1. Introduction
Fire accidents have been a persistent concern globally, occurring in various settings such as residential areas, industrial facilities, forests, and commercial establishments. Preventing fire accidents involves adhering to fire safety regulations, proper maintenance of equipment, and promoting awareness of fire prevention measures. Implementing and regularly practicing emergency evacuation plans also play a crucial role in minimizing the impact of fire accidents. Water is a common and effective extinguishing agent for various types of fires. Water is used to extinguish Class A fires involving wood, paper, fabric, trash, and other common combustibles by cooling and smothering the flames.
Fire suppression systems have an incredibly large variety of applications. The system can display the fire location and provides early warning to allow occupants to escape the building safely.
Implementing a fire suppression system in plywood industries is vital to mitigate the inherent fire risks associated with wood processing. These systems typically involve a combination of early detection and suppression mechanisms. Heat and smoke detectors strategically placed in key areas can swiftly identify potential fire outbreaks. Regular maintenance, employee training, and adherence to safety protocols are essential components of an effective fire safety strategy in plywood industries. Furthermore, integrating modern technologies like smart sensors and monitoring systems can enhance the overall efficiency of the fire suppression system.
2. Literature Review
Fakrulradzi Idris, Norlezah Hashim, Ahmad FauzanKadmin, Lee Boon Yee, "
Intelligent fire detection and alert system using LabVIEW” [
1]
describes the design and development of a fire detection and alert system. Temperature and flame sensors are used to indicate the occurrence of fire. The system can display the fire location and provides early warning to allow occupants to escape the building safely.
Arth Patel, Kalpesh Chudasama, Ravi Patel, Shreyas Patel, "
LABVIEW based Smart House Control“ [
2] proposed a LabVIEW based smart house control that a safety system can be designed as a single control unit which includes detection of hazardous parameters using sensor like smoke detection, LPG leakage detection, motion detection, temperature monitoring etc.
Dr. Ravikumar A V "
Fire Extinguishing System using LabView. [
3] develop the circuits by using sensors and embedded system software. With the help of these sensors, detection of fire and the required extinguishing action consists of alerting the passengers in the train about the accordance of fire with the help of a buzzer and a exhaust fan is switched on, sprinkling of water all around the compartment in order to reduce the flames.
Md. Selim Reza, SM Mamun,
” Development and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Fire Detection and Extinguishing system” [
4] consists of two units like detection unit and extinguishing unit. While for extinguishing purposes, foam and water through LabVIEW will process the signal and using relay module. The system will send SMS to the predefined numbers using GSM module.
Bharani J C , Gowtham M , Narmada K K, Ram Prasath J, ”
Fire Rescue System In Railways using LabVIEW “[
5] implements technology that will automatically identify the fire accident and inform it to the loco pilot through wireless signal transmission. As an initial step, fire will be suppressed and intimation about the accident will be sent through Short Message Service consists of the status of fire accident accurately by transmitting the physical parameters such as compartment number, intensity of fire. This also display the particular area code based upon that GSM Mobile network.
Samit Kumar Ghosh ,P B Natarajan , Sankata Bhanjan Prusty,”
Intelligent Smart Home Automation System based on LabVIEW”[
6] design for home automation with some intelligent functionalities. The system is based on the LabVIEW and can act as a security guard of the home. The system can monitor the temperature, PIR motion sensor, fire sensor to guarantees the family security.
P. Arun Mozhi Devan
, G. Manisha , K.G.T.Rajarajeswari , M.Priyanga
, “Fire safety and alerting system in railways” [
7] enables the rescuing methodology while fire accidents in the train by utilizing gas/smoke sensors integrated with LM35 along with automated fire suppression systems. If the temperature is greater than 80ºC and the output value from the gas and the smoke sensor senses the smoke then the Arduino gives the command to enable buzzer, alerting signal to GSM network, fire extinguisher.
Adeel Rehman, Dan-Sorin Necsulescu, Jurek Sasiadek
,” Robotic Based Fire Detection in Smart Manufacturing Facilities” [
8] proposes that Autonomous robots may be deployed to seek out a potential source of fire in the industrial environment, approach, investigate and declare the presence or absence of fire based on several sensor fusion techniques. The robot uses sensor readings comparison to approach the source and a smart obstacle avoidance system to avoid obstacles together with Modified Voting Logic to declare a fire threat
.
Nagesh M S , Deepika T V , Stafford Michahial, Dr M Shivakumar, “
Fire Extinguishing Robot” [
9] aims in giving a technical solution to the movement of robot and reaching the fire, the flame sensor detects the fire and gives the further signal to the extinguisher units to trigger the pump and spray the water.
