Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Collection of Blood
2.3. Detection of serum indicators
2.4. Adipose Tissue Collection and Processing
2.5. Immunohistochemistry technology
2.6. Isolation of bovine preadipocytes
2.7. Cell culture and processing
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. Data analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and blood variable of ketosis dairy cows
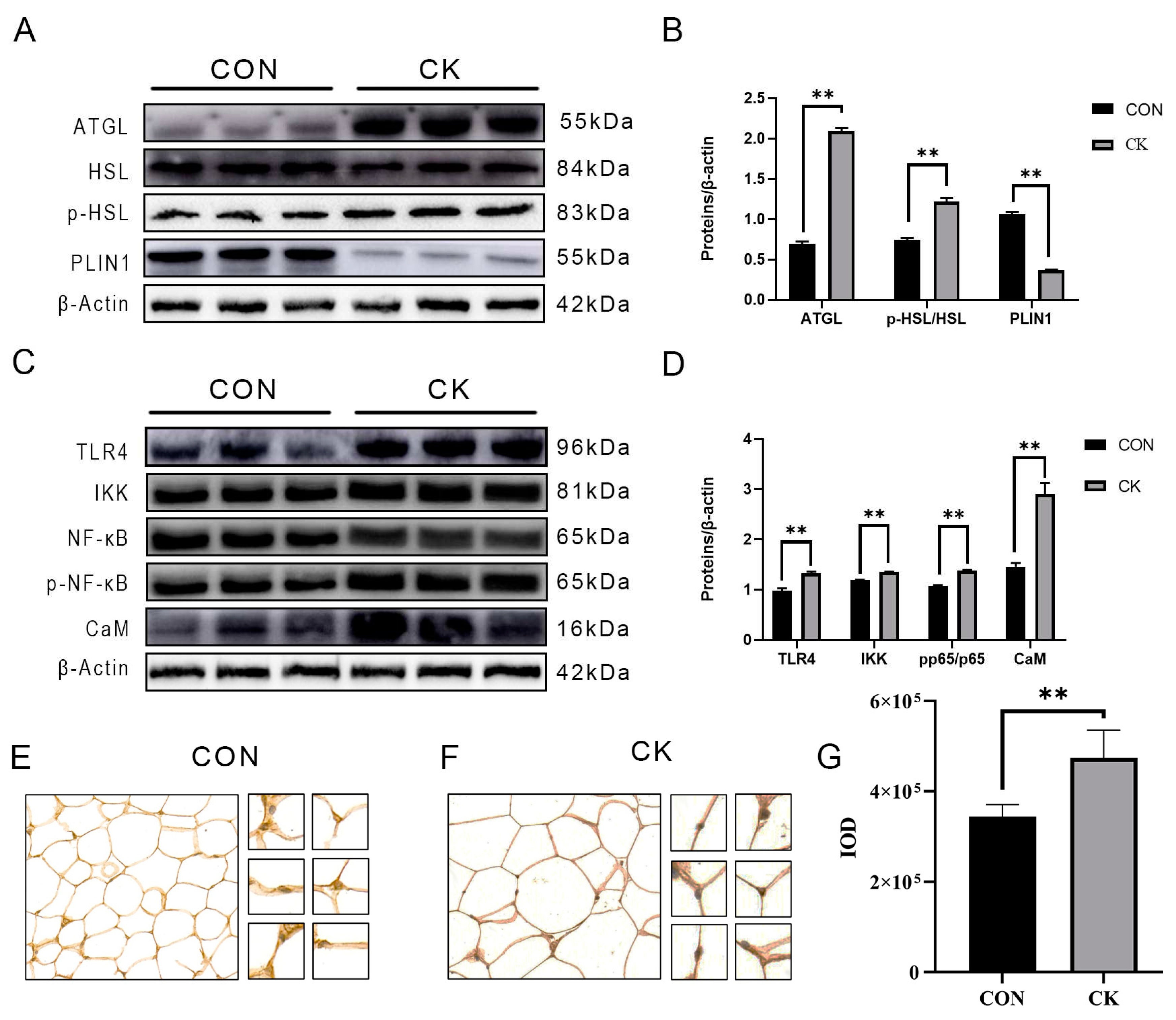
3.2. The abundance of CaM, lipolysis, and inflammation-related proteins in dairy cow adipose tissue
3.3. Results of CaM immunohistochemistry in adipose tissue of dairy cows
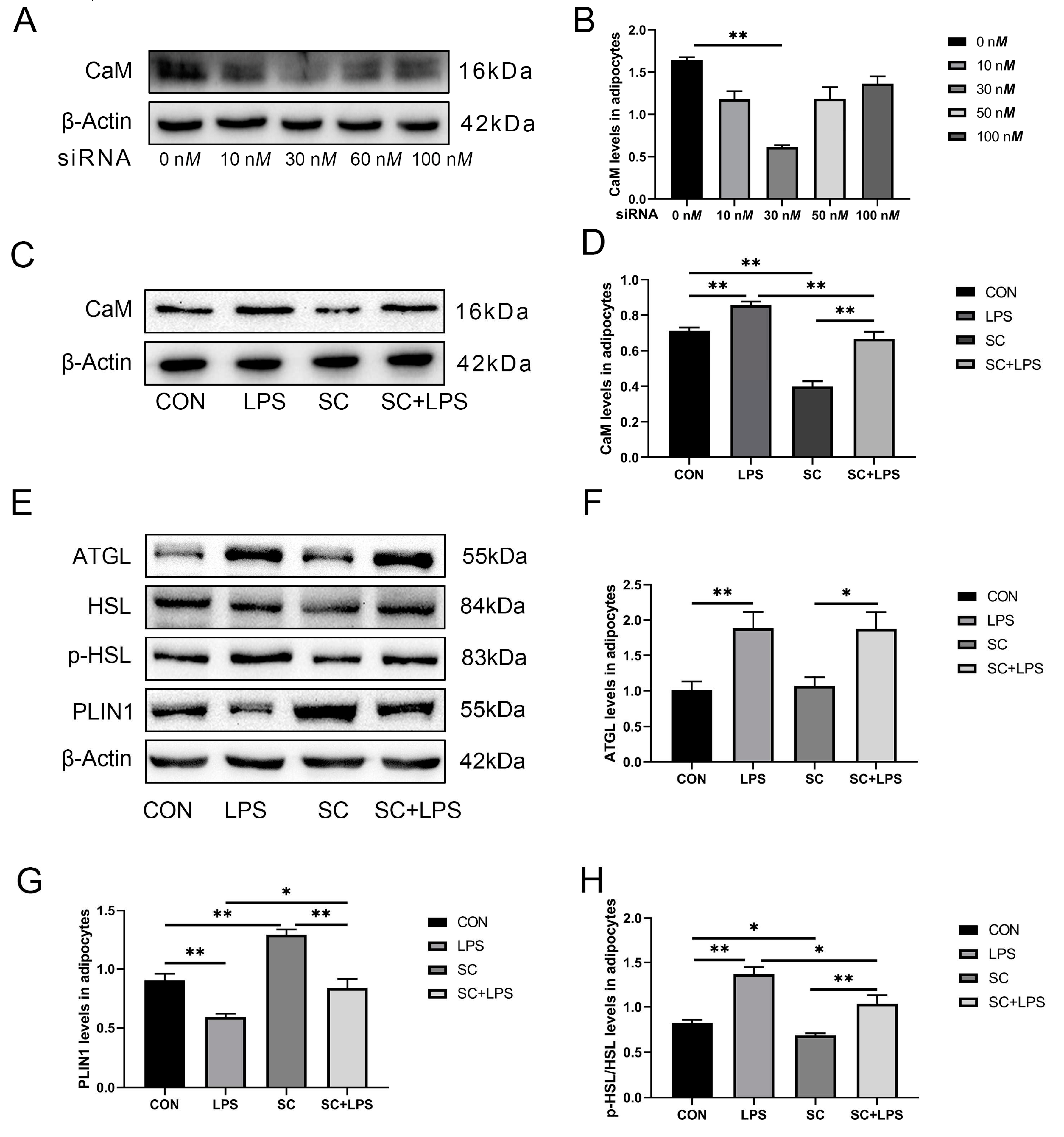
3.4. Effect of LPS stimulation and CaM silencing on the abundance of lipolysis-related proteins
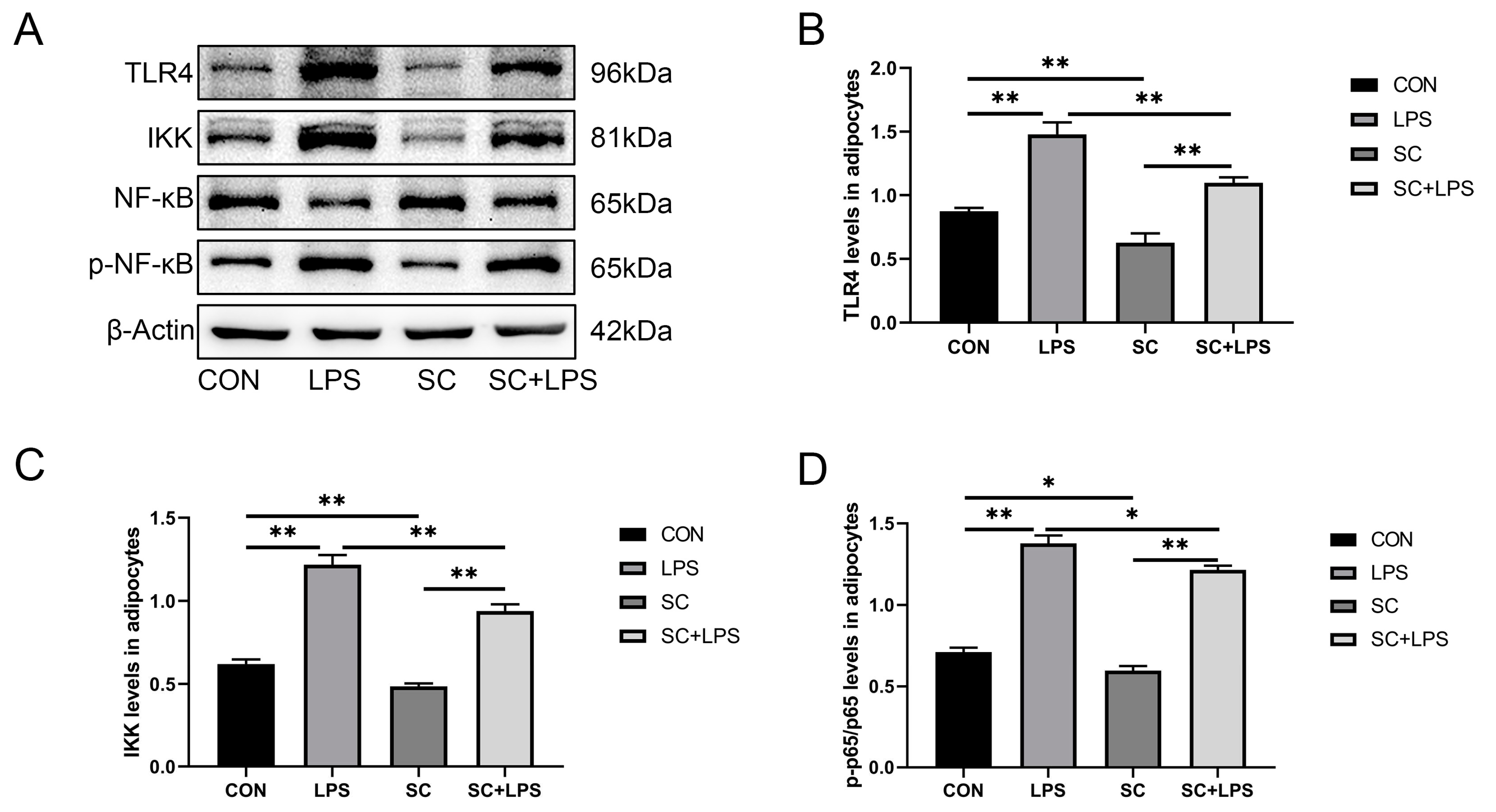
3.5. Effect of LPS stimulation and CaM silencing on the abundance of inflammation-related proteins
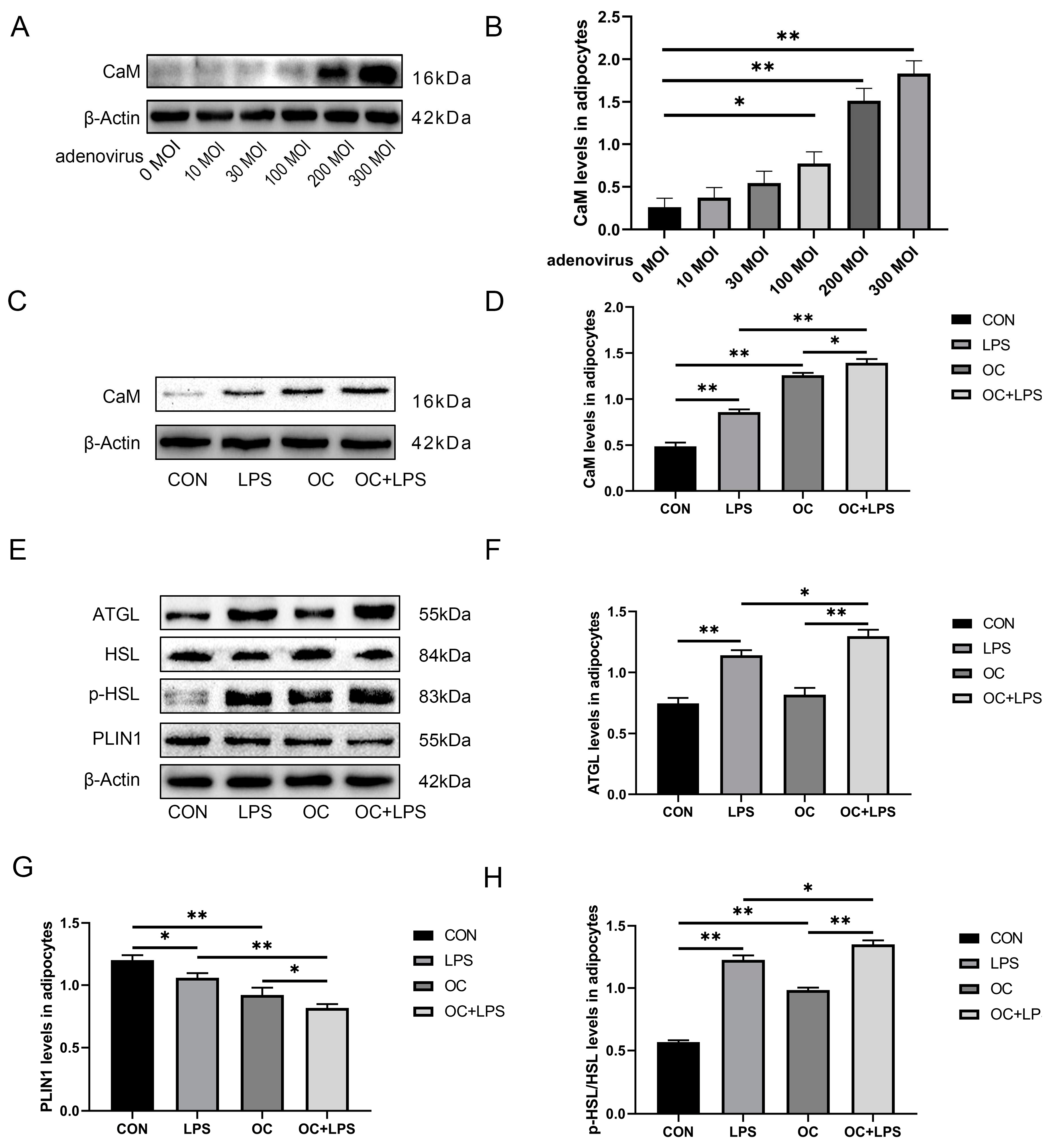
3.6. Effect of LPS stimulation and CaM overexpression on the abundance of lipolysis-related proteins
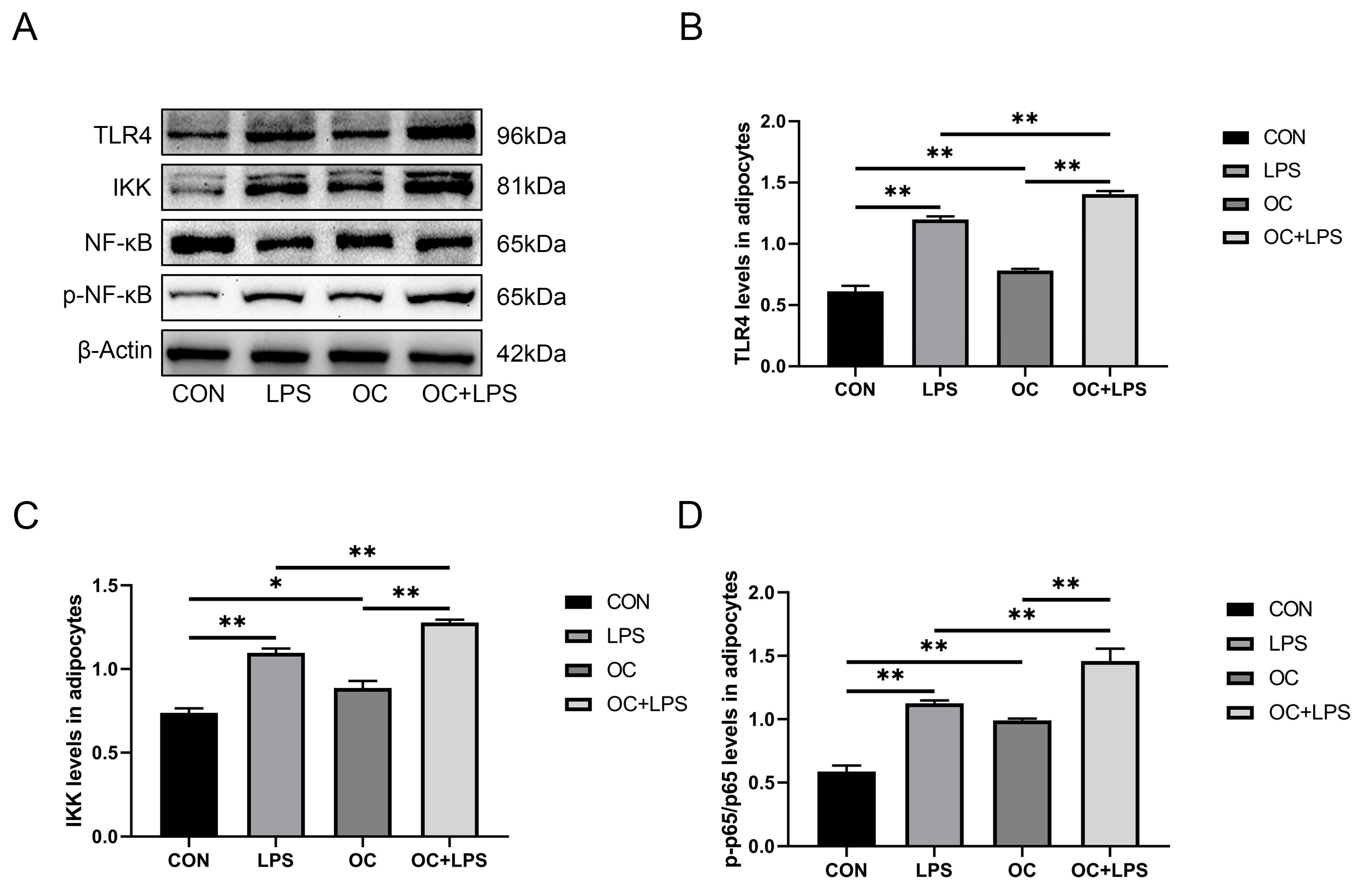
3.7. Effect of LPS stimulation and CaM overexpression on the abundance of inflammation-related proteins
4. Discussion
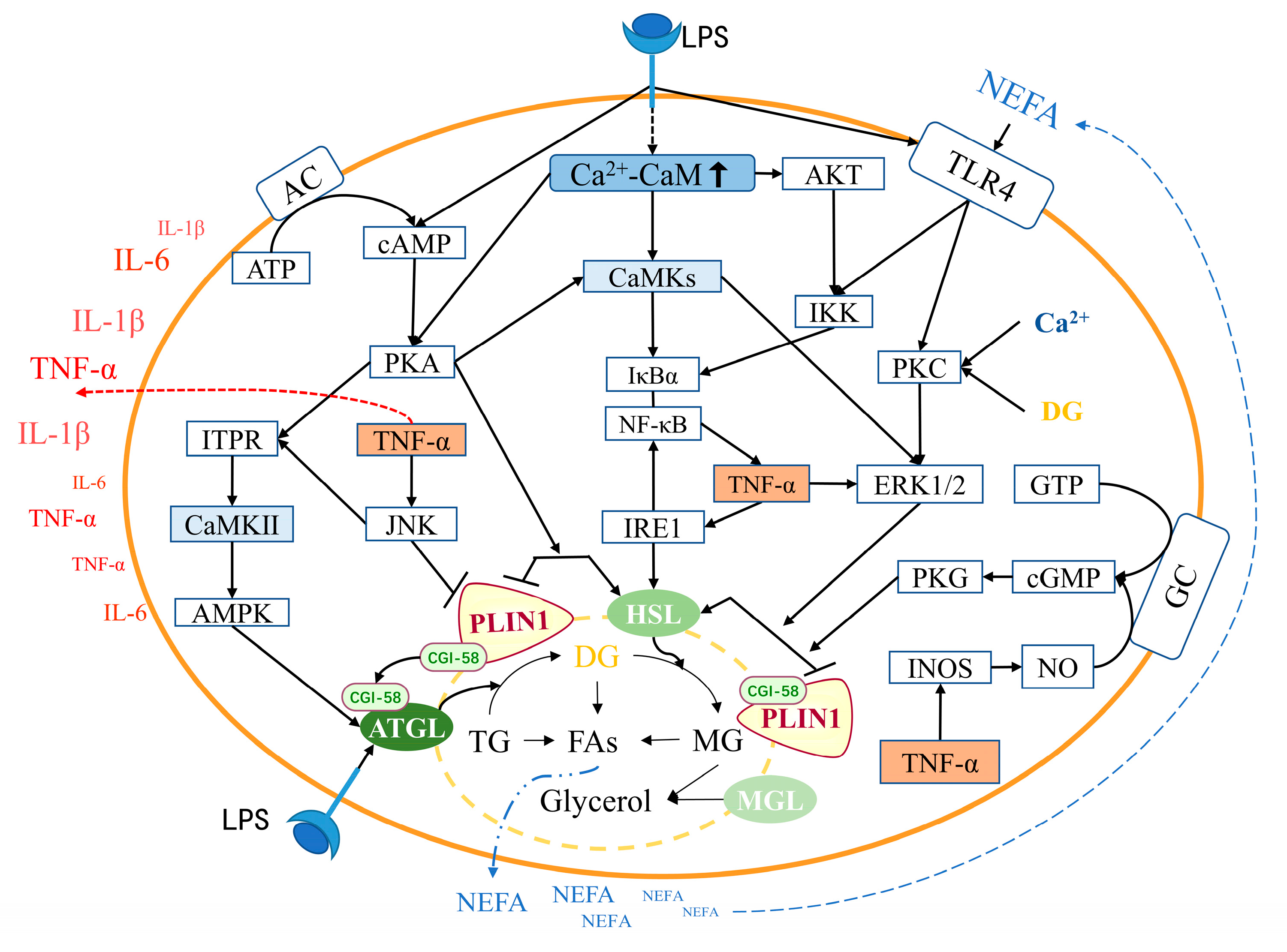
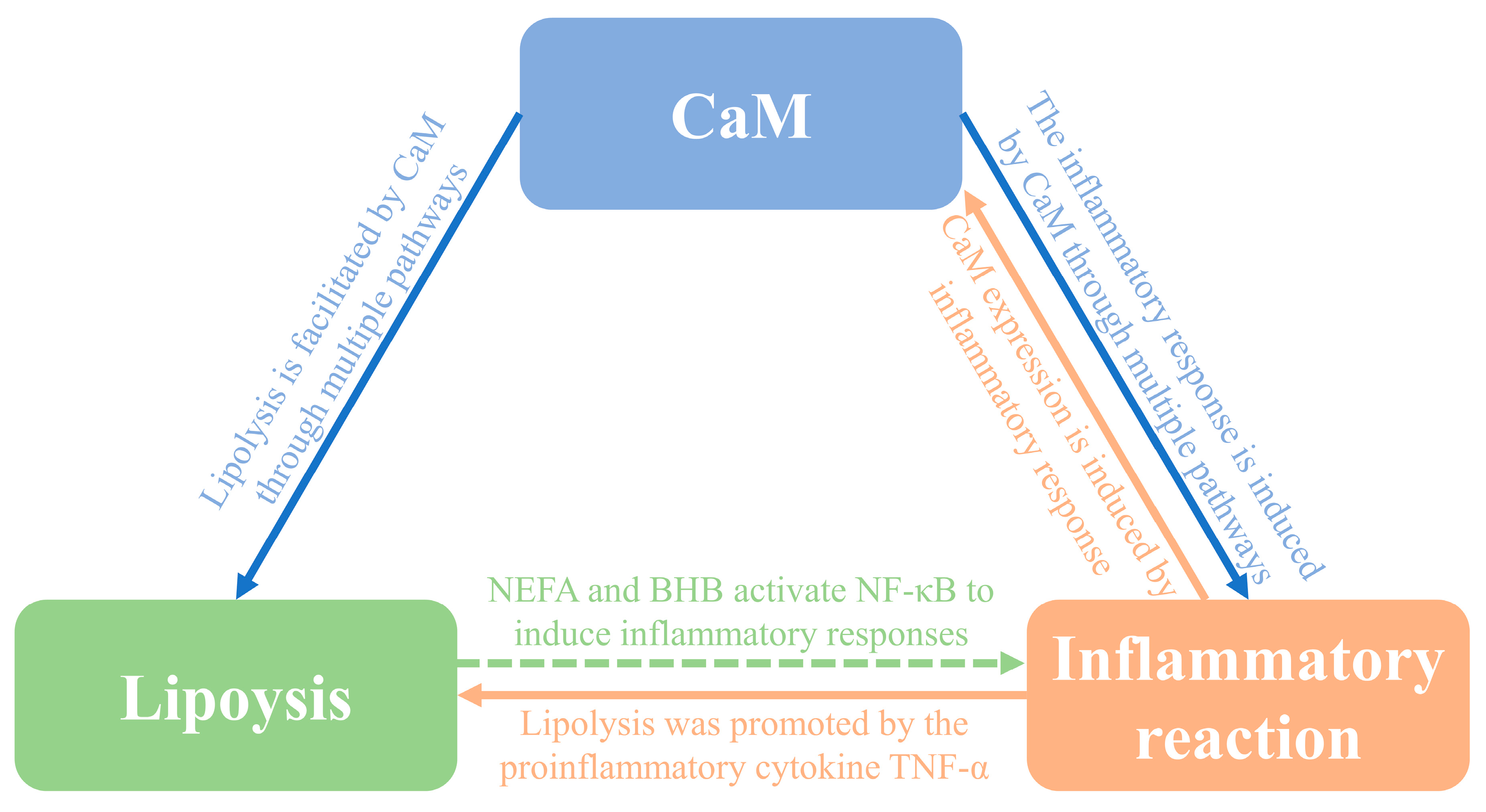
4.1. Relationship between CaM and lipolysis in adipocytes
4.2. Relationship between CaM and inflammation in adipocytes
4.3. Relationship between inflammation and lipolysis in adipocytes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loor, J.J.; Everts, R.E.; Bionaz, M.; Dann, H.M.; Morin, D.E.; Oliveira, R.