Submitted:
05 October 2023
Posted:
05 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
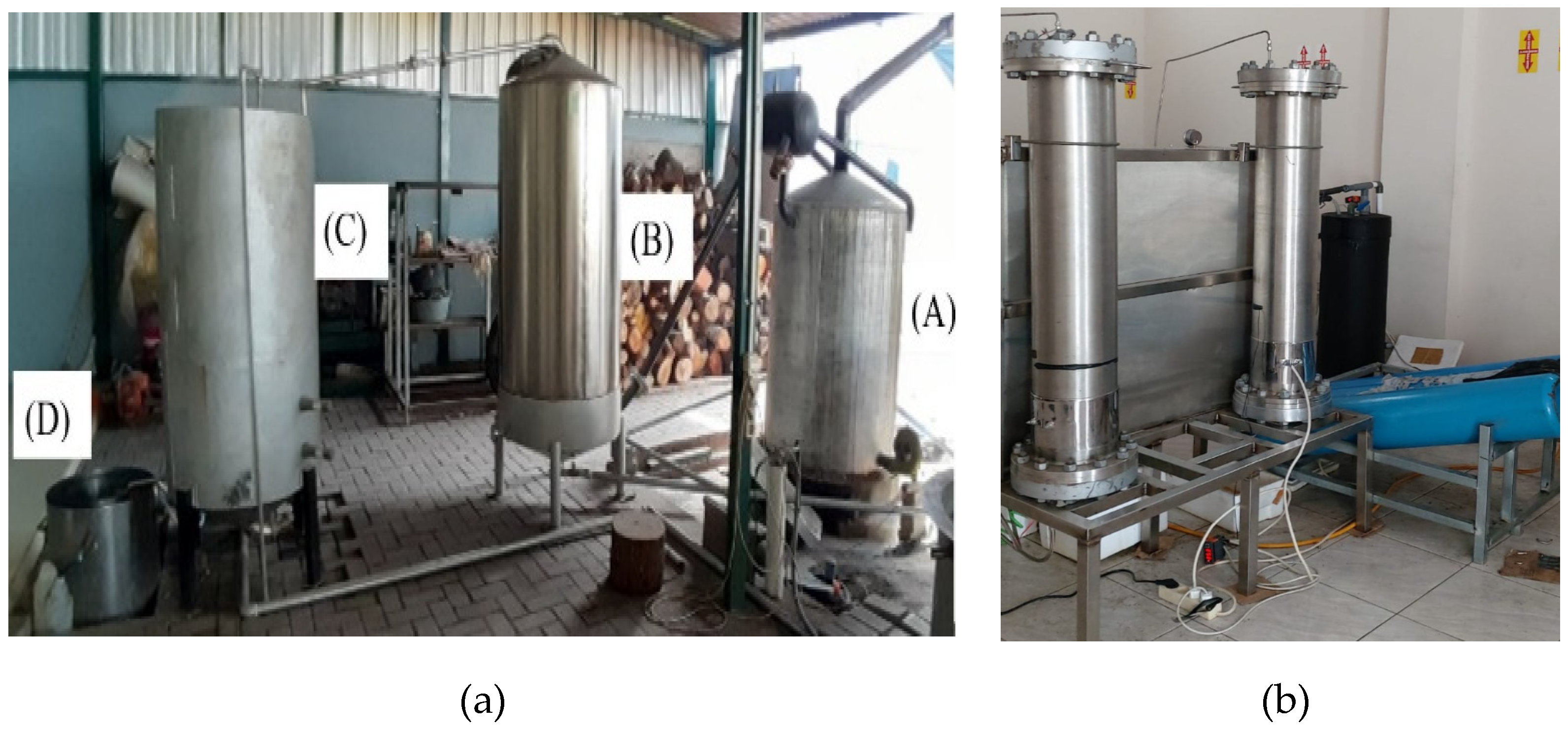
2.1. Equipment and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Raw Materials for Nutmeg Seeds
2.3. The Process of Isolating Nutmeg Seed Oil Using WSD
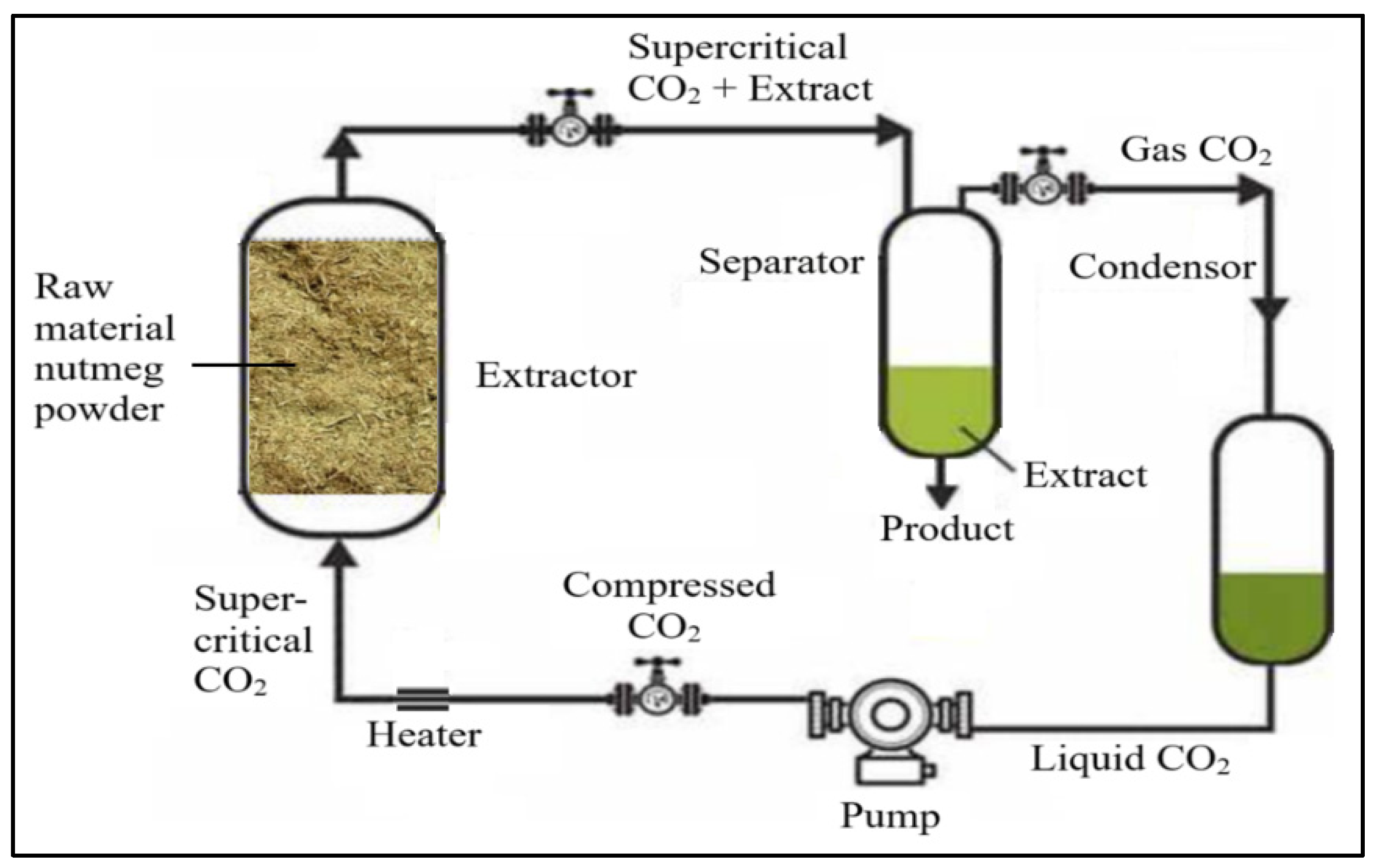
2.4. The Process of Isolating Nutmeg Seed Oil Using SCFE Method
2.5. Characterization of Nutmeg Oil
3. Results
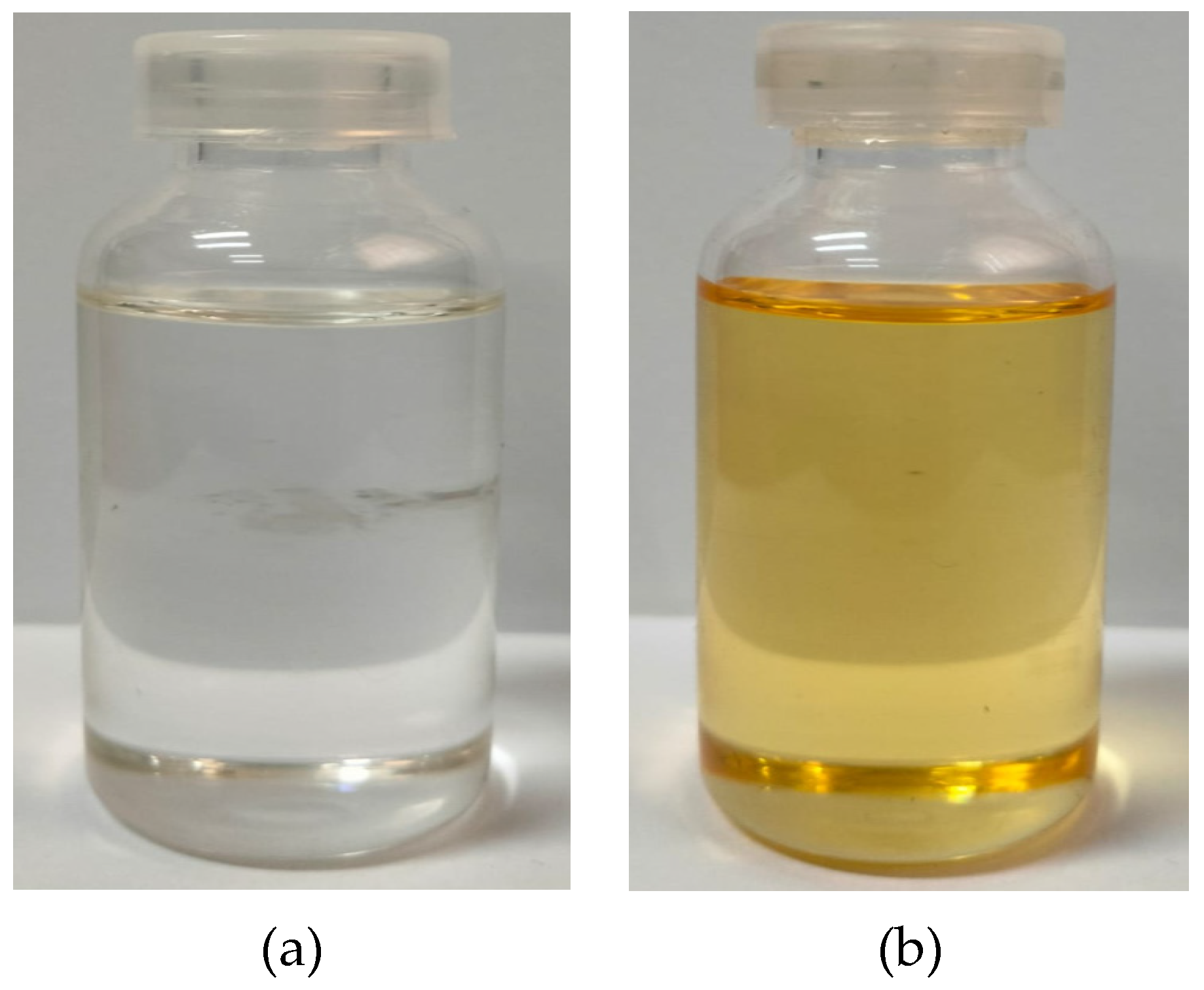
3.1. Physical Appearance of Nutmeg Oil
3.2. Analysis of Nutmeg Oil Content with GC-MS
3.3. Characterization of Nutmeg Oil
| No. | Parameters | ISO 3215:1998 Oil of nutmeg | Nutmeg Oil | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WSD | SCFE | |||
| 1 | Colour | Colourless or pale yellow | Colourless or pale yellow | Colourless or pale yellow |
| 2 | Odor | Typical Nutmeg oil | Typical Nutmeg oil | Typical Nutmeg oil |
| 3 | Density (20 ⁰C) | 0.880-0.910 | 0.8822 | 0.885 |
| 4 | Refractive index (nD 20) | 1.470-1.497 | 1.4781 | 1.484 |
| 5 | Solubility in ethanol 90% at 20 ⁰C | 1:3 colourless | 1:3 colourless | 1:3 colourless |
| 6 | Rotation Optical | (+) 8⁰ - (+) 25⁰ | (+) 24.37o | (+) 24,32o |
| 7 | Residue Evaporation (%) | Maximum 2.0 | 1.78 | 1.89 |
