Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
28 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Safety Risk Factors Identification of Metro Shield Construction
2.2. Safety Risks Evaluation of Metro Shield Construction
3. Safety Risk Factors Identification of MSCUB
3.1. The Framework for Safety Risk Factors Identification
3.2. The Identifying Process of the Safety Risk Factors
4. Evaluation Model for Safety Risk of MSCUB
4.1. Weights Calculation Based on Confirmatory Factor Analysis
4.2. Safety Risk Factors Measure Using FER
5. Case Validation
5.1. Project Overview
5.2. Identifying and Evaluating the Safety Risk Factors Based on Experts’ Group
5.3. Calculating the Risk Values of the Safety Risk Factors Based on CFA and ER
6. Discussion and Management Implication
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Safety risks | No important | Slightly important | Important | Relatively important | Extremelyimportant |
| W1: Physical and psychological unhealthy | |||||
| W2: Poor safety awareness | |||||
| W3: Weak safety ability | |||||
| M1: Lower safety management awareness | |||||
| M2: Weaker safety management competency | |||||
| M3: Lower safety management intentions | |||||
| M4: Insufficient safety communication | |||||
| M5: Inadequate safety inspection | |||||
| EQ1: Malfunction of cutter head equipment | |||||
| EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment | |||||
| EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor | |||||
| EQ4: Malfunction of segment erector | |||||
| EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment | |||||
| EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment | |||||
| TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme | |||||
| TE2: Inadequate geological and hydrological investigation scheme | |||||
| TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme | |||||
| TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme | |||||
| TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme | |||||
| TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | |||||
| TE7: Improper emergence plan | |||||
| NE1: Soft clay layer | |||||
| NE2: Silt soil layer | |||||
| NE3: Complex soil layer | |||||
| NE4: High-pressure underground water | |||||
| NE5: Subterranean boulders | |||||
| NE6: Subterranean voids | |||||
| BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel | |||||
| BC2:Friction bridge pile | |||||
| BC3:Large bridge pile diameter | |||||
| BC4:Poor bridge pile integrity | |||||
| BC5:Poor bridge safety condition | |||||
| ME1: Poor safety climate | |||||
| ME2: Incomplete safety institution | |||||
| ME3: Incomplete safety organization | |||||
| ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility | |||||
| ME5: Inadequate safety training & education |
Appendix B
| Safety risk factors | Occurrence probability grade | Consequences severity grade |
| W1: Physical and psychological unhealthy | ||
| W2: Poor safety awareness | ||
| W3: Weak safety ability | ||
| M1: Lower safety management awareness | ||
| M2: Weaker safety management competency | ||
| M3: Lower safety management intentions | ||
| M4: Insufficient safety communication | ||
| M5: Inadequate safety inspection | ||
| EQ1: Malfunction of cutter head equipment | ||
| EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment | ||
| EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor | ||
| EQ4: Malfunction of segment erector | ||
| EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment | ||
| EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment | ||
| TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme | ||
| TE2: Inadequate geological and hydrological investigation scheme | ||
| TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme | ||
| TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme | ||
| TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme | ||
| TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | ||
| TE7: Improper emergence plan | ||
| NE1: Soft clay layer | ||
| NE2: Silt soil layer | ||
| NE3: Complex soil layer | ||
| NE4: High-pressure underground water | ||
| NE5: Subterranean boulders | ||
| NE6: Subterranean voids | ||
| BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel | ||
| BC2:Friction bridge pile | ||
| BC3:Large bridge pile diameter | ||
| BC4:Poor bridge pile integrity | ||
| BC5:Poor bridge safety condition | ||
| ME1: Poor safety climate | ||
| ME2: Incomplete safety institution | ||
| ME3: Incomplete safety organization | ||
| ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility | ||
| ME5: Inadequate safety training & education |
References
- Cheng, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Lin, X.; Guo, Y. Evaluation of the Emergency Capability of Subway Shield Construction Based on Cloud Model. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2022, 14, 13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qiao, M.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z. A review on blockchain applications in the construction area. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2023, 20, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Li, H.; He, Z.; Chen, H. Carbon Emission Factors Identification and Measurement Model Construction for Railway Construction Projects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 11379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B. A comprehensive assessment approach for water-soil environmental risk during railway construction in ecological fragile region based on AHP and MEA. Sustainability (Switzerland) 2020, 12, 7910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Hu, X. Safety Influential Factors and Accident Causation Model of Subway Shield Construction. Journal of Railway Engineering Society 2020, 37, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Li, H. Research on safety impact factors and safety accident causation mechanism of subway shield construction in mix-ground. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2020, 17, 266–272. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Su, J. Study on active protection technology for an existing bridge adjacent to a subway project. Urban Rapid Rail Transit 2012, 25, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Song, F.; Xu, J.; Han, X. Influence of shield tunneling on a Large-Ang gle skewed railway box culvert. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering 2022, 18, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q. Research on the safety influence of subway shield method crossing existing high-speed railway frame bridge. Journal of Railway Engineering Society 2021, 38, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, M. A study on risk grade classification method and disposal measures for adjacent bridge piles in Beijing metro engineering. Rock and Soil Mechanics 2008, 2008, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Shuailei, L.; Hao, Z.; Xingru, L. Study on the restraint control of an isolation pile on an existing high-speed railway during the close passing of a shield machine. Frontiers in Earth Science 2023, 11, 1142864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Tan, C.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Y. In Influence of Shield Tunnel and Train Load on Existing Bridge Piles. Advances in Transdisciplinary Engineering 2020, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Li, T.; Lin, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W. Safety risk assessment of metro shield tunnel-induced adjacent bridge damage based on rough set and bayesian network. