Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
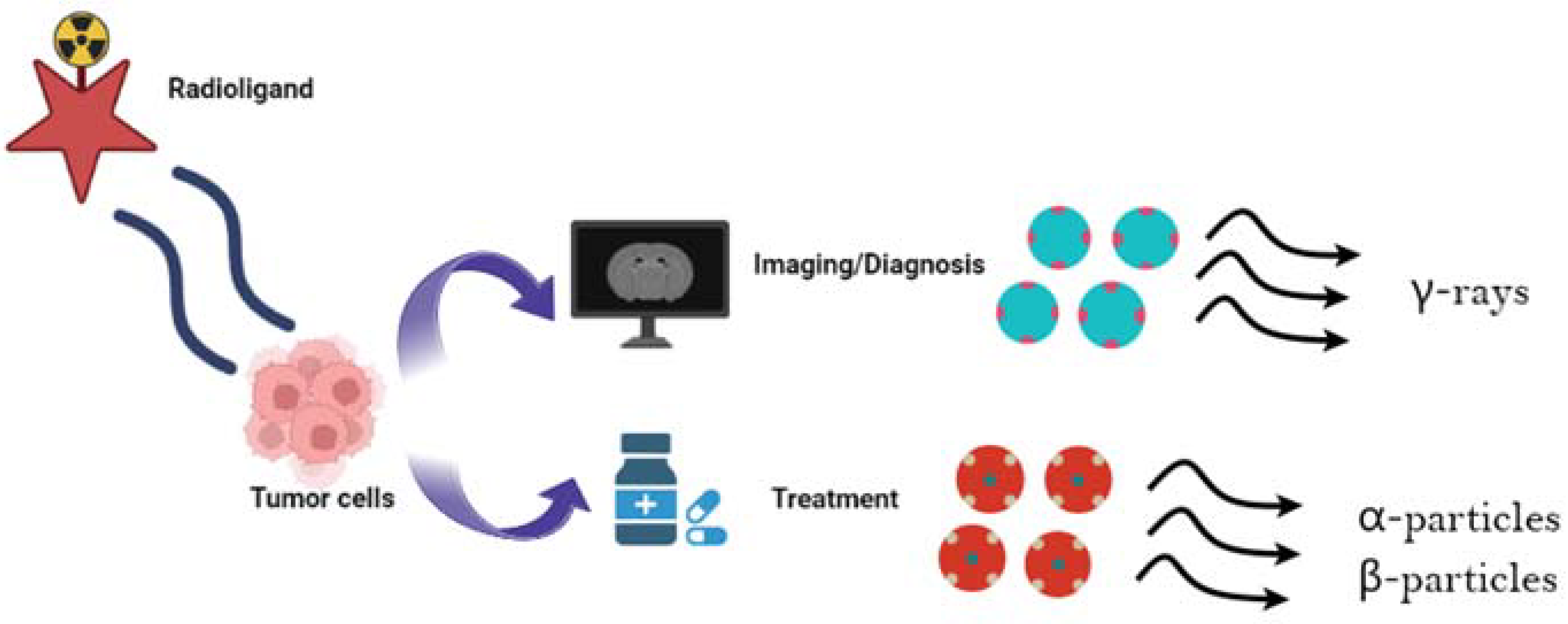
1. Introduction
2. Theragnostics
2.1. Thyroid cancer
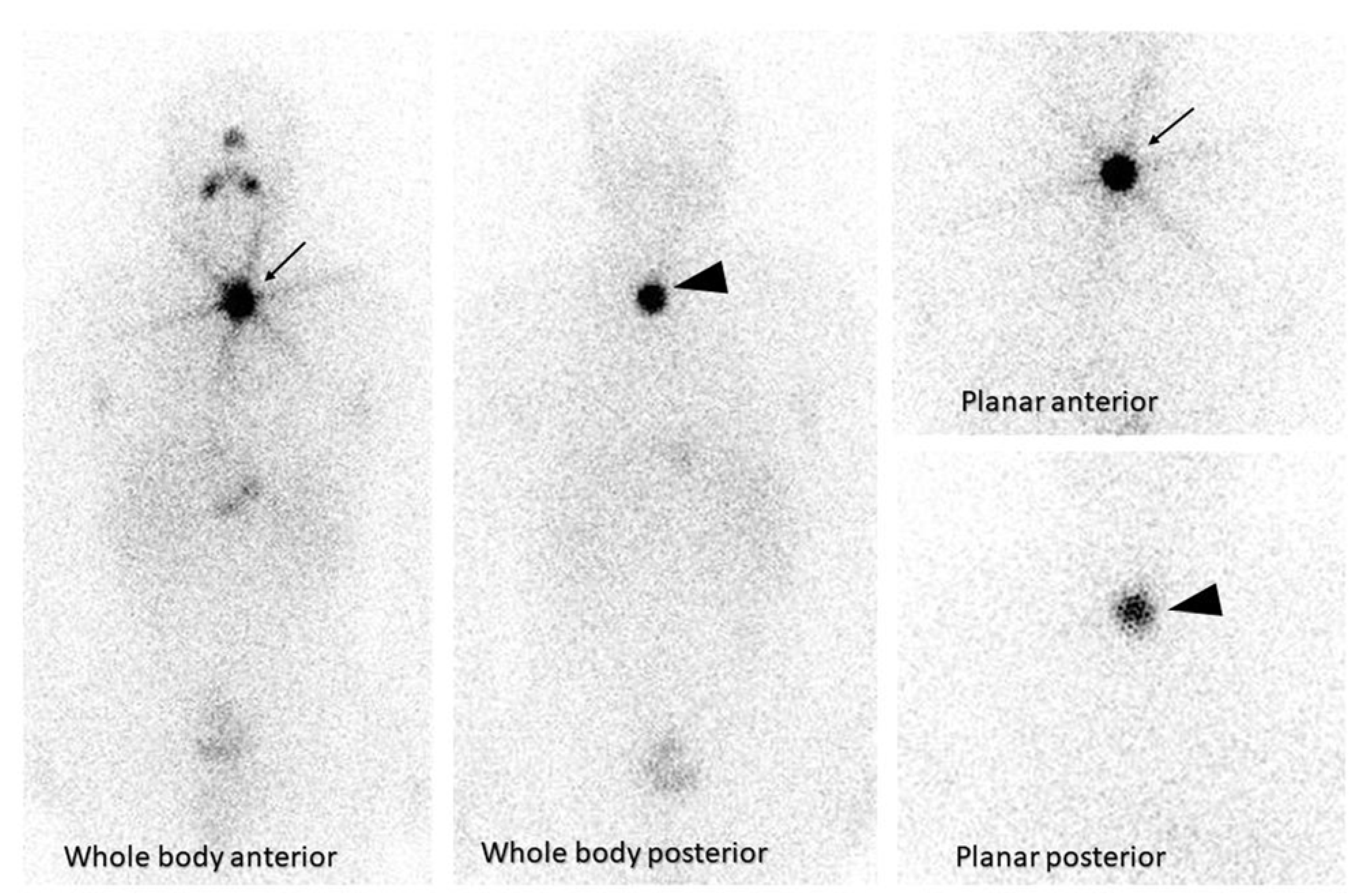
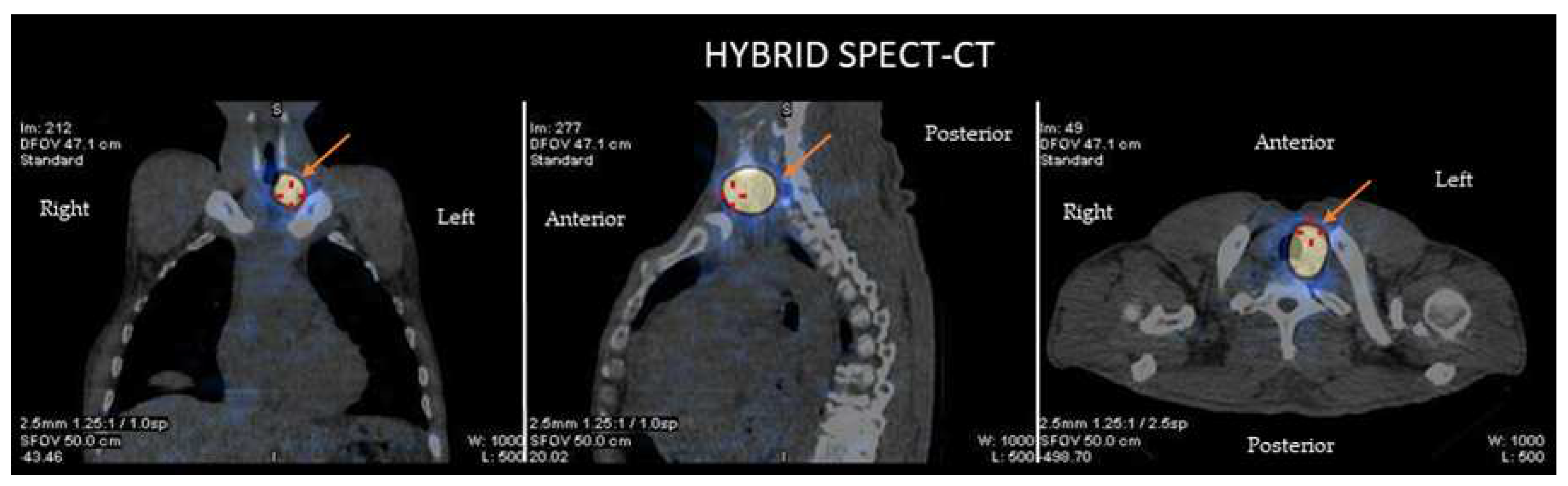
2.2. Neuroendocrine tumors
2.3. Prostate cancer
2.4. Colorectal cancer
2.5. Cholangiocarcinoma
2.6. Gliomas
2.7. Neuroblastoma and other pediatric tumors
3. Copper radionuclides as theragnostic agents
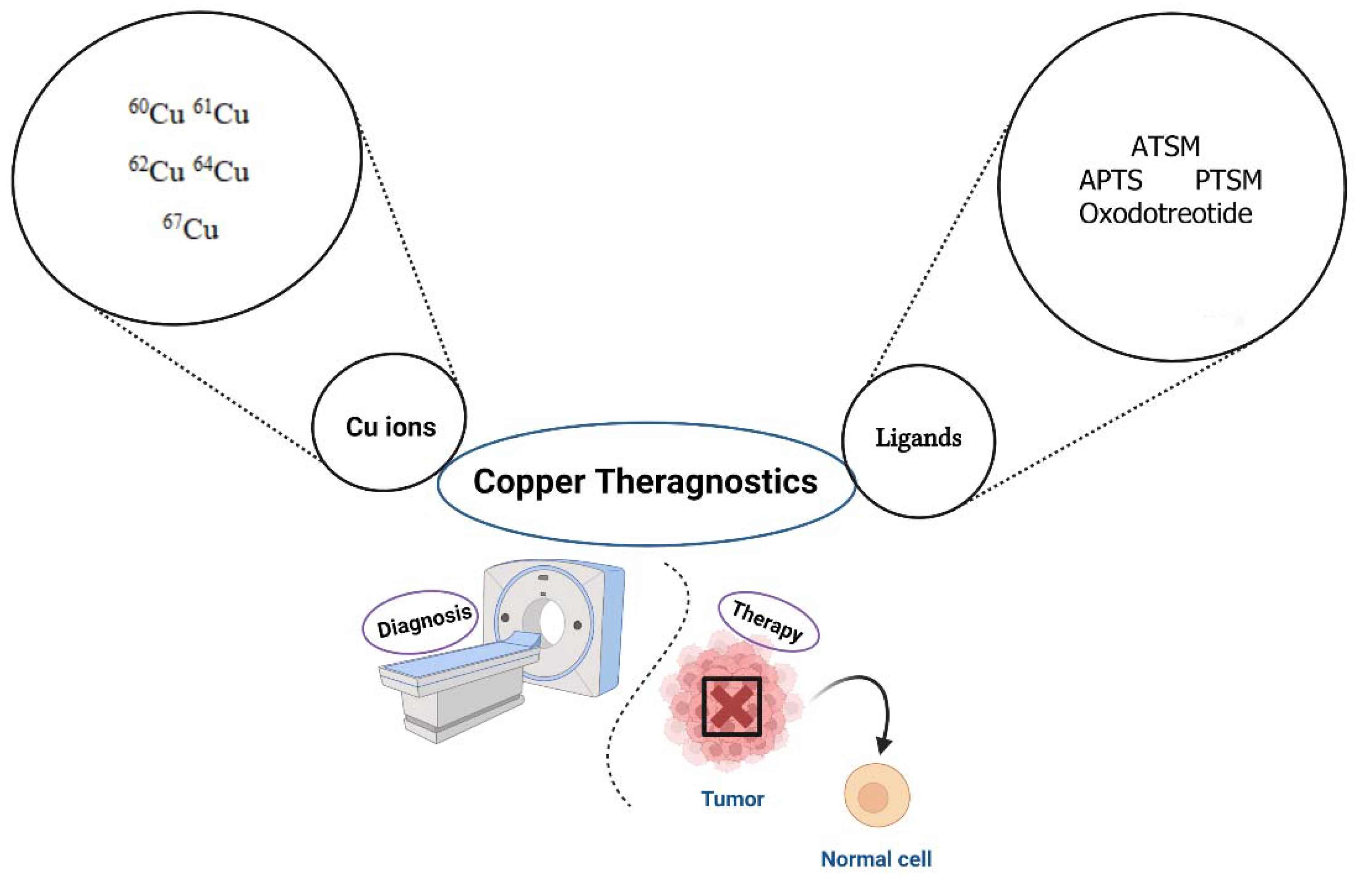
3.1. Biological effects of copper ions in cancer
4. Radiopharmaceutical applications of 64Cu isotope
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhury, P.S.; Gupta, M. Differentiated thyroid cancer theranostics: radioiodine and beyond. Br J Radiol. 2018, 91, 20180136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Annunziata, S.; Salvatori, M. Side effects of theragnostic agents currently employed in clinical practice. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021, 65, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomykala, K.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Sartor, O.; Gillessen, S.; Sweeney, C.J.; Maughan, T.; Hofman, M.S.; Herrmann, K. Next generation radiotheranostics promoting precision medicine. Ann Oncol. 2023, 34, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziorowski, J.; Ballinger, J. Theragnostic radionuclides: a clinical perspective. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021, 65, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Rousseau, J.; Ramogida, C.F.; Celler, A.; Rahmim, A.; Uribe, C.F. Implications of physics, chemistry and biology for dosimetry calculations using theranostic pairs. Theranostics. 