| 8 | Myristicin (%) | Minimum 10 | 30.30 | 16.22 |
| No. | Parameters | Nutmeg Oil | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WSD | SCFE | ||
| 1 | Yield | 10-11% | 10-12% (essential oil ≥ 90%) and 15% (essential oil 80-90%) |
| 2 | Extraction time | 24 h | 15-60 minutes |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simanjorang, T.M.; Irham, Waluyati, L.R.; Mulyo, J.H. Comparative and competitive advantages of nutmeg farming in two regions in Maluku Province, Indonesia. Biodiversitas. 2020, 21,3, 1165-1173. [CrossRef]
- Piaru, S.P.; Mahmud, R.; Majid, A.M.S.A.; Nassar, Z.D.M. Antioxidant and antiangiogenic activities of the essential oils of Myristica fragrans and Morinda citrifolia, Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2012, 5, 4, 294-298. [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, K.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Murugan, M.; Dhanya, M.K.; Pandian, A. Nutmeg (Myristica fragrans Houtt.) essential oil: A review on its composition, biological, and pharmacological activities. Phytother Res. 2022, 36,7, 2839-2851. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Hamiduddin, Zaigham, M.; Ikram, M. Phytopharmacological potential of Jaiphal (Myristica fragrans Houtt): A spice of medicinal importance and its utilization in Unani Medicine, Int J Green Pharm, 2018, 12(1), 26-36.
