Submitted:
13 December 2023
Posted:
14 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
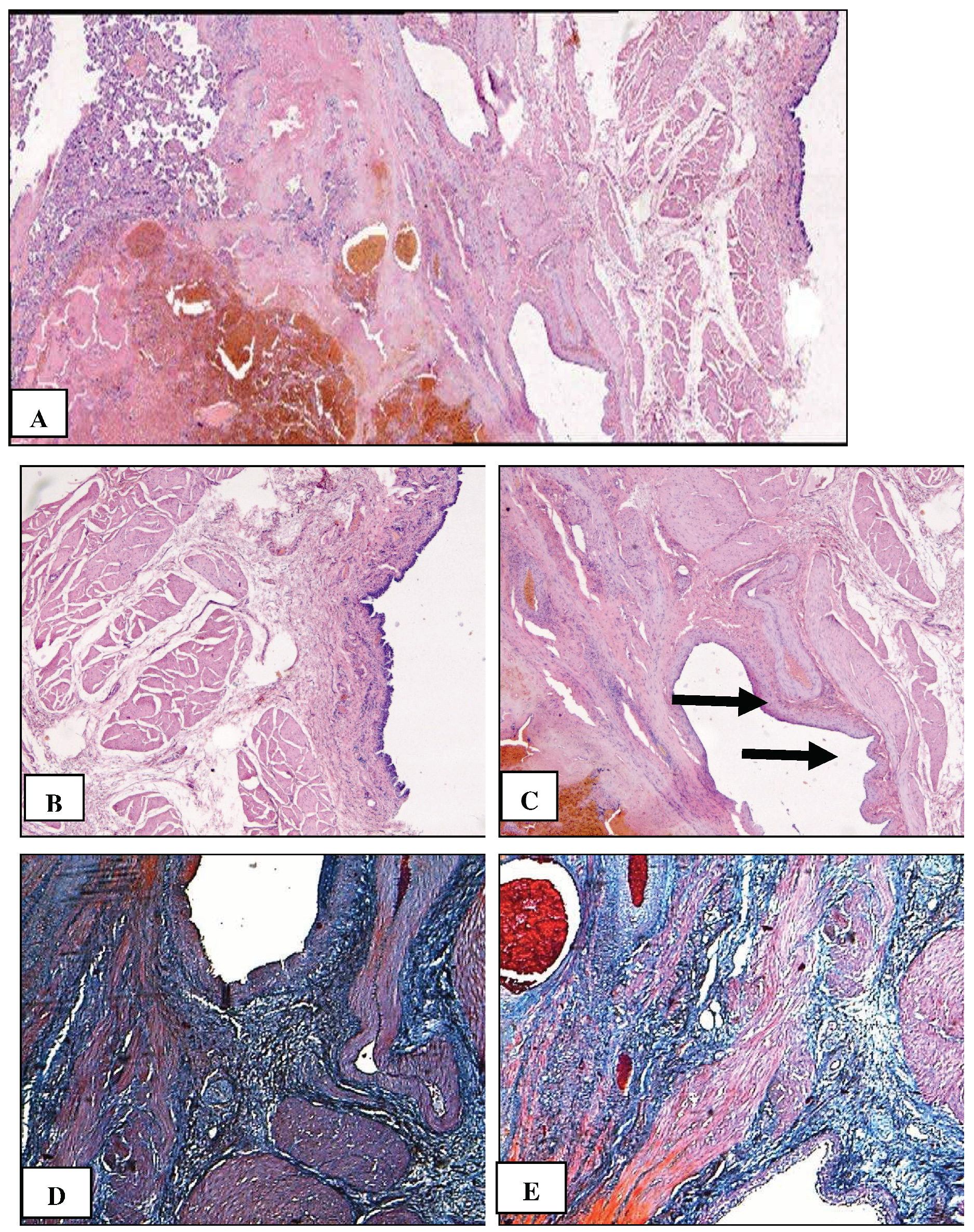
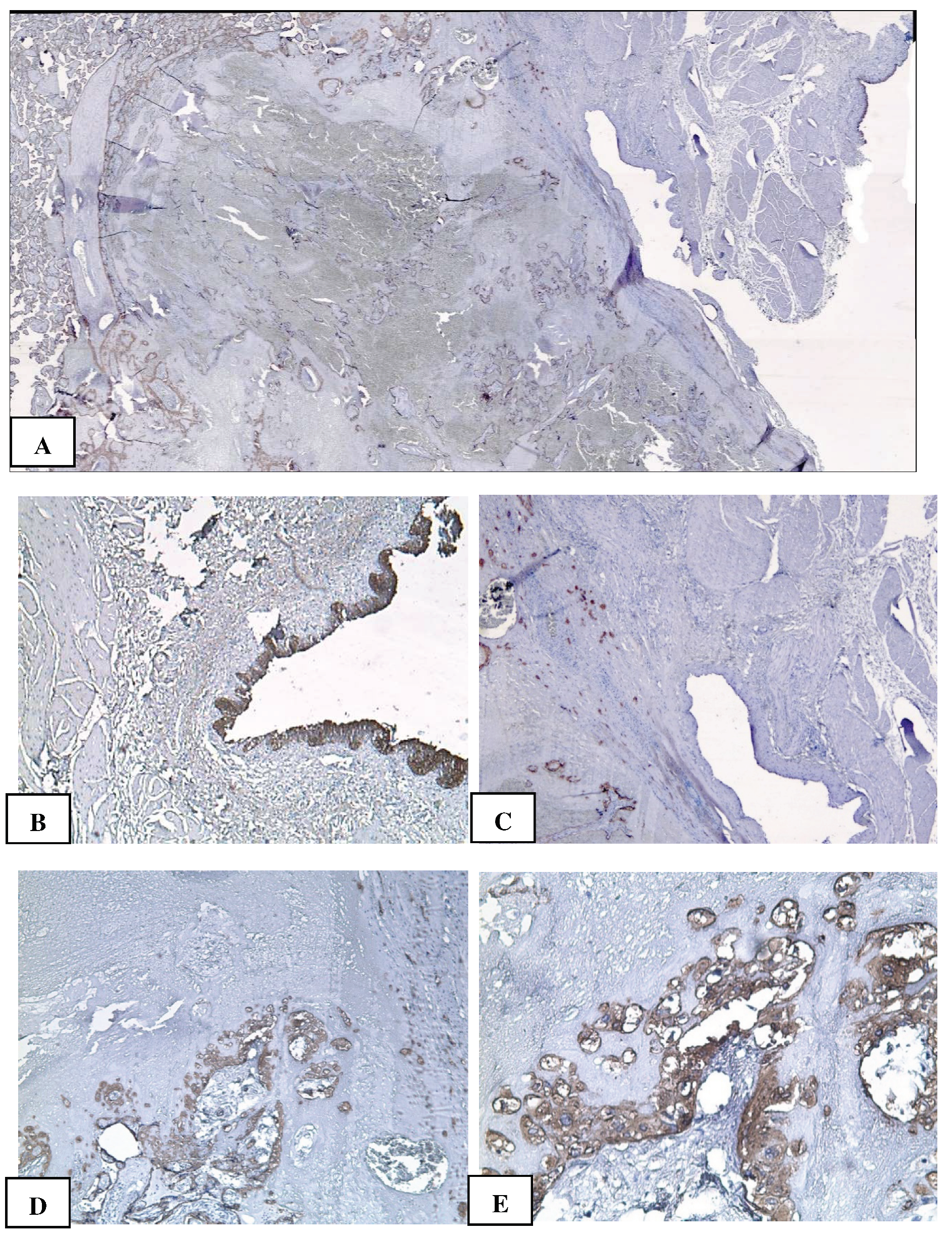
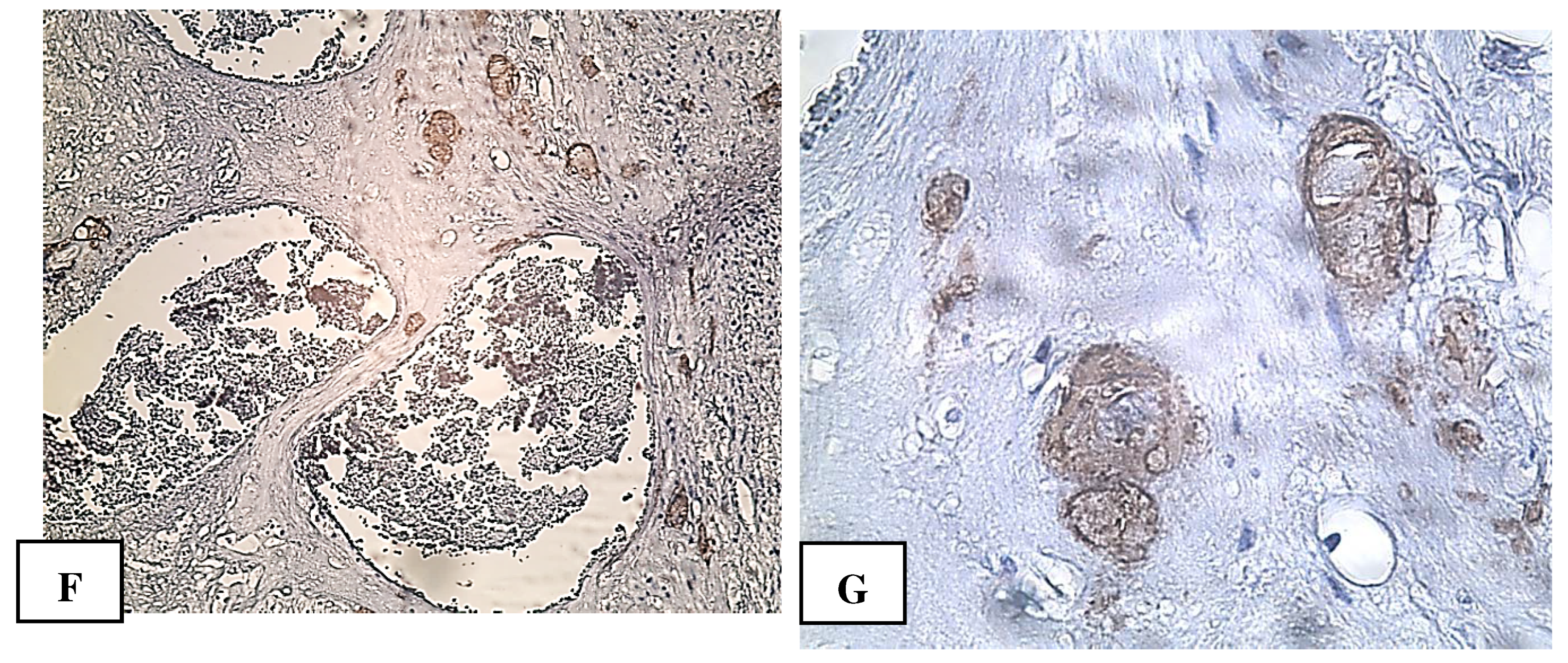
2. Сase Report
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Irving, C.; Hertig, A.T. A study of placenta accreta. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1937, 64, 178–200. [Google Scholar]
- Jauniaux, E.; Ayres-de-Campos, D.; Langhoff-Roos, J.; Fox, K.A.; Collins, S. FIGO Placenta Accreta Diagnosis and Management Expert Consensus Panel. FIGO classification for the clinical diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum disorders. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 146, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlando, M.; Sarno, L.; Napolitano, R.; Capone, A.; Tessitore, G.; Maruotti, G.M; Martinelli, P. Placenta accreta: Incidence and risk factors in an area with a particularly high rate of cesarean section. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 9, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carusi, D.A. The placenta accreta spectrum: Epidemiology and risk factors. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 61, 733–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, R.M.; Landon, M.B.; Rouse, D.J.; Leveno, K.J.; Spong, C.Y.; Thom, E.A.; Moawad, A.H.; Caritis, S.N.; Harper, M.; Wapner, R.J.; Sorokin, Y.; Miodovnik, M.; Carpenter, M.; Peaceman, A.M.; O'Sullivan, M.J.; Sibai, B.; Langer, O.; Thorp, J.M.; Ramin, S.M.; Mercer, B.M. , National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network. Maternal morbidity associated with multiple repeat cesarean deliveries. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 107, 1226–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upson, K.; Silver, R.M.; Greene, R.; Lutomski, J.; Holt, V.L. Placenta accreta and maternal morbidity in the Republic of Ireland, 2005-2010. J Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014, 27, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obstetric Care Consensus, No. Obstetric Care Consensus No. 7: placenta accreta spectrum. Obstet Gynecol. 2018, 132, e259–e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanov, A.P.; Aksenenko, V.A.; Lukashevich, A.A.; Fokina, T.V.; Stepanova, I.I.; Tikhonova, N.B. The leading role of scars after the caesarian section in the pathogenesis of placenta previa accreta. Clin. exp. morphology (In Russ.). 2019, 8, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanov, A.P.; Bushtarev, A.V.; Fokina, T.V. Special features of cytotrophoblastic invasion in complete placenta previa and increta. Arkh Pathol. Arkh Pathol. (In Russ.). 2017, 79, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.L.; Baergen, R.; Ernst, L.M.; Katzman, P.J.; Jacques, S.M.; Jauniaux, E.; Khong, T.Y.; Metlay, L.A.; Poder, L.; Qureshi, F.; Rabban JT 3rd, Roberts, D.J.; Shainker, S.; Heller, D.S. Classification and reporting guidelines for the pathology diagnosis of placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) disorders: recommendations from an expert panel. Mod Pathol. 2020 Dec;33, 2382-2396. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Uterine dehiscence in pregnant with previous caesarean delivery. Ann Med. 2021, 53, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauniaux, E.; Bhide, A. Prenatal ultrasound diagnosis and outcome of placenta previa accreta after cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 217, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habek, D.; Cerovac, A.; Luetić, A.; Marton, I.; Prka, M.; Kulaš, T.; Ujević, B. Modified Stark's (Misgav Ladach) caesarean section: 15 – year experience of the own techniques of caesarean section. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2020, 247, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antila-Långsjö, R.M.; Mäenpää, J.U.; Huhtala, H.S.; Tomás, E.I.; Staff, S.M. Cesarean scar defect: A prospective study on risk factors. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018, 219, 458–e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaryan, N.M.; Vandysheva, R.A.; Nizyaeva, N.V.; Gioeva, Z.V.; Mikhalev, S.A.; Khamoshina, M.B.; Mikhaleva, L.M. Clinical and morphological assessment of uterine scars after caesarean section in patients with gynecological and extragenital diseases. Clin. exp. morphology (In Russ.). 2023, 12, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.; Pōder, L.; Bourgioti, C.; Bharwani, N.; Lewis, S.; Kamath, A.; Nougaret, S.; Soyer, P.; Weston, M.; Castillo, R.P.; Kido, A.; Forstner, R.; Masselli, G. Society of Abdominal Radiology (SAR) and European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) joint consensus statement for MR imaging of placenta accreta spectrum disorders. Eur Radiol. 