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Drackley, J.K.; Lewin, H.A. Nutrition-induced ketosis alters metabolic and signaling gene networks in liver of periparturient dairy cows. Physiol Genomics 2007, 32, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweiger, M.; Schreiber, R.; Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Fledelius, C.; Jacobsen, P.; Tornqvist, H.; Zechner, R.; Zimmermann, R. Adipose Triglyceride Lipase and Hormone-sensitive Lipase Are the Major Enzymes in Adipose Tissue Triacylglycerol Catabolism. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2006, 281, 40236–40241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.; Cornaciu, I.; Lass, A.; Schweiger, M.; Poeschl, M.; Eder, C.; Kumari, M.; Schoiswohl, G.; Wolinski, H.; Kohlwein, S.D.; et al. The N-terminal region of comparative gene identification-58 (CGI-58) is important for lipid droplet binding and activation of adipose triglyceride lipase. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 12289–12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasaemle, D.L.; Rubin, B.; Harten, I.A.; Gruia-Gray, J.; Kimmel, A.R.; Londos, C. Perilipin A increases triacylglycerol storage by decreasing the rate of triacylglycerol hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 2000, 275, 38486–38493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, G.; Trevisi, E. Use of the liver activity index and other metabolic variables in the assessment of metabolic health in dairy herds. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 2013, 29, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, F.C.; LeBlanc, S.J.; Murphy, M.R.; Drackley, J.K. Prepartum nutritional strategy affects reproductive performance in dairy cows. J Dairy Sci 2013, 96, 5859–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchtold, M.W.; Antonio, V. The many faces of calmodulin in cell proliferation, programmed cell death, autophagy, and cancer. BBA - Molecular Cell Research 2014, 1843, 