Submitted:
05 October 2023
Posted:
06 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Occurrence of Microplastics (MPs) in Abiotic and Biotic Components
2.1. MPs in Abiotic Components
2.2. MPs in Biotic Components
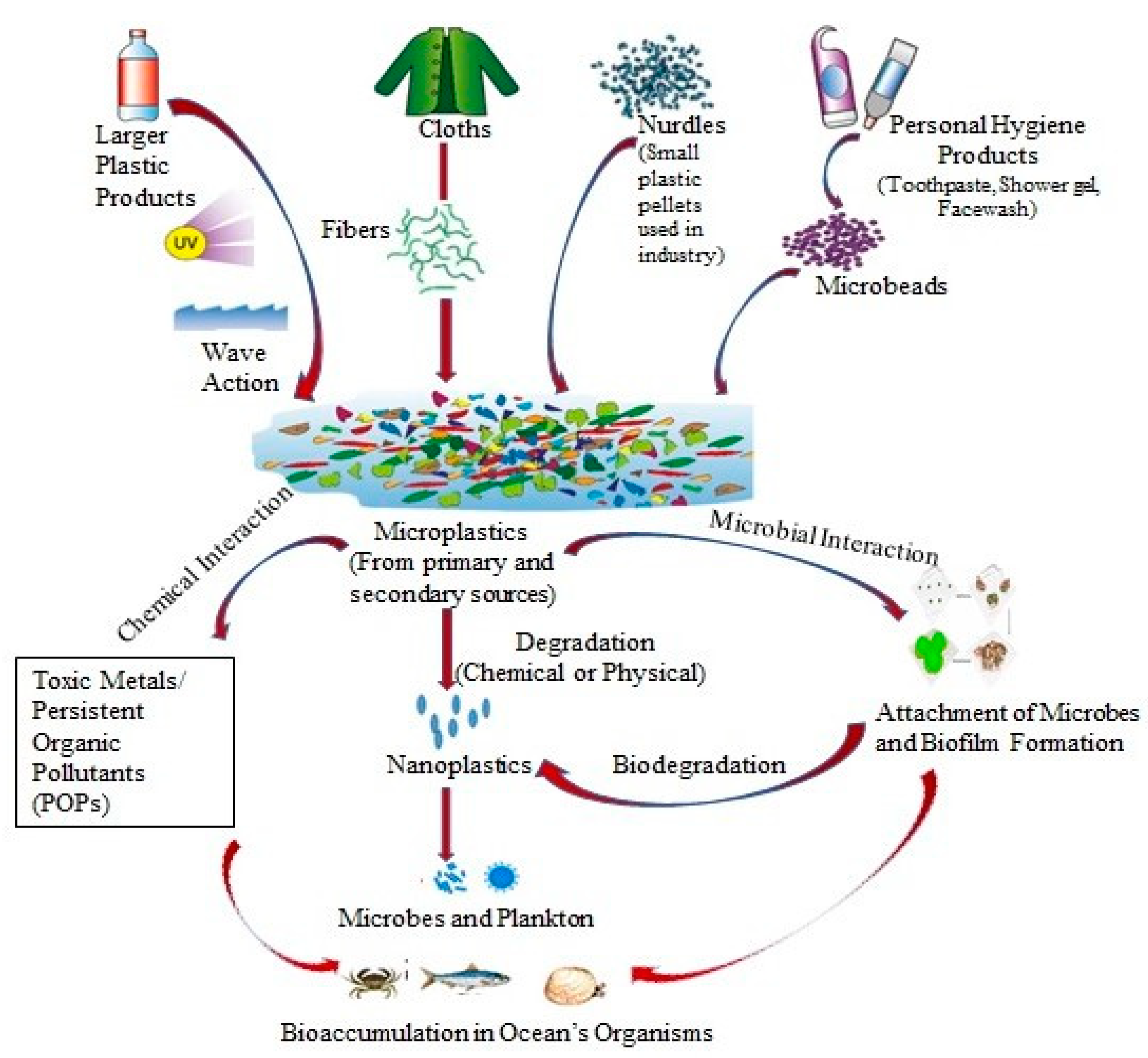
3. Sources of Microplastics (MPs) in the Antarctic Region
3.1. Microplastics (MPs) Released in Wastewater from the Antarctic Research Bases
3.2. Microplastics (MPs) Released from Personal Care Products (PCPs) and Laundry
3.3. Microplastics (MPs) Originate from the Degradation of Macroplastic
4. Harmful Effects of Microplastics (MPs)
5. Detection Methods/Techniques of Microplastics (MPs): The methods/techniques for the identification or quantification of MPs are limited and these are given below
- (i)
- Visual Identification: It is the most common and inexpensive method for the identification of MPs (Lee et al., 2013; Mathalon & Hill, 2014; Primpke et al., 2020). Several parameters such as shape, color distribution, color, length, width, and surface properties are analyzed by this method (Marti et al., 2020; Lusher et al., 2020)
- (ii)
- Density Separation: It is the most reliable and economical method and is used to segregate MPs from sediments and water. The density of MPs is affected by the concentration of additives and polymer types (Claessens et al., 2013; Masura et al., 2015). In this method, sodium chloride (NaCl), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), sodium bromide (NaBr), and sodium iodide (NaI) solutions are used for the separation of MPs from samples (Masura et al., 2015; Maes et al., 2017; Coppock et al., 2017; Quinn et al., 2017).