2022, 12, 232–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadvar, H.; Chen, X.; Cai, W.; Mahmood, U. Radiotheranostics in Cancer Diagnosis and Management. Radiology. 2018, 286, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidfar, N.; Eppard, E.; Farzanehfar, S.; Yordanova, A.; Fallahpoor, M.; Ahmadzadehfar, H. An Impressive Approach in Nuclear Medicine: Theranostics. PET Clin. 2021, 16, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klain, M.; Ricard, M.; Leboulleux, S.; Baudin, E.; Schlumberger, M. Radioiodine therapy for papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002, 29 (Suppl. S2)), S479–S485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlumberger, M.; Garcia, C.; Hadoux, J.; Klain, M.; Lamartina, L. Functional imaging in thyroid cancer patients with metastases and therapeutic implications. Presse Med. 2022, 51, 104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klain, M.; Zampella, E.; Piscopo, L.; Volpe, F.; Manganelli, M.; Masone, S.; Pace, L.; Salvatore, D.; Schlumberger, M.; Cuocolo, A. Long-Term Prognostic Value of the Response to Therapy Assessed by Laboratory and Imaging Findings in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Cancers. 2021, 13, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaim, S.M.; Scholten, B.; Neumaier, B. New developments in the production of theranostic pairs of radionuclides. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. 2018, 318, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, A.M.; Dewaraja, Y.K. Thyroid Cancer Radiotheragnostics: the case for activity adjusted 131I therapy. ClinTransl Imaging. 2018, 6, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioka, C.; Kouraklis, G.; Zafirakis, A.; Manetou, A.; Dimakopoulos, N. Menstrual cycle disorders after therapy with iodine-131. FertilSteril. 