Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Discussion
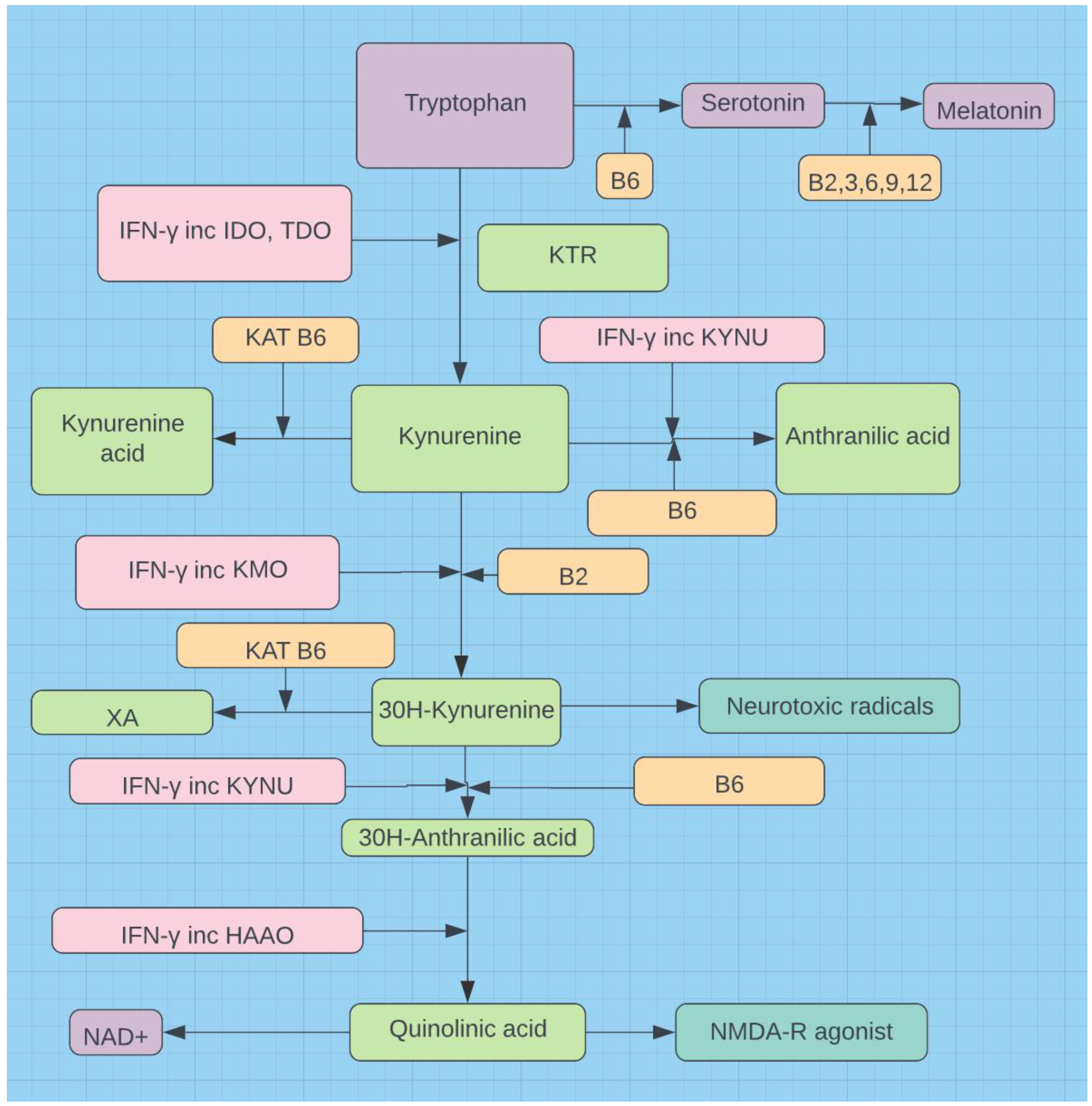
| 1. Altered tryptophan metabolism (7,8) 2. Increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity (7,9,10) 3. Low serum serotonin (11,12,13,14,15,16) 4. Low butyrate produced by gut microbiota (17,18,19) 5. TNFα mediated (20, 5) 6. Oxidative stress associated neurodegeneration (3,21) 7. Elevated dementia triad cytokines - TNFα, IL-1β, IL-6 (22,23,24,25) 8. Low (exhausted) IFN-γ (26,27] 9. Low (exhausted) mannose binding lectins (MBLs) (28,29,30,31) 10. Complement mediated fog (29,32,33) 11. High oligomannose glycan shield (34,35,36) 12. Alcohol intolerance (37,38) 13. Dysbiosis, Leaky gut (39,40) 14. Increased autoimmunity (39,40,41) 15. Brain fog and fatigue (29,42) 16. Accelerated AD (43,44,45) 17. More common in females during their reproductive years (46,47) |
Prevention and Therapy
Conclusion
References
- Silvere D Zaongo, Jing Ouyang, Stéphane Isnard, Xin Zhou, Vijay Harypursat, Hongjuan Cui, et al. (2023) Candida albicans can foster gut dysbiosis and systemic inflammation during HIV infection, Gut Microbes, 15:1 . [CrossRef]
- Park SY, Faraci G, Nanda S, Ter-Saakyan S, Love TMT, et al. Gut microbiome in people living with HIV is associated with impaired thiamine and folate syntheses. Microb Pathog. 2021 Nov;160:105209. [CrossRef]
- Cater RE 2nd. Chronic intestinal candidiasis as a possible etiological factor in the chronic fatigue syndrome. Med Hypotheses. 1995 Jun;44(6):507-15. [CrossRef]
- Valand N, Girija UV. Candida Pathogenicity and Interplay with the Immune System. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1313:241-272. [CrossRef]
- Chambers P (2023) The CD147 Epitope on SARS CoV2 and the Spike in Cancer, Autoimmunity and Organ Fibrosis. Medical & Clinical Research, 8(11), 01-13 https://www.medclinrese.org/open-access/the-cd147-epitope-on-sars-cov2-and-the-spike-in-cancer-autoimmunity-and-organ-fibrosis.pdf].
- Autoimmune Registry COVID-19 Added to the list of Autoimmune Diseases https://www.autoimmuneregistry.org/long-covid-announcement.
- Silvia Bozza, Francesca Fallarino, Lucia Pitzurra, Teresa Zelante, Claudia Montagnoli, Silvia Bellocchio, et al. A Crucial Role for Tryptophan Catabolism at the Host/Candida albicans Interface. J Immunol 1 March 2005; 174 (5): 2910–2918. [CrossRef]
- Kaur G, Ji X, Rahman I. SARS-CoV2 Infection Alters Tryptophan Catabolism and Phospholipid Metabolism Metabolites. 2021 Sep 28;11(10):659. [CrossRef]
- Guo L, Schurink B, Roos E, Nossent EJ, Duitman JW, Vlaar AP, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)-1 and IDO-2 activity and severe course of COVID-19. J Pathol. 2022 Mar;256(3):256-261. [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu İ, Eroğlu BÇ, Güven GS. Altered tryptophan absorption and metabolism could underlie long-term symptoms in survivors of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Nutrition. 2021 Oct;90:111308. [CrossRef]
