Submitted:
15 February 2024
Posted:
19 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biometrics and extraction of gills and intestines
2.2. Length-weight ratio
2.3. Fulton Condition Index (K)
2.4. Plenitud intestinal
3. Results
3.1. Variation in the amount of MP between males and females
3.2. Variation between the amount of MP in gills and intestines
3.3. Fulton Condition Index (k)
3.4. Intestinal fullness
3.5. Pearson correlation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. United Nations Environment Programme. Marine plastic debris and microplastics–global lessons and research to inspire action and guide policy change. 2016.
- ONU Medio, Ambiente. Plásticos de un solo uso: Una hoja de ruta para la sostenibilidad. In Tecnol. for Enviroment 2018, 227, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Deblonde, T.; Cossu-Leguille, C.; Hartemann, P. Emerging pollutants in wastewater: A review of the literature. Internat. J. of Hygiene and Environm. Health. 2011, 214, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, D.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Pereira, T. Ingestion of microplastics by commercial fish off the Portuguese coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campoy, P.; Beiras, R. Efectos ecológicos de macro-meso y microplásticos, Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2019, 189, 11, 581.
- Ritchie, H.; Sanborska, V.; Roser, M. Plastic pollution. On line: Our World in Data. 2023, 930, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar, J. La contaminación de los ríos y sus efectos en las áreas costeras y el mar. UN. CEPAL. Serie: División de Recursos Naturales e infraestructura. Santiago de Chile. Naciones Unidas. 2002, 50, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-Term Field Measurement of Sorption of Organic Contaminants to Five Types of Plastic Pellets: Implications for Plastic Marine Debris. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 2013, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Chapman, M.G.; Thompson, R.C.; A. Zettler, L.A.; Jambeck, J.; Mallos, N.J. Spatial and temporal patterns of stranded intertidal marine debris: is there a picture of global change? Environ. Sci. Technol, 2015, 49, 7082–7094. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Chang, M.; Wang, L.; Gan, Y.; Liu, J. The ecology of the plastisphere: Microbial composition, function, assembly, and network in the freshwater and seawater ecosystems. Water Research, 2021; 202, 117428. [Google Scholar]
- Thevenon, F.; Carroll, C.; Sousa, J. Plastic debris in the ocean: the characterization of marine plastics and their environmental impacts, situation analysis report. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN. 2014, 52. ISBN: 978-2-8317-1696-1. [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. The plastic in microplastics: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 119, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-López, J.; Bedia-Sánchez, C.M.; Peláez Rodríguez, E.; Viveros-Legorreta, J.L.; Ortiz-Touzet, M.A.; Vázquez-López, H. Ecological Aspects of Dormitator maculatus (Bloch, 1792) in the Alvarado Lagoon, Veracruz, Mexico. Turk. J. of Fishs. and Aquatic Sci., 2019, 20, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitter-Soto, J. Catálogo de los peces continentales de Quintana Roo. Colegio de la Frontera sur, Chetumal, México, 1996, p. 223.
- Lara, J.R.; Arreola, L.A. ; Calderón, I; Camacho; Lanza-Espino; et al., Los Ecosistemas costeros, Insulares y epicontinentales, Capítulo 4. En Capital natural de México. Conocimiento actual de la biodiversidad. CONABIO México. 2018. 1, pp. 109-134.
- Wallace, J.H.; Van Der Elst, R.P. The estuarine fishes of the east coast of South Africa. Ocurrence of juveniles in estuaries Investl. Rep. Oceanogr. Res. Inst, 1975, 42: 1-18.
- Nordlie, F.G. Life-history characteristics of eleotrid fishes of the western hemisphere, and perils of life in a vanishing environment. Rev. Fish Biol. Fisheries, 2012, 22, 189–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-López, R.; Franco-López, H.; Montoya-Mendoza, J.; Corro, F.T.; López, P.N. Características biológicas de la naca Dormitator maculatus en la laguna de Alvarado, Veracruz. Res. X Simp. Intern. Biol. Mar. 1994. 63.
