Submitted:
07 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- What is the volume and scope of the research on AI use in pediatrics?
- How is research spread geographically, focusing on developed and less-developed countries?
- What are the more prolific information titles/journals that inform the scientific community about research, and what are the sources through which the authors have the greatest opportunity to inform the community about the results of their research?
- Which founding bodies are more prolific in sponsoring the research?
- What are the most prolific research themes?
- What are the most used AI algorithms and approaches?
- What are the most targeted pediatric diagnoses?
- What are the most used health applications in pediatrics?
2. Methods
- Harvest research publications on the topic of interest from the selected bibliographic database using an appropriate search string representing the research question(s) to be answered through knowledge synthesis.
- Perform descriptive bibliometric analysis using software built-in functionality.
- Use author keywords as meaningful units of information and execute bibliometric mapping using selected bibliometric software; in our case, VOSViewer [6]. Next using inductive content analysis, analyze the node size, links, and proximity between meaningful units in individual clusters to form categories and identify themes.
- Use author keywords as meaningful units of information and use VOSViewer to analyse their frequencies. Perform deductive content analysis with preconceived categories, namely Machine learning algorithm, AI approach, Pediatric diagnosis and Application in pediatrics.
- Use country names as meaningful units of information and execute time overlay bibliometric mapping using VOSViewer. Next, analyze the overlay colour, node size and links between countries to identify country cooperation and the average age of publications.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Characteristics of the Body of Research
3.2. Content Analysis
3.2.1. Inductive Content Analysis
3.2.2. Deductive Content Analysis
3.3. Research Co-Operation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugiyama, K.; Hasegawa, Y. COMPUTER ASSISTED MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS SYSTEM FOR INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM.; 1984; Vol. 22, pp. 942–943.
- Kokol, P.; Kokol, M.; Zagoranski, S. Machine Learning on Small Size Samples: A Synthetic Knowledge Synthesis. Science Progress 2022, 105, 00368504211029777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, A. Statistical Bibliography or Bibliometrics? Journal of Documentation 1969, 25, 348–349. [Google Scholar]
- Bellis, N.D. Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis: From the Science Citation Index to Cybermetrics; Scarecrow Press: Lanham, Md, 2009; ISBN 978-0-8108-6713-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, R. An Introduction to Bibliometrics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2018; ISBN 978-0-08-102150-7. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyngäs, H. Qualitative Research and Content Analysis. In The Application of Content Analysis in Nursing Science Research; Kyngäs, H., Mikkonen, K., Kääriäinen, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 3–11. ISBN 978-3-030-30199-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. Paging Dr. Watson: IBM’s Watson Supercomputer Now Being Used in Healthcare. Journal of AHIMA 2014, 85, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, J.X.; Hu, Q.V. Deep Learning for Healthcare Decision Making with EMRs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM); November 2014; pp. 556–559. [Google Scholar]
- List of Healthiest Kids from These Countries in the World 2023. Available online: https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/which-countries-have-the-healthiest-kids-1698217870-1 (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Kokol, P.; Železnik, D.; Završnik, J.; Blažun Vošner, H. Nursing Research Literature Production in Terms of the Scope of Country and Health Determinants: A Bibliometric Study. Journal of Nursing Scholarship 2019, 51, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, S.L.; Trout, A.T.; Somasundaram, E.; Anton, C.G.; Li, Y.; Dillman, J.R. Improving Image Quality and Reducing Radiation Dose for Pediatric CT by Using Deep Learning Reconstruction. Radiology 2021, 298, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-R.J.; Baratto, L.; Hawk, K.E.; Theruvath, A.J.; Pribnow, A.; Thakor, A.S.; Gatidis, S.; Lu, R.; Gummidipundi, S.E.; Garcia-Diaz, J.; et al. Artificial Intelligence Enables Whole-Body Positron Emission Tomography Scans with Minimal Radiation Exposure. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2021, 48, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koetzier, L.R.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Szczykutowicz, T.P.; van der Werf, N.R.; Wang, A.S.; Sandfort, V.; van der Molen, A.J.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Deep Learning Image Reconstruction for CT: Technical Principles and Clinical Prospects. Radiology 2023, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupuis, M.; Delbos, L.; Veil, R.; Adamsbaum, C. External Validation of a Commercially Available Deep Learning Algorithm for Fracture Detection in Children. Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging 2022, 103, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Kim, D.D.; Patel, J.B.; Zeng, X.; Huang, J.; Chang, K.; Xun, X.; Zhang, C.; Sollee, J.; Wu, J.; et al. Deep Learning-Based Automatic Tumor Burden Assessment of Pediatric High-Grade Gliomas, Medulloblastomas, and Other Leptomeningeal Seeding Tumors. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Zia, T.; Tariq, A. Analyzing Transfer Learning of Vision Transformers for Interpreting Chest Radiography. Journal of Digital Imaging 2022, 35, 1445–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, I.; Hamza, A.B. Ridge Regression Neural Network for Pediatric Bone Age Assessment. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2021, 80, 30461–30478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y. Self-Supervised Attention Mechanism for Pediatric Bone Age Assessment with Efficient Weak Annotation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 2021, 40, 2685–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, C.; Gedik, M.A.; Kaya, Y. Age Estimation from Left-Hand Radiographs with Deep Learning Methods. Traitement du Signal 2021, 38, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Khaparde, A. Faster Region-Convolutional Neural Network Oriented Feature Learning with Optimal Trained Recurrent Neural Network for Bone Age Assessment for Pediatrics. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2022, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Ghaffari, H.; Sadighi, N.; Reiazi, R. Automated Detection of Pneumonia Cases Using Deep Transfer Learning with Paediatric Chest X-Ray Images. British Journal of Radiology 2021, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, V.; Junior, G.B.; de Paiva, A.C.; Silva, A.C.; Gattass, M. Bayesian Convolutional Neural Network Estimation for Pediatric Pneumonia Detection and Diagnosis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2021, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Li, W.; Feng, Q.; Han, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J. Ultrasound Image Intelligent Diagnosis in Community-Acquired Pneumonia of Children Using Convolutional Neural Network-Based Transfer Learning. Frontiers in Pediatrics 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Inai, K.; Sugiyama, H.; Muragaki, Y. Diagnosing Atrial Septal Defect from Electrocardiogram with Deep Learning. Pediatric Cardiology 2021, 42, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Berhane, H.; Scott, M.B.; Englund, E.K.; Schäfer, M.; Fonseca, B.; Berthusen, A.; Robinson, J.D.; Rigsby, C.K.; Browne, L.P.; et al. Segmentation of the Aorta and Pulmonary Arteries Based on 4D Flow MRI in the Pediatric Setting Using Fully Automated Multi-Site, Multi-Vendor, and Multi-Label Dense U-Net. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2022, 55, 1666–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L.A.; Feng, F.; Iqbal, M.; Fu, Y.; Sanyahumbi, A.; Hao, S.; McElhinney, D.B.; Ling, X.B.; Sable, C.; Luo, J. Machine Learning for Pediatric Echocardiographic Mitral Regurgitation Detection. Journal of the American Society of Echocardiography 2023, 36, 96–104.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J. Pediatric Mental and Behavioral Health in the Period of Quarantine and Social Distancing with COVID-19. JMIR Pediatrics and Parenting 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcinkevics, R.; Reis Wolfertstetter, P.; Wellmann, S.; Knorr, C.; Vogt, J.E. Using Machine Learning to Predict the Diagnosis, Management and Severity of Pediatric Appendicitis. Frontiers in Pediatrics 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiñeira, D.; Schlosser, K.R.; Geva, A.; Rahmani, A.R.; Fiore, G.; Walsh, B.K.; Smallwood, C.D.; Arnold, J.H.; Santillana, M. Adding Continuous Vital Sign Information to Static Clinical Data Improves the Prediction of Length of Stay after Intubation: A Data-Driven Machine Learning Approach. Respiratory Care 2020, 65, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roquette, B.P.; Nagano, H.; Marujo, E.C.; Maiorano, A.C. Prediction of Admission in Pediatric Emergency Department with Deep Neural Networks and Triage Textual Data. Neural Networks 2020, 126, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Nagaraj, S.; Mashouri, P.; Drysdale, E.; Fischer, J.; Goldenberg, A.; Brudno, M. Assessment of Machine Learning-Based Medical Directives to Expedite Care in Pediatric Emergency Medicine. JAMA Network Open 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabryszewski, S.J.; Chang, X.; Dudley, J.W.; Mentch, F.; March, M.; Holmes, J.H.; Moore, J.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Hakonarson, H.; Hill, D.A. Unsupervised Modeling and Genome-Wide Association Identify Novel Features of Allergic March Trajectories. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2021, 147, 677–685.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeddi, Z.; Gryech, I.; Ghogho, M.; Hammoumi, M.E.L.; Mahraoui, C. Machine Learning for Predicting the Risk for Childhood Asthma Using Prenatal, Perinatal, Postnatal and Environmental Factors. Healthcare (Switzerland) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrulloh, Y.; Abeyratne, U.; Swarnkar, V.; Triasih, R. Cough Sound Analysis for Pneumonia and Asthma Classification in Pediatric Population.; 2015; Vol. 2015-October, pp. 127–131.