- Harris E. Long COVID Linked With Viral Persistence, Serotonin Decline. JAMA. Published online November 01, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wong AC, Devason AS, Umana IC, Cox TO, Dohnalová L, Litichevskiy L, et al. Serotonin reduction in post-acute sequelae of viral infection. Cell. 2023 Oct 26;186(22):4851-4867.e20. [CrossRef]
- Bird, L. Low serotonin linked to long COVID. Nat Rev Immunol. Nat Rev Immunol (2023) . [CrossRef]
- Mayr A, Hinterberger G, Dierich MP, Lass-Flörl C. Interaction of serotonin with Candida albicans selectively attenuates fungal virulence in vitro. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005 Oct;26(4):335-7. [CrossRef]
- Lass-Flörl C, Fuchs D, Ledochowski M, Speth C, Dierich MP, Würzner R. Antifungal properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) against Candida species in vitro. J Med Microbiol. 2003 Feb;52(Pt 2):169-171. [CrossRef]
- Banskota S, Khan WI. Gut-derived serotonin and its emerging roles in immune function, inflammation, metabolism and the gut-brain axis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2022 Apr 1;29(2):177-182. [CrossRef]
- Noureldein MH, Bitar S, Youssef N, Azar S, Eid AA. Butyrate modulates diabetes-linked gut dysbiosis: epigenetic and mechanistic modifications. J Mol Endocrinol. 2020 Jan;64(1):29-42. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen LN, Lopes LC, Cordero RJ, Nosanchuk JD. Sodium butyrate inhibits pathogenic yeast growth and enhances the functions of macrophages. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Nov;66(11):2573-80. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Zhang, L., Wang, Y. et al. Alterations in microbiota of patients with COVID-19: potential mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Sig Transduct Target Ther 7, 143 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Jouault T, Lepage G, Bernigaud A, Trinel PA, Fradin C, Wieruszeski JM, Strecker G, Poulain D. Beta-1,2-linked oligomannosides from Candida albicans act as signals for tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Infect Immun. 1995 Jun;63(6):2378-81. [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeim, H.K., Al-Rubaye, H.T., Al-Hadrawi, D.S. et al. Long-COVID post-viral chronic fatigue and affective symptoms are associated with oxidative damage, lowered antioxidant defenses and inflammation: a proof of concept and mechanism study. Mol Psychiatry 28, 564–578 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., Du, S., Johnson, J.L. et al. Microglia and amyloid precursor protein coordinate control of transient Candida cerebritis with memory deficits. Nat Commun 10, 58 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q., Zhang, L., Dong, Y. et al. The role of SARS-CoV-2-mediated NF-κB activation in COVID-19 patients. Hypertens Res (2023). [CrossRef]
- Ishijima T, Nakajima K. Inflammatory cytokines TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 are induced in endotoxin- stimulated microglia through different signaling cascades. Sci Prog. 2021 Oct;104(4):368504211054985. [CrossRef]