2006, 86, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioka, C.; Fotopoulos, A. Effects of I-131 therapy on gonads and pregnancy outcome in patients with thyroid cancer. FertilSteril. 2011, 95, 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, T.; Eiber, M.; Schwaiger, M.; Gschwend, J.E. Current use of PSMA-PET in prostate cancer management. Nat Rev Urol. 2016, 13, 226–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Kuratsukuri, K.; Landas, S.; Imaida, K.; Rovito, P.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Haas, G.P. Expression of prostate-specific membrane antigen in normal and malignant human tissues. World J Surg. 2006, 3, 628–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.; Perez, F.G.; Gomez, E.; Pitalua, Q.; Ornelas, M.; Ignacio, E.; et al. Histopathologic Correlation With 68Ga PSMA PET/CT in Non Prostate Tumors. J Nucl Med. J Nucl Med., 61, 472. [Google Scholar]
- Ciappuccini, R.; Saguet-Rysanek, V.; Giffard, F.; Licaj, I.; Dorbeau, M.; Clarisse, B.; et al. PSMA Expression in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Association With Radioiodine, 18F-FDG Uptake and, Patient Outcome. J ClinEndocrinolMetab 2021, 106, 3536–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseland, M.E.; Dewaraja, Y.K.; Wong, K.K. Advanced imaging and theranostics in thyroid cancer. CurrOpinEndocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, L.; Deandreis, D.; Vrachimis, A.; Campenni, A.; PetranovicOvcaricek, P. Molecular Imaging and Theragnostics of Thyroid Cancers. Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Roesch, F.; Raju, S.; Satapathy, S.; Sheokand, P.; Moon, E.S., Martin, M.; Agarwal, S.; Tripathi, M.; Bal, C. Head-to-head comparison of [68Ga] Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi and [68Ga]Ga-DOTANOC PET/CT imaging for the follow-up surveillance of patients with medullary thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2023, 10.1089.
- Bal, C.; Chakraborty, D.; Khan, D. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography in thyroid cancer. PET Clin. 2022, 17, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asa, S.; Sonmezoglu, K.; Uslu-Besli, L.; et al. Evaluation of F-18 DOPA PET/CT in the detection of recurrent or metastatic medullary thyroid carcinoma: comparison with GA-68 DOTA-TATE PET/CT. Ann Nucl Med. 2021, 35, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treglia, G.; Tamburello, A.; Giovanella, L. Detection rate of somatostatin receptor PET in patients with recurrent medullary thyroid carcinoma: a systematic review and a meta-analysis. Hormones 2017, 16, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubello, D.; Rampin, L.; Nanni, C.; et al. The role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting metastatic deposits of recurrent medullary thyroid carcinoma: a prospective study. Eur J SurgOncol. 2008, 34, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saponjski, J.; Macut, D.; Saranovic, D.S.; et al. Clinical relevance of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the postoperative follow-up of patients with history of medullary thyroid cancer. RadiolOncol. 2020, 55, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pajak, C.; Cadili, L.; Nabata, K.; Wiseman, S.M. (68)Ga-DOTATATE-PET shows promise for diagnosis of recurrent or persistent medullary thyroid cancer: A systematic review. Am J Surg. 2022.224, 670–675.
