Submitted:
20 September 2023
Posted:
21 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates
2.2. Physicochemical and chemical analysis of materials
- Fat – Soxhlet method, extracted with hexane using a Soxhlet automatic extractor, model B-811 BUCHI, (Büchi Labortechnik AG, Flawil, Switzerland); AOAC 920.85 [35].
- Mineral matter – ash, range: (0.02–40%), gravimetric analysis [36];
- Starch – Luff-Schoorl titration method; the determination principle is based on the reduction reaction of Cu+2 ions contained in the Luff fluid by the reducing saccharides present in the solution tested. The reaction takes place in an alkaline environment (pH of about 9.5), at the boiling point. The Luff fluid consists of copper(II) sulphate (VI), sodium carbonate and citric acid [37];
- Dietary fibre method – a chemical method in which fibre is determined as the fraction remaining after fermentation with standard solutions of 0.25 N sulphuric acid and 0.25 N sodium hydroxide under strictly controlled conditions, AOAC 962.09) [38].
2.3. Biogas Production at Laboratory Scale
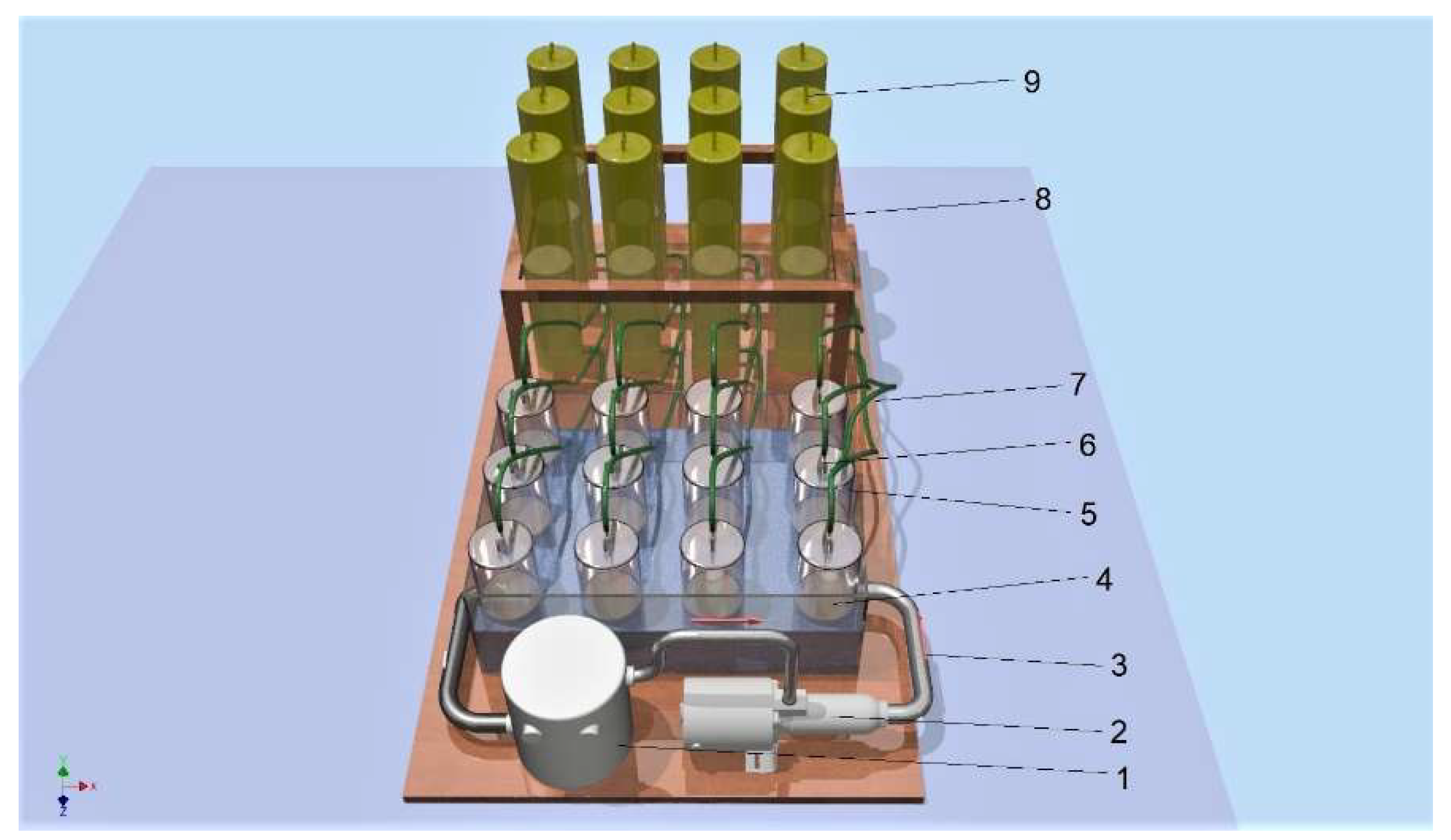
2.4. Biogas Production at Technical Scale
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Substrate chemical composition
3.2. Slurry BMP and calorific value of other substrates
3.3. Efficiency of methane and electricity production in a biogas plant: chemical energy and electricity
4. Conclusions
References
- Pilarski, K.; Pilarska, A.A.; Boniecki, P.; Niedbała, G.; Durczak, K.; Witaszek, K.; Mioduszewska, N.; Kowalik, I. The efficiency of industrial and laboratory anaerobic digesters of organic substrates: The use of the Biochemical Methane Potential Correction Coefficient. Energies 2020, 13, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarski, K.; Pilarska, A.A.; Boniecki, P.; Niedbała, G.; Witaszek, K.; Piekutowska, M.; Idzior-Haufa, M.; Wawrzyniak, A. Degree of biomass conversion in the integrated production of bioethanol and biogas. Energies 2021, 14, 7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjuki, H.M.; Kalam, M.A. An Overview of Biofuel as a renewable energy source: Development and challenges. Procedia Eng. 2013, 56, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Industrial Development Organization. The European Green Deal: Europe’s New Growth Strategy A Climate-Neutral EU by 2050; UNIDO Liaison Office in Brussels: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzak, M.B.; Igliński, B.; Kujawski, W.; Iwański, P. Energy Transition in Poland—Assessment of the Renewable Energy Sector. Energies 2021, 14, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igliński, B.; Piechota, G.; Kiełkowska, U.; Kujawski, W.; Pietrzak, M.B.; Skrzatek, M. The assessment of solar photovoltaic in Poland: the photovoltaics potential, perspectives and development. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igliński, B.; Kiełkowska, U.; Pietrzak, M.; Skrzatek, M.; Kumar, G.; Piechota, G. The regional energy transformation in the context of renewable energy sources potential. Renewable Energy 2023, 119246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witaszek, K.; Pilarski, K.; Niedbała, G.; Pilarska, A.A.; Herkowiak, M. Energy efficiency of comminution and extrusion of maize substrates subjected to methane fermentation. Energies 2020, 13, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, X.; Zhao, N.; Song, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, G. Interactive effects of carbohydrate, lipid, protein composition and carbon/nitrogen ratio on biogas production of different food wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Boniecki, P.; Zaborowicz, M. Use of confectionery waste in biogas production by the anaerobic digestion process. Molecules 2019, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, P. Biogas Production: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, T.; Nosrati, M.; Sreekrishnan, T.R. Anaerobic digestion from the viewpoint of microbiological, chemical, and operational aspects – a review. Environ. Rev. 2010, 18, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Zain, S.M.; Pramanik, B.K. The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste: Prospects and constraints. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Waliszewska, B.; Zborowska, M.; Witaszek, K.; Waliszewska, H.; Kolasiński, M.; Szwarc-Rzepka, K. Evaluation of bio-methane yields for high-energy organic waste and sewage sludge: Apilot-scale study for a wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2019, 18, 2023–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zou, L.; Qian, G.; Xu, Z.P. Improving the stability and efficiency of anaerobic digestion of food waste using additives: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 192, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Stazi, V.; Tomei, M.C. Enhancing anaerobic treatment of domestic wastewater: State of the art, innovative technologies and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva dos Santos, I.F.; Braz Vieira, N.D.; Bruni de Nóbrega, L.G.; Barros, R.M.; Tiago Filho, G.L. Assessment of potential biogas production from multiple organic wastes in Brazil: Impact on energy generation, use, and emissions abatement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 131, 54–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouallagui, H.; Lahdheb, H.; Romdan, E.B.; Rachdi, B.; Rachdi, B.; Hamdi, M. Improvement of fruit and vegetable waste anaerobic digestion performance and stability with co-substrates addition. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Ryniecki, A.; Tomaszyk, K.; Dach, J.; Wolna-Maruwka, A. Utilization of vegetable dumplings waste from industrial production by anaerobic digestion. Int. Agrophys. 2017, 31, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yin, J.; Shen, D.; Li, N. Anaerobic digestion of food waste for volatile fatty acids (VFAs) production with different types of inoculum: Effect of pH. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 161, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocamora, I.; Wagland, S.T.; Villa, R.; Simpson, E.W.; Fernández, O.; Bajón-Fernández, Y. Dry anaerobic digestion of organic waste: A review of operational parameters and their impact on process performance. Bioresour Technol. 2020, 299, 122681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, K.R.; Leong, H.Y.; Khoo, K.S.; Vo, D.V.N.; Anjum, H.; Chang, C.K.; Show, P.L. Effects of anaerobic digestion of food waste on biogas production and environmental impacts: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, D.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Tho, B.L.; Toan, P.P.S.; Minh, G.H. A review of anaerobic digestion systems for biodegradable waste: Configurations, operating parameters, and current trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydes, Andy; Cleveland, C.J. Primary energy. In: Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds. Cutler J. Cleveland, Washington, USA, D.C.: Environmental Information Coalition, National Council for Science and the Environment, June 2006.
- Øvergaard, S. Issue paper: Definition of primary and secondary Energy. Prepared as input to Chapter 3: Standard International Energy Classification (SIEC) in the International Recommendation on Energy Statistics (IRES) Norway: Oslo Group on Energy Statistics, Statistics Norway, September 2008.
- Zhu, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, H. A study on primary energy and secondary Energy price in distributed Energy projects. CUE2018-Applied Energy Symposium and Forum 2018: Low carbon cities and urban energy systems, 5–7 June 2018, Shanghai, China.
- Razmi, A.R.R.; Afshar, H.H.; Pourahmadiyan, A.; Torabi, M. Investigation of a combined heat and power (CHP) system based on biomass and compressed air energy storage (CAES). Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 46, 101253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeyoung, J. The effectiveness of combined heat and power (CHP) plant for carbon mitigation: Evidence from 47 countries using CHP plants. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 50, 101809. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Long, W. The economic analyses of cogeneration cooling heating and power on residence application, J. Archit. Sci. 2004, 20, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kabalci, E. Hybrid renewable energy systems and microgrids. Elsevier Inc., Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2020, ISBN 978-0-12-821724-5.
- Popović, M. Entropy change of open thermodynamic systems in self-organizing processes. Therm. Sci. 2014, 18(4), 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luscombe, J. Thermodynamics. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 2020, ISBN 978-0-36-757199-3.