- Schultheiß, Christoph, Edith Willscher, Lisa Paschold, Cornelia Gottschick, et al. 2022. The IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF Cytokine Triad Is Associated with Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 Cell Reports Medicine 3 (6): 100663. [CrossRef]
- Williams ES, Martins TB, Shah KS, Hill HR, Coiras M, Spivak AM, Planelles V. Cytokine Deficiencies in Patients with Long-COVID. J Clin Cell Immunol. 2022;13(6):672. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36742994/].
- Szkaradkiewicz, E. Szponar, E. Krzemińska-Jaśkowiak, T. Tułecka, Serum interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) in chronic oral candidosis, Medical Mycology, Volume 36, Issue 5, January 1998, Pages 269–273, . [CrossRef]
- Hammad NM, El Badawy NE, Ghramh HA, Al Kady LM. Mannose-Binding Lectin: A Potential Therapeutic Candidate against Candida Infection. Biomed Res Int. 2018 May 2;2018:2813737. [CrossRef]
- Bulla R, Rossi L, Furlanis G, Agostinis C, Toffoli M, Balduit A, et al. A likely association between low mannan-binding lectin level and brain fog onset in long COVID patients. Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 16;14:1191083. [CrossRef]
- Damiens S, Poissy J, François N, Salleron J, Jawhara S, Jouault T, et al. Mannose-binding lectin levels and variation during invasive candidiasis. J Clin Immunol. 2012 Dec;32(6):1317-23. [CrossRef]
- Choteau, L., Parny, M., François, N. et al. Role of mannose-binding lectin in intestinal homeostasis and fungal elimination. Mucosal Immunol 9, 767–776 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Hurler L, Szilágyi Á, Mescia F, Bergamaschi L, Mező B, Sinkovits G, et al. Complement lectin pathway activation is associated with COVID-19 disease severity, independent of MBL2 genotype subgroups. Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 27;14:1162171. [CrossRef]
- Harpf V, Rambach G, Würzner R, Lass-Flörl C, Speth C. Candida and Complement: New Aspects in an Old Battle. Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 14;11:1471. [CrossRef]
- Lillegard JB, Sim RB, Thorkildson P, Gates MA, Kozel TR. Recognition of Candida albicans by mannan-binding lectin in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 2006 Jun 1;193(11):1589-97. [CrossRef]
- Sendid B, Lecointe K, Collot M, Danzé PM, Damiens S, Drucbert AS, et al. Dissection of the anti-Candida albicans mannan immune response using synthetic oligomannosides reveals unique properties of β-1,2 mannotriose protective epitopes. Sci Rep. 2021 May 24;11(1):10825. [CrossRef]
- Bai Y, Huang W, Ma LT, Jiang JL, Chen ZN. Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 15;15(4):6356-77. [CrossRef]
- Pho, K. Could a glass of wine diagnose long COVID? https://www.kevinmd.com/2021/03/could-a-glass-of-wine-diagnose-long-covid.html.
- Chen CH, Joshi AU, Mochly-Rosen D. The Role of Mitochondrial Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in Neuropathology and Neurodegeneration. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2016 Dec 15;25(4)(4):111-123. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc10618051/.