398–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Choubey, M.; Patel, S.; Singer, H.; Ozcan, L. Adipocyte CAMK2 deficiency improves obesity-associated glucose intolerance. Molecular metabolism 2021, 53, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Shen, W.J.; Yeo, H.L.; Wang, S.M. Signaling pathway of magnolol-stimulated lipolysis in sterol ester-loaded 3T3-L1 preadipocyes. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 2010, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Zal, T.; Ch'En, I.L.; Gascoigne, N.R.J.; Hedrick, S.M. A Pivotal Role for the Multifunctional Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in T Cells: From Activation to Unresponsiveness. The Journal of Immunology 2005, 174, 5583–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.; Edin, S.; Antonsson, A.; Grundstrm, T. Calmodulin-dependent kinase II mediates T cell receptor/CD3- and phorbol ester-induced activation of IkappaB kinase. The Journal of biological chemistry 2001, 276, 36008–36013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.; Schaer, D.J.; Bachli, E.B.; Kurrer, M.O.; Schoedon, G. Wnt5A/CaMKII Signaling Contributes to the Inflammatory Response of Macrophages and Is a Target for the Antiinflammatory Action of Activated Protein C and Interleukin-10. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2008, 28, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mével, E.; Shutter, J.A.; Ding, X.; Mattingly, B.T.; Williams, J.N.; Li, Y.; Huls, A.; Kambrath, A.V.; Trippel, S.B.; Wagner, D.; et al. Systemic inhibition or global deletion of CaMKK2 protects against post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2022, 30, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, S.; Bai, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, C.; He, H.; He, L. Imperatorin ameliorates mast cell-mediated allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting MRGPRX2 and CamKII/ERK signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 2021, 184, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Ma, L.; Loor, J.J.; Li, X. Adipose tissue proteomic analysis in ketotic or healthy Holstein cows in early lactation1. Journal of Animal Science 2019, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.D.; Galligan, D.T.; Thomsen, N. Principal Descriptors of Body Condition Score in Holstein Cows. Journal of Dairy Science 1994, 77, 2695–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, T.; Papen, J.; Bemers, R.; Vertenten, G.; Berge, A.C.B. Risk factors for subclinical and clinical ketosis and association with production parameters in dairy cows in the Netherlands. Journal of Dairy Science 2015, 98, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, C.; Fu, S.; Xia, C.; Bai, Y. Early warning for inactive ovaries based on liver function index, serum MDA, IL-6, FGF21 and ANGPTL8 in dairy cows. Italian Journal of Animal Science 2022, 21, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Fan, Y.; Loor, J.J.; Liang, Y.; Sun, X.; Jia, H.; Zhao, C.; Xu, C. Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase ameliorates bovine adipocyte oxidative stress by inducing antioxidant responses and autophagy. Journal of Dairy Science 2021, 104, 4516–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Johnson, J.A.; Chang, D.W.; Zhang, Q. Decellularized musculofascial extracellular matrix for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Xu, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Jia, H.; Li, X.; Li, X. Perilipin 1 Mediates Lipid Metabolism Homeostasis and Inhibits Inflammatory Cytokine Synthesis in Bovine Adipocytes. Frontiers in immunology 2018, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Jia, H.; Ma, L.; Liu, G.