Submitted:
26 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NAFLD induction
2.2. Sample collection
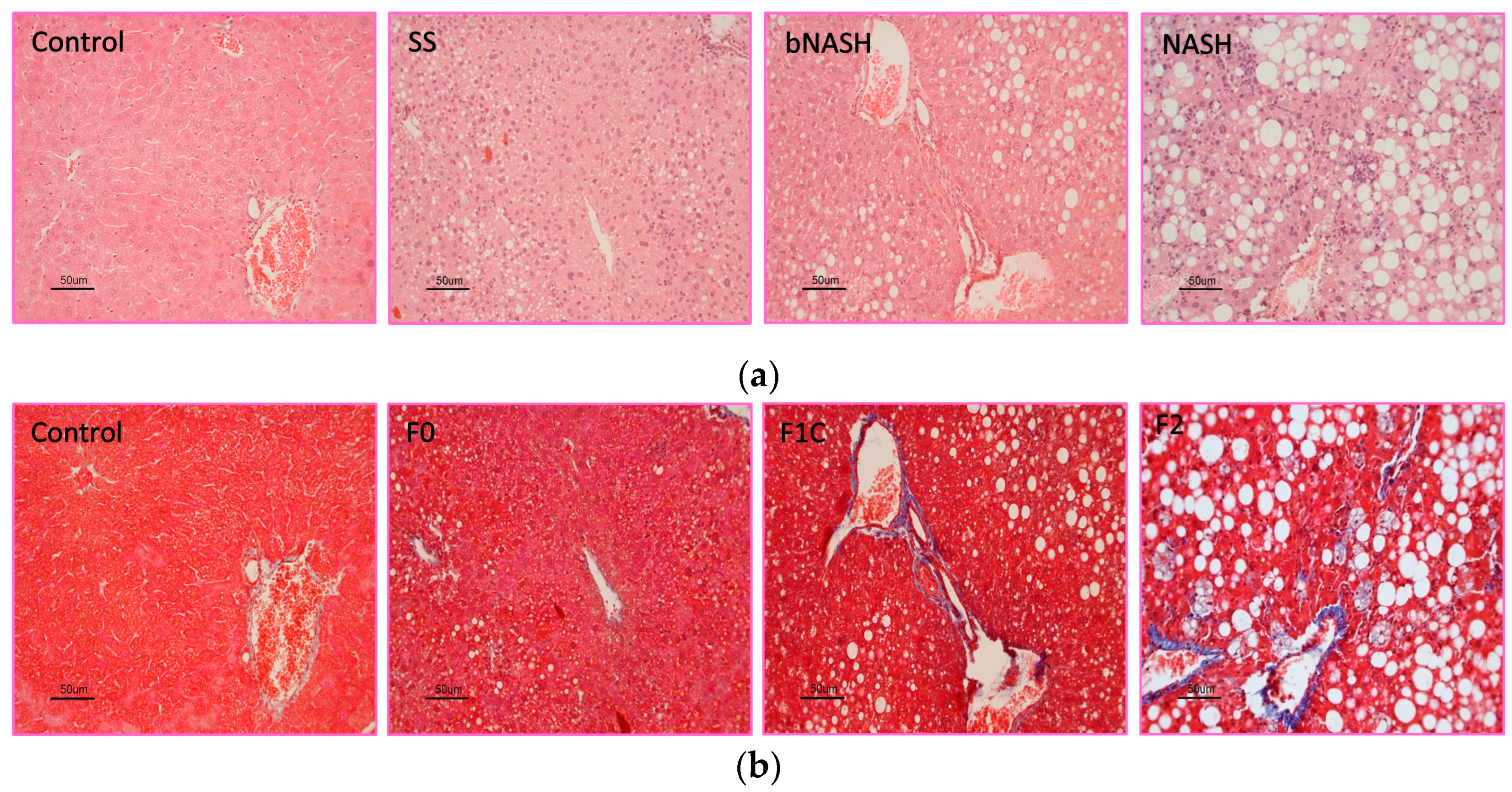
2.3. Histological assessment
2.4. Senescence analysis
2.5. Liver protein isolation
2.6. IGFBP assessment
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Histological classification
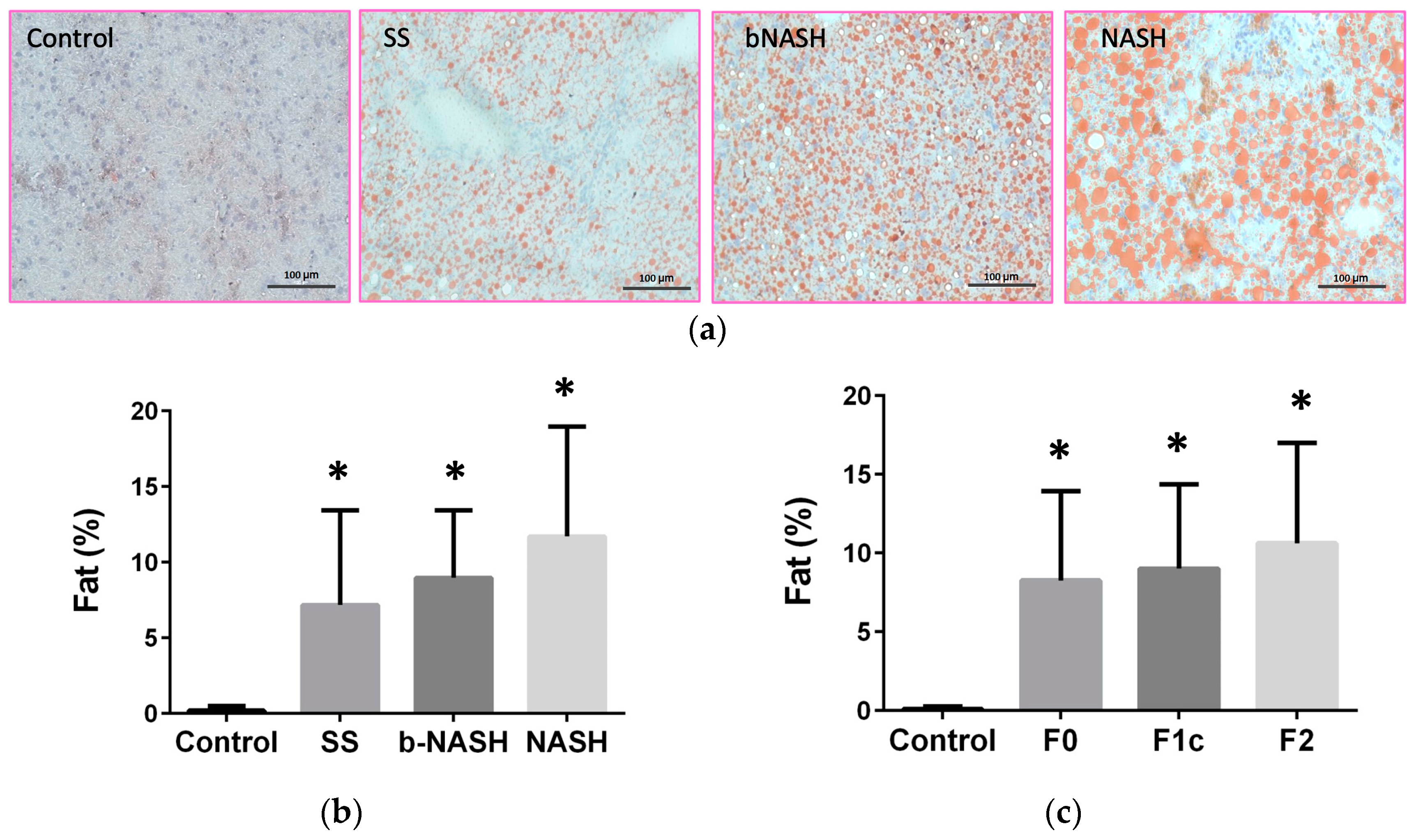
3.2. Liver fat contents
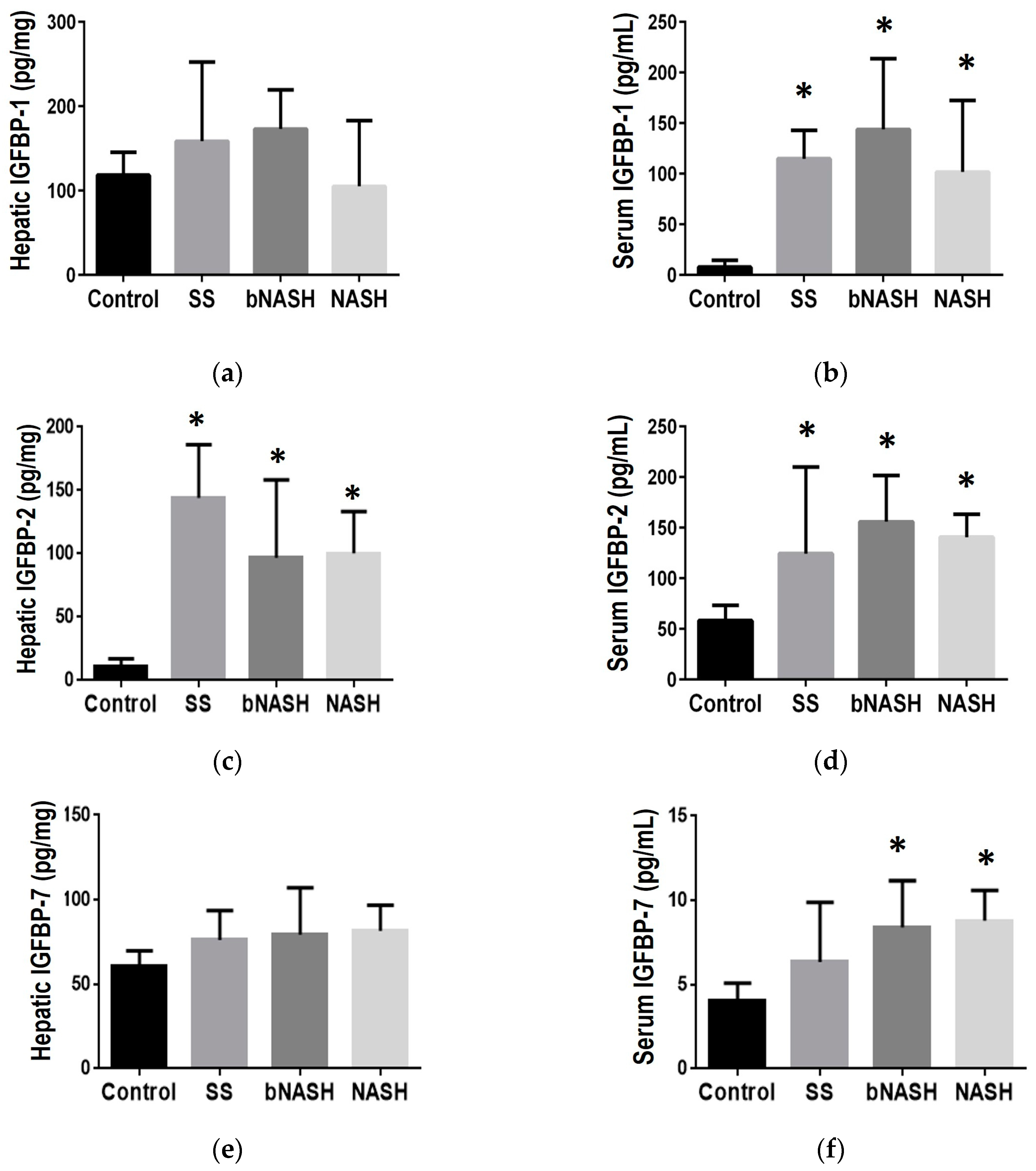
3.3. IGFBP levels in NAFLD
3.3.1. Liver tissue
3.3.2. Serum
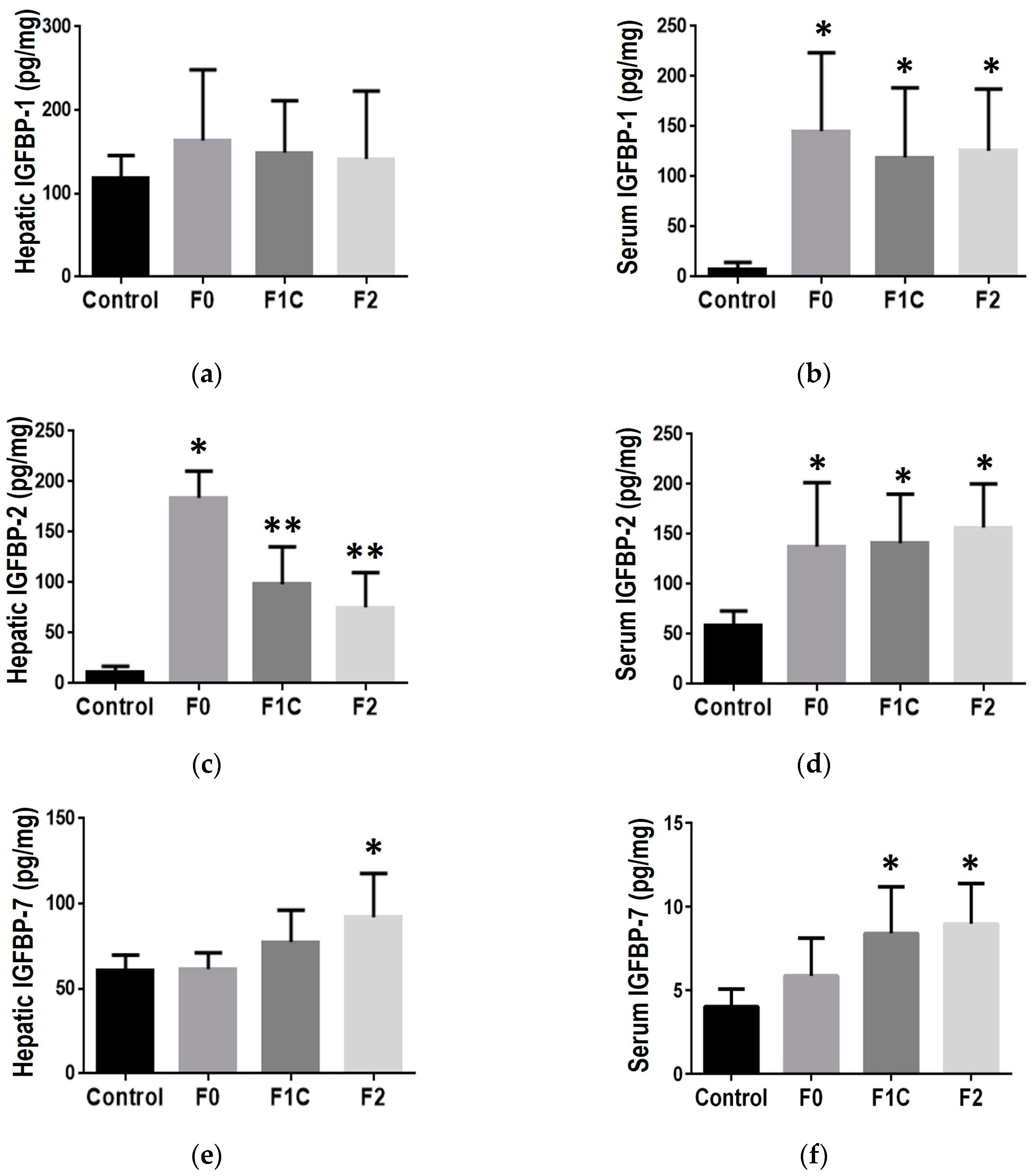
3.4. IGFBP during mild to moderate fibrosis in NAFLD
3.4.1. Liver tissue
3.4.2. Serum
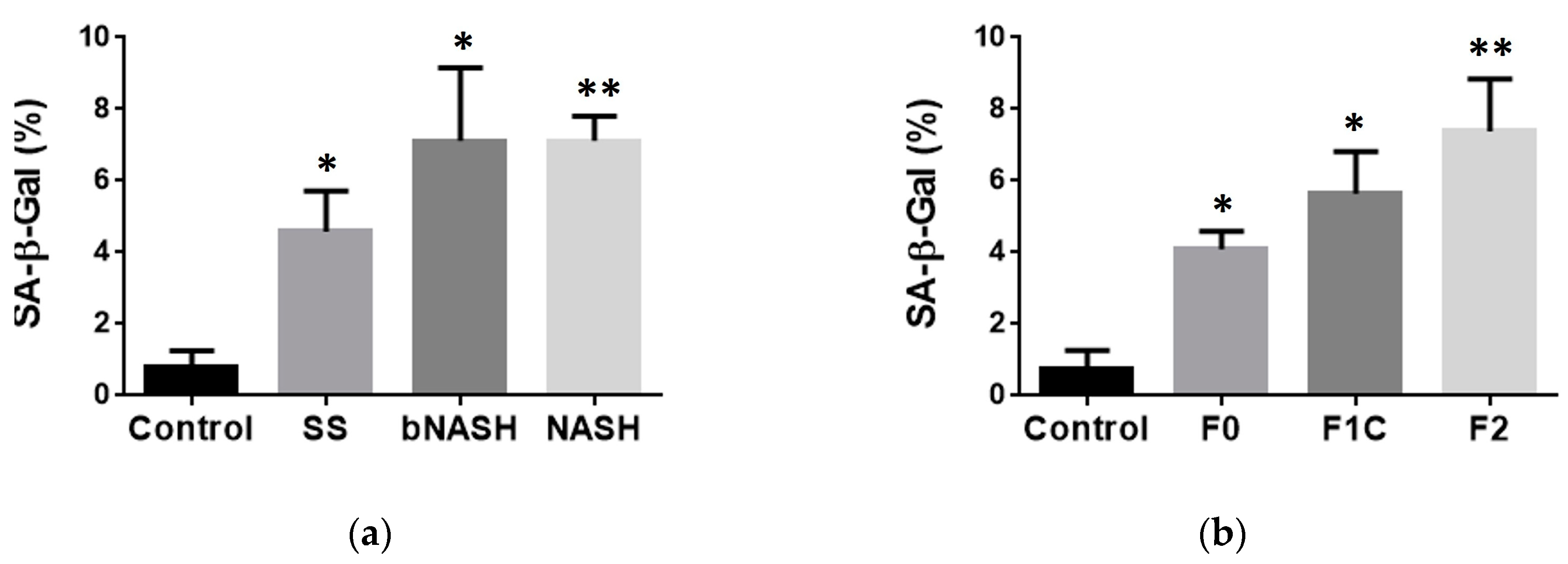
3.5. Cellular senescence during NAFLD and fibrosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calzadilla Bertot, L.; Adams, L.A. The Natural Course of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Kimura, T.; Fujimori, N.; Nagaya, T.; Komatsu, M.; Tanaka, E. Current status, problems, and perspectives of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease research. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Castera, L.; Wong, V.W. Noninvasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in NAFLD. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2023, 21, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2015, 13, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulai, P.S.; Singh, S.; Patel, J.; Soni, M.; Prokop, L.J.; Younossi, Z.; Sebastiani, G.; Ekstedt, M.; Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; et al. Increased risk of mortality by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terracciani, F.; Falcomata, A.; Gallo, P.; Picardi, A.