- Kinashi Y, Hase K. Partners in Leaky Gut Syndrome: Intestinal Dysbiosis and Autoimmunity. Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 22;12:673708. [CrossRef]
- Fasano A. Leaky gut and autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Feb;42(1):71-8. [CrossRef]
- Mousa WK, Chehadeh F, Husband S. Microbial dysbiosis in the gut drives systemic autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:906258. [CrossRef]
- Zimitat C, Nixon PF. Glucose loading precipitates acute encephalopathy in thiamine-deficient rats. Metab Brain Dis. 1999 Mar;14(1):1-20. [CrossRef]
- Wu Y, Du S, Bimler LH, Mauk KE, Lortal L, Kichik N, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 and CD11b expressed on microglia coordinate eradication of Candida albicans cerebral mycosis. Cell Rep. 2023 Oct 31;42(10):113240. [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S., Das, S., Ghosh, R., Dubey, M. J., Chakraborty, A. P., Roy, D., et al. (2023). The effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the cognitive functioning of patients with pre-existing dementia. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports, 7(1), 119–128. [CrossRef]
- Xia X, Wang Y, Zheng J. COVID-19 and Alzheimer's disease: how one crisis worsens the other. Transl Neurodegener. 2021 Apr 30;10(1):15. [CrossRef]
- Kumwenda P, Cottier F, Hendry AC, Kneafsey D, Keevan B, Gallagher H, et al. Estrogen promotes innate immune evasion of Candida albicans through inactivation of the alternative complement system. Cell Rep. 2022 Jan 4;38(1):110183. [CrossRef]
- Loster JE, Wieczorek A, Loster BW. Correlation between age and gender in Candida species infections of complete denture wearers: a retrospective analysis. Clin Interv Aging. 2016;11:1707-1714 . [CrossRef]
- Krämer K. Daily briefing: Severe COVID linked to bad fungal microbiome. Nature. 2023 Oct 24. [CrossRef]
- Jawhara S. How Gut Bacterial Dysbiosis Can Promote Candida albicans Overgrowth during Colonic Inflammation. Microorganisms. 2022 May 12;10(5):1014. [CrossRef]
- Lagree K, Chen P. Candida makes a lasting impression in COVID-19. Nat Immunol. 2023 Nov;24(11):1782-1784. [CrossRef]
- Zhu Z, Zhu L, Jiang L. Dynamic regulation of gut Clostridium-derived short-chain fatty acids. Trends Biotechnol. 2022 Mar;40(3):266-270. [CrossRef]
- Hu W, Xu D, Zhou Z, Zhu J, Wang D, Tang J. Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolic profiles coincide with intestinal damage in mice with a bloodborne Candida albicans infection. Microb Pathog. 2021 May;154:104826. [CrossRef]
- Sen A. Does serotonin deficiency lead to anosmia, ageusia, dysfunctional chemesthesis and increased severity of illness in COVID-19? Med Hypotheses. 2021 Aug;153:110627. [CrossRef]
- Lechien JR, Diallo AO, Dachy B, Le Bon SD, Maniaci A, Vaira LA, Saussez S. COVID-19: Post-vaccine Smell and Taste Disorders: Report of 6 Cases. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021 Sep 1:1455613211033125. [CrossRef]
- Bojing Liu, PhD*, Zhehui Luo, PhD*, Jayant M. Pinto, MD, Eric J. Shiroma, ScD, Gregory J. Tranah, PhD, Karin Wirdefeldt, MD, PhD, Relationship Between Poor Olfaction and Mortality Among Community-Dwelling Older Adults Ann Int Med 170(10):673-681 . [CrossRef]