- AOAC International. Association of Analytical Chemists Official Method 920.87. Protein (Total) in Flour. In The Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Cunniff, P., Ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Association of Analytical Chemists Official Method 920.85. Fat (Crude) or Ether Extract of Flour. In The Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Cunniff, P., Ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC International. Association of Analytical Chemists Official Method 923.03. Ash of Flour. Direct Method. In The Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Cunniff, P., Ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Marrubini, G.; Papetti, A.; Genorini, E.; Ulrici, A. Determination of the Sugar Content in Commercial Plant Milks by Near Infrared Spectroscopy and Luff-Schoorl Total Glucose Titration. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC International. Association of Analytical Chemists Official Method 962.09. Fiber (crude) in animal feed and pet food. In The Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Cunniff, P., Ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Wolna-Maruwka, A. Cell immobilization on lignin–polyvinylpyrrolidone material used for anaerobic digestion of waste wafers and sewage sludge. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN Guideline 38 414-S8. Characterisation of the Substrate, Sampling, Collection of Material Data, Fermentation Tests; German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (GUM); ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Evaluation and Quality Control of Analytical Measurement Results; Scientific-Technical Publishing House WNT: Warsaw, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sitorusa, B.; Sukandarb; Panjaitanc, S.D. Biogas recovery from anaerobic digestion process of mixed fruit-vegetable wastes. Energy Procedia 2013, 32, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butnariua, M.; Butu, A. Chemical composition of vegetables and their products; Handbook of Food Chemistry, Springer-Verlag: Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.D.; Silva, J.R.; Castro, L.M. Quinta-Ferreira, R.M. A biochemical methane potential of pig slurry. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Polo, C.; Cledera-Castro, M.M.; Soria, B.Y. M Biogas production from vegetable and fruit markets waste – compositional and batch characterizations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jay, J.; Cheng, J.J.; Creamer, K.S. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozym, M.; Florczak, I.; Zdanowska, P.; Wojdalski, J.; Klimkiewicz, M. An analysis of metal concentrations in food wastes for biogas production. Renew. Energy 2015, 77, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.; Ding, H.H.; Chang, S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) assay method for anaerobic digestion research. Water 2019, 11, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsair, A.; Cinar, S.O.; Alassali, A.; Qdais, H.A.; Kuchta, K. Operational parameters of biogas plants: A review and evaluation study. Energies 2020, 13, 3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKendry, P. Energy production from biomass (part 1): overview of biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, B.M.; Baxter, L.L.; Miles, T.R., Jr.; Miles, T.R. Combustion properties of biomass. Fuel Proc. Technol. 