Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
06 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Date Fruit Extract
2.3. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Measurement
2.4. Experimental Animals
2.5. Biochemical Assays
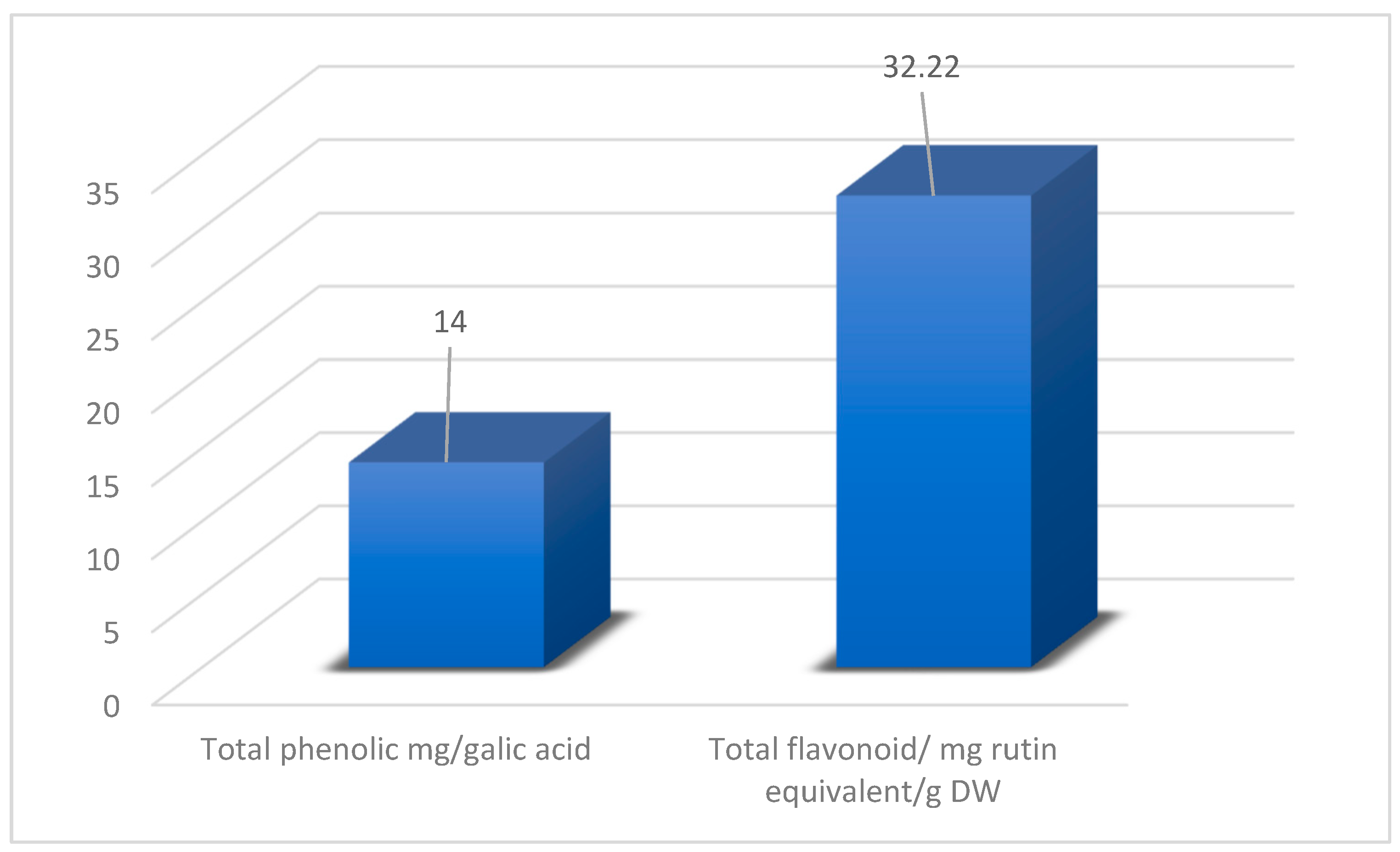
2.6. Estimation of Total Phenolic Content
2.7. Estimation of Flavonoids
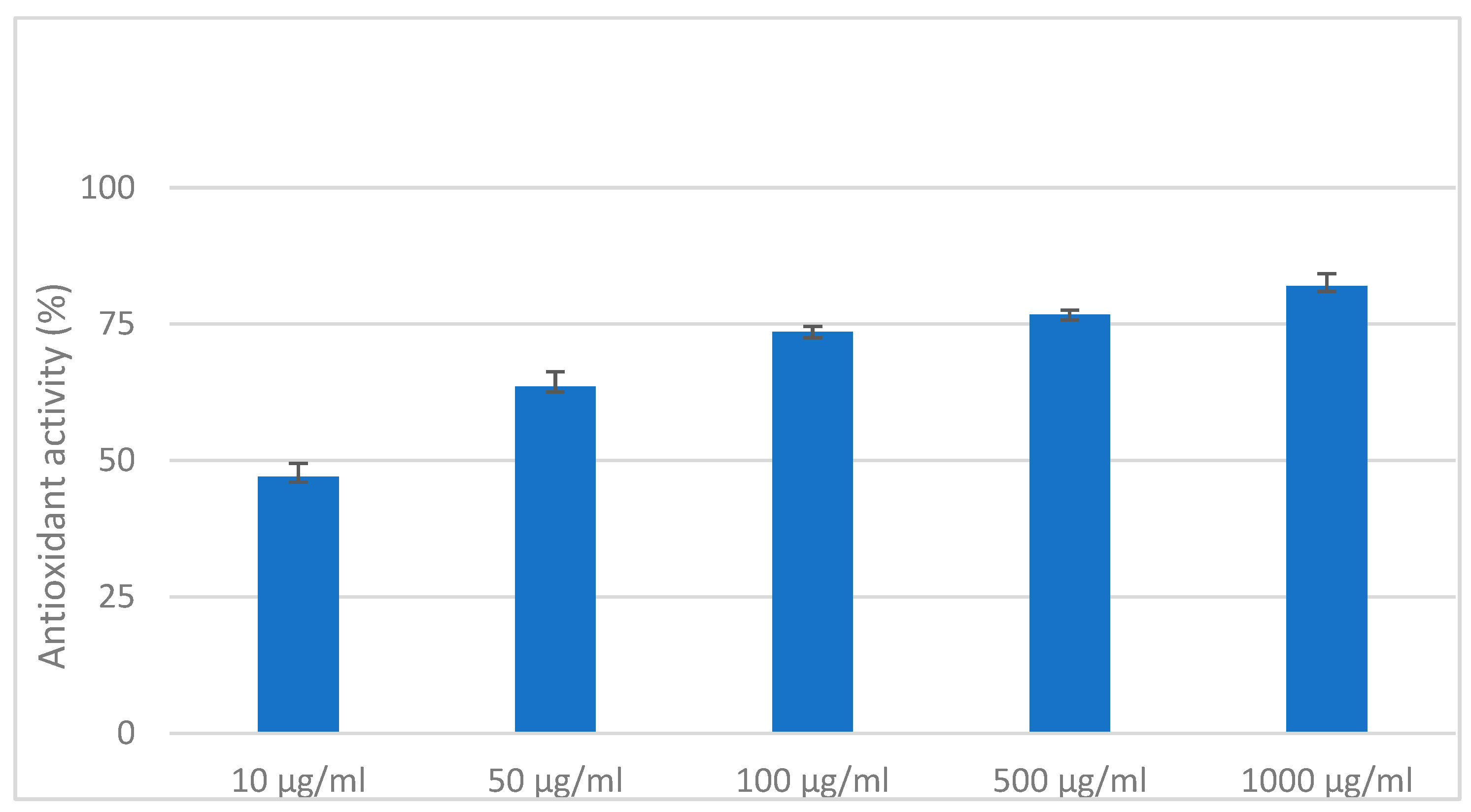
2.8. DPPH Antioxidant Activity
2.9. Histology and Light Microscopy
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
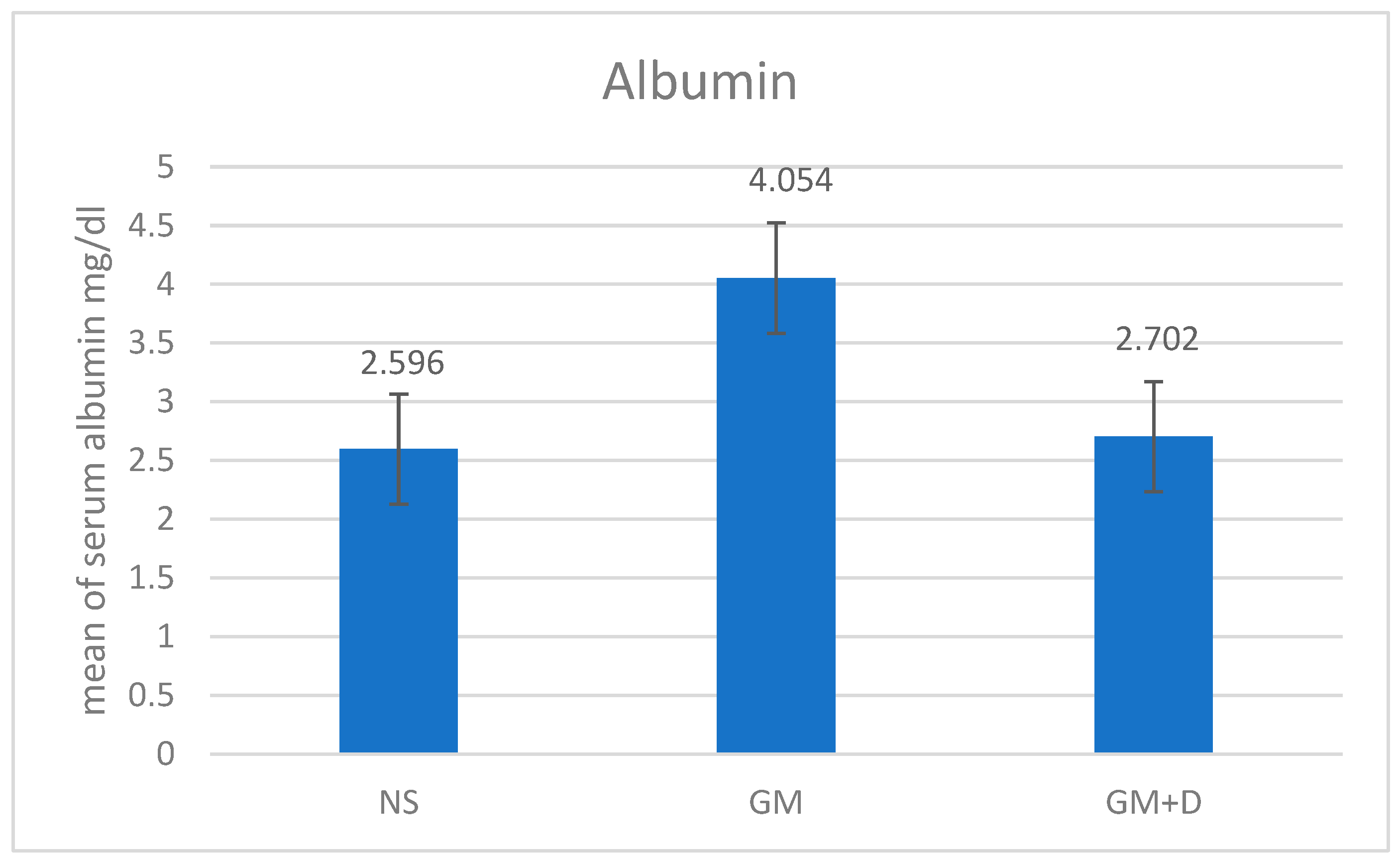
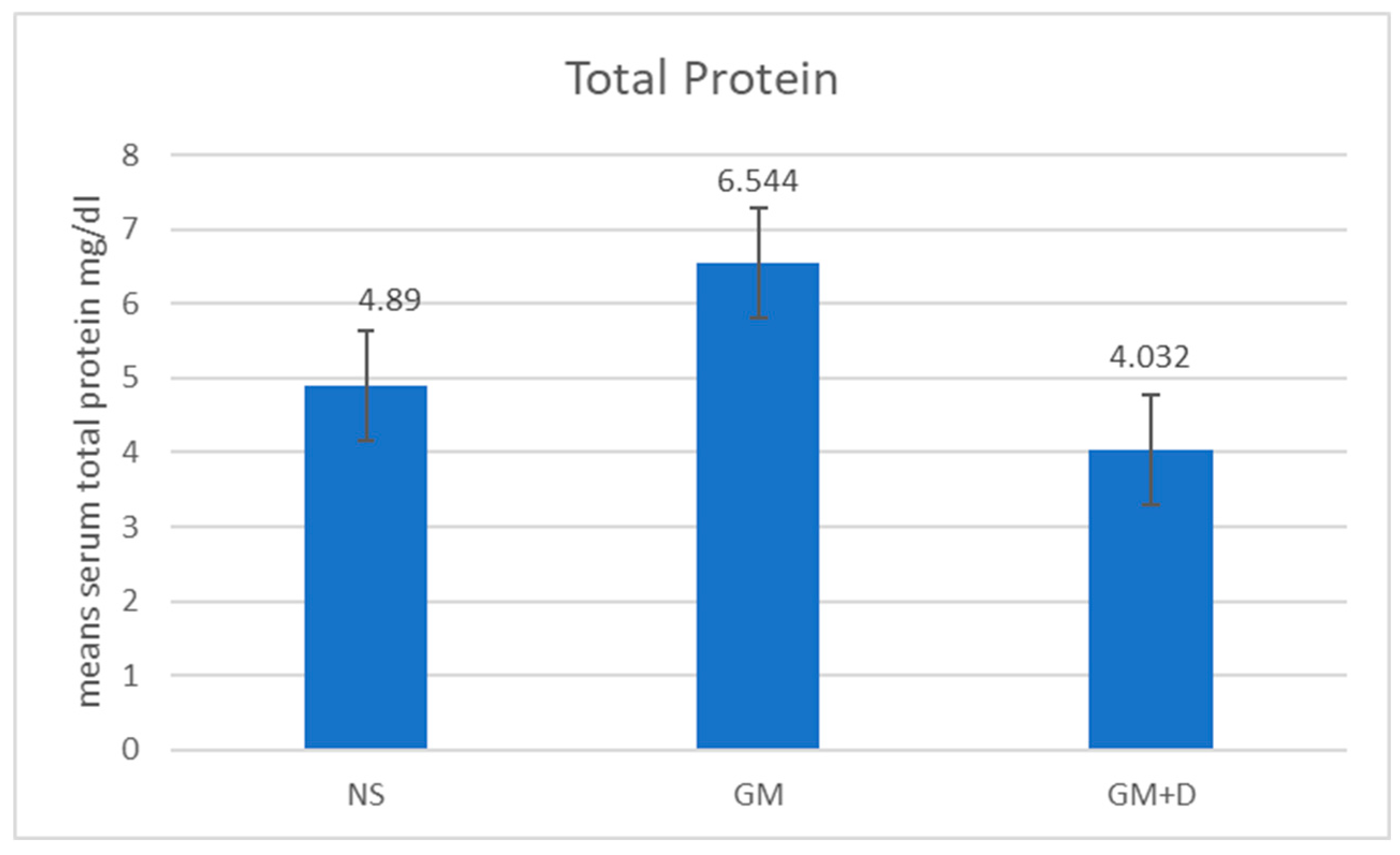
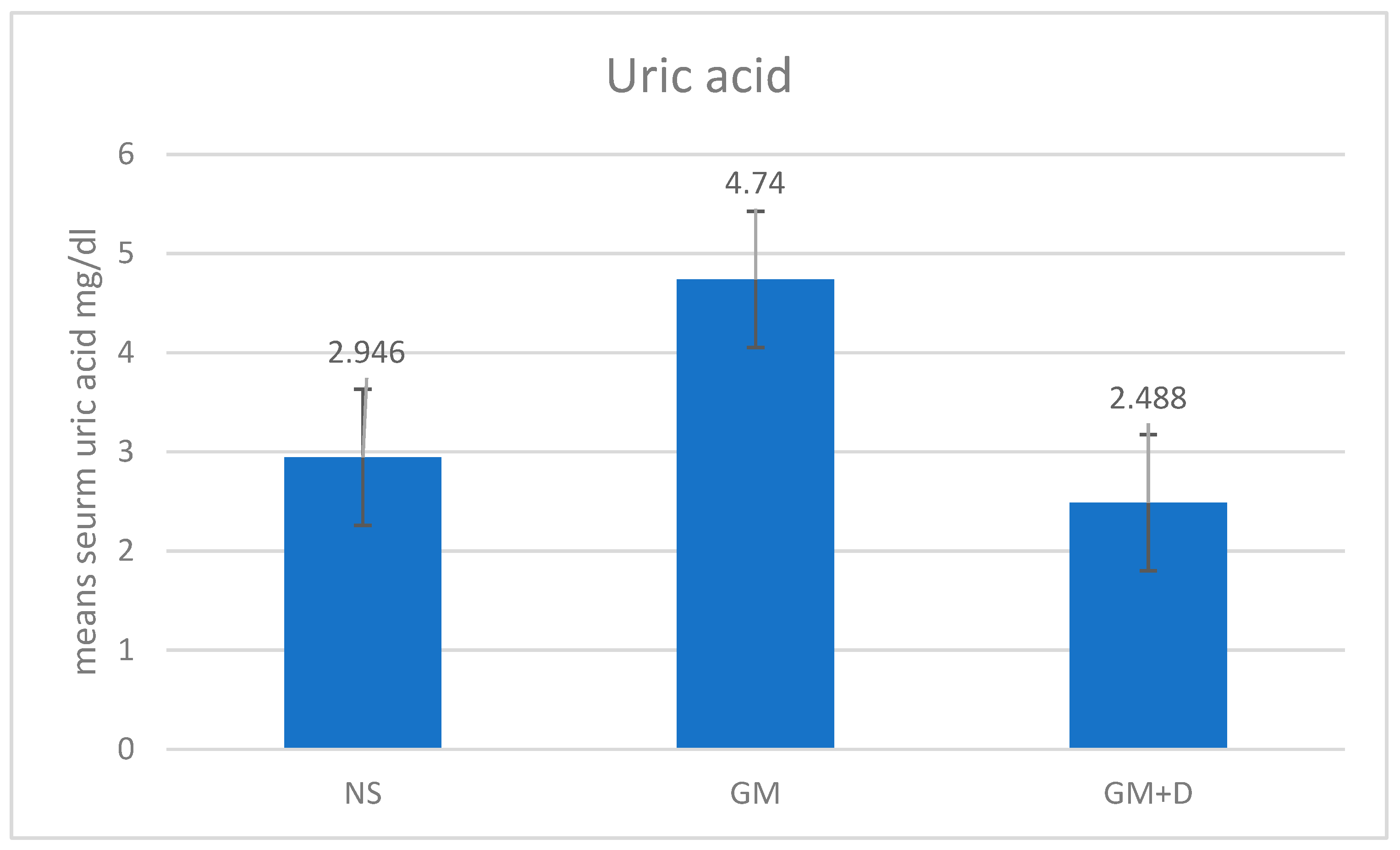
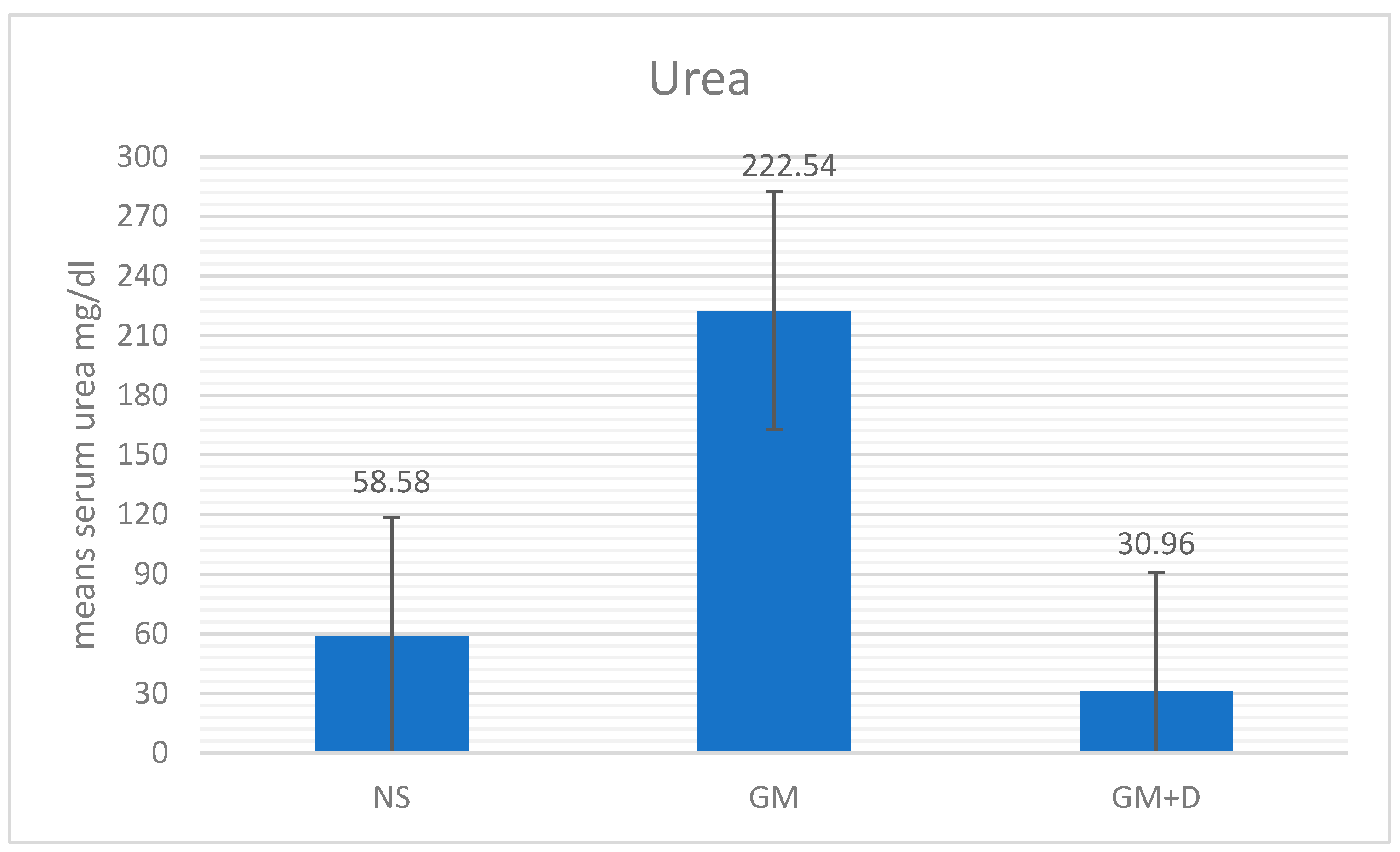
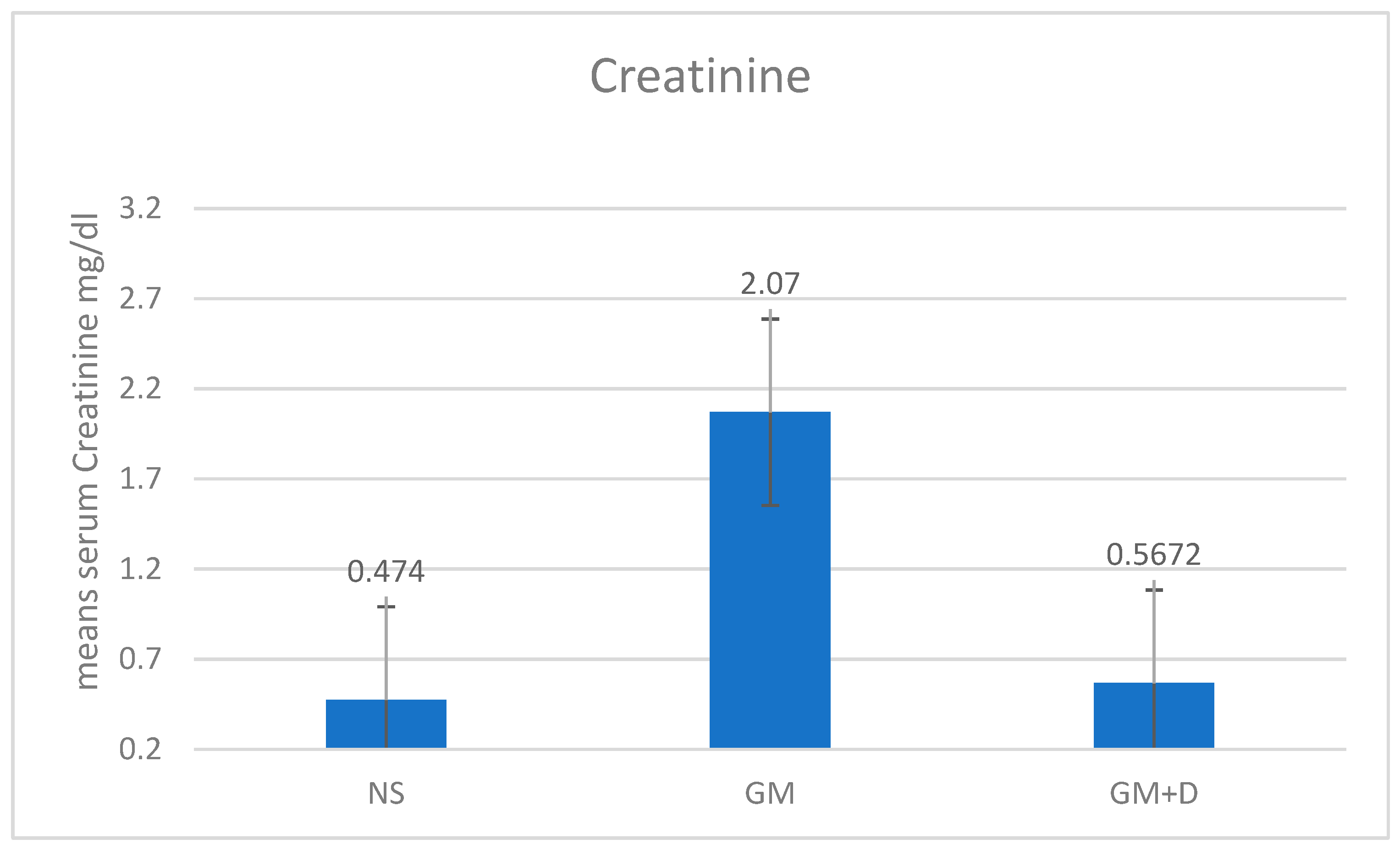
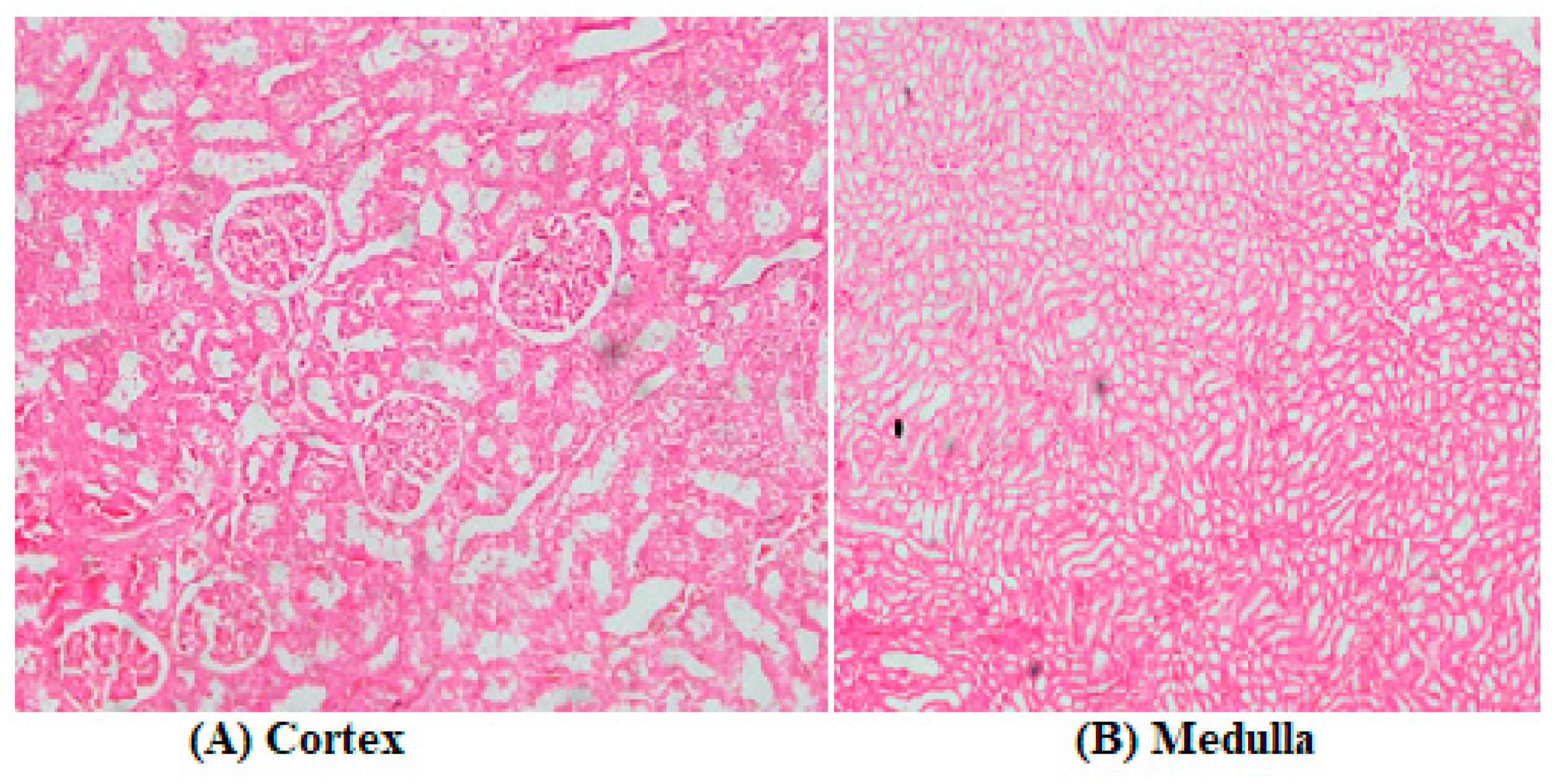
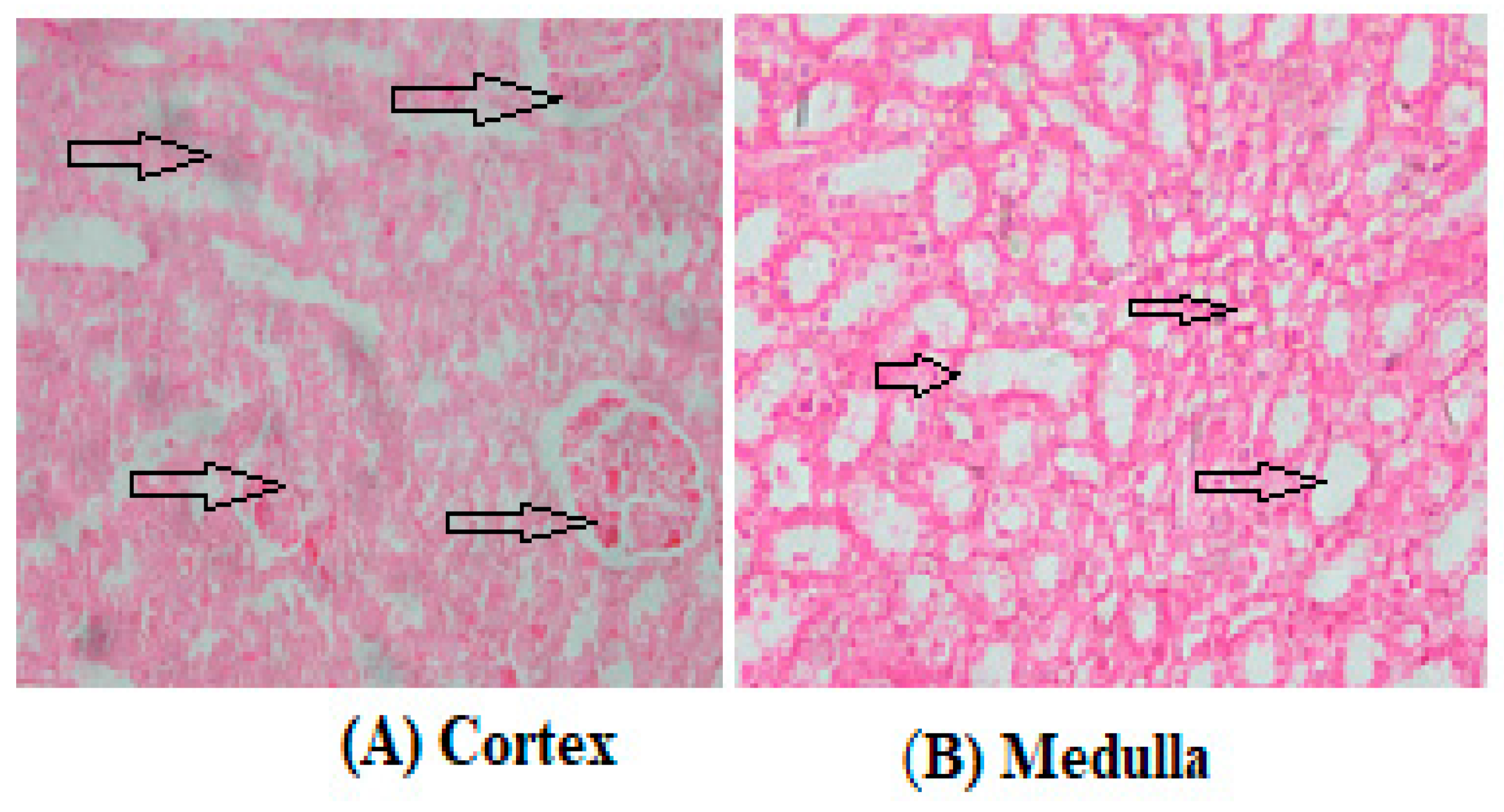
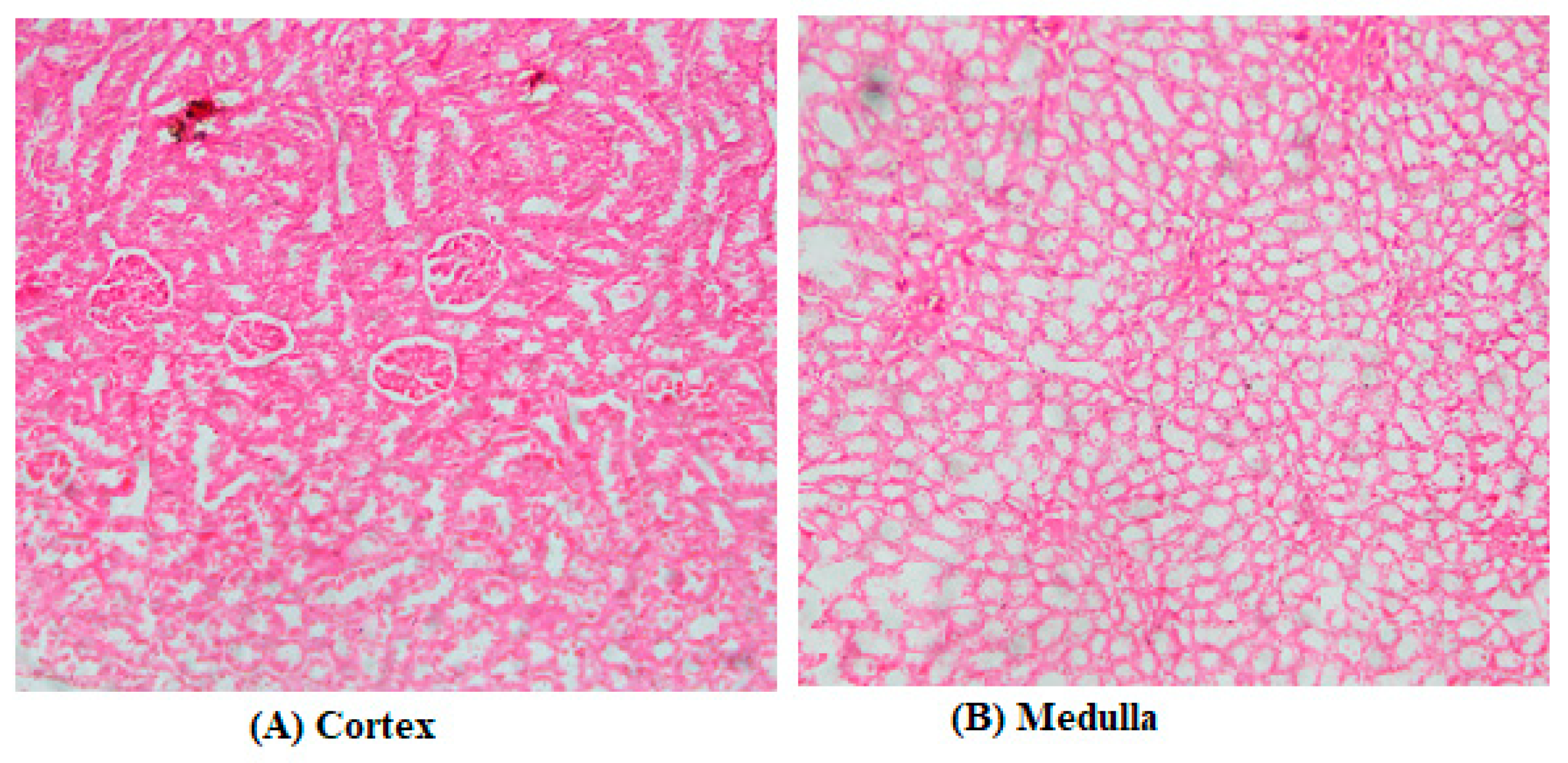
3.2. Biochemical Assays and Histology Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radi, Z.A. Kidney pathophysiology, toxicology, and drug-induced injury in drug development. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, N.; Singh, G.; Sharma, R.K.; Mishra, A.; Chandolia, P. Systemic Analysis Of Renal Biomarkers And Kidney Impairment Caused By Nephrotoxins In Several Animal Screening Models. Int. J. Curr. Sci. 2023, 13, 206–216. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, S.; Satish, S.; Rawtani, D. Aptasensors in environmental forensics: Tracking the silent killers. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Forensic Sci. 2023, 5, e1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, C.S.; Smith, J.E.; Eales, B.M.; Kajiji, S.; Liu, X.; Truong, L.D.; Tam, V.H. Zileuton ameliorates aminoglycoside and polymyxin-associated acute kidney injury in an animal model. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2023, 78, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlow, C.A.; da Costa, R.M.; Ellis, S.; Franceschi, F.; Sharland, M.; Piddock, L.; Das, S.; Hope, W. Potential antibiotics for the treatment of neonatal sepsis caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria. Pediatr. Drugs 2021, 23, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randjelovic, P.; Veljkovic, S.; Stojiljkovic, N.; Sokolovic, D.; Ilic, I. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity in animals: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Excli J. 2017, 16, 388. [Google Scholar]