- Gozalbo D, Gil ML. IFN-gamma in Candida albicans infections. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(5):1970-8. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Zhou, Y., Ma, J. et al. The long-term health outcomes, pathophysiological mechanisms and multidisciplinary management of long COVID. Sig Transduct Target Ther 8, 416 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Müller N, Myint AM, Schwarz MJ. The impact of neuroimmune dysregulation on neuroprotection and neurotoxicity in psychiatric disorders--relation to drug treatment. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2009;11(3):319-32. [CrossRef]
- Wolak N, Tomasi M, Kozik A, Rapala-Kozik M. Characterization of thiamine uptake and utilization in Candida spp. subjected to oxidative stress. Acta Biochim Pol. 2015;62(3):445-55. [CrossRef]
- Stevenhagen A, van Furth R. Interferon-gamma activates the oxidative killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Jan;91(1):170-5. [CrossRef]
- Reddy MGS, Kakodkar P, Nayanar G. Capacity of Candida species to produce acetaldehyde at various concentrations of alcohol. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2022 Apr-Jun;26(2):161-165. [CrossRef]
- Takabe M, Itokawa Y. Thiamine depletion after ethanol and acetaldehyde administration to rabbits. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 1983 Oct;29(5):509-14. [CrossRef]
- Wiegmann C, Mick I, Brandl EJ, Heinz A, Gutwinski S. Alcohol and Dementia - What is the Link? A Systematic Review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Jan 9;16:87-99. [CrossRef]
- Marrs C, Lonsdale D. Hiding in Plain Sight: Modern Thiamine Deficiency. Cells. 2021 Sep 29;10(10):2595. [CrossRef]
- Schröter C, Hipler UC, Wilmer A, Künkel W, Wollina U. Generation of reactive oxygen species by Candida albicans in relation to morphogenesis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2000 May;292(5):260-4. [CrossRef]
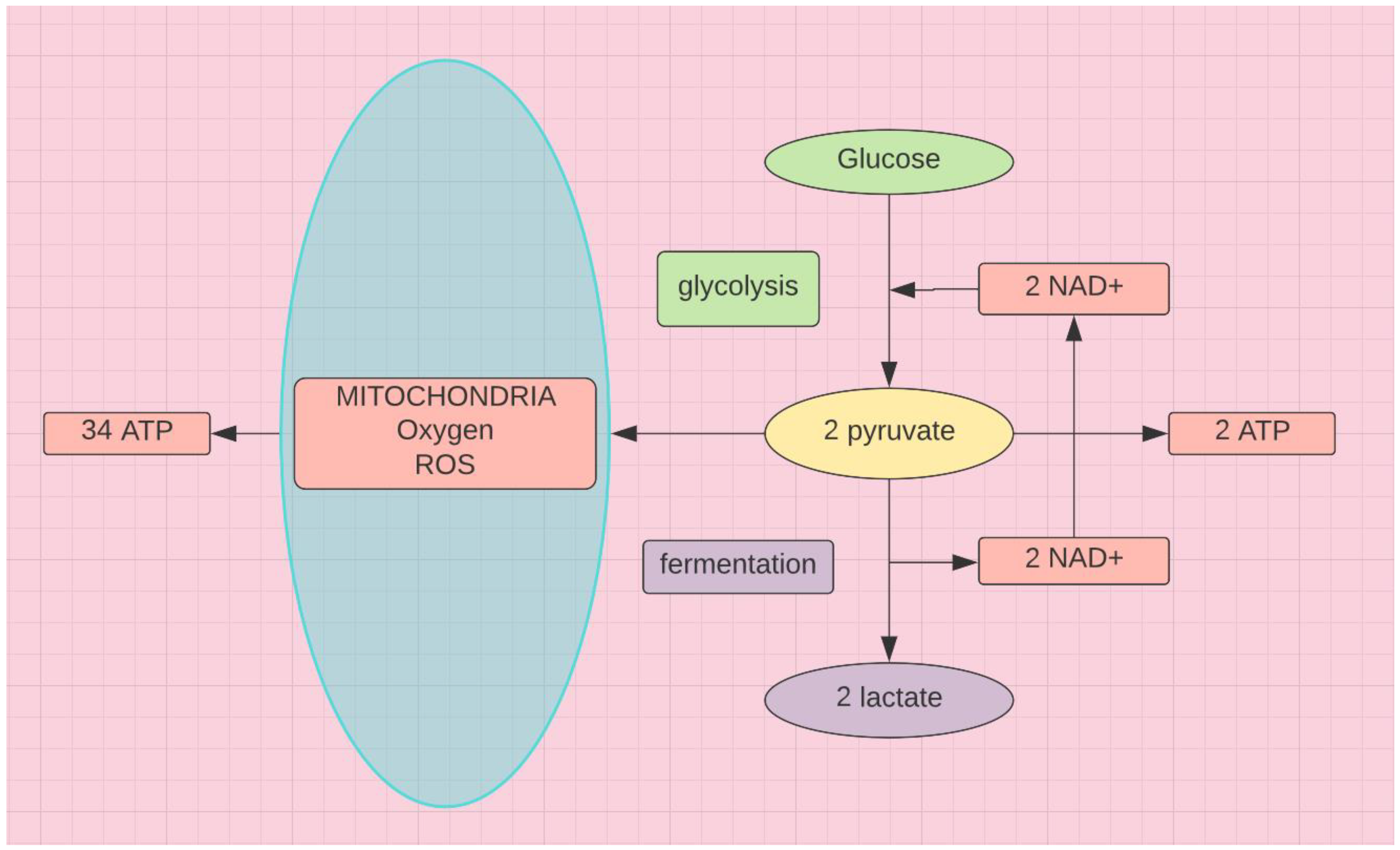
- Ballard JWO, Towarnicki SG. Mitochondria, the gut microbiome and ROS. Cell Signal. 2020 Nov;75:109737. [CrossRef]
- Swank, Z., Senussi, Y., Manickas-Hill, Z., Yu, X.G., Li, J.Z., et al. (2022) Persistent Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Spike Is Associated with Post-Acute COVID-19 Sequelae. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 2022, ciac722. [CrossRef]
- Shandilya S, Kumar S, Kumar Jha N, Kumar Kesari K, Ruokolainen J. Interplay of gut microbiota and oxidative stress: Perspective on neurodegeneration and neuroprotection. J Adv Res. 2021 Sep 17;38:223-244. [CrossRef]
- Zhang J, Wang Z, Zhang X, Dai Z, Zhi-Peng W, Yu J, et al. Large-Scale Single-Cell and Bulk Sequencing Analyses Reveal the Prognostic Value and Immune Aspects of CD147 in Pan-Cancer. Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 6;13:810471. [CrossRef]
- Hayes B, Stanley J, Peppers BP. COVID-19 Recurrence Without Seroconversion in a Patient With Mannose-Binding Lectin Deficiency. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2021 Jun 11;12:21526567211024140. [CrossRef]
- Kim HS. Do an Altered Gut Microbiota and an Associated Leaky Gut Affect COVID-19 Severity? mBio. 2021 Jan 12;12(1):e03022-20. [CrossRef]
- Rathmann W, Kuss O, Kostev K. Incidence of newly diagnosed diabetes after Covid-19. Diabetologia. 2022 Jun;65(6):949-954. [CrossRef]