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X. All-trans retinoic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in bovine adipocytes via TGFβ1/Smad3 signaling pathway. BMC Veterinary Research 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, A. The role of calmodulin in hormone-stimulated lipolysis. Metabolism 1985, 34, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roepstorff, C.; Vistisen, B.; Donsmark, M.; Nielsen, J.N.; Galbo, H.; Green, K.A.; Hardie, D.G.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.; Richter, E.A.; Kiens, B. Regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase activity and Ser563 and Ser565 phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle during exercise. J Physiol 2004, 560, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Tang, T.; Abbott, M.; Viscarra, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Sul, H.S. AMPK Phosphorylates Desnutrin/ATGL and Hormone-Sensitive Lipase To Regulate Lipolysis and Fatty Acid Oxidation within Adipose Tissue. Mol Cell Biol 2016, 36, 1961–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Zheng, X.L.; Liu, B.T.; Yang, G.S. Regulation of ATGL expression mediated by leptin in vitro in porcine adipocyte lipolysis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 2010, 333, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T. Crucial Role of CGI-58/α/β Hydrolase Domain-Containing Protein 5 in Lipid Metabolism. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2010, 33, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, X.; Lombès, M.; Rha, G.B.; Chi, Y.I.; Guerin, T.M.; Smart, E.J.; Liu, J. The G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 Regulates Adipose Lipolysis through Association with Adipose Triglyceride Lipase. Cell Metabolism 2010, 11, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rydén, M.; Arvidsson, E.; Blomqvist, L.; Perbeck, L.; Dicker, A.; Arner, P. Targets for TNF-alpha-induced lipolysis in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004, 318, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.C.; Au, L.C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Ho, L.T.; Juan, C.C. Short-term regulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is mediated through the inducible nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide-dependent pathway. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4892–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervishi, E.; Plastow, G.; Hoff, B.; Colazo, M. Common and specific mineral and metabolic features in dairy cows with clinical metritis, hypocalcaemia or ketosis. Res Vet Sci 2021, 135, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.K.; Jeong, J.K.; Choi, I.S.; Kang, H.G.; Hur, T.Y.; Jung, Y.H.; Kim, I.H. Relationships among ketosis, serum metabolites, body condition, and reproductive outcomes in dairy cows. Theriogenology 2015, 84, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, A.L.; Burhans, W.S.; Mann, S.; Nydam, D.V.; Wall, S.K.; Schoenberg, K.M.; Perfield, K.L.; Overton, T.R. Transition cow nutrition and management strategies of dairy herds in the northeastern United States: Part II-Associations of metabolic- and inflammation-related analytes with health, milk yield, and reproduction. J Dairy Sci 2022, 105, 5349–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirivi, M.; Rendon, C.; Myers, M.; Prom, C.; Roy, S.; Sen, A.; Lock, A.; Contreras, G. Lipopolysaccharide induces lipolysis and insulin resistance in adipose tissue from dairy cows. Journal of dairy science 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, L.; He, J.; Jiang, H.; Xu, C.; Pu, S.; Xu, G. Bacterial