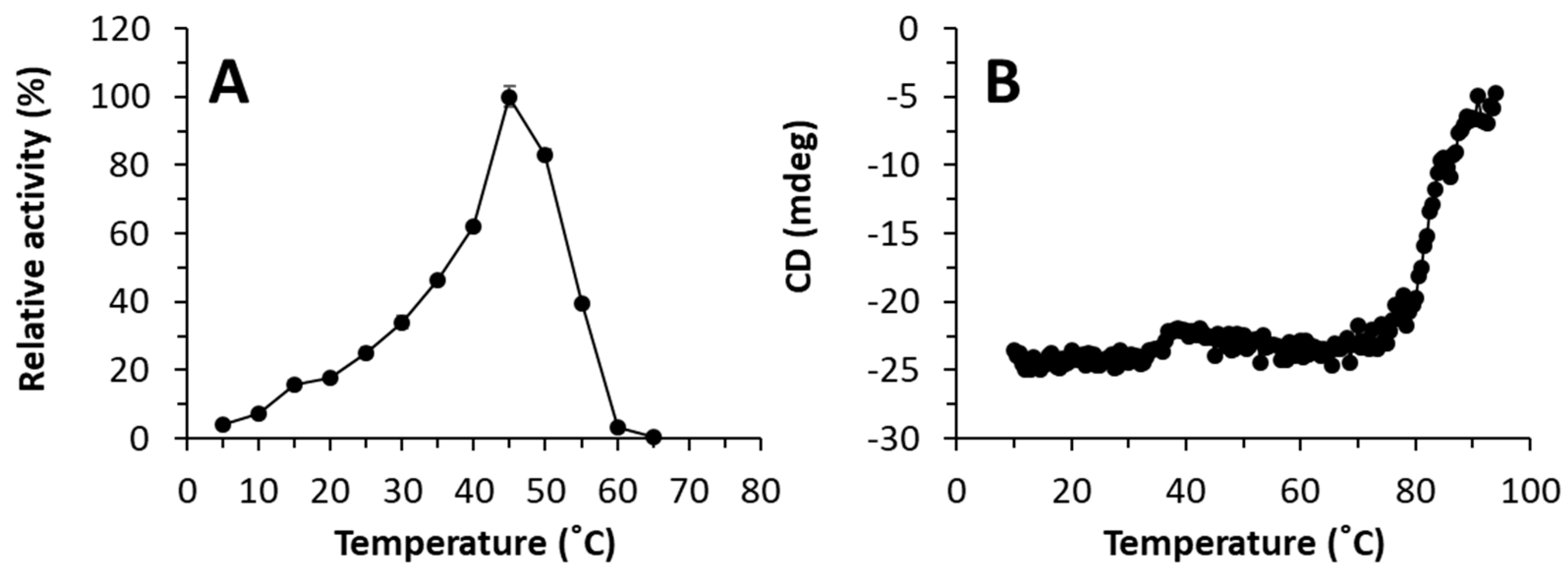
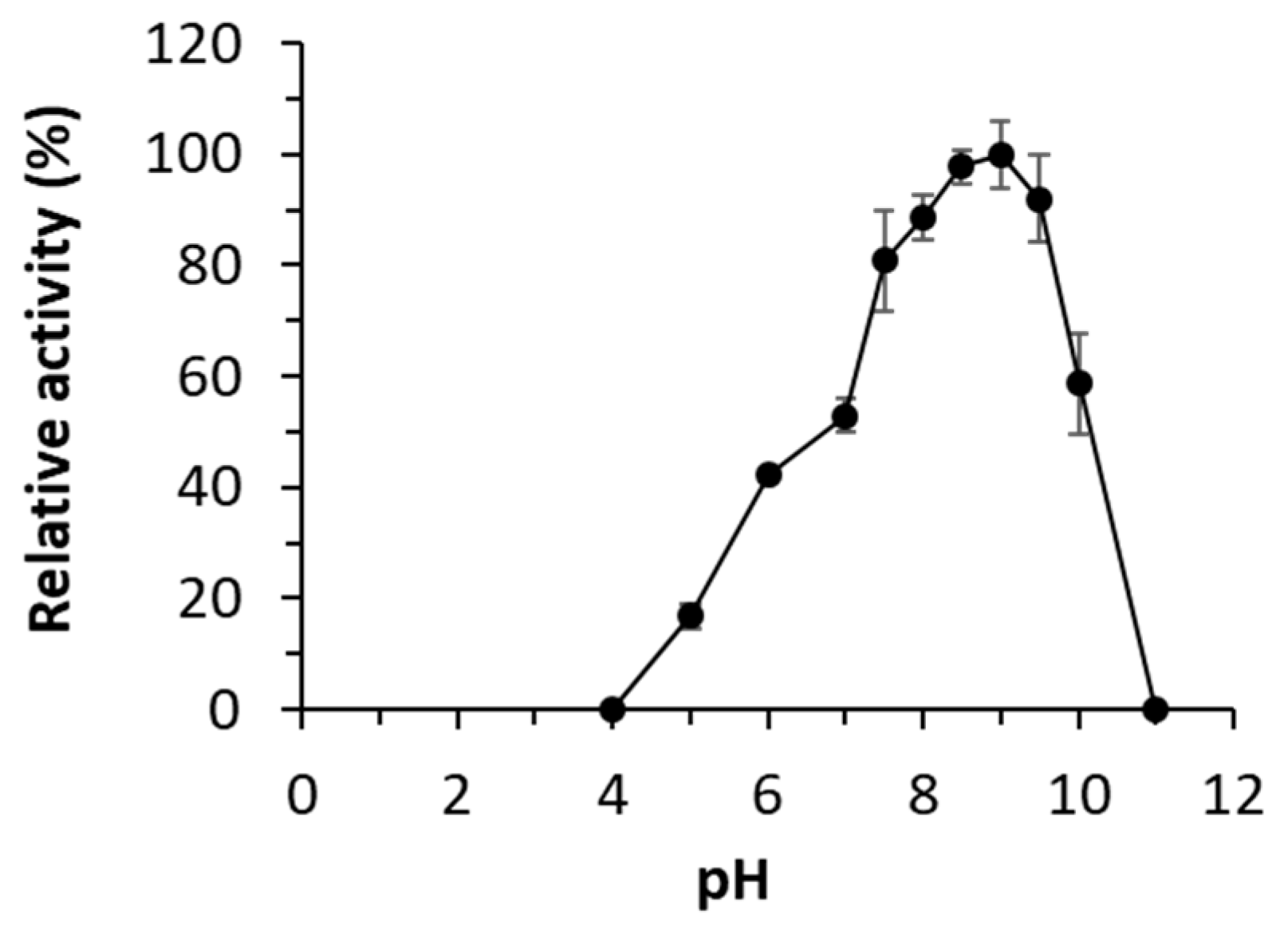
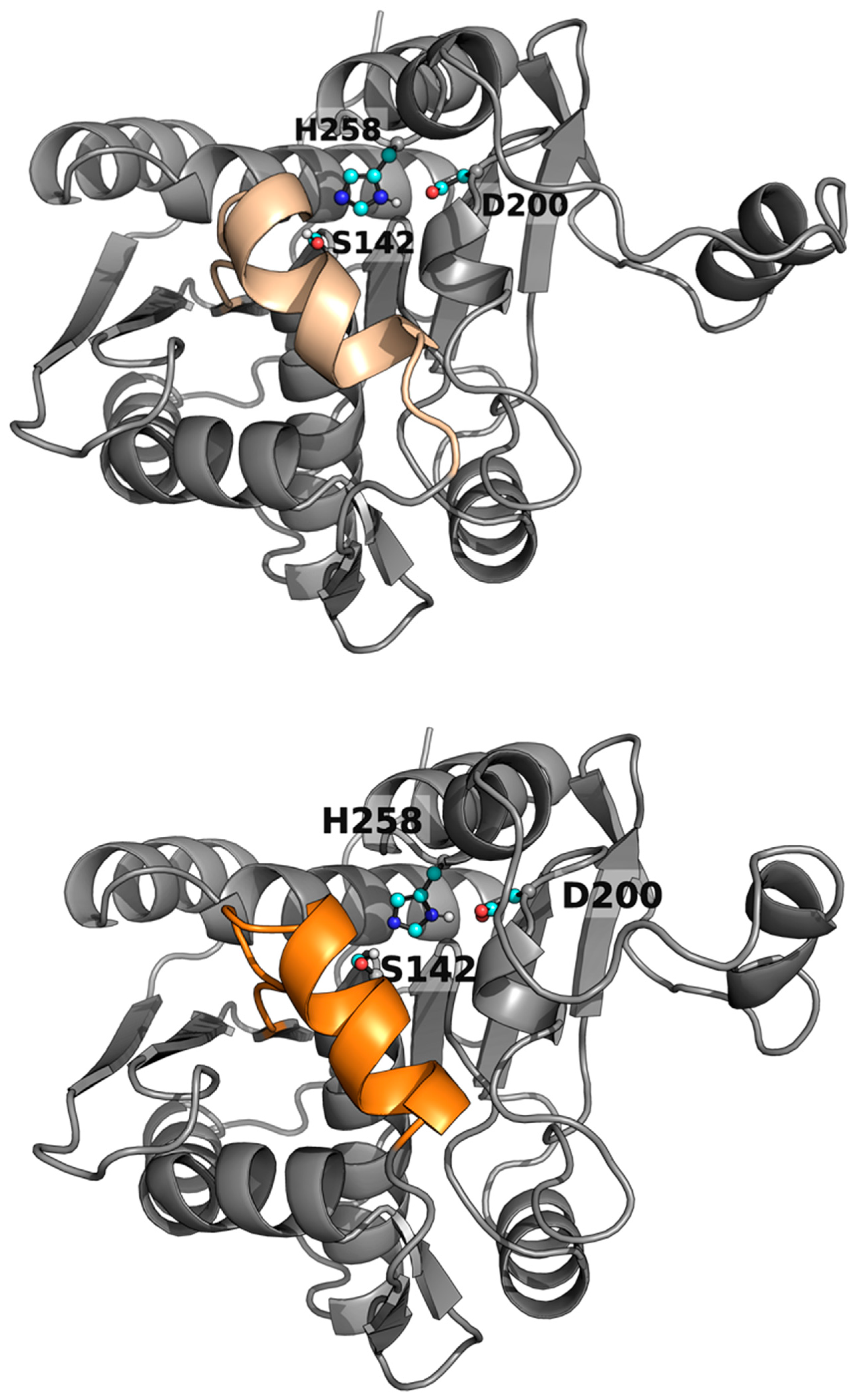
