Submitted:
12 September 2023
Posted:
14 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
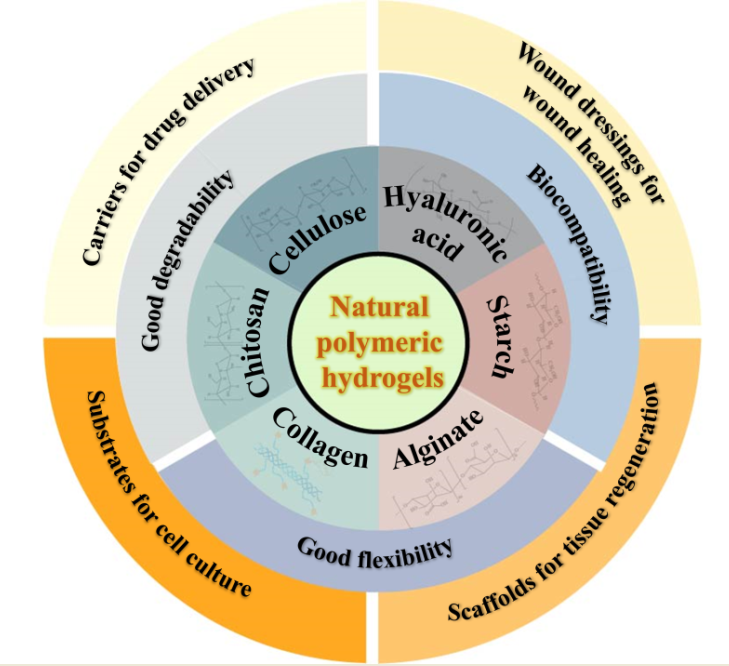
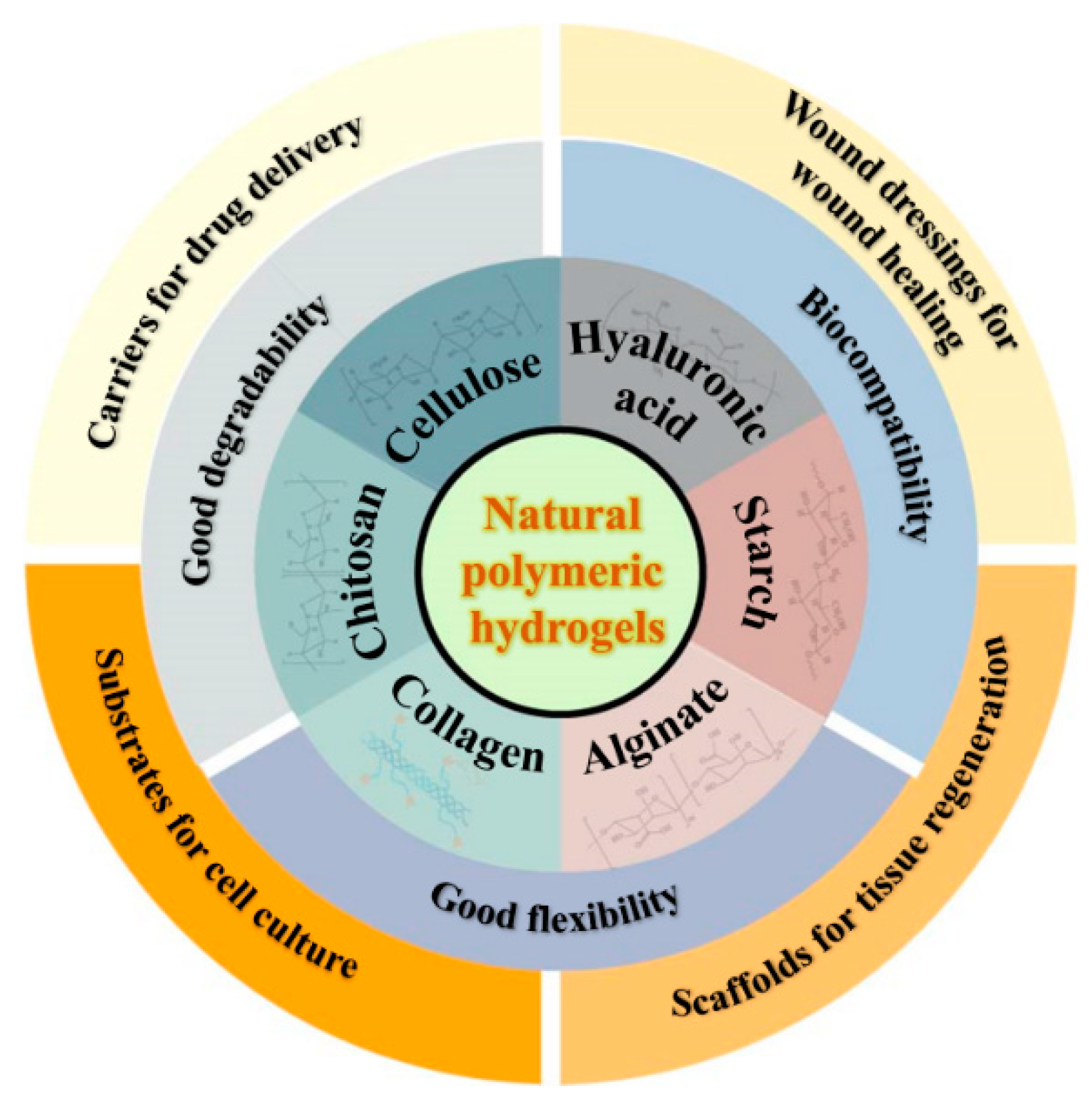
2. Natural polymer-based hydrogels
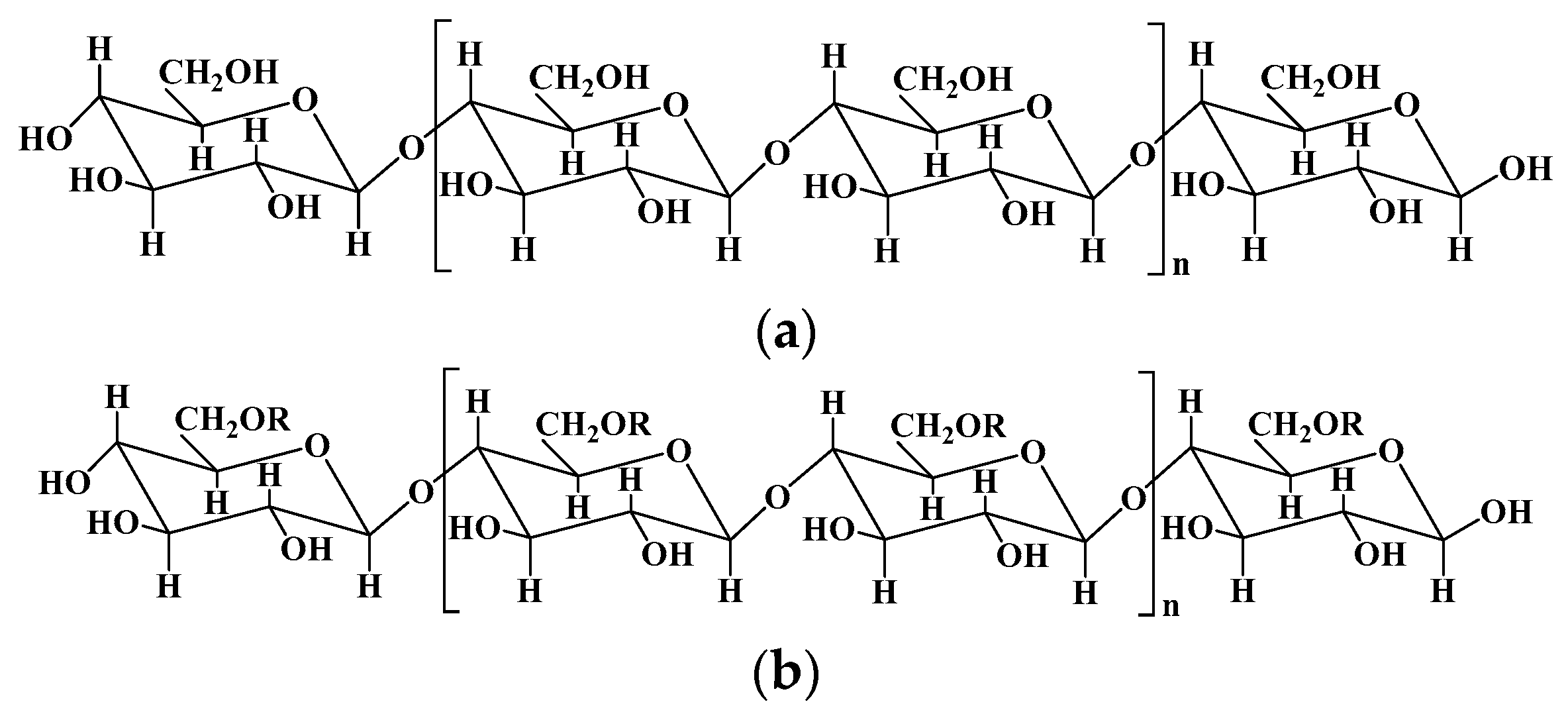
2.1. Cellulose and cellulose-based hydrogels
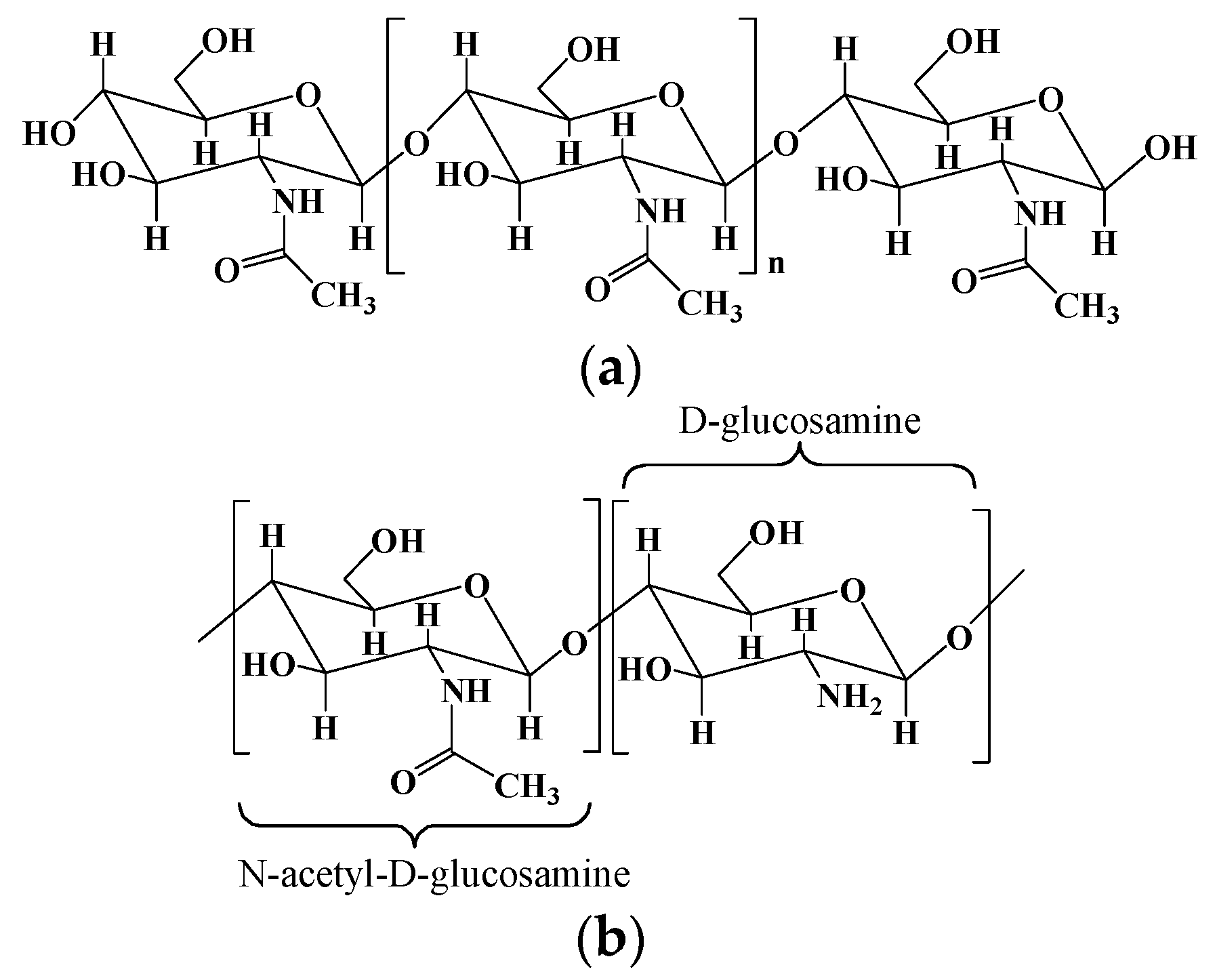
2.2. Chitosan and chitosan-based hydrogels
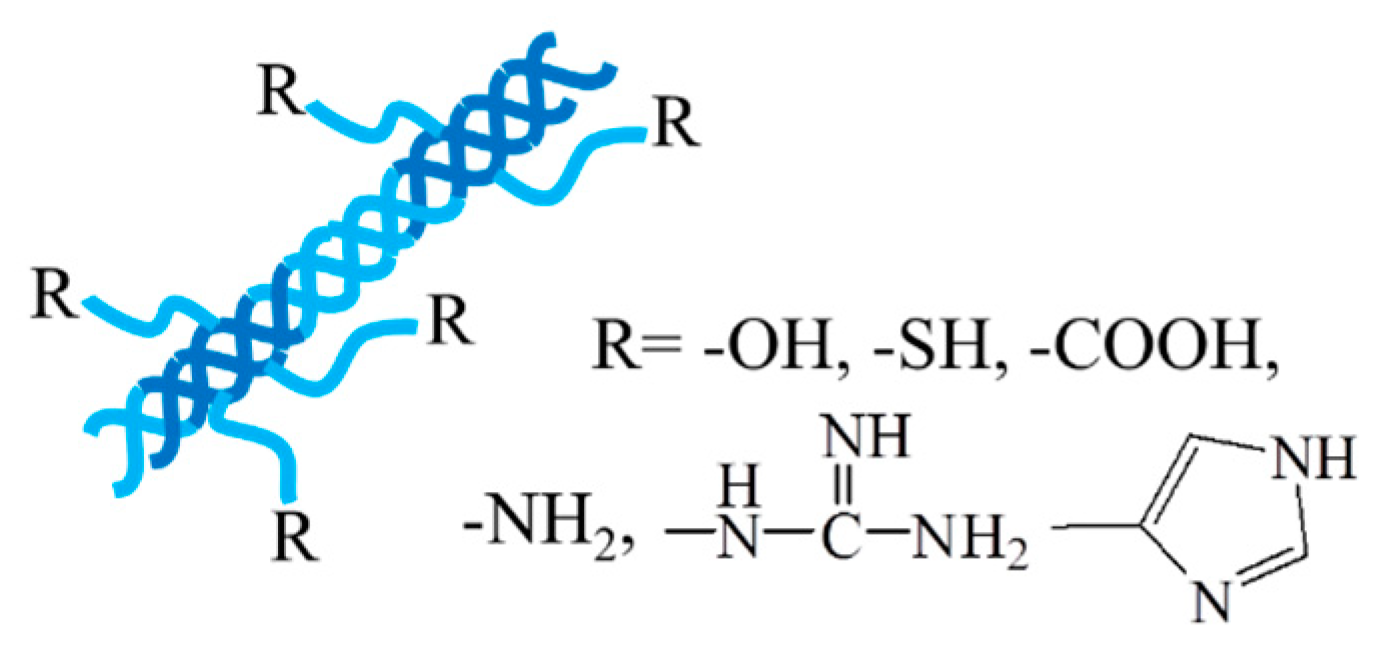
2.3. Collagen/gelatin and collagen/gelatin-based hydrogel
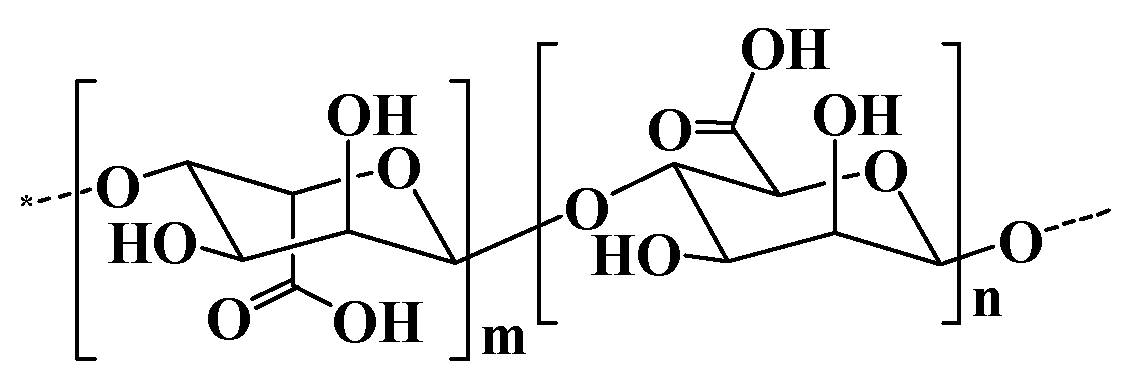
2.4. Alginate and alginate-based hydrogel
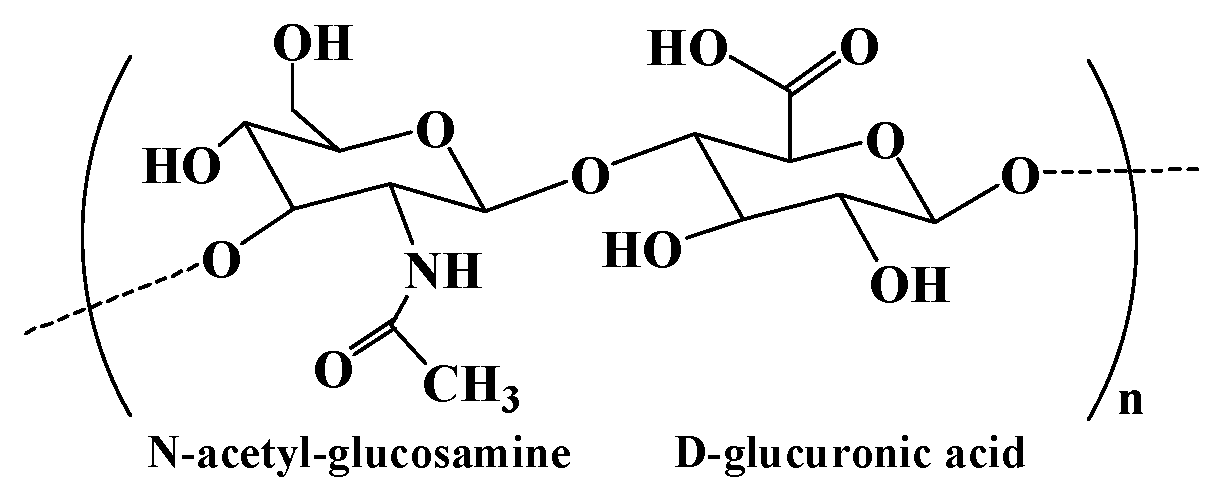
2.5. Hyaluronic acid and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel
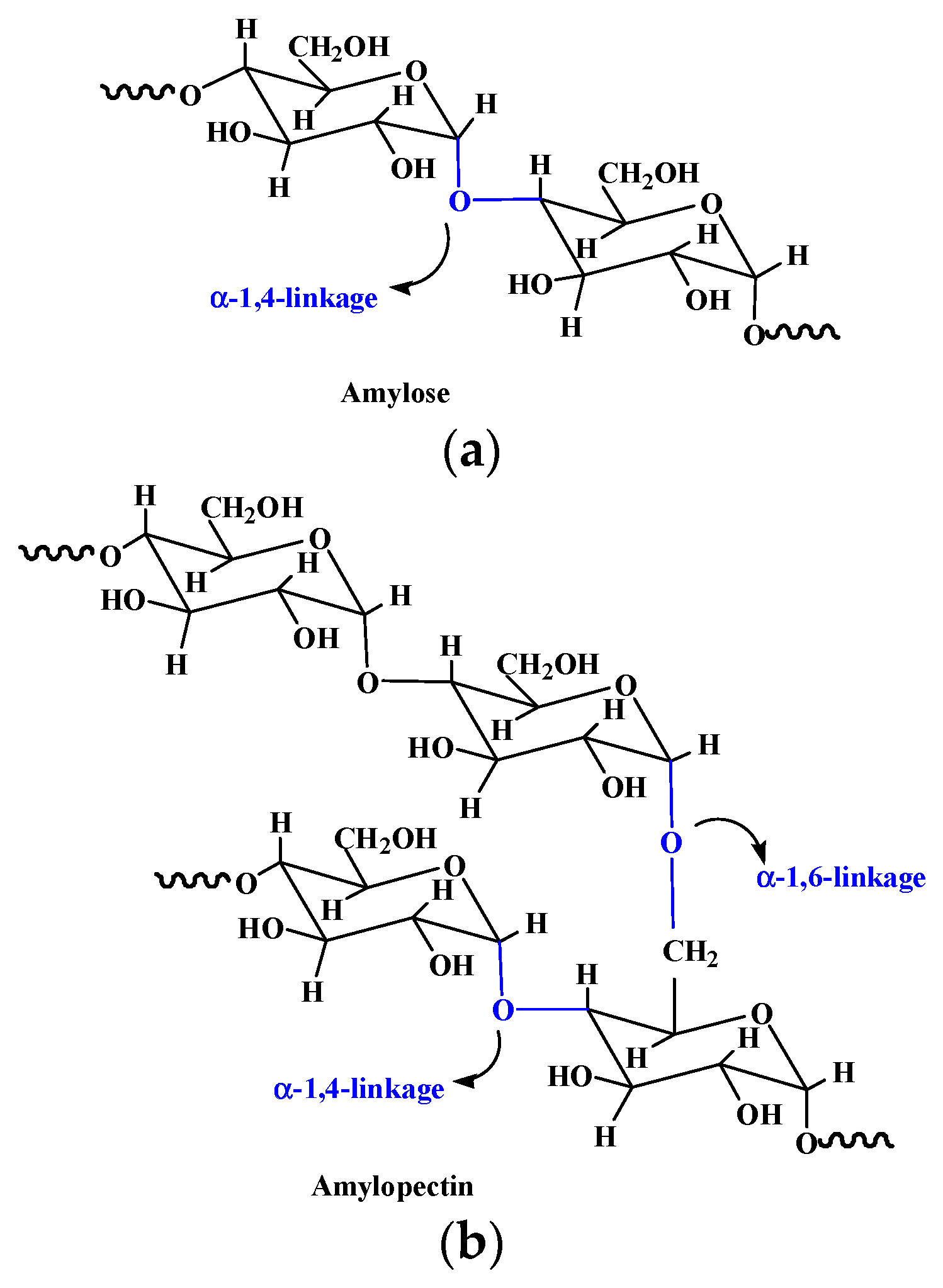
2.6. Starch and starch-based hydrogel
| Natural polymer | Chemical structures | Preparation and processing | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | Composed of β (1-4)- glycosidic-linked glucose units | 1. Lignocelluloses purification by chemical treatment. 2. Biological method depending on microbial enzymes. 3. Bacterial cellulose produced by certain types of bacteria. |
[12] |
| Chitosan | Poly-(β-1-4) N-acetyl- D-glucosamine | Derived from chitin by partial deacetylation though chemical or enzymatic hydrolysis. | [25,29] |
| Collagen | A helical fibrous protein formed by three peptide chains | 1. Extracted and purified from various animal sources by chemical and enzyme treatment. 2. Recombinant collagen produced by recombinant technology and biosynthesis. |
[40] |
| Alginate | Consisting of α-L glucuronate and β-D mannuronate repeating units | 1. Extraction from brown algae (Phaeophyceae) by treatment with aqueous alkali solutions. 2. Bacterial biosynthesis from Azotobacter and Pseudomonas. |
[54] |
| Hyaluronic acid | Consisting of N-acetyl- glucosamine and D-glucuronic acid residues | 1. Extraction from animal tissues. 2. Microbial fermentation using pathogenic bacteria and non-pathogenic bacteria. 3. Enzymatic polymerization of UDP-sugar monomers. |
[67] |
| Starch | Composed of α-D-(1 - 4) and α-D-(1 - 6)-glycosidic- linked glucose units | Extracted from seeds, roots, tubers, stems, fruits, and all leaves. | [73] |
3. Natural polymer-based hydrogels for biomedical application
3.1. Drug carriers for drug delivery
| Hydrogels | Drugs | Properties and function | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan-based micellar hydrogels | Minocycline and edaravone | Self-healing and injectable property. First-order rapid release for minocycline and zero-order sustained release for edaravone. Behavioral improvement in stroke rats. | [83] |
| Multi-domain peptide hydrogels | Cyclic dinucleotide (CDN) | An eight-fold slower release rate of CDN and a six-fold improvement in survival of mice compared with standard collagen hydrogel. | [84] |
| Chitosan/poly (glutamic acid)/alginate polyelectrolyte complex hydrogels | Piroxicam | Controlled colon-specific drug release, and reduced gastrointestinal irritation side effect of piroxicam. | [85] |
| Host-guest interaction hydrogel system | α-CD | Temperature responsive stepwise release of α-CD both in the solution and hydrogel states. | [86] |
| Magnetic hydrogel microrobots | Alpha-lipoic acid | Sustained drug release, targeted movement, satisfactory antioxidant properties and biosafety. | [89] |
| Hybrid gel beads based on chitosan and Fe3O4 cross-linked polyethylene glycol | Rifampicin | pH and magnetic field responsive asset in the drug delivery. | [87] |
| CaCO3/sodium alginate/Fe3O4 hydrogel-based capsule microrobots | Indomethacin | Intravascular targeted drug delivery by following a predetermined trajectory in the blood vessel under magnetic drive. | [90] |
| Grapheme quantum dot/carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel nanocomposite films | Doxorubicin | pH-sensitive and consecutive prolonged release of doxorubicin, and non-obvious cytotoxicity on K562 cells. | [93] |
| Carbon dots/gelatin/carboxymethyl cellulose based bionanogels | Curcumin and doxorubicin | pH-controlled release for both drugs and superior anticancer effect in comparison with free curcumin/doxorubicin. | [94] |
3.2. Wound dressings for wound healing
| Hydrogels | Properties | Effects in the wound healing | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium alginate-polyacrylamide hydrogels | Excellent mechanical strength by zinc crosslinked hydrogel. | Antibacterial activities and promoted fibroblasts migration, vascularization, collagen deposition and granulation tissue formation. | [99] |
| Alginate/dopamine/carboxymethyl chitosan-based hydrogels | Antibacterial, conductive, adhesive and self-healing properties. | Photothermal antibacterial property, reduced inflammation and increased vascular regeneration. | [100] |
| Alginate/MXene-based hydrogel | Photo- and magnetic-responsive, and precisely control release of AgNPs. | Eliminatied bacteria attachment and promoted M2 macrophages polarization and angiogenesis. | [101] |
