Submitted:
06 February 2024
Posted:
07 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.2. Discussion of challenges and limitations in the field of study
- Efficiency and Scalability: Transaction efficiency and scalability are essential issues in blockchain. Adding interactions with the cloud can increase complexity and the time required to complete transactions, which can reduce efficiency. Scalability becomes a problem when handling large volumes of data from the cloud to the blockchain, leading to network congestion and longer processing times [22,23].
- Costs and Sustainability: Implementing blockchain and cloud solutions can be costly, both in terms of infrastructure and energy consumption. Sustainability and energy efficiency are important considerations, especially at a time when the carbon footprint of blockchain is under scrutiny. Researching more energy-efficient solutions is crucial [24].
- Interoperability and Standards: Interoperability between different blockchains and cloud providers can be a problem. The lack of common standards and protocols can hinder seamless integration. Researching and developing standards to ensure smooth interaction is essential [2].
- Quantum computing resistance: With the development of quantum computing, resistance to quantum attacks becomes a concern. Blockchain and the cloud must be resilient to these emerging technological challenges [25].
1.3. Study Objectives and Motivation Behind Them
- RQ1: What is the distribution of papers across different years?
- RQ2: How are the chosen papers related to the proposed keywords?
- RQ3: Which of the papers explores blockchain and cloud computing as review?
- RQ4: Which papers explore the blockchain-cloud computing and healthcare?
- RQ5: In the current landscape of secure blockchain and cloud integration, what constitutes the primary challenges that organizations and practitioners face?
1.4. Contributions
- Synthesis of key findings to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of secure integration in the given domains. Classification based on topics and keywords.
- Recommendations for future research and potential areas for improvement in the integration of blockchain technology and cloud computing for enhanced security in healthcare applications.
- Analysis of emerging trends and innovative approaches in the secure integration of blockchain and cloud computing.
- Explore challenges and field limitations.
2. Material and Methods
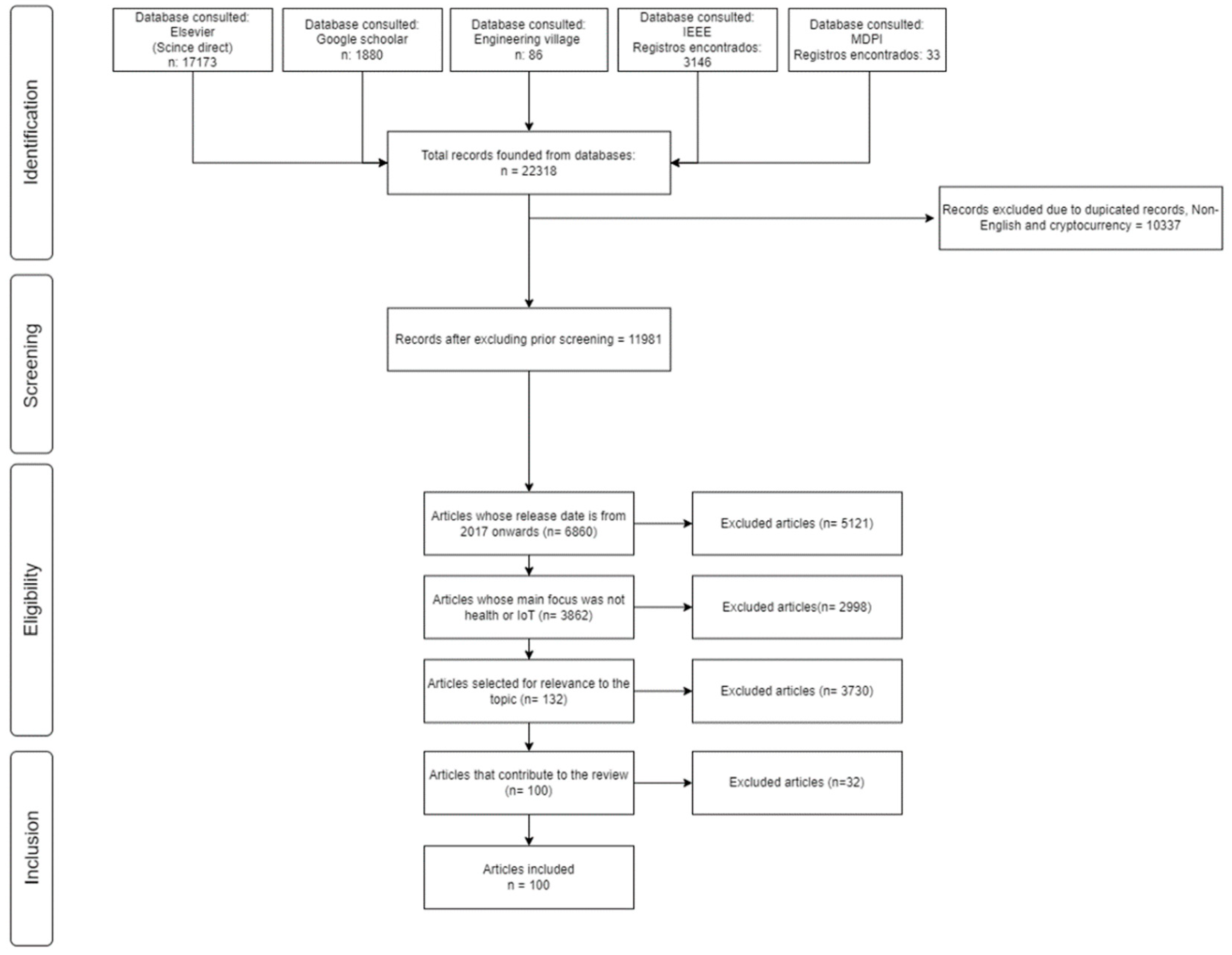
2.1. PRISMA
2.1.1. Why PRISMA?
- Reduction of Bias: PRISMA includes guidelines that aim to reduce bias in systematic reviews. Transparent reporting helps readers assess the risk of bias in the included studies, leading to a more accurate interpretation of the evidence.
- It enables self-regulated learning by providing systematic search procedures (identification, screening, eligibility, inclusion) via online platforms.
- Serves as a valuable guide for postgraduate students and researchers in conducting comprehensive searches to find necessary papers.
- Aids readers by offering a clear understanding of the process, enabling easy tracking of information sources through systematic review records, and simplifying the evaluation of reported systematic reviews.
- Support for Evidence-Based Practice: PRISMA contributes to the production of high-quality evidence that can be used to inform evidence-based practice, clinical guidelines, and policy decisions.