- Sakurai K, Narita D, Saito N, Ueno T, Sato R, Niitsuma S, Takahashi K, Arihara Z. Type 1 diabetes mellitus following COVID-19 RNA-based vaccine. J Diabetes Investig. 2022 Jul;13(7):1290-1292. [CrossRef]
- Moon H, Suh S, Park MK. Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Jan 9;38(2):e12. [CrossRef]
- Roe K. How major fungal infections can initiate severe autoimmune diseases. Microb Pathog. 2021 Dec;161(Pt A):105200. [CrossRef]
- Nikolic DM, Dimitrijevic-Sreckovic V, Ranin LT, Stojanovic MM, Ilic ID, Gostiljac DM, et al. Homeostatic microbiome disruption as a cause of insulin secretion disorders. Candida albicans, a new factor in pathogenesis of diabetes: A STROBE compliant cross-sectional study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 11;101(45):e31291. [CrossRef]
- Paray BA, Albeshr MF, Jan AT, Rather IA. Leaky Gut and Autoimmunity: An Intricate Balance in Individuals Health and the Diseased State. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(24):9770. [CrossRef]
- Xiao P, Hu Z, Lang J, Pan T, Mertens RT, Zhang H, et al. Mannose metabolism normalizes gut homeostasis by blocking the TNF-α-mediated proinflammatory circuit. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Feb;20(2):119-130. [CrossRef]
- Torretta S, Scagliola A, Ricci L, Mainini F, Di Marco S, Cuccovillo I, Kajaste-Rudnitski A, Sumpton D, Ryan KM, Cardaci S. D-mannose suppresses macrophage IL-1β production. Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 11;11(1):6343. [CrossRef]
- Dong, L., Xie, J., Wang, Y. et al. Mannose ameliorates experimental colitis by protecting intestinal barrier integrity. Nat Commun 13, 4804 (2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang W, Cheng H, Gui Y, Zhan Q, Li S, Qiao W, et al. Mannose Treatment: A Promising Novel Strategy to Suppress Inflammation. Front Immunol. 2021 Sep 27;12:756920. [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, M., Sruthi, D., Jinuraj, K.R. et al. Mannose: a potential saccharide candidate in disease management. Med Chem Res 32, 391–408 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Sun J, Wang F, Hong G, Pang M, Xu H, Li H, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of sodium butyrate and its possible mechanisms of action in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Neurosci Lett. 2016 Apr 8;618:159-166. [CrossRef]
- Mayr A, Hinterberger G, Dierich MP, Lass-Flörl C. Interaction of serotonin with Candida albicans selectively attenuates fungal virulence in vitro. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2005 Oct;26(4):335-7. [CrossRef]
- Roth W, Zadeh K, Vekariya R, Ge Y, Mohamadzadeh M. Tryptophan Metabolism and Gut-Brain Homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 15;22(6):2973. [CrossRef]
- Hodgkinson K, El Abbar F, Dobranowski P, Manoogian J, Butcher J, Figeys D, et al.. Butyrate's role in human health and the current progress towards its clinical application to treat gastrointestinal disease. Clin Nutr. 2023 Feb;42(2):61-75. [CrossRef]
- González Delgado S, Garza-Veloz I, Trejo-Vazquez F, Martinez-Fierro ML. Interplay between Serotonin, Immune Response, and Intestinal Dysbiosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 9;23(24):15632. [CrossRef]
