Submitted:
17 November 2023
Posted:
22 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
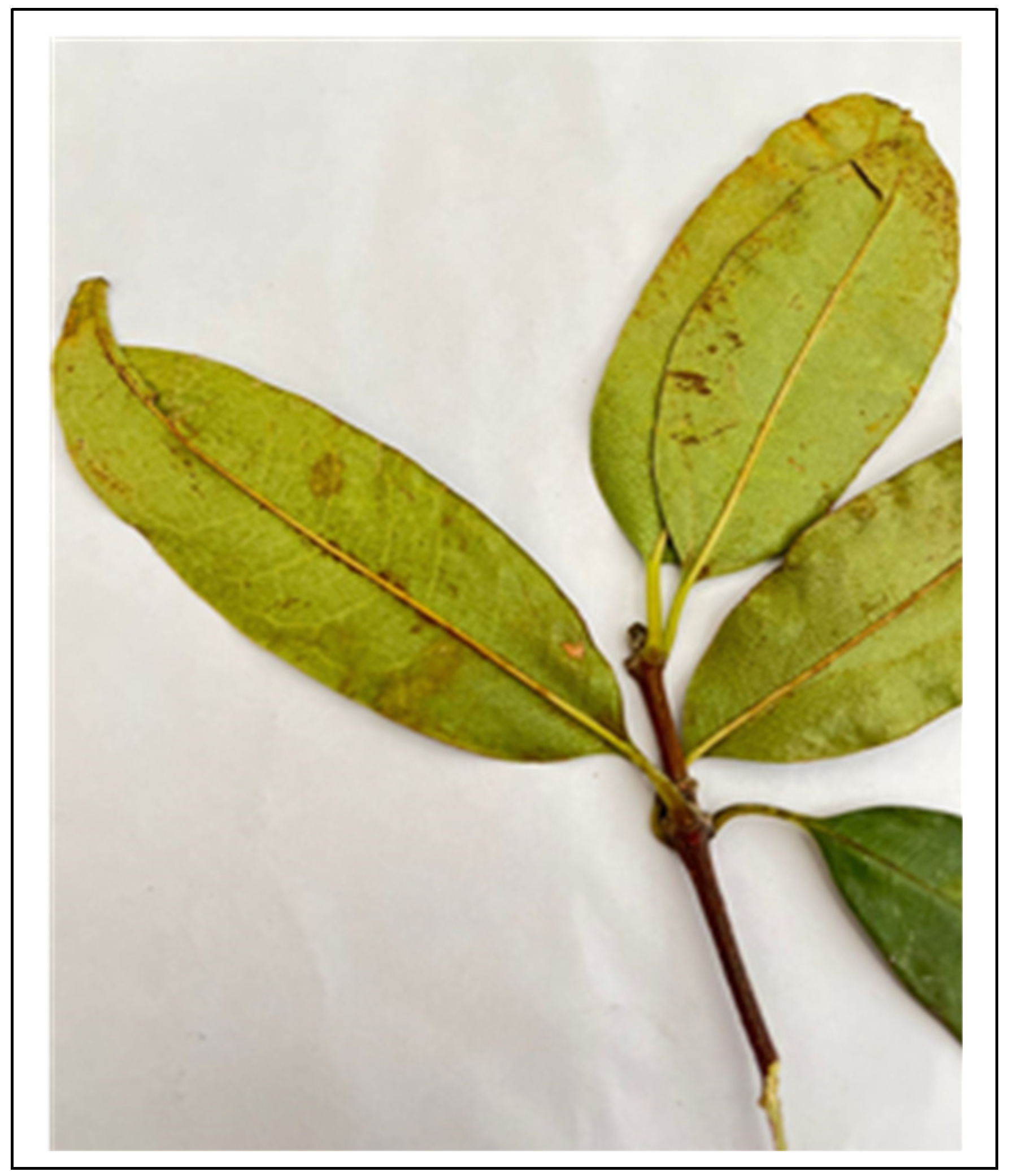
- Specimen 2: NH0151949-0, Cassipourea malosana (Baker) Alston (Figure 2).
