1. Introduction
Shiga toxin (Stx) is the defining virulence factor in Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC) which can cause gastrointestinal illness with possible life-threatening complications in humans. Two major types of Stx, Stx1 and Stx2, are further divided into subtypes, Stx1 (a, c, d) and 14 Stx2 (a-m, o).
A 2020 study from the EU found that O157 STEC was only isolated in 20.6 % of the confirmed cases of human STEC infections, the remaining 79.4% of confirmed cases were associated with non-O157 STEC [
3]. Therefore, methods for detection of toxin genes instead of or in addition to serogroup detection are important diagnostic tools for STEC infection.
In 2012, a standardized Stx nomenclature was established for Stx1/Stx2 and associated subtypes, which included Stx2a-Stx2g [
4]. In the last ten years, additional Stx2 subtypes, Stx2h-Stx2m have been described and named following the standardized Stx nomenclature: Stx2h [
5], Stx2i [
6], Stx2j [
1], Stx2k [
7], Stx2l [
8], Stx2m [
2], and Stx2o [
1].
As part of evaluation of the AMRFinderPlus tool [
9] for the detection of
stx variants in the Pathogen Detection system, we found 116 (0.2%) genomes among over 60,000
E. coli and
Shigella genomes screened with
stx2 B subunit sequences that fell just below the cutoffs for
stx2 subtypes a through g. Several of the new variants identified were in the process of being characterized and published by other groups (e.g., Stx2j, Stx2m and Stx2o). Among these 116 genomes, two were positive for a novel
stx2 subtype, provisionally designated
stx2n. Ten isolates; six Stx2j, one Stx2m, two Stx2n, and one Stx2o, were selected for further analysis and characterization for this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Detection of Novel Stx2 subtypes
Over 60,000
Escherichia coli and
Shigella isolates with short-read data included in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Pathogen Detection System (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens) as of February 2, 2020 were screened by both
de novo assembly using SKESA [
10] and targeted assembly using SAUTE with characterized
stx sequences as targets [
11]. Resulting assemblies were analyzed with AMRFinderPlus which includes curated Hidden Markov models (HMMs) that can identify novel divergent
stx genes [
9].
2.2. Collection of STEC strains
The standard operating procedure (SOP) for the PulseNet USA, the molecular surveillance network for foodborne disease in the United States [
12] includes upload of raw sequence reads to NCBI, where the novel
stx subtypes were detected. Limited metadata is available within the NCBI BioSample records for these clinical isolates due to laws that prevent sharing of personally identifiable information (PII) [
13].
2.3. Illumina and Oxford Nanopore Sequencing and Assembly
DNA was extracted from bacterial cells using the Promega Wizard kit (Promega Wizard Genomic DNA Purification Kit, Promega Corporation, Madison, WI), wide-bore pipette tips and minimal handling were used to produce high molecular weight DNA. A single DNA extract was used for all sequencing methods. Illumina MiSeq libraries were prepared with the DNA Prep Library kit (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA), using modified bead ratios for optimal fragment size, following the PulseNet standard operating procedure (SOP) PNL35 (
https://www.cdc.gov/pulsenet/pathogens/wgs.html) and sequenced to a minimum of 40X coverage [
14]. Nanopore MinION libraries were prepared with the Rapid Barcoding kit according to manufacturer’s protocol without size selection or normalization and sequenced for 72 hours on the R9.4.1 flow cell (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, Oxford, UK).
Illumina raw reads were analyzed with a PulseNet customized version of BioNumerics (Applied Maths, Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium), a commercial off-the-shelf data analysis and management software to assemble (SPAdes v2.2) then analyze the WGS [
12].
The complete hybrid genome assembly comprising the chromosome and plasmid(s) for the Stx2n and Stx2o isolates was obtained by
de novo assembly using nanopore data and Flye v2.8 [
15]. Second Hybrid genome assembly was created using both Illumina and Nanopore reads with Unicycler v0.4.8 [
16]. The hybrid and Flye assemblies for each isolate were aligned with Mauve v2.4.0 [
17] to look for any disagreement in synteny, size, or completeness. Since both genome assemblies (hybrid and nanopore only) for these three isolates agreed in all those requirements, the hybrid assembly was determined to be the final assembly (
i.e., complete genome). Unicycler assembled the chromosome and plasmids as circular closed and oriented the chromosome to start at the
dnaA gene. The genomes were annotated using the NCBI Prokaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline (PGAP v5.0,
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/annotation_prok) [
18].
2.4. WGS based Characterization
The serotype and virulence gene content of the Stx2j, Stx2m, Stx2n and Stx2o assemblies were identified using the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (
http://www.genomicepidemiology.org) web-based Serotype Finder 2.0.2 and Virulence Finder 1.5 tools [
19,
20,
21].
Multi-Locus Sequence Types were confirmed using an
in silico E. coli MLST approach, based on the information available at the
E. coli MLST website (Enterobase
https://enterobase.warwick.ac.uk/species/index/ecoli) and using Ridom SeqSphere+ software v2.4.0 (Ridom; Münster, Germany) (
http://www.ridom.com/seqsphere), through BioNumerics (using the same scheme), or with Torsten Seemann’s command line software mlst v2.23.0 (
https://github.com/tseemann/mlst#cit https://github.com/tseemann/mlst#citations ations). Seven housekeeping genes (adk, fumC, gyrB, icd, mdh, purA, and recA), described previously for
E. coli [
22], were used for MLST analysis and to assign numbers for alleles and sequence type (ST) (
https://github.com/tseemann/mlst/tree/master/db/pubmlst/ecoli_achtman_4).
