Submitted:
13 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Material and Methods
Research Objects and Treatment Procedures
Data Collection
SNP Selecting, DNA Extraction and Genotyping
Statistical Analysis
Results
Distribution of Characteristics in Lung Cancer Patients and Prognosis Analysis
Association between the Polymorphisms and Prognosis in the Lung Cancer Patients
Stratification Analyses of Association between Polymorphisms and Prognosis in Lung Cancer Patients
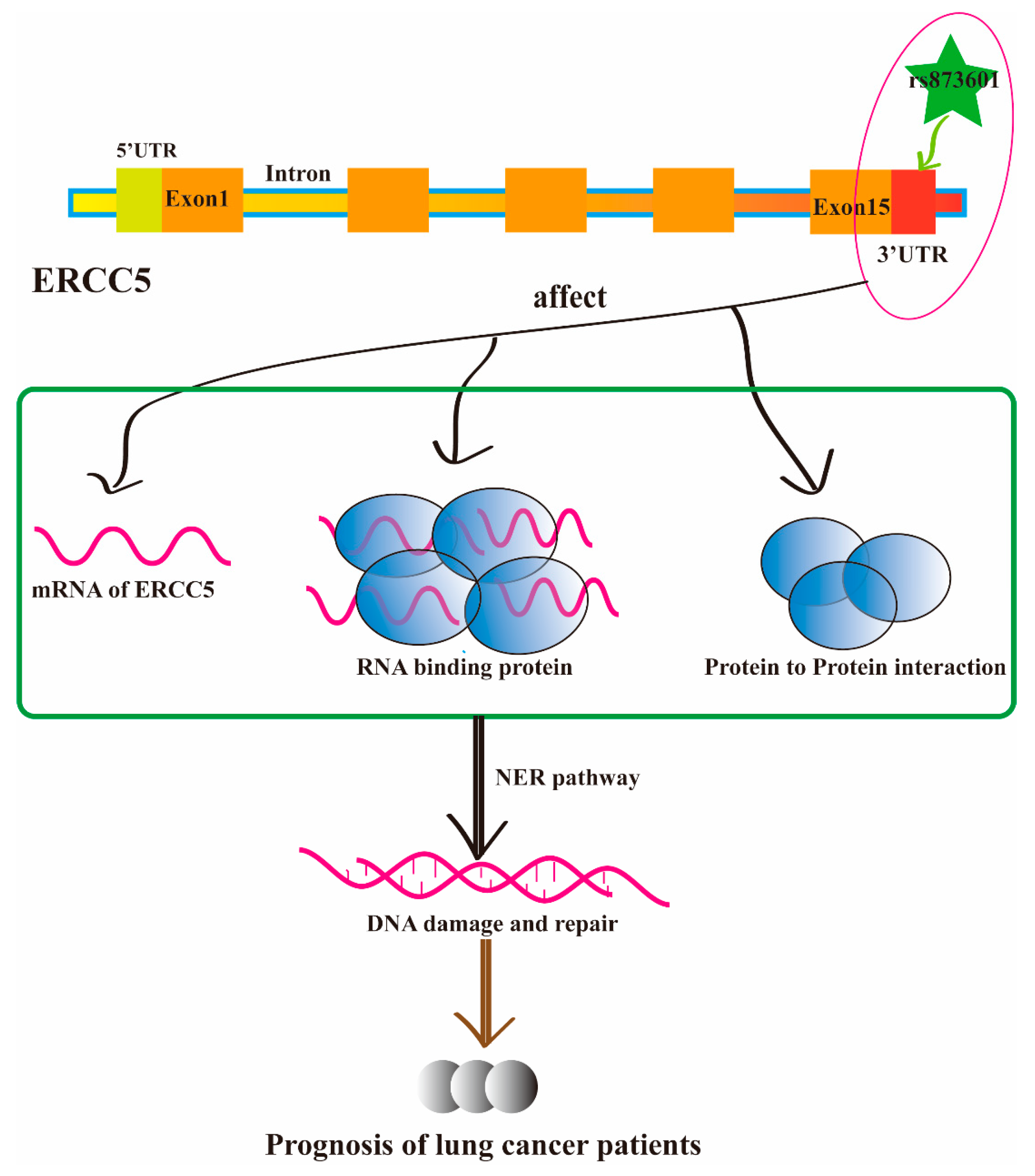
Discussion
Acknowledgments
Disclosure Statement
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-Chowdhuri, S. Molecular Pathology of Lung Cancer. Surg Pathol Clin 2021, 14, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, D. Advances in the therapy of small cell lung cancer. Klin Onkol 2021, 34, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.; Hanna, N. Advances in systemic therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. BMJ 2021, 375, n2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C. [Advances in Lung Cancer Treatment]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 2021, 146, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, B.; Lee, S.H.; Sun, J.M.; Park, W.Y.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K. DNA Damage Response and Repair Pathway Alteration and Its Association With Tumor Mutation Burden and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in SCLC. J Thorac Oncol 2019, 14, 1640–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Huo, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, R.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Lung cancer risk in patients with multiple sclerosis: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2021, 51, 102927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.Q. eIF3a: A new anticancer drug target in the eIF family. Cancer Lett 2018, 412, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Yin, J.