2020, 30, 2604–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, M. MR Imaging of Abnormal Placentation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2017 Aug;25, 601-610 ;25. [CrossRef]
- Uchevatkina, P.V.; Bychenko, V.G.; Kulabukhova, E.A.; Luzhin, I.A.; Shmakov, R.G. System of a unified approach to interpretation of magnetic resonance tomography in diagnostics of pathological placental attachment "MAPI-RADS" (morbidly adherent placenta imaging reporting and data system). REJR 2021, 11, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patent for invention. Method of correction of blood loss during surgical resolution of pregnant women with placenta ingrowth. Plakhotina, E.N.; Belousova, T.N.; Kulikov, I.A.; Pavlyutina, K.M.; Latyshev RV RU 2 704 464 C1, Russia, 2019 Application number: 2019119021. Registration date: 2019.06.19.
- Kulikov, I.A.; Shmakov, R.G.; Belousova, T.N.; Plakhotina, E.N.; Nizyaeva, N.V.; Geilis, I.A.; et al. Efficacy of the tourniquet hemostasis combined with vaginal balloon tamponade using a Zhukovsky vaginal catheter during delivery in placenta accreta spectrum. Obstetrics and Gynegology. 2022, 10, 58–66. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patent for invention Method of surgical delivery of patients with placenta ingrowth in the uterine scar. Kulikov, I.A.; Belousova, T.N.; Sovaev, N.I.; Plakhotina, E.N.; Musaeva, S.V.; Pavlyutina, K.M.; Petrov AE RU 2706368 C1, Russia, 2019 Application number: 2019118817. Registration date: 06.18.2019.
