Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample collection and preparation
2.2. RNA extraction
2.3. RNA-Seq analysis
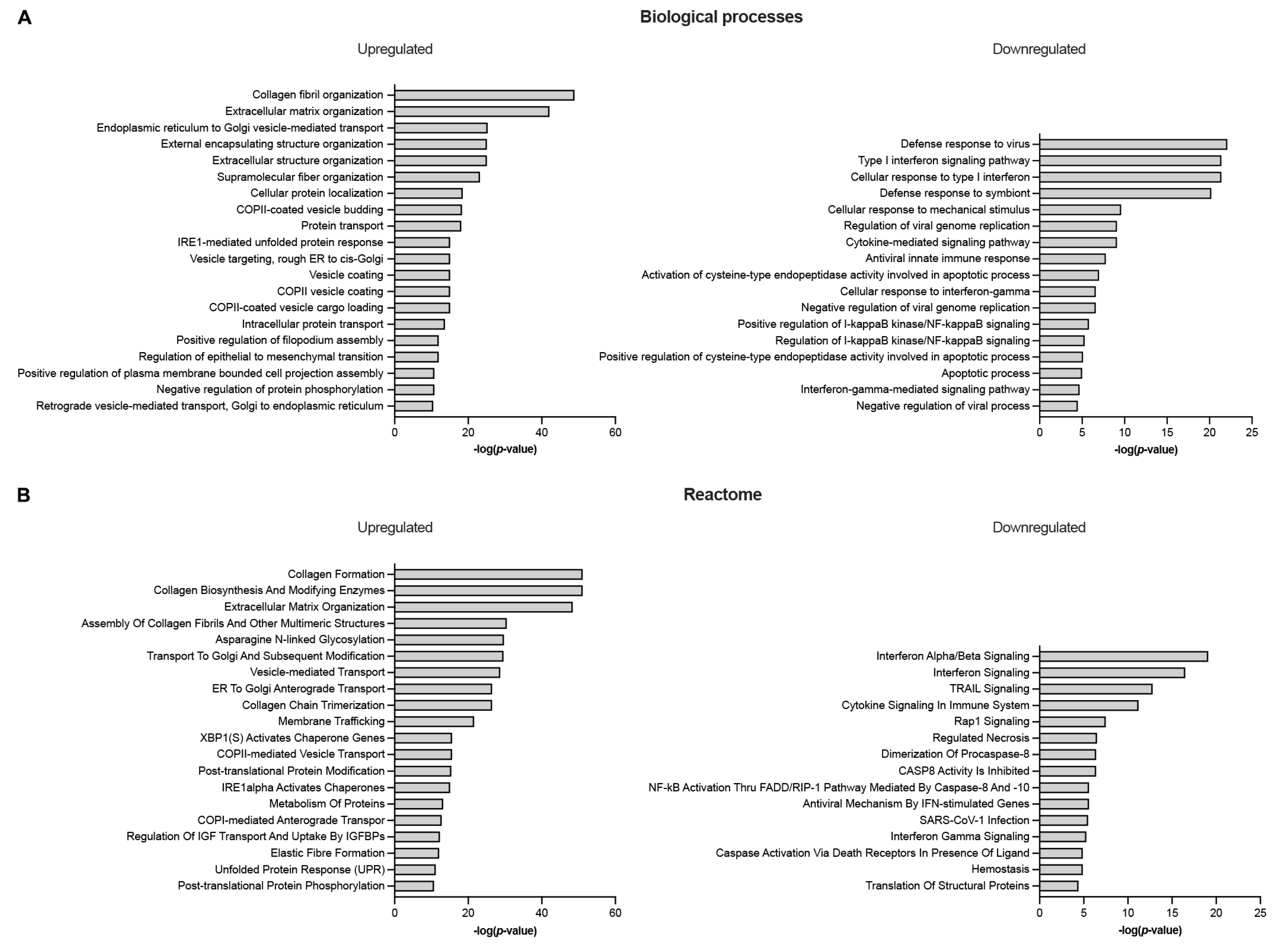
2.4. Gene ontology and pathway analysis
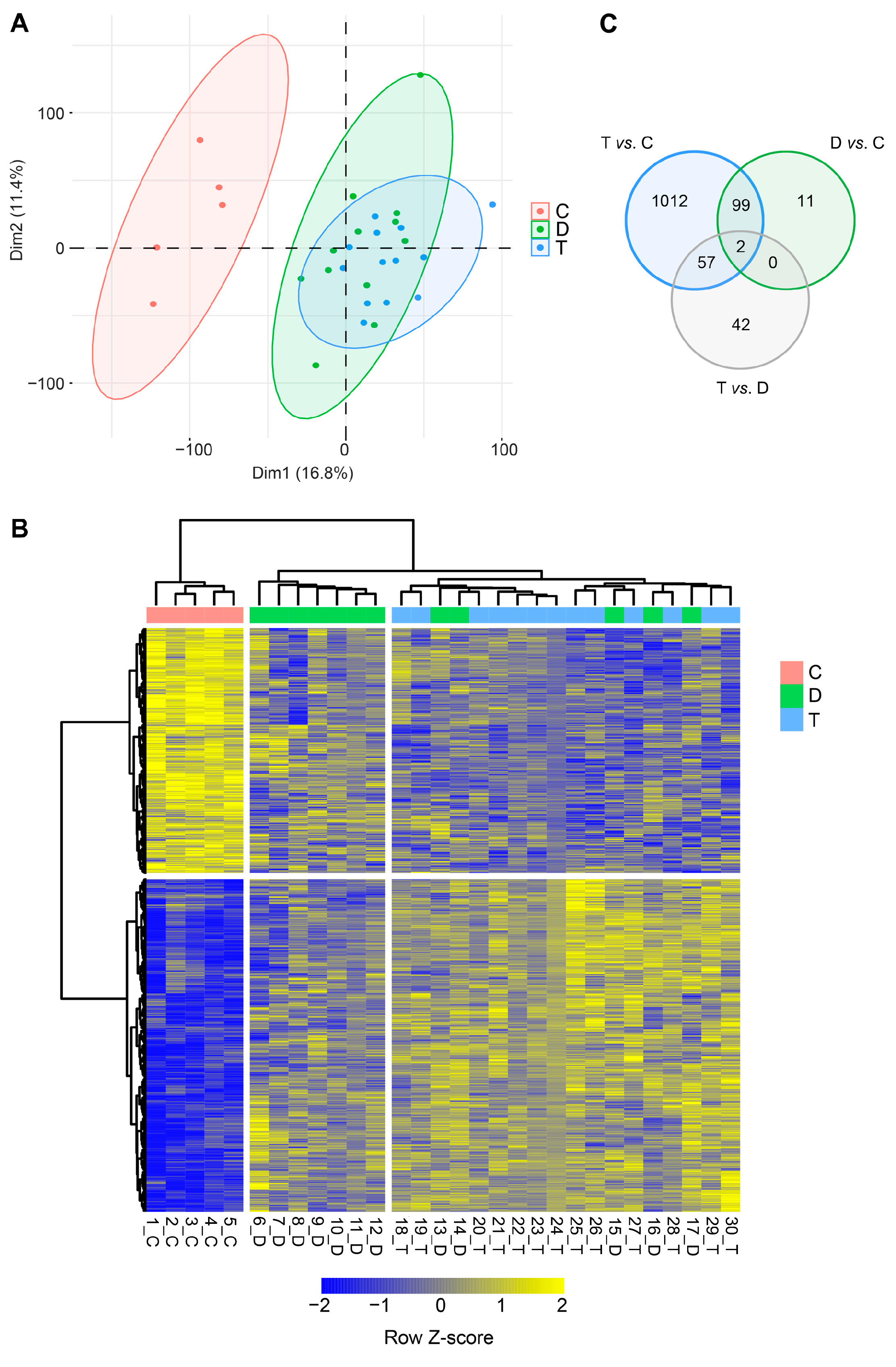
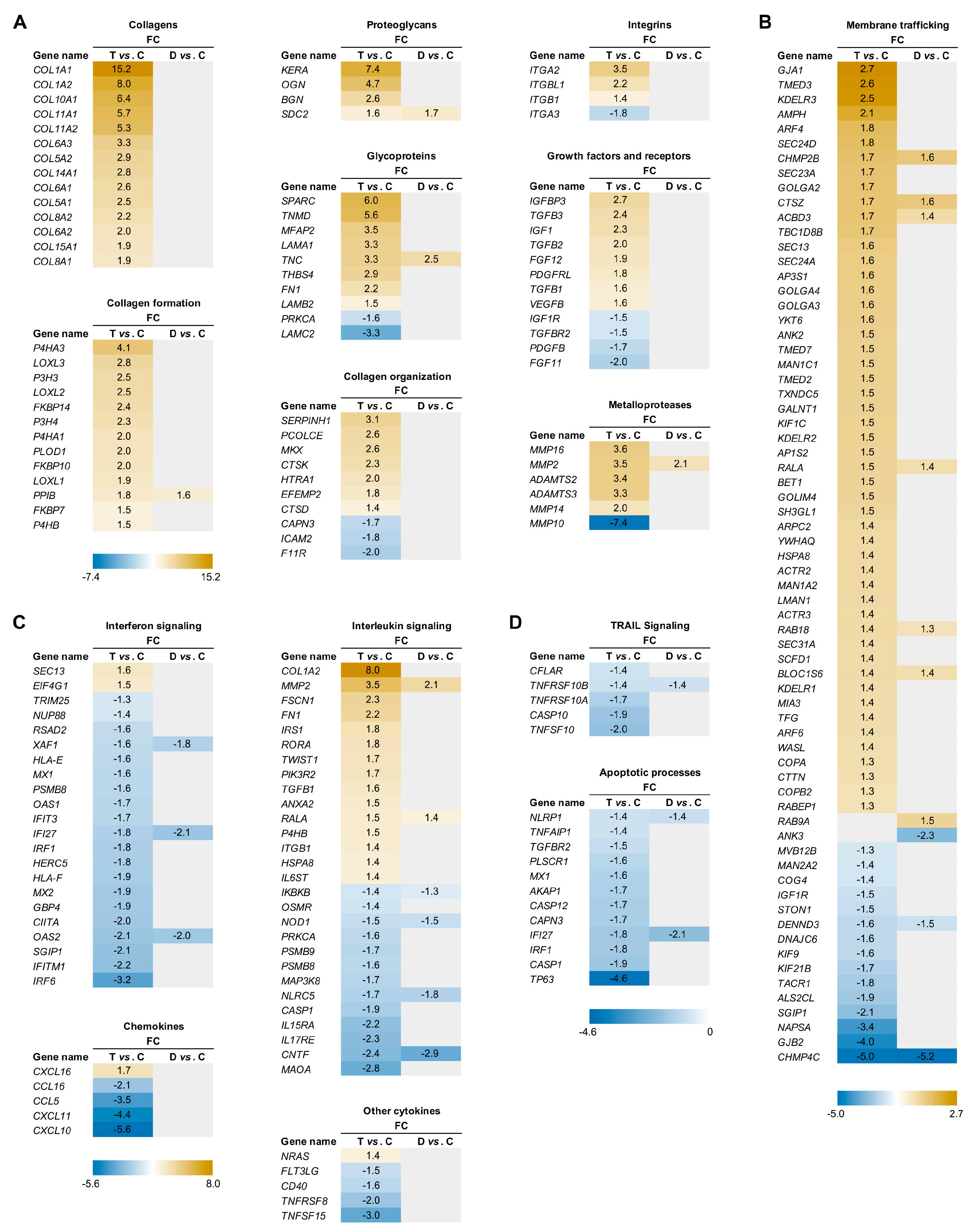
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kannus, P. Structure of the tendon connective tissue. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2000, 10, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.G. What happens when tendons bend and twist? Proteoglycans. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2004, 4, 202–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ezura, Y.; Chakravarti, S.; Oldberg, A.; Chervoneva, I.; Birk, D.E. Differential expression of lumican and fibromodulin regulate collagen fibrillogenesis in developing mouse tendons. J Cell Biol 2000, 151, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkman, A.A.; Buckley, M.R.; Mienaltowski, M.J.; Adams, S.M.; Thomas, S.J.; Satchell, L.; Kumar, A.; Pathmanathan, L.; Beason, D.P.; Iozzo, R.V.; et al. Decorin expression is important for age-related changes in tendon structure and mechanical properties. Matrix Biol 2013, 32, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boote, C.; Ma, Q.; Goh, K.L. Age-dependent mechanical properties of tail tendons in wild-type and mimecan gene-knockout mice - A preliminary study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2023, 139, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.; Arokiasamy, S.; Pataki, C.; Whiteford, J.R.; Couchman, J.R. Syndecan receptors: pericellular regulators in development and inflammatory disease. Open Biol 2021, 11, 200377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H. Mechanobiology of tendon. J Biomech 2006, 39, 1563–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax M, G.M. , Rosenbaum P, Leviton A, Paneth N, Dan B, Jacobsson B, Damiano D. Proposed definition and classification of cerebral palsy, April 2005. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 2005, 47, 571–571. [Google Scholar]
- Paneth, N.; Hong, T.; Korzeniewski, S. The Descriptive Epidemiology of Cerebral Palsy. Clinics in Perinatology 2006, 33, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeargin-Allsopp, M.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Kirby, R.S.; Durkin, M.S. Prevalence of cerebral palsy in 8-year-old children in three areas of the United States in 2002: a multisite collaboration. Pediatrics 2008, 121, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe. , S.o.C.P.i. Prevalence and characteristics of children with cerebral palsy in Europe. Dev Med Child Neurol 2002, 44, 