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U. Prognostication in NAFLD: Physiological bases, clinical indicators, and newer biomarkers. J Physiol Biochem 2023, 79, 851–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, V.; Oh, Y.; Rosenfeld, R.G. The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 761–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, L.A. IGF-binding proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T11–T28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Greenbaum, L.; Haber, B.A.; Nagle, D.; Lee, V.; Miles, V.; Mohn, K.L.; Bucan, M.; Taub, R. Structure and localization of the IGFBP-1 gene and its expression during liver regeneration. Hepatology 1994, 19, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, J.I.; George, D.L. Hepatic IGFBP1 is a prosurvival factor that binds to BAK, protects the liver from apoptosis, and antagonizes the proapoptotic actions of p53 at mitochondria. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, U.; Luo, F.; Greuter, T.; Jalan Sakrikar, N.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Lu, J.; Hu, X.; Gao, J.; Kostallari, E.; Chen, J.; et al. GIPC-Regulated IGFBP-3 Promotes HSC Migration In Vitro and Portal Hypertension In Vivo Through a beta1-Integrin Pathway. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 10, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Cabrera, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Jalan-Sakrikar, N.; Verma, V.K.; Simonetto, D.; Cao, S.; Yaqoob, U.; Leon, J.; Freire, M.; et al. Hepatic stellate cell activation promotes alcohol-induced steatohepatitis through Igfbp3 and SerpinA12. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boers, W.; Aarrass, S.; Linthorst, C.; Pinzani, M.; Elferink, R.O.; Bosma, P. Transcriptional profiling reveals novel markers of liver fibrogenesis: Gremlin and insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16289–16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Guo, X.H.; Han, D.W. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-7 induces activation and transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 3246–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Guo, X.H. Effects of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 in mice with hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 2521–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.H.; Liu, L.