- (iii)
- Raman Spectroscopy: This technique is performed on the particle surface and produces vibrational spectra (Schymanski et al., 2018; Sobhani et al., 2019). It is used for the determination of element numbers, size (<1 µm), and shape (Cabernard et al., 2018). It delivers the chemical and structural characteristics of MPs (Crawford and Quinn, 2017). It is time-consuming and can take from several days to weeks for the analysis of samples. Raman spectroscopy and FTIR both techniques are complementary to each other.
- (iv)
- Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): This technique is the most widely used for the estimation of MPs (Cincinelli et al., 2017; Fu et al., 2020; Morais et al., 2020). It produces a spectral pattern known as the IR spectrum. It has three optimizing technologies- focal plane array (FPA), micro-FTIR, and attenuated total reflection (ATR). It can detect MPs up to 10 μm.
- (v)
- Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS): This technique is advanced over FTIR as it enters deeper into plastic materials (Paul et al., 2019; Corradini et al., 2019; Pakhomova et al., 2020). In this technique, sample formulation is not required, and the majority of samples can be tested easily.
- (vi)
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): It is a fast and size-independent technique. In this technique, signal intensities are directly proportional to the proton numbers that give rise to a unique resonance (Peez et al., 2019; Peez & Imhof, 2020). It is an advanced technique over Raman spectroscopy and FTIR.
- (vii)
- Thermoanalytical Methods Combined with Gas-Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): This technique is used in forensic science and the polymer industry (Kusch, 2014). In this technique, polymers are first degraded at the temperature of 600 oC in an oxygen-free environment, and then volatile products are separated through the GC-MS.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
- ➢
- There should be augmented research in the proximity of the Antarctic Region to upsurge the understanding of the impacts of plastics on the Antarctic ecosystem.
- ➢
- The proper strategy should be made by the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS) to prevent and mitigate the problem of MPs in the Antarctic Region.
- ➢
- There is an urgent need for the implementation of waste management and treatment to avoid plastic input into the Antarctic Ocean.
- ➢
- A better step can be to spread environmental awareness among tourists, researchers, and ship crews who use areas in the proximity of Antarctica.
- ➢
- New guidelines/policies should be made globally, for example ban on the use of single-use plastics and regular monitoring of plastic pollution in the ocean should be done.
- ➢
- Government bodies, community, and industry can work together for the reduction of the amount of plastic litter seen in oceans and beaches.
- ➢
- People who use items made from waste material or refuse to buy plastic should be encouraged.
- ➢
- New analytical techniques for the detection of MPs should be developed and standardized by the researchers.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Code Availability
Conflicts of interest/Competing interest
References
- Abreu, A., & Pedrotti, M. L. (2019). Microplastics in the oceans: the solutions lie on land. Field Actions Science Reports. The journal of field actions, (Special Issue 19), 62-67.
- Absher, T. M., Ferreira, S. L., Kern, Y., Ferreira, A. L., Christo, S. W., & Ando, R. A. (2019). Incidence and identification of microfibers in ocean waters in Admiralty Bay, Antarctica. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 292-298. [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A. L., Barnes, P. W., Bornman, J. F., Gouin, T., Madronich, S., White, C. C.,... & Jansen, M. A. K. (2022). Oxidation and fragmentation of plastics in a changing environment; from UV-radiation to biological degradation. Science of The Total Environment, 851, 158022. [CrossRef]
- Aves, A. R., Revell, L. E., Gaw, S., Ruffell, H., Schuddeboom, A., Wotherspoon, N. E.,... & McDonald, A. J. (2022). First evidence of microplastics in Antarctic snow. The Cryosphere, 16(6), 2127-2145. [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D. K., Galgani, F., Thompson, R. C., & Barlaz, M. (2009). Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philosophical transactions of the royal society B: biological sciences, 364(1526), 1985-1998. [CrossRef]
- Barrows, A. P., Neumann, C. A., Berger, M. L., & Shaw, S. D. (2017). Grab vs. neuston tow net: a microplastic sampling performance comparison and possible advances in the field. Analytical methods, 9(9), 1446-1453. [CrossRef]
- Bergami, E., Rota, E., Caruso, T., Birarda, G., Vaccari, L., & Corsi, I. (2020). Plastics everywhere: first evidence of polystyrene fragments inside the common Antarctic collembolan Cryptopygus antarcticus. Biology letters, 16(6), 20200093. [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M., Gutow, L., & Klages, M. (2015). Marine anthropogenic litter, 447. Springer Nature.