2.5. Stx subtyping
The Stx subtypes of the selected STEC isolates were determined by ABRicate version
0.8.10 (
https://github.com/tseemann/abricate, accessed on 1 March 2020) with the default parameters. Briefly, a stx subtyping database was created with ABRicate by including representative nucleotide sequences of all identified Stx1 and Stx2 subtypes.
The assemblies were then searched against the stx subtyping database. For the stx genes that yield an identity below 96% with the nearest known stx subtype, the full nucleotide sequences were extracted and compared to the GenBank database with the NCBI Blast tool.
The representative nucleotide sequences of all the
stx2 subtypes and variants (
stx2a-stx2m, stx2o) described previously were downloaded from GenBank (Stx2h [
5], Stx2i [
6], Stx2j [
1], Stx2k [
7], Stx2l [
8], Stx2m [
2], Stx2o [
1]). The amino acid sequences for the combined A and B subunits of Stx2 holotoxin were translated from the open reading frames. The full amino acid and nucleotide sequences were aligned to calculate the genetic distances between
stx2/Stx2 sequences. Evolutionary unrooted trees were created from maximum parsimony cluster analysis using 100 bootstrap resamples. Also, the amino acid sequences were analyzed for sequence motifs that support the phylogenetic analyses using BioNumerics version 7.6 (Applied Maths, Ghent, Belgium), as previously described Scheutz, F., et al., [
4].
2.6. Cytotoxicity, Ciprofloxacin (Cip) induction, and activation assays
The level of cytotoxicity from culture supernatant fractions or cell fractions were determined on Vero cells as previously described [
23]. Sub-lethal concentrations of ciprofloxacin (5ng/mL) were added to some cultures for evaluation of induction. The toxins were tested for activation by incubation of the supernatant fractions with mouse intestinal mucus or a buffer control for 1-2 hours then determining the toxicity on Vero cells as described previously [
24].
2.7. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) primers to detect all described stx1 and stx2 subtypes
Primers for this study, were redesigned and tested independently in three laboratories for detection of all 18 Stx1/Stx2 subtypes (
Table S1). PCR was done for each target in a total volume of 20 µl with 10 µl HotStarTaq Master Mix Kit (Qiagen), 5 µl of primer mix (20 µM each primer), and 5 µl supernatant of boiled lysate. The thermocycler conditions were 95°C for 15 min followed by 35 cycles of 94°C for 50 s, 62°C for 40 s, and 72°C for 50 s, ending with 72°C for 3 min. PCR amplicons were stored at 4°C. Amplicons were separated on a 2% agarose gel stained with GelRed for a total of 30 minutes at 100 volts.
Table 1.
Primers for detection of all known Stx1 and Stx2 subtypes.
Table 1.
Primers for detection of all known Stx1 and Stx2 subtypes.
| Primer Name |
Primer Sequence |
Amplicon Size (bp) |
Reference |
|
stx2-PS8-F |
5’-TCACYGGTTTCATCATATCTGG |
400 |
This study |
|
stx2-PS7-R |
5’-GCCTGTCBCCASTTATCTGACA |
|
| PS19 stx2f-F |
5’-GTACAGGGATGCAGATTGGGCG |
438 |
This study |
| PS20 stx2f -R |
5’-CTTTAATGGCCGCCCTGTCTCC |
|
| PS17 eae-F |
5’-CGGCTATTTCCGCATGAGCGG |
223 |
This study |
| PS18 eae-R-NEW |
5´AGTTDACACCAAYWGTCRCCGC |
|
|
stx1 F3b |
5’-CTGATGATTGATAGTGGCACAGG |
283 |
This study |
|
stx1 OMNI-R1 |
5’-GCGATTTATCTGCATCCCCGTAC |
|
2.8. Stx2n and Stx2o pro-phages annotation and discovery
The pro-phages carrying
stx2n and
stx2o genes were identified using Phaster (
https://phaster.ca). The Stx2 pro-phage region flanked by
attL and
attR sites from each genome strain were extracted and annotated using Galaxy tracker Prokka 1.14.6 [
25] and visualized with SnapGene Viewer v6 (
https://www.snapgene.com/snapgene-viewer).
2.9. Data availability
Raw sequences, along with their limited metadata, are publicly available in the sequence read archive (SRA) housed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under BioProject PRJNA218110, the accession numbers are shown in
Table 3.
3. Results
3.1. Identification of two Novel Stx2 Subtypes
An evaluation of the AMRFinderPlus tool for the detection of stx gene variants in the Pathogen Detection system, found 116 (0.2%) genomes among over 60,000 E. coli and Shigella genomes screened with stx2 B subunit sequences that fell just below the cutoffs for stx2 subtypes a through g. Several of the new variants identified were in the process of being characterized and published by other groups (e.g., Stx2j, Stx2m and Stx2o). Among these 116 genomes, two were positive for a novel Stx2 subtype, provisionally designated Stx2n, and the remaining 114 were closely related to recently described identical subtypes Stx2j [MZ229608 and MZ571121] or Stx2o [MZ229604], or Stx2m [OQ054797]. Three strains 2013C-3244, 2017C-4317 and 2018C-3367 were selected for resequencing to generate closed genomes for further analysis.