- Winemiller, K.O.; Ponwith, B. Comparative Ecology of eleotrid fishes in Central American coastal streams. Environ. Biol. of fish. 1998, 53, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Editors 2023. FishBase. Base de dates. Version (10/2023). World Wide Web electronic publication. https://www.fishbase.se/search.php.
- Yang, G.; Jian, S.Q.; Cao, H.; Wen, C.; Hu, B.; Peng, M.; Peng, L.; Yuan, J.; Liang, L. Changes in microbiota along the intestine of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Community, interspecific interactions, and functions. Aquaculture, 2019, 498, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, X. , Hu, M.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y. Nanoplastics impair the health of the juvenile large yellow croaker Larimichthys crocea. J. of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 397, 122773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mowat, A.M.; Agace, W.W. Regional specialization within the intestinal immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol, 2014, 14, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X. , Zhang, K., Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Luo, Z.; Wu, C. Sources and distribution of microplastics in China's largest inland lake-Qinghai Lake. Environmental pollution 2018, 235, 899–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y. , Deng, Y., Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y., Geng, J.; Ding L.; Ren, H. Uptake and Accumulation of Polystyrene Microplastics in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) and Toxic Effects in Liver. Environ Sci Technol. 2016, 50, 4054–4060. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, A.N.; Govoni, D.; Árnason, S.H.; Carlsson, P. Microplastic ingestion by fish: Body size, condition factor and gut fullness are not related to the amount of plastics consumed. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F. , Fossi C.; Santillo, D.; Sousa, J.; Ingram, I.; Nadal, A.; Romano, D. Marine litter plastics and microplastics, and their toxic chemicals components: the need for urgent preventive measure. Environ. Sci. Europe, 2018; 30, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ré-Regis, M.C.; Estrada-García, J. Determinación de las fases de desarrollo gonádico de la "Naca" Dormitator maculatus. III Congreso Nacional de Ictiología, Oaxtepec, Morelos. 1992. 24p.
- Salas-Pérez, J.J.; Arenas-Fuentes, V. Winter water mass of the Veracruz Reef System. Atmósfera. 2011, 24, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ory, N.; Chagno, C.; Felix, F.; Fernández, C.; Ferreir, J.L.; Gallardo, C.; Ordóñez, O.G.; Henostroza, A.; Laaz, E.; Mizraji, R. Low prevalence of microplastic contamination in planktivorous fish species from the southeast Pacific Ocean. Mar. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 127, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanalp, M.; Köktürk, M.; Parlak, V.; Ucar, A.; Arslan, G.; Alak, G. A new record for the presence of microplastics in dominant fish species of the Karasu River Erzurum, Turkey. Environ. Sci. and Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 7866–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Experimental development of a new protocol for extraction and characterization of microplastics in fish tissues: First observations in commercial species from Adriatic Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusher, A.; McHugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Marine pollution bulletin, 2013. 67, 1-2, 94-9. [CrossRef]
- Teissier, G. , La Relatión d'allometrie, sa signification statique et Biologique. Biometrics, 1948, 4, 14–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R. Cube law, condition factor and weight-length relationships: history, meta-analysis and recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol.
- Froese, R.; Tsikliras, A.C.; Stergiou, K.I. Editorial Note on Weight–Length Relations of Fishes. Acta Ichthyologica Et Piscatoria, 2011, 41, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, W.E. Computation and interpretation of biological statistics of fish population. J. Fish. Res. Board of Canada. 1975, 191, 1–382. [Google Scholar]
- Waller, C.L.; Griffiths, H.J.; Waluda, C.M.; Thorpe, S.E.; Loaiza, I.; Moreno, B.; Pacherres, O.C.; Hughes, K.A. Microplastics in the Antarctic marine system: an emerging area of research. Sci. of the total environ. 2017, 598, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.L; Hernandez-Milian, G. Microplastic extraction from marine vertebrate digestive tracts regurgitates and scats: A protocol for researchers from all experience levels. Bio-protocol, 2018, 8, 22–e3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koongolla, J.B.; Lin, L.; Pan, Y.F.; Yang, C.P.; Sun, D.R.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Maharana, D.; Huang, J.S.; Li, H.X. Occurrence of microplastics in gastrointestinal tracts and gills of fish from Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Mar. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.E.; Ravikumar, G.; Jeyasanta, K.I. Occurrence of microplastics in fishes from two landing sites in Tuticorin, South east coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgana, S.; Ghigliotti, L.; Estévez-Calvar, N.; Stifanese, R.; Wieckzorek, A.; Doyle, T.; Christiansen, J.S.; Faimali, M.; Garaventa, F. Microplastics in the Arctic: A case study with sub-surface water and fish samples off Northeast Greenland. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242: 1078-1086.