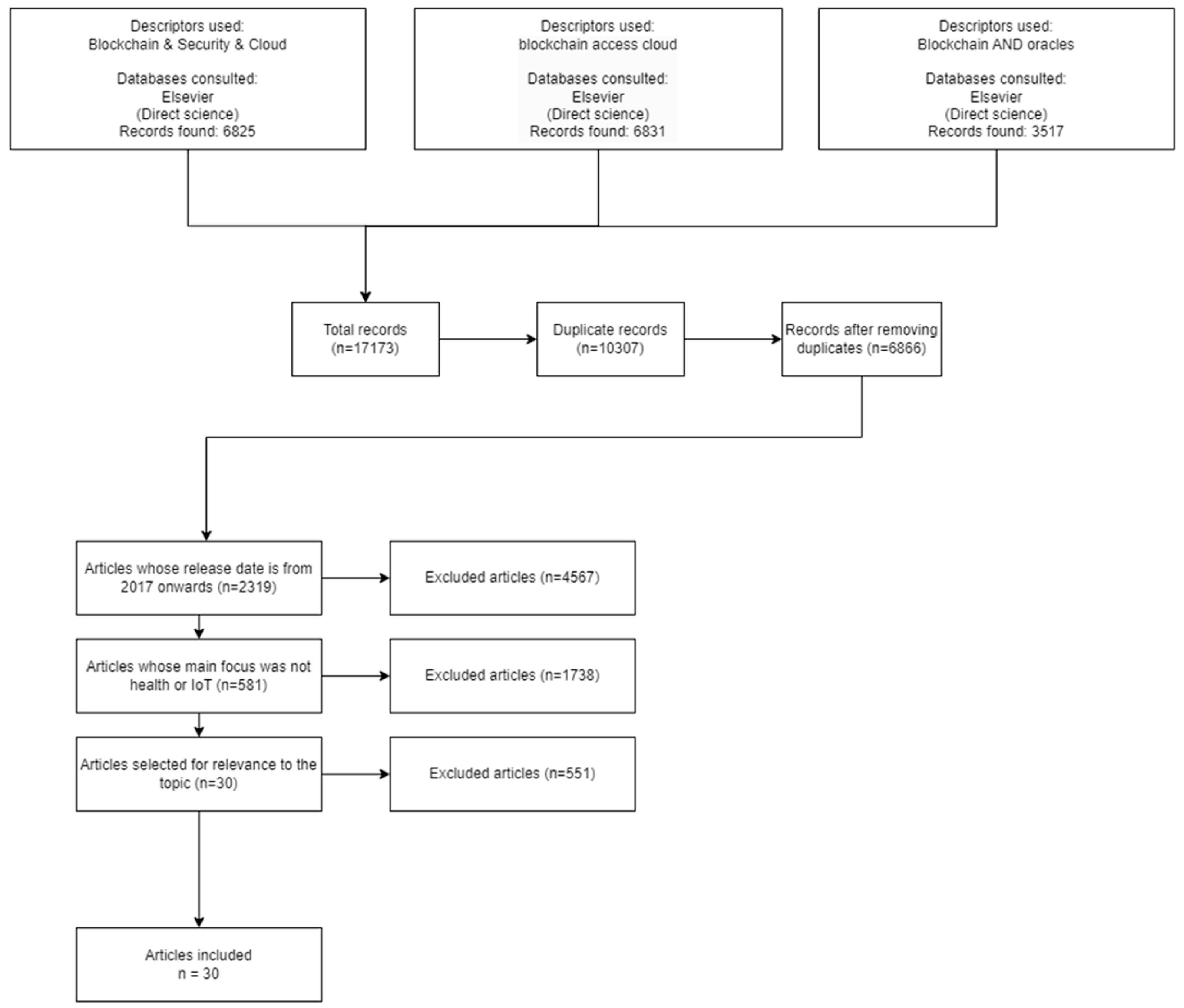
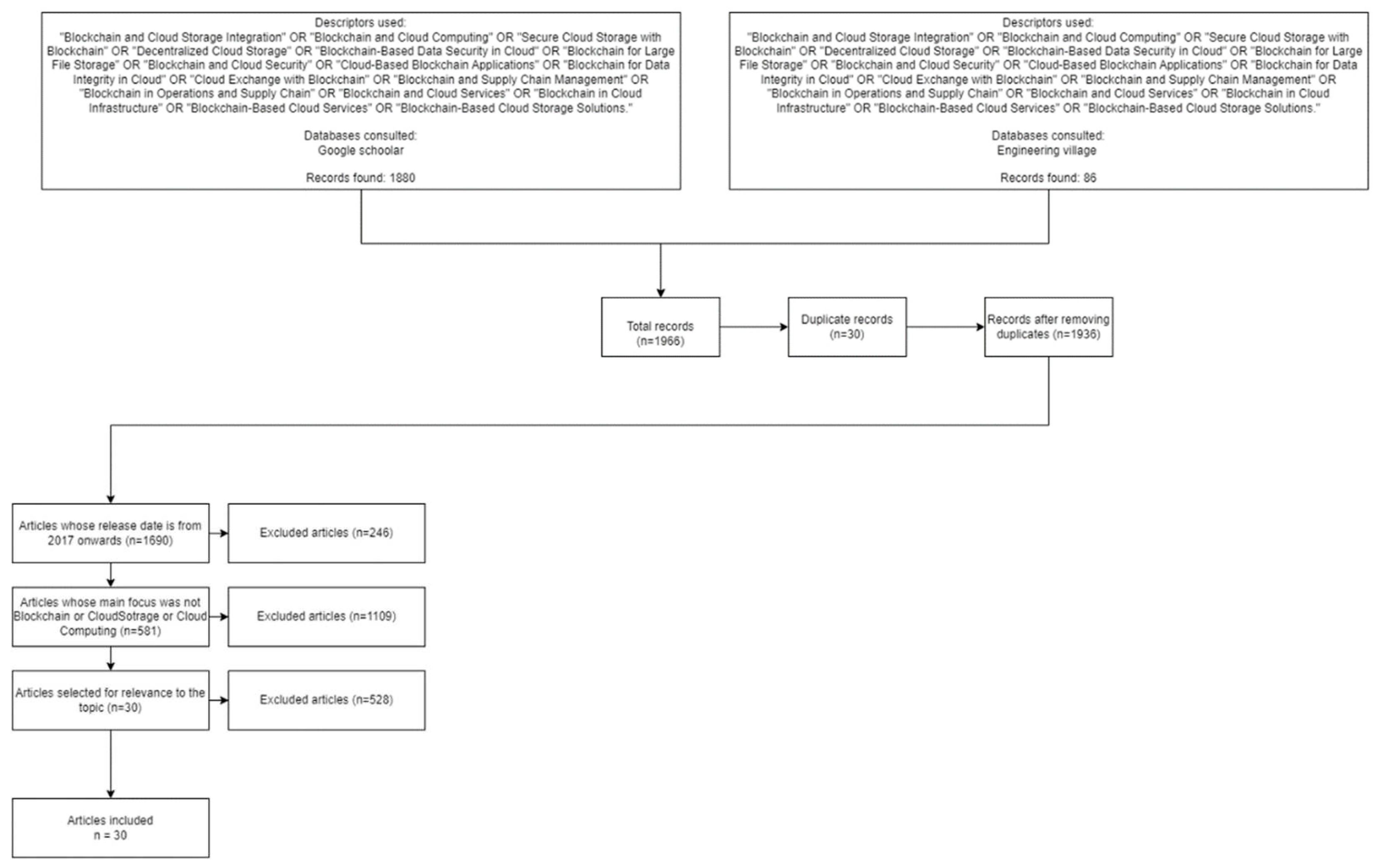
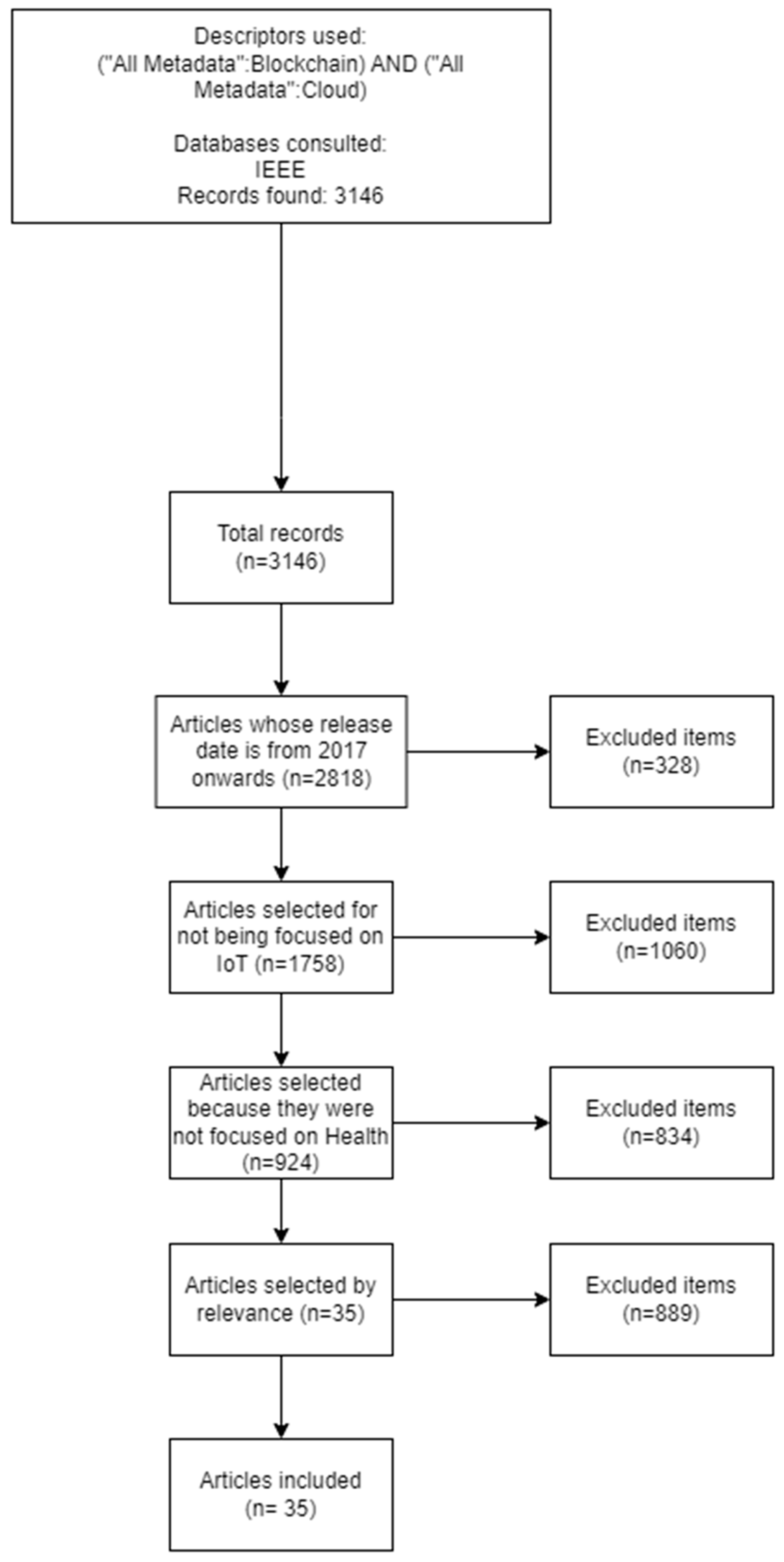
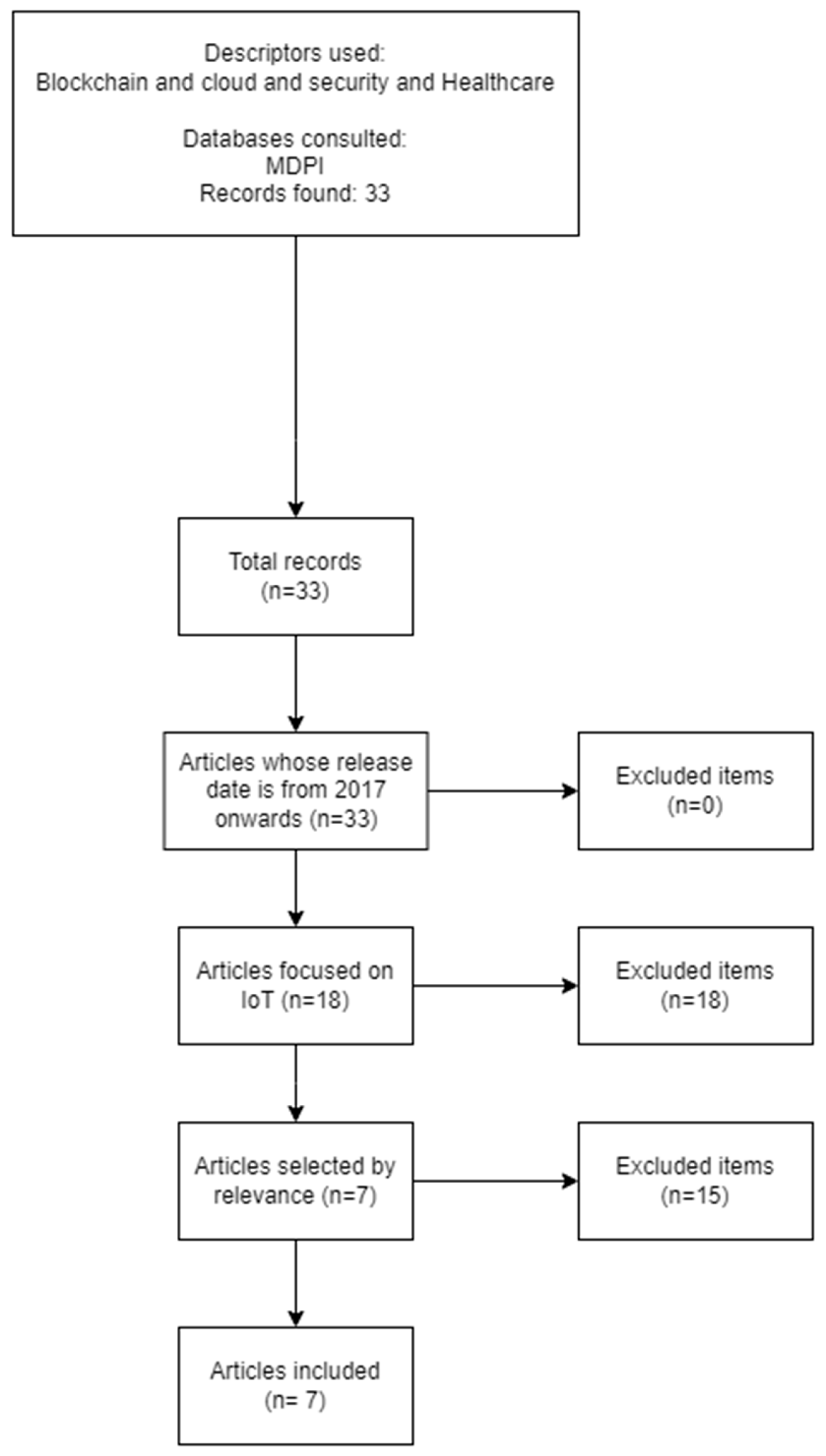
2.2. Search engines and search equations
- "Blockchain and Cloud Storage Integration" OR "Blockchain and Cloud Computing" OR "Secure Cloud Storage with Blockchain" OR "Decentralized Cloud Storage" OR "Blockchain-Based Data Security in Cloud" OR "Blockchain for Large File Storage" OR "Blockchain and Cloud Security" OR "Cloud-Based Blockchain Applications" OR "Blockchain for Data Integrity in Cloud" OR "Cloud Exchange with Blockchain" OR "Blockchain and Supply Chain Management" OR "Blockchain in Operations and Supply Chain" OR "Blockchain and Cloud Services" OR "Blockchain in Cloud Infrastructure" OR "Blockchain-Based Cloud Services" OR "Blockchain-Based Cloud Storage Solutions."
- Blockchain AND Security AND Cloud
- ("All Metadata": Blockchain) AND ("All Metadata": Cloud)
- Blockchain and cloud and security and Healthcare
- Blockchain AND oracles
2.3. Incorporation and Exclusion Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Results based on the proposed reasearch questions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- This comprehensive review highlights the growing interest and importance of integrating blockchain and cloud technologies for securing large healthcare files. The number of relevant publications on this topic has steadily increased since 2017, peaking in 2022, indicating rising scholarly attention. Most examined papers emphasize the need for enhanced security, exploring blockchain's potential to ensure integrity and traceability of medical records, while leveraging the storage capacity and efficiency of the cloud.
- Analysis of the literature reveals pressing challenges that still need to be addressed, including efficiency, scalability, costs, interoperability, quantum computing resistance, and balancing centralization with decentralization. Overcoming these limitations is crucial for fully realizing the potential of blockchain-cloud integration.
- This review serves as a launch pad for scholars and practitioners seeking to further develop the secure convergence of blockchain and cloud computing in healthcare settings. By highlighting accomplishments thus far, and exposing knowledge gaps, it provides a foundation to build upon through continued exploration of this promising integration.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- S. Bhari and S. J. Quraishi, “Blockchain and Cloud Computing-A Review,” in 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing, COM-IT-CON 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Taherdoost, “Blockchain and Healthcare: A Critical Analysis of Progress and Challenges in the Last Five Years,” Blockchains 2023, Vol. 1, Pages 73-89, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 73–89, Nov. 2023. 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Doshi and S. Khara, “Blockchain-Based Decentralized Cloud Storage,” in EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. Pise and S. Patil, “Enhancing Security of Data in Cloud Storage using Decentralized Blockchain,” in 2021 Third International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), IEEE, Feb. 2021, pp. 161–167. [CrossRef]
- E. F. Coutinho, Di. E. Paulo, A. W. Abreu, and I. M. B. Carla, “Towards Cloud Computing and Blockchain Integrated Applications,” in Proceedings - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture Companion, ICSA-C 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Gai, J. Guo, L. Zhu, and S. Yu, “Blockchain Meets Cloud Computing: A Survey,” IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, vol. 22, no. 3, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Han, S. Fei, Z. Yan, and X. Zhou, “A survey on blockchain-based integrity auditing for cloud data,” Digital Communications and Networks, vol. 8, no. 5, 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. Alromaihi, Y. Ismail, and W. Elmedany, “Literature Review of Blockchain-based Cloud Computing: Data Security Issues and Challenges,” in 2022 International Conference on Data Analytics for Business and Industry, ICDABI 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Xie, Z. Zheng, W. Chen, J. Wu, H. N. Dai, and M. Imran, “Blockchain for cloud exchange: A survey,” Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 81, 2020,. [CrossRef]