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, L.; Tan, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, C.; Cui, J.; et al. Rho GTPases: RAC1 polymorphisms affected platinum-based chemotherapy toxicity in lung cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2016, 78, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zou, T.; Li, X.P.; Cao, L.; Chen, J. The Effects of WISP1 Polymorphisms on the Prognosis of Lung Cancer Patients with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy. Pharmgenomics Pers Med 2021, 14, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, B.; Pothof, J.; Vijg, J.; Hoeijmakers, J.H.J. The central role of DNA damage in the ageing process. Nature 2021, 592, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.E.; Mosammaparast, N. Mechanisms of damage tolerance and repair during DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 3033–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, J.; Thadhani, E.; Samson, L.; Engelward, B. Inflammation-induced DNA damage, mutations and cancer. DNA Repair (Amst) 2019, 83, 102673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paull, T.T. DNA damage and regulation of protein homeostasis. DNA Repair (Amst) 2021, 105, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilger, D.; Seymour, L.W.; Jackson, S.P. Interfaces between cellular responses to DNA damage and cancer immunotherapy. Genes Dev 2021, 35, 602–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.H.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Jiang, H.G.; Wu, M.; Chen, Y.C. RNA interferences targeting the Fanconi anemia/BRCA pathway upstream genes reverse cisplatin resistance in drug-resistant lung cancer cells. J Biomed Sci 2015, 22, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunova, V.; Seluanov, A.; Mao, Z.; Hine, C. Changes in DNA repair during aging. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, 7466–7474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniesa-Vargas, A.; Theil, A.F.; Ribeiro-Silva, C.; Vermeulen, W.; Lans, H. XPG: A multitasking genome caretaker. Cell Mol Life Sci 2022, 79, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyohara, C.; Yoshimasu, K. Genetic polymorphisms in the nucleotide excision repair pathway and lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Int