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management 2016, 33, 9–15, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Gou, J.; Wan, Z.; Ren, C.; Chen, M.; Gou, T.; Luo, Z. Research on Coupling Degree Model of Safety Risk System for Tunnel Construction in Subway Shield Zone. Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2019, 2019, 5783938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, W.; Tang, J. Safety risk factors of metro tunnel construction in China: An integrated study with EFA and SEM. Safety Science 2018, 105, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Lin, P.; Lin, C. An interval risk assessment method and management of water inflow and inrush in course of karst tunnel excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 92, 103033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.C.; Min, S.; Choi, H.; Park, J.; Lee, I.M. Risk analysis using fault-tree analysis (FTA) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) applicable to shield TBM tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 49, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, T.; Duan, J. Enhanced safety prediction of vault settlement in urban tunnels using the pair-copula and Bayesian network. Applied Soft Computing 2023, 132, 109711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, W.; Zhai, S. Predictive Analysis of Settlement Risk in Tunnel Construction: A Bow-Tie-Bayesian Network Approach. Advances in Civil Engineering 2019, 2019, 2045125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Olgun, C.G.; Yang, S.; Jiao, Q.; Wang, M. Risk assessment of water inrush caused by karst cave in tunnels based on reliability and GA-BP neural network. Geomatics. Natural Hazards and Risk 2020, 11, 1212–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, C.; Su, B. Prediction and analysis of shield tunneling parameters in underwater karst stratum based on BP neural network. China Civil Engineering Journal 2020, 53, 75–80, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zou, S. A static risk assessment model for underwater shield tunnel construction. Sādhanā 2020, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Lee, I.-M.; Jung, J.-H.; Park, J. Bayesian networks-based shield TBM risk management system: methodology development and application. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 2019, 23, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Cheng, B.; Hu, X.; Cai, X. Study on formation model of subway construction safety climate based on fuzzy ISM-DEMATEL. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2021, 18, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C.; Lu, Z.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. On the risk evaluation of the metro shield construction in the soft soil condition background with the extension method. Journal of Safety and Environment 2017, 17, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yang, S.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Y. Safety evaluation of buildings adjacent to shield construction in karst areas: An improved extension cloud approach. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 2023, 124, 106386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Mei, Y. On the risk evaluation and control method of the shield tunneling under the hazardous buildings and rivers based on the catastrophe-forecasting theory. Journal of Safety and Environment 2017, 17, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Safety risk assessment of subway tunnel shield construction undercrossing an existing building. Building Structure 2023, 53, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Dong, J.; Li, L. Analysis on the safety influence of shield tunnel construction on its above metrostation. China Safety Science Journal 2009, 19, 172–176. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Q.; Chen, H.; Zeng, T.; Wang, J.; Tao, W. Preassessment of safety risk of shield tunneling underneath existing tunnel based on fuzzy Bayesian networks and evidence theory. Tunnel Construction 2021, 41, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, X.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Z. Physical model tests and discrete element simulation of shield tunnel face stability in anisotropic granular media. Acta Geotechnica 2020, 15, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, Y. Pipeline deformation laws and safety risk assessments caused by shield construction. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2020, 17, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Gu, H.; Jie, F. Safety evaluation of adjacent bridge in shield tunnel construction based on SPA method. Journal of Safety Science and Technology 2021, 17, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, M. In Shield construction safety risk assessment of metro tunnels based on cloud model, Proceedings – 2020 International Conference on Urban Engineering and Management Science. ICUEMS 2020, 2020, 584–587. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Xiahou, X.; Huang, H.; Tang, L.; Huang, J.; Li, Q.; Feng, P. AHP-FSE-Based Risk Assessment and Mitigation for Slurry Balancing Shield Tunnel Construction. Journal of Environmental and Public Health 2022, 2022, 1666950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, R. Application of matter-element extension method in safety risk assessment of subway shield construction. Journal of Safety and Environment 2023, 23, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Yang, F.; Zhu, Y. The Risk Assessment of Shield Construction under the Condition of Adjacent Buildings in Xi’an Metro. Journal of Railway Engineering Society 2016, 33, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Xu, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Mei, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, B. Prediction of shield construction risks in subway tunnelling based on fault tree and Bayesian network. Modern Tunneling Technology 2021, 58, 21–29, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Hu, X.; Cheng, B.; Tang, X. Determining the factor structure of construction safety climate in building engineering: A case study in Changsha. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2021, 18, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Cai, X.; Li, H. Research on the influence of supervisor-worker guanxi on construction workers’ safety behavior. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Zhang, Y. Fuzzy witness reasoning-based approach to the risk assessment of the deep foundation pit construction. Journal of Safety and Environment 2021, 21, 512–520. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Zhang, L.; Tiong, R.L.K. Flood risk assessment and mitigation for metro stations: An evidential-reasoning-based optimality approach considering uncertainty of subjective parameters. Reliability Engineering and System Safety 2023, 238, 109453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X. Multivariate Statistic Analysis, 2nd ed.; China Remin University Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 192–206. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.; Wichern, D. Applied multivariate statistical analysis, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall Inc.: New Jersey, USA, 2002; pp. 477–516. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.A. Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research, 2nd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, USA, 2015; pp. 35–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wenjuanxing. Wenjuanxing website. Available online: https://www.wjx.cn/ (accessed on 30 July 2023).