- Tuncel, M.; Kılıçkap, S.; Süslü, N. Clinical impact of (68)Ga-DOTATATE PET-CT imaging in patients with medullary thyroid cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 2020, 34, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parghane, R.V.; Naik, C.; Talole, S.; et al. Clinical utility of (177) Lu-DOTATATE PRRT in somatostatin receptor-positive metastatic medullary carcinoma of thyroid patients with assessment of efficacy, survival analysis, prognostic variables, and toxicity. Head Neck 2020, 42, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Svirydenka, H.; Virgolini, I. Theragnostics in Neuroendocrine Tumors. PET Clin. 2021, 16, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Singh, A.; Schuchardt, C.; Kulkarni, H.R.; Baum, R.P. Prognostic Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in a Large Cohort of Patients with Advanced Metastatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms Treated with Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. J Nucl Med. 2020, 61, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandathil, A.; Subramaniam, R.M. Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Diagnosis: DOTATATE PET/CT. PET Clin. 2023, 18, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabander, T.; van der Zwaan, W.A.; Teunissen, J.J.M.; et al. Long-term efficacy, survival, and safety of [177Lu-DOTA0,Tyr3]octreotate in patients with gastroenteropancreatic and bronchial neuroendocrine tumors. ClinCancerRes. 2017, 23, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strosberg, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Wolin, E.; Hendifar, A.; Yao, J.; Chasen, B.; Mittra, E.; Kunz, P.L.; Kulke, M.H.; Jacene, H.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of 177Lu-Dotatate for Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors. N Engl J Med. 2017, 376, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhbahaei, S.; Sadaghiani, M.S.; Rowe, S.P.; Solnes, L.B. Neuroendocrine Tumor Theranostics: An Update and Emerging Applications in Clinical Practice. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021, 2021. 217, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH website. Phase 1 study of AlphaMedix in adult subjects with SSTR (+) NET (NCT03466216). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03466216. UpdatedJuly 10, 2020. AccessedApril 10, 2021.
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, i.L.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Mier, W.; Apostolidis, C.; Boll, R.; et al. Bi-DOTATOC receptor-targeted alpha-radionuclide therapy induces remission in neuroendocrine tumours refractory to beta radiation: a first-in-human experience. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014, 41, 2106–19.
- Jeong, S.H.; Kwak, C. Prostate-specific membrane antigen-mediated theragnostics in prostate cancer. Investig Clin Urol. 2021, 62, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farolfi, A.; Mei, R.; Ali, S.; Castellucci, P. Theragnostics in prostate cancer. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021, 65, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.H.; Oxman, A.D.; Vist, G.; Kunz, R.; Brozek, J.; Alonso-Coello, P.; Montori, V.; Akl, E.A.; Djulbegovic, B.; Falck-Ytter, Y. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence--study limitations (risk of bias). J Clin Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 407–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beresford, M.J.; Gillatt, D.; Benson, R.J.; Ajithkumar, T. A systematic review of the role of imaging before salvage radiotherapy for post-prostatectomy biochemical recurrence. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 20, 2, 46-55.
- Han, S.; Woo, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Suh, C.H. Impact of 68Ga-PSMA PET on the management of patients with prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2018, 74, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calopedos, R.J.S.; Chalasani, V.; Asher, R.; Emmett, L.; Woo, H.H. Lutetium-177-labelled anti-prostate-specific membrane antigen antibody and ligands for the treatment of metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2017, 20, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor O, de Bono J, Chi KN, Fizazi K, Herrmann K, Rahbar K, Tagawa ST, Nordquist LT, Vaishampayan N, El-Haddad G, Park CH, Beer TM, Armour A, Pérez-Contreras WJ, DeSilvio M, Kpamegan E, Gericke G, Messmann RA, Morris MJ, Krause BJ; VISION Investigators. Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2021, 385, 1091-1103.
- Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Babich, J.W.; Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Eisenhut, M.; Kopka, K.; Haberkorn, U. The rise of PSMA ligands for diagnosis and therapy of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2016, 57, 79S–89S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, S.; Pizzuto, D.A.; Treglia, G. Diagnostic performance of pet imaging using different radiopharmaceuticals in prostate cancer according to published meta-analyses. Cancers (Basel). 2020, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberini, V.; Laudicella, R.; Balma, M.; Nicolotti, D.G.; Buschiazzo, A.; Grimaldi, S.; Lorenzon, L.; Bianchi, A.; Peano, S.; Bartolotta, T.V.; Farsad, M.; Baldari, S.; Burger, I.A.; Huellner, M.W.; Papaleo, A.; Deandreis, D. Radiomics and artificial intelligence in prostate cancer: new tools for molecular hybrid imaging and theragnostics. EurRadiol Exp. 2022, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonni, I.; Baratto, L.; Iagaru, A. Imaging of Prostate Cancer Using Gallium-68-Labeled Bombesin. PET Clin. 2017, 12, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, F.S., Suarez-Weiss, K.E., Vangel, M. et al. Clinical impact of PET/MRI in oligometastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2021, 125, 975–982.