The in-house stx-subtyping based on whole-genome sequences showed that the stx2 sequences from a representative Stx2n strain shared less than 94.6% nucleic acid sequence identities with other stx2 subtypes. stx2 genes and Stx2 proteins were extracted from the genome assemblies and compared against the GenBank database using NCBI BLAST. These comparisons showed the highest similarity (94.6%) with the Stx2n strain. When comparing sequences of Stx2 holotoxin, Stx2n shared 72.2 to 94.6% similarity with the other 14 described Stx2 subtypes at nucleic acid level and 83.9 to 95% at amino acid level (
Table 2). The last six amino acids in the A subunit were absent, which is also where the amino acid differences between the seven variants of Stx2j were found. All seven Stx2j variants had identical B subunits. These results suggest that the two provincial STEC strains harbor novel Stx2 subtypes. Based on the standardized nomenclature for Stx2 [
4], the new Stx2 subtype was designated Stx2n.
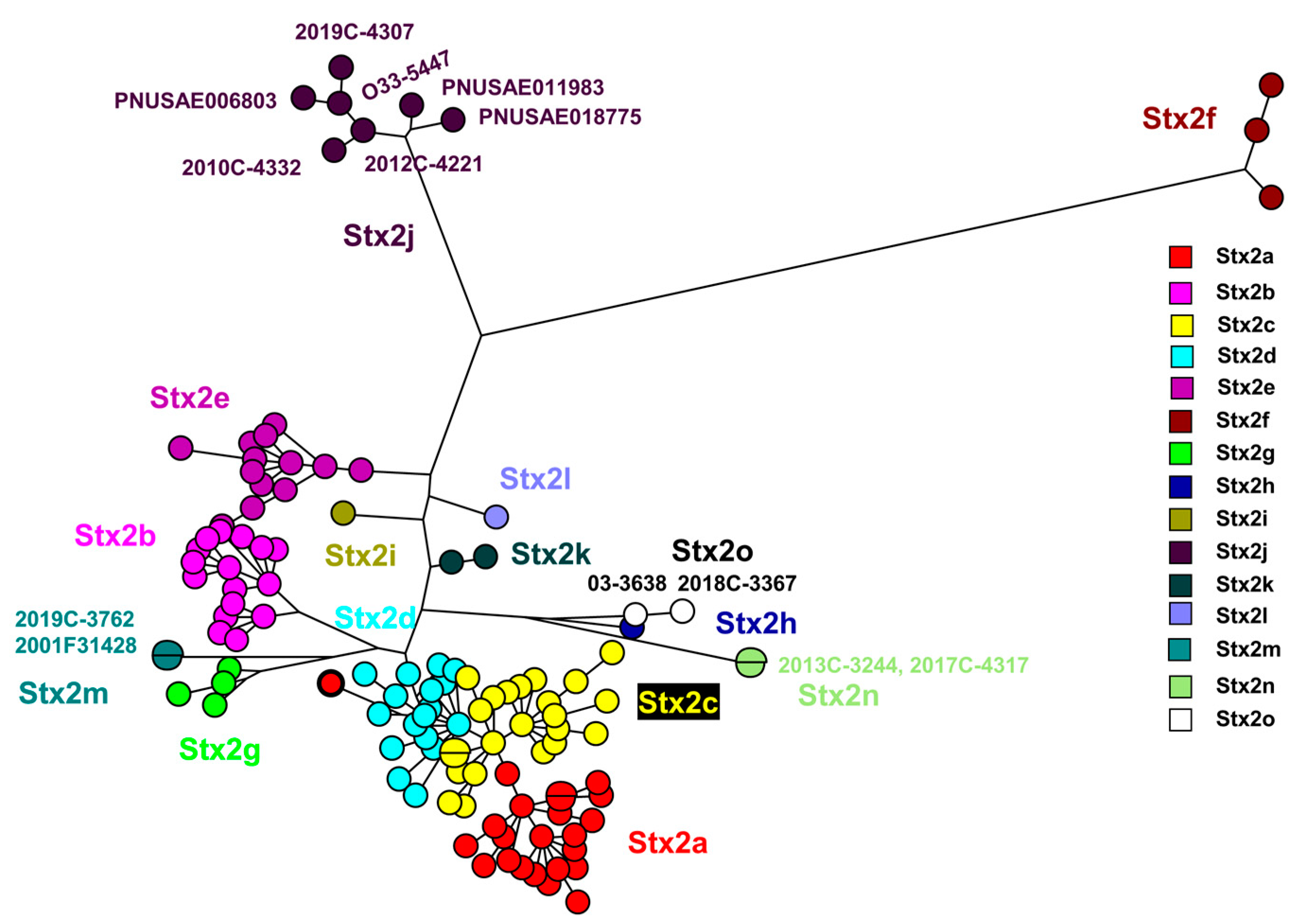
The Stx2 subtype amino acid comparison using a maximum parsimony tree (
Figure 1) included the novel strains described here: 2017C-4317, 2013C-3244, 2018C-3367, 03-3638 [
5]. Strains 2012C-4221
*, 2019C-4307, 2019C-4332, 2010C-4332, PNUSAE011983 and 2019C-3762 from this study grouped with previously described Stx2j and Stx2m sequences.