- Rashid, A.; Anwary, A.R.; Al-Obeidat, F.; Brierley, J.; Uddin, M.; Alkhzaimi, H.; Sarpal, A.; Toufiq, M.; Malik, Z.A.; Kadwa, R.; et al. Application of a Gene Modular Approach for Clinical Phenotype Genotype Association and Sepsis Prediction Using Machine Learning in Meningococcal Sepsis. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked 2023, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcelon, N.; Burgun, A.; Salomon, R.; Neuraz, A. Electronic Health Records for the Diagnosis of Rare Diseases. Kidney International 2020, 97, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenarejo, G. Machine Learning Models to Predict Childhood and Adolescent Obesity: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanbar, L.J.; Wissel, B.; Ni, Y.; Pajor, N.; Glauser, T.; Pestian, J.; Dexheimer, J.W. Implementation of Machine Learning Pipelines for Clinical Practice: Development and Validation Study. JMIR Medical Informatics 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanera, C.; Baldi, I.; Francavilla, A.; Barbieri, E.; Tramontan, L.; Scamarcia, A.; Cantarutti, L.; Giaquinto, C.; Gregori, D. A Deep Learning Approach to Estimate the Incidence of Infectious Disease Cases for Routinely Collected Ambulatory Records: The Example of Varicella-Zoster. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chafjiri, F.M.A.; Reece, L.; Voke, L.; Landschaft, A.; Clark, J.; Kimia, A.A.; Loddenkemper, T. Natural Language Processing for Identification of Refractory Status Epilepticus in Children. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 3227–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Major, A.; Cox, S.M.; Volchenboum, S.L. Using Big Data in Pediatric Oncology: Current Applications and Future Directions. Seminars in Oncology 2020, 47, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenberg, K.P.S.; Looze, E.J.; Molenaar, J.J. The Landscape of Pediatric Precision Oncology: Program Design, Actionable Alterations, and Clinical Trial Development. Cancers 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawahar, M.; H, S.; L, J.A.; Gandomi, A.H. ALNett: A Cluster Layer Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Classification. Computers in Biology and Medicine 2022, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.; Malviya, R.; Dahiya, S. Risk Assessment in the Field