- Ryan, P.G.; De Bruyn, P.N.; Bester, M.N. Regional differences in plastic ingestion among Southern Ocean fur seals and albatrosses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016. 104, 1-2, 207-210.
- Browne, M.A.; Crump, P.; Nive, S.J.; Teuten, E.; Tonkin, A.; Galloway, T. ; Thompson, R; Accumulation of microplastic on shorelines woldwide: sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 2011, 45, 9175–9179. [Google Scholar]
- Gasperi, J.; Dris, R.; Mirande-Bret, C. ; Mandin, C; Langlois, V.; Tassin B. First overview of microplastics in indoor and outdoor air [online]. 2015. Comunication Dans un Congres 15th EuCheMS International Conference on Chemistry and the Environment, Sep 2015 Leipzig, Germany. Available from https://hal-enpc.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01195546.
- Lebreton, L.; van Der Zwet, J.; Damsteeg, J.W.; Slat, B.; Andrad, A.; Reisser, J. River plastic emissions to the world’s oceans. Nature communications, 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Emmerik, T.; Schwarz, A. Plastic debris in rivers. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.B.; Bonner, T.H. Occurrence and amount of microplastic ingested by fishes in watersheds of the Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S. , Sun, D.; Zhou, A.; Xi, S., Xu, G.; Zou, J. Occurrence of Microplastics in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Gills of Fish from Guangdong, South China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 9–981:11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusher, A.; Mchugh, M.; Thompson, R.C. Occurrence of microplastics in the gastrointestinal tract of pelagic and demersal fish from the English Channel. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2013, 67, 1-2, 94-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Deng, H.; Li, B.; Chen, Q.; Pettigrove, V.; Wu, C.; Shi, H. The occurrence of microplastic in specific organs in commercially caught fishes from coast and estuary area of east China. J. of hazardous materials, 2019, 365, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic´, B.; Gökdag, K.; Güven, O.; Emre, Y.; Whitley, E.M.; Kideys, A.E. Virgin microplastics are not causing imminent harm to fish after dietary exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull, 2018, 130:123-131. [CrossRef]
- Boerger, C.M.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, S.L.; Moore, C.J. Plastic ingestion by planktivorous fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Pollut Bull. 2010, 12, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.Y.; Bruce, T.F.; Bridges, W.C.; Klaine, S.J. Responses of Hyalella azteca to acute and chronic microplastic exposures. Environ. Toxicology and Chemistry, 2015, 34, 11–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Zoh, K.D. Occurrence of microplastics in the Han River and riverine fish in South Korea. Sci. of The Total Environ. 2020. 708, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Koongolla, J.B. ; Lin L; Pan Y.F.; Yang C.P., Sun D.R.; Liu S.; Xu X.R.; Maharana D.; Huang J.S.; Li H.X. Occurrence of microplastics in gastrointestinal tracts and gills of fish from Beibu Gulf, South China Sea. Environ. Pollut, 1137. [Google Scholar]
- Dávila-Camacho, C.A. Parámetros reproductivos de Dormitator maculatus (Bloch, 1972) y relación con factores ambientales de la laguna de Alvarado Ver., para proponer aspectos básicos de cultivo. Ph.D. Tesis. Tecnológico Nacional de México/Instituto Tecnológico de Boca del Río. Boca del Río, Veracruz. 2020.