- Zhang, W. Advanced Courses on SPSS Statistical Analysis; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2004; pp. 218–227. [Google Scholar]
- Pallant, J. SPSS survival manual: a step by step guide to data analysis using IBM spss, 6th ed.; Open University Press: England, US, 2016; pp. 202–224. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, N.; Ding, S.; Yuan, J. The impact of a challenging work environment: Do job stressors benefit citizenship behavior of project managers? International Journal of Project Management 2022, 40, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Xia, N.; Yang, G. Do Family Affairs Matter? Work-Family Conflict and Safety Behavior of Construction Workers. Journal of Management in Engineering 2022, 38, 04021074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Tang, Y.; Li, D.; Pan, A. Safety Behavior among Construction Workers: Influences of Personality and Leadership. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 2021, 147, 04021019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Lin, B. Principle and Application of Structural Equation Model; China Light Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M. Structural Equation Model – Operation and Application of AMOS; Chongqing University Press: Chongqing, China, 2009; pp. 37–59. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, X.; Hui, Y.; Cui, C. Safety evaluation for the overtaking behavior on the two-lane highway based on the structural equation model. Journal of Safety and Environment 2017, 17, 1359–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Meng, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhou, X. PLS-SEM-based analysis on contruction safety of water conservancy project. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering 2019, 50, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X. Safety risk and strategy of prefabricated building construction based on SEM. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management 2020, 37, 70–75+121. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Fan, Z. Research on double-weight risk assessment method of coal mine safety management. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology 2022, 42, 600–606. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Li, X.; Xing, L.; Chen, Y. System risk analysis and evaluation approach based on fuzzy evidential reasoning. Systems Engineering – Theory & Practice 2013, 33, 529–537. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, H.; Men, G.; Wang, Q. A fuzzy evidence reasoning method for aviation safety risk evaluation. Electronics Optics & Control 2022, 29, 81–85+113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S. Safety-Risk Assessment for TBM Construction of Hydraulic Tunnel Based on Fuzzy Evidence Reasoning. Processes 2022, 10, 2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.; Chin, K.S. The evidential reasoning approach for MADA under both probabilistic and fuzzy uncertainties. European Journal of Operational Research 2006, 171, 309–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Qi, J.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, H. Multi-agent based safety computational experiment system for shield tunneling projects. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management 2020, 27, 1963–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Yang, L.; Cai, H. Risk assessment and management via multi-source information fusion for undersea tunnel construction. Autom Constr 2020, 111, 103050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, N.S.N.; Chan, D.W.M.; Shan, M.; Sze, N.N. Implementation of safety management system in managing construction projects: Benefits and obstacles. Safety Science 2019, 117, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Hu, X. Safety Influential Factors and Accident Causation Model of Subway Shield Construction. Journal of Railway Engineering Society 2020, 37, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Zhu, K.; Guo, P. Construction Safety Risks of Metro Tunnels Constructed by the Mining Method in Wuhan City, China: A Structural Equation Model-Fuzzy Cognitive Map Hybrid Method. Buildings 2023, 13, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhu, H.; AbouRizk, S.M. Perceiving safety risk of buildings adjacent to tunneling excavation: An information fusion approach. Autom Constr 2017, 73, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Hu, Q.; Ma, G. Improved Hybrid Reasoning Approach to Safety Risk Perception under Uncertainty for Mountain Tunnel Construction. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 2021, 147, 04021105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ding, L.; Wu, X.; Skibniewski, M.J. An improved Dempster–Shafer approach to construction safety risk perception. Knowledge-Based Systems 2017, 132, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Qi, J.; Chen, W.; Yang, K.; Chen, Q.; Xue, R. Analysis on influence of shield tunnel excavation in Nantong water-rich sand stratum on adjacent pile foundations. Science and Technology of Work Safety in China 2022, 18, 146–151. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, N.; Xie, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Meng, H. A dual perspective on risk perception and its effect on safety behavior: A moderated mediation model of safety motivation, and supervisor’s and coworkers’ safety climate. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 134, 105350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, N.; Xie, Q.; Griffin, M.A.; Ye, G.; Yuan, J. Antecedents of safety behavior in construction: A literature review and an integrated conceptual framework. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2020, 148, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gong, W.; Li, H.; Shi, S. Co-workers’ guanxi and construction workers’ safety behavior: The mediating role of group identification. Frontiers in Public Health 2022, 10, 964514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, H.; Goh, Y.M. A review of construction safety climate: Definitions, factors, relationship with safety behavior and research agenda. Safety Science 2021, 142, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
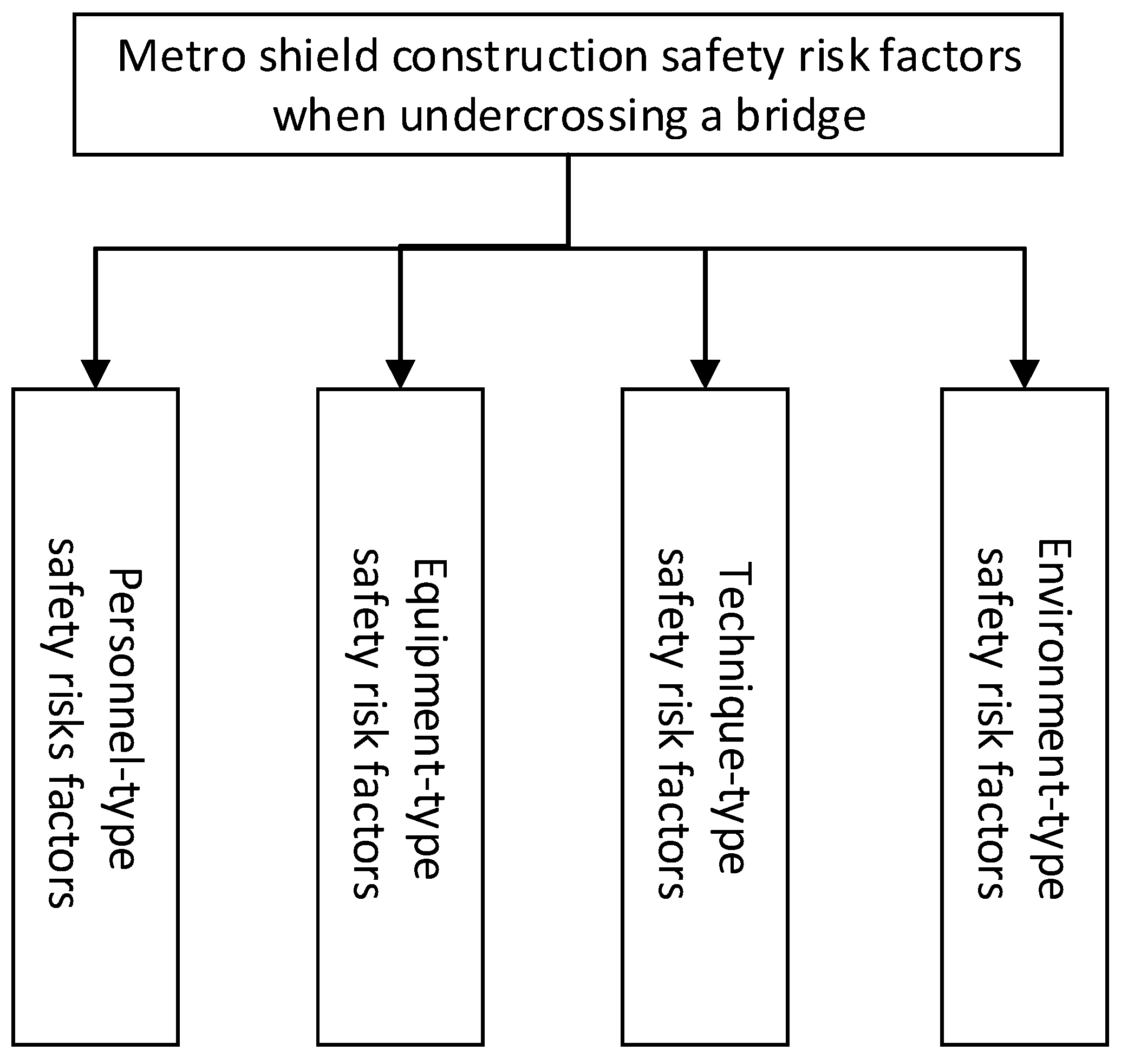
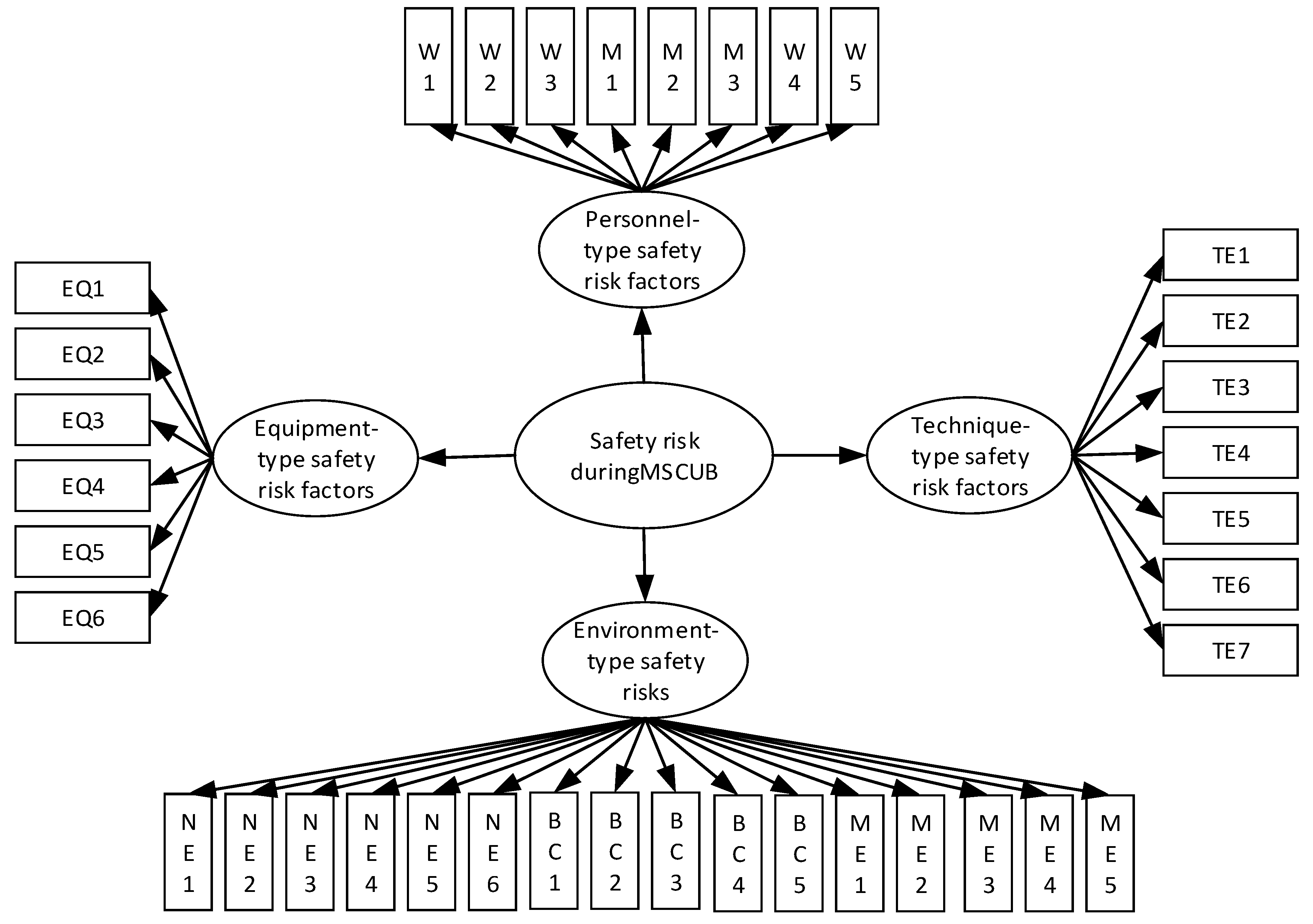
| Safety risk factors category | Safety risk factors | |
|---|---|---|