- Bessa, F., Ratcliffe, N., Otero, V., Sobral, P., Marques, J. C., Waluda, C. M.,... & Xavier, J. C. (2019). Microplastics in gentoo penguins from the Antarctic region. Scientific reports, 9(1), 14191. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K. (2022). Evaluation of Bis (2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) in the PET Bottled Mineral Water of Different Brands and Impact of Heat by GC–MS/MS. Chemistry Africa, 5(4), 929-942. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., & Jindal, T. (2020). Persistent organic pollutants in lakes of Grovnes Peninsula at Larsemann Hill area, East Antarctica. Earth Systems and Environment, 4, 349-358. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., & Jindal, T. (2022a). Evaluation of Coliform and Faecal Coliform Bacteria in the Lakes of Broknes and Grovnes Peninsula, East Antarctica. Nature Environment & Pollution Technology, 21. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., & Sharma, A. (2021a). Estimation of physico-chemical, trace metals, microbiological and phthalate in PET bottled water. Chemistry Africa, 4(4), 981-991. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., & Sharma, A. (2021b). Microplastics (MPs) in Drinking Water: Uses, Sources & Transport. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., Sharma, S., & Jindal, T. (2021). Occurrence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the lake water at Grovnes Peninsula Over East Antarctica. Chemistry Africa, 4, 965-980. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L. K., Sharma, S., & Jindal, T. (2023). Estimation of Physico-Chemical and Heavy Metals in the Lakes of Grovnes & Broknes Peninsula, Larsemann Hill, East Antarctica. Chemistry Africa, 1-18. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, L., & Jindal, T. (2019). Contamination of Lakes in Broknes peninsula, East Antarctica through the Pesticides and PAHs. Asian-Journal of Chemistry, 31(7), 1574-1580. [CrossRef]
- Browne, M. A., Crump, P., Niven, S. J., Teuten, E., Tonkin, A., Galloway, T., & Thompson, R. (2011). Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks. Environmental science & technology, 45(21), 9175-9179. [CrossRef]
- Cabernard, L., Roscher, L., Lorenz, C., Gerdts, G., & Primpke, S. (2018). Comparison of Raman and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for the quantification of microplastics in the aquatic environment. Environmental science & technology, 52(22), 13279-13288. [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G., Bergami, E., Singh, N., & Corsi, I. (2022). Plastic occurrence, sources, and impacts in Antarctic environment and biota. Water Biology and Security, 1(2), 100034. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q., Reisser, J., Cunsolo, S., Kwadijk, C., Kotterman, M., Proietti, M.,... & Koelmans, A. A. (2018). Pollutants in plastics within the North Pacific subtropical gyre. Environmental science & technology, 52(2), 446-456. [CrossRef]
- Cincinelli, A., Scopetani, C., Chelazzi, D., Lombardini, E., Martellini, T., Katsoyiannis, A.,... & Corsolini, S. (2017). Microplastic in the surface waters of the Ross Sea (Antarctica): occurrence, distribution and characterization by FTIR. Chemosphere, 175, 391-400. [CrossRef]
- Claessens, M., Van Cauwenberghe, L., Vandegehuchte, M. B., & Janssen, C. R. (2013). New techniques for the detection of microplastics in sediments and field collected organisms. Marine pollution bulletin, 70(1-2), 227-233. [CrossRef]
- Cole, M., Lindeque, P., Fileman, E., Halsband, C., Goodhead, R., Moger, J., & Galloway, T. S. (2013). Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environmental science & technology, 47(12), 6646-6655. [CrossRef]
- Coppock, R. L., Cole, M., Lindeque, P. K., Queirós, A. M., & Galloway, T. S. (2017). A small-scale, portable method for extracting microplastics from marine sediments. Environmental Pollution, 230, 829-837. [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F., Bartholomeus, H., Lwanga, E. H., Gertsen, H., & Geissen, V. (2019). Predicting soil microplastic concentration using vis-NIR spectroscopy. Science of the Total Environment, 650, 922-932. [CrossRef]
- Cowger, W., Booth, A. M., Hamilton, B. M., Thaysen, C., Primpke, S., Munno, K.,... & Nel, H. (2020). Reporting guidelines to increase the reproducibility and comparability of research on microplastics. Applied Spectroscopy, 74(9), 1066-1077. [CrossRef]
