Submitted:
05 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
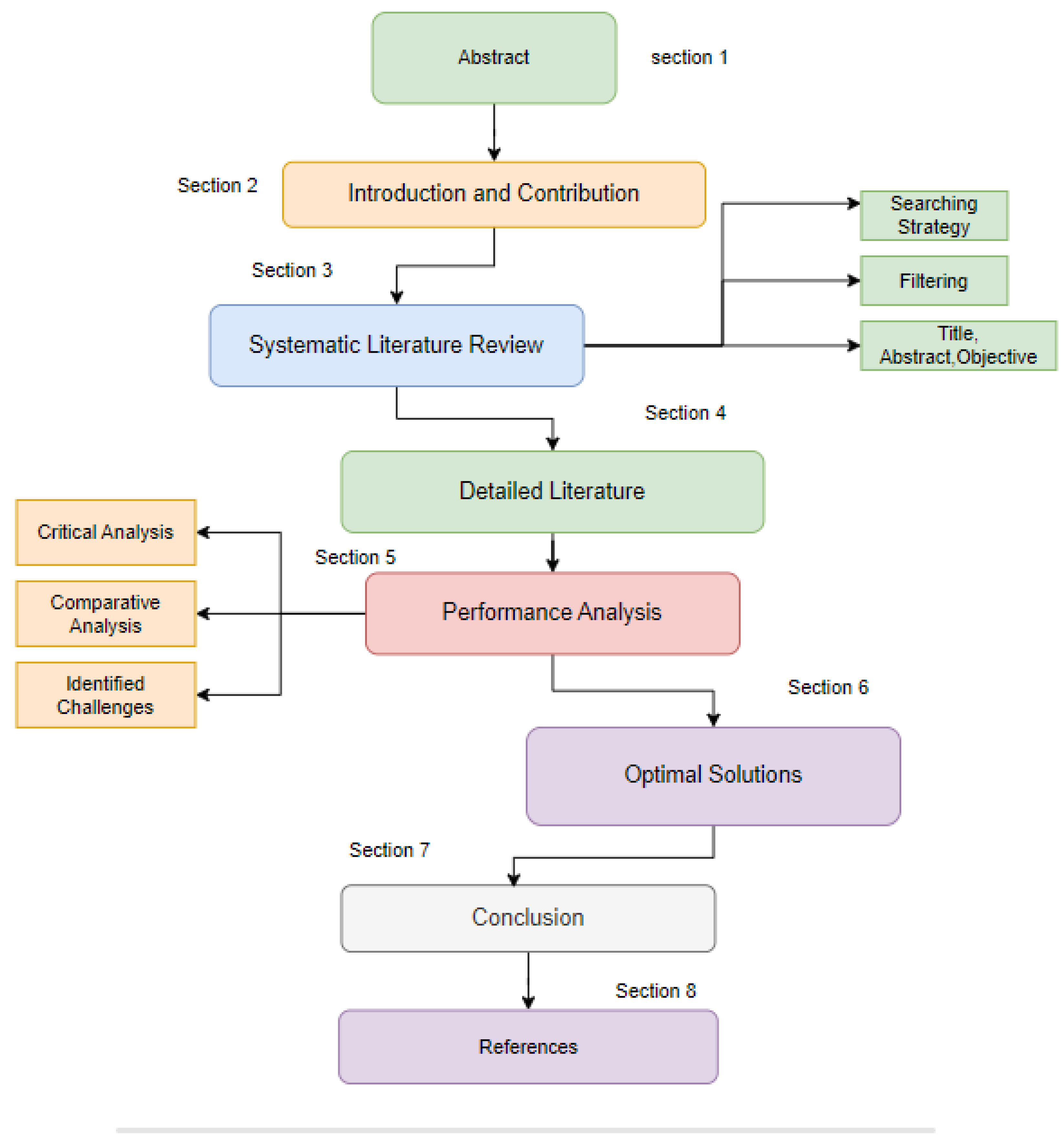
Introduction
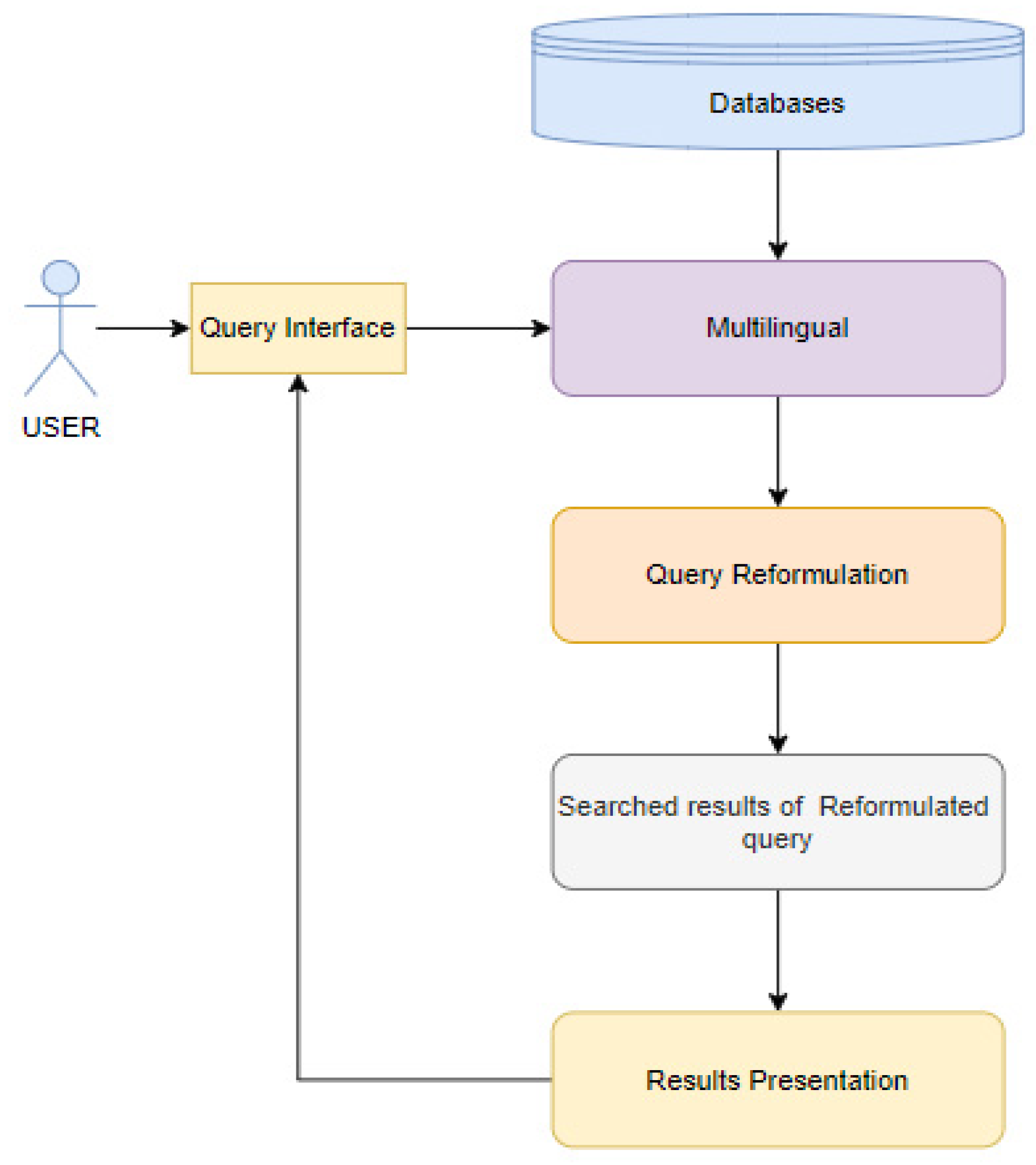
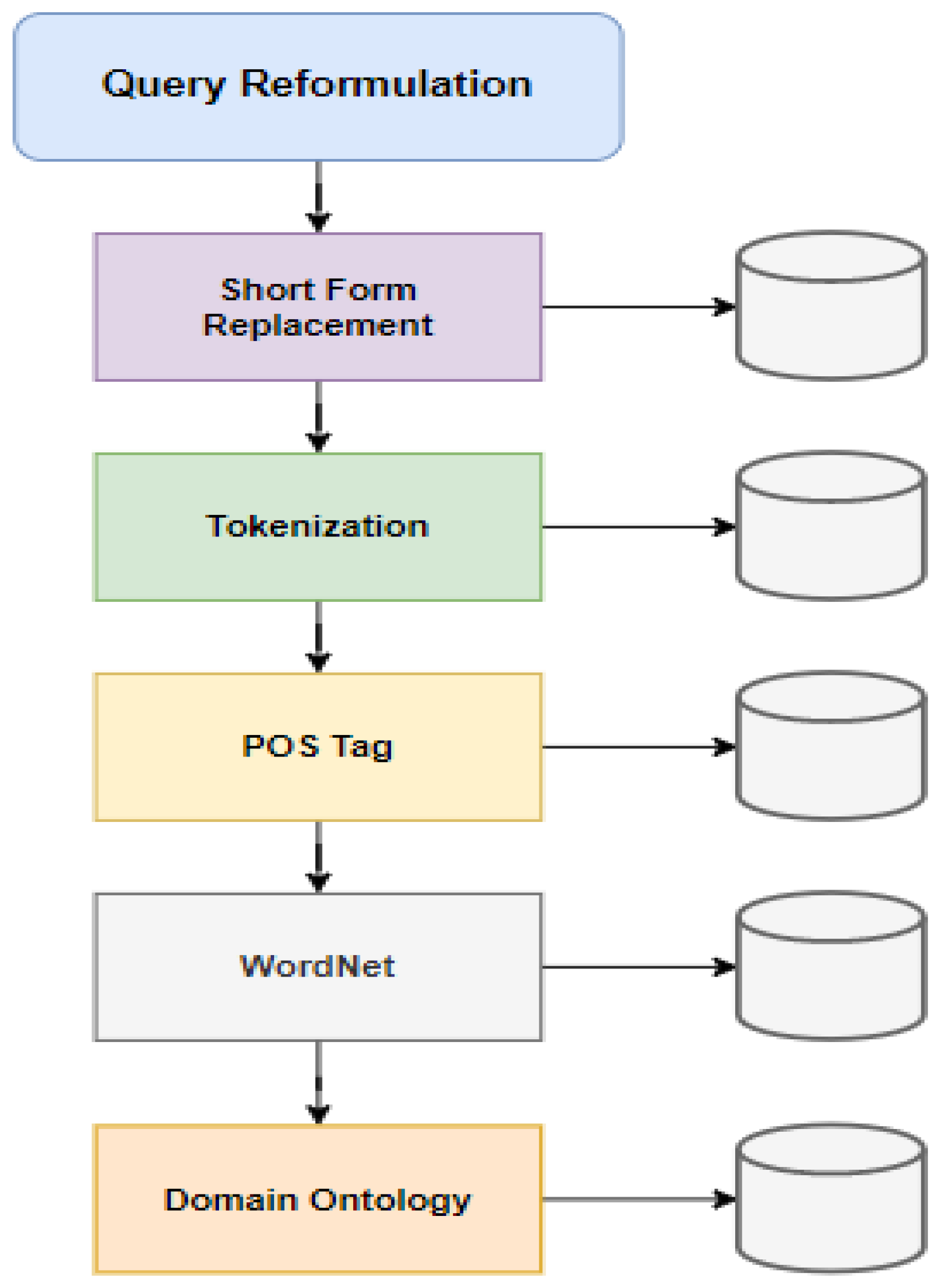
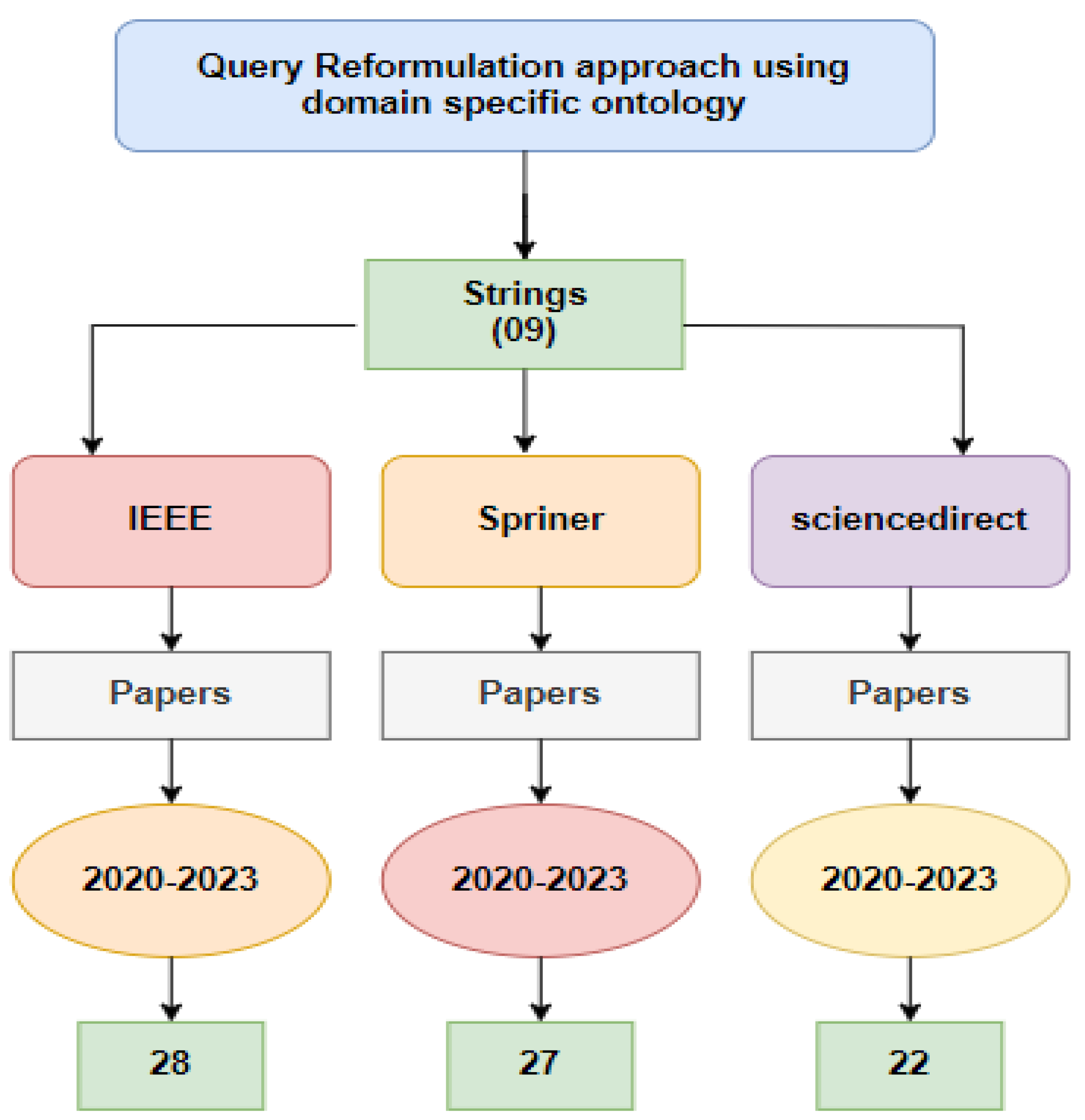
1. Systematic Literature Review
1.1. String Development
- Searching protocol:
1.2. Filtering:
2.2.1. Title-based Filtering:
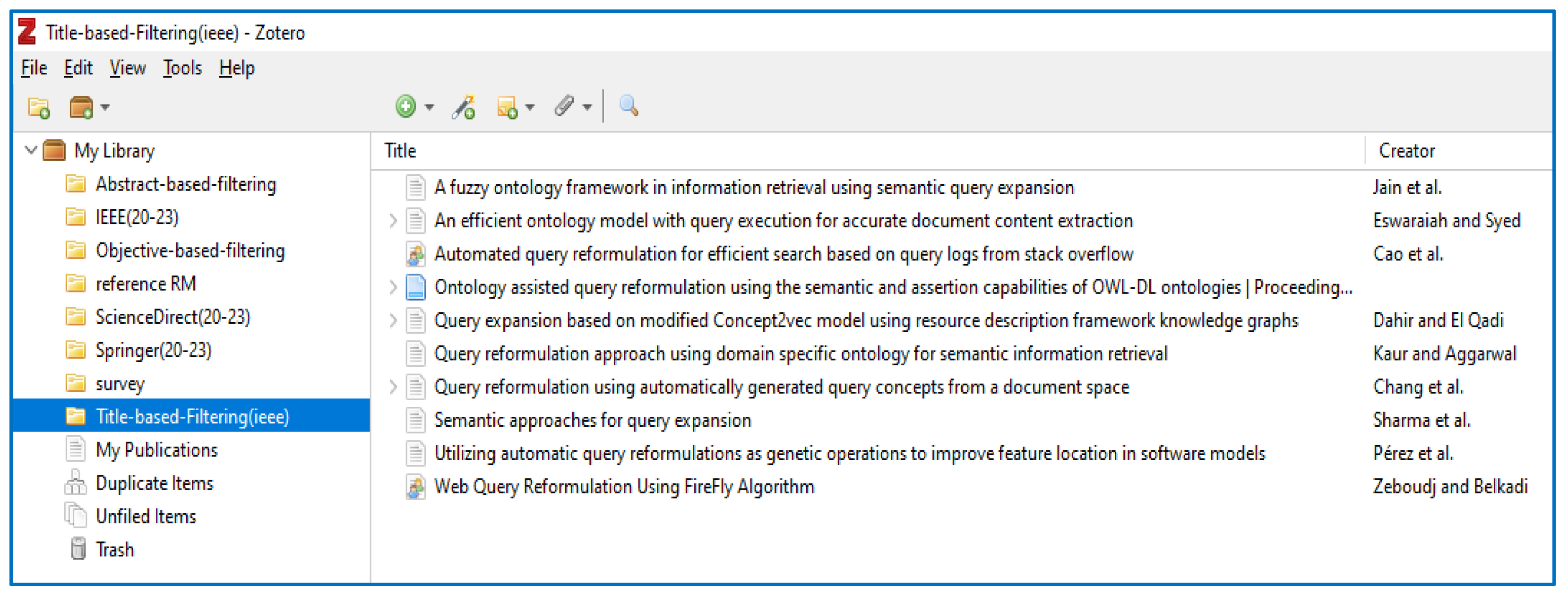
- Abstract-based Filtering:
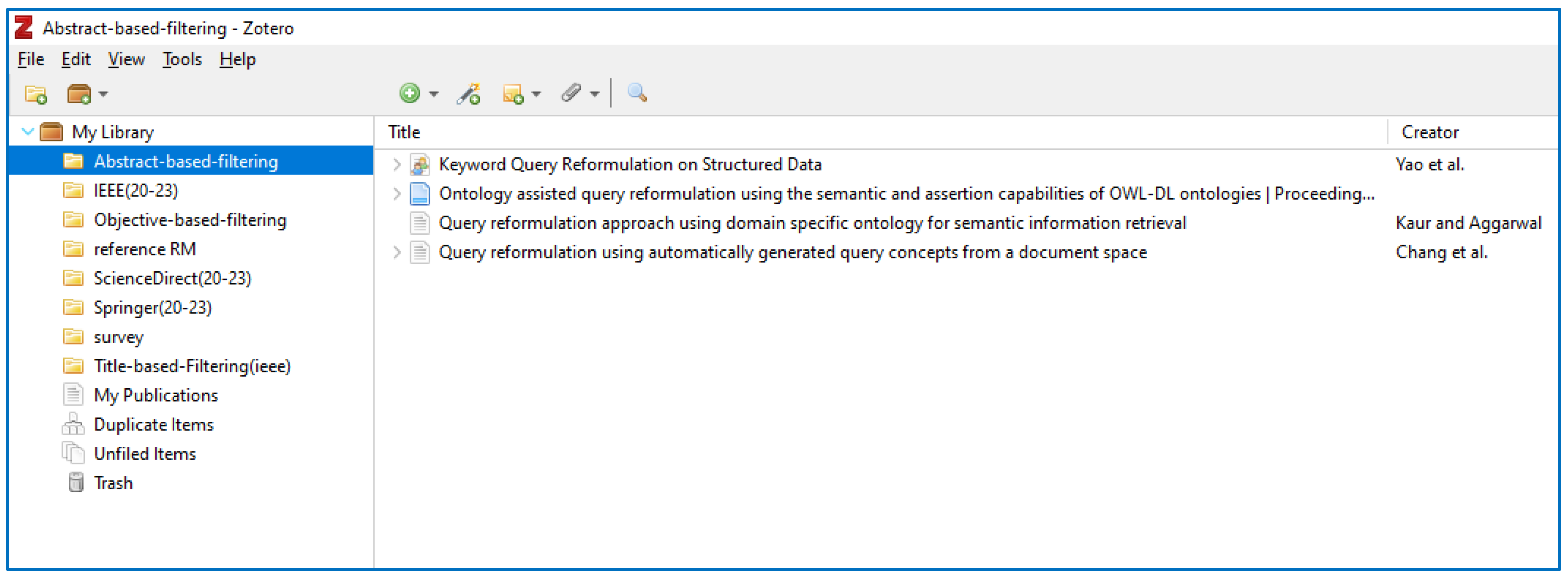
- Objective-based Filtering:
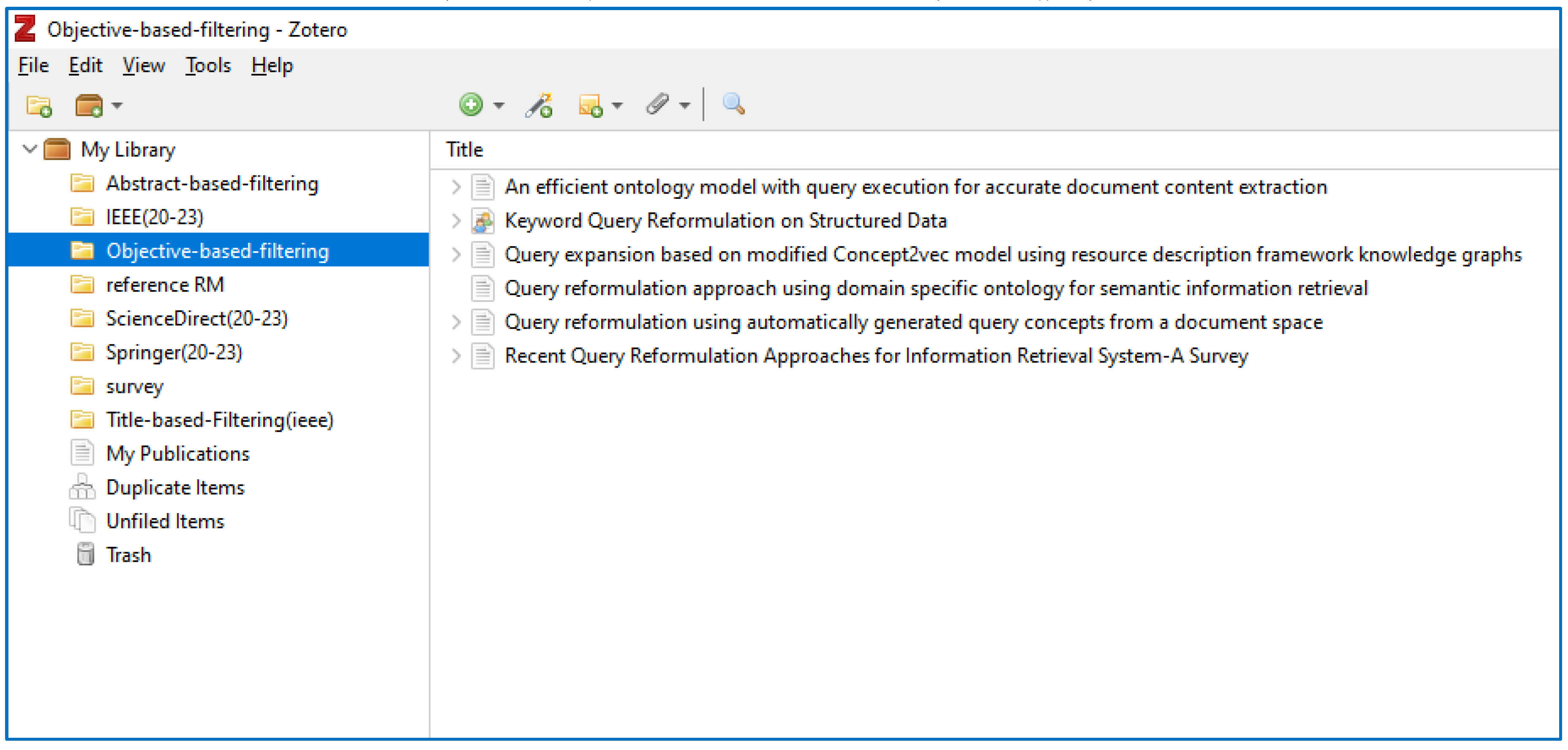
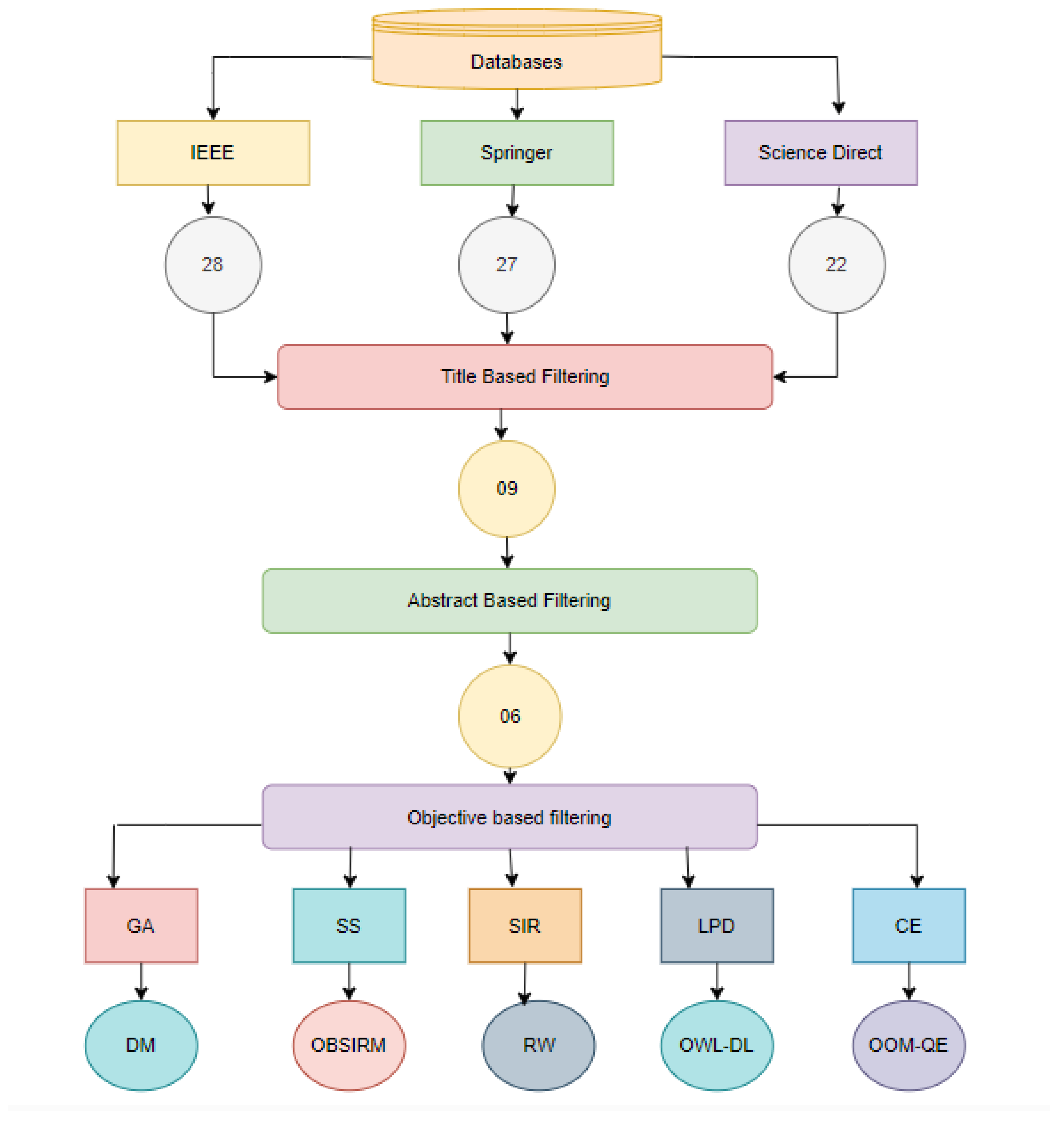
3. Detailed Literature:
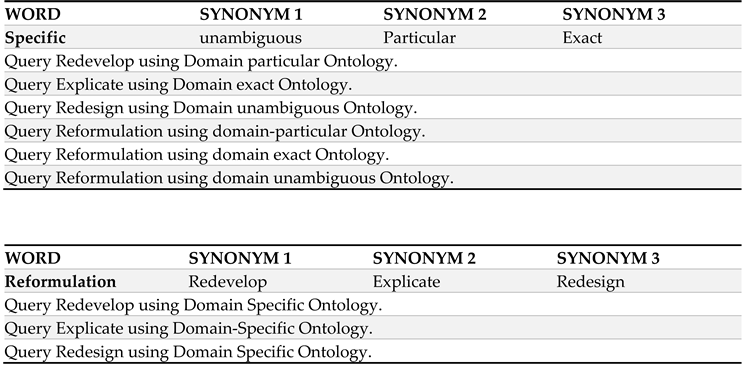
3.1. Query reformulation approaches using domain-specific ontologies
- Technique based filtering:
| Ref. | PC | OBSIRM | RW | OWL-DL | OOM-QE | Concept2vec | HM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | - | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - | - |
| [7] | - | - | ✔ | - | - | - | ✔ |
| [1] | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [8] | ✔ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [9] | - | - | - | - | ✔ | - | - |
| [6] | - | - | - | - | - | - |
4. Performance Analysis
4.1. Critical Analysis:
5. Research Gaps
| Ref. | Research Gaps | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| [1] | High Resource consumption | One way to reduce resource consumption is to narrow the scope of the search by limiting the number of documents or data sources that need to be examined. This can be achieved by using filters or query expansion techniques that refine the search results and reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed.[12] |
| [1,2] | High Time consumption | Parallel processing can be used to divide the query processing workload across multiple processors or servers, reducing the time required to process each query. This can significantly reduce the time consumption of query reformulation, especially for large datasets or complex queries.[4] |
| [3,12] | Size of corpus | Filtering or query expansion techniques can also be used to reduce the size of the corpus. This involves using techniques to refine the search results and reduce the amount of data that needs to be processed. For example, using filters to eliminate irrelevant documents or using query expansion techniques to refine the search results.[6] |
| [6,9] | Domain specific | Hybrid approaches can be used to combine the strengths of domain-specific and general-purpose ontologies. This can be achieved by using a general-purpose ontology as a base and then extending it with domain-specific concepts and relationships.[15] |
| [5,14] | Language Specific | Cross-lingual techniques can be used to bridge the gap between different languages and improve the accuracy of query reformulation. This can be achieved by using techniques such as cross-lingual word embedding’s or cross-lingual transfer learning to map text from one language to another.[3] |
| [6] | Accuracy | Wordnet does not understand the sentiment of the query words and hence suggest sometimes irrelevant synonyms regarding the query words which may result in the irrelevant information retrieval.[2] |
6. Conclusion
References
- N. Kaur and H. Aggarwal, “Query reformulation approach using domain specific ontology for semantic information retrieval,” Int. J. Inf. Technol., vol. 13, pp. 1745–1753, 2021.
- G. Suganya and R. Porkodi, “Ontology based information extraction-a review,” in 2018 International Conference on Current Trends towards Converging Technologies (ICCTCT), IEEE, 2018, pp. 1–7.