| Personnel-type | Worker-type | W1: Physical and psychological unhealthy; W2: Poor safety awareness; W3: Weak safety ability. |
| Manager-type | M1: Lower safety management awareness; M2: Weaker safety management competency; M3: Lower safety management intentions; M4: Insufficient safety communication; M5: Inadequate safety inspection. | |
| Equipment-type | EQ1: Malfunction of cutter head equipment; EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment; EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor; EQ4: Malfunction of segment erector; EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment: EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment. | |
| Technique-type | TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme; TE2: Inadequate geological and hydrological investigation scheme; TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme; TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme; TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme; TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme; TE7: Improper emergence plan. | |
| Environment-type | Natural environment-type | NE1: Soft clay layer; NE2: Silt soil layer; NE3: Complex soil layer; NE4: High-pressure underground water; NE5: Subterranean boulders; NE6: Subterranean voids. |
| Bridge condition | BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel; BC2:Friction bridge pile type; BC3:Large bridge pile diameter; BC4:Poor bridge pile integrity; BC5:Poor bridge safety condition; | |
| Management environment-type | ME1: Poor safety climate; ME2: Incomplete safety institution; ME3: Incomplete safety organization; ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility; ME5: Inadequate safety training & education. | |
| Relationship path | SPC | Relationship path | SPC | Relationship path | SPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTSRF→W1 | 0.406 | TTSRF→TE1 | 0.699 | ETSRF→BC2 | 0.674 |
| PTSRF→W2 | 0.711 | TTSRF→TE2 | 0.531 | ETSRF→BC3 | 0.642 |
| PTSRF→W3 | 0.592 | TTSRF→TE3 | 0.627 | ETSRF→BC4 | 0.732 |
| PTSRF→M1 | 0.570 | TTSRF→TE4 | 0.779 | ETSRF→BC5 | 0.755 |
| PTSRF→M2 | 0.605 | TTSRF→TE5 | 0.756 | ETSRF→ME1 | 0.732 |
| PTSRF→M3 | 0.739 | TTSRF→TE6 | 0.587 | ETSRF→ME1 | 0.835 |
| PTSRF→M4 | 0.706 | TTSRF→TE7 | 0.473 | ETSRF→ME1 | 0.732 |
| PTSRF→M5 | 0.727 | ETSRF→NE1 | 0.747 | ETSRF→ME1 | 0.813 |
| ETSRT→EQ1 | 0.625 | ETSRF→NE2 | 0.741 | ETSRF→ME1 | 0.625 |
| ETSRT→EQ2 | 0.682 | ETSRF→NE3 | 0.673 | SRMSCUB→PTSRF | 0.785 |
| ETSRT→EQ3 | 0.409 | ETSRF→NE4 | 0.723 | SRMSCUB→ETSRF | 0.564 |
| ETSRT→EQ4 | 0.622 | ETSRF→NE5 | 0.547 | SRMSCUB→TTSRF | 0.648 |
| ETSRT→EQ5 | 0.768 | ETSRF→NE6 | 0.543 | SRMSCUB→ETSRF | 0.946 |
| ETSRT→EQ6 | 0.594 | ETSRF→BC1 | 0.769 | - | - |
| Safety risks factors | Weights | Safety risks factors | Weights | Safety risks factors | Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.238 | TE1 | 0.157 | BC2 | 0.189 |
| W2 | 0.416 | TE2 | 0.119 | BC3 | 0.180 |
| W3 | 0.346 | TE3 | 0.141 | BC4 | 0.205 |
| M1 | 0.170 | TE4 | 0.175 | BC5 | 0.211 |
| M2 | 0.181 | TE5 | 0.170 | ME1 | 0.196 |
| M3 | 0.221 | TE6 | 0.132 | ME2 | 0.223 |
| M4 | 0.211 | TE7 | 0.106 | ME3 | 0.196 |
| M5 | 0.217 | NE1 | 0.188 | ME4 | 0.218 |
| EQ1 | 0.169 | NE2 | 0.186 | ME5 | 0.167 |