- Yusufu I, Ding K, Smith K, Wankhade UD, Sahay B, Patterson GT, et al. A Tryptophan-Deficient Diet Induces Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Increases Systemic Inflammation in Aged Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 8;22(9):5005. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.L., Jiang, L., Adams, J.S. et al. Vitamin D metabolites and the gut microbiome in older men. Nat Commun 11, 5997 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Książek A, Zagrodna A, Bohdanowicz-Pawlak A, Lwow F, Słowińska-Lisowska M. Relationships between Vitamin D and Selected Cytokines and Hemogram Parameters in Professional Football Players-Pilot Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 2;18(13):7124. [CrossRef]
- Chen YC, Sung HC, Chuang TY, Lai TC, Lee TL, Lee CW, et al. Vitamin D3 decreases TNF-α-induced inflammation in lung epithelial cells through a reduction in mitochondrial fission and mitophagy. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2022 Jun;38(3):427-450. [CrossRef]
- Bouzid D, Merzouki S, Bachiri M, Ailane SE, Zerroug MM. Vitamin D3 a new drug against Candida albicans. J Mycol Med. 2017 Mar;27(1):79-82. [CrossRef]
- Lei J, Xiao W, Zhang J, Liu F, Xin C, Zhou B, et al. Antifungal activity of vitamin D3 against Candida albicans in vitro and in vivo. Microbiol Res. 2022 Dec;265:127200. [CrossRef]
- Ragab D, Soliman D, Samaha D, Yassin A. Vitamin D status and its modulatory effect on interferon gamma and interleukin-10 production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in culture. Cytokine. 2016 Sep;85:5-10. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen FH. Magnesium deficiency and increased inflammation: current perspectives. J Inflamm Res. 2018 Jan 18;11:25-34. [CrossRef]
- Nabin K Shrestha, Patrick C Burke, Amy S Nowacki, James F Simon, Amanda Hagen, et al. Effectiveness of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Bivalent Vaccine, Open Forum Infectious Diseases, Volume 10, Issue 6, June 2023, ofad209, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, K., Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Deng, Y., et al. (2020) CD147-Spike Protein Is a Novel Route for SARS-CoV-2 Infection to Host Cells. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 5, 283. [CrossRef]
- Chambers, P.W. (2021) Basigin Binds Spike S on SARS-CoV2. Open Access Library Journal, 8: e8064. [CrossRef]
- Ricke, D.O., Immediate onset signatures of autoimmune diseases after vaccination (2023) Global Translational Medicine 2023, 2(3), 1455 . [CrossRef]
- Salsone M, Signorelli C, Oldani A, Alberti VF, Castronovo V, Mazzitelli S, et al. NEURO-COVAX: An Italian Population-Based Study of Neurological Complications after COVID-19 Vaccinations. Vaccines. 2023; 11(10):1621. [CrossRef]
- Eriksson O, Hultström M, Persson B, Lipcsey M, Ekdahl KN, Nilsson B, Frithiof R. Mannose-Binding Lectin is Associated with Thrombosis and Coagulopathy in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Thromb Haemost. 2020 Dec;120(12):1720-1724. [CrossRef]
- Hoffa, Charles, Doctor who vaccinated 900 calls blood clots at capillary level an ‘absolutely new phenomenon’ World Tribune 2021 https://www.worldtribune.com/doctor-who-vaccinated-900-calls-blood-clots-at-capillary-level-an-absolutely-new-phenomenon/].