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.X.; Qiu, Z.H. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 contributes to hepatic fibrogenesis. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, V.; Alessio, N.; Farina, A.; Sandomenico, A.; Cipollaro, M.; Peluso, G.; Galderisi, U.; Chambery, A. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 4 and 7 released by senescent cells promote premature senescence in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Yoo, B.K.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Gredler, R.; Bhutia, S.K.; Das, S.K.; Fuller, C.; Su, Z.Z.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 functions as a potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6693–6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald, A.H.; Kaushal, K.; Siddals, K.W.; Rudenski, A.S.; Anderson, S.G.; Gibson, J.M. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2) is a marker for the metabolic syndrome. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Off. J. Ger. Soc. Endocrinol. Ger. Diabetes Assoc. 2006, 114, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colak, Y.; Senates, E.; Ozturk, O.; Yilmaz, Y.; Zemheri, E.; Yilmaz Enc, F.; Ulasoglu, C.; Aksaray, S.; Bozbeyoglu, S.G.; Kiziltas, S.; et al. Serum concentrations of human insulin-like growth factor-1 and levels of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-5 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Association with liver histology. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.K.; Maruyama, H.; Jang, B.K.; Shimada, M.; Mirshahi, F.; Ren, S.; Oh, Y.; Puri, P.; Sanyal, A.J. Suppression of IGF binding protein-3 by palmitate promotes hepatic inflammatory responses. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2016, 30, 4071–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runchey, S.S.; Boyko, E.J.; Ioannou, G.N.; Utzschneider, K.M. Relationship between serum circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 and liver fat in the United States. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfarani, S.; Inzaghi, E.; Alisi, A.; Germani, D.; Puglianiello, A.; Nobili, V. Insulin-like growth factor-I and -II levels are associated with the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaquias, A.C.; Bezzan, P.C.; Montenegro, R., Jr.; Daneluzzi, J.C.; Ricco, R.G.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Elias, J., Jr.; Martinelli, A.L.; Martinelli, C.E., Jr. Can the insulin sensitivity index (ISI) in association with insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 identify insulin resistance early in overweight children? J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 22, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Espinosa, A.; Guzman, C. A Model of Experimental Steatosis In Vitro: Hepatocyte Cell Culture in Lipid Overload-Conditioned Medium. J Vis Exp 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.X.; Muhammad, L.; Nietert, P.J.; Feghali-Bostwick, C. IGFBP-5 Promotes Fibrosis via Increasing Its Own Expression and That of Other Pro-fibrotic Mediators. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrom, H.; Stal, P.; Hultcrantz, R.; Brismar, K.; Ansurudeen, I. IGFBP-1 and IGF-I as markers for advanced fibrosis in NAFLD—A pilot study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiot, J.; Bondue, B.; Henket, M.; Corhay, J.L.; Louis, R. Raised serum levels of IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiot, J.; Henket, M.; Corhay, J.L.; Moermans, C.; Louis, R. Sputum biomarkers in IPF: Evidence for raised gene expression and protein level of IGFBP-2, IL-8 and MMP-7. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravinthan, A.; Pietrosi, G.; Hoare, M.; Jupp, J.; Marshall, A.; Verrill, C.; Davies, S.; Bateman, A.; Sheron, N.; Allison, M.; et al. Hepatocyte expression of the senescence marker p21 is linked to fibrosis and an adverse liver-related outcome in alcohol-related liver disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravinthan, A.; Scarpini, C.; Tachtatzis, P.; Verma, S.; Penrhyn-Lowe, S.; Harvey, R.; Davies, S.E.; Allison, M.; Coleman, N.; Alexander, G. Hepatocyte senescence predicts progression in non-alcohol-related fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 accelerates hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkheil, M.; Paeshuyse, J.; Neyts, J.; Van Haele, M.; Roskams, T.; Liekens, S. HCV-induced EGFR-ERK signaling promotes a pro-inflammatory and pro-angiogenic signature contributing to liver cancer pathogenesis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.J.; Chew, S.L.; D’Souza Li, L.; Yateman, M.; Rodriguez-Arnao, J.; Gimson, A.; Holly, J.; Camacho-Hubner, C. Expression of IGF-I and IGF-binding protein genes in cirrhotic liver. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 149, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.D.; Suwanichkul, A.; DePaolis, L.A.; Snuggs, M.B.; Morris, S.L.; Powell, D.R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) suppression of IGFBP-1 production: Evidence for mediation by the type I IGF receptor. Regul. Pept. 1993, 48, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haywood, N.J.; Slater, T.A.; Matthews, C.J.; Wheatcroft, S.B. The insulin like growth factor and binding protein family: Novel therapeutic targets in obesity & diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2019, 19, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matz-Soja, M.; Aleithe, S.; Marbach, E.; Bottger, J.; Arnold, K.