of Oncology Using Big Data. In Big Data in Oncology: Impact, Challenges, and Risk Assessment; 2023; pp. 355–409. ISBN 978-87-7022-812-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Ruan, X.; Deng, K.; Zhang, J.; Zou, D.; He, X.; Li, F.; Bin, G.; Zeng, H.; et al. Voxel-Based Morphometry Analysis and Machine Learning Based Classification in Pediatric Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Hippocampal Sclerosis. Brain Imaging and Behavior 2020, 14, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palraj, P.; Siddan, G. Deep Learning Algorithm for Classification of Cerebral Palsy from Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Classification of Cerebral Palsy from Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2021, 12, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethy, P.K.; Panigrahi, M.; Vijayakumar, K.; Behera, S.K. Machine Learning Based Classification of EEG Signal for Detection of Child Epileptic Seizure without Snipping. International Journal of Speech Technology 2023, 26, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yuan, Z.; Wu, D.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Hu, W. Novel Seizure Detection Algorithm Based on Multi-Dimension Feature Selection. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Renna, F.; Costa, P.D.; Nogueira, M.; Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, C.; Jorge, A.; Mattos, S.; Hatem, T.; Tavares, T.; et al. The CirCor DigiScope Dataset: From Murmur Detection to Murmur Classification. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 2022, 26, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struyf, T.; Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Spijker, R.; Hooft, L.; Emperador, D.; Domen, J.; et al. Signs and Symptoms to Determine If a Patient Presenting in Primary Care or Hospital Outpatient Settings Has COVID-19. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Katkar, G.D.; Shimizu, C.; Kim, J.; Khandelwal, S.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Kanegaye, J.T.; Abe, N.; Austin-Page, L.; Bryl, A.