| EQ2 | 0.184 | NE3 | 0.169 | PTSRF | 0.267 |
| EQ3 | 0.111 | NE4 | 0.182 | ETSRF | 0.192 |
| EQ4 | 0.168 | NE5 | 0.138 | TTSRF | 0.220 |
| EQ5 | 0.208 | NE6 | 0.137 | ETSRF | 0.321 |
| EQ6 | 0.161 | BC1 | 0.215 | - | - |
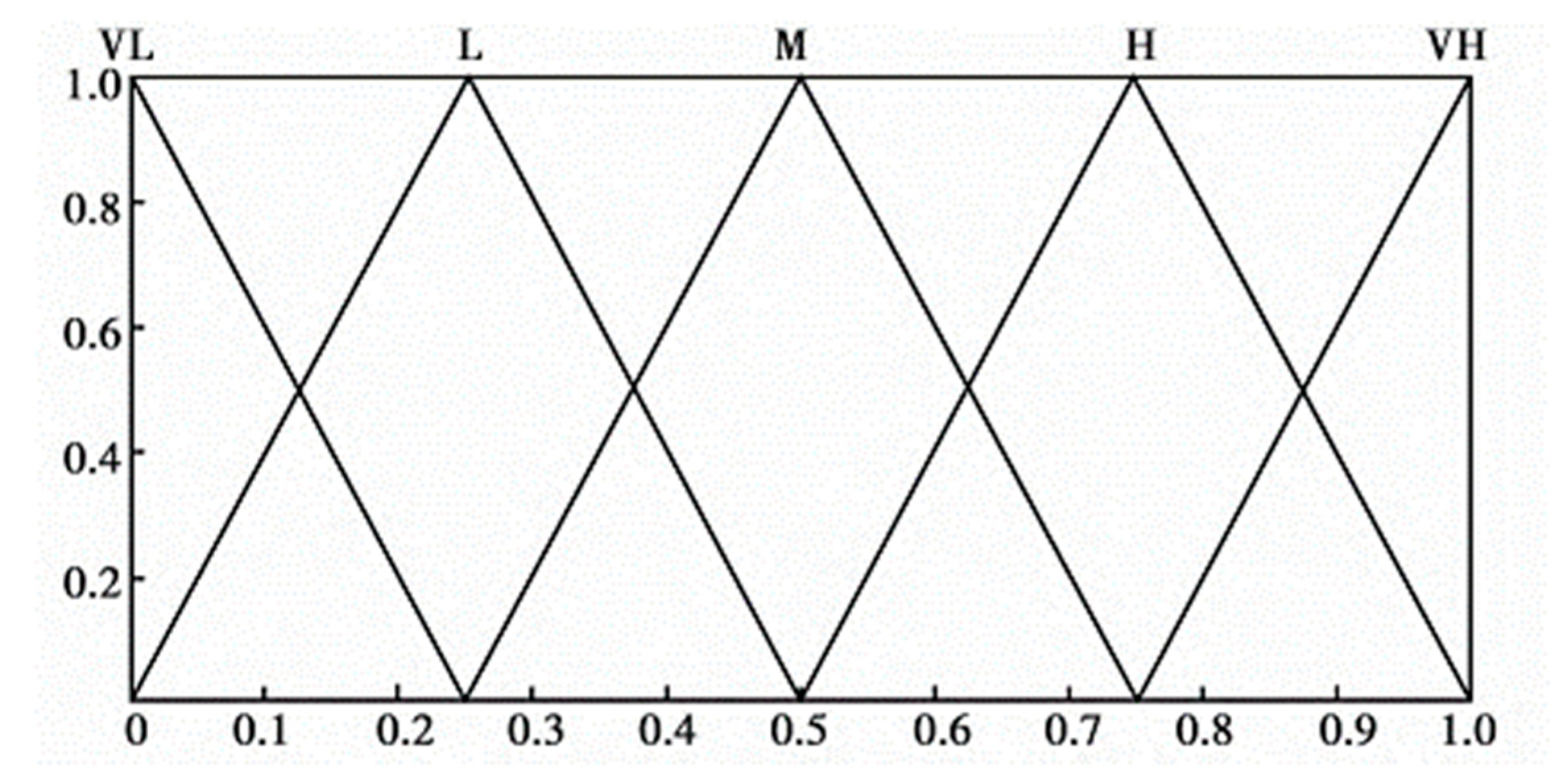
| Level | Occurrence probability | Consequence severity | The triangular fuzzy number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Extremely low | No impact | (0.00, 0.00, 0.25) |
| 2 | low | Minor impact | (0.00, 0.25, 0.50) |
| 3 | Relatively high | Large impact | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) |
| 4 | High | Dangerous | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) |
| 5 | Extremely high | Catastrophic | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) |
| Num. | Level of a safety risk | Definition | The membership functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Extremely low (EL) | The safety risk is acceptable | (0.00, 0.00, 0.25) |
| 2 | Low (L) | The safety risk is acceptable, and if the safety risk cost is acceptable, measures should be taken to reduce the risk. | (0.00, 0.25, 0.50) |
| 3 | Medium (M) | If technology is feasible, measures must be taken to reduce the risk. | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) |
| 4 | High (H) | Measures must be taken to reduce the risk. | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) |
| 5 | Extremely high (EH) | Measures must be taken to reduce and control the risk. | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) |
| Safety risk factors category | Safety risk factors | |
|---|---|---|
| Personnel-type | Worker-type | W2: Poor safety awareness; W3: Weak safety ability. |
| Manager-type | M2: Weaker safety management competency; M4: Insufficient safety communication; M5: Inadequate safety inspection. | |
| Equipment-type | EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment; EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor; EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment: EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment. | |
| Technique-type | TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme; TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme; TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme; TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme; TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | |
| Environment-type | Natural environment-type | NE1: Soft clay layer; NE4: High-pressure underground water; NE5: Subterranean boulders; |
| Bridge condition | BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel; BC2:Friction bridge pile; BC3:Large bridge pile diameter; BC5:Poor bridge safety condition; | |
| Management environment-type | ME2: Incomplete safety institution; ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility; ME5: Inadequate safety training & education. | |
| Safety risk factors | Occurrence probability level | Consequences severity level |
|---|---|---|
| W2: Poor safety awareness | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| W3: Weak safety ability | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| M2: Weaker safety management competency | 4(High) | 3(Large impact) |
