Submitted:
17 December 2023
Posted:
18 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
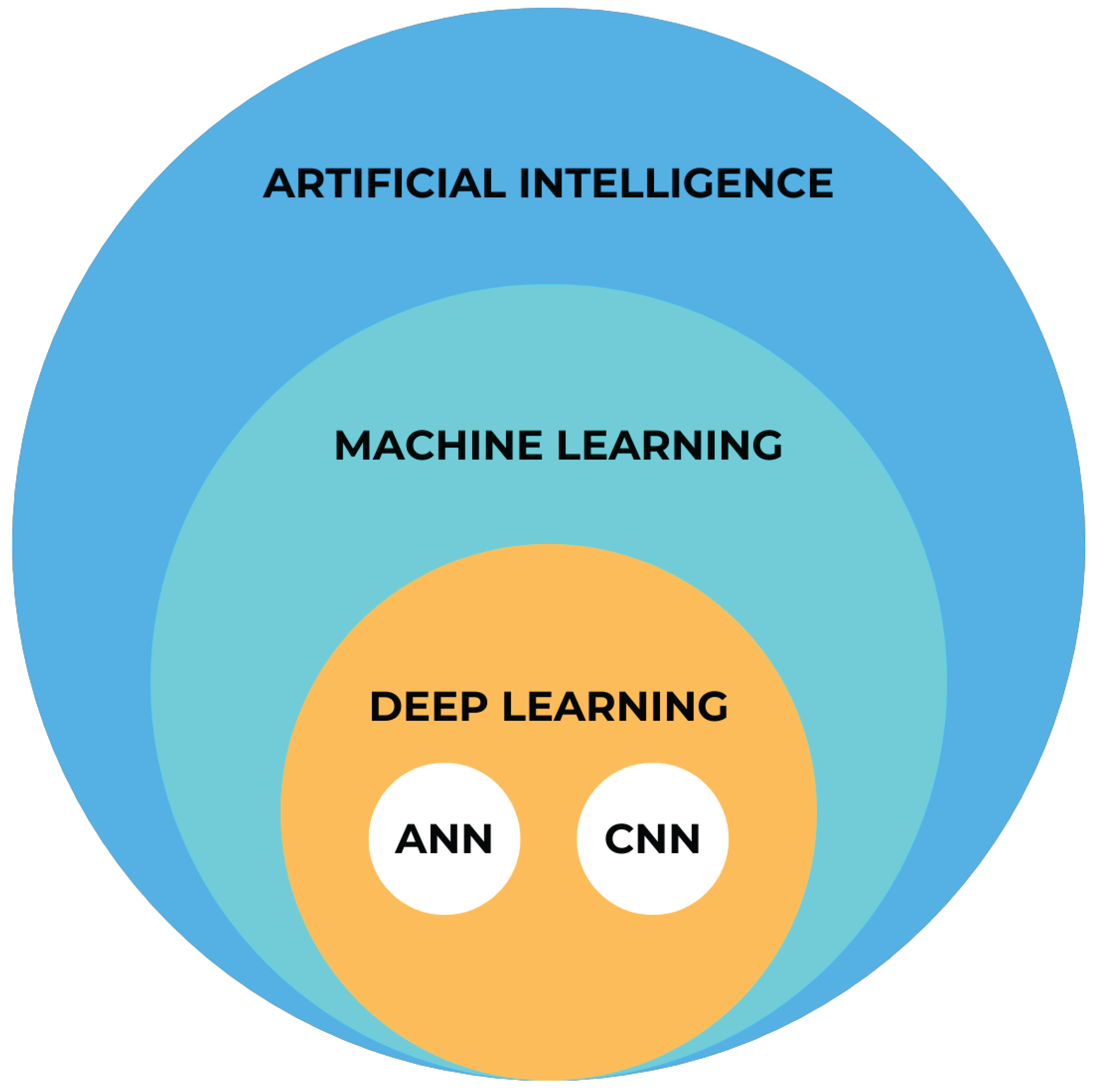
2. AI categories
2.1. Machine Learning
2.2. Deep Learning
3. AI applications in Orthodontics
3.1. Dental Diagnostics
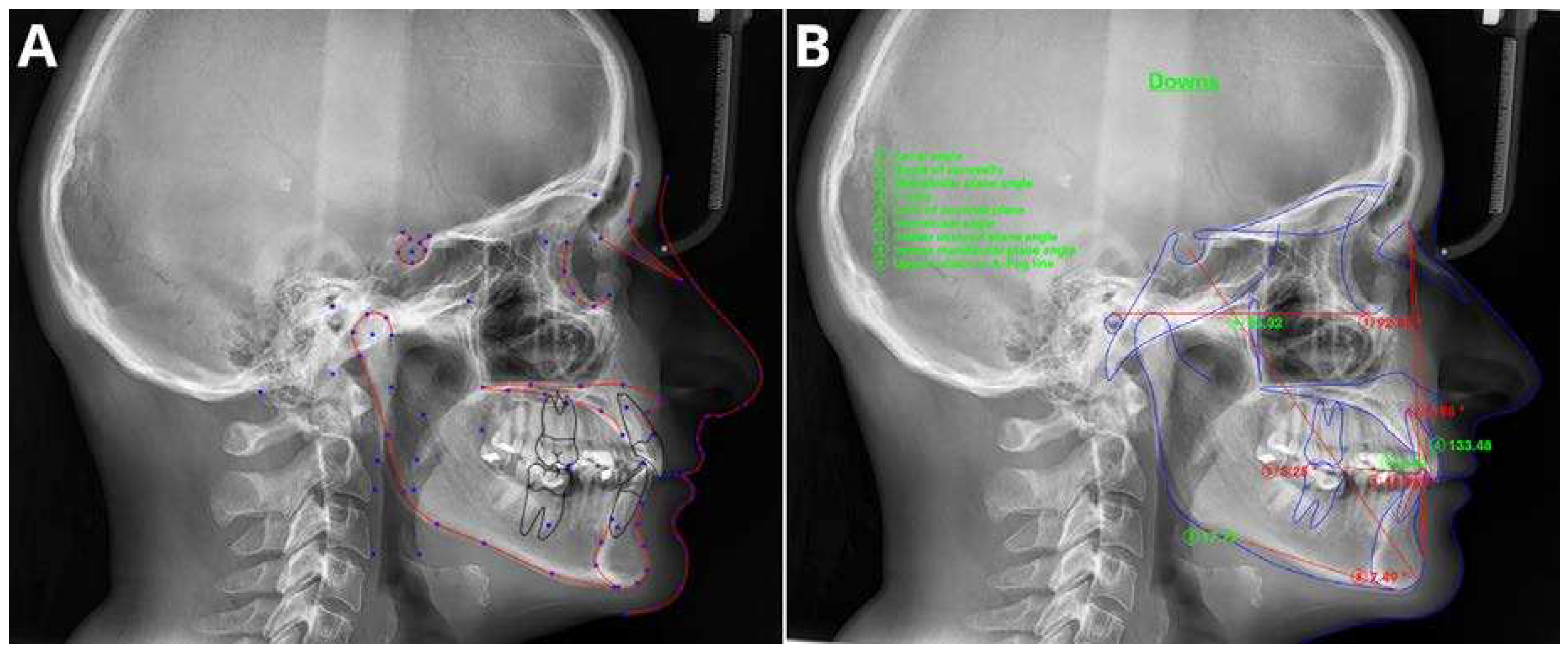
3.2. Cephalometric Analysis
3.3. Determination of Skeletal Age
3.4. TMJ Evaluation
3.5. Extraction Decision Making
4. Implementation Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCarthy, J.; Minsky, M.L.; Rochester, N.; Shannon, C.E. A Proposal for the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence. AI Mag 2006, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Haenlein, M.; Kaplan, A. A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence: On the Past, Present, and Future of Artificial Intelligence. Calif Manage Rev 2019, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Golla, T.; Dreher, M.; Krois, J. Convolutional Neural Networks for Dental Image Diagnostics: A Scoping Review. J Dent 2019, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-Level Classification of Skin Cancer with Deep Neural Networks. Nature 2017, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association 2016, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazurowski, M.A.; Buda, M.; Saha, A.; Bashir, M.R. Deep Learning in Radiology: An Overview of the Concepts and a Survey of the State of the Art with Focus on MRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2019, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, N.K.; Christensen, E.W.; Rula, E.Y.; Coombs, L.; Dreyer, K.; Wald, C.; Treml, C. Projected Growth in FDA-Approved Artificial Intelligence Products Given Venture Capital Funding. Journal of the American College of Radiology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pianykh, O.S.; Langs, G.; Dewey, M.; Enzmann, D.R.; Herold, C.J.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Brink, J.A. Continuous Learning AI in Radiology: Implementation Principles and Early Applications. Radiology 2020, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milam, M.E.; Koo, C.W. The Current Status and Future of FDA-Approved Artificial Intelligence Tools in Chest Radiology in the United States. Clin Radiol 2023, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giełczyk, A.; Marciniak, A.; Tarczewska, M.; Kloska, S.M.; Harmoza, A.; Serafin, Z.; Woźniak, M. A Novel Lightweight Approach to COVID-19 Diagnostics Based on Chest X-Ray Images. J Clin Med 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloska, A.; Tarczewska, M.; Giełczyk, A.; Kloska, S.M.; Michalski, A.; Serafin, Z.; Woźniak, M. Influence of Augmentation on the Performance of the Double ResNet-Based Model for Chest X-Ray Classification. Pol J Radiol 2023, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujima, N.; Kamagata, K.; Ueda, D.; Fujita, S.; Fushimi, Y.; Yanagawa, M.; Ito, R.; Tsuboyama, T.; Kawamura, M.; Nakaura, T.; et al. Current State