- S. G. Sharma, L. Ahuja, and D. P. Goyal, “Building Secure Infrastructure for Cloud Computing Using Blockchain,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems, ICICCS 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tang et al., “ChainFS: Blockchain-Secured Cloud Storage,” in IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing, CLOUD, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Zang and J. Kim, “A Comprehensive Study on Blockchain-based Cloud-Native Storage for Data Confidence,” in International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks, ICUFN, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Wan et al., “Smart Contract Service Optimization in Blockchain-Cloud Collaborative Computing,” in Proceedings - IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Xu, S. Liu, D. Yu, X. Cheng, S. Guo, and J. Yu, “CloudChain: A Cloud Blockchain Using Shared Memory Consensus and RDMA,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. 71, no. 12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Meng, L. Luo, P. Sun, and Y. Gao, “Reliability Service Assurance in Public Clouds based on Blockchain,” in Proceedings - Companion of the 2020 IEEE 20th International Conference on Software Quality, Reliability, and Security, QRS-C 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Tapas, G. Merlino, F. Longo, and A. Puliafito, “Blockchain-based publicly verifiable cloud storage,” in Proceedings - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing, SMARTCOMP 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Dorsala, V. N. Sastry, and S. Chapram, “Blockchain-based solutions for cloud computing: A survey,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 196. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhu, Y. Wang, X. Hei, W. Ji, and L. Zhang, “A blockchain-based decentralized cloud resource scheduling architecture,” in Proceedings - 2018 International Conference on Networking and Network Applications, NaNA 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- V. Reantongcome, V. Visoottiviseth, W. Sawangphol, A. Khurat, S. Kashihara, and D. Fall, “Securing and Trustworthy Blockchain-based Multi-Tenant Cloud Computing,” in ISCAIE 2020 - IEEE 10th Symposium on Computer Applications and Industrial Electronics, 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Xi, J. Liu, Y. Li, and B. Qin, “Decentralized access control for secure microservices cooperation with blockchain,” ISA Trans, vol. 141, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Duan, W. Xu, W. Ni, and W. Wang, “BSAF: A blockchain-based secure access framework with privacy protection for cloud-device service collaborations,” Journal of Systems Architecture, vol. 140, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zheng, S. Xie, H. Dai, X. Chen, and H. Wang, “An Overview of Blockchain Technology: Architecture, Consensus, and Future Trends,” in Proceedings - 2017 IEEE 6th International Congress on Big Data, BigData Congress 2017, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Hasan, K. Ogan, and B. Starly, “Hybrid blockchain architecture for Cloud Manufacturing-as-a-service (CMaaS) platforms with improved data storage and transaction efficiency,” in Procedia Manufacturing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. I. Alzoubi and A. Mishra, “Green blockchain – A move towards sustainability,” J Clean Prod, vol. 430, p. 139541, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Sharma, S. Sharma, and T. Choudhury, “A Study And Analysis Of Decentralized Cloud Based Platform,” in Proceedings of the Confluence 2022 - 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science and Engineering, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Yang, L. Lei, and H. Zhu, “Overview of Blockchain and Cloud Service Integration,” in Proceedings - 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud, IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing, and IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data and Security, BigDataSecurity/HPSC/IDS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Zou, D. He, S. Zeadally, N. Kumar, H. Wang, and K. R. Choo, “Integrated Blockchain and Cloud Computing Systems: A Systematic Survey, Solutions, and Challenges,” ACM Computing Surveys, vol. 54, no. 8. 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Wilczyński and J. Kołodziej, “Modelling and simulation of security-aware task scheduling in cloud computing based on Blockchain technology,” Simul Model Pract Theory, vol. 99, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Ahmad and G. S. Aujla, “GDPR compliance verification through a user-centric blockchain approach in multi-cloud environment,” Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 109, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. N. Prasad and C. Rekha, “Block chain based IAS protocol to enhance security and privacy in cloud computing,” Measurement: Sensors, vol. 28, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Aljaloud and A. Razzaq, “Modernizing the Legacy Healthcare System to Decentralize Platform Using Blockchain Technology,” Technologies (Basel), vol. 11, no. 4, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. K. Lo, X. Xu, M. Staples, and L. Yao, “Reliability analysis for blockchain oracles,” Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 83, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Taghavi, J. Bentahar, H. Otrok, and K. Bakhtiyari, “A reinforcement learning model for the reliability of blockchain oracles,” Expert Syst Appl, vol. 214, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Hassan, I. Makhdoom, W. Iqbal, A. Ahmad, and A. Raza, “From trust to truth: Advancements in mitigating the Blockchain Oracle problem,” Journal of Network and Computer Applications, vol. 217. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. Kochovski, S. Gec, V. Stankovski, M. Bajec, and P. D. Drobintsev, “Trust management in a blockchain based fog computing platform with trustless smart oracles,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 101, 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Gupta, R. Gupta, D. Jadav, S. Tanwar, N. Kumar, and M. Shabaz, “Proxy smart contracts for zero trust architecture implementation in Decentralised Oracle Networks based applications,” Comput Commun, vol. 206, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. H. Y. Chung, D. Li, and P. Adriaens, “Technology-enabled financing of sustainable infrastructure: A case for blockchains and decentralized oracle networks,” Technol Forecast Soc Change, vol. 187, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Berdik, S. Otoum, N. Schmidt, D. Porter, and Y. Jararweh, “A Survey on Blockchain for Information Systems Management and Security,” Inf Process Manag, vol. 58, no. 1, p. 102397, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. J. Page et al., “Declaración PRISMA 2020: una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas,” Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition), vol. 74, no. 9, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Seenivasan, V. Krishnasamy, and S. S. Muppudathi, “Data division using Fuzzy Logic and Blockchain for data security in cyber space,” in Procedia Computer Science, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Dai, Y. Shi, N. Meng, L. Wei, and Z. Ye, “From Bitcoin to cybersecurity: A comparative study of blockchain application and security issues,” in 2017 4th International Conference on Systems and Informatics, ICSAI 2017, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, Y. Chen, Y. Huang, and X. Li, “Protecting personal sensitive data security in the cloud with blockchain,” in Advances in Computers, vol. 120, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Che, Y. Duan, T. Zhang, and J. Fan, “Study on the security models and strategies of cloud computing,” in Procedia Engineering, 2011. [CrossRef]
- N. Nahar, F. Hasin, and K. A. Taher, “Application of Blockchain for the Security of Decentralized Cloud Computing,” in 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development, ICICT4SD 2021 - Proceedings, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Meenakshi, B. Bharathi, S. J. J. Thangaraj, and S. Sivasubramanian, “Cloud Security Analysis using Blockchain Technology,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Edge Computing and Applications, ICECAA 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Ren, G. Xu, H. Qi, and T. Zhang, “PriFR: Privacy-preserving Large-scale File Retrieval System via Blockchain for Encrypted Cloud Data,” in Proceedings - 2023 IEEE 9th International Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud, IEEE International Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing, and IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data and Security, BigDataSecurity-HPSC-IDS 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Gaba, I. Budhiraja, A. Makkar, and D. Garg, “Machine Learning for Detecting Security Attacks on Blockchain using Software Defined Networking,” in 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops, ICC Workshops 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Cai and J. Qu, “Systematic Research on Information Security Based on Blockchain Technology,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronics and Renewable Systems, ICEARS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gong-Guo and Z. Wan, “Blockchain-based IoT security authentication system,” in Proceedings - 2021 International Conference on Computer, Blockchain and Financial Development, CBFD 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, A. Badshah, S. Tu, and M. Waqas, “Blockchain Boundary Security Protection based on Trusted Computing,” in Proceedings - 2021 2nd Asia Symposium on Signal Processing, ASSP 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Fartitchou, H. El Marraki, L. Lafkir, A. Azzouz, K. El Makkaoui, and Z. El Allali, “Public-Key Cryptography behind Blockchain Security,” in Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Networking, Information Systems and Security: Envisage Intelligent Systems in 5G/6G-Based Interconnected Digital