| M4: Insufficient safety communication | 3(Relatively high) | 5(Catastrophic) |
| M5: Inadequate safety inspection | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor | 2(Low) | 4(Dangerous) |
| EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme | 3(Relatively high) | 5(Catastrophic) |
| TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | 3(Relatively high) | 5(Catastrophic) |
| NE1: Soft clay layer | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| NE4: High-pressure underground water | 4(High) | 4(Dangerous) |
| NE5: Subterranean boulders | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel; | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| BC2:Friction bridge pile;; | 4(High) | 4(Dangerous) |
| BC3:Large bridge pile diameter; | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| BC5:Poor bridge safety condition | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| ME2: Incomplete safety institution; | 3(Relatively high) | 5(Catastrophic) |
| ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility; | 3(Relatively high) | 4(Dangerous) |
| ME5: Inadequate safety training & education | 3(Relatively high) | 3(Large impact) |
| Safety risk factors | Fuzzy occurrence probability | Fuzzy consequences severity level | Fuzzy values of safety risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| W2: Poor safety awareness | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| W3: Weak safety ability | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| M2: Weaker safety management competency | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| M4: Insufficient safety communication | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) | (0.188, 0.500, 0.750) |
| M5: Inadequate safety inspection | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor | (0.00, 0.25, 0.50) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.00, 0.188, 0.500) |
| EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) | (0.188, 0.500, 0.750) |
| TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) | (0.188, 0.500, 0.750) |
| NE1: Soft clay layer | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| NE4: High-pressure underground water | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.250, 0.563, 1.000) |
| NE5: Subterranean boulders | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel; | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| BC2:Friction bridge pile;; | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.250, 0.563, 1.000) |
| BC3:Large bridge pile diameter; | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| BC5:Poor bridge safety condition | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| ME2: Incomplete safety institution; | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.75, 1.00, 1.00) | (0.188, 0.500, 0.750) |
| ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility; | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.50, 0.75, 1.00) | (0.125, 0.375, 0.750) |
| ME5: Inadequate safety training & education | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.25, 0.50, 0.75) | (0.063, 0.250, 0.563) |
| Safety risk factors | Belief structure | Risk level | ||||
| EL | L | M | H | EH | ||