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence-Guided Signature Reveals the Shared Host Immune Response in MIS-C and Kawasaki Disease. Nature Communications 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.S.A.; Farrow, E.G.; Abdelmoity, A.T.; Alaimo, J.T.; Amudhavalli, S.M.; Anderson, J.T.; Bansal, L.; Bartik, L.; Baybayan, P.; Belden, B.; et al. Genomic Answers for Children: Dynamic Analyses of >1000 Pediatric Rare Disease Genomes. Genetics in Medicine 2022, 24, 1336–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padash, S.; Mohebbian, M.R.; Adams, S.J.; Henderson, R.D.E.; Babyn, P. Pediatric Chest Radiograph Interpretation: How Far Has Artificial Intelligence Come? A Systematic Literature Review. Pediatric Radiology 2022, 52, 1568–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.H.; Yoon, H.M.; Kim, J.R.; Hwang, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.; Sung, J.; Jung, K.-H.; Bae, B.; et al. Bone Age Assessment Using Artificial Intelligence in Korean Pediatric Population: A Comparison of Deep-Learning Models Trained With Healthy Chronological and Greulich-Pyle Ages as Labels. Korean Journal of Radiology 2023, 24, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokop-Piotrkowska, M.; Marszałek-Dziuba, K.; Moszczyńska, E.; Szalecki, M.; Jurkiewicz, E. Traditional and New Methods of Bone Age Assessment-an Overview. JCRPE Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology 2021, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thodberg, H.H.; Thodberg, B.; Ahlkvist, J.; Offiah, A.C. Autonomous Artificial Intelligence in Pediatric Radiology: The Use and Perception of BoneXpert for Bone Age Assessment. Pediatric Radiology 2022, 52, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Song, I.-S.; Ahn, B.; Choo, J.; Lee, D.-Y. Prediction of Hand-Wrist Maturation Stages Based on Cervical Vertebrae Images Using Artificial Intelligence. Orthodontics and Craniofacial Research 2021, 24, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.; Heo, J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Jung, M.K.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, Y.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, H.I.; Lee, M.; et al. Bone Age Estimation and Prediction of Final Adult Height Using Deep Learning. Yonsei Medical Journal 2023, 64, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Mutlu, O.C.; Kline, A.; Surabhi, S.; Washington, P.; Wall, D.P. Training and Profiling a Pediatric Facial Expression Classifier for Children on Mobile Devices: Machine Learning Study. JMIR Formative Research 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Han, J.