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Kratzsch, J.; Gebhardt, R. Hepatic Hedgehog signaling contributes to the regulation of IGF1 and IGFBP1 serum levels. Cell Commun. Signal. 2014, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedbacker, K.; Birsoy, K.; Wysocki, R.W.; Asilmaz, E.; Ahima, R.S.; Farooqi, I.S.; Friedman, J.M. Antidiabetic effects of IGFBP2, a leptin-regulated gene. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeflich, A.; Russo, V.C. Physiology and pathophysiology of IGFBP-1 and IGFBP-2—Consensus and dissent on metabolic control and malignant potential. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.C.; Azar, W.J.; Yau, S.W.; Sabin, M.A.; Werther, G.A. IGFBP-2: The dark horse in metabolism and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, S.W.; Russo, V.C.; Clarke, I.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Werther, G.A.; Sabin, M.A. IGFBP-2 inhibits adipogenesis and lipogenesis in human visceral, but not subcutaneous, adipocytes. Int J Obes (Lond) 2015, 39, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T.; Shah, A.M.; Ezzat, V.A.; Miell, J.R.; Modo, M.; Williams, S.C.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. IGF-binding protein-2 protects against the development of obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benatar, T.; Yang, W.; Amemiya, Y.; Evdokimova, V.; Kahn, H.; Holloway, C.; Seth, A. IGFBP7 reduces breast tumor growth by induction of senescence and apoptosis pathways. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012, 133, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracun, V.; van Essen, B.; Voors, A.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Dickstein, K.; Zannad, F.; Metra, M.; Anker, S.; Samani, N.J.; Ponikowski, P.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 (IGFBP7), a link between heart failure and senescence. ESC Heart Fail 2022, 9, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiel, M.