Joshua G. McNeil, Joseph Starr, and Brian Y. Lattimer,”
Autonomous Fire Suppression Using Multispectral Sensors” [
10] contains a multispectral sensor suite, including UV sensors and IR stereovision, to detect and target the fire for suppression. Using a deterministic trajectory algorithm, the nozzle angle is adjusted to apply the suppressant onto the base of the fire.
3. Proposed Solution and Implementation
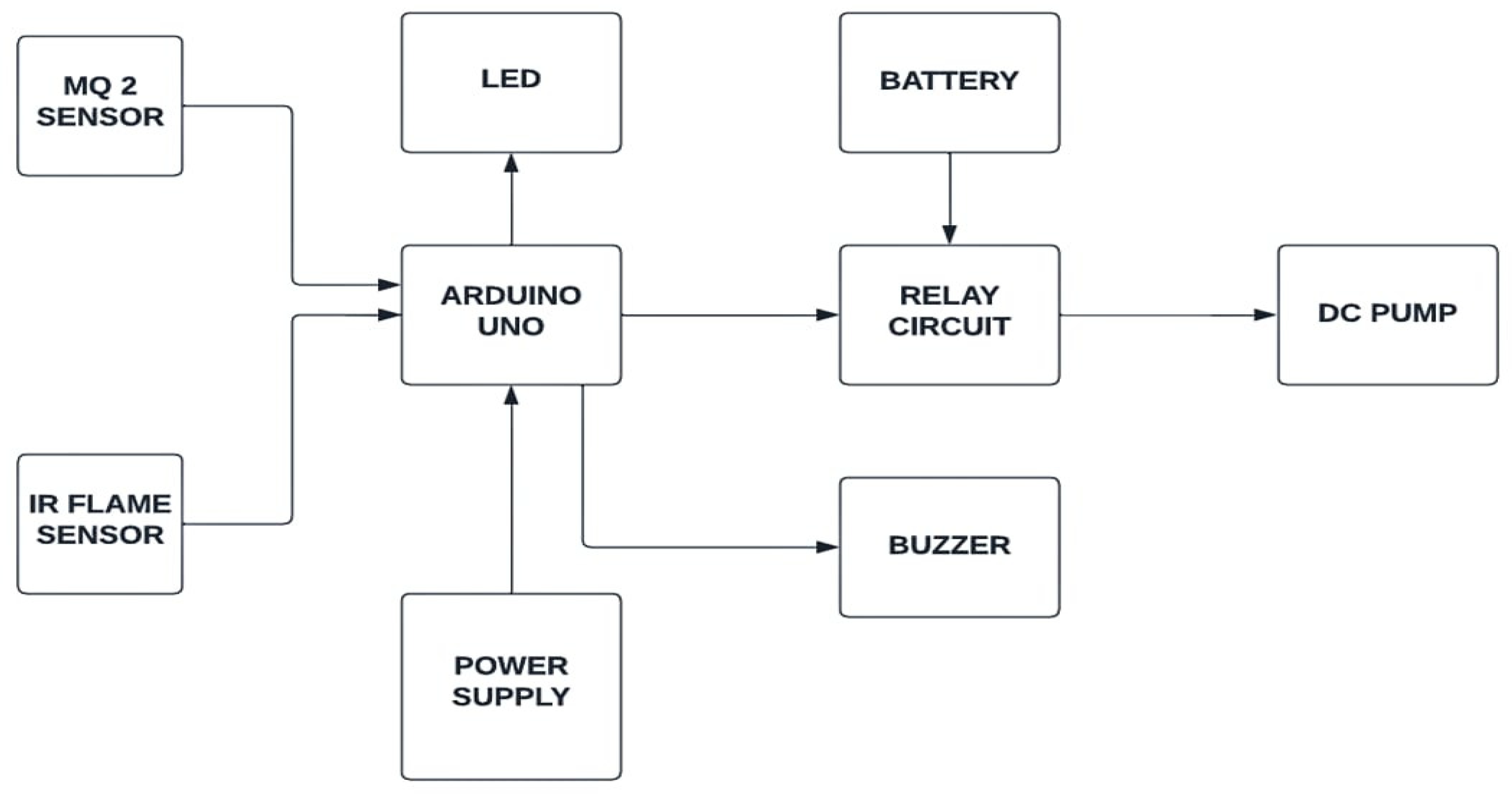
Figure 1.
Block diagram of proposed system.
Figure 1.
Block diagram of proposed system.
Table 1.
Interfacing of Hardware components to Microcontroller.
Table 1.