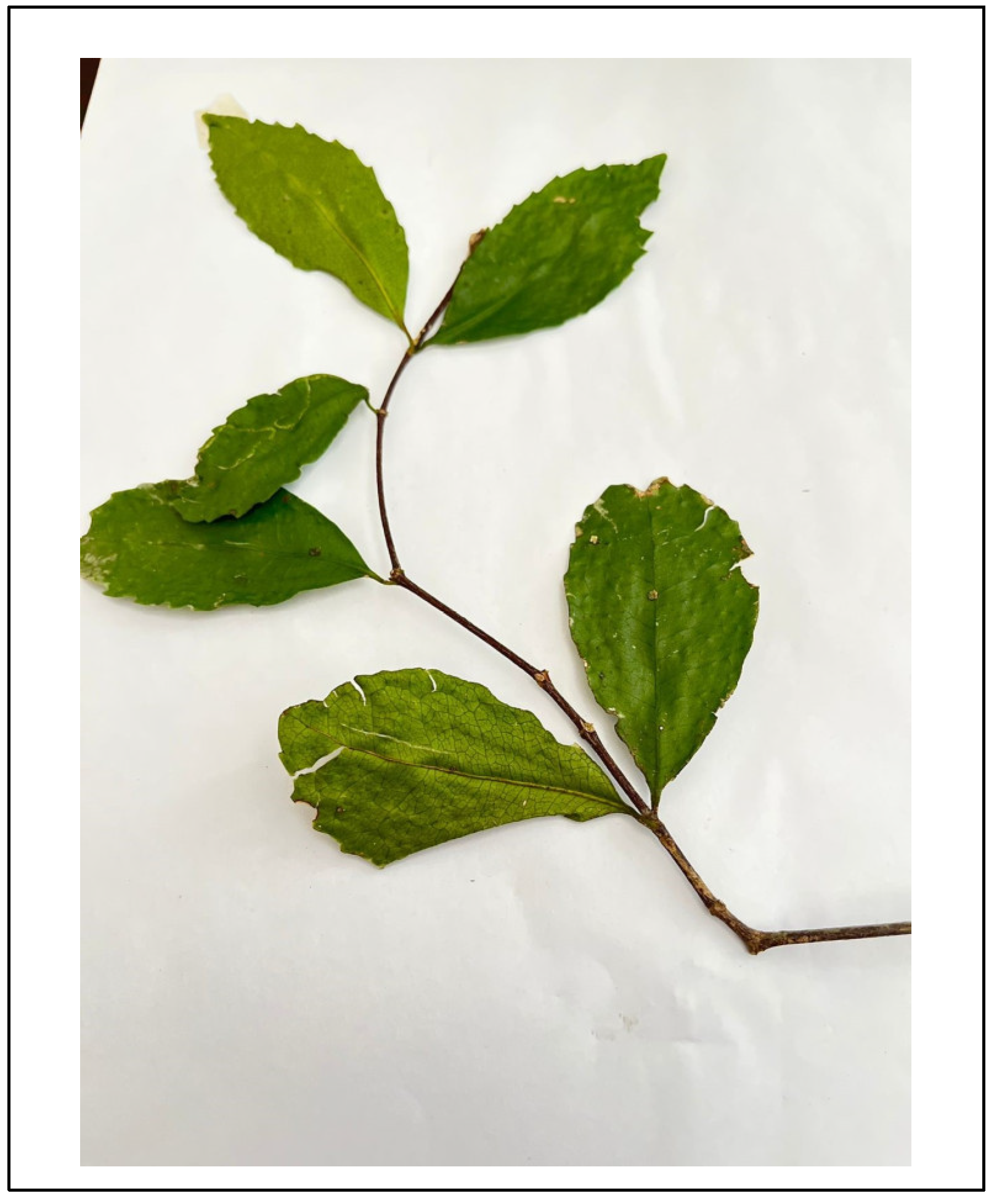
- Specimen 1:NH0151948-0, Cassipourea gummiflua Tul. verticillata (N.E.Br.) J. Lewis (Figure 3).
- Specimen 3: NH0151950-0, Cassipourea gummiflua Tul. verticillata (N.E.Br.) J. Lewis.
- Specimen 4. NH0151951-0, Cassipourea flanaganii (Schinz) Alston.