-X. Rehabilitation Educational Design for Children with Autism Based on the Radial Basis Function Neural Network. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Naik, N.; Somani, B.K.; Hameed, B.M.Z. Artificial Intelligence (Ai) in Urology-Current Use and Future Directions: An Itrue Study. Turkish Journal of Urology 2020, 46, S27–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Alksas, A.; Shehata, M.; AbdelKhalek, A.; Abdel Baky, K.; El-Baz, A.; Helmy, E. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Radiomics in Neuro-Oncology Imaging. Insights into Imaging 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliozzi, S.; Oh, Y.T.; Hasanain, M.; Garofano, L.; D’Angelo, F.; Najac, R.D.; Picca, A.; Bielle, F.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Lerond, J.; et al. Integrative Multi-Omics Networks Identify PKCδ and DNA-PK as Master Kinases of Glioblastoma Subtypes and Guide Targeted Cancer Therapy. Nature Cancer 2023, 4, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Merchant, K.; KN, B.P.; CS, A.; Zhao, J.J.; Saffari, S.E.; Tan, P.H.; Tang, P.H. CT-Based Morphologic and Radiomics Features for the Classification of MYCN Gene Amplification Status in Pediatric Neuroblastoma. Childs Nerv Syst 2022, 38, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Wu, C.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Guan, W.; Duan, S.; Wang, D. Radiogenomics of Neuroblastoma in Pediatric Patients: CT-Based Radiomics Signature in Predicting MYCN Amplification. Eur Radiol 2021, 31, 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Qian, L.; Yang, S.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, S.; Qin, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Clinical Parameters Combined with Radiomics Features of PET/CT Can Predict Recurrence in Patients with High-Risk Pediatric Neuroblastoma. BMC Med Imaging 2022, 22, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, H.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Z.; He, L. Development and Validation of a CT-Based Radiomics Signature for Identifying High-Risk Neuroblastomas under the Revised Children’s Oncology Group Classification System. Pediatric Blood & Cancer 2023, 70, e30280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
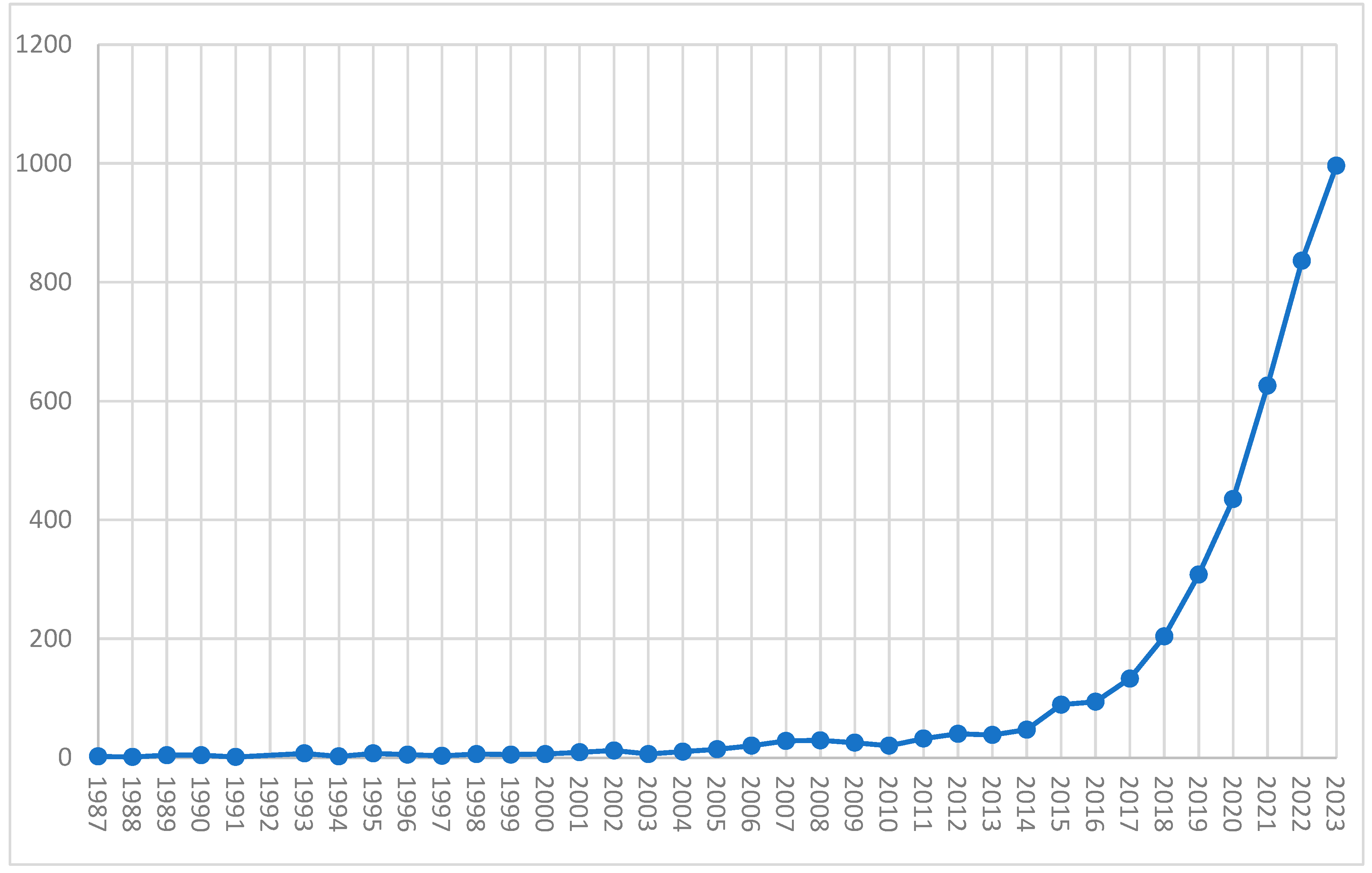