1998, 54, 17–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.; Sen, U.; Pereira, H. Influence of chemical composition on heating value of biomass: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Energies 2023, 16, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea-Moreno, M.A.; Samerón-Manzano, E.; Perea-Moreno, A.J. Biomass as renewable energy: Worldwide research trends. Sustainability 2019, 11, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpaz, R.; Konrada, O.; da Silva Cyrne, C.C.; Barzotto, H.P.; Hasan, C.; Filho, M.G. Using biogas for energy cogeneration: An analysis of electric and thermal energy generation from agro-industrial waste. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 40, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Cristofari, C.; Levrey, S. Cogeneration: Another way to increase energy efficiency of hybrid renewable energy hydrogen chain – A review of systems operating in cogeneration and of the energy efficiency assessment through exergy analysis. J. Energy Storage 2023, 66, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciuła, J.; Wiewiórska, I.; Banaś, M.; Pająk, T.; Szewczyk, P. Balance and energy use of biogas in Poland: Prospects and Ddrections of development for the circular economy. Energies 2023, 16, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarek, A.; Klepacka, A.M.; Siudek, A. Development barriers of agricultural biogas plants in Poland. Econ. Environ. 2023, 1(84), 229–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasnyk, O.; Sołowski, G.; Shkarupa, O. Historical, technical and economic aspects of biogas development: Case of Poland and Ukraine. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holik, M.; Zivić, M.; Virag, Z.; Barac, A.; Vujanović, M.; Avsec, J. Thermo-economic optimization of a Rankine cycle used for waste-heat recovery in biogas cogeneration plants. Energy Convrs. Manag. 2021, 232, 113897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apunda, M.O.; Oloo, B. Nyangoye selection of a combined heat and power (CHP), and CHP generation compared to buying of electrical power from the national grid and separate thermal heat production. Open Sci. J. 2017, 2(3), 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of substrate | ONI | CAR | POT | CEL | LE | PAR | MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) |
8 | 12 | 15 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 50 |
| Sub. | ONI | CAR | POT | CEL | LE | PAR | MS | ||||||||
|
Comp. and unit |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
|
|
Prot. (g) |
1.4 | 0.005 | 1.0 | 0.004 | 1.9 | 0.006 | 1.6 | 0.005 | 2.2 | 0.008 | 2.6 | 0.009 | 3.7 | 0.013 | |
|
Fat (g) |
0.4 | 0.003 | 0.2 | 0.002 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 0.5 | 0.004 | 1.5 | 0.011 | |
|
Carb. (g) |
6.9 | 0.007 | 8.7 | 0.009 | 20.5 | 0.020 | 7.7 | 0.076 | 5.7 | 0.006 | 10.5 | 0.010 | 23.5 | 0.023 | |
|
Ash (g) |
0.5 | 0.004 | 0.4 | 0.003 | 1.0 | 0.008 | 0.9 | 0.008 | 0.9 | 0.007 | 1.1 | 0.009 | 0.5 | 0.004 | |
| Water(g) | 90.8 | 0.090 | 89.7 | 0.09 | 76.5 | 0.080 | 89.5 | 0.88 | 90.9 | 0.730 | 85.3 | 0.680 | 70.8 | 0.570 | |
|
TS (%) |
9.2 | 0.074 | 10.3 | 0.083 | 23.5 | 0.189 | 10.5 | 0.084 | 9.1 | 0.073 | 14.7 | 0.118 | 29.2 | 0.243 | |
| VS (%) | 8.7 | 0.070 | 9.9 | 0.080 | 22.5 | 0.181 | 9.6 | 0.077 | 8.2 | 0.066 | 13.6 | 0.109 | 28.7 | 0.238 | |
| Sub. | ONI | CAR | POT | CEL | LE | PAR | MS | ||||||||
|
Comp. (g) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
|
| Gluc. | 1.7 | 0.010 | 1.6 | 0.009 | 0.4 | 0.002 | 0.5 | 0.003 | 1.0 | 0.006 | 0.4 | 0.002 | 0.6 | 0.004 | |
| Fruc. | 1.5 | 0.009 | 1.4 | 0.008 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 1.0 | 0.006 | 0.5 | 0.003 | 0.2 | 0.001 | |