J Med Sci 2007, 4, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, L. The Association of ERCC1 and ERCC5 Polymorphisms with Lung Cancer Risk in Han Chinese. J Cancer 2022, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Shi, G.Y.; Zhou, H.F.; Yu, Y. Role of XRCC1 and ERCC5 polymorphisms on clinical outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Genet Mol Res 2014, 13, 3100–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Sarma, H.; Mattaparthi, V.S.K. Investigation of the probable homo-dimer model of the Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group A (XPA) protein to represent the DNA-binding core. J Biomol Struct Dyn 2019, 37, 3322–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Yu, C.; Yu, K. Association of human XPA rs1800975 polymorphism and cancer susceptibility: An integrative analysis of 71 case-control studies. Cancer Cell Int 2020, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Hou, M.; Guo, S.; Hua, F.; Zheng, D.; Xu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Qiao, Y.; Fan, Y.; et al. Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes of XRCC1, XPA, XPC, XPD and associations with lung cancer risk in Chinese people. Thorac Cancer 2014, 5, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, S.; Hong, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Huai, C.; Chen, H.; Gao, Z.; Qian, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of nucleotide excision repair pathway are significantly associated with outcomes of platinum-based chemotherapy in lung cancer. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Kong, J.; Yu, H.; Qian, B. DNA Repair Gene Polymorphisms in Relation to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Survival. Cell Physiol Biochem 2015, 36, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zou, T.; Qian, C.; Li, C.; et al. Effect of transporter and DNA repair gene polymorphisms to lung cancer chemotherapy toxicity. Tumour Biol 2016, 37, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piljic Burazer, M.; Mladinov, S.; Matana, A.; Kuret, S.; Bezic, J.; Glavina Durdov, M. Low