Worlds, NISS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. R. Vidal, N. Ivaki, and N. Laranjeiro, “Advancing Blockchain Security: from Vulnerability Detection to Transaction Revocation,” in Proceedings - 53rd Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks - Supplemental Volume, DSN-S 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. H. Bai and L. H. Liu, “Research on Software Defined Network Security Model Based on Blockchain,” in 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, ICSP 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Sharma and K. Shah, “Exploring Security Threats on Blockchain Technology along with possible Remedies,” in 2022 IEEE 7th International conference for Convergence in Technology, I2CT 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- I. Hammouti, A. Addaim, and Z. Guennoun, “Proposed Architecture of Cyber Security in Smart Grids, Blockchain as Solution,” in 2022 IEEE Information Technologies and Smart Industrial Systems, ITSIS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. J. Kim, P. Lingga, J. P. Jeong, Y. Choi, and J. Park, “A Web-Based Monitoring System of Network Security Functions in Blockchain-Based Cloud Security Systems,” in International Conference on Information Networking, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Tiwari, V. Agarwal, Y. Aggarwal, and U. Srivastava, “Server Security in Cloud Computing Using Blockchain,” in 8th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems, ICACCS 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Harshavardhan, T. Vijayakumar, and S. R. Mugunthan, “Blockchain technology in cloud computing to overcome security vulnerabilities,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on I‐SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud), I‐SMAC 2018, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Ahmed, A. F. M. S. Akhter, A. N. M. B. Rashid, and A. S. K. Pathan, “A dependable and secure consensus algorithm for blockchain assisted microservice architecture,” Computers and Electrical Engineering, vol. 109, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, L. Xiong, F. Li, X. Niu, and H. Wu, “A blockchain-based privacy-preserving auditable authentication scheme with hierarchical access control for mobile cloud computing,” Journal of Systems Architecture, vol. 142, 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. J. Samuel Babu and M. Baskar, “Application of blockchain methodology in secure task scheduling in cloud environment,” Advances in Engineering Software, vol. 172. 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. Eltayieb, R. Elhabob, A. Hassan, and F. Li, “A blockchain-based attribute-based signcryption scheme to secure data sharing in the cloud,” Journal of Systems Architecture, vol. 102, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Kumar and A. K. Singh, “Distributed Intrusion Detection System using Blockchain and Cloud Computing Infrastructure,” in Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics, ICOEI 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Shah, M. Shaikh, V. Mishra, and G. Tuscano, “Decentralized Cloud Storage Using Blockchain,” in 2020 4th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI)(48184), IEEE, Jun. 2020, pp. 384–389. [CrossRef]
- L. Huang and H. H. Lee, “A Medical Data Privacy Protection Scheme Based on Blockchain and Cloud Computing,” Wirel Commun Mob Comput, vol. 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Qi et al., “Blockchain based Consensus Checking in Cloud Storage,” in Proceedings - 2019 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Autonomous Decentralized Systems, ISADS 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Mechkaroska, A. Popovska-Mitrovikj, and S. Mitrevska, “Overview of Blockchain and Cloud Computing Services Integration,” in 2022 30th Telecommunications Forum, TELFOR 2022 - Proceedings, 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu, “Research on University Book Sharing Cloud Platform Based on Blockchain,” in ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. A. D. S. N. Wijesekara and S. Gunawardena, “A Review of Blockchain Technology in Knowledge-Defined Networking, Its Application, Benefits, and Challenges,” Network, vol. 3, no. 3. 