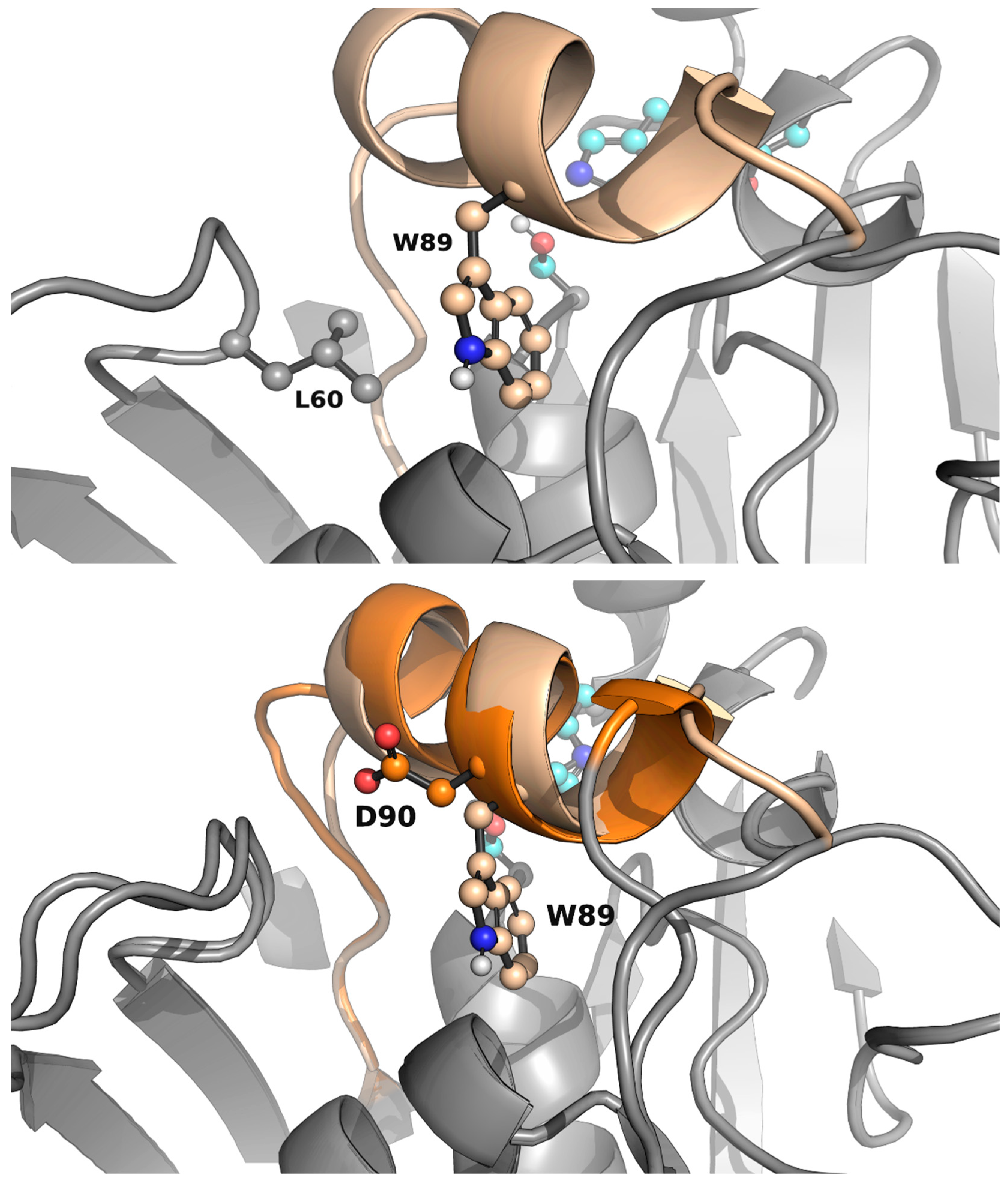
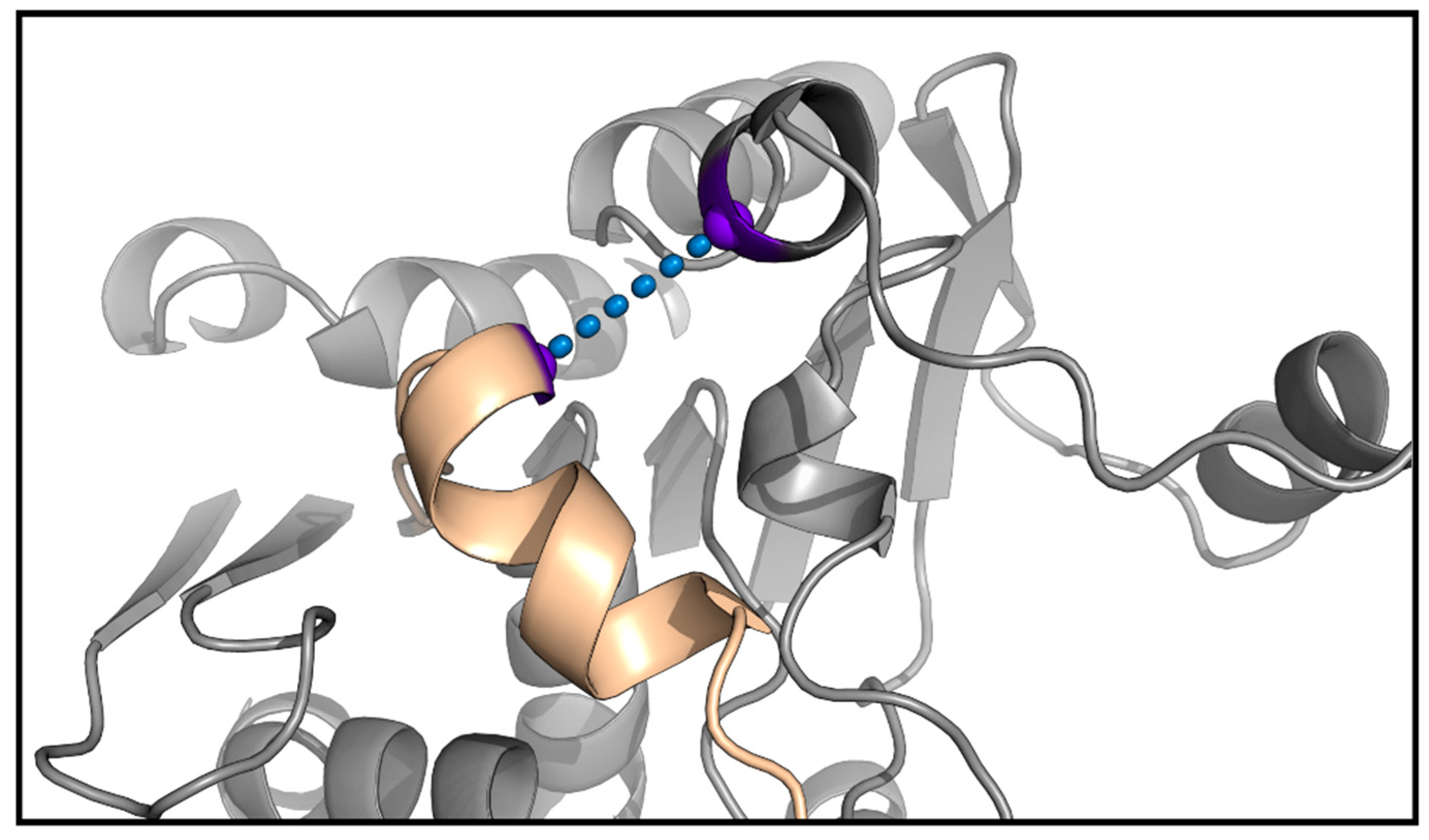
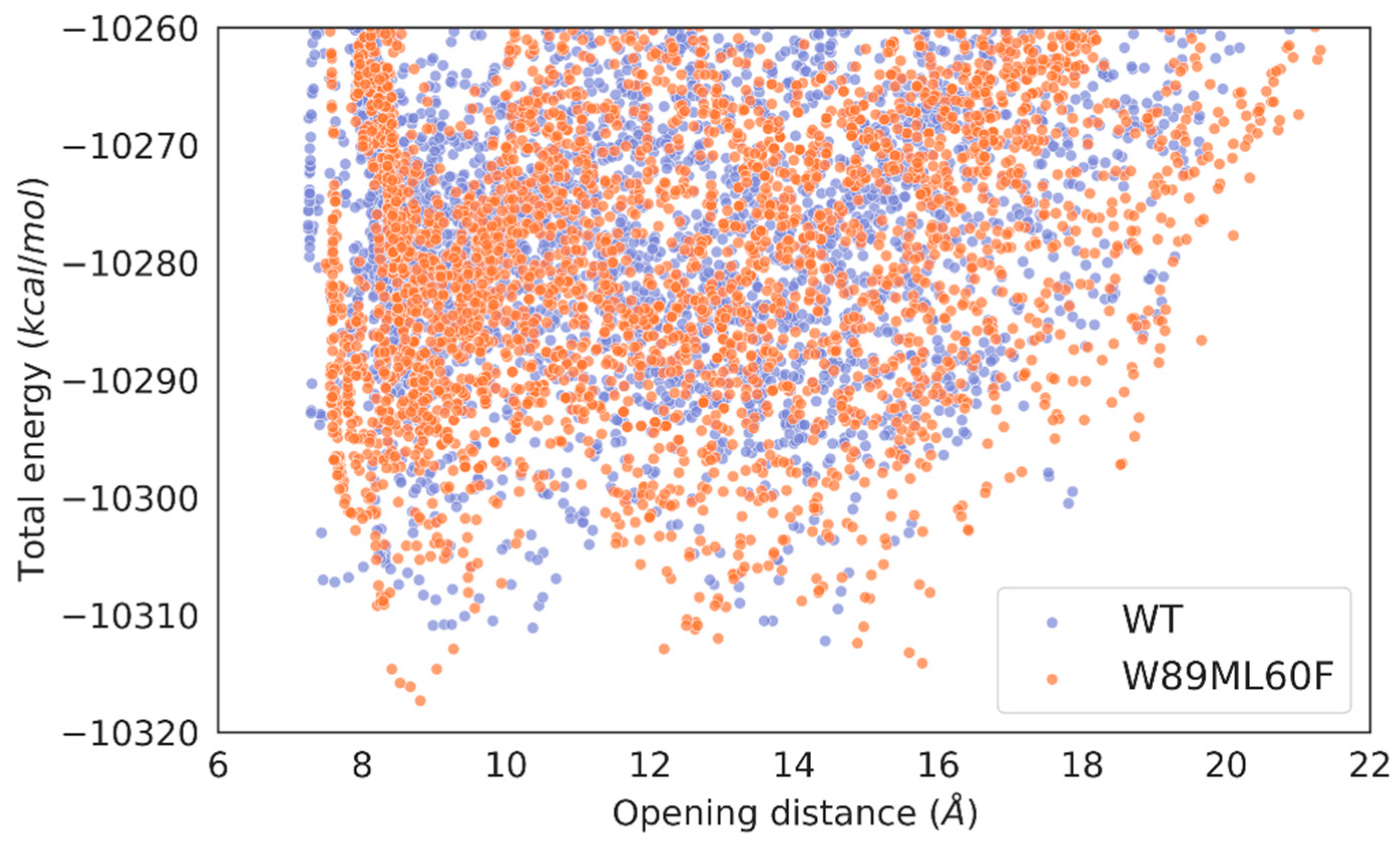