ERCC1 expression is a good predictive marker in lung adenocarcinoma patients receiving chemotherapy based on platinum in all TNM stages—A single-center study. Diagn Pathol 2019, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenda, A.; Blach, J.; Szczyrek, M.; Krawczyk, P.; Nicos, M.; Kuznar Kaminska, B.; Jakimiec, M.; Balicka, G.; Chmielewska, I.; Batura-Gabryel, H.; et al. Promoter polymorphisms of TOP2A and ERCC1 genes as predictive factors for chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Med 2020, 9, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Tang, L.L.; Long, J.T.; Zhu, J.; Hua, R.X.; Li, J. XPG gene polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: Evidence from 47 studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 37263–37277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liutkeviciene, R.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Morkunaite, G.; Glebauskiene, B.; Kriauciuniene, L. SIRT1 (rs3740051) role in pituitary adenoma development. BMC Med Genet 2019, 20, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, J.Y.; Li, X.P.; Chen, J.; Qian, C.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Fu, Y.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Liu, Z.Q. The association of transporter genes polymorphisms and lung cancer chemotherapy response. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibeira, M.T.; de Larrea, C.F.; Navarro, A.; Diaz, T.; Fuster, D.; Tovar, N.; Rosinol, L.; Monzo, M.; Blade, J. Impact on response and survival of DNA repair single nucleotide polymorphisms in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma patients treated with thalidomide. Leuk Res 2011, 35, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, B.; Lin, D.; Tan, W.; Leaw, S.; Hong, X.; Hu, X. XRCC1 polymorphisms and severe toxicity in lung cancer patients treated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy in Chinese population. Lung Cancer 2008, 62, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.R.; Sethi, I.; Bhat, A.; Verma, S.; Bakshi, D.; Sharma, B.; Nazir, M.; Dar, K.A.; Abrol, D.; Shah, R.; et al. Genetic evaluation of the variants using MassARRAY in non-small cell lung cancer among North Indians. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 11291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minina, V.I.; Bakanova, M.L.; Soboleva, O.A.; Ryzhkova, A.V.; Titov, R.A.; Savchenko, Y.A.; Sinitsky, M.Y.; Voronina, E.N.; Titov, V.A.; Glushkov, A.N. Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes in lung cancer patients living in a coal-mining region. Eur J Cancer Prev 2019, 28, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ramirez, C.; Canadas-Garre, M.; Molina, M.A.; Robles, A.I.; Faus-Dader, M.J.; Calleja-Hernandez, M.A. Contribution of genetic factors to platinum-based chemotherapy sensitivity and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 2017, 771, 32–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Duan, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, Q.; Yuan, Y. Role of ERCC5 promoter polymorphisms in response to platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2013, 24, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, G.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; Li, A.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and toxicity of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Cappuzzo, F. HER2 and lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2013, 13, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, A.; Sharma, S.; Minari, R.; Perego, P.; Giovannetti, E.; Tiseo, M. Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 2019, 121, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Kanwar, S.S. Phosphatidylserine: A cancer cell targeting biomarker. Semin Cancer Biol 2018, 52, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, W.Y.; Ding, C.L.; Yuan, B.Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, N.; Huang, J.B. Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of HER2 Gene Phenotype in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int J Gen Med 2021, 14, 9153–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraibar, I.; Mezquita, L.; Gil-Bazo, I.; Planchard, D. Novel drugs targeting EGFR and HER2 exon 20 mutations in metastatic NSCLC. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2020, 148, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalkhalek, E.S.; Wakeel, L.M.E.; Nagy, A.A.; Sabri, N.A. Variants of ERCC5 and the outcome of platinum-based regimens in non-small cell lung cancer: A prospective cohort study. Med Oncol 2022, 39, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zienolddiny, S.; Campa, D.; Lind, H.; Ryberg, D.; Skaug, V.; Stangeland, L.; Phillips, D.H.; Canzian, F.; Haugen, A. Polymorphisms of DNA repair genes and risk of non-small cell lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Han, X.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Lu, S.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, J. Long Non-Coding RNA PNKY Modulates the Development of Choroidal Neovascularization. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 836031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Yang, Q.; Wei, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, E. Toll/IL-1 receptor-containing proteins STIR-1, STIR-2 and STIR-3 synergistically assist Yersinia ruckeri SC09 immune escape. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2020, 103, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Wei, S.; Yuan, K. Gene expression and prognosis of x-ray repair cross-complementing family members in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 6210–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, H.; Guo, Q.; Guo, J.L.; Liu, H.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. The roles of risk model based on the 3-XRCC genes in lung adenocarcinoma progression. Transl Cancer Res 2021, 10, 4413–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saviozzi, S.; Ceppi, P.; Novello, S.; Ghio, P.; Lo Iacono, M.; Borasio, P.; Cambieri, A.; Volante, M.; Papotti, M.; Calogero, R.A.; et al. Non-small cell lung cancer exhibits transcript overexpression of genes associated with homologous recombination and DNA replication pathways. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 3390–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Total no. of patients | 345 |