Interfacing of Hardware components to Microcontroller.
| Pin Name on The Microcontroller |
Component |
| 2 |
Red led |
| 3 |
Green led |
| 7 |
Buzzer |
| 13 |
Relay |
| A0 |
Flame Sensor |
| A1 |
MQ 2 Sensor |
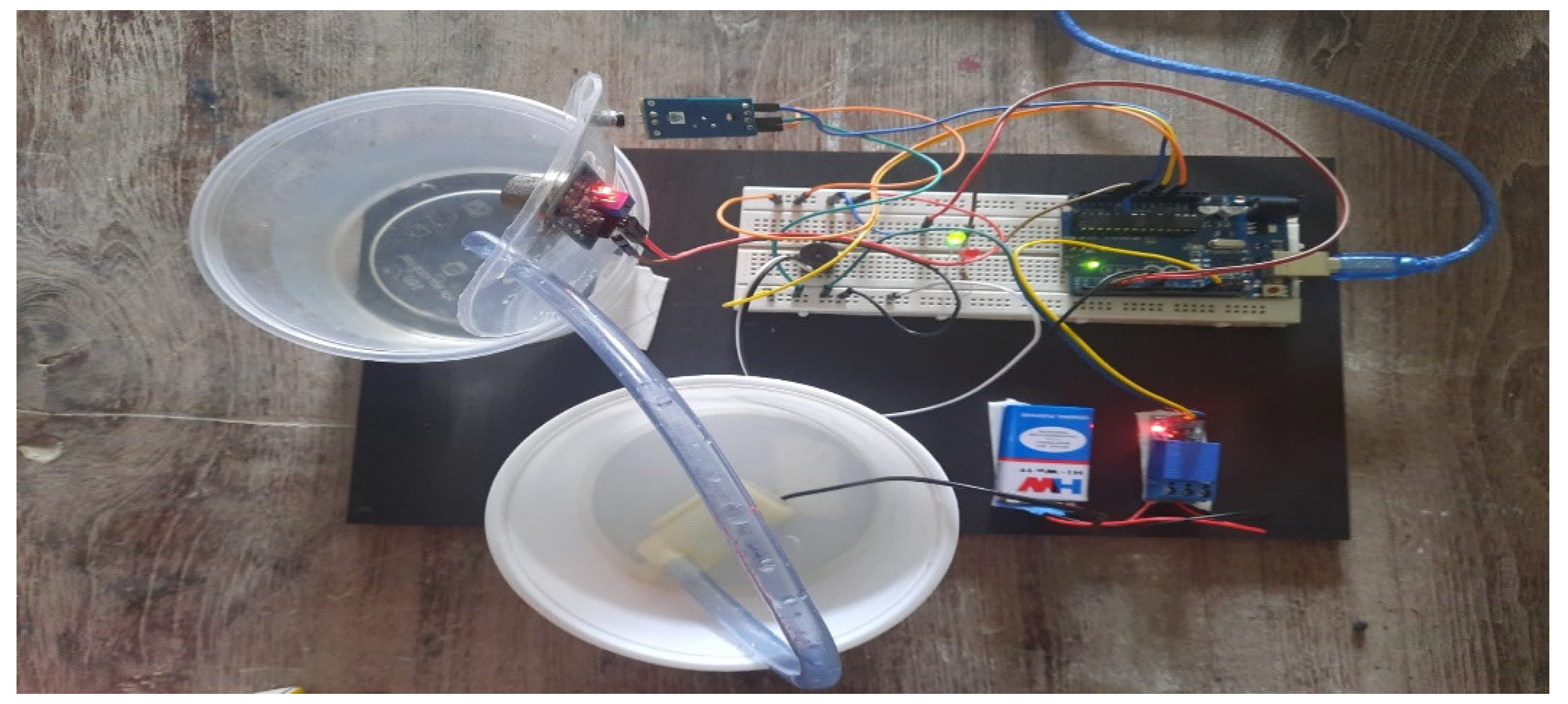
Figure 2.
Hardware setup.
Figure 2.
Hardware setup.