- Cózar, A., Echevarría, F., González-Gordillo, J. I., Irigoien, X., Úbeda, B., Hernández-León, S.,... & Duarte, C. M. (2014). Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(28), 10239-10244. [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C. B., & Quinn, B. (2017). Microplastic collection techniques. Microplastic pollutants, 179-202. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, E. M., Ehlers, S. M., Dick, J. T., Sigwart, J. D., Linse, K., Dick, J. J., & Kiriakoulakis, K. (2020). High abundances of microplastic pollution in deep-sea sediments: evidence from Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(21), 13661-13671. [CrossRef]
- da Costa, J. P., Santos, P. S., Duarte, A. C., & Rocha-Santos, T. (2016). (Nano) plastics in the environment–sources, fates and effects. Science of the total environment, 566, 15-26. [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A. L., Kawaguchi, S., King, C. K., Townsend, K. A., King, R., Huston, W. M., & Bengtson Nash, S. M. (2018). Turning microplastics into nanoplastics through digestive fragmentation by Antarctic krill. Nature communications, 9(1), 1001. [CrossRef]
- do Sul, J. A. I., Barnes, D. K., Costa, M. F., Convey, P., Costa, E. S., & Campos, L. S. (2011). Plastics in the Antarctic environment: are we looking only at the tip of the iceberg? Oecologia Australis, 15(1), 150-170. [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M., Lebreton, L. C., Carson, H. S., Thiel, M., Moore, C. J., Borerro, J. C.,... & Reisser, J. (2014). Plastic pollution in the world's oceans: more than 5 trillion plastic pieces weighing over 250,000 tons afloat at sea. PloS one, 9(12), e111913. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C., & Burton, H. (2003). Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Island. AMBIO: A Journal of the Human Environment, 32(6), 380-384. [CrossRef]
- Europe, P. (2015). An analysis of European plastics production, demand and waste data. Plastics–the facts, 147.
- Fragão, J., Bessa, F., Otero, V., Barbosa, A., Sobral, P., Waluda, C. M.,... & Xavier, J. C. (2021). Microplastics and other anthropogenic particles in Antarctica: Using penguins as biological samplers. Science of The Total Environment, 788, 147698. [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C. I., Morrison, A. K., Hogg, A. M., Macaya, E. C., van Sebille, E., Ryan, P. G.,... & Waters, J. M. (2018). Antarctica’s ecological isolation will be broken by storm-driven dispersal and warming. Nature climate change, 8(8), 704-708. [CrossRef]
- Fu, W., Min, J., Jiang, W., Li, Y., & Zhang, W. (2020). Separation, characterization and identification of microplastics and nanoplastics in the environment. Science of the total environment, 721, 137561. [CrossRef]
- Gall, S. C., & Thompson, R. C. (2015). The impact of debris on marine life. Marine pollution bulletin, 92(1-2), 170-179. [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M., Edo, C., Velázquez, D., Casero-Chamorro, M. C., Leganés, F., Quesada, A.,... & Rosal, R. (2020). First detection of microplastics in the freshwater of an Antarctic Specially Protected Area. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 161, 111811. [CrossRef]
- González-Pleiter, M., Lacerot, G., Edo, C., Pablo Lozoya, J., Leganés, F., Fernández-Piñas, F.,... & Teixeira-de-Mello, F. (2021). A pilot study about microplastics and mesoplastics in an Antarctic glacier. The Cryosphere, 15(6), 2531-2539. [CrossRef]
- Gröndahl, F., Sidenmark, J., & Thomsen1, A. (2009). Survey of waste water disposal practices at Antarctic research stations. Polar Research, 28(2), 298-306. [CrossRef]
- Habib, S., Iruthayam, A., Abd Shukor, M. Y., Alias, S. A., Smykla, J., & Yasid, N. A. (2020). Biodeterioration of untreated polypropylene microplastic particles by Antarctic bacteria. Polymers, 12(11), 2616. [CrossRef]
- Hammer, J., Kraak, M. H., & Parsons, J. R. (2012). Plastics in the marine environment: the dark side of a modern gift. Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology, 1-44. [CrossRef]
- Harper, P. C., & Fowler, J. C. (1987). Plastic pellets in New Zealand storm-killed prions (Pachyptila spp.). Notornis, 34(1), 65-70.