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.; Schieve, L.; Christensen, D.; Goodman, A.; Yeargin-Allsopp, M. Birth Prevalence of Cerebral Palsy: A Population-Based Study. Pediatrics 2016, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Tallawy, H.N.; Farghaly, W.M.; Shehata, G.A.; Rageh, T.A.; Metwally, N.A.; Badry, R.; Sayed, M.A.; Abd El Hamed, M.; Abd-Elwarth, A.; Kandil, M.R. Cerebral palsy in Al-Quseir City, Egypt: prevalence, subtypes, and risk factors. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2014, 10, 1267–1272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.J.; Ma, H.I.; Lu, T.H. Estimating the prevalence of cerebral palsy in Taiwan: A comparison of different case definitions. Res Dev Disabil 2015, 36C, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.; Van Naarden Braun, K.; Doernberg, N.S.; Maenner, M.J.; Arneson, C.L.; Durkin, M.S.; Benedict, R.E.; Kirby, R.S.; Wingate, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.; et al. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, co-occurring autism spectrum disorders, and motor functioning - Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, USA, 2008. Dev Med Child Neurol 2014, 56, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, H.K.; Rosenbaum, P.; Paneth, N.; Dan, B.; Lin, J.P.; Damiano, D.L.; Becher, J.G.; Gaebler-Spira, D.; Colver, A.; Reddihough, D.S.; et al. Cerebral palsy. Nature reviews. Disease primers 2016, 2, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handsfield, G.G.; Williams, S.; Khuu, S.; Lichtwark, G.; Stott, N.S. Muscle architecture, growth, and biological Remodelling in cerebral palsy: a narrative review. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2022, 23, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliano, N.; Menon, A.; Martinelli, C.; Pettinari, L.; Panou, A.; Milzani, A.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Portinaro, N.M. Tendon structure and extracellular matrix components are affected by spasticity in cerebral palsy patients. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J 2013, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, N.; Pelillo, F.; Chiriva-Internati, M.; Picciolini, O.; Costa, F.; Schutt, R.C., Jr.; Gioia, M.; Portinaro, N. Expression profiling of genes involved in collagen turnover in tendons from cerebral palsy patients. Connect Tissue Res 2009, 50, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliano, N.; Pelillo, F.; Grizzi, F.; Picciolini, O.; Gioia, M.; Portinaro, N. Gene expression profile of extracellular matrix of tendons in cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol 2007, 49, 557–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping identifiers for the integration of genomic datasets with the R/Bioconductor package biomaRt. Nat Protoc 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentleman, R.C.; Carey, V.J.; Bates, D.M.; Bolstad, B.; Dettling, M.; Dudoit, S.; Ellis, B.; Gautier, L.; Ge, Y.; Gentry, J.; et al. Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 2004, 5, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R package for multivariate analysis. J Stat Softw 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricard-Blum, S. The collagen family. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011, 3, a004978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heino, J. The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins. Bioessays 2007, 29, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjaltema, R.A.; Bank, R.A. Molecular insights into prolyl and lysyl hydroxylation of fibrillar collagens in health and disease. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 2017, 52, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingson, A.J.; Pancheri, N.M.; Schiele, N.R. Regulators of collagen crosslinking in developing and adult tendons. Eur Cell Mater 2022, 43, 130–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, Z.M.; Bonilla, K.A.; Dekhne, M.S.; Sun, M.; Adams, T.H.; Adams, S.M.; Weiss, S.N.; Rodriguez, A.B.; Shetye, S.S.; Birk, D.E.; et al. Biglycan has a major role in maintenance of mature tendon mechanics. J Orthop Res 2022, 40, 2546–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasheva, E.S.; Koester, A.; Paulsen, A.Q.; Garrett, A.S.; Boyle, D.L.; Davidson, H.J.; Song, M.; Fox, N.; Conrad, G.W. Mimecan/osteoglycin-deficient mice have collagen fibril abnormalities. Mol Vis 2002, 8, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rees, S.G.; Waggett, A.D.; Kerr, B.C.; Probert, J.; Gealy, E.C.; Dent, C.M.; Caterson, B.; Hughes, C.E. Immunolocalisation and expression of keratocan in tendon. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009, 17, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wagner, A.; Gehwolf, R.; Yan, W.; Passini, F.S.; Thien, C.; Weissenbacher, N.; Lin, Z.; Lehner, C.; Teng, H.; et al. Load-induced regulation of tendon homeostasis by SPARC, a genetic predisposition factor for tendon and ligament injuries. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, V.P.; Naimov, S.I. A Prospectus of Tenomodulin. Folia Med (Plovdiv) 2016, 58, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Guo, Q.; Li, B. Tendon biomechanics and mechanobiology--a minireview of basic concepts and recent advancements. J Hand Ther 2012, 25, 133–140; quiz 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.S.; Jones, P.L. The tenascin family of ECM glycoproteins: structure, function, and regulation during embryonic development and tissue remodeling. Dev Dyn 2000, 218, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halper, J.; Kjaer, M. Basic components of connective tissues and extracellular matrix: elastin, fibrillin, fibulins, fibrinogen, fibronectin, laminin, tenascins and thrombospondins. Adv Exp Med Biol 2014, 802, 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Docheva, D.; Popov, C.; Alberton, P.; Aszodi, A. Integrin signaling in skeletal development and function. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 2014, 102, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavizadeh, R.; Hojabrpour, P.; Eltit, F.; McDonald, P.C.; Dedhar, S.; McCormack, R.G.; Duronio, V.; Jafarnejad, S.M.; Scott, A. beta1 integrin, ILK and mTOR regulate collagen synthesis in mechanically loaded tendon cells. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 12644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, E.; Ye, S.; Wang, W.; Bader, D.L.; Knight, M.M.; Lee, D.A. Gap junction permeability between tenocytes within tendon fascicles is suppressed by tensile loading. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 2012, 11, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disser, N.P.; Sugg, K.B.; Talarek, J.R.; Sarver, D.C.; Rourke, B.J.; Mendias, C.L. Insulin-like growth factor 1 signaling in tenocytes is required for adult tendon growth. FASEB J 2019, 33, 12680–12695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Mao, Z.; Wei, X.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, C. The roles of TGF-beta1 gene transfer on collagen formation during Achilles tendon healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009, 383, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Yu, T.; An, S.; Deng, R.; Tan, X.; Crane, J.; Zhang, W.; Pan, D.; Wan, M.; et al. Inhibition of Integrin alphavbeta6 Activation of TGF-beta Attenuates Tendinopathy. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2022, 9, e2104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, S.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, D. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Tendon Healing. Front Physiol 2021, 12, 766080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Watson, S.S.; Lan, Y.; Keene, D.R.; Ovitt, C.E.; Liu, H.; Schweitzer, R.; Jiang, R. The atypical homeodomain transcription factor Mohawk controls tendon morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 4797–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Toriuchi, N.; Yoshitaka, T.; Ueno-Kudoh, H.; Sato, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Nishida, K.; Akimoto, T.; Takahashi, M.; Miyaki, S.; et al. The Mohawk