of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Applications for Head and Neck MR Imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Ibaraki, M.; Nemoto, M.; Watabe, H.; Kimura, Y. A Review on AI in PET Imaging. Ann Nucl Med 2022, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jin, S.; Yan, Q.; Xu, H.; Luo, C.; Wei, L.; Zhao, W.; Hou, X.; Ma, W.; Xu, Z.; et al. AI-Assisted CT Imaging Analysis for COVID-19 Screening: Building and Deploying a Medical AI System. Appl Soft Comput 2021, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichu, Y.M.; Hansa, I.; Bichu, A.Y.; Premjani, P.; Flores-Mir, C.; Vaid, N.R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Orthodontics: A Scoping Review. Prog Orthod 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.; Haugeland, J. Artificial Intelligence: The Very Idea. Technol Cult 1987, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, W.B.; Patil, R.S.; Szolovits, P. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Where Do We Stand? N Engl J Med 1987, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.; Faber, C.; Faber, P. Artificial Intelligence in Orthodontics. APOS Trends in Orthodontics 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer, 2007; Volume 16. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep Learning for Chest Radiograph Diagnosis: A Retrospective Comparison of the CheXNeXt Algorithm to Practicing Radiologists. PLoS Med 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamkurthy, S.; Ghosh, R.; Tanamala, S.; Biviji, M.; Campeau, N.G.; Venugopal, V.K.; Mahajan, V.; Rao, P.; Warier, P. Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Critical Findings in Head CT Scans: A Retrospective Study. The Lancet 2018, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.C.; Mohajer, B.; Eng, J. External Validation of Deep Learning Algorithms for Radiologic Diagnosis: A Systematic Review. Radiol Artif Intell 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Phang, J.; Park, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zorin, M.; Jastrzebski, S.; Fevry, T.; Katsnelson, J.; Kim, E.; et al. Deep Neural Networks Improve Radiologists’ Performance in Breast Cancer Screening. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, W.; Hӓne, C.; Mukherjee, P.; Malik, J.; Yuh, E.L. Expert-Level Detection of Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage on Head Computed Tomography Using Deep Learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulten, W.; Pinckaers, H.; van Boven, H.; Vink, R.; de Bel, T.; van Ginneken, B.; van der Laak, J.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Litjens, G. Automated Deep-Learning System for Gleason Grading of Prostate Cancer Using Biopsies: A Diagnostic Study. Lancet Oncol 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, A.; Aerts, H.J.; Mak, R.H. Handcrafted versus Deep Learning Radiomics for Prediction of Cancer Therapy Response. Lancet Digit Health 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, B.; Doken, S.; Zhuang, T.; Wingerter, D.; Gidwani, M.; Mistry, N.; Ladic, L.; Kamen, A.; Abazeed, M.E. An Image-Based Deep Learning Framework for Individualising Radiotherapy Dose: A Retrospective Analysis of Outcome Prediction. Lancet Digit Health 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, C.J.; Drazen, J.M. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Clinical Medicine, 2023. New England Journal of Medicine 2023, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberghe, B.; Jacobs, R.; Bosmans, H. Modern Dental Imaging: A Review of the Current Technology and Clinical Applications in Dental Practice. Eur Radiol 2010, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drage, N. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) in General Dental Practice. Prim Dent J 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallichan, N.; Albadri, S.; Dixon, C.; Jorgenson, K. Trends in CBCT Current Practice within Three UK Paediatric Dental Departments. European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanović, A.; Oosterkamp, B.C.M.; Lamberts, A.A.; Schols, J.G.J.H. Orthodontic Radiology: Development of a Clinical Practice Guideline. Radiologia Medica 2021, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Grauwe, A.; Ayaz, I.; Shujaat, S.; Dimitrov, S.; Gbadegbegnon, L.; Vannet, B. Vande; Jacobs, R. CBCT in Orthodontics: A Systematic Review on Justification of CBCT in a Paediatric Population Prior to Orthodontic Treatment. Eur J Orthod 2019, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajem, S.; Brogårdh-Roth, S.; Nilsson, M.; Hellén-Halme, K. CBCT of Swedish Children and Adolescents at an Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology Department. A Survey of Requests and Indications. Acta Odontol Scand 2020, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, K.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Ezhov, M.; Kravtsov, A.; Özyürek, T. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence for Detecting Periapical Pathosis on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans. Int Endod J 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, J.; Jaber, M.; Rifai, I.; Mozdziak, P.; Kempisty, B.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M. Diagnostic Test Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Periapical Periodontitis on Two-Dimensional Radiographs: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Medicina (Lithuania) 2023, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, K.; Shamshiev, M.; Ezhov, M.; Plaksin, A.; Kurbanova, A.; Ünsal, G.; Gusarev, M.; Golitsyna, M.; Aksoy, S.; Mısırlı, M.; et al. AI-Based Automatic Segmentation of Craniomaxillofacial Anatomy from CBCT Scans for Automatic Detection of Pharyngeal Airway Evaluations in OSA Patients. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujanovic, T.; Jagtap, R. Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence for Automatic Tooth and Periapical Pathosis Detection on Panoramic Radiography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2023, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignardello-Petersen, R. Artificial Intelligence System Seems to Be Able to Detect a High Proportion of Periapical Lesions in Cone-Beam Computed Tomographic Images. Journal of the American Dental Association 2020, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadrożny, Ł.; Regulski, P.; Brus-Sawczuk, K.; Czajkowska, M.; Parkanyi, L.; Ganz, S.; Mijiritsky, E. Artificial Intelligence Application in Assessment of Panoramic Radiographs. Diagnostics 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhov, M.; Gusarev, M.; Golitsyna, M.; Yates, J.M.; Kushnerev, E.; Tamimi, D.; Aksoy, S.; Shumilov, E.; Sanders, A.; Orhan, K. Clinically Applicable Artificial Intelligence System for Dental Diagnosis with CBCT. Sci Rep 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, R.; Giordano, D.; Maiorana, F.; Spampinato, C. Automatic Cephalometric Analysis: A Systematic Review. Angle Orthodontist 2008, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chen, S.K.; Yao, J.C.C.; Chang, H.F. The Effects of Differences in Landmark Identification on the Cephalometric Measurements in Traditional versus Digitized Cephalometry. Angle Orthodontist 2004, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Dias Da Silveira, H.L.; Dias Silveira, H.E. Reproducibility of Cephalometric Measurements Made by Three Radiology Clinics. Angle Orthodontist 2006, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, H.-W.; Moon, J.-H.; Kim, M.-G.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.-J. Evaluation of Automated Cephalometric Analysis Based on the Latest Deep Learning Method. Angle Orthod 2021, 91, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.W.; Park, J.H.; Moon, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. Automated Identification of Cephalometric Landmarks: Part 2-Might It Be Better than Human? Angle Orthodontist 2020, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.J.; Yang, B.E.; Park, I.Y.; Yi, S.; On, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kang, S.H.; Byun, S.H. Effectiveness of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography-Generated Cephalograms Using Artificial Intelligence Cephalometric Analysis. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, D.J.; Sinclair, P.M.; Coggins, J.M. Automatic Computerized Radiographic Identification of Cephalometric Landmarks. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1998, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobratulin, K.; Gaidel, A.; Kapishnikov, A.; Ivleva, A.; Aupova, I.; Zelter, P. The Efficiency of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detecting Anatomical Reference Points on Radiological Images of the Head Profile. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of ITNT 2020 - 6th IEEE International Conference on Information Technology and Nanotechnology; 2020.