- Isobe, A., Uchiyama-Matsumoto, K., Uchida, K., & Tokai, T. (2017). Microplastics in the southern ocean. Marine pollution bulletin, 114(1), 623-626. [CrossRef]
- Jambeck, J. R., Geyer, R., Wilcox, C., Siegler, T. R., Perryman, M., Andrady, A.,... & Law, K. L. (2015). Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science, 347(6223), 768-771. [CrossRef]
- Jones-Williams, K., Galloway, T., Cole, M., Stowasser, G., Waluda, C., & Manno, C. (2020). Close encounters-microplastic availability to pelagic amphipods in sub-antarctic and antarctic surface waters. Environment International, 140, 105792. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A., Lannuzel, D., Rodemann, T., Meiners, K. M., & Auman, H. J. (2020). Microplastic contamination in east Antarctic sea ice. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 154, 111130. [CrossRef]
- Kozak, E. R., Franco-Gordo, C., Mendoza-Pérez, J., Sánchez-Nuño, N., Martínez-Sánchez, X. A., Melo-Agustín, P.,... & Gómez-Gutiérrez, J. (2021). Surface layer microplastic pollution in four bays of the central Mexican Pacific. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 169, 112537. [CrossRef]
- Kusch, P. (2014). Identification of synthetic polymers and copolymers by analytical pyrolysis–gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Journal of Chemical Education, 91(10), 1725-1728. [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, A. L. D. F., Rodrigues, L. D. S., Van Sebille, E., Rodrigues, F. L., Ribeiro, L., Secchi, E. R.,... & Proietti, M. C. (2019). Plastics in sea surface waters around the Antarctic Peninsula. Scientific reports, 9(1), 3977. [CrossRef]
- Lasee, S., Mauricio, J., Thompson, W. A., Karnjanapiboonwong, A., Kasumba, J., Subbiah, S.,... & Anderson, T. A. (2017). Microplastics in a freshwater environment receiving treated wastewater effluent. Integrated Environmental Assessment and Management, 13(3), 528-532. [CrossRef]
- Le Guen, C., Suaria, G., Sherley, R. B., Ryan, P. G., Aliani, S., Boehme, L., & Brierley, A. S. (2020). Microplastic study reveals the presence of natural and synthetic fibres in the diet of King Penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) foraging from South Georgia. Environment international, 134, 105303. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J., Hong, S., Song, Y. K., Hong, S. H., Jang, Y. C., Jang, M.,... & Shim, W. J. (2013). Relationships among the abundances of plastic debris in different size classes on beaches in South Korea. Marine pollution bulletin, 77(1-2), 349-354. [CrossRef]
- Leistenschneider, C., Burkhardt-Holm, P., Mani, T., Primpke, S., Taubner, H., & Gerdts, G. (2021). Microplastics in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica): a forensic approach for discrimination between environmental and vessel-induced microplastics. Environmental Science & Technology, 55(23), 15900-15911. [CrossRef]
- Leslie, H. A. (2015). Plastic in Cosmetics: Are we polluting the environment through our personal care?: Plastic ingredients that contribute to marine microplastic litter.
- Li, W. C., Tse, H. F., & Fok, L. (2016). Plastic waste in the marine environment: A review of sources, occurrence and effects. Science of the total environment, 566, 333-349. [CrossRef]
- Long, Z., Pan, Z., Wang, W., Ren, J., Yu, X., Lin, L.,... & Jin, X. (2019). Microplastic abundance, characteristics, and removal in wastewater treatment plants in a coastal city of China. Water Research, 155, 255-265. [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A. L., Bråte, I. L. N., Munno, K., Hurley, R. R., & Welden, N. A. (2020). Is it or isn't it: the importance of visual classification in microplastic characterization. Applied spectroscopy, 74(9), 1139-1153. [CrossRef]
- Maes, T., Jessop, R., Wellner, N., Haupt, K., & Mayes, A. G. (2017). A rapid-screening approach to detect and quantify microplastics based on fluorescent tagging with Nile Red. Scientific reports, 7(1), 44501. [CrossRef]
- Martí, E., Martin, C., Galli, M., Echevarría, F., Duarte, C. M., & Cózar, A. (2020). The colors of the ocean plastics. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(11), 6594-6601. [CrossRef]
- Masura, J., Baker, J., Foster, G., & Arthur, C. (2015). Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments. [CrossRef]
- Materić, D., Kjær, H. A., Vallelonga, P., Tison, J. L., Röckmann, T., & Holzinger, R. (2022). Nanoplastics measurements in Northern and Southern polar ice. Environmental research, 208, 112741. [CrossRef]
- Mathalon, A., & Hill, P. (2014). Microplastic fibers in the intertidal ecosystem surrounding Halifax Harbor, Nova Scotia. Marine pollution bulletin, 81(1), 69-79. [CrossRef]
- Morais, L. M. S., Sarti, F., Chelazzi, D., Cincinelli, A., Giarrizzo, T., & Martinelli Filho, J. E. (2020). The sea anemone Bunodosoma cangicum as a potential biomonitor for microplastics contamination on the Brazilian Amazon coast. Environmental Pollution, 265, 114817. [CrossRef]
- Munari, C., Infantini, V., Scoponi, M., Rastelli, E., Corinaldesi, C., & Mistri, M. (2017). Microplastics in the sediments of terra nova bay (ross sea, Antarctica). Marine pollution bulletin, 122(1-2), 161-165. [CrossRef]
- Nerland, I. L., Halsband, C., Allan, I., & Thomas, K. V. (2014). Microplastics in marine environments: Occurrence, distribution and effects.