| Epsilon-polylysine modified cellulose/γ-PGA double-network hydrogel | Good biocompatibility and antibacterial activity. | Improved collagen deposition, accelerated vascularization and enhanced cell proliferation. | [102] |
| Hyaluronic acid-EN106 hydrogels | Glucose-responsive, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory abilities, and sustained release of EN106. | Ameliorated oxidative stress and improved angiogenesis. | [104] |
| Sodium alginate hydrogel containing desferrioxamine (DFO) and bioglass | Injectable and sustained release of DFO. | Promoted wound healing by increasing HIF-1α and VEGF expression and vascularization. | [105] |
| Composite hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid/collagen /deferoxamine-loaded polydopamine nanoparticles | Desirable mechanical property, improved tissue adhesive and injectable performance. | Exhibited prominent enhancement of angiogenesis, excellent anti-inflammatory and bacteriostatic effect, promoted the M2 polarization of macrophages, and enhanced the diabetic wounds healing. | [42] |
| Exosome-loaded hydrogels based on α-Lipoic acid modified chitosan | Strong adhesion, photo-induced self-healing and pH/H2O2/glucose responsiveness | Accelerate diabetic wound healing by regulating the wound environment, such as reducing oxidative stress, lowering blood glucose levels, and promoting angiogenesis. | [106] |
3.3. Scaffolds for regenerative medicine
| Hydrogels | Properties | Functions | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collagen/alginate/fibrin-based hydrogels | Thermo-sensitivity and mechanical stiffness similar to native soft tissues | Enhanced osteogenic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells and improved aggregation MIN6 β-cells with the indication of pseudo-islets formation. | [39] |
| Gelatin/FAPi-loaded microspheres composite hydrogels | Antioxidant Properties | Promoted repair of osteoporotic bone defects by rescuing ROS microenvironment and guiding the immune response in bilateral OVX-induced osteoporotic rats. | [111] |
| RGD-modified alginate-based osteoconductive hydrogels | Tunable mechanical properties and biodegradability | Complete bone regeneration around ailing dental implants with peri-implant bone loss in a rat model. | [112] |
| GelMA-based hydrogel scaffolds containing anisotropic microchannels | Improved robustness and versatility | Encapsulated live cells at high viability levels in desired cellular alignments to fabricate muscle-tendon unit and muscle-microvascular unit | [114] |
| Magneto-patterned cellular hydrogels based on methacrylated hyaluronic acid | Pre-positioned diamagnetic objects in 3D hydrogels. | Fabricated cartilage constructs similar to natural tissue with gradient cellularity and maintained these cell gradients in the extracellular matrix content. | [115] |
3.4. Other biomedicine applications
4. Future perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein, M.; Poverenov, E. Natural biopolymer-based hydrogels for use in food and agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2020, 100, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural polymer-based hydrogels with enhanced mechanical performances: Preparation, structure, and property. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Rational design of smart hydrogels for biomedical applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 615665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sood, A.; Agrawal, G.; Thakur, S.; Thakur, V.K.; Tanaka, M.; Mishra, Y.K.; Christie, G.; Mostafavi, E.; Boukherroub, R.; et al. Polysaccharides, proteins, and synthetic polymers based multimodal hydrogels for various biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 247, 125606–125606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo, E.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Biomedical applications of hydrogels: A review of patents and commercial products. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 65, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varaprasad, K.; Vimala, K.; Raghavendra, G.M.; Jayaramudu, T.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ramam, K. Chapter 10 - Cell Encapsulation in Polymeric Self-Assembled Hydrogels. In Nanotechnology Applications for Tissue Engineering, Thomas, S.; Grohens, Y.; Ninan, N., Eds. William Andrew Publishing: Oxford, 2015, pp 149-171.
- Goswami, P.; O'Haire, T. 3 - Developments in the use of green (biodegradable), recycled and biopolymer materials in technical nonwovens. In Advances in Technical Nonwovens, Kellie, G., Ed. Woodhead Publishing: 2016, pp 97-114.
- Ghalia, M.A.; Dahman, Y. Chapter 6 - Advanced nanobiomaterials in tissue engineering: Synthesis, properties, and applications. In Nanobiomaterials in Soft Tissue Engineering, Grumezescu, A.M., Ed. William Andrew Publishing: 2016, pp 141-172.