- Naeem, N.; Rehman, R.; Mushtaq, A.; and Ghania, J.B. (2016). Nutmeg: A review on uses and biological properties, Int J Biol Chem Sci. 2016, 9, 107-110.
- Saputro, M.; Andarwulan, N.; Faridah, D. Physical characterization and essential oil properties of West Sumatra mace and nutmeg seed (Myristica fragrans Houtt) at different ages at harvest, J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2016, 5(6), 371-376.
- Marzuki, I.; Joefrie, B.; Aziz, S.A.; Agusta, H.; Surahman, M. Physico-chemical characterization of Maluku Nutmeg oil, Int J Sci Eng. 2014, 7, 61-64. [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Jinno, K.; Kawagishi, H.; Sugiyama, K. Hepatoprotective effect of myristicin from nutmeg (Myristica fragrans) on lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-induced liver injury, J Agric Food Chem. 2023, 51(6), 1560-1565. [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Dybowski, M.P. Simple and rapid determination of myristicin in human serum, Forensic Toxicol. 2013, 31(1), 119-123. [CrossRef]
- Riyanto, Umayah, S.; Marhaendro, P. The uniqueness of isolation of nutmeg oil from nutmeg seeds (Myristica fragrans Houtt.) and its effects on physical and chemical properties, Indian Journal of Natural Products and Resources. 2021, 12(2), 247-255.
- Herrero, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibanez, E. Supercritical fluid extraction: Recent advances and applications. J. Chromatogr. A. 2010, 1217, 2495–2511. [CrossRef]
- Leila, M.; Ratiba, D.; Al-Marzouqi, A. Experimental and mathematical modelling data of green process of essential oil extraction: Supercritical CO2 extraction, Materials Today Proceedings. 2022, 49, 4, 1023-1029. [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Hajimirsadeghi, S.S. Supercritical fluid extraction in plant essential and volatile oil analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2007, 7, 1163(1-2), 2-24. [CrossRef]
- Fornari, T.; Vicente, G.; Vázquez, E.; García-Risco, M.R.; Reglero, G. Isolation of essential oil from different plants and herbs by supercritical fluid extraction. J Chromatogr A. 2012, 10,1250, 34-48. [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, P.; Gupta, K.; Katiyar, P.; Khanam, S. Supercritical fluid extraction of turmeric root oil using CO2: Experimental analysis and process modelling, Industrial Crops and Products. 2022, 188, Part A, 115559.