- Foekema, E.M.; De Gruijter, C.; Mergia, M.T.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Murk, A.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Plastic in North Sea Fish. Environ. Sci. & Technol. 2013, 47, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of benzo [a] pyrene from microplastics to Artemia nauplii and further to zebrafish via a trophic food web experiment: CYP1A induction and visual tracking of persistent organic pollutants. Environm. Toxicol. and Chemistry. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liboiron, M.; Liboiron, F.; Wells, E.; Richárd, N.; Zahar, A.; Mather, C.; Bradshaw, H.; Murichi, J. Low plastic ingestion rate in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) from Newfoundland destined for human consumption collected through citizen science methods. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 113, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, A.M.; Morrison, L.; Croot, P.L.; Allcock, A.L.; MacLoughlin, E.; Savard, O.; Brownlow, H.; Doyle, T.K. Frequency of Microplastics in Mesopelagic Fishes from the Northwest Atlantic. Frontiers in Marine Science, Sec. Mar. Pollut. 2018, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foekema, E.M.; De Gruijter, C.; Mergia, M.T.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Murk, A.J.; Koelmans, A.A. Plastic in North Sea Fish. Environ. Sci. & Techn., 2013, 47, 8818–8824. [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan, G.; Purvaja, R.; Anandavelu, I.; Robin, R.S.; Ramesh, R. Accumulation and ecotoxicological risk of weathered polyethylene (wPE) microplastics on green mussel (Perna viridis). Ecotoxicoly and Environmental Safety, 2021; 208, 8818–111765. [Google Scholar]