Supplementary Table S2 list data for all the sequences in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. *O162 was determined by in silico serotyping as positive for both wzmO162 and wztO162. Phenotypic O grouping was positive for O101.
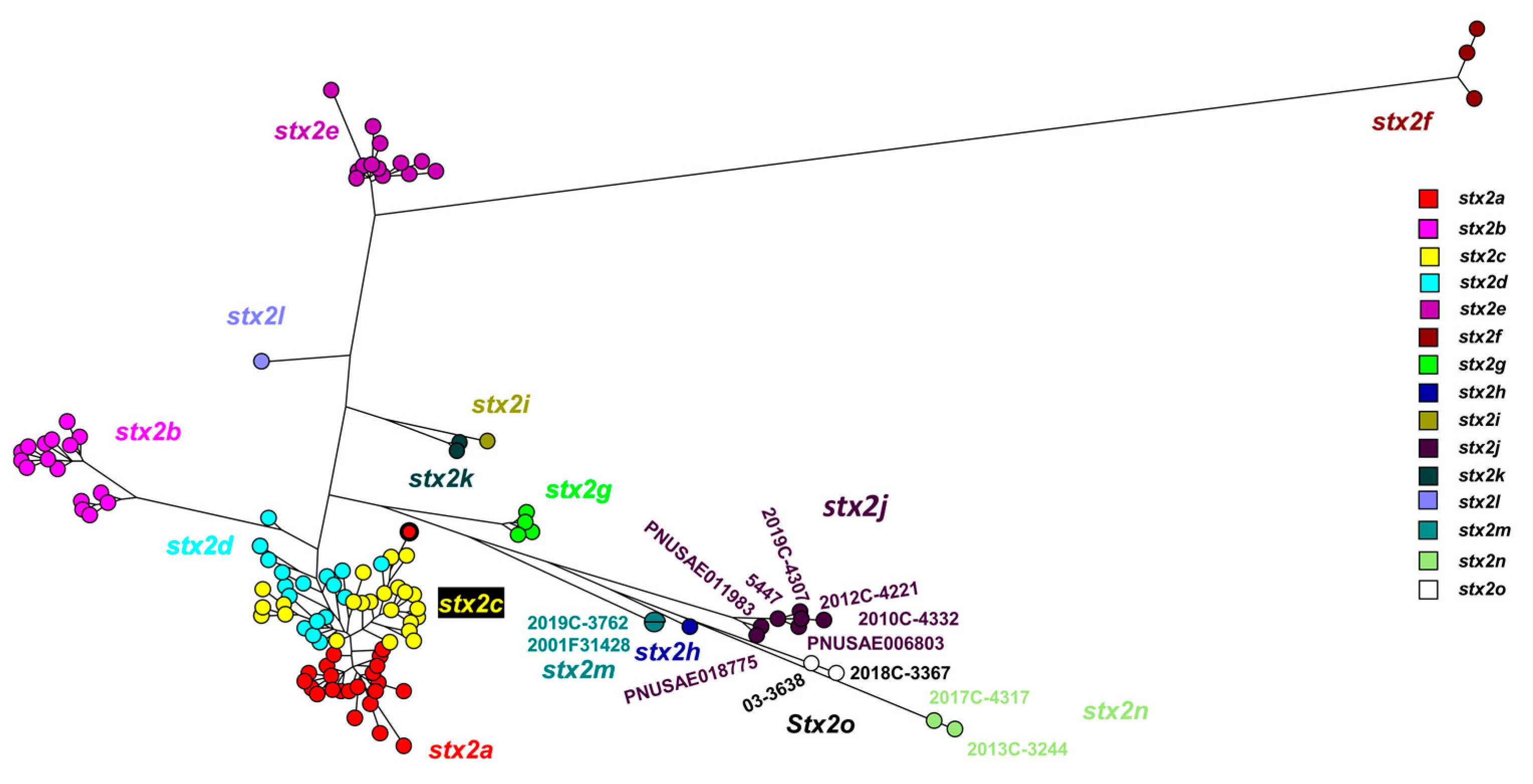
The Stx2 subtype nucleotide comparison using a maximum parsimony tree (
Figure 2) included the novel strains described in this study: 2017C-4317, 2013C-3244, 2018C-3367, and previously mentioned 03-3638 [
5]. Strains 2012C-4221, 2019C-4307, 2010C-4332, PNUSAE018775, PNUSAE006803, PNUSAE011983 and 2019C-3762 , from this study grouped with previously described Stx2j and Stx2m sequences [
2]. These strains were included in primer design to ensure detection of known diversity present in Stx2j and Stx2m.
3.2. WGS based Characterization of Stx2n and a Stx2o strains
The ten strains in this study are all different serotypes and STs (
Table 3) and show variability across time (isolated from 2010-2019).
Table 3.
Characterization of Stx2j, Stx2m, Stx2n and a Stx2o-producing STEC strains.
Table 3.