- Catalano, O.A., Lee, S.I., Parente, C. et al. Improving staging of rectal cancer in the pelvis: the role of PET/MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2021, 48, 1235–1245.
- Wiering, B.; Ruers, T.J.; Oyen, W.J. Role of FDG-PET in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal liver metastases. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2004, 4, 607–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosten, M.; Crane, L.M.; Bart, J.; van Leeuwen, F.W.; van Dam, G.M. Selecting potential targetable biomarkers for imaging purposes in colorectal cancer using target selection criteria (TASC): A novel target identification tool. Transl Oncol. 2011, 4, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Kaur, S.; Guha, S.; Batra, S.K. The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in inflammation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012, 1826, 129–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Ingram, N.; Verghese, E.T.; Wijetunga, I.; Markham, A.F.; Wyatt, J.; Prasad, K.R.; Coletta, P.L. Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin as a Theragnostic Marker in Perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6737–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.X.; Zou, S.J.; Li, D.; Zhou, J.Y.; Cheng, Z.T.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y.L.; Kuang, D.; Zhu, X.H. Prostate-specific membrane antigen expression in hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, and liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 7664–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaba, S.E.; Kyritsis, A.P. Recognition and management of gliomas. Drugs. 1997, 53, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, M.D.; Maor, M.H.; Meyers, C.; Kyritsis, A.P.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Yung, W.K.; Sawaya, R.E.; Hess, K.; Bruner, J.M.; Peterson, P.; Levin, V.A. A phase II trial of high-dose bromodeoxyuridine with accelerated fractionation radiotherapy followed by procarbazine, lomustine, and vincristine for glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999, 45, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyritsis, A.P.; Levin, V.A. An algorithm for chemotherapy treatment of recurrent glioma patients after temozolomide failure in the general oncology setting. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Martin-Duque, P.; Perez-Soler, R.; Levin, V.A.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. Adenovirus-mediated p16 transfer to glioma cells induces G1 arrest and protects from paclitaxel and topotecan: implications for therapy. Int J Oncol. 1998, 12, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. The functional role of tumor suppressor genes in gliomas: clues for future therapeutic strategies. Neurology. 1998, 51, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Cifola, I.; Caratelli, S.; Sconocchia, G.; D'Agnano, I.; Cenciarelli, C. Glioma extracellular vesicles for precision medicine: prognostic and theragnostic application. DiscovOnc. 2022, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprita, A.; Baloi, S.C.; Staicu, G.A.; Alexandru, O.; Tache, D.E.; Danoiu, S.; Micu, E.S.; Sevastre, A.S. Updated Insights on EGFR Signaling Pathways in Glioma. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagner, J.P.; Sarfraz, Y.; Ortenzi, V.; Alotaibi, F.M.; Chiriboga, L.A.; Tayyib, A.T.; Douglas, G.J.; Chevalier, E.; Romagnoli, B.; Tuffin, G.; Schmitt, M.; Lemercier, G.; Dembowsky, K.; Zagzag, D. Multifaceted C-X-C Chemokine Receptor 4 (CXCR4) Inhibition Interferes with Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy-Induced Glioma Dissemination. Am J Pathol. 2017, 187, 2080–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamszus, K.; Meyerhof, W.; Westphal, M. Somatostatin and somatostatin receptors in the diagnosis and treatment of gliomas. J Neurooncol. 1997, 35, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, E.P.; Gonçalves, C.S.; Pojo, M.; Carvalho, R.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Taipa, R.; Pardal, F.; Pinto, A.A.; Custódia, C.; Faria, C.C.; Baltazar, F.; Sousa, N.; Paredes, J.; Costa, B.M. Cadherin-3 is a novel oncogenic biomarker with prognostic value in glioblastoma. MolOncol. 2022, 16, 2611–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshari, A.R.; Motamed-Sanaye, A.; Sabri, H.; Soltani, A.; Karkon-Shayan, S.; Radvar, S.; Javid, H.; Mollazadeh, H.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, S. Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists: Potential Targets in the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Curr Med Chem. 2021, 28, 4877–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Patel, C.B.; Xu, G.; Iagaru, A.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z. Visualization of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets in Glioma with Molecular Imaging. Frontiers in Immunology. 2020, 11, 592389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y.; Fu, K.; Shang, Q.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; Lin, Q.; Chen, H. Fibroblast activation protein-based theranostics in cancer research: A state-of-the-art review. Theranostics. 2022, 12, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y.; O'Connor, M.J.; de Bono, J. Laying a trap to kill cancer cells: PARP inhibitors and their mechanisms of action. SciTransl Med. 2016, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, T.; Lacy, J.; Keliher, E.J.; Yang, K.S.; Ullal, A.; Kohler, R.H.; Vinegoni, C.; Weissleder, R. Imaging therapeutic PARP inhibition in vivo through bioorthogonally developed companion imaging agents. Neoplasia. 2012, 14, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, B.; Carlucci, G.; Salina, B.; Di Gialleonardo, V.; Kossatz, S.; Vansteene, A.; Longo, V.A.; Bolaender, A.; Chiosis, G.; Keshari, K.R.; Weber, W.A.; Reiner, T. Non-invasive PET imaging of PARP1 expression in glioblastoma models. Mol Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, N.; Pastorino, S.; Jiang, P.; Lambert, G.; Crawford, J.R.; Gymnopoulos, M.; Piccioni, D.; Juarez, T.; Pingle, S.C.; Makale, M.; Kesari, S. Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) expression in primary gliomas and breast cancer brain metastases. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; ArunRaj, S.T.; Bhullar, K.; Haresh, K.P.; Gupta, S.; Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.; Singh, M.; Damle, N.A.; Garg, A. , Tripathi, M.; Bal C. Ga-68 PSMA PET/CT in recurrent high-grade gliomas: Evaluating PSMA expression in vivo. Neuroradiology. 2022, 64, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasikumar, A.; Kashyap, R.; Joy, A.; Patro, K.C.; Bhattacharya, P.; Pilaka, V.K.R.; Oommen, K.E.; Pillai, M.R.A. Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Imaging of Glioma—A Pilot Study. ClinNucl Med. 2018, 43, e304–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Dall'Armellina, S.; Pizzuto, D.A.; Perotti, G.; Zagaria, L.; Lanni, V.; Treglia, G.; Racca, M.; Annunziata, S. PSMA Radioligand Uptake as a Biomarker of Neoangiogenesis in Solid Tumours: Diagnostic or Theragnostic Factor? Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.W.; Yang, S.X.; Chen, J.H.; Ping, Y.F.; Zhou, X.D.; Wang, Q.L.; Jiang, X.F.; Gong, W.; Xiao, H.L.; Du, L.L.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhao, W.; Shi, J.Q.; Wang, J.M. Preferential expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by highly malignant human gliomas and its association with poor patient survival. Neurosurgery. 2007, 61, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapa, C.; Lückerath, K.; Kleinlein, I.; Monoranu, C.M.; Linsenmann, T.; Kessler, A.F.; Rudelius, M.; Kropf, S.; Buck, A.K.; Ernestus, R.I.; Wester, H.J.; Löhr, M.; Herrmann, K. (68) Ga-Pentixafor-PET/CT for Imaging of Chemokine Receptor 4 Expression in Glioblastoma. Theranostics. 2016, 6, 428–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.; Nigam, S.; Tatum, D.S.; Raphael, I.; Xu, J.; Kumar, R.; Plakseychuk, E.; Latoche, J.D.; Vincze, S.; Li, B.; Giri, R.; McCarl, L.H.; Edinger, R.; Ak, M.; Peddagangireddy, V.; Foley, L.M.; Hitchens, T.K.; Colen, R.R.; Pollack, I.F.; Panigrahy, A.; Magda, D.; Anderson, C.J.; Edwards, W.B.; Kohanbash, G. Novel theranostic agent for PET imaging and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy of tumour-infiltrating immune cells in glioma. EBioMedicine. 2021, 71, 103571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, G.A.; Xourgia, X.; Gerogianni, P.; Vartholomatos, E.; Kalef-Ezra, J.A.; Fotopoulos, A.D.; Kyritsis, A.P. 99mTc-Tetrofosmin Uptake Correlates with the Sensitivity of Glioblastoma Cell Lines to Temozolomide. World J Nucl Med. 2017, 16, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- lexiou GA, Tsiouris S, Kyritsis AP, Fotakopoulos, K.; Goussia, A.; Voulgaris, S.; Fotopoulos, A.D. The value of 99mTc-tetrofosmin brain SPECT in predicting survival in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J Nucl Med. 2010, 51, 1923-1926.