| Histology | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 112(32.5) |
| Squamous cell Small cell |
111(32.2) 99(28.7) |
| Age | |
| ≤56 | 172(49.9) |
| >56 | 173(50.1) |
| Clinical stage | |
| I/II/LD | 41(11.9) |
| III/IV/ED | 298(86.4) |
| Smoking status | |
| Non-smoker | 122(35.4) |
| Smoker | 223(64.6) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 285(82.6) |
| Female | 60(17.4) |
| Metastasis | |
| No Yes |
61(17.7) 149(34.2) |
| Chemotherapy regimens | |
| Platinum/gemcitabine | 109(31.6) |
| Platinum/paclitaxel | 59(17.1) |
| Platinum/navelbine | 8(2.3) |
| Platinum/etoposide | 77(22.3) |
| Platinum/irinotecan | 8(2.3) |
| Gene | Locus | dbSNP | Call Rate(%) | Polymorphism | MAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERCC1 | 19q13.32 | rs12984195 | 97.97 | T>C | 3.70 |
| rs117128015 | 100.00 | C>T | 8.00 | ||
| ERCC5 | 13q33.1 | rs873601 | 99.13 | G>A | 49.11 |
| PNKY | 6q16.1 | rs1869641 | 98.84 | G>A | 22.22 |
| rs1883306 | 93.91 | T>G | 38.53 | ||
| rs2444933 | 99.13 | A>G | 31.62 | ||
| SIRT1 | 10q21.3 | rs3758391 | 97.39 | T>C | 24.46 |
| rs3740051 | 96.52 | A>G | 33.41 | ||
| rs4746720 | 99.13 | T>C | 46.67 | ||
| rs12778366 | 95.65 | T>C | 22.09 | ||
| XPA | 9q22.33 | rs3176751 | 98.84 | G>C | 20.61 |
| rs3176752 | 98.84 | C>A | 21.44 | ||
| XRCC3 | 14q32.33 | rs3212117 | 98.84 | C>A | 5.28 |
| rs3212121 | 98.55 | A>G | 4.24 | ||
| XRCC5 | 2q35 | rs1051677 | 98.84 | T>C | 22.43 |
| rs2440 | 98.55 | C>T | 34.03 | ||
| rs1051685 | 99.13 | A>G | 12.14 |
| Variables | Patients N(%) | Death N(%) | MST-OS (year) | MST-PFS (year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | 345 | 279 | 4.42 | 3.16 |
| NSCLC | 233(67.5) | 188(67.4) | 4.56 | 3.25 |
| SCLC | 99(28.7) | 80(28.7) | 4.17 | 3.10 |
| Age | ||||
| ≤56 | 172(49.9) | 142(50.9) | 4.48 | 2.95 |
| >56 | 173(50.1) | 137(49.1) | 4.36 | 3.80 |
| Clinical stage | ||||
| I/II/LD | 41(11.9) | 31(11.1) | 3.14 | 4.05 |
| III/IV/ED | 298(86.4) | 243(87.1) | 4.55 | 3.21 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| Non-smoker | 122(35.4) | 97(34.8) | 4.77 | 4.60 |