- Obbard, R. W. (2018). Microplastics in polar regions: the role of long range transport. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 1, 24-29. [CrossRef]
- Pakhomova, S., Zhdanov, I., & van Bavel, B. (2020). Polymer type identification of marine plastic litter using a miniature near-infrared spectrometer (MicroNIR). Applied Sciences, 10(23), 8707. [CrossRef]
- Paul, A., Wander, L., Becker, R., Goedecke, C., & Braun, U. (2019). High-throughput NIR spectroscopic (NIRS) detection of microplastics in soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 7364-7374. [CrossRef]
- Peez, N., & Imhof, W. (2020). Quantitative 1 H-NMR spectroscopy as an efficient method for identification and quantification of PVC, ABS and PA microparticles. Analyst, 145(15), 5363-5371. [CrossRef]
- Peez, N., Becker, J., Ehlers, S. M., Fritz, M., Fischer, C. B., Koop, J. H.,... & Imhof, W. (2019). Quantitative analysis of PET microplastics in environmental model samples using quantitative 1 H-NMR spectroscopy: validation of an optimized and consistent sample clean-up method. Analytical and bioanalytical chemistry, 411, 7409-7418. [CrossRef]
- Perfetti-Bolaño, A., Araneda, A., Muñoz, K., & Barra, R. O. (2022). Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in soils and intertidal sediments at Fildes Bay, Maritime Antarctica. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8, 774055. [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N. N., Zalouk-Vergnoux, A., Poirier, L., Kamari, A., Châtel, A., Mouneyrac, C., & Lagarde, F. (2016). Is there any consistency between the microplastics found in the field and those used in laboratory experiments?. Environmental pollution, 211, 111-123. [CrossRef]
- Primpke, S., Christiansen, S. H., Cowger, W., De Frond, H., Deshpande, A., Fischer, M.,... & Wiggin, K. J. (2020). Critical assessment of analytical methods for the harmonized and cost-efficient analysis of microplastics. Applied Spectroscopy, 74(9), 1012-1047. [CrossRef]
- Quinn, B., Murphy, F., & Ewins, C. (2017). Validation of density separation for the rapid recovery of microplastics from sediment. Analytical Methods, 9(9), 1491-1498. [CrossRef]
- Reed, S., Clark, M., Thompson, R., & Hughes, K. A. (2018). Microplastics in marine sediments near Rothera research station, Antarctica. Marine pollution bulletin, 133, 460-463. [CrossRef]
- Reisser, J., Shaw, J., Wilcox, C., Hardesty, B. D., Proietti, M., Thums, M., & Pattiaratchi, C. (2013). Marine plastic pollution in waters around Australia: characteristics, concentrations, and pathways. PloS one, 8(11), e80466. [CrossRef]
- Rota, E., Bergami, E., Corsi, I., & Bargagli, R. (2022). Macro-and microplastics in the Antarctic environment: Ongoing assessment and perspectives. Environments, 9(7), 93. [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P. G. (2014). Litter survey detects the South Atlantic ‘garbage patch’. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 79(1-2), 220-224. [CrossRef]
- Ryan, P. G., De Bruyn, P. N., & Bester, M. N. (2016). Regional differences in plastic ingestion among Southern Ocean fur seals and albatrosses. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 104(1-2), 207-210. [CrossRef]
- Schymanski, D., Goldbeck, C., Humpf, H. U., & Fürst, P. (2018). Analysis of microplastics in water by micro-Raman spectroscopy: Release of plastic particles from different packaging into mineral water. Water research, 129, 154-162. [CrossRef]