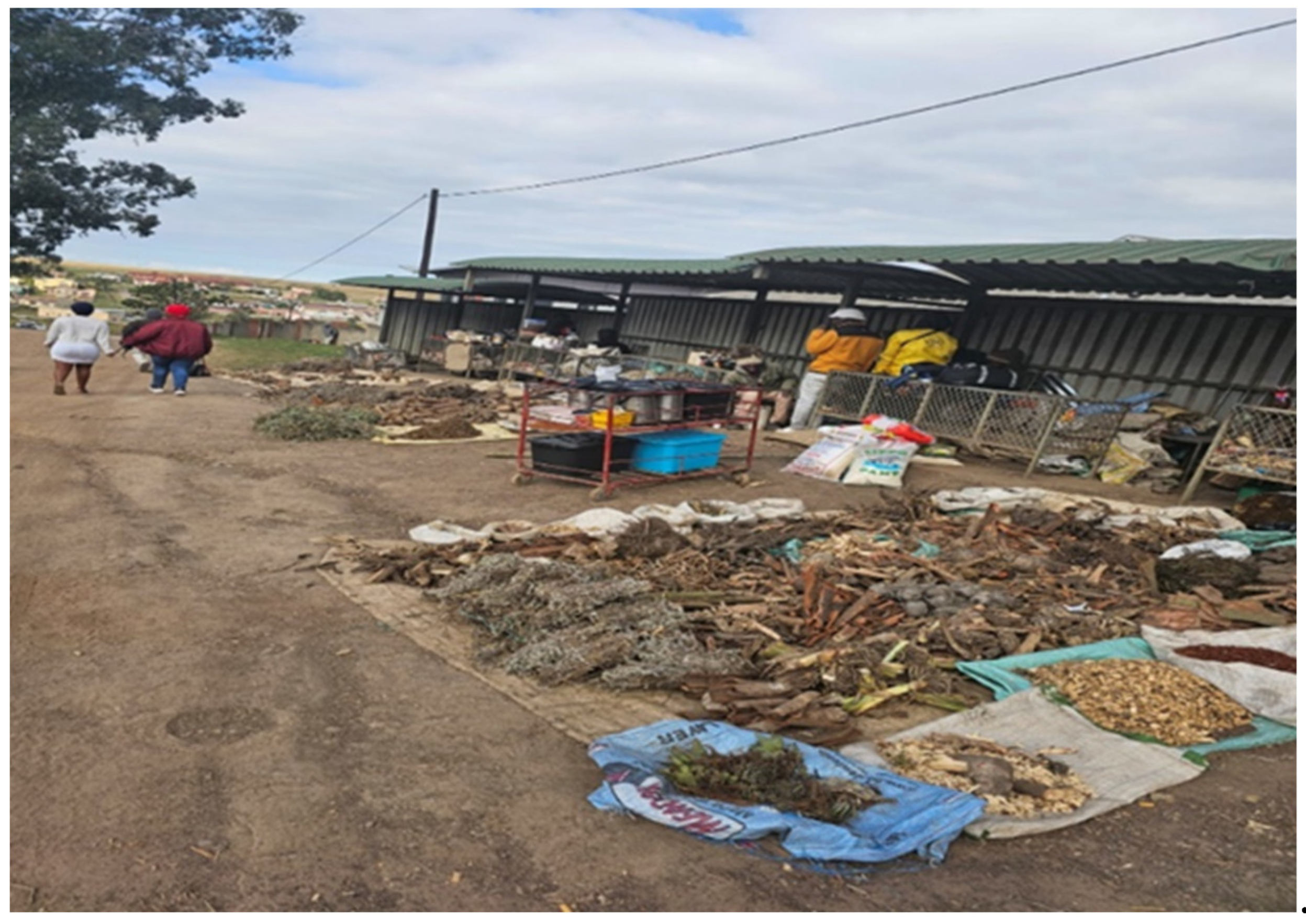
3. Discussion

4. Materials and Methods
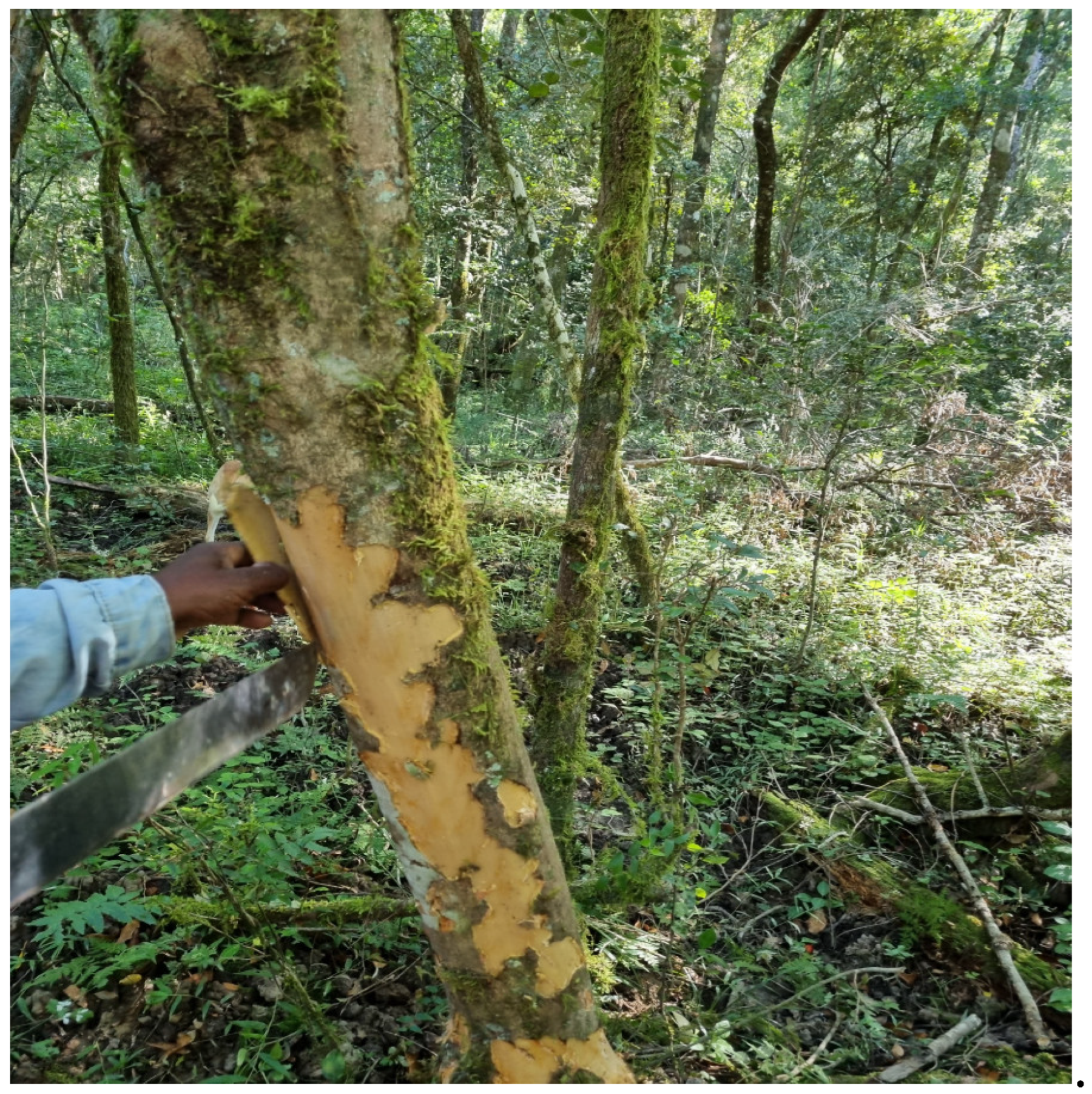
4.1. Identification of plant material

4.2. Herbarium specimen preparation
4.3. Preparation of the plant extracts
4.3. LCMS equipment and chemical reagents
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mpofana, N.; Chipangura, J.K.; Paulse, M.; Yalo, M.; Gqaleni, N.; Nxumalo, C.T.; Dlova, N.C.; Hussein, A.A.; Crouch, N.R. An Investigation into the Acute and Subacute Toxicity of Extracts of Cassipourea flanaganii Stem Bark In Vivo. Plants 2023, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogun, F.O.; Ashafa, A.O.T. A review of plants used in South African traditional medicine for the management and treatment of hypertension. Planta medica 2019, 85, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, S.A.; Cunningham, D.G.; Marles, R.J. Assessment of herbal medicinal products: challenges, and opportunities to increase the knowledge base for safety assessment. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2010, 243, 198–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization, W.H. WHO guidelines on safety monitoring of herbal medicines in pharmacovigilance systems. World Health Organization, 2004; ISBN 9241592214. [Google Scholar]
- Thring, T.; Weitz, F. Medicinal plant use in the Bredasdorp/Elim region of the Southern Overberg in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2006, 103, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguntibeju, O.O. Medicinal plants and their effects on diabetic wound healing. Veterinary world 2019, 12, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anywar, G.; Kakudidi, E.; Byamukama, R.; Mukonzo, J.; Schubert, A.; Oryem-Origa, H. Indigenous traditional knowledge of medicinal plants used by herbalists in treating opportunistic infections among people living with HIV/AIDS in Uganda. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2020, 246, 112205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.M.; Norval, M.; Wright, C.Y. Solar ultraviolet radiation in Africa: a systematic review and critical evaluation of the health risks and use of photoprotection. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences 2016, 15, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Afolayan, A.J.; Grierson, D.S.; Mbeng, W.O. Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used in the management of skin disorders among the Xhosa communities of the Amathole District, Eastern Cape, South Africa. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2014, 153, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R. Plants of Xhosa people in the Transkei region of Eastern Cape (South Africa) with major pharmacological and therapeutic properties. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research 2013, 7, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Dlova, N.C.; Ollengo, M.A. Traditional and ethnobotanical dermatology practices in Africa. Clinics in Dermatology 2018, 36, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langat, M.K.; Dlova, N.C.; Mulcahy-Ryan, L.E.; Schwikkard, S.L.; Opara, E.I.; Crouch, N.R.; Hiles, J.D.; Mulholland, D.A. The effect of isolates from Cassipourea flanaganii (Schinz) alston, a plant used as a skin lightning agent, on melanin production and tyrosinase inhibition. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2021, 264, 113272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mhlongo, L.; Van Wyk, B.-E. Zulu medicinal ethnobotany: New records from the Amandawe area of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. South African Journal of Botany 2019, 122, 266–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibane, V.; Ndhlala, A.; Abdelgadir, H.; Finnie, J.; Van Staden, J. The cosmetic potential of plants from the Eastern Cape Province traditionally used for skincare and beauty. South African Journal of Botany 2019, 122, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwa-Komoren, L.V.; Mayekiso, B.; Mhinana, Z.; Adeniran, A.L. An ethnobotanical and ethnomedicinal survey of traditionally used medicinal plants in Seymour, South Africa: An attempt toward digitization and preservation of ethnic knowledge. Pharmacognosy Magazine 2019, 15, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, R.; Stirk, W.; Van Staden, J. South African traditional medicinal plant trade—challenges in regulating quality, safety and efficacy. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2008, 119, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mander, M.; Ntuli, L.; Diederichs, N.; Mavundla, K. Economics of the traditional medicine trade in South Africa care delivery. South African health review 2007, 2007, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Mwinga, J.; Makhaga, N.; Aremu, A.; Otang-Mbeng, W. Botanicals used for cosmetic purposes by Xhosa women in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. South African Journal of Botany 2019, 126, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lall, N.; Kishore, N. Are plants used for skin care in South Africa fully explored? Journal of ethnopharmacology 2014, 153, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyo, M.; Aremu, A.O.; Van Staden, J. Medicinal plants: An invaluable, dwindling resource in sub-Saharan Africa. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2015, 174, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sans, M.; et al. Metabolic markers and statistical prediction of serous ovarian cancer aggressiveness by ambient ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Cancer research 2017, 77, 2903–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.; Musa, A.; Abdullahi, M.; Sule, M.; Sani, Y. Isolation of Lupeol from the Stem-bark of Lonchocarpus sericeus (Papilionaceae). Scholars Acad J Biosci 2013, 1, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, S.; Dong, L.; Hurst, W.J.; van Breemen, R.B. Quantitative analysis of phytosterols in edible oils using APCI liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Lipids 2013, 48, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Gu, N.; Pei, J.; Su, E.; Duan, X.; Cao, F.; Zhao, L. Synthesis of isorhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside by a three-enzyme (rhamnosyltransferase, glycine max sucrose synthase, UDP-rhamnose synthase) cascade using a UDP-rhamnose regeneration system. Molecules 2019, 24, 3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, C.G.; Duarte, L.P.; Mussel, W.d.N.; Ruiz, A.L.T.G.; Shiozawa, L.; Carvalho, J.E.d.; Trindade, I.C.; Vieira, S.A. Lupeol and its esters: NMR, powder XRD data and in vitro evaluation of cancer cell growth. Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2018, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Kokpol, U.; Chavasiri, W.; Chittawong, V.; Bruce, M.; Cunningham, G.; Miles, D.H. Long chain aliphatic alcohols and saturated carboxylic acids from heartwood of Rhizophora apiculata. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 1129–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Noda, Y.; Nakatani, N.; Shitan, N.; Sudo, T.; Kato, A.; Chalo Mutiso, P.B. Structure of constituents isolated from the bark of Cassipourea malosana and their cytotoxicity against a human ovarian cell line. Journal of Natural Medicines 2019, 73, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garelnabi, M.; Litvinov, D.; Parthasarathy, S. Evaluation of a gas chromatography method for azelaic acid determination in selected biological samples. North American Journal of Medical Sciences 2010, 2, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Rhyncosides A—F, phenolic constituents from the Chinese mangrove plant Bruguiera sexangula var. rhynchopetala. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2007, 55, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dem’yanov, P.; Malo, N.; Petrosyan, V. An investigation of the composition of an ethereal extract of the fruit stones of Anisophyllea laurina. Chemistry of Natural Compounds 1984, 20, 609–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, S.; et al. Cholestenoic acids regulate motor neuron survival via liver X receptors. The Journal of clinical investigation 2014, 124, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedula, V.P.; Norris, A.; Miller, J.S.; Ratovoson, F.; Andriantsiferana, R.; Rasamison, V.E.; Kingston, D.G. Cytotoxic Diterpenes from Cassipourea m adagascariensis from the Madagascar Rainforest. Journal of natural products 2006, 69, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manojlović, I.; Bogdanović-Dusanović, G.; Gritsanapan, W.; Manojlović, N. Isolation and identification of anthraquinones of Caloplaca cerina and Cassia tora. Chemical Papers 2006, 60, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y. Rapid screening of Chemical constituents in Rhizoma anemarrhenae by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS combined with data postprocessing techniques. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, C.-S.; Shin, H.-K. Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Simultaneous Analysis of 22 Analytes of Oncheong-Eum, a Traditional Korean Herbal Formula. Processes 2023, 11, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Ghani, A.E.; Al-Saleem, M.S.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; AbouZeid, E.M.; Mahmoud, M.Y.; Abdallah, R.H. UPLC-ESI-MS/MS Profiling and Cytotoxic, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Antidiabetic, and Antiobesity Activities of the Non-Polar Fractions of Salvia hispanica L. Aerial Parts. Plants 2023, 12, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kircik, L.H. Efficacy and safety of azelaic acid (AzA) gel 15% in the treatment of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne: a 16-week, baseline-controlled study. Journal of drugs in dermatology: JDD 2011, 10, 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach, A. Melanin hyperpigmentation of skin: melasma, topical treatment with azelaic acid, and other therapies. Cutis 1996, 57, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Nashar, H.A.; El-Din, M.I.G.; Hritcu, L.; Eldahshan, O.A. Insights on the inhibitory power of flavonoids on tyrosinase activity: A survey from 2016 to 2021. Molecules 2021, 26, 7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, S.-Q. Molecular inhibitory mechanism of tricin on tyrosinase. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2013, 107, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocks, M.; Dold, A. The informal trade of Cassipourea flanaganii as a cosmetic in South Africa. In Ethnobiology and Biocultural Diversity: Proceedings of the 7th International Congress of Ethnobiology; pp. 412-431.