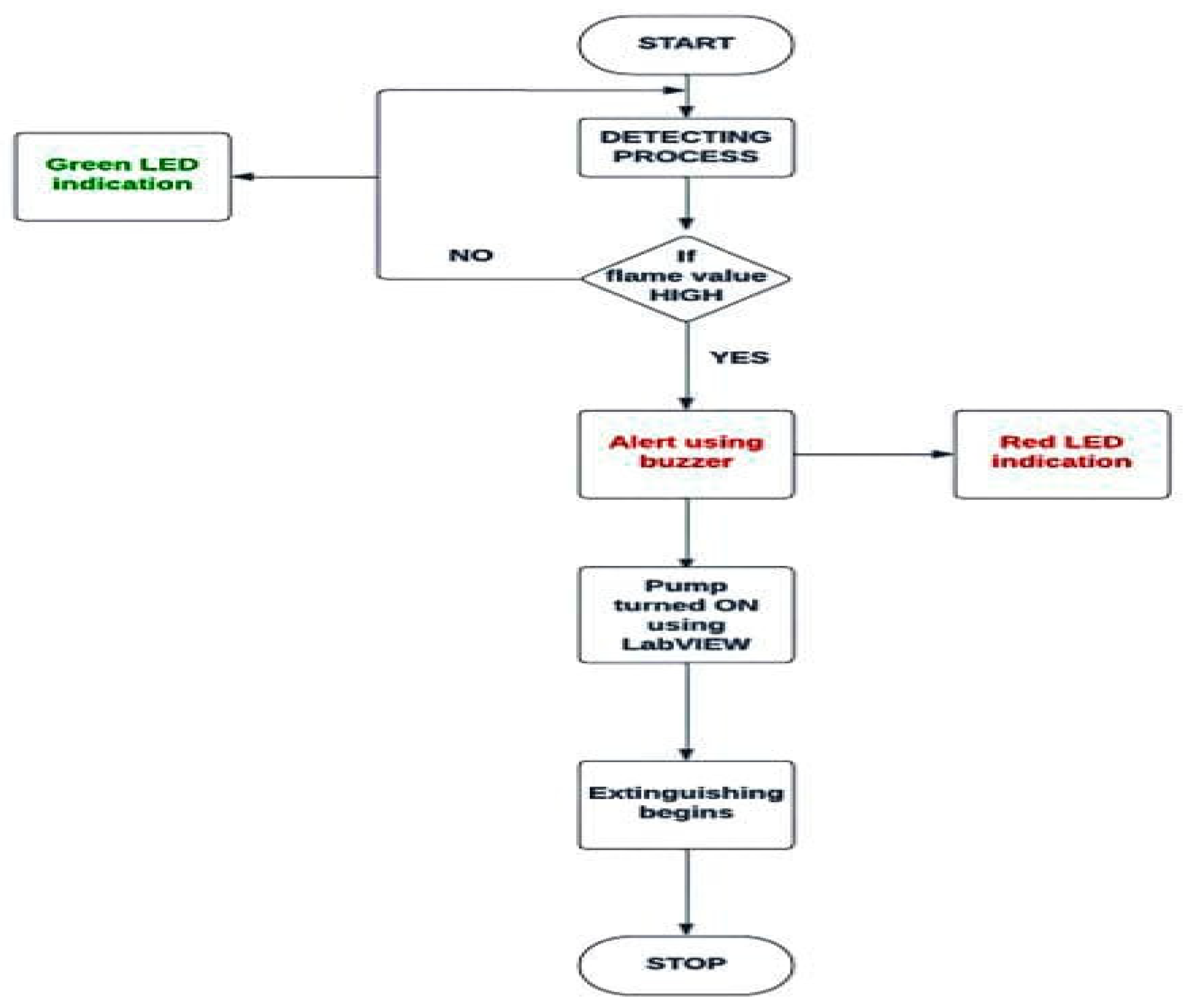
MQ 2 sensor and Flame sensors are interfaced to the Arduino Microcontroller through proper wire connection. A flame sensor works by detecting the presence of a flame within a specified chamber. The sensor is a short length of thin metallic rod that creates a small current of electricity in order to confirm there is fire burning within the chamber. While the program is executed, MQ2 sensor is checking the presence of hazardous gases like LPG. Presence of gas changer the resistance of the sensor. Due to this resistance change, the output voltage also get varies. The pump and Buzzer gets run condition when the control signal is given by Arduino and LabVIEW. The flowchart of proposed system is enclosed in
Figure 3.