- Sfriso, A. A., Tomio, Y., Rosso, B., Gambaro, A., Sfriso, A., Corami, F.,... & Munari, C. (2020). Microplastic accumulation in benthic invertebrates in Terra Nova bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Environment international, 137, 105587. [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, Z., Al Amin, M., Naidu, R., Megharaj, M., & Fang, C. (2019). Identification and visualisation of microplastics by Raman mapping. Analytica chimica acta, 1077, 191-199. [CrossRef]
- Suaria, G., Perold, V., Lee, J. R., Lebouard, F., Aliani, S., & Ryan, P. G. (2020). Floating macro-and microplastics around the Southern Ocean: Results from the Antarctic Circumnavigation Expedition. Environment international, 136, 105494. [CrossRef]
- Tian, W., Song, P., Zhang, H., Duan, X., Wei, Y., Wang, H., & Wang, S. (2022). Microplastic materials in the environment: Problem and strategical solutions. Progress in Materials Science, 101035. [CrossRef]
- Tirelli, V., Suaria, G., & Lusher, A. L. (2022). Microplastics in polar samples. In Handbook of Microplastics in the Environment (pp. 281-322). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Tirkey, A., & Upadhyay, L. S. B. (2021). Microplastics: An overview on separation, identification and characterization of microplastics. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 170, 112604. [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L., Devriese, L., Galgani, F., Robbens, J., & Janssen, C. R. (2015). Microplastics in sediments: a review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Marine environmental research, 111, 5-17. [CrossRef]
- Waller, C. L., & Hughes, K. A. (2018). Plastics in the Southern Ocean. Antarctic Science, 30(5), 269-269. [CrossRef]
- Waller, C. L., Griffiths, H. J., Waluda, C. M., Thorpe, S. E., Loaiza, I., Moreno, B.,... & Hughes, K. A. (2017). Microplastics in the Antarctic marine system: an emerging area of research. Science of the total environment, 598, 220-227. [CrossRef]
- Watts, A. J., Lewis, C., Goodhead, R. M., Beckett, S. J., Moger, J., Tyler, C. R., & Galloway, T. S. (2014). Uptake and retention of microplastics by the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Environmental science & technology, 48(15), 8823-8830. [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. L., Thompson, R. C., & Galloway, T. S. (2013). The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: a review. Environmental pollution, 178, 483-492. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W., Liu, W., Chen, Y., Liao, K., Yu, W., & Jin, H. (2023). Microplastics in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) from Antarctic region. Science of The Total Environment, 870, 161880. [CrossRef]
- Ziajahromi, S., Neale, P. A., & Leusch, F. D. (2016). Wastewater treatment plant effluent as a source of microplastics: review of the fate, chemical interactions and potential risks to aquatic organisms. Water science and technology, 74(10), 2253-2269. [CrossRef]
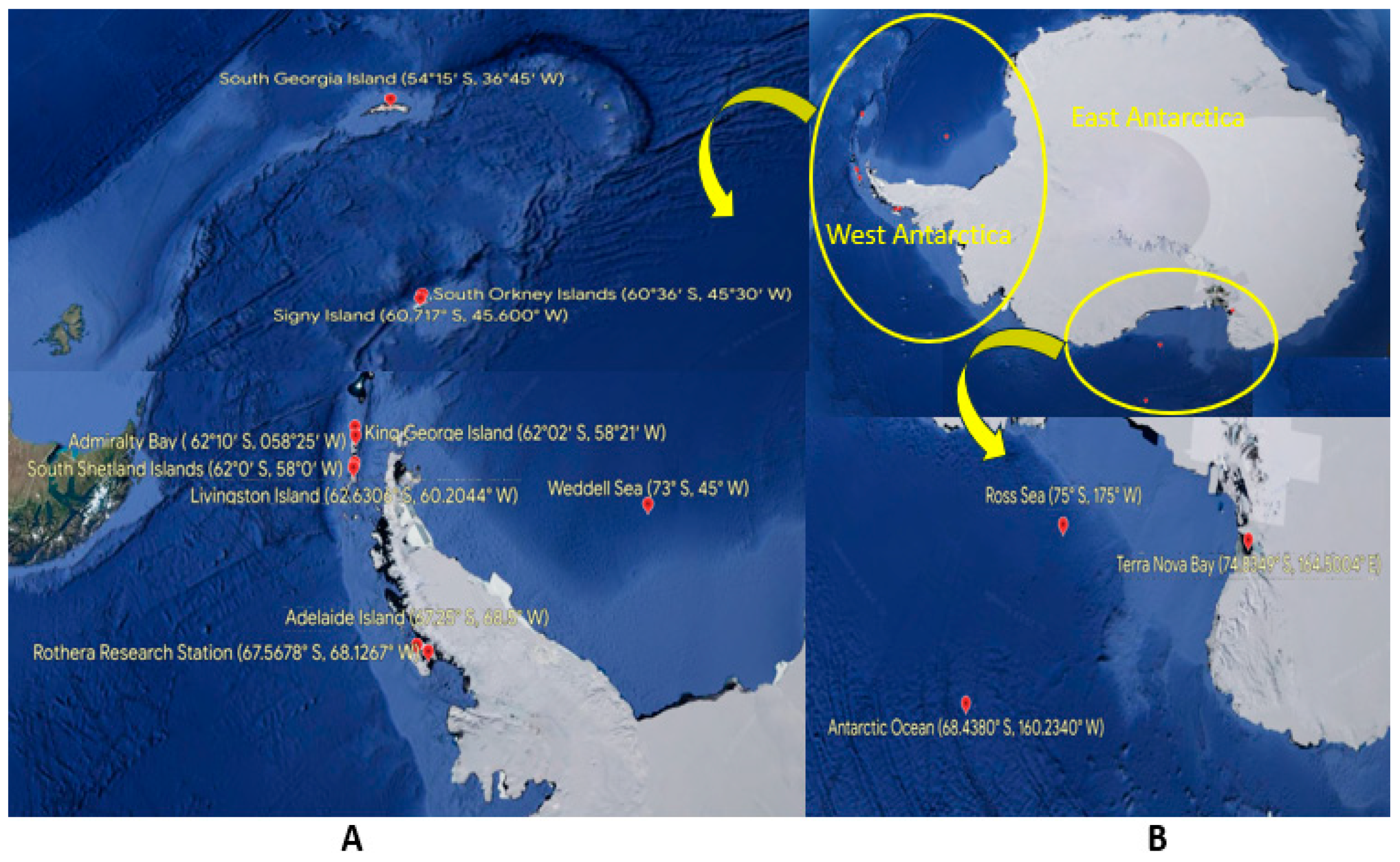
| S. No. | Sample Matrix | Location | Detection Method | Concentration of Microplastics (MPs) | Types and Color of Microplastics (MPs) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ocean water | Antarctic Ocean | Microscopic | 0.55 to 56.58 gm/km2 | Dark color and small size | Eriksen et al., 2014 |
| King George Island (West Antarctic Region) | 16-766 particles/m2 | Synthetic fibre, and fragments | Waller et al., 2017 | |||