- V. Jain and S. Prasad, “Ontology based information retrieval model in semantic web: a review,” Int. J., vol. 4, no. 8, 2014.
- D. C. Wimalasuriya and D. Dou, “Ontology-based information extraction: An introduction and a survey of current approaches,” Journal of Information Science, vol. 36, no. 3. Sage Publications Sage UK: London, England, pp. 306–323, 2010.
- Dridi, “Ontology-based information retrieval: Overview and new proposition,” in 2008 Second International Conference on Research Challenges in Information Science, IEEE, 2008, pp. 421–426.
- “Ontology assisted query reformulation using the semantic and assertion capabilities of OWL-DL ontologies | Proceedings of the 2008 international symposium on Database engineering & applications.” https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/1451940.1451953 (accessed Mar. 08, 2023).
- J. Yao, B. Cui, L. Hua, and Y. Huang, “Keyword Query Reformulation on Structured Data,” in 2012 IEEE 28th International Conference on Data Engineering, Apr. 2012, pp. 953–964. [CrossRef]
- Y. Chang, I. Ounis, and M. Kim, “Query reformulation using automatically generated query concepts from a document space,” Inf. Process. Manag., vol. 42, no. 2, pp. 453–468, Mar. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Eswaraiah and H. Syed, “An efficient ontology model with query execution for accurate document content extraction,” Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci., vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 981–989, 2023.
- S. Zhu and J. Feng, “Using an ontology to help reason about the information content of data,” J. Softw. Eng. Appl., vol. 3, no. 07, p. 629, 2010.
- N. Jayaram, A. Khan, C. Li, X. Yan, and R. Elmasri, “Querying knowledge graphs by example entity tuples,” IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 27, no. 10, pp. 2797–2811, 2015.
- H. Zhang, X. Diao, Z. Yuan, J. Chun, and Y. Huang, “EVis: a system for extracting and visualizing ontologies from databases with web interfaces,” in 2012 Fourth International Symposium on Information Science and Engineering, IEEE, 2012, pp. 408–411.
- S. Manouchehri, M. Mirzabeigi, and T. Jowkar, “Evaluating the effectiveness of Farsi-English query production using ontology: a case of scientometric ontology,” Aslib J. Inf. Manag., vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 386–405, 2021.