- Mahapatra, S.; Challagundla, K.B. Neuroblastoma. 2023 Feb 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Cimini, A.; Ricci, M.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Filippi, L.; Schillaci, O. Theragnostic Aspects and Radioimmunotherapy in Pediatric Tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrangelo, S.; Rufini, V.; Ruggiero, A.; Di Giannatale, A.; Riccardi, R. Treatment of Advanced Neuroblastoma in Children Over 1 Year of Age: The Critical Role of 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine Combined with Chemotherapy in a Rapid Induction Regimen. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2011, 56, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayano, D.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nakajima, K.; Kuroda, R.; Watanabe, S.; Inaki, A.; Toratani, A.; Akatani, N.; Yamase, T.; Kunita, Y.; et al. High-dose 131I-metaiodobenzylguanidine Therapy in Patients with High-Risk Neuroblastoma in Japan. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasse-Lazar, K.; Krajewska, J.; Paliczka-Cieślik, E.; Jurecka-Lubieniecka, B.; Michalik, B.; Handkiewicz-Junak, D.; Roskosz, J.; Jarzab, B. Terapia 131I-MIBG w leczeniuguzówchromochłonnych u dzieci--doświadczeniawłasne [131I-MIBG therapy in the treatment of pheochromocytoma in children--own experiences]. Endokrynol Pol. 2008, 5, 235–40. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; et al. [18F]MFBG PET/CT outperforming [123I]MIBG SPECT/CT in the evaluation of neuroblastoma. EurJ Nucl Med MolImag. 2023, 50, 3097–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ametamey, S.M.; Honer, M.; Schubiger, P.A. Molecular imaging with PET. Chem Rev. 2008, 108, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, G.; Piccardo, A.; Giovannelli, E.; Signore, A. Targeting Copper in Cancer Imaging and Therapy: A New Theragnostic Agent. J Clin Med. 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschi, A.; Martini, P.; Janevik-ivanoska, E.; Duatti, A. The emerging role of copper-64 radiopharmaceuticals as cancer theranostics. Drug Discov Today. 2018, 23, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denoyer, D.; Masaldan, S.; La Fontaine, S.; Cater, M.A. Targeting copper in cancer therapy: ‘Copper That Cancer’ Metallomics. 2015, 7, 1459–1476.
- Bolzati, C. ,’ Duatti, A. The emerging value of 64Cu for molecular imaging and therapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020, 64, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutfilen, B.; Souza, S.A.; Valentini, G. Copper-64: a real theranostic agent. Drug Des DevelTher. 2018, 12, 3235–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Wu, J.S.; Muzik, O.; Hsieh, J.T.; Lee, R.J.; Peng, F. Reduced 64Cu uptake and tumor growth inhibition by knockdown of human copper transporter 1 in xenograft mouse model of prostate cancer. J Nucl Med. 2014, 55, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Niccoli, A.; Villano, C.; Giacobbi, B.; Coccetti, D.; Panichelli, P.; Giuseppe, R. Copper-64 Dichloride as Theranostic Agent for Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Preclinical Study. Bio Med Res Int. 2015, 2015, 129764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Lan, X. Theranostics of malignant melanoma with 64CuCl2. J Nucl Med. 2014, 55, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panichelli, P.; Villano, C.; Cistaro, A.; Bruno, A.; Barbato, F.; Piccardo, A. Imaging of brain tumors with copper-64 chloride: Early experience and results. Cancer BiotherRadiopharm. 2016, 31, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, J.F.; Alves, V.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; Paulo, A.; Gil, O.M.; Mendes, F. Radiobiological characterization of 64CuCl2 as a simple tool for prostate cancer theranostics. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalogna, G.; Talarico, C.; Dattilo, V.; Gangemi, V.; Calabria, F.; D’Antona, L.; Schenone, S.; Musumeci, F.; Bianco, C.; Perrotti, N.; et al. The SGK1 kinase inhibitor SI113 sensitizes theranostic effects of the 64CuCl2 in human glioblastoma Multiforme cells. CellPhysiolBiochem. 2017, 43, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.L.; Willowson, K.P.; Harris, M.; Biggin, C.; Aslani, A.; Lengkeek, N.A.; Stoner, J.; Eslick, M.E.; Marquis, H.; Parker, M.; et al. 64Cu Treatment Planning and 67Cu Therapy with Radiolabeled [64Cu/67Cu]MeCOSar-Octreotate in Subjects with Unresectable Multifocal Meningioma: Initial Results for Human Imaging, Safety, Biodistribution, and Radiation Dosimetry. J Nucl Med. 2023, 64, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.; Van Dam, E.; Houston, Z.; McInnes, L.; Mpoy, C.; Harris, M.; Thurecht, K.; Donnelly, P.; Rogers, B. A Cu-64/Cu-67 Bombesin ligand as a theranostic for cancer. J Nucl Med. 2021, 62 (supplement 1), 1237. [Google Scholar]
| Molecular Target | Biological process in GBM | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Tenascin-C | Cell adhesion/extracellular matrix (ECM) | [61] |
| Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | Cell growth/survival | [62] |
| Chemokine Receptor-4 (CXCR4) | Cell migration | [63] |
| Somatostatin Receptor 2 (SSTR2) | Cell signalling/cell survival | [64] |
| Cadherin-3 | Cell adhesion/extracellular matrix (ECM) | [65] |
| Neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R) | Cell growth/survival | [66] |
| Integrin alpha-V beta-3 (αvβ3) | Angiogenesis | [67] |
| Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) | Inflammation | [68] |
| Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP1) | Cellular repair of DNA | [69] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