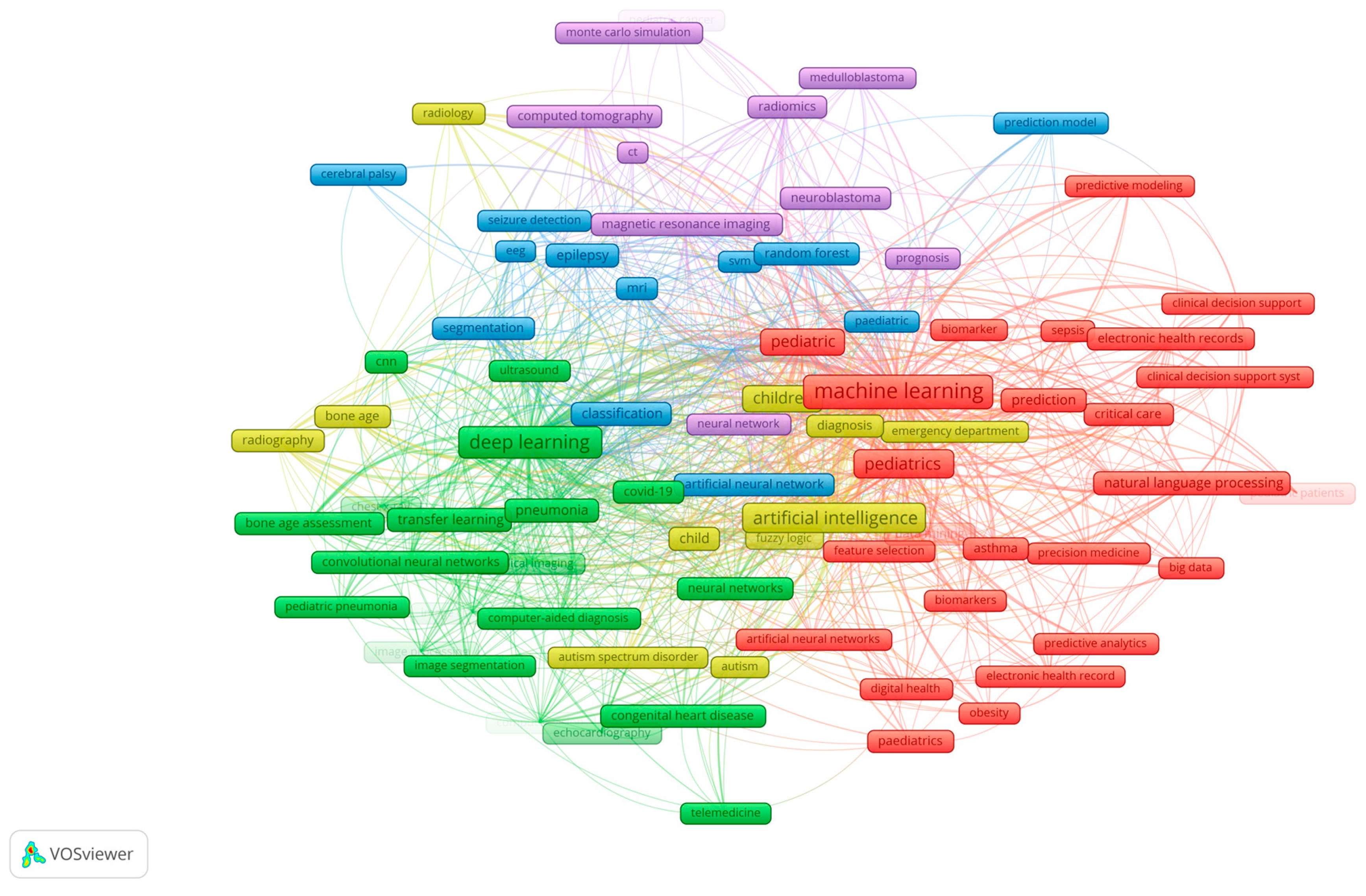
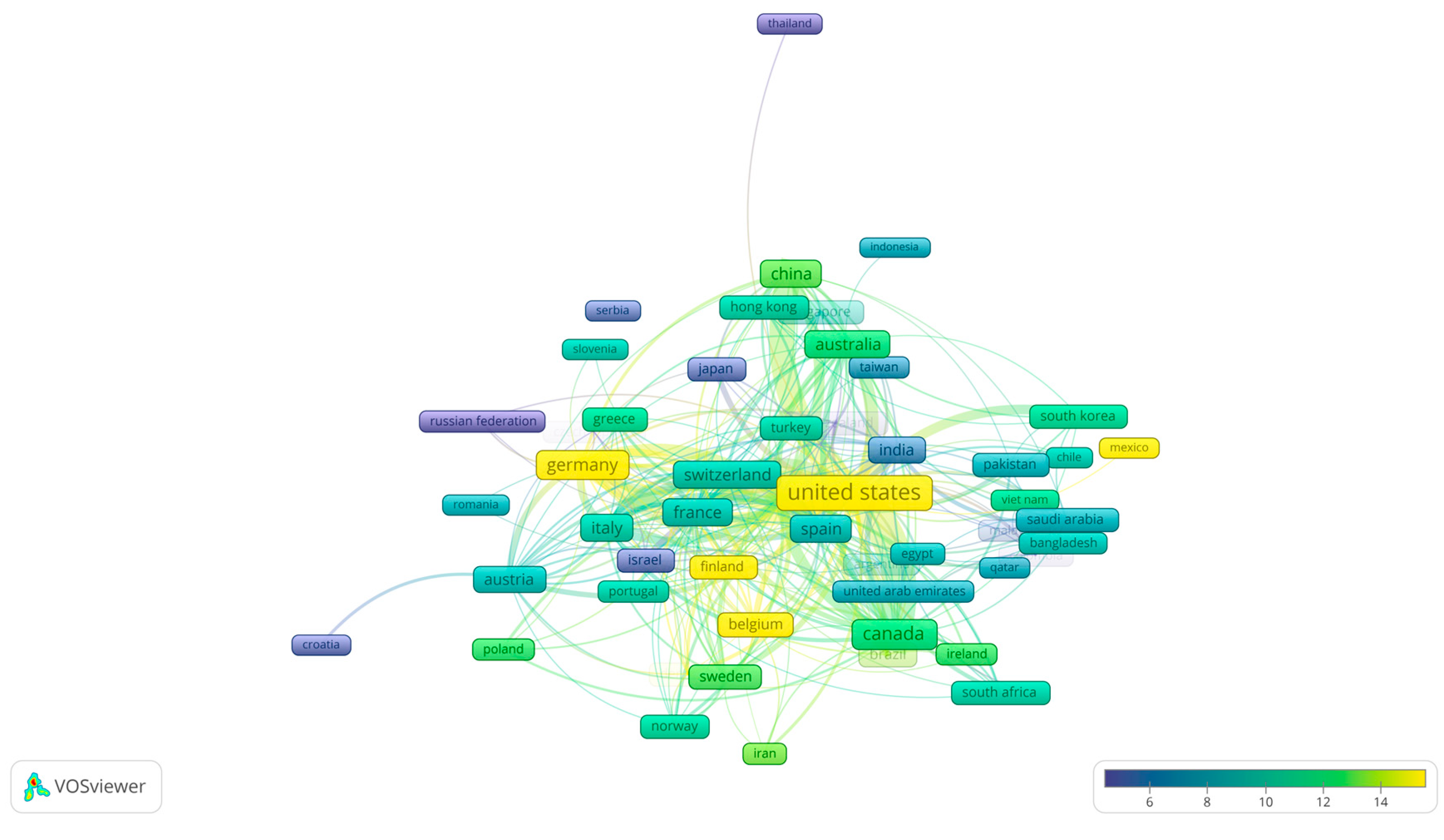
| Country | Number of publications |
|---|---|
| United States of America | 1786 |
| China | 531 |
| Canada | 335 |
| United Kingdom | 330 |
| Germany | 211 |
| India | 185 |
| Italy | 179 |
| Spain | 146 |
| Australia | 142 |
| South Korea | 132 |
| Source title | Number of Publications | Impact Factors (SJR – Scopus 2021) | H-index | Quarter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lecture Notes In Computer Science | 155 | 0.32 | 209 | Q3 |
| Frontiers in Pediatrics | 70 | 0.80 | 62 | Q1 |
| Scientific Reports | 67 | 0.97 | 282 | Q1 |
| Pediatric Radiology | 65 | 0.65 | 95 | Q2 |
| Progress In Biomedical Optics And Imaging Proceedings Of SPIE | 50 | 0.21 | 60 | N/A |
| Plos ONE | 48 | 0.89 | 404 | Q1 |
| Pediatric Critical Care Medicine | 40 | 1.42 | 100 | Q1 |
| Pediatric Research | 34 | 1.04 | 165 | Q1 |
| IEEE Journal Of Biomedical And Health Informatics | 30 | 1.67 | 146 | Q1 |
| Computer Methods And Programs In Biomedicine | 29 | 1.12 | 124 | Q1 |
| Color | Representative author keywords (codes) | Categories | Themes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green (n=21) | Deep learning (431); Convolutional neural network (152); Pneumonia (n=56); Transfer Learning (n=54); Bone age assessment (47); Covid 19 (43); Congenital heart diseases (n=29) | Deep learning with convolutional networks for complex decision making about bone age assessment and pneumonia; Segmentation of echocardiography images in congenital heart diseases | Analysing complex signals using deep learning |
| Red (n=26) | Machine learning (758); Pediatrics (464); Prediction (n=61); Natural language processing (n=60); Electronic health records (n=58); Clinical decision support (53); Asthma (39); Critica care (32), Data mining /26)Artificial neural networks (25); Sepsis (25); Cancer (24) | Machine learning on electronic health records for predication and critical decision support in asthma and sepsis; Natural language processing of electronic health records; Big data analysis for paediatric cancer patients | Critical clinical decision making and prediction with machine learning and natural language processing |
| Blue (n=14) | Classification (73); Support vector machines (63, Epilepsy (57); Segmentation (48); MRI (40); Random forest (39); Artificial neural networks (32); EEG (25) |