- M. M. Rahman and C. K. Roy, “Improved query reformulation for concept location using coderank and document structures,” in 2017 32nd IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE), IEEE, 2017, pp. 428–439.
- Z. Bao, B. Kimelfeld, and Y. Li, “Automatic suggestion for query-rewrite rules,” May 24, 2016.
- L. Zhang, T. Tran, and A. Rettinger, “Probabilistic query rewriting for efficient and effective keyword search on graph data,” Proc. VLDB Endow., vol. 6, no. 14, pp. 1642–1653, 2013.
- D. R. Cunha and B. F. Lóscio, “An approach for query decomposition on federated SPARQL query systems,” J. Inf. Data Manag., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 106–106, 2015.
- J. M. do Espírito Santo, E. V. de Paula, and C. B. Medeiros, “Exploring Semantics in Clinical Data Interoperability,” in Advances in Conceptual Modeling: ER 2019 Workshops FAIR, MREBA, EmpER, MoBiD, OntoCom, and ER Doctoral Symposium Papers, Salvador, Brazil, November 4–7, 2019, Proceedings 38, Springer, 2019, pp. 201–210.
- Gouda, W. , Sama, N. U., Al-Waakid, G., Humayun, M., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2022, June). Detection of skin cancer based on skin lesion images using deep learning. In Healthcare (Vol. 10, No. 7, p. 1183). MDPI.