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. Praveena Anjelin and S. Ganesh Kumar, “Blockchain Technology for Data Sharing in Decentralized Storage System,” in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Soares, R. Saraiva, I. Fernandes, A. Neto, and J. Souza, “A Blockchain-based Customizable Document Registration Service for Third Parties,” in IEEE International Conference on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency, ICBC 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Fitwi, Y. Chen, and S. Zhu, “A lightweight blockchain-based privacy protection for smart surveillance at the edge,” in Proceedings - 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Blockchain, Blockchain 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yang, M. Hu, Y. Cheng, X. Liu, and W. Ma, “Keyword Searchable Encryption Scheme based on Blockchain in Cloud Environment,” in Proceedings - 2020 3rd International Conference on Smart BlockChain, SmartBlock 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Uthayashangar, T. Dhanya, S. Dharshini, and R. Gayathri, “Decentralized Blockchain Based System for Secure Data Storage in Cloud,” in 2021 International Conference on System, Computation, Automation and Networking, ICSCAN 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Spoorti, R. Sneha, V. Soujanya, K. Heena, S. Pooja, and D. G. Narayan, “Secure Access Control to Cloud Resources using Blockchain,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics, DISCOVER 2021 - Proceedings, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Mendki, “Securing Cloud Native Applications Using Blockchain,” in 2021 12th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems, ICICS 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Lahoti and D. Singh, “Blockchain Technology Based Secure Data Sharing in Cloud Computing,” in IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Communication Systems, ICKES 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, “Development of Cloud Information Platform based on Blockchain Public Service Platform,” in 6th International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud), I-SMAC 2022 - Proceedings, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Yao et al., “Blockchain-Empowered Collaborative Task Offloading for Cloud-Edge-Device Computing,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 40, no. 12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. H. Chee and M. E. Rana, “An Exploratory Study on the Impact of Hosting Blockchain Applications in Cloud Infrastructures,” in 2023 15th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), IEEE, Jan. 2023, pp. 381–386. [CrossRef]
- X. Thipphonexai and Y. Guanghui, “Research on analysis and design of cloud ERP based on blockchain technology,” in Proceedings - 2020 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Intelligent Systems, ICVRIS 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Q. Xia, E. B. Sifah, A. Smahi, S. Amofa, and X. Zhang, “BBDS: Blockchain-based data sharing for electronic medical records in cloud environments,” Information (Switzerland), vol. 8, no. 2, 2017. [CrossRef]
- E. Bacis, S. De Capitani Di Vimercati, S. Foresti, S. Paraboschi, M. Rosa, and P. Samarati, “Securing Resources in Decentralized Cloud Storage,” IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, vol. 15, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Karuppasamy and V. Vasudevan, “Security Management in Decentralized Cloud Storage via Improved Bees Swarm Optimisation Data Slicers,” in International Conference on Edge Computing and Applications, ICECAA 2022 - Proceedings, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Bacis, S. De Capitani DI Vimercati, S. Foresti, S. Paraboschi, M. Rosa, and P. Samarati, “Dynamic allocation for resource protection in decentralized cloud storage,” in 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference, GLOBECOM 2019 - Proceedings, 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. Karuppasamy and V. Vasudevan, “A novel double keys adapted elliptic curve cryptography and log normalized Gaussian sigmoid adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system based secure resource allocation system in decentralized cloud storage,” Expert Syst, vol. 40, no. 4, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. V. Doan, Y. Psaras, J. Ott, and V. Bajpai, “Toward Decentralized Cloud Storage With IPFS: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Considerations,” IEEE Internet Comput, vol. 26, no. 6, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Khatiwada and B. Yang, “An access control and authentication scheme for secure data sharing in the decentralized cloud storage system,” in 5th Conference on Cloud and Internet of Things, CIoT 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Golightly, P. L. Golightly, P. Modesti, R. Garcia, and V. Chang, “Securing distributed systems: A survey on access control techniques for cloud, blockchain, IoT and SDN,” Cyber Security and Applications, vol. 1. 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Baranwal, D. Kumar, and D. P. Vidyarthi, “Blockchain based resource allocation in cloud and distributed edge computing: A survey,” Computer Communications, vol. 209. 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. Tarannum and S. Abidin, “Integration of Blockchain and Cloud Computing: A Review,” in Proceedings of the 17th INDIACom; 2023 10th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, INDIACom 2023, 2023.