- Park, J.H.; Hwang, H.W.; Moon, J.H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.J. Automated Identification of Cephalometric Landmarks: Part 1—Comparisons between the Latest Deep-Learning Methods YOLOV3 and SSD. Angle Orthodontist 2019, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, C.; Yamamoto, T.; Yagic, M.; Takadad, K. Automatic Recognition of Anatomic Features on Cephalograms of Preadolescent Children. Angle Orthodontist 2010, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, C.; Yagi, M.; Takada, K. Automated Cephalometry: System Performance Reliability Using Landmark-Dependent Criteria. Angle Orthodontist 2009, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Shim, E.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, U.; Kim, Y. Web-Based Fully Automated Cephalometric Analysis by Deep Learning. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2020, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, V.; Alcañiz, M.; Juan, M.C.; Monserrat, C.; Knoll, C. Automatic Localization of Cephalometric Landmarks. J Biomed Inform 2001, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Zeng, W.; He, T.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, W. Automatic Localization of Cephalometric Landmarks Based on Convolutional Neural Network. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2022, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, S.; Alcañiz, M. An Approach for the Automatic Cephalometric Landmark Detection Using Mathematical Morphology and Active Appearance Models. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); 2006; Vol. 4190 LNCS-I.
- Vuinić, P.; Trpovski, Z.; Ćepan, I. Automatic Landmarking of Cephalograms Using Active Appearance Models. Eur J Orthod 2010, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, S.; Sotsuka, Y.; Kawai, K.; Ishise, H.; Kakibuchi, M. Personal Computer-Based Cephalometric Landmark Detection with Deep Learning, Using Cephalograms on the Internet. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, F.; Stellzig-Eisenhauer, A.; Zeman, F.; Boldt, J. Artificial Intelligence in Orthodontics: Evaluation of a Fully Automated Cephalometric Analysis Using a Customized Convolutional Neural Network. Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics 2020, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Cho, S.R.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, J. Automated Skeletal Classification with Lateral Cephalometry Based on Artificial Intelligence. J Dent Res 2020, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, M.C.; Abe, J.M.; Ortega, N.R.S.; Del Santo, M. Paraconsistent Artificial Neural Network as Auxiliary in Cephalometric Diagnosis. Artif Organs 2010, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yu, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, J. Automated Cephalometric Landmark Detection with Confidence Regions Using Bayesian Convolutional Neural Networks. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S. Locating Cephalometric Landmarks with Multi-Phase Deep Learning. Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, J.M.; Yang, C.Y.; Hans, M.G. Clinical Application of Three-Dimensional Craniofacial Imaging in Orthodontics. Journal of Medical Sciences 2005, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierczak, N.; Kazimierczak, W.; Serafin, Z.; Nowicki, P.; Lemanowicz, A.; Nadolska, K.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. Correlation Analysis of Nasal Septum Deviation and Results of AI-Driven Automated 3D Cephalometric Analysis. J Clin Med 2023, 12, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ed-Dhahraouy, M.; Riri, H.; Ezzahmouly, M.; Bourzgui, F.; El Moutaoukkil, A. A New Methodology for Automatic Detection of Reference Points in 3D Cephalometry: A Pilot Study. Int Orthod 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Sardana, V.; Balachandran, R.; Sardana, H.K. A Knowledge-Based Algorithm for Automatic Detection of Cephalometric Landmarks on CBCT Images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Kobayashi, E.; Fan, B.; Nakagawa, K.; Sakuma, I.; Masamune, K.; Suenaga, H. Automatic 3D Landmarking Model Using Patch-Based Deep Neural Networks for CT Image of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. International Journal of Medical Robotics and Computer Assisted Surgery 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montúfar, J.; Romero, M.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J. Hybrid Approach for Automatic Cephalometric Landmark Annotation on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Volumes. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2018, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Kharbanda, O.P.; Sardana, V.; Balachandran, R.; Sardana, H.K. Accuracy of 3D Cephalometric Measurements Based on an Automatic Knowledge-Based Landmark Detection Algorithm. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Liu, Y.; Oh, S.H.; Ahn, H.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Nelson, G. Evaluation of a Multi-Stage Convolutional Neural Network-Based Fully Automated Landmark Identification System Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomographysynthesized Posteroanterior Cephalometric Images. Korean J Orthod 2021, 51, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraev, A.A.; Tsai, P.; Kibardin, I.; Oborotistov, N.; Shirayeva, T.; Ivanov, S.; Ivanov, S.; Guseynov, N.; Aleshina, O.; Bosykh, Y.; et al. Frontal Cephalometric Landmarking: Humans vs Artificial Neural Networks. Int J Comput Dent 2020, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Zhang, K.; Yu, C.; Li, H.; Cao, D.; Shu, H.; Liu, L.; Yan, B. Evaluating the Accuracy of Automated Cephalometric Analysis Based on Artificial Intelligence. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccetti, T.; Franchi, L.; McNamara, J.A. The Cervical Vertebral Maturation (CVM) Method for the Assessment of Optimal Treatment Timing in Dentofacial Orthopedics. Semin Orthod 2005, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.A.; Bookstein, F.L.; Shaughnessy, T.G. Skeletal and Dental Changes Following Functional Regulator Therapy on Class II Patients. Am J Orthod 1985, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Mir, C.; Nebbe, B.; Major, P.W. Use of Skeletal Maturation Based on Hand-Wrist Radiographic Analysis as a Predictor of Facial Growth: A Systematic Review. Angle Orthodontist 2004, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Khanagar, S.B.; Al-Ehaideb, A.; Vishwanathaiah, S.; Maganur, P.C.; Patil, S.; Naik, S.; Baeshen, H.A.; Sarode, S.S. Scope and Performance of Artificial Intelligence Technology in Orthodontic Diagnosis, Treatment Planning, and Clinical Decision-Making - A Systematic Review. J Dent Sci 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Song, I.S.; Ahn, B.; Choo, J.; Lee, D.Y. Prediction of Hand-Wrist Maturation Stages Based on Cervical Vertebrae Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Orthod Craniofac Res 2021, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, T.; Sari, Z.; Ramoglu, S.I.; Basciftci, F.A. Relationships between Dental and Skeletal Maturity in Turkish Subjects. Angle Orthodontist 2004, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourieh, A.; Khan, H.; Mheissen, S.; Assali, M.; Alam, M.K. The Correlation between Dental Stages and Skeletal Maturity Stages. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.M.; Park, J.H. Correlation of Dental Maturity with Skeletal Maturity from Radiographic Assessment. Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 2012, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemraj, A.; Wojtaszek-Słomińska, A.; Racka-Pilszak, B. Is the Cervical Vertebral Maturation (CVM) Method Effective Enough to Replace the Hand-Wrist Maturation (HWM) Method in Determining Skeletal Maturation?—A Systematic Review. Eur J Radiol 2018, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Hermann, A.L.; Ventre, J.; Ducarouge, A.; Pourchot, A.; Marty, V.; Regnard, N.E.; Guermazi, A. High Performance for Bone Age Estimation with an Artificial Intelligence Solution. Diagn Interv Imaging 2023, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, D.K.; Khandwala, N.B.; Long, J.; Fefferman, N.R.; Lala, S.V.; Strubel, N.A.; Milla, S.S.; Filice, R.W.; Sharp, S.E.; Towbin, A.J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Algorithm Improves Radiologist Performance in Skeletal Age Assessment: A Prospective Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Radiology 2021, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasya, H.; Cesur, E.; Yıldırım, D.; Orhan, K. Validation of Cervical Vertebral Maturation Stages: Artificial Intelligence vs Human Observer Visual Analysis. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2020, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, H.; Pu, L.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; You, M.; Yang, Z.