- Kour, H.; Singh, A.; Jaiswal, P.; Sharma, R. Screening models of nephrotoxicity and their molecular mechanism. World J. Biol. Pharm. Health Sci. 2023, 13, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.C.; Muller, A.E.; Hunfeld, N.G.; de Winter, B.C.; Ewoldt, T.M.; Abdulla, A.; Endeman, H. Therapeutic drug monitoring of antibiotics in critically ill patients: Current practice and future perspectives with a focus on clinical outcome. Ther. Drug Monit. 2022, 44, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jospe-Kaufman, M.; Siomin, L.; Fridman, M. The relationship between the structure and toxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Barbero, A.; Lopez-Novoa, J.; Arevalo, M. Involvement of platelet-activating factor in gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp. Nephrol. 1997, 5, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery, P.K. Goblet cell increase in rat bronchial epithelium arising from irritation or drug administration: An experimental and electron microscopic study PhD thesis, University of London. 1973. https://spiral.imperial.ac.uk/bitstream/10044/1/20467/2/Jeffery-PK-1973-PhD-Thesis.pdf.
- STEVE ESOMBA, D. The Book of Life, Knowledge and Confidence; Lulu. com: Morrisville, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Aiswarya, N.; Chandran, V.; Teerthanath, S.; Rakesh, K.B. Nephroprotective effect of aqueous extract of Pimpinella anisum in gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in wistar rats. Pharmacognosy Journal 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman İ, Balikci E. Protective effects of Nigella sativa against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology 2010, 62, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nale, L.P.; More, P.R.; More, B.K.; Ghumare, B.C.; Shendre, S.B.; Mote, C.S. Protective effect of Carica papaya L. seed extract in gentamicin induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2012, 3, 508–515. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Pundir, J.; Vishwakarma, P.; Goel, R.K.; Saini, M.; Saxena, K.K. Evaluation of nephroprotective activity of Tinospora cordifolia against gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in albino rats: an experimental study. International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology 2019, 8, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Vasfiye Erseçkin, Handan Mert, Kıvanç İrak, Serkan Yildirim & Nihat Mert. Nephroprotective effect of ferulic acid on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats, Drug and Chemical Toxicology 2022, 45, 663–669. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandan, R.; Subramanian, P. Renal protective effect of hesperidin on gentamicin-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male Wistar albino rats. Redox Report 2012, 17, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanna, S.; Hiremath, S.K.; Unger, B.S. Nephroprotective activity of Bilvādi agada in gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Ancient science of life 2015, 34, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kashef, D.H.; El-Kenawi, A.E.; Suddek, G.M.; Salem, H.A. Protective effect of allicin against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. International immunopharmacology 2015, 1, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, O.Y.; Irak, K. Protective effect of date extract on rat nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin, clinical histological and antioxidant evidences. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2018, 30, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulieman, A.M.E.; Alanaizy, E.; Alanaizy, N.A.; Abdallah, E.M.; Idriss, H.; Salih, Z.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Ibrahim, S.E.; Abd El Hakeem, B.S. Unveiling Chemical, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Fagonia indica Grown in the Hail Mountains, Saudi Arabia. Plants 2023, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.; Siddig, B.; González-Maldonado, P.; Elkhair, H.; Alakhras, A.I.; Abdallah, E.M.; Elzupir, A.O.; Sotelo, P.H. Inhibitory activity of Saussurea costus extract against bacteria, candida, herpes, and SARS-CoV-2. Plants 2023, 12, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.; Siddig, B.; Maldonado, P.G.; Elkhair, H.; Alakhras, A.; Abdallah, E.M.; Torres, P.H.S.; Elzupir, A.O. Phytochemical Discrimination, Biological Activity and Molecular Docking of Water-Soluble Inhibitors from Saussurea costus Herb against Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2022, 27, 4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, A.H.; Marri, A.; Shaikh, N. Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera): A Review of Economic Potential, Industrial Valorization, Nutritional and Health Significance. In Neglected Plant Foods of South Asia: Exploring and Valorizing Nature to Feed Hunger; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 319–350. [Google Scholar]
- Škrovánková, S.; Mišurcová, L.; Machů, L. Antioxidant activity and protecting health effects of common medicinal plants. Advances in food and nutrition research 2012, 1, 75–139. [Google Scholar]
- Allaith, A.A. Antioxidant activity of Bahraini date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit of various cultivars. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 2008, 43, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, E.A.; Tawfik, M.S.; Abu-Tarboush, H.M. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of various date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits from Saudi Arabia. Food and Nutrition Sciences 2011, 19, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, E.A.; Behija, S.E.; Beligh, M.; Lamia, L.; Manel, I.; Mohamed, H.; Lotfi, A. Effects of the ripening stage on phenolic profile, phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of date palm fruit. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 2012, 60, 10896–10902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, S.; Ahmad, A.; Kaleem, M. Antioxidant activity and phenolic contents of Ajwa date and their effect on lipo-protein profile. Functional Foods in Health and Disease 2017, 30, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalid, N.; Khan, R.S.; Ahmed, H.; Ahmad, A. A review on chemistry and pharmacology of Ajwa date fruit and pit. Trends in food science & technology 2017, 1, 60–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ragab, A.R.; Elkablawy, M.A.; Sheik, B.Y.; Baraka, H.N. Antioxidant and tissue-protective studies on Ajwa extract: Dates from Al Madinah Al-Monwarah, Saudia Arabia. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 3, 2161–0525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhahri, M.; Sioud, S.; Alsuhaymi, S.; Almulhim, F.; Haneef, A.; Saoudi, A.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A.-H.M. Extraction, Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity of Polysaccharides from Ajwa Seed and Flesh. Separations 2023, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, S.; Safari, T.; Komeili, G.R.; Nematbakhsh, M.; Niazi, A.A.; Jahantigh, M.; Bagheri, H.; Maghool, F. Sex difference in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Influence of L-arginine in rat model. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 9, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Alghamdi, A.A.; Awadelkarem, A.M.; Hossain, A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Fawzi, M.; Ashraf, S.A. Nutritional assessment of different date fruits (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties cultivated in Hail province, Saudi Arabia. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun 2018, 11, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A K Ramya, Dr R Devika, & Dr K Sethumadhavan.). A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF GCMS ANALYSIS OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUND ISOLATED FROM MARINE ALGAE-DERIVED ENDOPHYTIC FUNGI. Journal of Population Therapeutics and Clinical Pharmacology 2023, 30, 482–490. [CrossRef]