- Ahn, W.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, J.; Lee, E.J. Designed protein- and peptide-based hydrogels for biomedical sciences. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1919–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tang, F.; Li, M.; Li, L. Facile synthesis of Ag@AgCl-contained cellulose hydrogels and their application. Colloid. Surface A 2018, 553, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Wang, W.; Govindaraj, D.; Kang, S.; Vikesland, P.J. Recent advances in environmental science and engineering applications of cellulose nanocomposites. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tec. 2023, 53, 650–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelraof, M.; Hasanin, M.S.; El -Saied, H. Ecofriendly green conversion of potato peel wastes to high productivity bacterial cellulose. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 211, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.E.; Guo, Y.Z.; Liza, A.A.; Yang, G.H.; Sipponen, M.H.; Guo, J.Q.; Li, H.M. Nanocellulose: a review on preparation routes and applications in functional materials. Cellulose 2023, 30, 4115–4147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Du, H.; Liu, K.; Nie, S.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Fabrication and applications of cellulose-based nanogenerators. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfanian, E.; Moaref, R.; Ajdary, R.; Tam, K.C.; Rojas, O.J.; Kamkar, M.; Sundararaj, U. Electrochemically synthesized graphene/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils hydrogels: Highly conductive green inks for 3D printing of robust structured EMI shielding aerogels. Carbon 2023, 210, 118037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Wu, W.; Cao, X.; Luo, Z. Copolymer-grafted cellulose nanocrystal induced nanocomposite hydrogels with enhanced strength, high elasticity and adhesiveness for flexible strain and pressure sensors. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 317, 121092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, N.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Fashandi, H. Pyridinium-based ionic liquid/water mixture intended for efficient dissolution of cellulose, chitosan and chitin: The pivotal contribution of water. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 195, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.C.; Leh, C.P.; Goh, C.F. Designing cellulose hydrogels from non-woody biomass. Carbohyd. Polym. 2021, 264, 118036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y. , Cellulose-Based Gels. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 217, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Deng, Y.; Shi, Y. Cellulose-Based Stimuli-Responsive Anisotropic Hydrogel for Sensor Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 11524–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, M.R.; Aouada, F.A.; Fajardo, A.R.; Martins, A.F.; Paulino, A.T.; Davi, M.F.T.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. Superabsorbent hydrogels based on polysaccharides for application in agriculture as soil conditioner and nutrient carrier: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 365–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Yao, J.; Cui, Y.N.; Zhao, T.; Che, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, C. Advances in Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Engineering: A Review Summary. Gels 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, M.; Lin, F.; Tang, L.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y. One-pot construction of cellulose-gelatin supramolecular hydrogels with high strength and pH-responsive properties. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 196, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, S.; Wu, Z.; Han, Z.; Qu, X.; Jin, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H. Bacterial cellulose hydrogel-based wearable thermo-electrochemical cells for continuous body heat harvest. Nano Energy 2023, 112, 108482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Qiu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Gou, D. Chitosan-based hydrogel wound dressing: From mechanism to applications, a review. Int. J Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125250–125250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peers, S.; Montembault, A.; Ladaviere, C. Chitosan hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou. E. S. Chitosan based edible films and coatings: a review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Sakib, M.N.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications-A review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Raziyeva, K.; Tabyldiyeva, L.; Berikova, K.; Zhumagul, D.; Temirkhanova, K.; Saparov, A. Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.V.; Kim, S.C. Update on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J. Smart stimuli-responsive chitosan hydrogel for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.H.; Zhan, W.; Tang, X.Z.; Mo, F.; Fu, L.H.; Lin, B.F. Self-healing chitosan/vanillin hydrogels based on Schiff-base bond/hydrogen bond hybrid linkages. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Ding, Z.; Hu, Z.; Yu, D.; Hu, Y.; Abidi, N.; Li, W. Electroresponsive Homogeneous Polyelectrolyte Complex Hydrogels from Naturally Derived Polysaccharides. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7052–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Lin, K. The development of collagen based composite scaffolds for bone regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentino, C.; Vigani, B.; Zucca, G.; Ruggeri, M.; Boselli, C.; Cornaglia, A.I.; Malavasi, L.; Sandri, G.; Rossi, S. Formulation development of collagen/chitosan-based porous scaffolds for skin wounds repair and regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 125000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajbhiye, S.; Wairkar, S. Collagen fabricated delivery systems for wound healing: A new roadmap. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 142, 213152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copes, F.; Pien, N.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Boccafoschi, F.; Mantovani, D. Collagen-Based Tissue Engineering Strategies for Vascular Medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2019, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbano, G.; Toumpaniari, S.; Popov, A.; Duan, P.; Chen, J.; Dalgarno, K.; Scott, W.E., 3rd; Ferreira, A.M. Synthesis of bioinspired collagen/alginate/fibrin based hydrogels for soft tissue engineering. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2018, 91, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda-Nieves, D.; Chaikof, E.L. Collagen and Elastin Biomaterials for the Fabrication of Engineered Living Tissues. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 694–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Gentile, P.; Chiono, V.; Ciardelli, G. Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Fan, D.; Shen, S.; Ma, X. An M2 macrophage-polarized anti-inflammatory hydrogel combined with mild heat stimulation for regulating chronic inflammation and impaired angiogenesis of diabetic wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akilbekova, D.; Shaimerdenova, M.; Adilov, S.; Berillo, D. Biocompatible scaffolds based on natural polymers for regenerative medicine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen-Carvajal, K.; Valdez-Salas, B.; Beltran-Partida, E.; Salomon-Carlos, J.; Cheng, N. Chitosan, Gelatin, and Collagen Hydrogels for Bone Regeneration. Polymers 2023, 15, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohidar, H.B.; Jena, S.S. Kinetics of sol-gel transition in thermoreversible gelation of gelatin. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 8970–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L.; Heitfeld, K.; Slone, C.; Vaia, R.A. Autonomic Hydrogels through Postfunctionalization of Gelatin. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3074–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mad-Ali, S.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Maqsood, S. Characteristics and gelling properties of gelatin from goat skin as affected by drying methods. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2017, 54, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzer, T.; Beckert, A.; Langguth, H.; Rummel, S.; Mehnert, R. Electron beam curing of methacrylated gelatin.1. Dependence of the degree of crosslinking on the irradiation dose. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1997, 63, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, A.G.; Singh, R.K.; Patel, K.D.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W. Multifunctional GelMA platforms with nanomaterials for advanced tissue therapeutics. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 267–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bupphathong, S.; Quiroz, C.; Huang, W.; Chung, P.F.; Tao, H.Y.; Lin, C.H. Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering Applications-A Review on Material Modifications. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, X.; Li, D.; Lai, X.; Liu, Y. Development of alginate-based hydrogels: Crosslinking strategies and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Singh, R.; Sarker, B.; Papageorgiou, D.G.; Juhasz-Bortuzzo, J.A.; Roether, J.A.; Cicha, I.; Kaschta, J.; Schubert, D.W.; Chrissafis, K.; et al. Hydrogel matrices based on elastin and alginate for tissue engineering applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Pei, X.; Chen, J.; Wan, Q. Alginate-based biomaterial-mediated regulation of macrophages in bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, G.; Sun, R.; Wong, C.P. Mechanical strengthened alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel crosslinked by barium and ferric dual ions. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8538–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, P. Alginate/gelatin blended hydrogel fibers cross-linked by Ca2+ and oxidized starch: Preparation and properties. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2019, 99, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Cha, C. Graft Architecture Guided Simultaneous Control of Degradation and Mechanical Properties of In Situ Forming and Fast Dissolving Polyaspartamide Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3693–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Bouhadir, K.H.; Mooney, D.J. Controlled degradation of hydrogels using multi-functional cross-linking molecules. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2461–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalanqui, M.J.; Pentlavalli, S.; McCrudden, C.; Chambers, P.; Ziminska, M.; Dunne, N.; McCarthy, H.O. Influence of alginate backbone on efficacy of thermo-responsive alginate-g-P (NIPAAm) hydrogel as a vehicle for sustained and controlled gene delivery. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2019, 95, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, G.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; He, F.; Ni, C. Drug release behavior of poly (lactic-glycolic acid) grafting from sodium alginate (ALG-g-PLGA) prepared by direct polycondensation. J. Biomat. Sci.-Polym. E 2015, 26, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follin, B.; Juhl, M.; Cohen, S.; Pedersen, A.E.; Gad, M.; Kastrup, J.; Ekblond, A. Human adipose-derived stromal cells in a clinically applicable injectable alginate hydrogel: Phenotypic and immunomodulatory evaluation. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.P.; Shin, M.; Kim, K.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H. Dynamic Bonds between Boronic Acid and Alginate: Hydrogels with Stretchable, Self-Healing, Stimuli-Responsive, Remoldable, and Adhesive Properties. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Luo, H. Constructions and Properties of Physically Cross-Linked Hydrogels Based on Natural Polymers. Polym. Rev. 2022, 63, 574–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, C.; Huo, Q.; Liu, X. Development of novel hyaluronic acid/human-like collagen bio-composite membranes: A facile “surface modification-assembly” approach. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Song, L.; Zou, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Guo, J. Role of Hyaluronic Acids and Potential as Regenerative Biomaterials in Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, G.; Holloway, J.L.; Stabenfeldt, S.E. Hyaluronic Acid Biomaterials for Central Nervous System Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2020, 9, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Z.; Thu, H.E.; Katas, H.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Biomaterials: A Versatile and Smart Approach to Tissue Regeneration and Treating Traumatic, Surgical, and Chronic Wounds. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 594–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, J.; Assmann, M.; Kuballa, J.; Elling, L. Repetitive Synthesis of High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid with Immobilized Enzyme Cascades. Chemsuschem 2022, 15, e202101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Q.; Yan, S.; Feng, L.; Lan, Y.; Shan, G.; Xue, W.; Guo, R. Enhanced healing activity of burn wound infection by a dextran-HA hydrogel enriched with sanguinarine. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2472–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cui, W.; Fang, Y.; Li, L.; Ji, S.; Mao, D.; Ke, T.; Yao, X.; Ding, D.; et al. Composite Hydrogel Modified by IGF-1C Domain Improves Stem Cell Therapy for Limb Ischemia. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4481–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadokawa, J.; Shoji, T.; Yamamoto, K. Preparation of supramolecular network materials by means of amylose helical assemblies. Polymer 2018, 140, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamruzzaman, M.; Ahmed, F.; Mondal, M.I.H. An Overview on Starch-Based Sustainable Hydrogels: Potential Applications and Aspects. J. Polym. Environ. 2021, 30, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yu, M.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, L. Recent advances in the preparation, characterization, and food application of starch-based hydrogels. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 291, 119624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Cai, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L.; Ai, Y.; Jiang, B. Interactions between exogenous free fatty acids and maize starches varying in amylose content at high heating temperatures. Food Hydrocolloid. 2023, 143, 108855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Li, Y.; An, J.; Shen, S.; Dou, H. Study on structure-function of starch by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation coupled with multiple detectors: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 226, 115330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, J.F.; Paschoalin, R.T.; Carmona, V.B.; Sena Neto, A.R.; Marques, A.C.P.; Marconcini, M.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Medeiros, E.S.; Oliveira, J.E. Biodegradable polymer blends based on corn starch and thermoplastic chitosan processed by extrusion. Carbohyd. Polym. 