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Development of an Artificial Intelligence System for the Automatic Evaluation of Cervical Vertebral Maturation Status. Diagnostics 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.; Palatinus, S.; Padala, S.; Alshehri, A.; Awadh, W.; Bhandi, S.; Thomas, J.; Patil, S. Neural Networks for Classification of Cervical Vertebrae Maturation: A Systematic Review. Angle Orthod 2022, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.T.; Sin, Ç.; Akkaya, N.; Vahdettin, L. Artificial Intelligence-Based Algorithm for Cervical Vertebrae Maturation Stage Assessment. Orthod Craniofac Res 2023, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.E.; Rayan, J.C.; Annapragada, A.V.; Mahmood, N.F.; Scheslinger, A.E.; Zhang, W.; Kan, J.H. Bone Age Determination Using Only the Index Finger: A Novel Approach Using a Convolutional Neural Network Compared with Human Radiologists. Pediatr Radiol 2020, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amasya, H.; Yildirim, D.; Aydogan, T.; Kemaloglu, N.; Orhan, K. Cervical Vertebral Maturation Assessment on Lateral Cephalometric Radiographs Using Artificial Intelligence: Comparison of Machine Learning Classifier Models. Dentomaxillofacial Radiology 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S.; Nath, B.; Chaudhari, P.K.; Vichare, S. Cervical Vertebral Maturation Assessment Using Various Machine Learning Techniques on Lateral Cephalogram: A Systematic Literature Review. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.; Hwang, J.; Jeong, T.; Shin, J. Comparison of Deep Learning Models for Cervical Vertebral Maturation Stage Classification on Lateral Cephalometric Radiographs. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, H.; Acilar, A.M.; İzgi, M.S. Usage and Comparison of Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Determination of Growth and Development by Cervical Vertebrae Stages in Orthodontics. Prog Orthod 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Rahimi, H.; Motamadian, S.R.; Nadimi, M.; Hassanzadeh-Samani, S.; Minabi, M.A.S.; Mahmoudinia, E.; Lee, V.Y.; Rohban, M.H. Deep Learning for the Classification of Cervical Maturation Degree and Pubertal Growth Spurts: A Pilot Study. Korean J Orthod 2022, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajmir, S.H.; Lee, H.; Shailam, R.; Gale, H.I.; Nguyen, J.C.; Westra, S.J.; Lim, R.; Yune, S.; Gee, M.S.; Do, S. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Interpretation of Bone Age Radiographs Improves Accuracy and Decreases Variability. Skeletal Radiol 2019, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhang, J.N.; Gan, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.H. Current Understanding of Pathogenesis and Treatment of TMJ Osteoarthritis. J Dent Res 2015, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derwich, M.; Mitus-Kenig, M.; Pawlowska, E. Interdisciplinary Approach to the Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis—Review of the Literature. Medicina (Lithuania) 2020, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crincoli, V.; Cortelazzi, R.; De Biase, C.; Cazzolla, A.P.; Campobasso, A.; Dioguardi, M.; Piancino, M.G.; Mattia, L.; Di Comite, M. The Loss of Symmetry in Unilateral Bony Syngnathia: Case Report and Literature Review. Symmetry (Basel) 2022, 14, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, N.N.; Mathai, P.; Aggarwal, N. Facial Asymmetry. In Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery for the Clinician; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1549–1576. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, E.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.K. Artificial Intelligence in Detecting Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis on Orthopantomogram. Sci Rep 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Dumast, P.; Mirabel, C.; Cevidanes, L.; Ruellas, A.; Yatabe, M.; Ioshida, M.; Ribera, N.T.; Michoud, L.; Gomes, L.; Huang, C.; et al. A Web-Based System for Neural Network Based Classification in Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 2018, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, J.; de Oliveira Ruellas, A.C.; Gonçalves, J.R.; Paniagua, B.; Prieto, J.C.; Styner, M.; Li, T.; Zhu, H.; Sugai, J.; Giannobile, W.; et al. Osteoarthritis of the Temporomandibular Joint Can Be Diagnosed Earlier Using Biomarkers and Machine Learning. Sci Rep 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukri, B.; Prieto, J.C.; Ruellas, A.; Yatabe, M.; Sugai, J.; Styner, M.; Zhu, H.; Huang, C.; Paniagua, B.; Aronovich, S.; et al. Minimally Invasive Approach for Diagnosing TMJ Osteoarthritis. J Dent Res 2019, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Mine, Y.; Yoshimi, Y.; Takeda, S.; Tanaka, A.; Onishi, A.; Peng, T.Y.; Nakamoto, T.; Nagasaki, T.; Kakimoto, N.; et al. Automated Segmentation of Articular Disc of the Temporomandibular Joint on Magnetic Resonance Images Using Deep Learning. Sci Rep 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, M.H.; Mageet, A.O. Extraction Planning in Orthodontics. Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, S. Extractions, Retention and Stability: The Search for Orthodontic Truth. Eur J Orthod 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Real, A.; Del Real, O.; Sardina, S.; Oyonarte, R. Use of Automated Artificial Intelligence to Predict the Need for Orthodontic Extractions. Korean J Orthod 2022, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribarevski, R.; Vig, P.; Dryland Vig, K.; Weyant, R.; O’Brien, K. Consistency of Orthodontic Extraction Decisions. Eur J Orthod 1996, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffit, W.R. Forty-Year Review of Extraction Frequencies at a University Orthodontic Clinic. Angle Orthodontist 1994, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.H.; Guez, C.; Lin, F.C.; Proffit, W.R.; Ko, C.C. Extraction Frequencies at a University Orthodontic Clinic in the 21st Century: Demographic and Diagnostic Factors Affecting the Likelihood of Extraction. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2017, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrard, A.S.; Tepedino, M.; Cattaneo, P.M.; Cornelis, M.A. Which Factors Influence Orthodontists in Their Decision to Extract? A Questionnaire Survey. J Clin Exp Dent 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, D.W.; Thakkar, D. Consistency of Orthodontists’ Clinical Decisions: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Theory Development. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2022, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, N.; Heaton, L.J.; Bayirli, B.; Turpin, D.L.; Khosravi, R.; Bollen, A.M. Influence of Clinicians’ Experience and Gender on Extraction Decision in Orthodontics. Angle Orthodontist 2017, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumrind, S.; Korn, E.L.; Boyd, R.L.; Maxwell, R. The Decision to Extract: Part 1--Interclinician Agreement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 1996, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantonis, D.; Anthopoulou, C.; Makou, M. Extraction Decision and Identification of Treatment Predictors in Class I Malocclusions. Prog Orthod 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, K.; de Freitas Silva, B.S.; Yamamoto-Silva, F.P.; Valladares-Neto, J.; Silva, M.A.G.; Cevidanes, L.H.S.; de Luca Canto, G.; Massignan, C. Accuracy of Artificial Intelligence for Tooth Extraction Decision-Making in Orthodontics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Oral Investig 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, Z. Machine Learning in Orthodontics: Challenges and Perspectives. Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2021, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H. Il; Jung, S.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lim, W.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Yang, I.H.; Kim, T.W. Artificial Intelligent Model with Neural Network Machine Learning for the Diagnosis of Orthognathic Surgery. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, K. Artificial Intelligence Expert Systems with Neural Network Machine Learning May Assist Decision-Making for Extractions in Orthodontic Treatment Planning. Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.K.; Kim, T.W. New Approach for the Diagnosis of Extractions with Neural Network Machine Learning. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2016, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kong, D.; Tang, T.; Su, D.; Yang, P.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Orthodontic Treatment Planning Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Sci Rep 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, A. Artificial Neural Network Modeling for Deciding If Extractions Are Necessary Prior to Orthodontic Treatment. Angle Orthodontist 2010, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; de Rooij, M.; Schalekamp, S.; van Ginneken, B.; Rutten, M.J.C.M. How Does Artificial Intelligence in Radiology Improve Efficiency and Health Outcomes? Pediatr Radiol 2022, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolle, K.M.; Tansley, D.S.W.; Hey, A.J.G. The Fourth Paradigm: Data-Intensive Scientific Discovery. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE; 2011; Vol. 99.
- Dania, D.; Walter, F.W.; Matthew, P.L.; Tarik, A.; Nina, K.; Bibb, A.; Christopher, J.R.; Bernardo, C.B.; Kimberly, D.; James, A.B.; et al. Implementation of Clinical Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: Who Decides and How? Radiology 2022, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet AI in Medicine: Creating a Safe and Equitable Future. The Lancet 2023, 402.
- van Leeuwen, K.G.; Schalekamp, S.; Rutten, M.J.C.M.; van Ginneken, B.; de Rooij, M. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology: 100 Commercially Available Products and Their Scientific Evidence. Eur Radiol 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