4. Performance of Proposed System
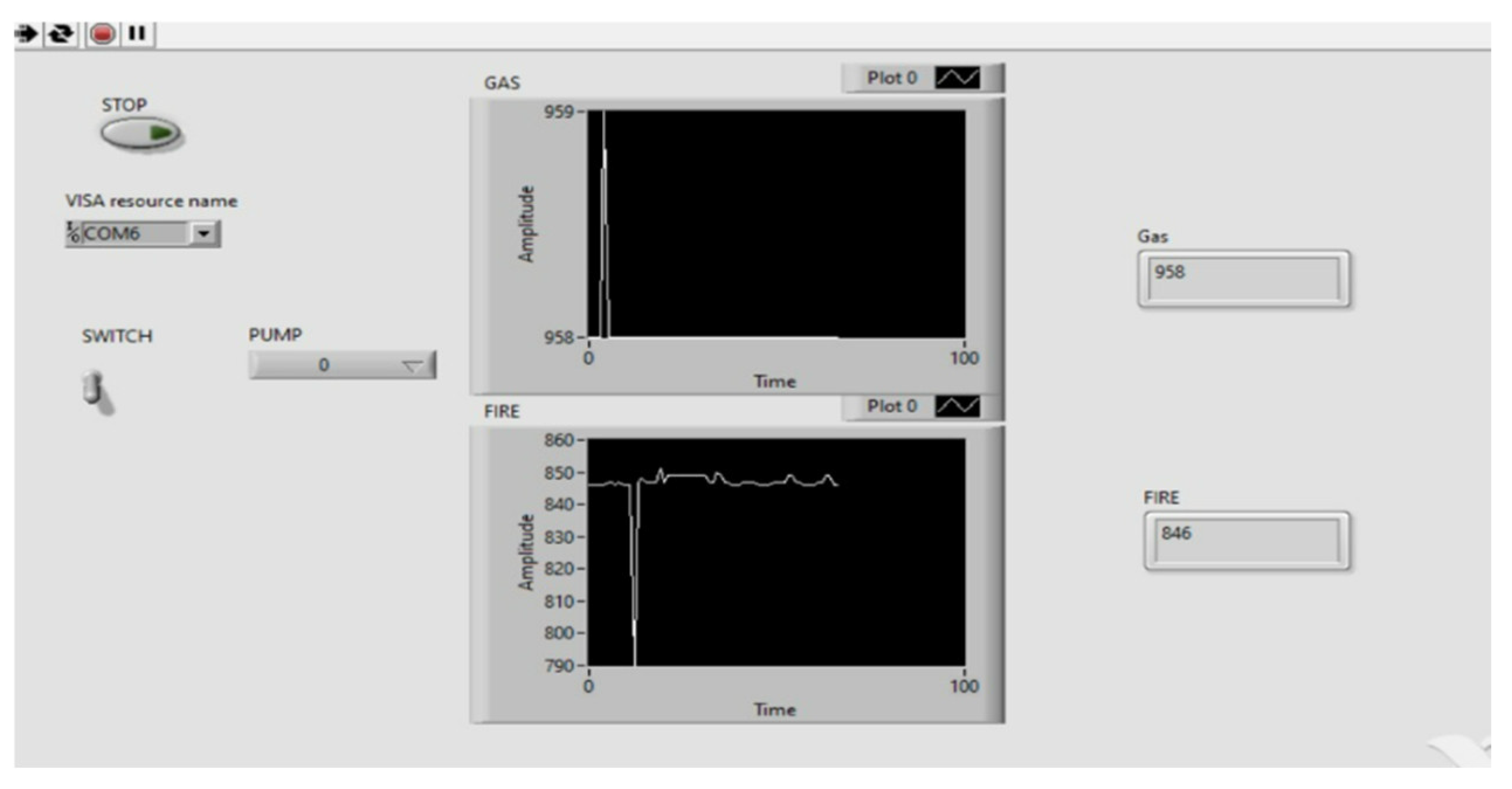
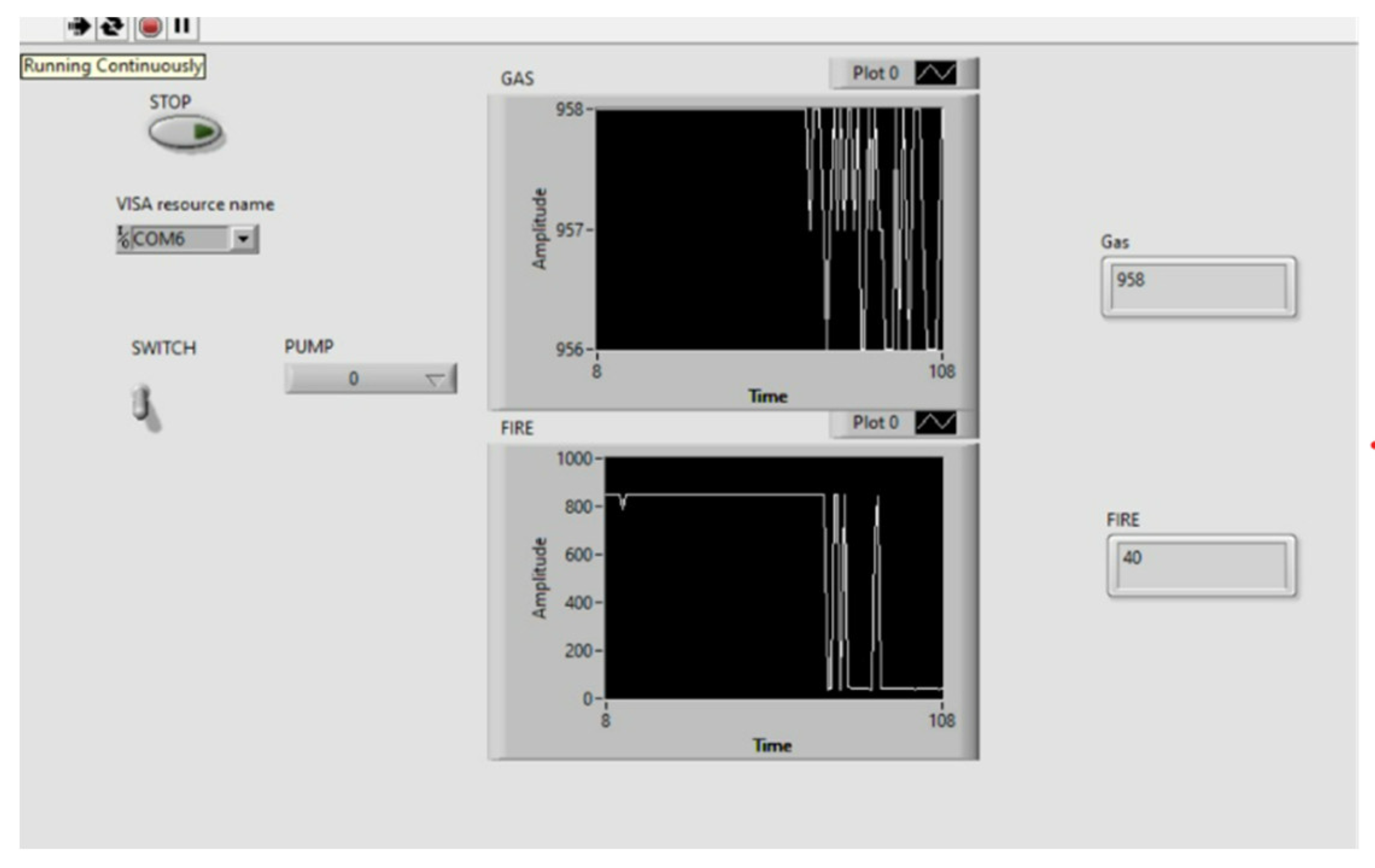
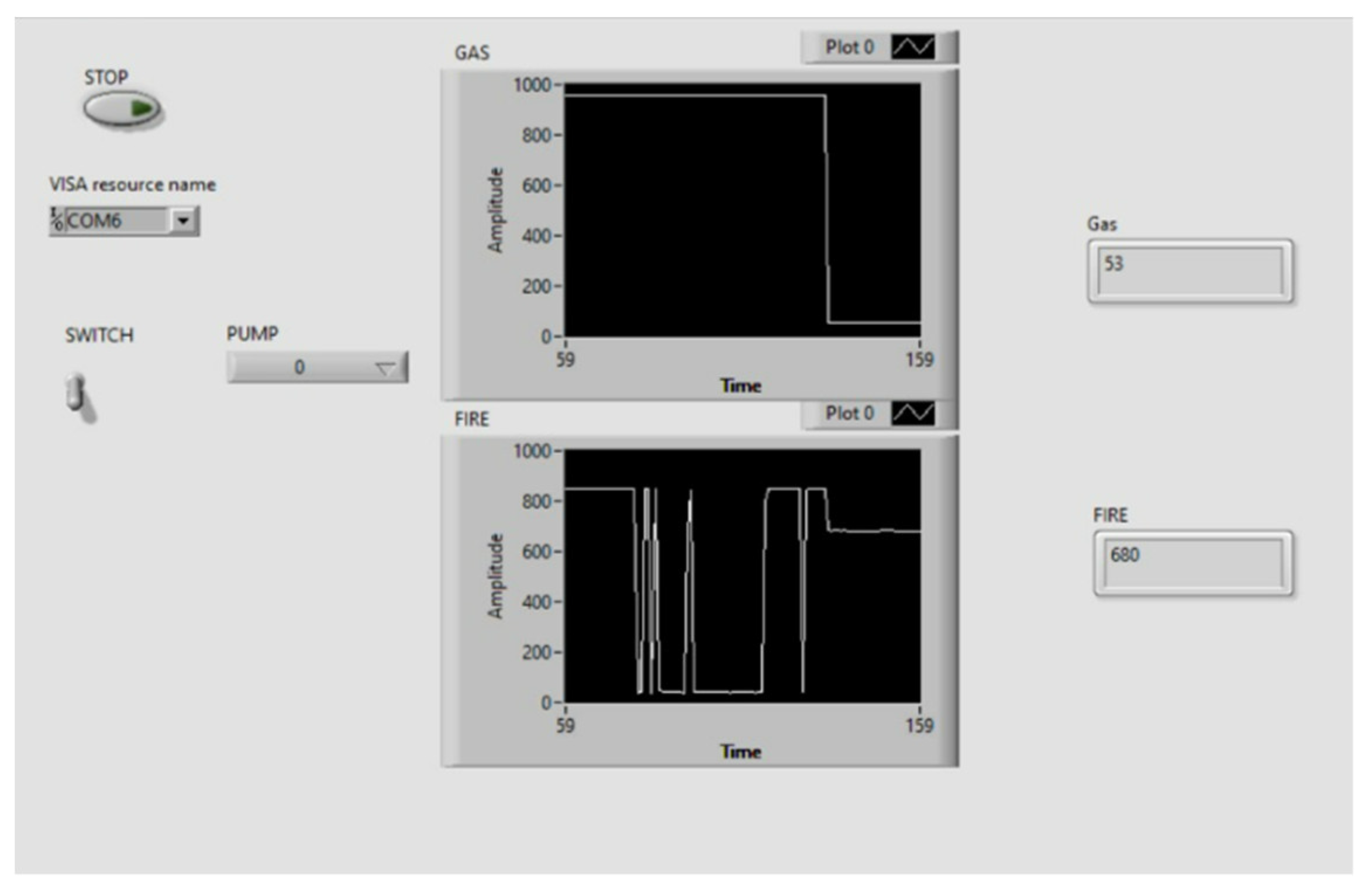
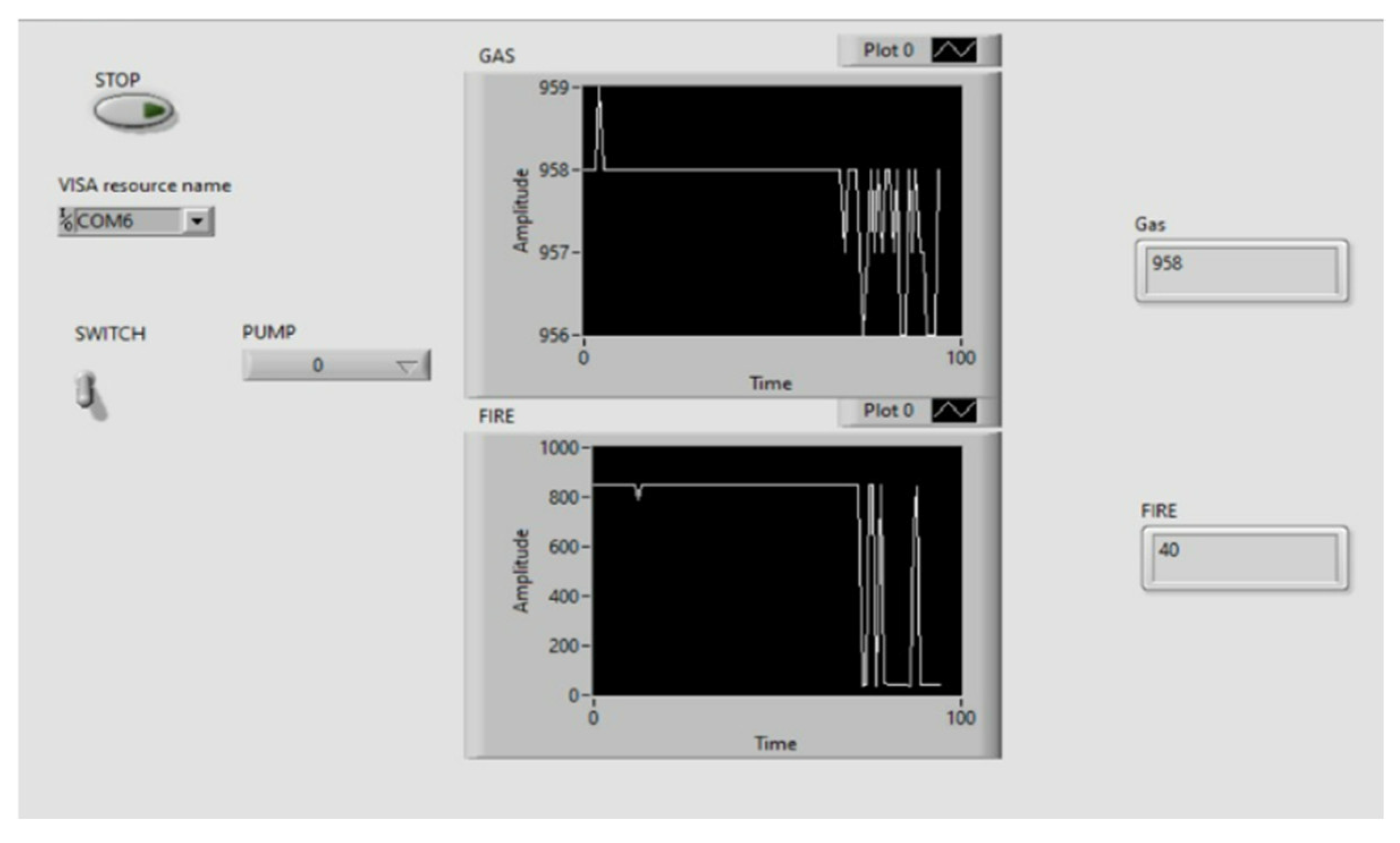
Once the fire is detected by the IR flame sensor, sensor will send the data to the microcontroller interfaced with LabVIEW and then pump gets start to turn ON the suppression system. IR flame sensor detects the fire only if the wavelength of fire is greater than 760 nm and within the range of 0.8 m and MQ2 Smoke sensor detects the smoke within the range of 300 ppm.
Figure 4.
Before Fire detection.
Figure 4.
Before Fire detection.
Figure 5.
After Fire Detection.
Figure 5.
After Fire Detection.
Figure 6.
Before Smoke Detection.
Figure 6.
Before Smoke Detection.
Figure 7.
After Smoke Detection.
Figure 7.
After Smoke Detection.
5. Conclusions
This project concluded by creating fire suppression system using LabVIEW is used to extinguish, control the fire from spreading or occurring. Implementing a fire suppression