- Chan, T.Y. Inorganic mercury poisoning associated with skin-lightening cosmetic products. Clinical toxicology 2011, 49, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, L.K. Consequences of systemic absorption of topical glucocorticoids. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2011, 65, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Noda, Y.; Nakatani, N.; Shitan, N.; Sudo, T.; Kato, A.; Chalo Mutiso, P.B. Structure of constituents isolated from the bark of Cassipourea malosana and their cytotoxicity against a human ovarian cell line. Journal of natural medicines 2019, 73, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, A.; Ichimaru, M.; Matsukawa, M.; Moriyasu, M.; Fukuoka, N.; Kishida, K.; Ogeto, J.O.; Juma, F.D. Studies on unused medicinal resources in Africa, occurrence of sulfur compounds in Cassipourea genus in Kenya. Journal of African Studies 1989, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, S.E.; Taylor, C.W. Methylated A-type proanthocyanidins and related metabolites from Cassipourea gummiflua. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rondo, M. Phytochemical and biological studies on some South African plants used in traditional medicine for skin hyperpigmentation. 2017.
- Wright, W.G.; Warren, F.L. Rhizophoraceae alkaloids. Part I. Four sulphur-containing bases from Cassipourea spp. Journal of the Chemical Society 1967, 283–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drewes, S.E.; Taylor, C.W.; Cunningham, A.B. (+)-Afzelechin 3-rhamnoside from Cassipourea gerrardii. Phytochemistry 1994, 31, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, V.L.; Raimondo, D.; Crouch, N.R.; Cunningham, A.B.; Scott-Shaw, C.R.; Lotter, M.; Ngwenya, A.M. Cassipourea malosana (Baker) Alston. National Assessment: Red List of South African Plants. 2014, Version, .1580-27.
- Cooks, R.G.; Warren, F.L.; Williams, D.H. Rhizophoraceae alkaloids. Part III. Cassipourine. Journal of the Chemical Society C 1967, Organic, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



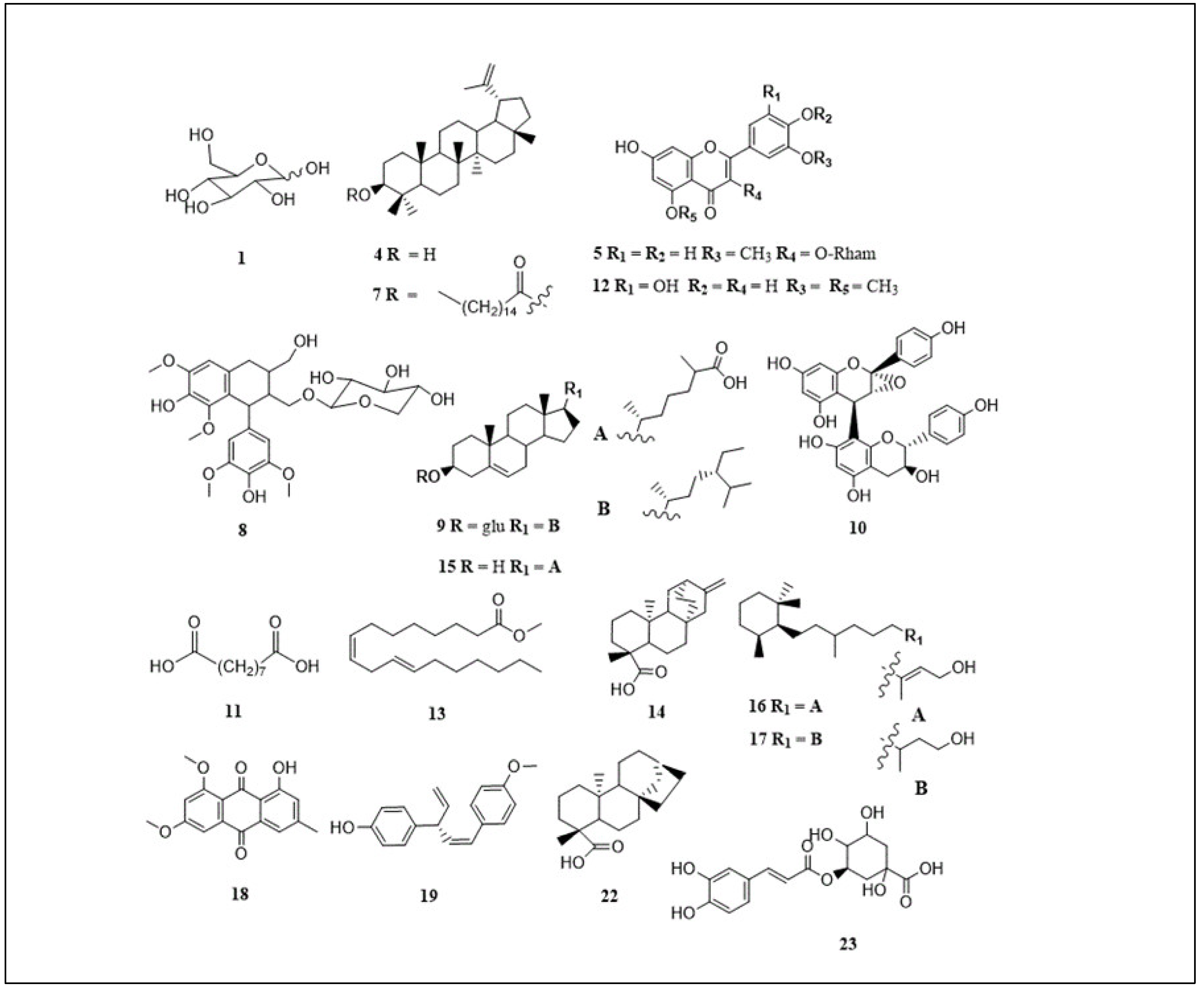