Endotoxin Stimulates Adipose Lipolysis via Toll-Like Receptor 4 and Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase Pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2009, 284, 5915–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yao, M.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, X. CaMKII promotes TLR-triggered proinflammatory cytokine and type I interferon production by directly binding and activating TAK1 and IRF3 in macrophages. Blood 2008, 112, 4961–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.V.; Swaminathan, P.D.; Luczak, E.D.; Kutschke, W.; Weiss, R.M.; Anderson, M.E. MyD88 mediated inflammatory signaling leads to CaMKII oxidation, cardiac hypertrophy and death after myocardial infarction. Journal of Molecular & Cellular Cardiology 2012, 52, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Clozapine reduces Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses through inhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent Akt activation in microglia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2018, 81, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusciano, M.R.; Sommariva, E.; Douin-Echinard, V.; Ciccarelli, M.; Poggio, P.; Maione, A.S. CaMKII Activity in the Inflammatory Response of Cardiac Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisouard, J.; Bouillet, E.; Timper, K.; Radimerski, T.; Dembinski, K.; Frey, D.M.; Peterli, R.; Zulewski, H.; Keller, U.; Müller, B.; et al. Both inflammatory and classical lipolytic pathways are involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced lipolysis in human adipocytes. Innate Immun 2012, 18, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, K.P.; Chen, Y.; Barra, N.G.; Heal, M.; Schertzer, J.D. Inflammation promotes adipocyte