- T. Feng and Y. Liu, “Research on PoW Protocol Security under Optimized Long Delay Attack,” Cryptography, vol. 7, no. 2, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Kim, S. Yu, J. Lee, Y. Park, and Y. Park, “Design of secure protocol for cloud-assisted electronic health record system using blockchain,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. 20, no. 10, 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Taherdoost, “Blockchain and Healthcare: A Critical Analysis of Progress and Challenges in the Last Five Years,” Blockchains 2023, Vol. 1, Pages 73-89, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 73–89, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
| Papers included | Papers excluded |
|---|---|
| Papers must talk about Blockchain and cloud integration. Papers that mention ways of securely connect cloud with blockchain and show the process. Review papers that help the purpose and objective of this paper. |
Papers that focus on cryptocurrencies or its focus is Internet of Things. Papers published before 2017 Papers that proposed storing the chain in cloud. |
| Years | Number of papers |
|---|---|
| 2017 | 4 |
| 2018 | 4 |
| 2019 | 10 |
| 2020 | 20 |
| 2021 | 16 |
| 2022 | 23 |
| 2023 | 24 |
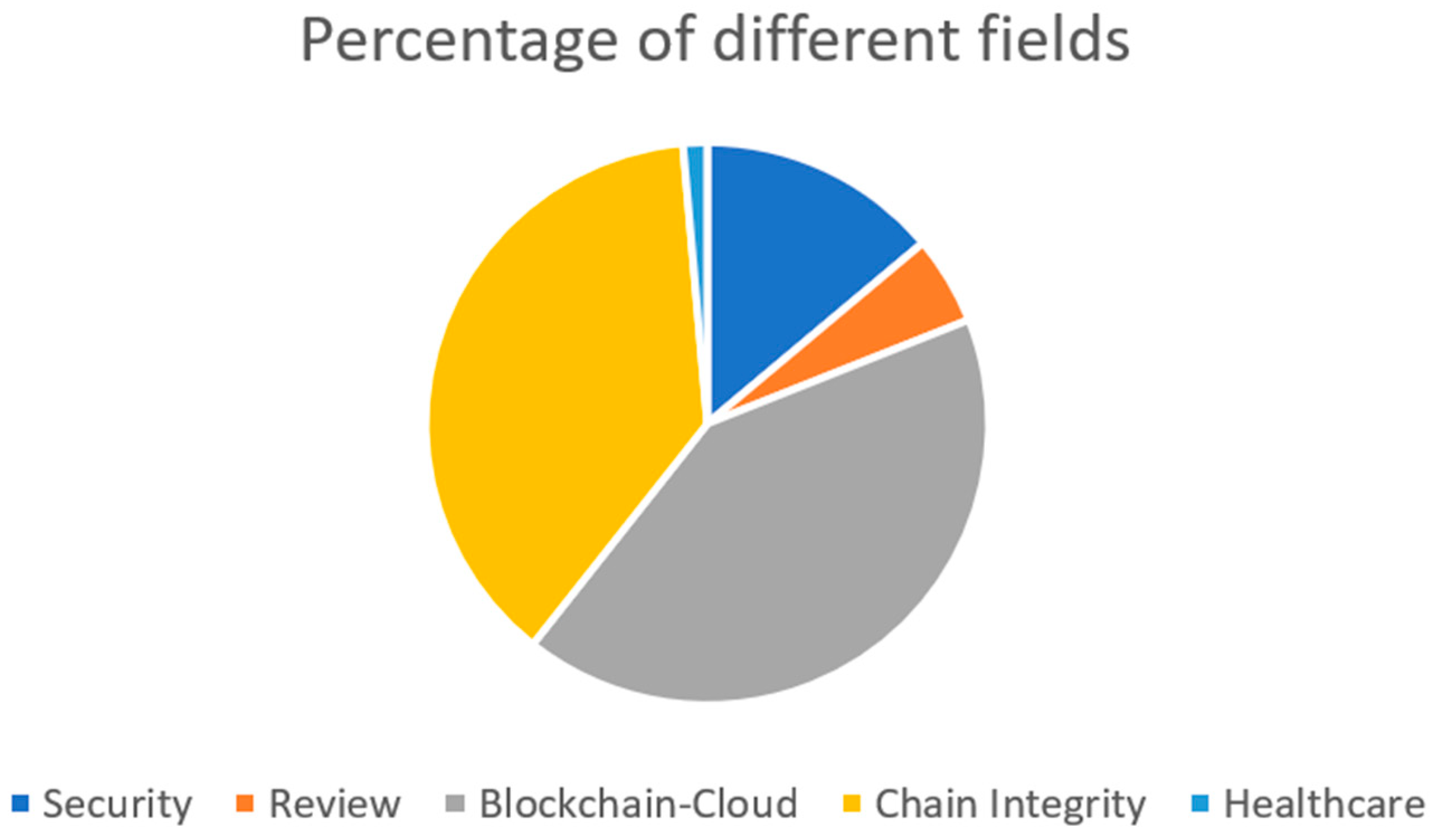
| Work | Security | Review/ Survey |
Blockchain-Cloud | Chain Integrity |
Healthcare |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [40,41] | X | X | X | X | |
| [4,15,26,28,30,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58] | X | X | X | ||
| [3,5,10,11,12,13,14,16,18,19,20,21,22,23,29,32,33,34,35,37,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82] | X | X | |||
| [43,83,84] | X | X | |||
| [25,85,86,87,88] | X | ||||
| [1,6,7,9,17,27,89,90,91] | X | X | X | ||
| [92] | X | ||||
| [10,58] | X | X | X |
| Work | Title | Area of focus | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| [91] | Integration of Block-chain and Cloud Computing: A Review. | Blockchain, Cloud Compu-ting and security. | Explores the rising use of block-chain for enhancing cloud data security across various sectors. Suggests integrating blockchain to ad-dress vulnerabilities in centralized cloud computing systems. The focus is on reviewing the benefits and applications of cloud-based blockchain services, emphasizing current trends and security challenges. |
| [1] | Blockchain and Cloud Computing-A Review | Blockchain and Cloud Compu-ting | Examine literature on blockchain-based enterprise solutions from 2008 to 2021. It explores three categories: Blockchain using IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, discussing characteristics and their relation to cloud services. The study investigates cutting-edge applications in ledger storage, strategy creation, computation, data aggregation, micro-services, and extraction. The report concludes with current issues, expected obstacles, and potential opportunities in blockchain-based cloud technology, aiming to contribute to a comprehensive understanding and the future development of cloud computing environments. |
| [8] | Literature Review of Blockchain-based Cloud Computing: Data Security Issues and Challenges | Blockchain, Cloud Compu-ting, Security Is-sues and Challenges | This paper highlights the growing acceptance of cloud computing for handling IT infrastructure and data services efficiently. Also, explores how blockchain technology, known for its incorruptible nature, can address security issues in cloud applications. As well the paper emphasizes the importance of security in realizing the benefits of both cloud computing and block-chain. It proposes a literature review to examine how academics utilize blockchain to enhance cloud data security. |
| [8] | Blockchain Technology Application in Security: A Systematic Review | Blockchain, Cloud Com-putting and security. | The study focuses on categorizing blockchain types, consensus mechanisms, smart contract usage, and integration with other software-based algorithms. The authors emphasize the increasing popularity of blockchain beyond digital currencies, particularly in securing networks. The systematic review identifies the Internet of Things (IoT) as the primary field where blockchain enhances security. |
| Work | Title | Contribution(s) |
|---|---|---|
| [2] | A Critical Analysis of Progress and Challenges in the Last Five Years | The paper significantly contributes by objectively evaluating the impact of blockchain technology in the healthcare sector, drawing insights from a thorough analysis of 124 papers published by MDPI over the past five years. Its noteworthy identification of advancements, such as improved data security and interoperability, adds depth to our understanding of blockchain's positive influence on healthcare. |
| [31] | A. Modernizing the Legacy Healthcare System to Decentralize Platform Using Blockchain Technology. | The authors aim to address challenges related to complex medical procedures, large-scale medical data management, and cost optimization. The paper reviews existing literature and proposes workflows for better data management, implemented using the Ethereum blockchain platform. The feasibility of the proposed system is analyzed in terms of associated costs, and a model-driven engineering approach is used to recover the architecture of traditional healthcare systems. |