| Smoker | 223(64.6) | 182(65.2) | 4.26 | 2.61 |
| Gender | ||||
| male | 285(82.6) | 229(82.1) | 4.39 | 2.93 |
| female | 60(17.4) | 50(17.9) | 4.57 | 4.47 |
| Metastasis | ||||
| No | 61(17.7) | 51(18.3) | 3.84 | 2.28 |
| Yes | 149(43.2) | 121(43.4) | 4.53 | 3.94 |
| Gene | Polymorphisms | Genotype | MST(year) | Additive | Dominant | Recessive | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BETA (95%CI) | p value | BETA (95%CI) | p value | BETA (95%CI) | p value | ||||
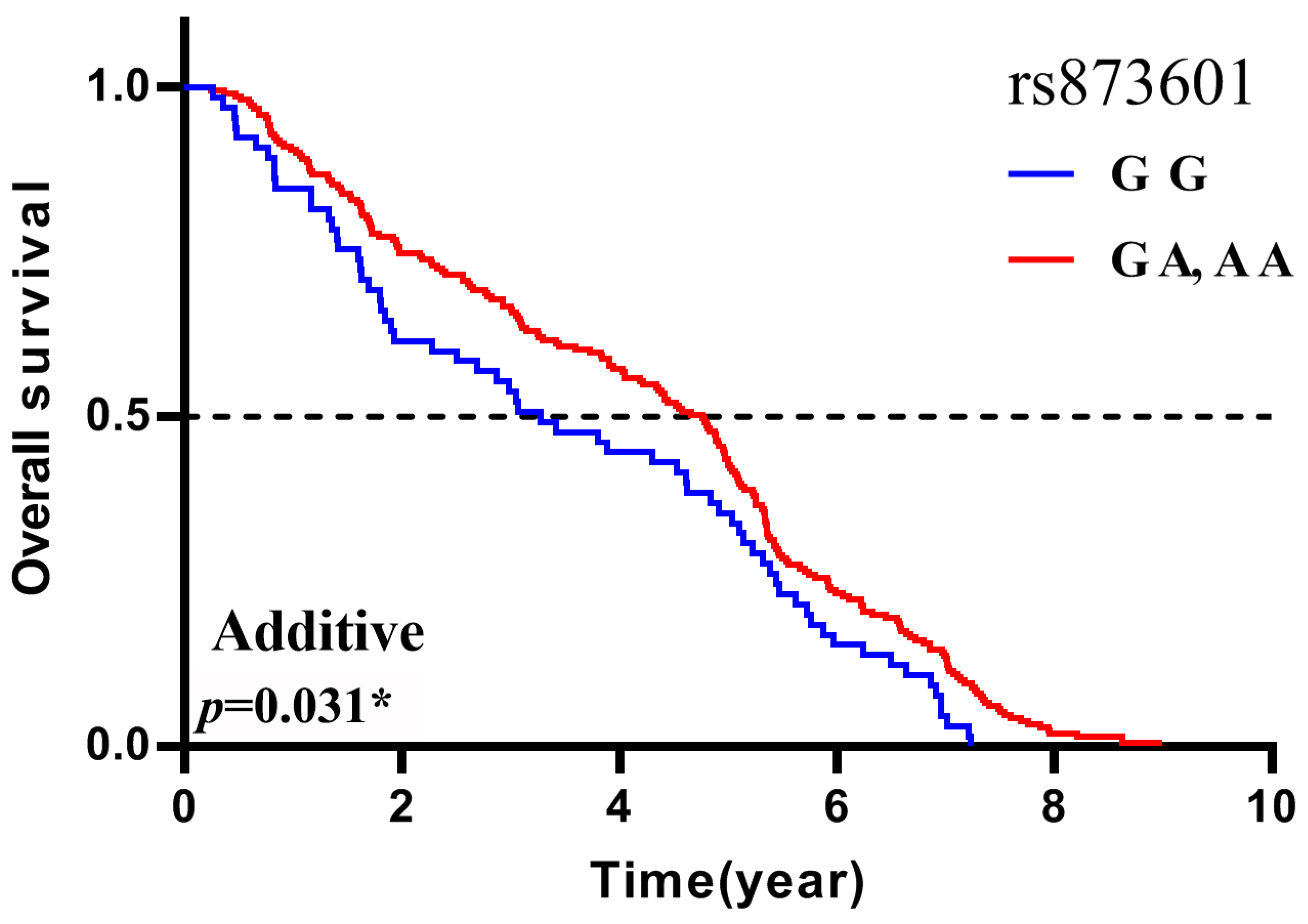
| ERCC5 | rs873601 | G G | 3.28 | -0.37(-0.75,0.01) | 0.061 | -0.30(-0.91,0.32) | 0.348 | -0.70(-1.34,-0.07) | 0.031* |
| G A A A |
4.88 4.02 |
| OS/PFS |
Gene |
Polymorphisms | Subgroup | Additive | Dominant | Recessive | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BETA (95%CI) | p value | BETA (95%CI) | p value | BETA (95%CI) | p value | ||||
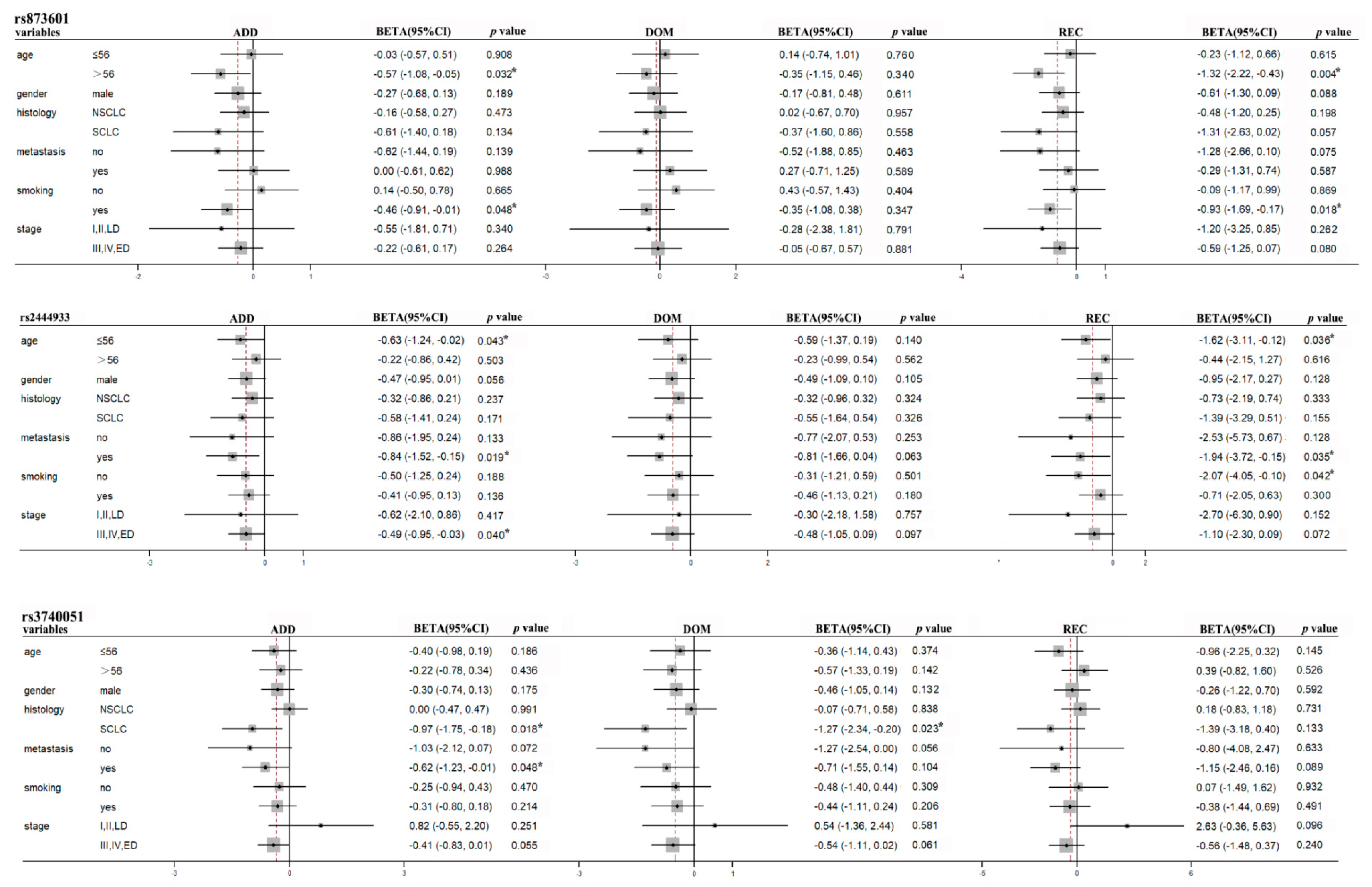
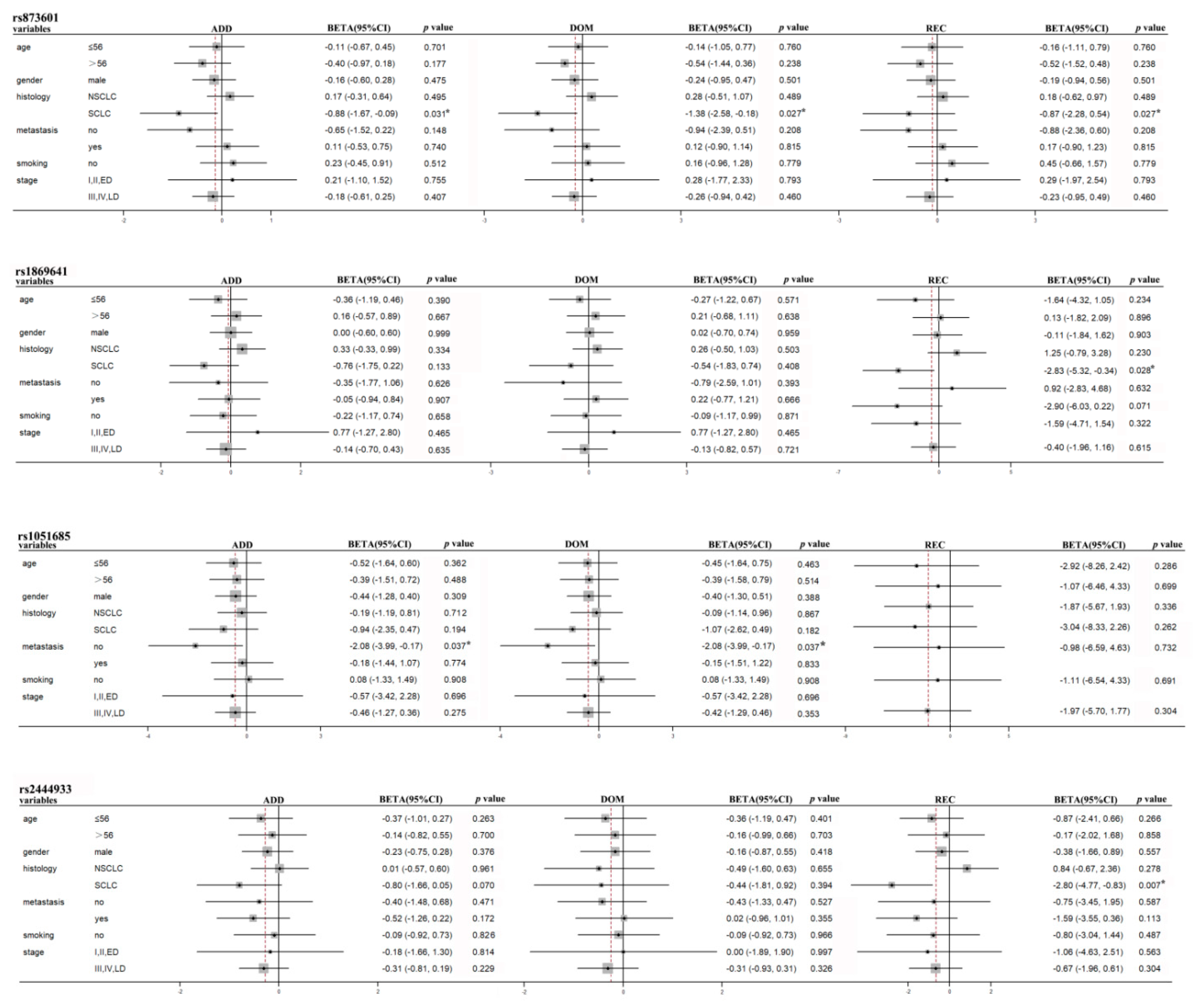
| OS | ERCC5 | rs873601 | age>56 | -0.57(-1.08,-0.05) | 0.032* | -0.35(-1.15,0.46) | 0.399 | -1.32(-2.22,-0.43) | 0.004* |
|
PFS |
PNKY STIR1 ERCC5 PNKY XRCC5 |
rs2444933 rs3740051 rs873601 rs2444933 rs1869641 rs1051685 |
smokers age≤56 metastasis non-smoker III/IV/ED SCLC metastasis SCLC SCLC SCLC Non-metastasis |
-0.46(-0.91,-0.01) -0.63(-1.24,-0.02) -0.84(-1.53,-0.15) -0.51(-1.25,0.24) -0.49(-0.95,-0.03) -0.97(-1.75,-0.18) -0.62(-1.23,-0.01) -0.88(-1.67,-0.09) -0.80(-1.66,0.05) -0.76(-1.75,0.22) -2.08(-3.99,-0.17) |
0.048* 0.043* 0.019* 0.188 0.040* 0.018* 0.048* 0.031* 0.070 0.133 0.037* |
-0.35(-1.08,0.38) -0.59(-1.37,0.19) -0.81(-1.66,0.04) -0.31(-1.21,0.59) -0.48(-1.05,0.09) -1.27(-2.34,-0.20) -0.71(-1.55,0.14) -1.38(-2.58,-0.18) -0.49(-1.60,0.63) -0.54(-1.83,0.74) -2.08(-3.99,-0.17) |
0.347 0.140 0.063 0.501 0.097 0.023* 0.104 0.027* 0.394 0.408 0.037* |
-0.93(-1.69,-0.17) -1.62(-3.11,-0.12) -1.94(-3.72,-0.15) -2.07(-4.05,-0.10) -1.10(-2.30,0.09) -1.39(-3.18,0.40) -1.15(-2.46,0.16) -0.87(-2.28,0.54) -2.80(-4.77,-0.83) -2.83(-5.32,-0.34) |
0.018* 0.036* 0.035* 0.042* 0.072 0.133 0.089 0.230 0.007* 0.028* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