Segmentation, feature selection and classification of EEG and MRI signals; Seizure detection in epilepsy and cerebral palsy; | MRI and EEG analysis in seizure detection in epilepsy and cerebral palsy |
| Yellow (n=11) | Artificial intelligence (420); Children (188); Radiology and radiography (50); Autism spectre disorder (34)Diagnosis /46); Bone age (30) | Artificial intelligence based processing of radiography and radiology outputs for assessing bone age, Diagnosis of autism spectre disorder with artificial intelligence | Using artificial intelligence for diagnosing |
| Viollet (n=10) | Magnetic resonance imaging (48), Blastoma (46); Computer tomography (44); Radiomics (41); | Analysis of CT and MRI images for blastoma prognosis | Radiomics in peditric cancer treatment |
| Machine learning algorithms | AI Approaches | Pediatric diagnoses | Applications in pediatrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deep learning (464) | Classification (95) | Pneumonia (71) | Bone age assesment (77) |
| Convolutional neural network (196) | Natural language processing (60) | Epilepsy (70) | Critical care (43) |
| Transfer learning (54) | Data and text mining (31) | Covid 19 (43) | Prediction (146) |
| Support vector machine (51) | Feature selection and extraction (64) | Asthma (50) | Computer-aided diagnosis (86) |
| Artificial neural networks (111) | Monte carlo simulation (33) | Obstructive sleep apnea (12) | Signal and image processing (73) |
| Random forest (45) | Data augmentation (8) | Autism spectrum disorder (34) | Clinical decision support (112) |
| Fuzzy logic (16) | Big data (19) | Sepsis (35) | Radiomics (41) |
| Logistic regression (19) | Explainable artificial intelligence (10) | Cerebral palsy (17) | Computer vision (16) |
| Decision tree (18) | Digital health (16) | Kidney dieases (16) | Triaging (11 |
| Ensemble learning (15) | Expert systems (6) | Cancer (47) | Anomaly detection (12) |
| Genetic algorithm (8) | Crohn's disease (12) | Epidemiology (14) | |
| Bayesian methods (10) | Cystic fibrosis (10) | Length of stay (7) | |
| Mental health (12) | Metabolomics (10) | ||
| Congenital heart disease (39) | Quality improvement (12) | ||
| Blastoma (50) | Severity of illness (9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