- Milovanov, A.P. Cytotrophoblastic invasion is the most important mechanism of placement and pregnancy progression (in Russian only). Arkhiv Pathologii. 2019, 81, 5 10. (In Russ.). [CrossRef]
- Benirschke, K.; Burton, G.J.; Baergen, R. Pathology of the human placenta. 6th edition. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag . 2012. 939 p. ISBN: 0-387-26738-7.
- Tikhonova, N.B.; Milovanov, A.P.; Aleksankina, V.V.; Fokina, T.V.; Boltovskaya, M.N.; Aleksankin, A.P. The role of adipose tissue in the healing of the rat uterine wall after a full-thickness surgical incision. Clin. exp. morphology 2021, 10, 72–80, (In Russ.). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
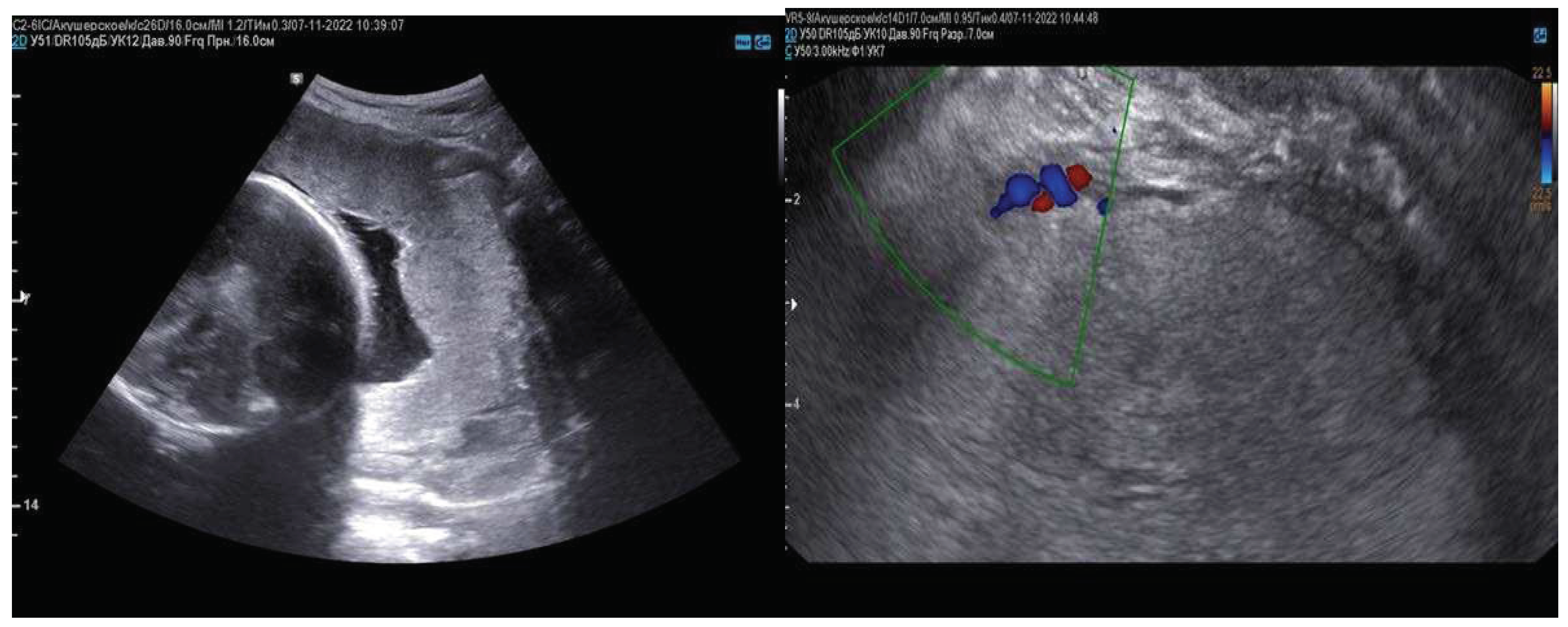
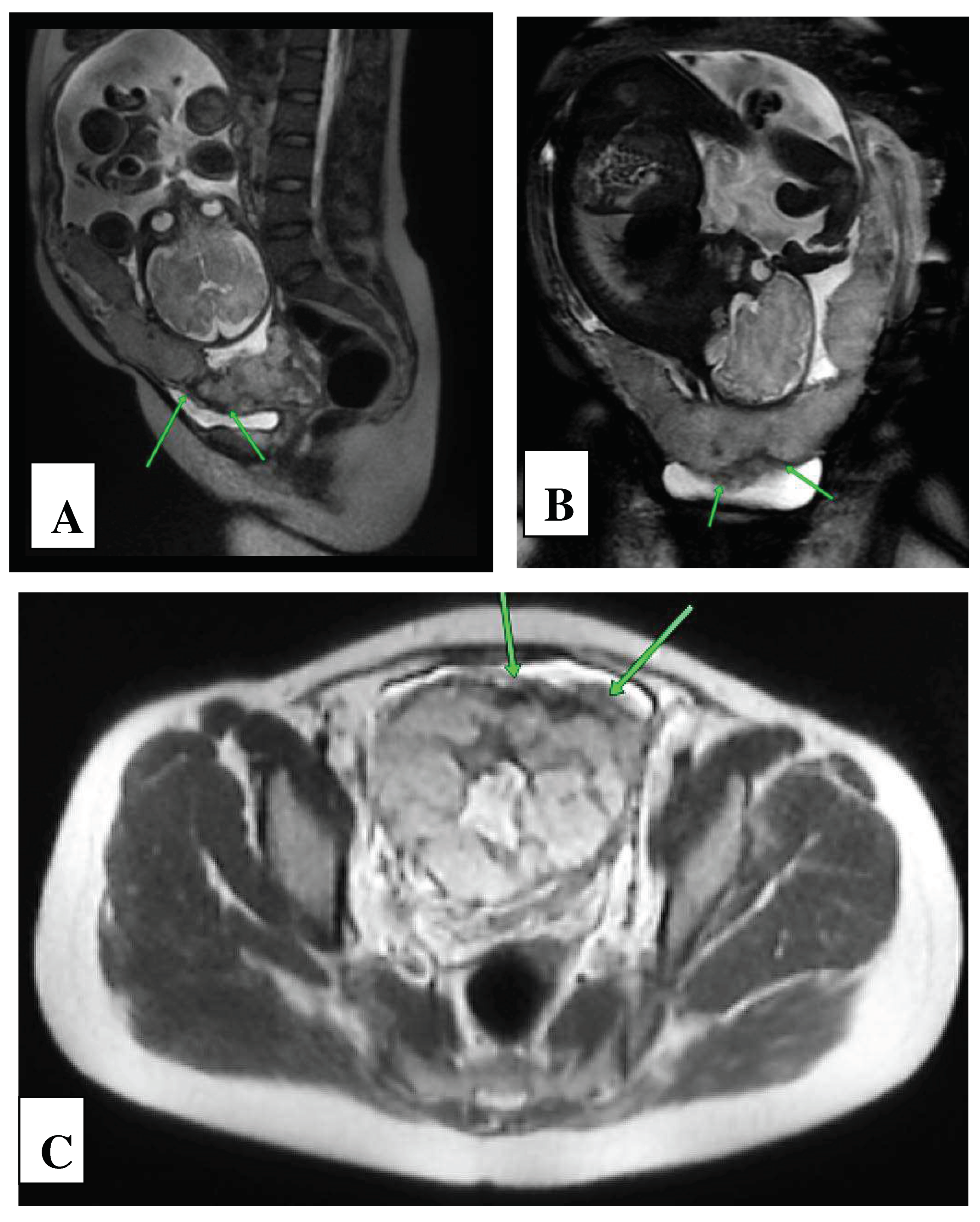