| Sucr. | 1.9 | 0.011 | 2.0 | 0.012 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 1.7 | 0.010 | 0.8 | 0.005 | 4.8 | 0.028 | 2.2 | 0.013 | |
| Stch. | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.3 | 0.002 | 16.6 | 0.097 | 0.4 | 0.002 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.6 | 0.004 | 12.3 | 0.072 | |
| Df. | 1.7 | 0.010 | 3.6 | 0.021 | 1.6 | 0.009 | 4.9 | 0.029 | 2.7 | 0.016 | 4.2 | 0.025 | 3.3 | 0.019 | |
| Sub. | ONI | CAR | POT | CEL | LE | PAR | MS | ||||||||
|
Comp. (mg) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
Value | MU (±) |
|
| Na | 6 | 0.040 | 82 | 0.550 | 7 | 0.050 | 86 | 0.560 | 6 | 0.040 | 49 | 0.330 | 7 | 0.050 | |
| K | 121 | 0.810 | 282 | 1.890 | 491 | 3.280 | 320 | 2.140 | 248 | 1.660 | 399 | 2.670 | 283 | 1.890 | |
| Ca | 25 | 0.160 | 36 | 0.240 | 4 | 0.030 | 40 | 0.270 | 48 | 0.320 | 43 | 0.290 | 6 | 0.040 | |
| P | 14 | 0.090 | 32 | 0.210 | 61 | 0.410 | 80 | 0.540 | 52 | 0.350 | 77 | 0.510 | 102 | 0.680 | |
| Mg | 8 | 0.050 | 16 | 0.110 | 23 | 0.150 | 19 | 0.130 | 11 | 0.070 | 27 | 0.180 | 37 | 0.250 | |
| Fe | 0.50 | 0.003 | 0.50 | 0.003 | 0.60 | 0.004 | 0.50 | 0.003 | 1.10 | 0.007 | 1.10 | 0.007 | 0.80 | 0.005 | |
| Zn | 0.24 | 0.002 | 0.34 | 0.002 | 0.35 | 0.002 | 0.56 | 0.004 | 0.69 | 0.005 | 0.60 | 0.040 | 0.40 | 0.003 | |
| Cu | 0.06 | – | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.14 | 0.001 | 0.05 | – | 0.13 | 0.001 | 0.14 | 0.001 | 0.04 | – | |
| Mn | 0.17 | 0.001 | 0.19 | 0.001 | 0.10 | 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.001 | 0.18 | 0.001 | 0.58 | 0.004 | 0.20 | 0.001 | |
| pH | Measurement uncertainty (±) |
Total solids (%) |
Measurement uncertainty (±) |
Volatile solids (%) |
Measurement uncertainty (±) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.2 | 0.05 | 5.6 | 0.06 | 81.2 | 0.24 |
| Biogas from FM (m3·Mg FM-1) |
MU (±) |
Biogas from TS (m3·Mg TS-1) |
MU (±) |
Biogas from VS (m3·Mg VS-1) |
MU (±) |
Methane (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 0.24 | 321.43 | 4.46 | 395.85 | 5.66 | 51.0 |
| Sub. | Substrate amount (Mg·day-1) | Energy value (kJ·kg-1) |
Energy value (kWh·kg-1) |
Energy value (kWh·Mg-1) |
Energy value (kWh·day-1) |
Energy value (MWh·day-1) |
Energy value (MWh·year-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ONI | 4 | 1,410 | 0.392 | 392 | 1,567 | 1.567 | 572 |
| CAR | 6 | 1,400 | 0.389 | 389 | 2,333 | 2.333 | 852 |
| POT | 7.5 | 3,700 | 1.028 | 1,028 | 7,708 | 7.708 | 2,814 |
| CEL | 2.5 | 1,250 | 0.347 | 347 | 868 | 0.868 | 317 |
| LE | 2 | 1,210 | 0.336 | 336 | 672 | 0.672 | 245 |
| PAR | 3 | 2,030 | 0.564 | 564 | 1,692 | 1.692 | 617 |
| MS | 25 | 4,870 | 1.353 | 1353 | 33,819 | 33.819 | 12,344 |
| Substrates type |
Daily biogas production (m3·day-1) |
Annual biogas production (m3·year-1) |
Hourly biogas production(m3·hour-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pig slurry | 1,800 | 657,000 | 82.125 |
| Other substrates | 5,620 | 2,051,300 | 256.41 |
| Sum | 7,420 | 2,708,300 | 338.84 |
| Substrates type |
Hourly biogas production(m3·hour-1) |
Power (MW) |
Electricity produced (MWh·year-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pig slurry | 82.125 | 0.15 | 1,192 |
| Other substrates | 256.41 | 0.47 | 3,721 |
| Sum | 338.84 | 0.61 | 4,913 |
| Energy accumulated in substrates (MWh·year-1) |
Energy in methane produced (MWh·year-1) | Biomass to methane conversion efficiency (%) |
Electricity production efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17,760 | 10,633 | 59.87 | 27.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