- Sennan, S. , Somula, R., Luhach, A. K., Deverajan, G. G., Alnumay, W., Jhanjhi, N. Z., ... & Sharma, P. (2021). Energy efficient optimal parent selection based routing protocol for Internet of Things using firefly optimization algorithm. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32(8), e4171.
- Hussain, K. , Hussain, S. J., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2019, April). SYN flood attack detection based on bayes estimator (SFADBE) for MANET. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Hanif, M. , Ashraf, H., Jalil, Z., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Humayun, M., Saeed, S., & Almuhaideb, A. M. (2022). AI-based wormhole attack detection techniques in wireless sensor networks. Electronics, 11(15), 2324.
- Jabeen, T. , Jabeen, I., Ashraf, H., Jhanjhi, N., Humayun, M., Masud, M., & Aljahdali, S. (2022). A monte carlo based COVID-19 detection framework for smart healthcare. Computers, Materials, & Continua, 70(2), 2365-2380.
- Siddiqui, F. J. , Ashraf, H., & Ullah, A. (2020). Dual server based security system for multimedia Services in Next Generation Networks. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 79, 7299-7318.
- Shahid,H.,Ashraf,H.,Ullah,A.,Band,S.S.&Elnaffar,S.Wormholeattackmitigationstrategiesandtheirimpact onwirelesssensornetworkperformance: Aliteraturesurvey. InternationalJournalofCommunicationSystems35, e5311(2022). URLhttps://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/dac.5311. https:// onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/dac.5311.
- Zamir, U. B. , Masood, H., Jamil, N., Bahadur, A., Munir, M., Tareen, P.,... & Ashraf, H. (2015, July). The relationship between sea surface temperature and chlorophyll-a concentration in Arabian Sea. In Biological Forum–An International Journal (Vol. 7, No. 2, pp. 825-834).
- Gaur, L. , Afaq, A., Solanki, A., Singh, G., Sharma, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z.,... & Le, D. N. (2021). Capitalizing on big data and revolutionary 5G technology: Extracting and visualizing ratings and reviews of global chain hotels. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 95, 107374.
- Diwaker, C. , Tomar, P., Solanki, A., Nayyar, A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Abdullah, A., & Supramaniam, M. (2019). A new model for predicting component-based software reliability using soft computing. IEEE Access, 7, 147191-147203.
- Hussain, S. J. , Ahmed, U., Liaquat, H., Mir, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2019, April). IMIAD: intelligent malware identification for android platform. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Humayun, M. Alsaqer, M. S., Jhanjhi, N. (2022). Energy optimization for smart cities using iot. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 36(1), 2037255.
- Ghosh, G. , Verma, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Talib, M. N. (2020, December). Secure surveillance system using chaotic image encryption technique. In IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (Vol. 993, No. 1, p. 012062). IOP Publishing.
- Almusaylim, Z. A. , Zaman, N., & Jung, L. T. (2018, August). Proposing a data privacy aware protocol for roadside accident video reporting service using 5G in Vehicular Cloud Networks Environment. In 2018 4th International conference on computer and information sciences (ICCOINS) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Wassan, S. , Chen, X., Shen, T., Waqar, M., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2021). Amazon product sentiment analysis using machine learning techniques. Revista Argentina de Clínica Psicológica, 30(1), 695.
- Shahid, H. , Ashraf, H., Javed, H., Humayun, M., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & AlZain, M. A. (2021). Energy optimised security against wormhole attack in iot-based wireless sensor networks. Comput. Mater. Contin, 68(2), 1967-81.
- E. Ndashimye, N. I. Sarkar, and S. K. Ray, “A Multi-criteria based handover algorithm for vehicle-toinfrastructure communications,” Computer Networks, vol. 185, no. 202152, Article ID 107652, 2020.
- Ray, S. K., Pawlikowski, K., Sirisena, H. (2009). A fast MAC-layer handover for an IEEE 802.16 e-based WMAN. In AccessNets: Third International Conference on Access Networks, AccessNets 2008, Las Vegas, NV, USA, October 15-17, 2008. Revised Papers 3 (pp. 102-117). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Srivastava, R. K. , Ray, S., Sanyal, S., & Sengupta, P. (2011). Mineralogical control on rheological inversion of a suite of deformed mafic dykes from parts of the Chottanagpur Granite Gneiss Complex of eastern India. Dyke Swarms: Keys for Geodynamic Interpretation: Keys for Geodynamic Interpretation, 263-276.
- Ray, S. K. , Sinha, R., & Ray, S. K. (2015, June). A smartphone-based post-disaster management mechanism using WiFi tethering. In 2015 IEEE 10th conference on industrial electronics and applications (ICIEA) (pp. 966-971). IEEE.
- Chaudhuri A, Ray S (2015) Antiproliferative activity of phytochemicals present in aerial parts aqueous extract of Ampelocissus latifolia (Roxb.) planch. on apical meristem cells. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 6(2):99–108.
- Hossain, A. , Ray, S. K., & Sinha, R. (2016, December). A smartphone-assisted post-disaster victim localization method. In 2016 IEEE 18th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 14th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS) (pp. 1173-1179). IEEE.
- Airehrour, D. , Gutierrez, J., & Ray, S. K. (2018). A trust-based defence scheme for mitigating blackhole and selective forwarding attacks in the RPL routing protocol. Journal of Telecommunications and the Digital Economy, 6(1), 41-49.
- Ray, S. K. , Ray, S. K., Pawlikowski, K., McInnes, A., & Sirisena, H. (2010, April). Self-tracking mobile station controls its fast handover in mobile WiMAX. In 2010 IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Dey, K. , Ray, S., Bhattacharyya, P. K., Gangopadhyay, A., Bhasin, K. K., & Verma, R. D. (1985). Salicyladehyde 4-methoxybenzoylhydrazone and diacetylbis (4-methoxybenzoylhydrazone) as ligands for tin, lead and zirconium. J. Indian Chem. Soc.;(India), 62(11).