system in plywood industries is vital to mitigate the inherent fire risks associated with wood processing. These systems typically involve a combination of early detection and suppression mechanisms. Heat and smoke detectors strategically placed in key areas can swiftly identify potential fire outbreaks. Regular maintenance, employee training, and adherence to safety protocols are essential components of an effective fire safety strategy in plywood industries. Furthermore, integrating modern technologies like smart sensors and monitoring systems can enhance the overall efficiency of the fire suppression system
This project can be extended by Integrate advanced sensors such as infrared cameras or multispectral sensors, to detect fires at an early stage. To enable remote or wireless monitoring and control of the fire suppression system allows for real-time assessment of system status, immediate response to alerts, and remote adjustments for optimal performance.
References
- Fakrulradzi, I.; Norlezah, H.; Ahmad; F.K.; Lee, B.Y. Intelligent fire detection and alert system using LabVIEW. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Chudasama, K.; Patel, R.; Patel, S. LABVIEW based Smart House Control. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Res. Manag. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, M.S.; Mamun, S.M. Development and Performance Evaluation of a Novel Fire Detection and Extinguishing System: Towards Industrial Automation. Int. J. Adv. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samit Kumar Ghosh ,P B Natarajan , Sankata Bhanjan Prusty. Intelligent Smart Home Automation System based on LabVIEW. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2018.
- A V, D.R. ; Bhoomika G; Chaitra R; Lekhana H. Fire Extinguishing System using LabView. International J. Innov. Sci. Res. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Devan, P.A.M.; Manisha, G.; Rajarajeswari, K.G.T.; Priyanga, M. Fire safety and alerting system in railways. In Proceedings of the 2018 3rd IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT-2018), May 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, M.S.; Deepika, T.V.; Stafford, M.; Shivakumar, M. Fire Extinguishing Robot. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2016, 5. ISO 3297:2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Necsulescu, D.-S.; Sasiadek, J. Robotic Based Fire Detection in Smart Manufacturing Facilities. from International Federation of Automatic Control -Papers on Line 48-3 (2015). [CrossRef]
- Bharani, J.C.; Gowtham, M.; Narmada, K.K.; Ram Prasath, J. Fire Rescue System in Railways using LabVIEW. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Green Computing Communication and Electrical Engineering (ICGCCEE); 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, J.G.; Starr, J.; Lattimer, B.Y. Autonomous Fire Suppression Using Multispectral Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM) Wollongong, Australia, 9–12 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).