| Peak | Proposed compound | m/z | tR (min) | [M-H]- | Molecular formula | C. flanaganii | C. gummiflua | C. malosana | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hexose/glucose | 215.033 | 0.99 | [M+Cl]- | C6H12O | + | - | + | [21] |
| 2 | Unknown | 194.1 | 1.15 | [M-H]- | Unknown | - | + | - | - |
| 3 | Unknown | 341.1 | 1.21 | [M-H]- | Unknown | - | + | - | - |
| 4 | Lupeol | 425.075 | 3.02 | [M-H]- | C30H50O | + | + | + | [22,23] |
| 5 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-rhamnoside | 461.129 | 3.21 | [M-H]- | C22H22O11 | + | - | - | [24] |
| 6 | Unknown | 252.014 | 3.55 | [M-H]- | Unknown | + | - | + | - |
| 7 | Lupeol stearate | 691.202 | 4.25 | [M-H]- | C48H84O2 | - | - | + | [25] |
| 8 | Lynoside | 551.202 | 4.83 | [M-H]- | C27H36O12 | + | + | - | [12] |
| 9 | Sitosterol glycoside | 575.103 | 5.53 | [M-H]- | C35H60O6 | - | - | + | [26] |
| 11 | Azelaic acid | 187.097 | 5.62 | [M-H]- | C9H16O4 | + | + | + | [28] |
| 12 | Tricin | 329.232 | 6.98 | [M-H]- | C17H14O7 | + | + | + | [29] |
| 13 | Methyl linoliate | 293.138 | 8.06 | [M-H]- | C19H34O2 | + | - | + | [30] |
| 14 | ent-atis-16-en-19-oic acid | 337.1 | 8.49 | [M+Cl]- | C30H24O10 | - | + | - | [12] |
| 15 | Cholestenoic acid | 415.103 | 9.09 | [M-H]- | C27H44O3 | - | + | - | [31] |
| 16 | Cassipourol | 293.211 | 9.53 | [M-H]- | C20H38O | + | - | + | [32] |
| 17 | Decahydroretinol | 295.228 | 10.10 | [M-H]- | C20H40O | + | - | + | [32] |
| 18 | Emodin 6,8-dimethyl ether | 297.242 | 10.63 | [M-H]- | C17H14O5 | + | - | + | [33] |
| 19 | Ellisinin A | 265.1 | 11.32 | [M-H]- | C18H18O2 | - | + | - | [34] |
| 20 | Unknown | 311.2 | 11.48 | [M-H]- | Unknown | - | + | - | - |
| 21 | Unknown | 327.256 | 11.63 | [M-H]- | Unknown | + | - | - | - |
| 22 | ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid | 309.2 | 12.35 | [M+Cl]- | C19H30O | - | + | - | [12] |
| 23 | Chlorogenic acid | 353.2 | 12.76 | [M-H]- | C16H18O9 | - | + | - | [35,36] |
| 24 | Unknown | 397.2 | 12.91 | [M-H]- | Unknown | - | + | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