2016, 137, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghadam, M.; Dorraji, M.S.S.; Dodangeh, F.; Ashjari, H.R.; Mousavi, S.N.; Rasoulifard, M.H. Design of a new light curable starch-based hydrogel drug delivery system to improve the release rate of quercetin as a poorly water-soluble drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 174, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, K.; Gan, R.Y.; Sun, C.X.; Jiao, G.; Wu, D.T.; Li, H.B.; Kenaan, A.; Corke, H.; Fang, Y.P. Recent advances in the structure, synthesis, and applications of natural polymeric hydrogels. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 3817–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Li, H.; Yin, C.; Tang, F. Research progress in the application of in situ hydrogel system in tumor treatment. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, C.; Chu, W. L. Natural Polymer-based Stimuli-responsive Hydrogels. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2631–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Hui, P.; Kan, C.W. Thermoresponsive Hydrogels and Their Biomedical Applications: Special Insight into Their Applications in Textile Based Transdermal Therapy. Polymers 2018, 10, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, H.; Moradi, S.; Hudson, S.M.; Tonelli, A.E. Chitosan based hydrogels and their applications for drug delivery in wound dressings: A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 199, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Huang, A.P.H.; Hsu, S.H. Injectable, Micellar Chitosan Self-Healing Hydrogel for Asynchronous Dual-Drug Delivery to Treat Stroke Rats. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 2303853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, D.G.; Dharmaraj, N.; Piotrowski, S.L.; Lopez-Silva, T.L.; Lei, Y.L.; Sikora, A.G.; Young, S.; Hartgerink, J.D. STINGel: Controlled release of a cyclic dinucleotide for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 163, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, X.T.; Zhao, J.A.; Feng, H.Y.; Li, P.W.; Tong, Z.R.; Yang, Z.M.; Li, S.D.; Yang, J.Y.; Jin, S.H. Preparation of the chitosan/poly(glutamic acid)/alginate polyelectrolyte complexing hydrogel and study on its drug releasing property. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 191, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.D.; Das, G.; Ajayaghosh, A. Stepwise control of host-guest interaction using a coordination polymer gel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavan, M.P.; Ayyanaar, S.; Vijayakumar, V.; Raja, J.D.; Annaraj, J.; Sakthipandi, K.; Rajesh, J. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MIONs) cross-linked natural polymer-based hybrid gel beads: Controlled nano anti-TB drug delivery application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Luo, G.S.; Dai, Y.Y. In situ preparation of magnetic Fe3O4-chitosan nanoparticles for lipase immobilization by cross-linking and oxidation in aqueous solution. Bioresource Technol. 2009, 100, 3459–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hong, G.; Zhu, C.; Qian, X.; Chai, R.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y. Magnetic Hydrogel Microrobots Delivery System for Deafness Prevention. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Ouyang, H.; Zheng, X.; Qi, C.; Ma, L. Magnetically actuated hydrogel-based capsule microrobots for intravascular targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6095–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic, B.Z.; Milenkovic, M.M.; Dakic, I.R.; Todorovic-Markovic, B.M.; Milosavljevic, M.S.; Budimir, M.D.; Paunovic, V.G.; Dramicanin, M.D.; Markovic, Z.M.; Trajkovic, V.S. Photodynamic antibacterial effect of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4428–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hu, Z.; Wei, J.; Dai, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Duan, Z.; Xie, F.; Zhang, W.; Guo, R. Quantum dots-hydrogel composites for biomedical applications. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanbakht, S.; Namazi, H. Doxorubicin loaded carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene quantum dot nanocomposite hydrogel films as a potential anticancer drug delivery system. Mat. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. 2018, 87, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooresmaeil, M.; Namazi, H. Folic acid-modified photoluminescent dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose crosslinked bionanogels for pH-controlled and tumor-targeted co-drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 200, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, L.; Liang, H.; Tan, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F. pH and Glucose Dual-Responsive Injectable Hydrogels with Insulin and Fibroblasts as Bioactive Dressings for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37563–37574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Lee, G.H.; Chou, C.W.; Chen, Y.P.; Wu, T.H.; Lin, H.R. Stimulation of wound healing by PU/hydrogel composites containing fibroblast growth factor-2. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futrega, K.; King, M.; Lott, W.B.; Doran, M.R. Treating the whole not the hole: necessary coupling of technologies for diabetic foot ulcer treatment. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Kang, H.F.; Bielec, M.; Wu, X.P.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, W.Y.; Dai, H.L. Influence of different divalent ions cross-linking sodium alginate-polyacrylamide hydrogels on antibacterial properties and wound healing. Carbohyd. Polym. 2018, 197, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Alsareii, S.A.; Alamri, A.M.; Harraz, F.A.; Guo, B. Antibacterial conductive self-healing hydrogel wound dressing with dual dynamic bonds promotes infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 30, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Deng, D.; Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhong, Q. Multiple Stimuli-Responsive MXene-Based Hydrogel as Intelligent Drug Delivery Carriers for Deep Chronic Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, 2104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Feng, K.; Hu, T.; Huang, B.; Tang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Yang, G.; et al. Double-network cellulose-based hybrid hydrogels with favourable biocompatibility and antibacterial activity for wound healing. Carbohyd. Polym. 2023, 319, 121193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebitz, G.M.; Nyanhongo, G.S. Enzymes as Green Catalysts and Interactive Biomolecules in Wound Dressing Hydrogels. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zha, K.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, W.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhou, W.; Cao, F.; Hu, H.; et al. Glucose-responsive, antioxidative HA-PBA-FA/EN106 hydrogel enhanced diabetic wound healing through modulation of FEM1b-FNIP1 axis and promoting angiogenesis. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 30, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Cui, H.; Shen, J.; Chang, J.; Li, H.; He, Y. Bioactive Injectable Hydrogels Containing Desferrioxamine and Bioglass for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30103–30114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Kang, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; Dai, H. A simple yet effective hydrogel dressing for advanced microenvironmental management of diabetic wounds with intrinsic regulation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 143987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliktar, D. Designing Cell-Compatible Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Science 2012, 336, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutluk, H.; Bastounis, E.E.; Constantinou, I. Integration of Extracellular Matrices into Organ-on-Chip Systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2203256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.C.; Zhao, Y.X.; Zhang, L.Z.; Gao, M.; Kong, Y.; Yang, Y.M. Preparation of graphene oxide/polyacrylamide composite hydrogel and its effect on Schwann cells attachment and proliferation. Colloid Surf. B 2016, 143, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Han, F.; Meng, Q.; Wang, H.; Wei, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, F.; Xie, E.; Qin, X.; et al. A Multifunctional Composite Hydrogel That Rescues the ROS Microenvironment and Guides the Immune Response for Repair of Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Sarrion, P.; Pouraghaei, S.; Chau, Y.; Ansari, S.; Li, S.; Aghaloo, T.; Moshaverinia, A. An engineered cell-laden adhesive hydrogel promotes craniofacial bone tissue regeneration in rats. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, D.V.; Reichert, P.; Zvick, J.; Labouesse, C.; Kunzli, V.; Dudaryeva, O.; Bar-Nur, O.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Dual, J. Continuous Production of Acoustically Patterned Cells Within Hydrogel Fibers for Musculoskeletal Tissue Engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2113038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Tang, G.; Ravanbakhsh, H.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Kuang, X.; Garciamendez-Mijares, C.E.; Lian, L.; Yi, S.; Liao, J.; et al. Vertical Extrusion Cryo(bio)printing for Anisotropic Tissue Manufacturing. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2108931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlotnick, H.M.; Clark, A.T.; Gullbrand, S.E.; Carey, J.L.; Cheng, X.M.; Mauck, R.L. Magneto-Driven Gradients of Diamagnetic Objects for Engineering Complex Tissues. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, F.H.; Singh, A.R.; Joshi, S.; Smith, C.A.; Morales, G.A.; Garlich, J.R.; Durden, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G. Dual-activity PI3K-BRD4 inhibitor for the orthogonal inhibition of MYC to block tumor growth and metastasis. PNAS 2017, 114, E1072–E1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, M.; Li, S.; Zhu, J. Surface plasmon resonance imaging validation of small molecule drugs binding on target protein microarrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 450, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Long, S.