- Ukwubile, C.A.; Ahmed, A.; Katsayal, U.A.; Ya'u, J.; Mejida, S. GC–MS analysis of bioactive compounds from Melastomastrum capitatum (Vahl) Fern. leaf methanol extract: An anticancer plant. Scientific African 2019, 1, e00059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uka, E.; Eghianrunwa, Q.A.; Akwo, V.D. GC-MS ANALYSIS OF BIOACTIVE COMPOUNDS IN ETHANOL LEAVES EXTRACT OF SPHENOCENTRUM JOLLYANUM AND THEIR BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES. world. 2022, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallasch, B.A.; Spiteller, G. Synthesis of 9, 12-dioxo-10 (Z)-dodecenoic acid, a new fatty acid metabolite derived from 9-hydroperoxy-10, 12-octadecadienoic acid in lentil seed (Lens culinaris Medik.). Lipids 2000, 35, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolayan, F.I. and Ijidakinro, O.D., 2021. African Journal of Biological Sciences. Afr.J.Bio.Sc 2021, 3, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouZeid, E.; Abou El-Kassem, L.; Ammar, N. Veined Dock (Rumex pictus Forssk.) Usage in the Middle East: Phytochemical Constituents and Biological Effects of the Extracts. InAncient and Traditional Foods, Plants, Herbs and Spices used in the Middle East (pp. 343-351). CRC Press. 2023. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781003243472-25/veined-dock-rumex-pictus-forssk-usage-middle-east-enaam-abouzeid-lamiaa-abou-el-kassem-nagwa-ammar.
- Tardif, S.; Rwigemera, A.; Letourneau, N.; Robaire, B.; Delbes, G. Reproductive toxicity of emerging plasticizers, flame retardants, and bisphenols, using culture of the rat fetal testis. Biology of Reproduction 2023, 108, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Ajay, Sandeep Kaur, Sukhvinder Dhiman, Prithvi Pal Singh, Gaurav Bhatia, Sharad Thakur, Hardeep Singh Tuli, Upendra Sharma, Subodh Kumar, Abdulmajeed G. Almutary, and et al. "Targeting Akt/NF-κB/p53 Pathway and Apoptosis Inducing Potential of 1, 2-Benzenedicarboxylic Acid, Bis (2-Methyl Propyl) Ester Isolated from Onosma bracteata Wall. against Human Osteosarcoma (MG-63) Cells" Molecules 2022, 27, 3478. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, Elham, Ahlam Elwekeel, Nasrah F. Alshariedh, Mohamed Sadek Abdel-Bakky, and Marwa H. A. Hassan. "GC-MS Analysis and Bioactivities of the Essential Oil of Suaeda aegyptiaca" Separations 2022, 9, 439. [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.Z.; Zayed, M.Z.; Ali, H.M.; Abd El-Kareem, M.S. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of extracts from Schinus molle wood branch growing in Egypt. Journal of wood science. 2016, 62, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhetso, T.; Shubharani, R.; Roopa, M.S.; Sivaram, V. Chemical constituents, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activity of Allium chinense G. Don. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainangu, P.; Antonyraj, A.P.; Subramanian, K.; Kaliyaperumal, S.; Gopal, S.; Renuka, P.S. In vitro screening of antimicrobial, antioxidant, cytotoxic activities, and characterization of bioactive substances from freshwater cyanobacteria Oscillatoria sp. SSCM01 and Phormidium sp. SSCM02. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2020, 29, 101772. [Google Scholar]