- Shrirame, B.; Geed, S.R.; Hassan, S.Z.; Verma, J.S.; Samal, K.; Namdeo, A.; Rai, B.N. Supercritical CO2 extraction of caraway (Carum carvi L.) seed: Optimization and parametric interaction studies using design of experiments, Journal of CO2 Utilization. 2022, 65, 102195. [CrossRef]
- Chani-Paucar, L.O.; Johner, J.C.F.; Zabot, G.L.; Meireles, M.A.A. Technical and economic evaluation of supercritical CO2 extraction of oil from sucupira branca seeds, The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 2022, 181, 105494. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Abdeslam-Hassan, M.; Ouassila, L.; Danielle, B. Extraction and Modeling of Algerian Rosemary Essential Oil Using Supercritical CO2: Effect of Pressure and Temperature, Energy Procedia. 2012, 18, 1038-1046. [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.G.; Oliveira, M.S.; Cruz, J.N.; Costa, W.A.; M.da Silva, S.H., Maia, A.A.B.; Sousa, R.L.; Junior, R.N.C.; and Andrade, E.H.A. Supercritical CO2 extraction to obtain Lippia thymoides Mart. and Schauer (Verbenaceae) essential oil rich in thymol and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity, The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 2021, 168, 105064.
- Uquiche, E.; Cirano, N.; and Millao, S. (2015). Supercritical fluid extraction of essential oil from Leptocarpha rivularis using CO2, Industrial Crops and Products, 2015, 77, 307-314. [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Naik, S.N.; Goud, V.V.; and Das, C. (2019). Supercritical CO2 extraction and online fractionation of dry ginger for production of high-quality volatile oil and gingerols enriched oleoresin, Industrial Crops and Products, 2019, 130, 352-362. [CrossRef]
- Náthia-Neves, G.; Vardanega, R.; Urango, A.C.M.; and Meireles, M.A.A. (2020). Supercritical CO2 extraction of α-bisabolol from different parts of candeia wood (Eremanthus erythropappus), The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 2020, 166, 105026. [CrossRef]
- Frohlich, P.C.; Santos, K.A.; Palu, F.; Cardozo-Filho, L.; Silva, C.; Silva, E.A. Evaluation of the effects of temperature and pressure on the extraction of eugenol from clove (Syzygium aromaticum) leaves using supercritical CO2, The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 2019, 143, 313-320. [CrossRef]
- Salgin, U.; Salgin, S.; Ekici, D.D.; Uludal, G. Oil recovery in rosehip seeds from food plant waste products using supercritical CO2 extraction, The Journal of Supercritical Fluids. 2016, 118, 194-202. [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Figueiredo, A.C.; Burillo, J.; Mainar, A.M.; Urieta, J.S.; Barroso, J.G.; Coelho, J.A.; and Palavra, A.M. Supercritical fluid extraction of the volatile oil from Santolina chamaecyparissus. J Sep Sci. 2009, 32(18), 3215-3222. [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Sefidkon, F.; Hosseini, S.G. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of essential oils from Perovskia atriplicifolia Benth, J Agric Food Chem. 2003, 27, 51(18), 5414-5419. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Han, D.; Tian, M.; Row, K. Supercritical CO2 extraction of essential oils from Chamaecyparis obtuse, Nat Prod Commun. 2010, 5(3), 461-464.
- ISO 3215:1998, Oil of nutmeg, Indonesian type (Myristica fragrans Houtt.).
- Berger, R.G. (2007). Flavours and Fragrances Chemistry, Bioprocessing and Sustainability; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007, Volume XVI, pp. 43–103.