| Antarctic Ocean | Stereoscopic microscope and FTIR spectroscopy | 46, 000 to 99,000 particles/km2 | PS and fibres | Isobe et al., 2017 | ||
| Antarctic Peninsula | FTIR spectroscopy | 1794 items/km2 | PU, PA, and PE | Lacerda et al., 2019 | ||
| Admiralty Bay, King George Island (West Antarctic Region) | Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Raman spectroscopy | 2.40 (± 4.57) microfibers 100/m3 | Microfibers (blue, red, and black), PEG, PU, PET, and PA | Absher et al., 2019 | ||
| Antarctic Ocean | µ-FTIR spectroscopy | 188 ± 589 particles/km2 | PE, PP, PS, PVC, PA, and PMMA | Suaria et al., 2020 | ||
| Ross Sea (Antarctic Region) | FTIR spectroscopy | 0.17 ± 0.34 particles/m3 | Fragments and fibers | Cincinelli et al., 2017 | ||
| Adelaide Island (West Antarctic Region) | 0.013 ± 0.005 particles/m3 | Fragments and film | Jones-Williams et al., 2020 | |||
| Weddell Sea (West Antarctic Region) | ATR-FTIR spectroscopy | 0.01 ± 0.01 particles/m3 | Fragments and lines | Leistenschneider et al., 2021 | ||
| 2 | Freshwater | Livingston Island (West Antarctic Region) | µ-FTIR spectroscopy | 0.47 to 1.43 items/1000 m3 | Polyester fibers, acrylic fibers and transparent PTFE films | González-Pleiter et al., 2020 |
| 3 | Floating plastic debris | Antarctic Ocean | Raman spectroscopy | 0.100 to 0.514 gm/km2 | PE and industrial resin pellets | Cózar et al., 2014 |
| 4 | Sea ice | East Antarctica | µ-FTIR spectroscopy and TD-PTR-MS | 11.71 particles/L | PE, PP, and PA | Kelly et al., 2020 |
| King George Island, Antarctica | 0.17 to 0.33 items/m2 | EPS | González-Pleiter et al., 2021 | |||
| Ross Sea (Antarctic Region) | 67 ng/mL | Fibers, fragments, and films | Materic et al., 2022 | |||
| 5 | Snow | 29.4 ± 4.7 particles/L | Aves et al., 2022 | |||
| 6 | Sediment | South Georgia Island (West Antarctic Region) | Visual identification, microscopic and µ-FTIR spectroscopy | 1.30 ± 0.51 particles/gm | Polyester and blue in color | Cunningham et al., 2020 |
| 1.09 ± 0.22 particles/gm | ||||||
| 1.04 ± 0.39 particles/gm | ||||||
| Rothera research station, Adelaide Island (West Antarctic Region) | FTIR spectroscopy | < 5 particles/10 mL | White, vibrant red, and green | Reed et al., 2018 | ||
| Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea (Antarctic Region) | FTIR spectroscopy | 5-1705 particles/m2 | Fibers, film, and fragments | Munari et al., 2017 |
| S. No. | Sample Matrix | Location | Detection Method | Concentration of Microplastics (MPs) | Types and Color of Microplastics (MPs) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) | Antarctic Peninsula | Enzyme digestion, and microscopic | 149 beads/mL, 2063 µg/L | PE beads and PE fragments (6.0 ± 5.0 S.D. µm) | Dawson et al., 2018 |
| South Shetland Island and South Orkney Island (West Antarctic Region) | FTIR spectroscopy | 0.29 ± 0.14 and 0.20 ± 0.083 items/individual | PE, PP, and PS, (Blue, black, and red color particles with <150 μm) | Zhu et al., 2023 | ||
| 2 | Gentoo Penguins (Pygoscelis papua) | Antarctic Peninsula | µ-FTIR spectroscopy | 0.23 ± 0.53 items/individual | Fibers and fragments (76 to 4945 µm) Green, transparent, red, blue, and black | Bessa et al., 2019 |
| 3 | Adélie Penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae), chinstrap Penguins (Pygoscelis antarcticus) and Gentoo Penguins (Pygoscelis papua) | 92 particles | PE, and PS, | Fragão et al., 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