Characterization of Stx2j, Stx2m, Stx2n and a Stx2o-producing STEC strains.
| Stx Subtype |
CDC isolate ID |
BioSample |
ST type |
O:(K):H type |
PNID |
Assembly |
| stx2j |
2010C-4332 |
SAMN04377066 |
5662 |
O158:H23 |
PNUSAE001889 |
GCA_012764415.1 |
| stx2j |
2012C-4221 |
SAMN08579578 |
5350 |
O162:H6 |
None |
GCA_003018235.1 |
| stx2j |
2019C-4307 |
SAMN12361752 |
5736 |
O32:K87:H2 |
PNUSAE027323 |
GCA_011901845.1 |
| stx2j |
See PNUSAE |
SAMN10170522 |
491 |
ONT:H45 |
PNUSAE018775 |
GCA_003903075.2 |
| stx2j |
See PNUSAE |
SAMN07177511 |
5923 |
O33:H14 |
PNUSAE006803 |
GCA_012463025.1 |
| stx2j |
See PNUSAE |
SAMN08595463 |
657 |
O183: H18 |
PNUSAE011983 |
GCA_012253565.1 |
| stx2m |
2019C-3762 |
SAMN11569941 |
9312 |
O38:H39 |
PNUSAE024072 |
GCA_011950125.1 |
| Stx2n* |
2013C-3244 |
SAMN04578435 |
1385 |
O1:K22:H4 1
|
None |
GCA_012711215.22
|
| Stx2n* |
2017C-4317 |
SAMN07709929 |
70 |
O23:H15 |
PNUSAE009425 |
GCA_013342905.22
|
| Stx2o |
2018C-3367 |
SAMN08799860 |
80 |
O75:H7 |
PNUSAE012694 |
GCA_012224845.22
|
WGS virulence analysis showed that thirty-two virulence genes were harbored between the three isolates, the number of virulence genes varied between the three isolates with 2017C-4317 harboring 9 of 32, 2013C-3244 harboring 18 of 32, and 2018C-3367 harboring 27 of 32 total virulence genes (
Table 4). All three isolates harbored stx2, chuA, gad, kpsE, kpsMII_K5, sitA and terC (
Table 4). In addition, 2017C-4317 harbored virulence genes; stx2n, traT, and eilA. 2013C-3244, harbored additional virulence genes; stx2n, focC, fyuA, iroN, irp2, iss, ompT, sfaD, sfaS, tcpC, vat, and yfcV. The virulence profile for 2018C-3367 harbored virulence genes; stx2o, focC, fyuA, iroN, irp2, iss, ompT, sfaD, vat, yfcV, neuC, clbB, cnf1, hra, ibeA, mchB, mchC, mchF, mcmA, and pic (
Table 4). The presence of fyuA, vat, and yfcV qualifies 2013C-3244 and 2018C-3367 as UPEC
HM according to the current definition of UPEC [
27].
3.3. Detection of Shiga Toxin Production
Culture supernatant from each strain was tested for cytotoxicity on Vero cells as described previously [
23]. The isolates in this study demonstrated toxicity for Vero cells,
Table 5. Additionally, strain 2012C-4221 could be induced when grown with sub-inhibitory concentrations of ciprofloxacin, and toxicity was detected,
Table 5. All the strains were positive for stx2 when tested with OMNI primers, described in this publication (
Table 5). None of the supernatants showed increased toxicity after incubation with mouse intestinal mucus (activation), although the control Stx2d sample did show activation (data not shown).
3.4. Design and testing of new OMNI PCR primers
The original stx1 primer to detect all stx1 subtypes [
4] was redesigned to produce a slightly larger fragment by using a conserved upstream sequence as the new forward primer, now identified as stx1 F3b and by reversing the original forward primer (stx1-det-F1), now stx1 OMNI-R1 (table 1). This change allows for the detection of a slightly larger fragment (283 bp) and a clear separation of the stx1 fragment from the newly developed fragment for the detection eae. The stx2 primers (stx2-PS8-F, stx2-PS7-R) were redesigned to detect all known stx2 subtypes stx2a-stx2o with a 399bp amplicon, except for stx2f. It needs the stx2f specific primers for a 438bp amplicon (This study, table 1). The eae primers (PS17 eae-F, PS18 eae-R-NEW) are designed to detect all known eae genes, this includes all variants of eae found in Citrobacter spp. These primers were tested in three different laboratories, using standard reference strains to confirm detection and amplicon size.