lipolysis via IRE1 kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2021, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasic, S.; Tian, B.; Green, A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates lipolysis in adipocytes by decreasing Gi protein concentrations. J Biol Chem 1999, 274, 6770–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Ji, Y.; Lan, T.; Yan, W.; Xu, Y.; Gong, G. Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Limonin Derivative In Vivo and Its Mechanisms in RAW264.7 Cells. Inflammation 2023, 46, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item (%) | Postpartum |
|---|---|
| Corn silage | 40.00 |
| Corn | 35.00 |
| Wheat bran | 8.00 |
| Soybean meal | 5.00 |
| Sunflower | 8.00 |
| NaCl | 1.00 |
| Premix* | 1.80 |
| NaHCO3 | 1.20 |
| Total | 100.00 |
| Nutrient composition (% of DM) | |
| NEL (MJ/Kg) | 6.70 |
| CP | 15.20 |
| NDF | 33.45 |
| ADF | 17.20 |
| NFC | 40.40 |
| Ca | 0.70 |
| P | 0.50 |
| Item | CON (n=6) | CK (n=6) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parity | 3 | 3 | |
| Milk production (kg/d) | 38.34; 0.27 | 27.50; 0.21 | < 0.001 |
| DMI (kg/d) | 21.32; 0.47 | 19.75; 0.40 | 0.028 |
| BW (kg) | 613.29; 6.24 | 643.70; 7.18 | 0.010 |
| BCS | 2.67; 0.17 | 3.32; 0.22 | 0.041 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 4.03; 0.07 | 2.23; 0.03 | < 0.001 |
| BHB (mmol/L) | 0.38; 0.05 | 3.29; 0.11 | < 0.001 |
| NEFA (mmol/L) | 0.32; 0.06 | 1.18; 0.11 | < 0.001 |
| AST(U/L) | 72.00; 1.59 | 156.40; 3.52 | < 0.001 |
| ALT(U/L) | 18.80; 1.18 | 35.53; 1.87 | < 0.001 |
| LFI | 1.08; 0.86 | -7.53; 1.24 | < 0.001 |
| IL-6(ng/L) | 0.46; 0.02 | 1.26; 0.05 | < 0.001 |
| IL-1β(ng/L) | 1.50; 0.31 | 6.08; 0.59 | < 0.001 |
| TNF-α(ng/L) | 69.24; 3.95 | 102.49; 4.29 | < 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