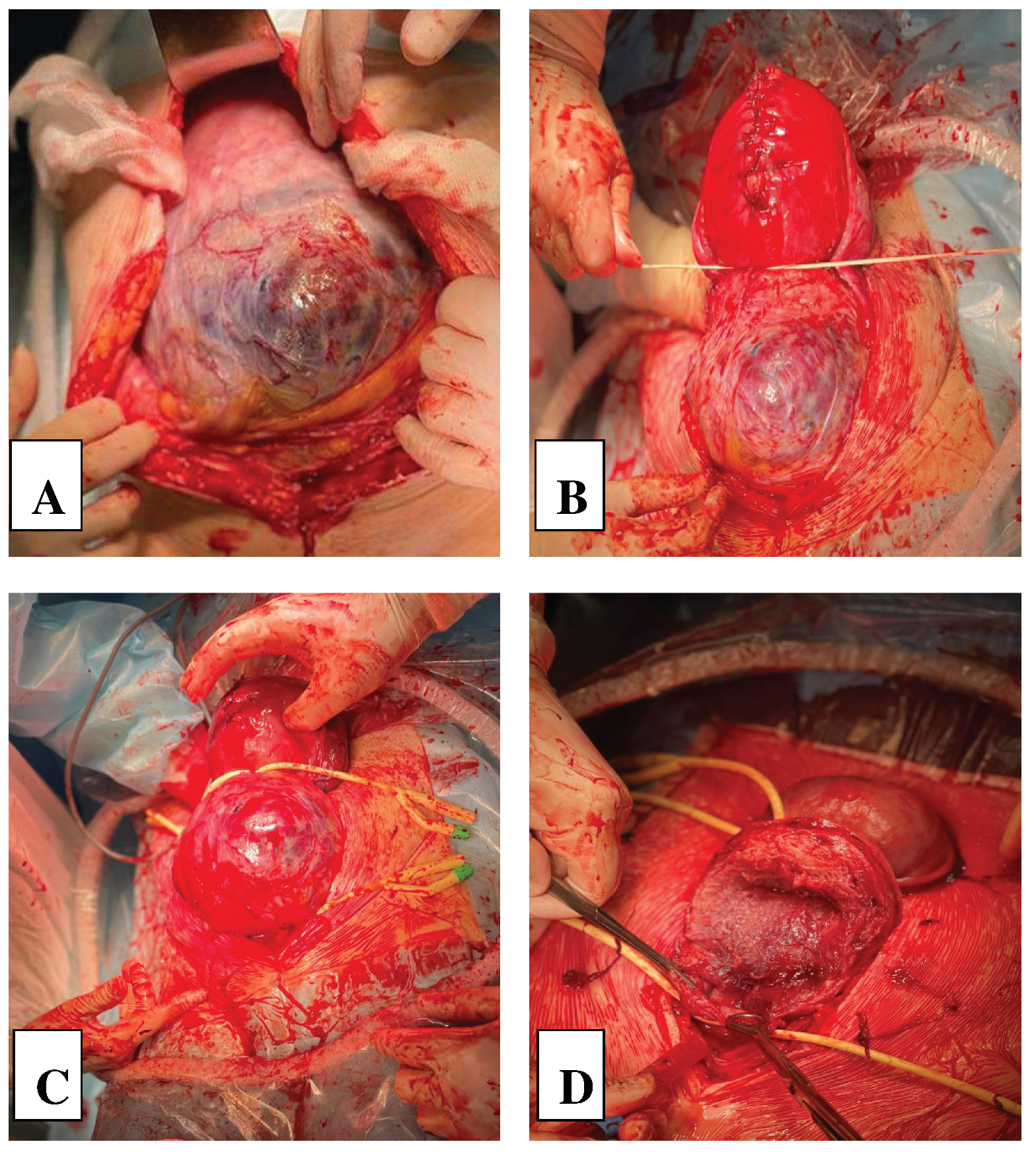
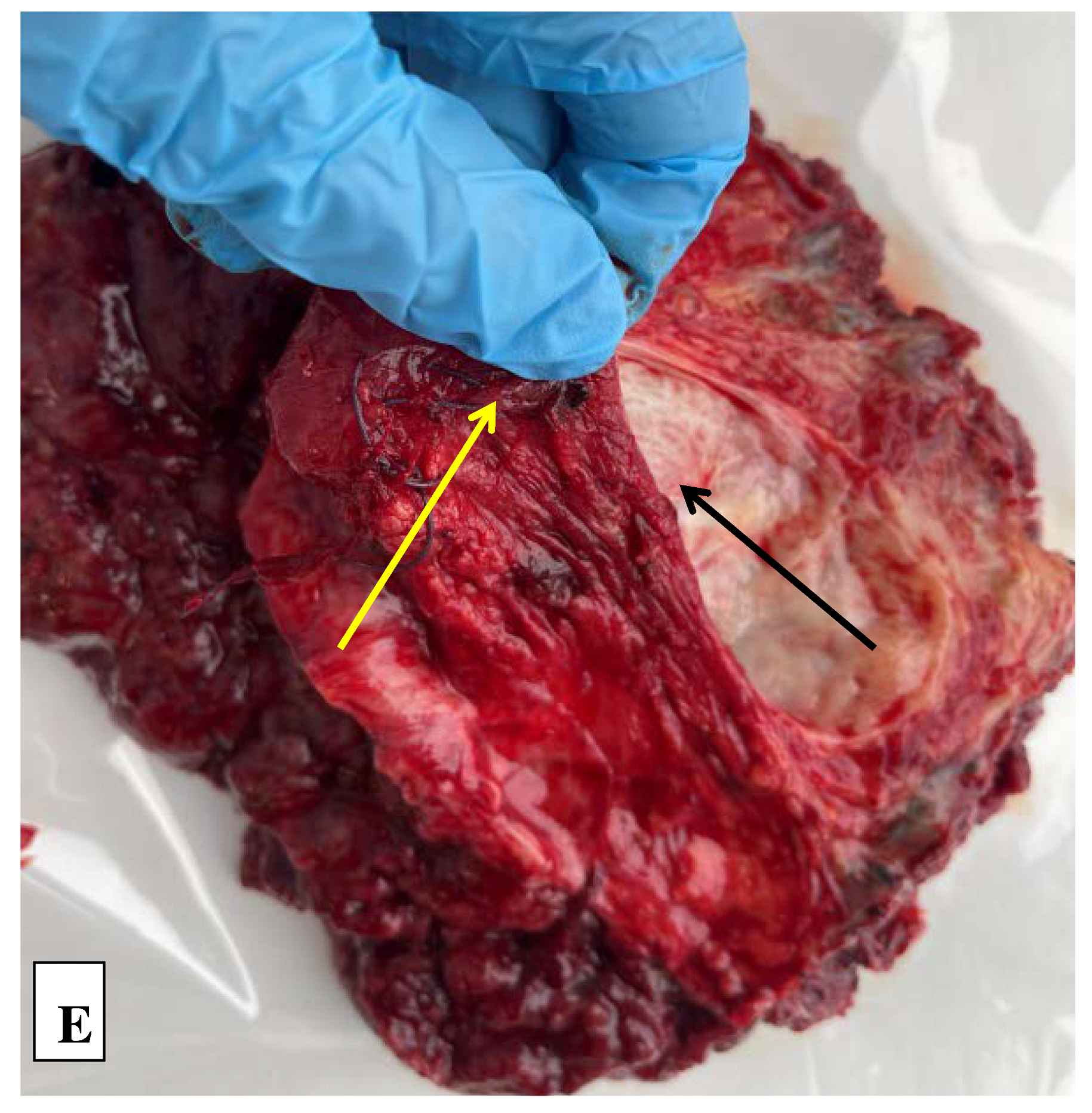
| Basic signs: | Availability | MAPI Scores - RADS |
|---|---|---|
| Local prolapse of the uterine wall («uterine hernia») | present | 2 |
| Thinning of the myometrium in the area where the placenta adjacent | present | 2 |
| MRI vascular lacuna visualization in the structure of the placenta | present | 2 |
| Vascular band MRI visualization in the structure of the placenta | present | 2 |
| Retroplacental hypointense “shadow” | present | 2 |
| Additional signs: | ||
| Varicose veins of the uterine wall and parametrium | Yes | 1 |
| Central/marginal placenta previa | Yes | 1 |
| Spread of the placenta beyond the walls of the uterus | Yes | 3 |
| Sum of points: | 15 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