3.5. Identification of the Stx2n and Stx2o pro-phages in the strains from this study
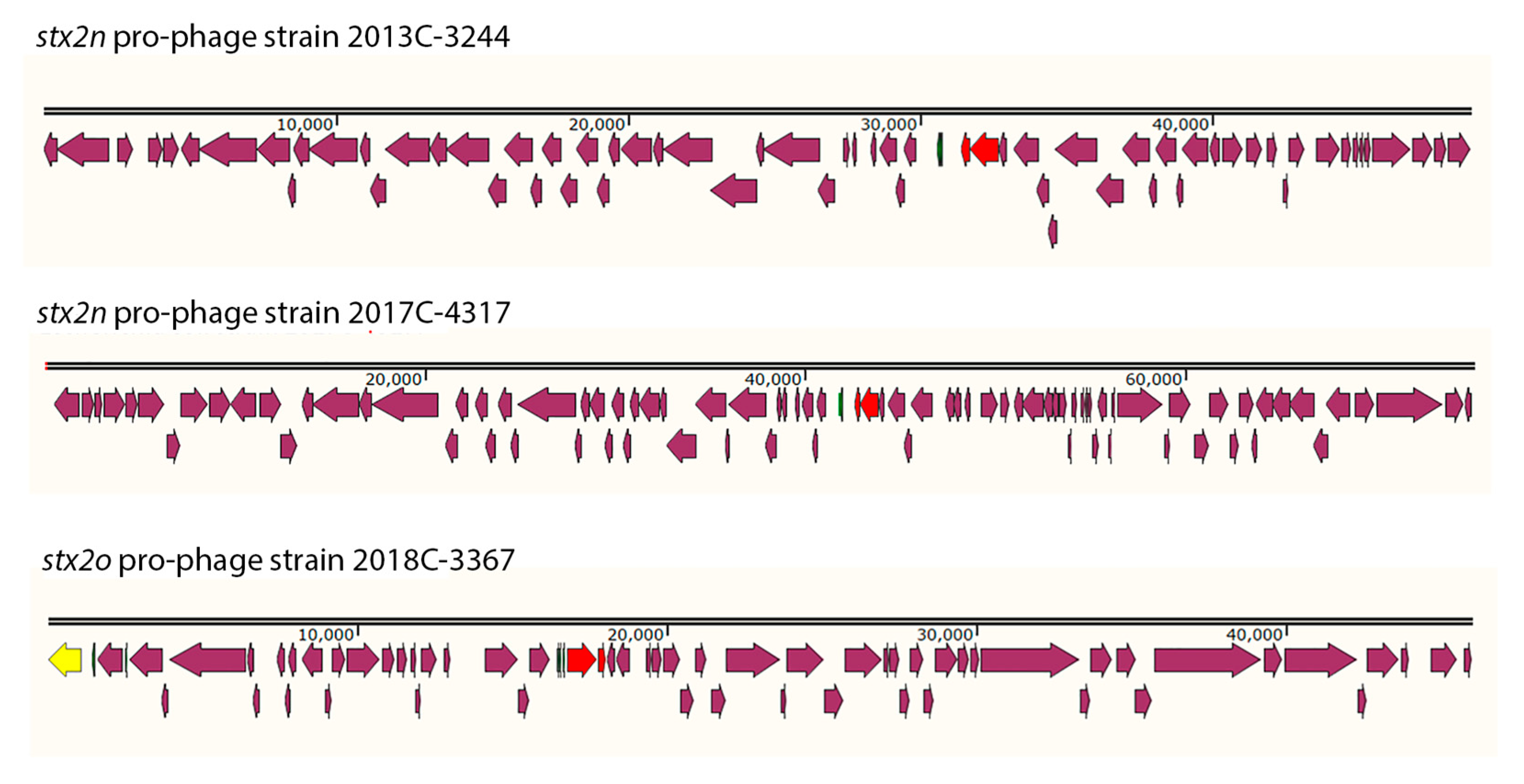
The Stx2 pro-phages were identified in different locations for each strain from this study (Supplementary figure 1). The Stx2 pro-phages were all different sizes and gene compositions, even among the two stx2n strains (
Figure 3). stx2n pro-phage in strain 2013C-3244 was 45.2Kb in size and the %GC content was 49.97. stx2n pro-phage in strain 2017C-4317 was 75.1Kb in size and the %GC content was 50.76. stx2o pro-phage in strain 2018C-3367 was 45.9Kb in size and the %GC content was 49.63. The attL and attR were also different for each Stx2 pro-phages. For strain 2013C-3344 the attL sequence for the stx2n pro-phage was TGGCGAAAAACTG and located at the following coordinates in the chromosome 2,048,352, while the identical attR sequence was located at 2,086,928. In the case of the stx2n for strain 2017C-4317 the attL sequence for the stx2n pro-phage was TTAATTAATTTA and located at the following coordinates in the chromosome 2,907,157, while the identical attR sequence was located at 2,982,293. For strain 2018C-3367 the attL sequence was TCAATCACTTACA and located at 2,071,326, while the identical attR was located at 2,113,169. Most of the genes identified in these three pro-phages coded for hypothetical proteins.
4. Discussion
In our present study, novel Stx-producing STEC strains were isolated from patients in clinical settings in the United States. Six
stx2j strains were included in figures 1, 2 and table 3, to demonstrate the diversity in the
stx2j subtype when compared to each other and strains described by Gill
et.al. Here,
Stx2j subtype strains, 2010C-4332, 2012C-4221, 2019C-4307, PNUSAE018775, PNUSAE006803 and PNUSAE011983 were identified in six different serogroups (O158, O162, O32, ONT, O33 and O183) and STs (5662, 5350, 5736, 491, 5923 and 657) over a period of 11 years. The
stx2m strain, 2019C-3762, was included here to demonstrate the diversity in this subtype when compared to strains described by Bai
et.al. The two Stx2n
-STEC isolates, 2017C-4317 and 2013C-3244, show diversity in serotype (O23 and O1) and ST (70 and 1385). The Stx2o strain, 2018C-3367, was included here to demonstrate the diversity in this subtype when compared to strains described by
Gill, et al [
1]. The genome assemblies for the Stx2 subtype strains (
Table 3) will be published in future Microbial Resource Announcements.