- Luca M, Chattipakorn SC, Sriwichaiin S, Luca A. Cognitive-Behavioural Correlates of Dysbiosis: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 8;21(14):4834. [CrossRef]
- Pham VT, Dold S, Rehman A, Bird JK, Steinert RE. Vitamins, the gut microbiome and gastrointestinal health in humans. Nutr Res. 2021 Nov;95:35-53. [CrossRef]
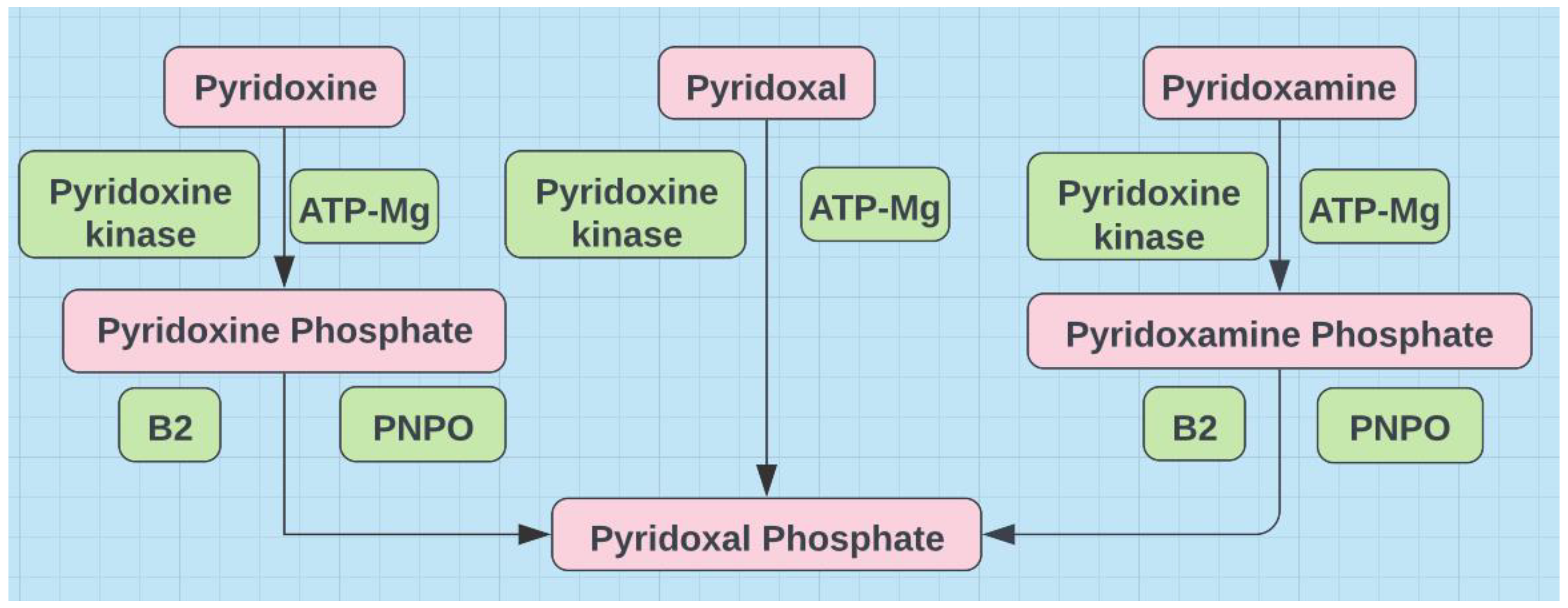
- Lonsdale D, Marrs C. Thiamine Deficiency Disease, Dysautonomia, and High Calorie Malnutrition, 1st Edition, 2017, Academic Press.
- Tetsuka, S., Hashimoto, R. Alcohol-Related Central Nervous System Disorders Associated with Vitamin B Deficiency. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 3, 528–537 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Huang SC, Wei JC, Wu DJ, Huang YC (2010) Vitamin B(6) supplementation improves pro-inflammatory responses in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Clin Nutr 64(9):1007- 1013. [CrossRef]
- Bzioueche H, Simonyté Sjödin K, West CE, Khemis A, Rocchi S, Passeron T, Tulic MK. Analysis of Matched Skin and Gut Microbiome of Patients with Vitiligo Reveals Deep Skin Dysbiosis: Link with Mitochondrial and Immune Changes. J Invest Dermatol. 2021 Sep;141(9):2280-2290. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