- Minh, Truong Ngoc, Tran Dang Xuan, Truong Mai Van, Yusuf Andriana, Tran Duc Viet, Tran Dang Khanh, and Hoang-Dung Tran. Phytochemical Analysis and Potential Biological Activities of Essential Oil from Rice Leaf. Molecules 2019, 24, 546. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musa, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Aliyu, A.B.; Abdullahi, M.S.; Tajuddeen, N.; Ibrahim, H.; Oyewale, A.O. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of hexane leaf extract of Anisopus mannii (Asclepiadaceae). Journal of intercultural ethnopharmacology 2015, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingfa, L.; Ankanagari, S. GC-MS Profiling of Reproductive Stage Withania somnifera for Antimicrobial and Anticancer Phytochemicals. Biomed Pharmacol J 2023, 16, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Chohan, M.M.; Ahmed, D.; Ullah, N. The first report on the in vitro antimicrobial activities of extracts of leaves of Ehretia serrata. Saudi journal of biological sciences 2019, 1, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negm, N.A.; Tawfik, S.M. Characterization, surface properties and biological activity of some synthesized anionic surfactants. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2014, 25, 4463–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Zahiruddin, S.; Parveen, R.; Khan, W.; Ahmad, S.; Shrivastava, B.; Shrivastava, A.K. TLC-bioautography identification and GC-MS analysis of antimicrobial and antioxidant active compounds in Musa× paradisiaca L. fruit pulp essential oil. Phytochemical Analysis 2019, 30, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, M.T.; Ibrahim, D. Volatile Bioactive Compounds from Lasiodiplodia pseudotheobromae IBRL OS-64, an Endophytic Fungus Residing in the Leaf of Ocimum sanctum. HAYATI Journal of Biosciences. 2022, 13, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, R.; Subramanian, P. Renal protective effect of hesperidin on gentamicin-induced acute nephrotoxicity in male Wistar albino rats. Redox Rep. 2012, 17, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Shah, J. Protective effect of ethanolic extract of Hordeum vulgare seed on gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhitha, K.; Raghavendra, M.; VenkataKirankumar, M. Protective Effect Of Bauhinia Tomentosa