The stx2 pro-phages for Stx2n and Stx2o strains described here (2013C-3244, 2017C-4317, 2018C-3367) were identified in different locations (figure 3), were all different sizes and gene compositions (
Table 4), even among the two
stx2n strains (figure S1). The facts that Our findings that the strains carrying these
stx2 subtypes have different predicted serogroups, are in separate ST classes, and were isolated in different years and different locations demonstrates that the phages that encode these toxin subtypes are mobile and have spread among different
E. coli, as has been shown for other
stx-phages [
28].
The virulence gene profile (
Table 3) highlights the variability of known virulence genes among the three isolates, with 2017C-4317 harboring 9 of 32, 2013C-3244 harboring 18 of 32, and 2018C-3367 harboring 27 of 32 total virulence genes (
Table 4). Of note the STEC strains 2013C-3244 and 2018C-3367, carry the genes
fyuA, vat, and
yfcV, which qualifies these two strains as UPEC
HM according to current definition of UPEC [
27]. Strains classified as multiple pathotypes can be more dangerous to human health because once an initial pathotype is detected, analysis may stop, missing additional virulence genes related to a second pathotype related to human illness. The O104 outbreak in Europe was caused by a strain that was both STEC and EAEC [
29]. A complete WGS analysis of
E. coli includes databases from CGE that were designed to provide a complete examination of important genes such as those for serotyping, virulence genes and pathotype [
19,
27]. We note that the public contribution of surveillance data by groups such as PulseNet and publicly available analysis results such as MicroBIGG-E (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/microbigge) demonstrate the power of large-scale and open data analysis to identify novel genes and variants important to public health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: Supplementary Table S1; Statens Serum Institut strain collection of reference strains harboring the
stx gene subtypes, their O:H serotype, additional virulence genes and identification numbers. Table S2: Supplementary Table S2: Sequence information including Accession numbers, protein and nucleotide sequences. Figure S1 Location of pro-phages identified by Phaster (
https://phaster.ca) in the chromosome of the strains carrying novel stx2 types (stx2n and stx2o) reported in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.P., B.K., F.S.C., and R.L.; methodology, M.F., A.S., and A.P.; validation, A.M-C., C.K., N.G-E., and M.F.; investigation, A.M-C., F.S.C., J.T., C.K., N.G-E., R.L., and P.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.P., N.G-E, and R.L.; writing—review and editing, A.P., B. K., and F.S.C.; visualization, F.S.C. and N.G-E; project administration, A.P. and R.L.
Funding
For CDC associated work, this research was funded by the Advanced Molecular Detection (AMD) Initiative grant number AMD-21 at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. This project was supported in part by an appointment to the Research Participation Program at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education through an interagency agreement between the U.S. Department of Energy and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. As well as NCBI associated research was supported by the National Center for Biotechnology Information of the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious disease (NIAID), National Institutes of Health. Dr. Flemming Scheutz was partially funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No 773830.
Data Availability Statement
The whole genome sequence data for this study is publicly available at NCBI. Specific NCBI Accession numbers are listed in
Table 3 and in supplementary tables S1 and S2. The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the author(s) and do not and do not reflect the view of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Department of Health and Human Services, or the United States government. Furthermore, the use of any product names, trade names, images, or commercial sources is for identification purposes only, and does not imply endorsement or government sanction by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders and contract company, Weems Design Studio, had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the result.
References
- Gill, A.; Dussault, F.; McMahon, T.; Petronella, N.; Wang, X.; Cebelinski, E.; Scheutz, F.; Weedmark, K.; Blais, B.; Carrillo, C. Characterization of Atypical Shiga Toxin Gene Sequences and Description of Stx2j, a New Subtype. J Clin Microbiol 2022, 60, e0222921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Scheutz, F.; Dahlgren, H.M.; Hedenstrom, I.; Jernberg, C. Characterization of Clinical Escherichia coli Strains Producing a Novel Shiga Toxin 2 Subtype in Sweden and Denmark. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety, A.; European Centre for Disease, P. ; Control. The European Union One Health 2020 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J 2021, 19, e06971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, F.; Teel, L.D.; Beutin, L.; Pierard, D.; Buvens, G.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A.; Caprioli, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Morabito, S.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of a sequence-based protocol for subtyping Shiga toxins and standardizing Stx nomenclature. J Clin Microbiol 2012, 50, 2951–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Fan, R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; He, X.; Xu, J.; Xiong, Y. Identification and pathogenomic analysis of an Escherichia coli strain producing a novel Shiga toxin 2 subtype. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacher, D.W.; Gangiredla, J.; Patel, I.; Elkins, C.A.; Feng, P.C. Use of the Escherichia coli Identification Microarray for Characterizing the Health Risks of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Foods. J Food Prot 2016, 79, 1656–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Fu, S.; Fan, R.; He, X.; Scheutz, F.; Matussek, A.; Xiong, Y. Escherichia coli strains producing a novel Shiga toxin 2 subtype circulate in China. Int J Med Microbiol 2020, 310, 151377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panel, E.B.; Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Pathogenicity assessment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and the public health risk posed by contamination of food with STEC. EFSA Journal 2020, 18, e05967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldgarden, M.; Brover, V.