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, X. Role of N-Cadherin in a Niche-Mimicking Microenvironment for Chondrogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Vitro. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karamikamkar, S.; Behzadfar, E.; Cheung, K.C. A novel approach to producing uniform 3-D tumor spheroid constructs using ultrasound treatment. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shamul, J.G.; Staten, N.A.; White, A.M.; Jiang, B.; He, X. Bioinspired 3D Culture in Nanoliter Hyaluronic Acid-Rich Core-Shell Hydrogel Microcapsules Isolates Highly Pluripotent Human iPSCs. Small 2021, 17, 2102219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadden, W.J.; Young, J.L.; Holle, A.W.; McFetridge, M.L.; Kim, D.Y.; Wijesinghe, P.; Taylor-Weiner, H.; Wen, J.H.; Lee, A.R.; Bieback, K.; et al. Stem cell migration and mechanotransduction on linear stiffness gradient hydrogels. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5647–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodrich, R.; Tai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Yin, Y.; Nam, J. A Magneto-Responsive Hydrogel System for the Dynamic Mechano-Modulation of Stem Cell Niche. Advanced Functional Materials 2023, 33, 2211288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, O.; Lee, K.; Alsberg, E. Spatial Micropatterning of Growth Factors in 3D Hydrogels for Location-Specific Regulation of Cellular Behaviors. Small 2018, 14, 1800579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deangelis, P.L.; Oatman, L.C.; Gay, D.F. Rapid chemoenzymatic synthesis of monodisperse hyaluronan oligosaccharides with immobilized enzyme reactors. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35199–35203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, H.P.; Wang, P.; Yu, S.H. Stretchable and Self-Healing Graphene Oxide–Polymer Composite Hydrogels: A Dual-Network Design. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H.; Shi, J.; Li, F.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, H. Bio-inspired layered chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels with high strength and pH-driven shape memory effect. Carbohyd. Polym. 2017, 177, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.W.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, Q.Y. Multi-structural network design and mechanical properties of graphene oxide filled chitosan-based hydrogel nanocomposites. Mater. Design 2018, 148, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X. Dual-crosslinked hyaluronan hydrogels with rapid gelation and high injectability for stem cell protection. Scie. Rep-UK 2020, 10, 14997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, K.; Tang, H.; Hu, S.; Xin, L.; Jing, X.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Mei, L.; et al. A Logic-Based Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hydrogel with Multistimuli Responsiveness to Orchestrate Diabetic Bone Regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimene, D.; Kaunas, R.; Gaharwar, A.K. Hydrogel Bioink Reinforcement for Additive Manufacturing: A Focused Review of Emerging Strategies. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1902026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Fei, Z.; Dai, H.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, C. 3D Printing Scaffold Vaccine for Antitumor Immunity. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Schuurmans, C.C.L.; Genderen, A.M.V.; Cao, X.; Li, W.; Cheng, F.; He, J.J.; Lopez, A.; Huerta, V.; Manriquez, J.; et al. Complexation-induced resolution enhancement of 3D-printed hydrogel constructs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandakrishnan, N.; Ye, H.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Z.; Mentkowski, K.I.; Lang, J.K.; Rajabian, N.; Andreadis, S.T.; Ma, Z.; Spernyak, J.A.; et al. Fast Stereolithography Printing of Large-Scale Biocompatible Hydrogel Models. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2002103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, T.; Hann, S.Y.; Chiesa, I.; Cui, H.; Celikkin, N.; Micalizzi, S.; Barbetta, A.; Costantini, M.; Esworthy, T.; Zhang, L.G.; et al. 4D printing in biomedical applications: emerging trends and technologies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7608–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champeau, M.; Heinze, D.A.; Viana, T.N.; de Souza, E.R.; Chinellato, A.C.; Titotto, S. 4D Printing of Hydrogels: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Ye, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, M.; Sun, M.; He, J.; Yu, X.; Ye, G.; et al. 4D Printing of Multi-Responsive Membrane for Accelerated In Vivo Bone Healing Via Remote Regulation of Stem Cell Fate. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