- Kinnebrew, M.A.; Pamer, E.G. , Innate immune signaling in defense against intestinal microbes. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemes, J.J.; Van Fan, Y.; Tan, R.R.; Jiang, P. Minimising the present and future plastic waste, energy and environmental footprints related to COVID-19. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, D.; Locke, D.C.; Cannone, L.J. Synthetic fibers as indicators of municipal sewage sludge, sludge products, and sewage treatment plant effluents. Water, Air, and Soil Pollut., 1998, 103, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
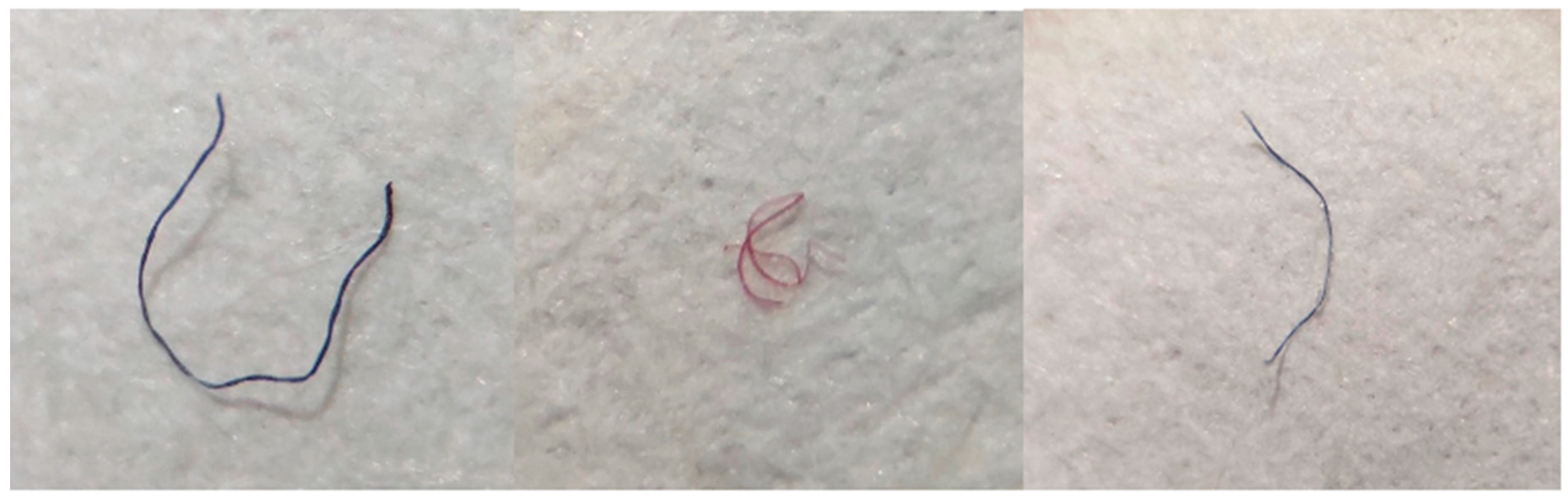

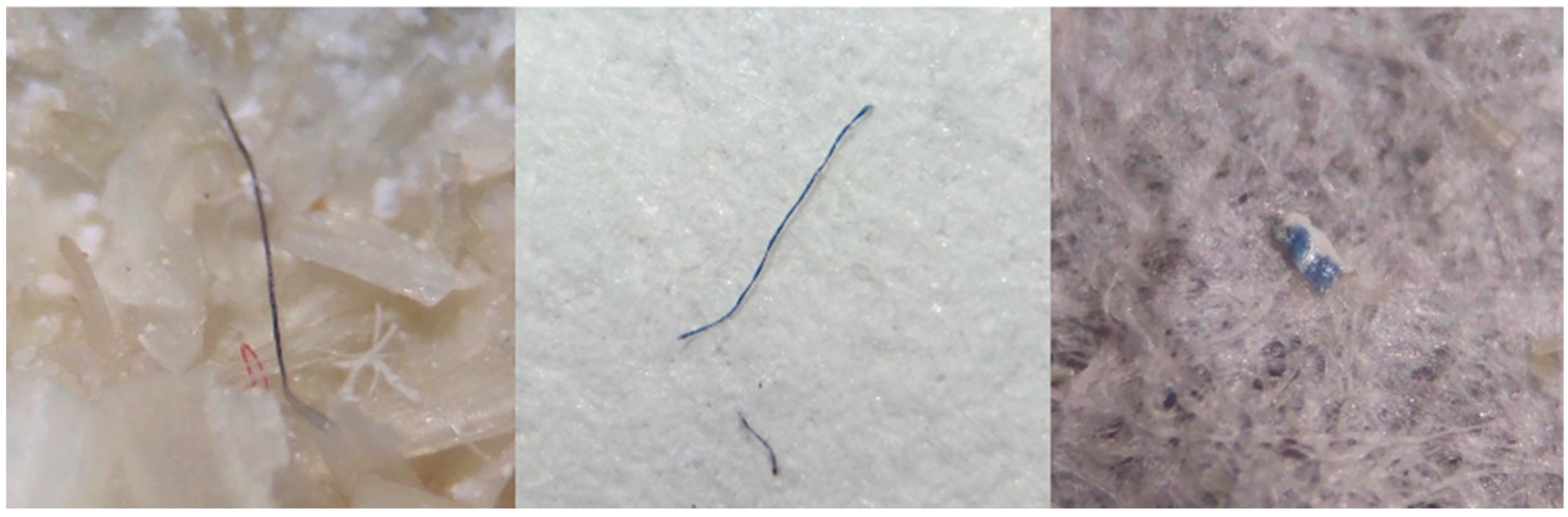
| N:127 | LT | PT | LI | PI | PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 13.79 | 44.51 | 54.87 | 0.19 | 00.17 |
| Minimum | 10.50 | 18.30 | 14.00 | 0.001 | 0.0005 |
| Maximum | 17.60 | 102.00 | 87.00 | 01.87 | 02.02 |
| Forms | digestiv tract | gills | total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibra | 545 | 561 | 1106 | 97.53 |
| Pellet | 9 | 1 | 10 | 00.88 |
| Film | 5 | 8 | 13 | 01.15 |
| Fragment | 2 | 3 | 5 | 00.44 |
| Irregular | 0 | 0 | 0 | 00.00 |
| Total | 561 | 573 | 1134 | 100.0 |
| Color | Intestine | Gills | Total | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | 353 | 351 | 704 | 62.08 |
| Black | 111 | 89 | 200 | 17.64 |
| Red | 28 | 25 | 53 | 04.67 |
| Green | 3 | 6 | 9 | 00.79 |
| Transparent | 51 | 90 | 141 | 12.43 |
| Yellow | 9 | 8 | 17 | 01.50 |
| White | 6 | 4 | 10 | 00.88 |
| Total | 561 | 573 | 1134 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