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Rajasekaran, D.; Mendoza, R.G.; Robertson, C.L.; Jariwala, N.; Yuan, F.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.; et al. IGFBP7 Deletion Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 4014–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pitcher, L.E.; Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Zhu, Y. Cellular senescence: A key therapeutic target in aging and diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachtatzis, P.M.; Marshall, A.; Arvinthan, A.; Verma, S.; Penrhyn-Lowe, S.; Mela, M.; Scarpini, C.; Davies, S.E.; Coleman, N.; Alexander, G.J. Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: The Relation between Hepatitis B Antigen Expression, Telomere Length, Senescence, Inflammation and Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravinthan, A.D.; Alexander, G.J.M. Senescence in chronic liver disease: Is the future in aging? J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| IGFBP-1 | IGFBP-2 | IGFBP-7 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | ||
| Liver tissue | Exposure | -3.195 (-26.99, 20.60) |
13.519 (-11.41, 38.45) |
-21.593 (-38.68, -4.50) |
-27.348 (-47.76, -6.93)* |
5.875 (-2.50, 14.25) |
9.258 (-0.01, 18.52) |
| SS | 38.493 (-25.85, 102.84) |
62.778 (-18.88, 144.43) |
122.548 (78.25, 166.84)*** |
116.826 (52.09, 181.56)** |
18.722 (-3.93, 41.38) |
24.296 (-6.05, 54.65) |
|
| bNASH | 55.529 (9.35, 101.71)* |
79.380 (12.88, 145.88) |
94.752 (61.80, 127.70)*** |
107.422 (46.69, 168.16)** |
17.358 (1.10, 33.62) |
10.902 (-13.81, 35.62) |
|
| NASH | 3.672 (-51.09, 58.44) |
28.816 (-51.37, 109.01) |
89.745 (52.11, 127.38)*** |
105.661 (38.16, 173.16)** |
21.080 (1.80, 40.36) |
10.560 (-19.24, 40.36) |
|
| Serum | Exposure | -17.108 (-38.35, 4.13) |
-9.390 (-33.877, 15.10) |
23.904 (8.63, 39.17)*** |
14.966 (-2.18, 32.11) |
-0.013 (-1.00, 0.97)* |
0.277 (-0.94, 1.49) |
| SS | 100.763 (45.55, 155.98)** |
138.635 (53.61, 223.66)** |