- Lima, M.A.; Kestekoglou, I.; Charalampopoulos, D.; Chatzifragkou, A. Supercritical fluid extraction of carotenoids from vegetable waste matrices. Molecules. 2019, 24, 466. [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Lenucci, S.M.; Mita, G. Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Carotenoids from Pumpkin (Cucurbita spp.): A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6725–6740.
- Singh, G.; Marimuthu, P.; De Heluani, C.S.; Catalan, C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials of essential oil and acetone extract of Myristica fragrans Houtt. (Aril part). J Food Sci. 2005, 70, 141-148. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Chen, Y. Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of essential oil from tangerine peel: Experimental optimization and kinetics modelling, Chemical Engineering Research and Design. 2020, 164, 412-423. [CrossRef]
- King, J.W. Supercritical Fluid Technology for Lipid Extraction, Fractionation and Reactions. In Tsung Min Kuo and Harold Gardner (ed.). Lipid Biotechnology. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc. 2002, 663-687.
- Yousefi, M.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Pourmortazavi, S.P.; Wysokowski, M.; Jesionowski, T.; Ehrlich, H.; Mirsadeghi, S. Supercritical fluid extraction of essential oils, TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry. 2019, 118, 182-193. [CrossRef]
- Uwineza, P.A.; Wa´skiewicz, A. Recent advances in supercritical fluid extraction of natural bioactive compounds from natural plant materials, Molecules. 2020, 25, 3847, 1-23.

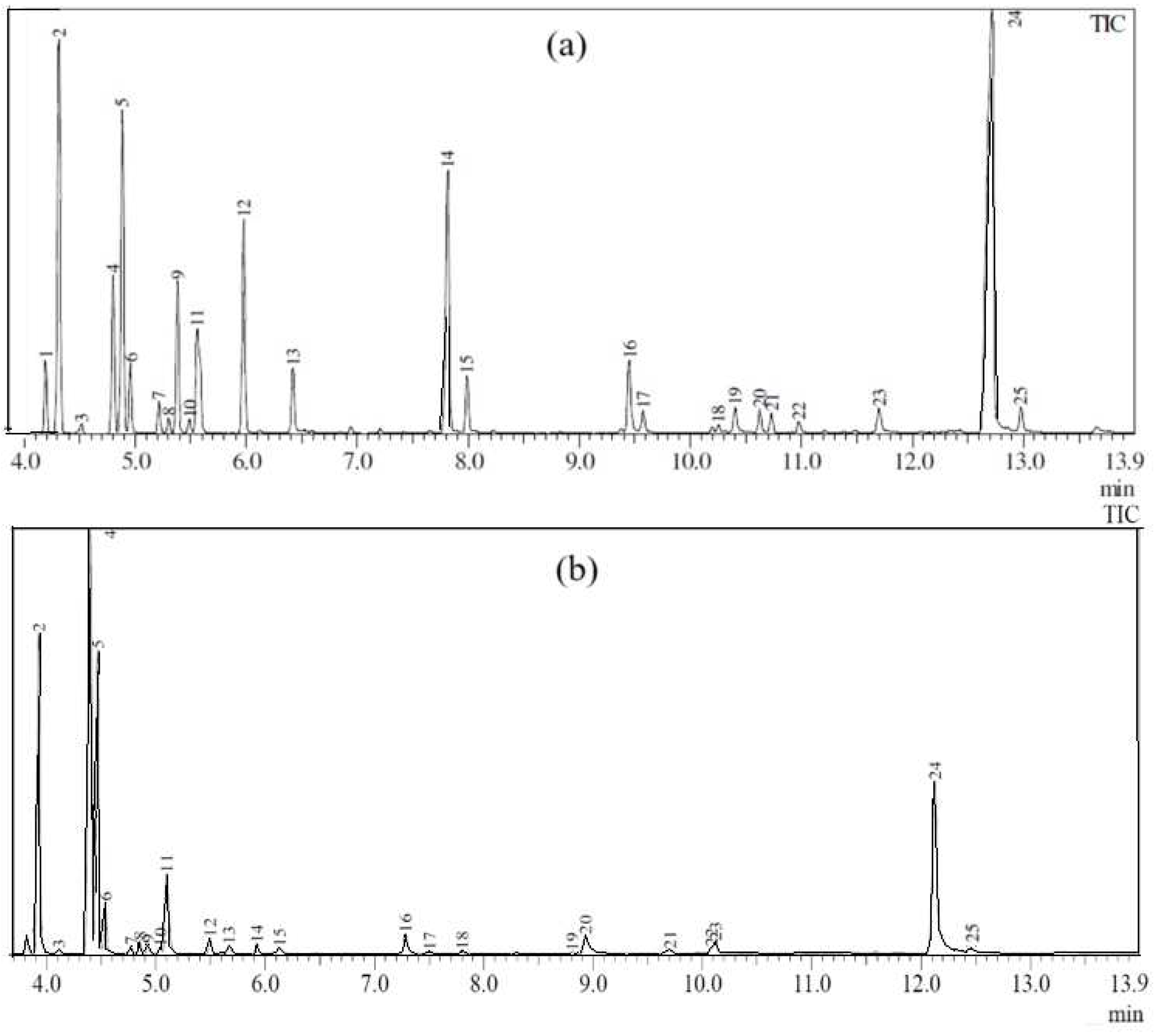
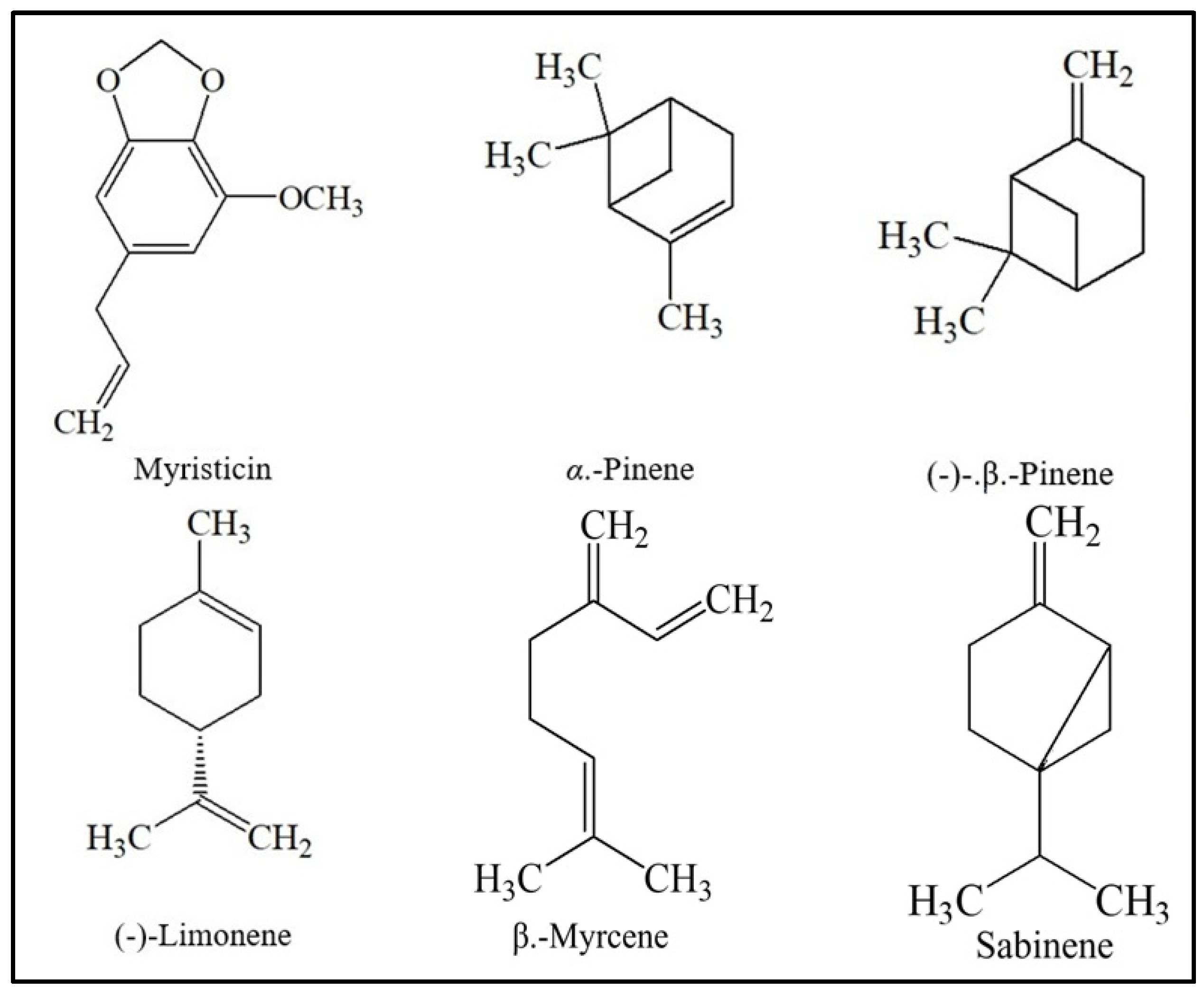
| No. | Name of Compounds | WSD | SCFE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retention Time (minutes) | Area (%) | Retention Time (minutes) | Area (%) | ||
| 1 | Myristicin | 12.719 | 30.30 | 12.127 | 16.22 |
| 2 | α.-Pinene | 4.313 | 12.01 | 3.927 | 18.01 |
| 3 | (-)-4-Terpineol | 7.813 | 9.75 | 7.284 | 1.41 |
| 4 | (-)-β.-Pinene | 4.884 | 9.65 | 4.466 | 15.73 |
| 5 | γ.-Terpinene | 5.977 | 6.63 | 5.494 | 0.89 |
| 6 | (-)-Limonene | 5.558 | 4.99 | 5.096 | 5.91 |
| 7 | β.-Phellandrene | 4.800 | 4.61 | - | - |
| 8 | (+)-2-Carene | 5.380 | 4.41 | 4.853 | 0.67 |
| 9 | Safrole | 9.449 | 2.76 | 8.928 | 1.96 |
| 10 | α.-Terpinolene | 6.419 | 1.99 | 5.923 | 0.63 |
| 11 | α.-Thujene | 4.191 | 1.94 | 3.819 | 0.93 |