homeobox gene is a critical regulator of tendon differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 10538–10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, T.; Mori, M.; Ito, Y.; Matsushima, T.; Nakamichi, R.; Suzuki, H.; Ichinose, S.; Saito, M.; Marumo, K.; Asahara, H. Gtf2ird1-Dependent Mohawk Expression Regulates Mechanosensing Properties of the Tendon. Mol Cell Biol 2016, 36, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, G. Tendinopathy--from basic science to treatment. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2008, 4, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbardella, D.; Tundo, G.R.; Fasciglione, G.F.; Gioia, M.; Bisicchia, S.; Gasbarra, E.; Ippolito, E.; Tarantino, U.; Coletta, M.; Marini, S. Role of metalloproteinases in tendon pathophysiology. Mini Rev Med Chem 2014, 14, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, W.A.; Murphy, G.; Sandy, J.D.; Gavrilovic, J.; Cawston, T.E.; Reynolds, J.J. Purification and characterization of a rabbit bone metalloproteinase that degrades proteoglycan and other connective-tissue components. Biochem J 1983, 209, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, R.; Murphy, G.; Breathnach, R. Human and rat malignant-tumor-associated mRNAs encode stromelysin-like metalloproteinases. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 5195–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, R.J.; Hirohata, S.; Engle, J.M.; Colige, A.; Cohn, D.H.; Eyre, D.R.; Apte, S.S. Procollagen II amino propeptide processing by ADAMTS-3. Insights on dermatosparaxis. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 31502–31509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colige, A.; Ruggiero, F.; Vandenberghe, I.; Dubail, J.; Kesteloot, F.; Van Beeumen, J.; Beschin, A.; Brys, L.; Lapiere, C.M.; Nusgens, B. Domains and maturation processes that regulate the activity of ADAMTS-2, a metalloproteinase cleaving the aminopropeptide of fibrillar procollagens types I-III and V. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 34397–34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadon-Le Goff, S.; Kronenberg, D.; Bourhis, J.M.; Bijakowski, C.; Raynal, N.; Ruggiero, F.; Farndale, R.W.; Stocker, W.; Hulmes, D.J.; Moali, C. Procollagen C-proteinase enhancer stimulates procollagen processing by binding to the C-propeptide region only. J Biol Chem 2011, 286, 38932–38938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubmacher, D.; Wang, L.W.; Mecham, R.P.; Reinhardt, D.P.; Apte, S.S. Adamtsl2 deletion results in bronchial fibrillin microfibril accumulation and bronchial epithelial dysplasia--a novel mouse model providing insights into geleophysic dysplasia. Dis Model Mech 