L. Extract Against Gentamicin Induced Nephrotoxicity in Wistar Male Albino Rats. IJPSR 2019, 10, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Fatima, N.; Sultana, A. Renoprotective and anti-oxidant effects of coleus forskohlii against gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in albino wistar rats. Acta Pharm. Sci. 2018, 56, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaider, I.A.; Mohamed, M.E.; Ahmed, K.; Kumar, A.H. Date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) fruits as a potential cardioprotective agent: The role of circulating progenitor cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bami, E.; Ozakpınar, O.B.; Ozdemir-Kumral, Z.N.; Köroglu, K.; Ercan, F.; Cirakli, Z.; Sekerler, T.; Izzettin, F.V.; Sancar, M.; Okuyan, B. Protective effect of ferulic acid on cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 54, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erseckin, V.; Mert, H.; İrak, K.; Yildirim, S.; Mert, N. Nephroprotective effect of ferulic acid on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in female rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.B.; Suliman, M.; Bashir, A.I.; Shadeed, M.; Ibrahimd, N.A.; Qumani, M.; Alaraj, M. Effect of royal jelly on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Biochem. Cell. Arch. 2017, 17, 761–767. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, C.T.; Krueger, R.R. The date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.): overview of biology, uses, and cultivation. HortScience 2007, 42, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, D.; Dhobi, M.; Wang, D.; Tewari, D. An insight to treat cardiovascular diseases through phytochemicals targeting PPAR-α. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Shams, R.; Pandey, V.K.; Dash, K.K.; Singh, P.; Bashir, O. Barley phytochemicals and health promoting benefits: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Gullón, B.; Pateiro, M.; Amarowicz, R.; Misihairabgwi, J.M.; Lorenzo, J.M. Date fruit and its by-products as promising source of bioactive components: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1411–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Al-Hamimi, S.; Ayyash, M.; Rosa, C.T.; Yahia, E.M.; Haris, S.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; Kamal-Eldin, A. Contributing factors to quality of date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruit. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 321, 112256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farsi, M.; Alasalvar, C.; Morris, A.; Baron, M.; Shahidi, F. Comparison of antioxidant activity, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and phenolics of three native fresh and sun-dried date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties grown in Oman. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7592–7599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Harthi, S.; Mavazhe, A.; Al Mahroqi, H.; Khan, S.A. Quantification of phenolic compounds, evaluation of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of four date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) varieties of Oman. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2015, 10, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, E.A.; Tawfik, M.S.; Abu-Tarboush, H.M. Phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of various date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) fruits from Saudi Arabia. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2011, 16364. [Google Scholar]
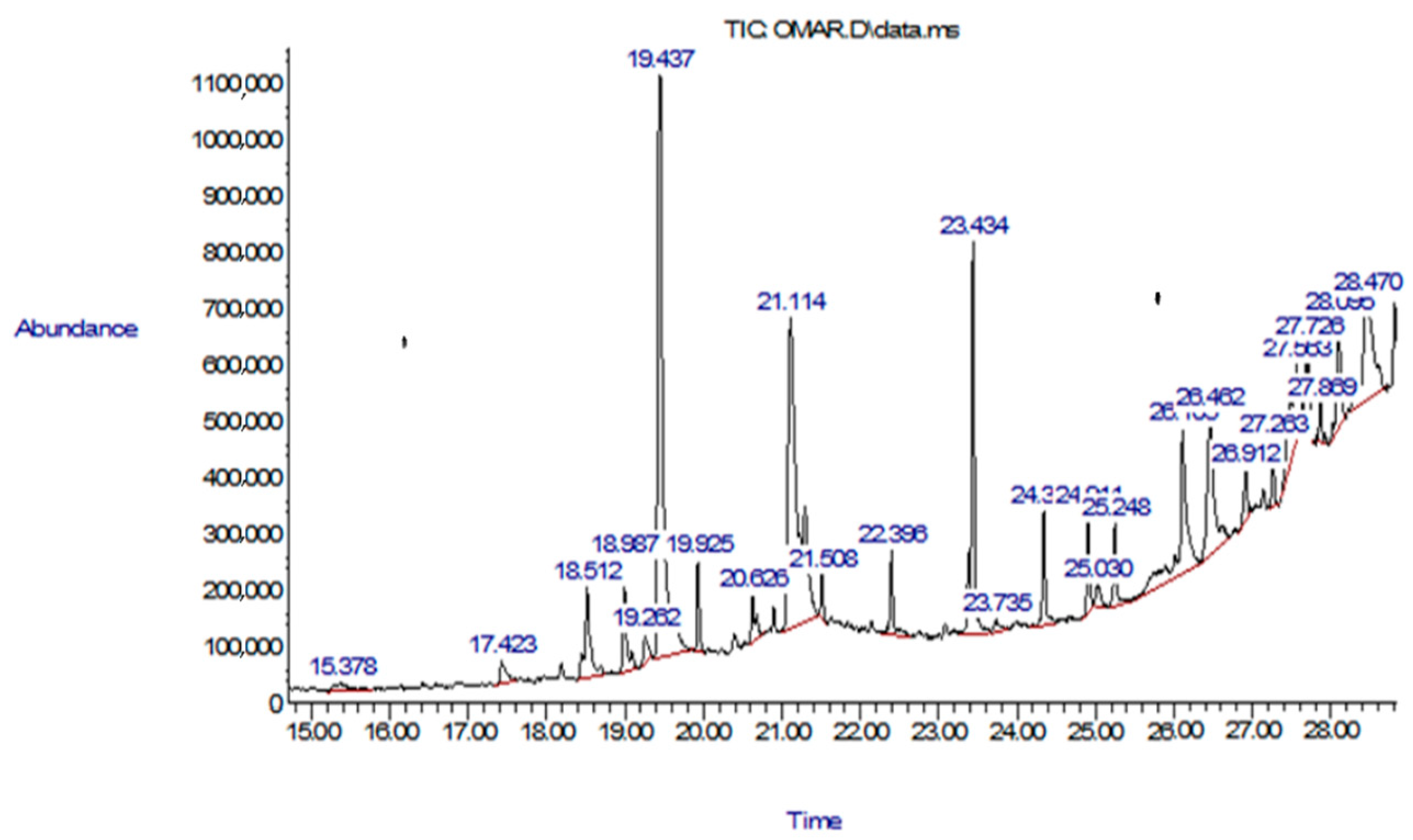
| No. | Compound | RT (min) | Peak Area (%) | Mol Weight (amu) | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Phthalic acid, isobutyl octadecyl ester | 18.512 | 4.61 | 474.371 | C30H50O4 |
| 2 | Hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester | 18.987 | 3.42 | 270.256 | C17H34O2 |
| 3 | 9-Octadecenoic acid, (E)- | 19.262 | 1.01 | 282.256 | C18H34O2 |
| 4 | n-Hexadecanoic acid | 19.437 | 29.69 | 256.24 | C16H32O2 |
| 5 | i-Propyl 14-methyl-pentadecanoate | 19.925 | 1.97 | 298.287 | C19H38O2 |
| 6 | 9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z)- | 20.626 | 1.68 | 280.24 | C18H32O2 |
| 7 | Cycloeicosane | 21.508 | 0.91 | 280.313 | C20H40 |
| 8 | Octadecane | 22.396 | 2.48 | 254.297 | C18H38 |
| 9 | Diisooctyl adipate | 23.434 | 11.83 | 370.308 | C22H42O4 |
| 10 | 2-Methyl-Z-4-tetradecene | 23.735 | 0.69 | 210.235 | C15H30 |
| 11 | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, diisooctyl ester | 24.911 | 2.53 | 390.277 | C24H38O4 |
| 12 | Z,E-3,13-Octadecadien-1-ol | 25.03 | 0.93 | 266.261 | C18H34O |
| 13 | Eicosane | 26.105 | 10.65 | 282.329 | C20H42 |
| 14 | 2-Nonacosanone | 26.462 | 8.85 | 422.449 | C29H58O |
| 15 | Heptadecane, 2,6,10,15-tetramethyl- | 26.912 | 1.67 | 296.344 | C21H44 |
| 16 | Oxirane, hexadecyl- | 27.263 | 1.46 | 268.277 | C18H36O |
| 17 | Benzenepropanoic acid, 3,5-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-4-hydroxy-, octadecyl ester | 27.563 | 7.26 | 530.47 | C35H62O3 |
| 18 | 13-Tetradecen-1-ol acetate | 27.726 | 2.99 | 254.225 | C16H30O2 |
| 19 | 2-Pentadecanone, 6,10,14-trimethyl- | 27.869 | 1.03 | 268.277 | C18H36O |
| 20 | 2-Octadecyl-propane-1,3-diol | 28.095 | 4.34 | 328.334 | C21H44O2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