97.291 (57.60, 136.98)*** |
56.635 (-2.89, 116.16) |
3.890 (1.32, 6.46)** |
3.433 (-0.79, 7.65) |
|
| bNASH | 144.465 (101.25, 187.68)*** |
187.488 (126.29, 248.69)*** |
86.343 (55.28, 117.41)*** |
52.058 (9.21, 94.91)* |
3.853 (1.84, 5.86)** |
3.456 (0.42, 6.49)* |
|
| NASH | 95.872 (46.69, 145.06)*** |
167.234 (89.32, 245.15)*** |
82.528 (47.17, 117.89)*** |
42.754 (-11.80, 97.31) |
4.768 (2.48, 7.06) |
3.938 (0.07, 7.80)* |
|
| IGFBP-1 | IGFBP-2 | IGFBP-7 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | Crude | Adjusted | ||
| Liver tissue | Exposure | -2.187 (-31.041, 26.668) |
17.899 (-6.99, 42.79) |
-11.963 (-23.80, -0.12)* |
-9.707 (-23.96, 4.54) |
1.768 (-6.34, 9.87) |
4.398 (-4.95, 13.75) |
| F0 | 43.925 (-30.11, 117.96) |
108.685 (40.01, 177.36)** |
167.126 (137.47, 196.78)*** |
169.176 (130.50, 207.85)*** |
2.012 (-18.63, 22.66) |
8.565 (-17.24, 34.37) |
|
| F1C | 15.546 (-42.31, 73.40) |
21.507 (-41.08, 84.10) |
93.984 (69.98, 117.98)*** |
81.854 (41.13, 122.58)*** |
15.926 (-0.20, 32.06) |
9.558 (-13.96, 33.07) |
|
| F2 | 37.069 (-18.68, 92.82) |
73.961 (9.41, 138.51)* |
70.058 (46.91, 93.21)*** |
52.506 (13.64, 91.37)** |
28.996 (12.89, 45.10)** |
29.142 (4.89, 53.39)* |
|
| Serum | Exposure | -14.280 (-39.42, 10.86) |
-11.338 (-39.88, 17.21) |
22.962 (6.02, 39.90)* |
12.738 (-6.50, 31.977) |
-0.230 (-1.24, 0.78) |
-0.100 (-1.43, 1.23) |
| F0 | 132.477 (67.16, 197.79)*** |
173.399 (94.64, 252.16)*** |
90.865 (46.85, 134.88)*** |
46.646 (-6.435, 99.73) |
1.722 (-0.90, 4.35) |
2.057 (-1.60, 5.71) |
|
| F1C | 116.838 (67.17, 166.50)*** |
169.778 (97.10, 241.56)*** |
84.247 (50.78, 117.72)*** |
49.147 (0.77, 97.52)* |
4.740 (2.74, 6.74)*** |
4.020 (0.69, 7.35)* |
|
| F2 | 118.259 (69.09, 167.43)*** |
184.027 (109.10, 258.06)*** |
89.224 (56.09, 122.36)*** |
61.460 (11.57, 111.35)* |
4.566 (2.59, 6.54)*** |
4.522 (1.08, 7.96)* |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