| W2: Poor safety awareness | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| W3: Weak safety ability | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| M2: Weaker safety management competency | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| M4: Insufficient safety communication | 0.051 | 0.257 | 0.461 | 0.231 | 0.000 | M |
| M5: Inadequate safety inspection | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| EQ2: Malfunction of thrust cylinder equipment | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| EQ3: Malfunction of screw conveyor | 0.300 | 0.467 | 0.233 | 0.000 | 0.000 | L |
| EQ5: Malfunction of grouting equipment | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| EQ6: Malfunction of electrical equipment | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| TE1: Improper bridge pier reinforcement technic scheme | 0.051 | 0.257 | 0.461 | 0.231 | 0.000 | M |
| TE3: Improper construction monitoring technical scheme | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| TE4: Improper excavation technical scheme | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| TE5: Improper grouting and reinforcement technical scheme | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| TE6: Sealed water-proof technical scheme | 0.051 | 0.257 | 0.461 | 0.231 | 0.000 | M |
| NE1: Soft clay layer | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| NE4: High-pressure underground water | 0.000 | 0.184 | 0.366 | 0.300 | 0.15 | M |
| NE5: Subterranean boulders | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| BC1: Relatively close position of bridge piles and tunnel | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| BC2:Friction bridge pile | 0.000 | 0.184 | 0.366 | 0.300 | 0.150 | M |
| BC3:Large bridge pile diameter | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| BC5:Poor bridge safety condition | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| ME2: Incomplete safety institution | 0.051 | 0.257 | 0.461 | 0.231 | 0.000 | M |
| ME4: Unclear safety rights and responsibility | 0.114 | 0.341 | 0.363 | 0.183 | 0.000 | M |
| ME5: Inadequate safety training & education | 0.205 | 0.477 | 0.265 | 0.053 | 0.000 | L |
| Safety risk factors categories/overall worksite safety risk | Belief structure | Risk level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EL | L | M | H | EH | ||
| Worker-type safety risk factor | 0.080 | 0.560 | 0.330 | 0.030 | 0.000 | L |
| Manager-type safety risk factor | 0.007 | 0.300 | 0.615 | 0.078 | 0.000 | M |
| Personnel-type safety risk factor | 0.001 | 0.451 | 0.541 | 0.007 | 0.000 | M |
| Equipment-type safety risk factor | 0.023 | 0.740 | 0.233 | 0.004 | 0.000 | L |
| Technique-type safety risk factor | 0.001 | 0.480 | 0.516 | 0.003 | 0.000 | M |
| Natural environment-type safety risk factor | 0.012 | 0.464 | 0.500 | 0.024 | 0.000 | M |
| Bridge condition | 0.000 | 0.433 | 0.543 | 0.024 | 0.000 | M |
| Management environment-type safety risk factor | 0.000 | 0.440 | 0.532 | 0.028 | 0.000 | M |
| Environment-type safety risk factor | 0.000 | 0.394 | 0.604 | 0.002 | 0.000 | M |
| Overall worksite safety risk | 0.000 | 0.475 | 0.524 | 0.001 | 0.000 | M |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