| 12 | α.-Terpineol | 7.989 | 1.83 | 7.500 | 0.17 |
| 13 | β.-Myrcene | 4.955 | 1.82 | 4.537 | 2.75 |
| 14 | Eugenol | 10.404 | 0.92 | - | - |
| 15 | (E)-Isoeugenol | 11.702 | 0.90 | - | - |
| 16 | α.-Phellandrene | 5.212 | 0.89 | 4.770 | 0.44 |
| 17 | β.-Asarone | 12.979 | 0.86 | 12.454 | 0.35 |
| 18 | 4-Pentylanisole | 9.575 | 0.77 | - | - |
| 19 | Neryl acetate | 10.626 | 0.74 | - | - |
| 20 | α.-Copaene | 10.730 | 0.64 | 9.701 | 0.30 |
| 21 | δ-3-Carene | 5.302 | 0.41 | 4.853 | 0.67 |
| 22 | p-Cymene | 5.487 | 0.39 | 5.039 | 0.36 |
| 23 | Methyleugenol | 10.978 | 0.39 | - | - |
| 24 | Camphene | 4.514 | 0.21 | 4.112 | 0.30 |
| 25 | α.-Terpinyl acetate | 10.254 | 0.19 | - | - |
| 26 | Sabinene | - | - | 4.399 | 29.94 |
| 27 | α.-Thujene | - | - | 3.819 | 0.93 |
| 28 | α.-Cubebene | - | - | 10.119 | 0.78 |
| 29 | Trans Sabinene Hydrate | - | - | 5.667 | 0.60 |
| 30 | α. Terpinene | - | - | 4.925 | 0.52 |
| 31 | α.-Copaene | - | - | 9.701 | 0.30 |
| 32 | Geranyl Acetate | - | - | 10.080 | 0.26 |
| 33 | Trans-Sabinene Hydrate Acetate | - | - | 7.799 | 0.21 |
| 34 | Borneol, Acetate | - | - | 8.805 | 0.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