- Airehrour, D. , Gutierrez, J., & Ray, S. K. (2017, November). A testbed implementation of a trust-aware RPL routing protocol. In 2017 27th International Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Ndashimye, E. , Sarkar, N. I., & Ray, S. K. (2016, August). A novel network selection mechanism for vehicle-to-infrastructure communication. In 2016 IEEE 14th Intl Conf on Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing, 14th Intl Conf on Pervasive Intelligence and Computing, 2nd Intl Conf on Big Data Intelligence and Computing and Cyber Science and Technology Congress (DASC/PiCom/DataCom/CyberSciTech) (pp. 483-488). IEEE.
- Ndashimye, E. , Sarkar, N. I., & Ray, S. K. (2020). A network selection method for handover in vehicle-to-infrastructure communications in multi-tier networks. Wireless Networks, 26, 387-401.
- Al-Turjman, F. (Ed.) . (2020). Drones in smart-cities: Security and performance. Elsevier.
- Ponnusamy, V. , Jung, L. T., Ramachandran, T., & Zaman, N. (2017, April). Bio-inspired energy scavenging in wireless ad hoc network. In 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Electrical Engineering and Computational Technologies (ICIEECT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Ponnusamy, V. (Ed.) . (2016). Biologically-Inspired Energy Harvesting through Wireless Sensor Technologies. IGI Global.
| Year | Main Focus | Major Contribution | Enhancement in our paper |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Over the past five years, ontology-based research has grown significantly. | The research of [2] gives a summary of these three categories of ontologies, which are intended for use in the fields of agriculture, biomedicine and health, education, and tourism. | Our survey provides a thorough Performance analysis, which includes a critical analysis and gaps in current plans that have been found. |
| 2018 | Integrating Semantic Web, Mining, and Multi-Agent Systems research. | Our concept of fusing the three research areas of Semantic Web, Mining, and Multi-Agent Systems is presented in the study of [3] which gives a literature survey on Semantic Web Mining. The fundamental concept is to employ Web-based semantic structures to our advantage when mining, and to combine mining methods with Multi-Agent Systems to create the Semantic Web. | Our survey presents a detailed Performance analysis, including critical analysis and identified gaps in existing schemes. |
| 2018 | In order to categorize these systems based on several criteria and determine whether they share a common architecture, | An overview of ontology-based information extraction is given in the study of [4] along with a detailed analysis of the many ontology-based information extraction systems that have been created to date. In order to better understand how these systems function, it also makes an effort to classify them based on a variety of criteria and find a shared architecture among them. It also covers the specifics of how these systems were put into place, such as the tools they used and the measurements they employed to gauge their effectiveness. | Our survey offers a thorough comparison of all existing program as well as a thorough critical analysis. |
| 2021 | Techniques and software tools for ontology-based information retrieval are currently being developed as prototypes or as products for sale.. | An overview of ontology-based information retrieval methods and software tools that are now on the market as either prototypes or finished goods is given in the research of [5]. Feature categorization, which encompasses both generic tool characteristics and their information retrieval properties, is used to evaluate systems. Finally, we discuss our contribution to this field of study. | Our survey offers a thorough comparison of all existing programs as well as a thorough critical analysis. |
| Ref. | GA | SS | SIR | LPD | A | CE | QE | E |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | ✔ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [7] | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [1] | - | - | ✔ | - | ✔ | ✔ | - | - |
| [8] | - | - | - | ✔ | - | - | - | - |
| [9] | - | - | - | - | - | ✔ | - | - |
| [6] | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✔ | ✔ |
| Notation | Term |
|---|---|
| Global Access | GA |
| Structural Semantics | SS |
| Semantic Information Retrieval | SIR |
| Local Pattern Discovery | LPD |
| Accuracy | A |
| Content Extraction | CE |
| Query Expansion | QE |
| Efficiency | E |
| Heterogeneous model | HM |
| Primitive Concepts | PC |
| Random Walk | RW |
| (Optimized ontology model with query execution) | OOM-QE |
| Ref. | Technique | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| [6] | PC | Local pattern discovery and a global modeling using data mining techniques. For a new query, select its most associated primitive concepts and choose the most probable interpretations as query concepts. |
| [7] | OBSIRM | (OBSIRM) has been built to refine the web search in the music domain. It first replaced with abbreviations along with the use of the multilingual concept to search a query. |
| [1] | RW&HM | Heterogeneous graph to model the words and items in structured data, and design an enhanced Random Walk approach to extract relevant terms from the graph context. |
| [8] | OWL-DL | This approach is applied to the integrated database schema of the EU funded Health-e-Child (HEC) project with the aim of providing ontology assisted query reformulation techniques to simplify the global access that is needed to millions of medical records across the UK and Europe. |
| [9] | OOM-QE | Optimized ontology model with query execution used for content extraction from documents |
| [6] | Concept2vec | It reformulates the initial query by adding similar terms that help in retrieving more relevant results. |
| Ref. | Effort Year | Technique | Short coming |
|---|---|---|---|
| [6] | 2023 | OWL-DL ontologies | The research of [1] Claims that developing OWL-DL ontologies can be time- and resource-consuming. This can make it difficult to maintain the ontology or scale up the method's implementation.[10] |
| [7] | 2012 | RW | Random walk techniques in [2] usually take a long time to converge, especially in large networks. Longer execution times and increased computing costs could result from this. [11,16] |
| [1] | 2021 | OBSIRM | The application of the technique to a constrained set of topics may be hindered in [3] by the usage of a domain-specific ontology. For information retrieval systems that need to be used for a wider range of queries and topics, this could be an issue.[12] |
| [8] | 2005 | Primitive Concepts | The research of [4], dealing with the entire corpus took a lot of effort, and the strategy only showed promise for the queries that performed poorly.[13] |
| [9] | 2023 | OOM-QE | The study of [5] The proposed strategy is tested on a small dataset with just one use case, and the experiments are only allowed to compare the performance of the proposed method to that of two baseline approaches. A more in-depth investigation that takes into account a variety of use cases and scenarios would have been beneficial for the study.[14] |
| [6] | 2023 | Concept2vec | How the Concept2vec model can be trained for different domains or how the Knowledge Graphs may be constructed for different use cases are not quite obvious in [6,9,15]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