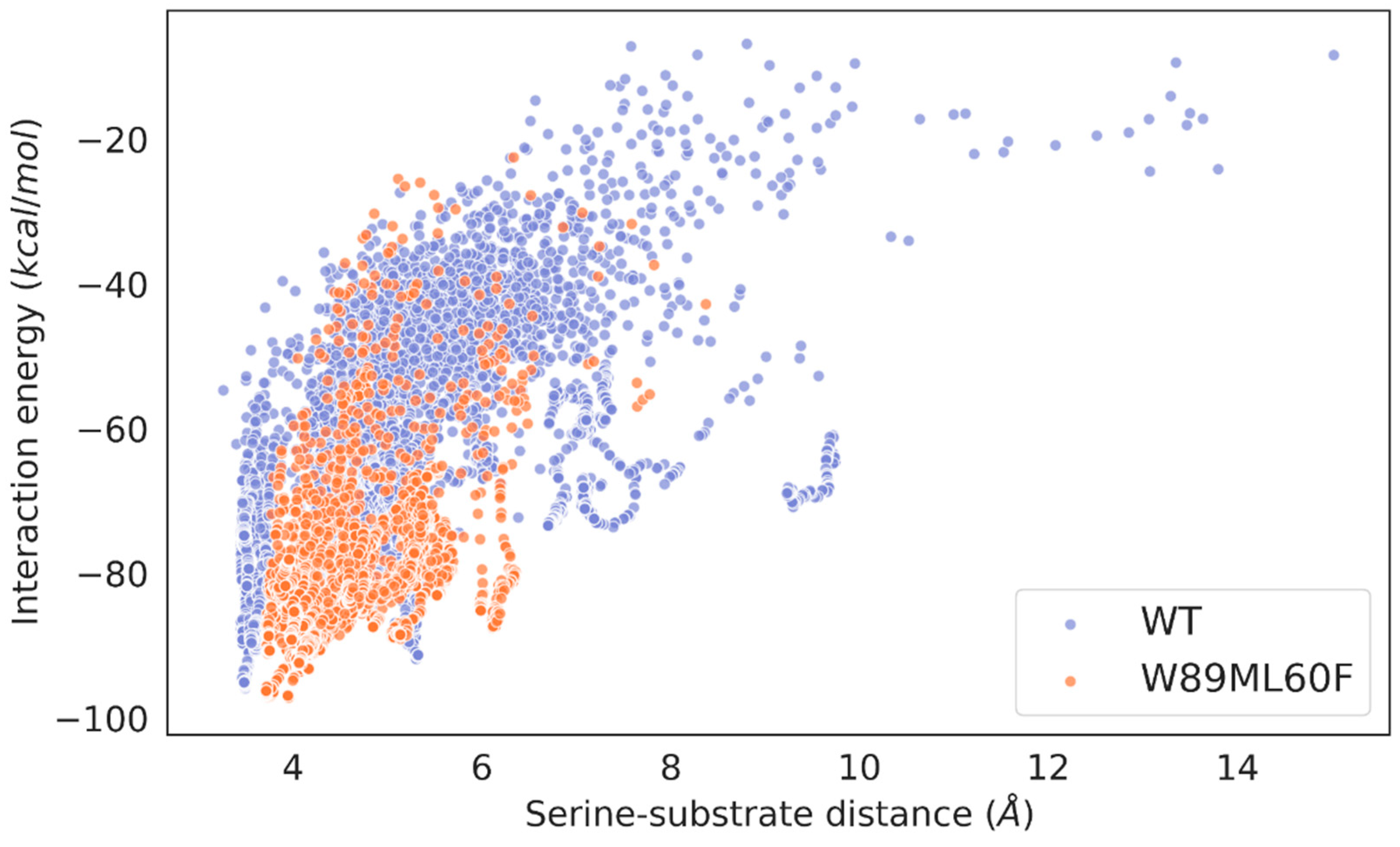
| Triglyceride | Spec. act. (Units/g) WP_075743487.1 |
Spec. act. (Units/g) Addzyme RD |
Spec. act. (Units/g) WP_075743487.1lid |
Spec. act. (Units/g) WP_075743487.1W89M/L60F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TriC3:0 | 960±20 | 590±80 | 630±20 | 550±70 |
| TriC4:0 | 1080±10 | 1080±90 | 780±70 | 640±10 |
| TriC8:0 | 3230±10 | 13440±60 | 2330±90 | 13800±290 |
| TriC10:0 | 580±10 | 9850±350 | 2220±60 | 9220±320 |
| Coconut oil | 50±10 | 6630±180 | 1460±170 | 1860±370 |
| Palm oil | 0 | 1300±250 | 1290±210 | 1050±20 |
| Olive oil | 0 | 3680±270 | 1210±20 | 1760±210 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