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Frye, J.G.; Haendiges, J.; Haft, D.H.; Hoffmann, M.; Pettengill, J.B.; Prasad, A.B.; Tillman, G.E.; et al. AMRFinderPlus and the Reference Gene Catalog facilitate examination of the genomic links among antimicrobial resistance, stress response, and virulence. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souvorov, A.; Agarwala, R.; Lipman, D.J. SKESA: strategic k-mer extension for scrupulous assemblies. Genome Biol 2018, 19, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souvorov, A.; Agarwala, R. SAUTE: sequence assembly using target enrichment. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolar, B.; Joseph, L.A.; Schroeder, M.N.; Stroika, S.; Ribot, E.M.; Hise, K.B.; Gerner-Smidt, P. An Overview of PulseNet USA Databases. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2019, 16, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, E.L.; Carleton, H.A.; Beal, J.; Tillman, G.E.; Lindsey, R.L.; Lauer, A.C.; Pightling, A.; Jarvis, K.G.; Ottesen, A.; Ramachandran, P.; et al. Use of Whole Genome Sequencing by the Federal Interagency Collaboration for Genomics for Food and Feed Safety in the United States. J Food Prot 2022, 85, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poates, A.; Truong, J.; Lindsey, R.; Griswold, T.; Williams-Newkirk, A.J.; Carleton, H.; Trees, E. Sequencing of Enteric Bacteria: Library Preparation Procedure Matters for Accurate Identification and Characterization. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2022, 19, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput Biol 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy In Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J Clin Microbiol 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabol, A.; Joung, Y.J.; VanTubbergen, C.; Ale, J.; Ribot, E.M.; Trees, E. Assessment of Genetic Stability During Serial In Vitro Passage and In Vivo Carriage. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2021, 18, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: an evolutionary perspective. Mol Microbiol 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, J.R.; Atitkar, R.R.; Petro, C.D.; Lindsey, R.L.; Strockbine, N.; O'Brien, A.D.; Melton-Celsa, A.R. The Virulence of Escherichia coli O157:H7 Isolates in Mice Depends on Shiga Toxin Type 2a (Stx2a)-Induction and High Levels of Stx2a in Stool. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton-Celsa, A.R.; Darnell, S.C.; O'Brien, A.D. Activation of Shiga-like toxins by mouse and human intestinal mucus correlates with virulence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O91:H21 isolates in orally infected, streptomycin-treated mice. Infect Immun 1996, 64, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Bai, X.; Zhao, A.; Lan, R.; Du, H.; Wang, T.; Shi, C.; Yuan, X.; Bai, X.; Ji, S.; et al. Characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from healthy pigs in China. BMC Microbiol 2014, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malberg Tetzschner, A.M.; Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Lund, O.; Scheutz, F. In Silico Genotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates for Extraintestinal Virulence Genes by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J Clin Microbiol 2020, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.T.; Salvador, A.; Sun, X.; Wu, V.C.H. Prediction, Diversity, and Genomic Analysis of Temperate Phages Induced From Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli Strains. Front Microbiol 2019, 10, 3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheutz, F.; Nielsen, E.M.; Frimodt-Moller, J.; Boisen, N.; Morabito, S.; Tozzoli, R.; Nataro, J.P.; Caprioli, A. Characteristics of the enteroaggregative Shiga toxin/verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 strain causing the outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Germany, May to June 2011. Euro Surveill 2011, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Brien AD, Newland JW, Miller SF, Holmes RK, Smith HW, Formal SB. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 1984, 226, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch C, Hertwig S, Lurz R, Appel B, Beutin L. Isolation of a lysogenic bacteriophage carrying the stx1OX3 gene, which is closely associated with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains from sheep and humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3992–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton AW, Beutin L, Paton JC. Heterogeneity of the amino-acid sequences of Escherichia coli Shiga-like toxin type-I operons. Gene. 1995, 153, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürk C, Dietrich R, Açar G, Moravek M, Bülte M, Märtlbauer E. Identification and characterization of a new variant of Shiga toxin 1 in Escherichia coli ONT:H19 of bovine origin. J Clin Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piérard D, Muyldermans G, Moriau L, Stevens D, Lauwers S. Identification of new verocytotoxin type 2 variant B-subunit genes in human and animal Escherichia coli isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1998, 36, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paton AW, Paton JC, Heuzenroeder MW, Goldwater PN, Manning PA. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a variant Shiga-like toxin II gene from Escherichia coli OX3:H21 isolated from a case of sudden infant death syndrome. Microb Pathog. 1992, 13, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson S, Olsen KE, Ethelberg S, Scheutz F. Subtyping method for Escherichia coli shiga toxin (verocytotoxin) 2 variants and correlations to clinical manifestations. J Clin Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2020–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein DL, Jackson MP, Samuel JE, Holmes RK, O'Brien AD. Cloning and sequencing of a Shiga-like toxin type II variant from Escherichia coli strain responsible for edema disease of swine. J Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4223–4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt H, Scheef J, Morabito S, Caprioli A, Wieler LH, Karch H. A new Shiga toxin 2 variant (Stx2f) from Escherichia coli isolated from pigeons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung PH, Peiris JS, Ng WW, Robins-Browne RM, Bettelheim KA, Yam WC. A newly discovered verotoxin variant, VT2g, produced by bovine verocytotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003, 69, 7549–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng Q, Bai X, Zhao A, Lan R, Du H, Wang T, Shi C, Yuan X, Bai X, Ji S, Jin D, Yu B, Wang Y, Sun H, Liu K, Xu J, Xiong Y. Characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from healthy pigs in China. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D. ,Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.,Sajed, T.,Pon, A.,Liang, Y., Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).