2015, 8, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.C.; Corps, A.N.; Pennington, C.J.; Clark, I.M.; Edwards, D.R.; Bradley, M.M.; Hazleman, B.L.; Riley, G.P. Expression profiling of metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in normal and degenerate human achilles tendon. Arthritis Rheum 2006, 54, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinsky, S.A.; Rodeo, S.A.; Li, J.; Gulotta, L.V.; Archambault, J.M.; Seeherman, H.J. Regulation of gene expression in human tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2011, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, D.; Harrall, R.; Curry, V.; Holloway, G.; Hackney, R.; Hazleman, B.; Riley, G. Multiple changes in gene expression in chronic human Achilles tendinopathy. Matrix Biol 2001, 20, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, B.J.; Franklin, S.L.; Carr, A.J. A systematic review of the histological and molecular changes in rotator cuff disease. Bone Joint Res 2012, 1, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvind, V.; Huang, A.H. Reparative and Maladaptive Inflammation in Tendon Healing. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2021, 9, 719047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, I.; Schnabel, L.V.; Berglund, A.K. Defining the Profile: Characterizing Cytokines in Tendon Injury to Improve Clinical Therapy. J Immunol Regen Med 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, G.; Kwan, C.K.; Fu, S.C.; Ling, S.K.; Chan, K.M.; Yung, P.S.; Rolf, C. A systematic review of inflammatory cells and markers in human tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2020, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; El Khatib, M.; Prencipe, G.; Citeroni, M.R.; Faydaver, M.; Mauro, A.; Berardinelli, P.; Cervero-Varona, A.; Haidar-Montes, A.A.; Turriani, M.; et al. Tendon Immune Regeneration: Insights on the Synergetic Role of Stem and Immune Cells during Tendon Regeneration. Cells 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langberg, H.; Rosendal, L.; Kjaer, M. Training-induced changes in peritendinous type I collagen turnover determined by microdialysis in humans. J Physiol 2001, 534, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, A.; Karamanidis, K.; Albracht, K. Adaptational responses of the human Achilles tendon by modulation of the applied cyclic strain magnitude. J Exp Biol 2007, 210, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couppe, C.; Kongsgaard, M.; Aagaard, P.; Hansen, P.; Bojsen-Moller, J.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Habitual loading results in tendon hypertrophy and increased stiffness of the human patellar tendon. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2008, 105, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arampatzis, A.; Peper, A.; Bierbaum, S.; Albracht, K. Plasticity of human Achilles tendon mechanical and morphological properties in response to cyclic strain. J Biomech 2010, 43, 7–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seynnes, O.R.; Erskine, R.M.; Maganaris, C.N.; Longo, S.; Simoneau, E.M.; Grosset, J.F.; Narici, M.V. Training-induced changes in structural and mechanical properties of the patellar tendon are related to muscle hypertrophy but not to strength gains. J Appl Physiol (1985) 2009, 107, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Tettke, M.; Kraft, M.; Arampatzis, A. Human Achilles tendon plasticity in response to cyclic strain: effect of rate and duration. J Exp Biol 2014, 217, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Arampatzis, A. Human tendon adaptation in response to mechanical loading: a systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise intervention studies on healthy adults. Sports Med Open 2015, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosager, S.; Aagaard, P.; Dyhre-Poulsen, P.; Neergaard, K.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Load-displacement properties of the human triceps surae aponeurosis and tendon in runners and non-runners. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2002, 12, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sponbeck, J.K.; Perkins, C.L.; Berg, M.J.; Rigby, J.H. Achilles Tendon Cross Sectional Area Changes Over a Division I NCAA Cross Country Season. Int J Exerc Sci 2017, 10, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Reitelseder, S.; Pedersen, T.G.; Holm, L.; Aagaard, P.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Region specific patellar tendon hypertrophy in humans following resistance training. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2007, 191, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient | Gender | Age | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 15.8 | C |
| 2 | M | 26.4 | C |
| 3 | M | 14.6 | C |
| 4 | M | 16.1 | C |
| 5 | M | 16.8 | C |
| 6 | M | 21.1 | D |
| 7 | M | 15.5 | D |
| 8 | M | 17.1 | D |
| 9 | M | 15.0 | D |
| 10 | F | 5.6 | D |
| 11 | M | 16.5 | D |
| 12 | M | 10.5 | D |
| 13 | M | 11.0 | D |
| 14 | M | 15.7 | D |
| 15 | F | 11.4 | D |
| 16 | M | 17.1 | D |
| 17 | M | 10.1 | D |
| 18 | M | 11.5 | T |
| 19 | F | 11.0 | T |
| 20 | F | 14.5 | T |
| 21 | M | 16.2 | T |
| 22 | M | 4.9 | T |
| 23 | F | 14.0 | T |
| 24 | M | 14.9 | T |
| 25 | F | 12.8 | T |
| 26 | F | 11.6 | T |
| 27 | M | 13.3 | T |
| 28 | M | 9.2 | T |
| 29 | M | 16.2 | T |
| 30 | M | 13.0 | T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