| [93] | Design of Secure Protocol for Cloud-Assisted Electronic Health Record System Using Blockchain | Addresses the challenges of electronic health record (EHR) management in traditional systems and proposes a secure protocol using blockchain and cloud computing. The authors highlight the potential of blockchain technology to enable sharing of EHRs across various medical service centers, promoting decentralization and data integrity. However, the integration of cloud computing into the EHR system introduces security vulnerabilities, as sensitive data is transmitted over public channels. The proposed secure protocol aims to address these challenges by using blockchain for data integrity and access control, while the cloud server manages and stores patient EHRs securely. Elliptic curve cryptosystems (ECC) are employed for secure health data sharing within the cloud computing environment. |
| Work | Title | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| [27] | Integrated Blockchain and Cloud Computing Systems: A Systematic Survey, Solutions, and Challenges | Cloud computing introduces new security challenges in secure service management and control, privacy protection, data integrity protection in distributed databases, data backup, and synchronization. Blockchain can be leveraged to address these challenges, partly due to the underlying characteristics such as transparency, traceability, decentralization, security, immutability, and automation. Also, the team explores how cloud computing can affect blockchain, especially about the performance improvements that cloud computing can provide for the blockchain. |
| [87] | Toward Decentralized Cloud Storage With IPFS: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Considerations | Content availability: IPFS relies on peers to host content, which can lead to content unavailability if the peers hosting the content go offline. Content discovery: IPFS uses content addressing to locate content, which can be challenging when the content is not popular or has not been accessed recently. Content integrity: IPFS does not provide any guarantees about the integrity of the content, which can be compromised if the content is modified by a malicious peer. Content privacy: IPFS does not provide any privacy guarantees, which can lead to privacy violations if the content is accessed by unauthorized parties. Content distribution: IPFS does not provide any mechanisms for incentivizing peers to host content, which can lead to uneven distribution of content. |
| [8] | Literature Review of Blockchain-based Cloud Computing: Data Security Issues and Challenges | Data privacy: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents challenges in ensuring data privacy, as the data is stored in a decentralized manner and is accessible to all nodes in the network. Data integrity: Ensuring data integrity is a challenge in blockchain-based cloud computing, as the data is stored in a decentralized manner and is accessible to all nodes in the network. Scalability: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents scalability challenges, as the number of nodes in the network increases, the time required to reach consensus increases. Interoperability: Interoperability is a challenge in blockchain-based cloud computing, as different blockchains may have different protocols and standards. Regulatory compliance: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents regulatory compliance challenges, as the regulatory framework for blockchain technology is still evolving. |
| [94] | Blockchain and Healthcare: A Critical Analysis of Progress and Challenges in the Last Five Years | Data privacy: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents challenges in ensuring data privacy, as the data is stored in a decentralized manner and is accessible to all nodes in the network. Data integrity: Ensuring data integrity is a challenge in blockchain-based cloud computing, as the data is stored in a decentralized manner and is accessible to all nodes in the network. Scalability: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents scalability challenges, as the number of nodes in the network increases, the time required to reach consensus increases. Interoperability: Interoperability is a challenge in blockchain-based cloud computing, as different blockchains may have different protocols and standards. Regulatory compliance: Blockchain-based cloud computing presents regulatory compliance challenges, as the regulatory framework for blockchain technology is still evolving. |
| [31] | A. Modernizing the Legacy Healthcare System to Decentralize Platform Using Blockchain Technology | Migrated classes: Ensure that the migrated classes are compatible with the blockchain platform. This requires a deep understanding of the blockchain architecture, and the programming languages used to write smart contracts. Patient mobility: When patients move from one hospital to another, their data may be dispersed among multiple hospitals, making it difficult for them to access their medical records. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




