Submitted:
26 February 2024
Posted:
27 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.1.1. Patients and controls
2.1.2. Blood samples
2.1.3. RNA solation and quantification of circulating miRNs levels
2.1.4. Quantitative real-time amplification (qRT-PCR)
2.2. Statistical Analysis
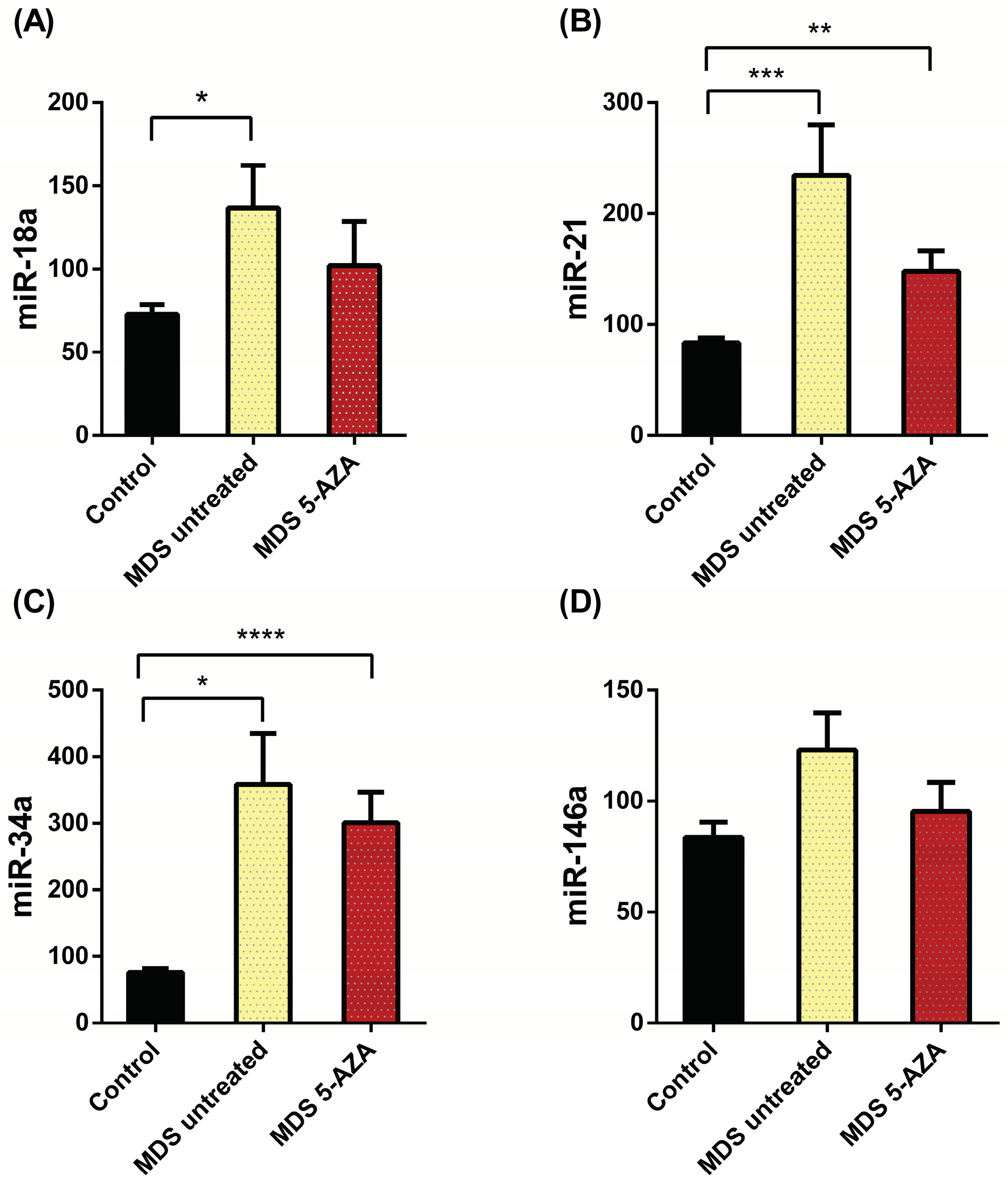
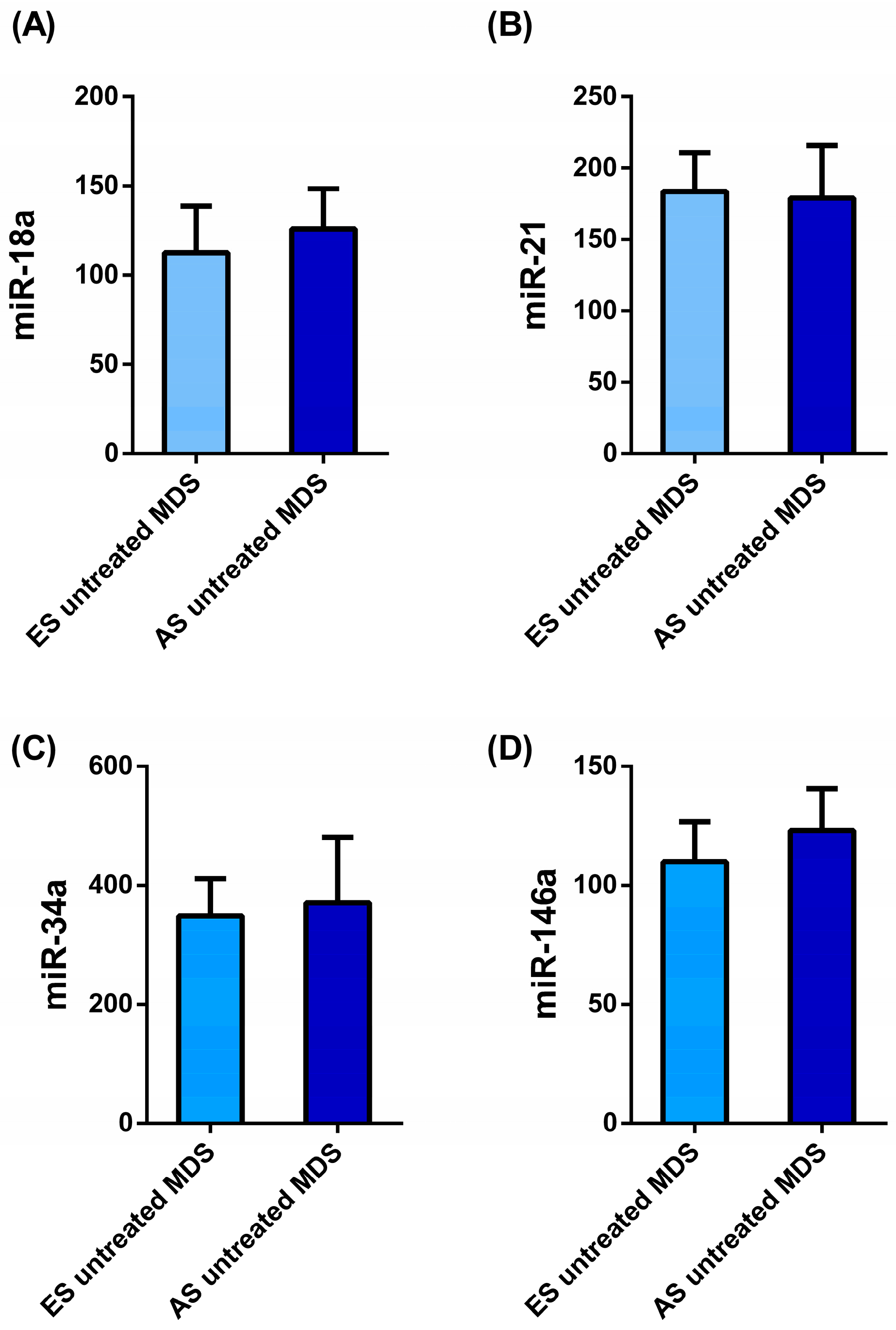
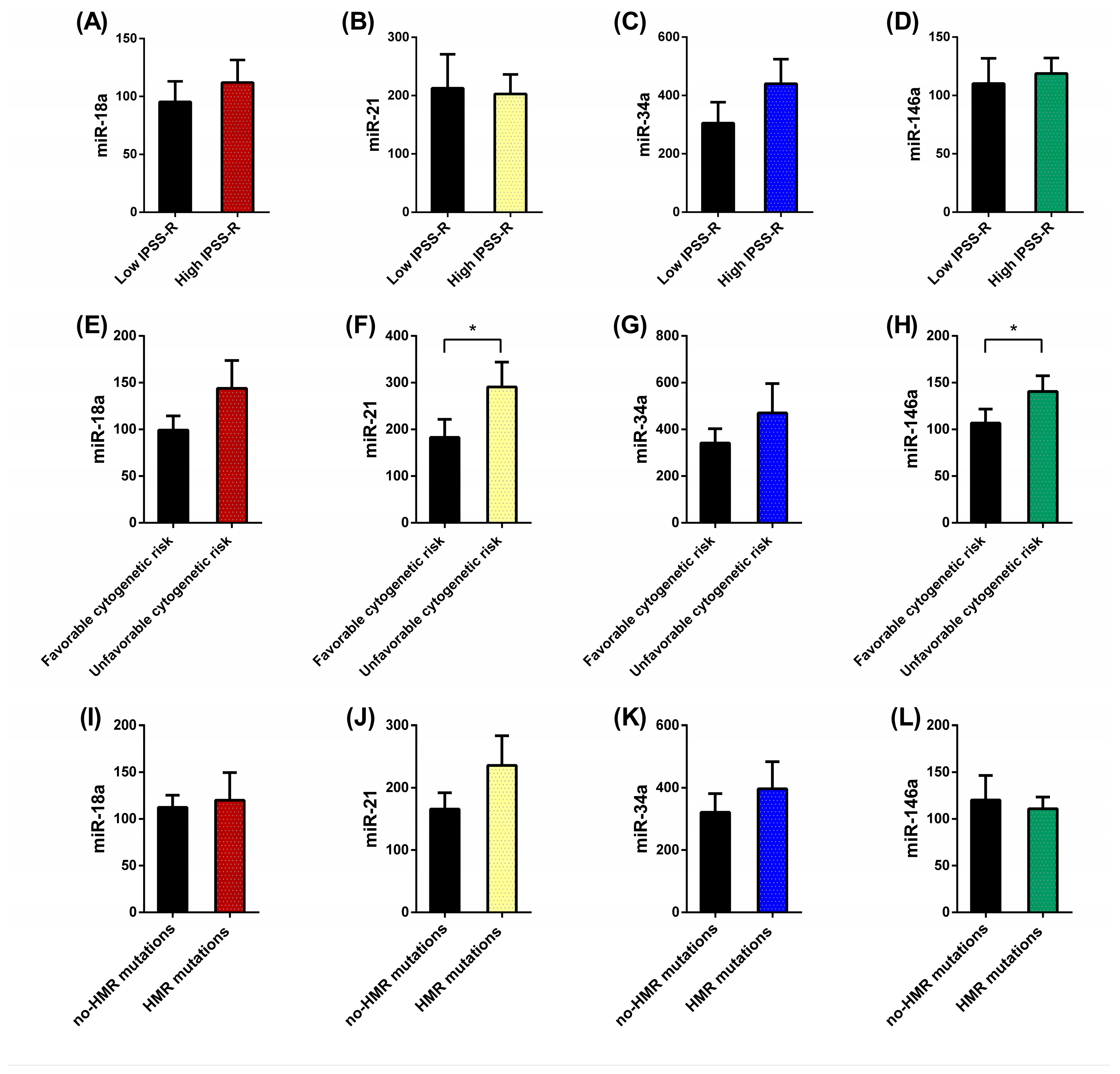
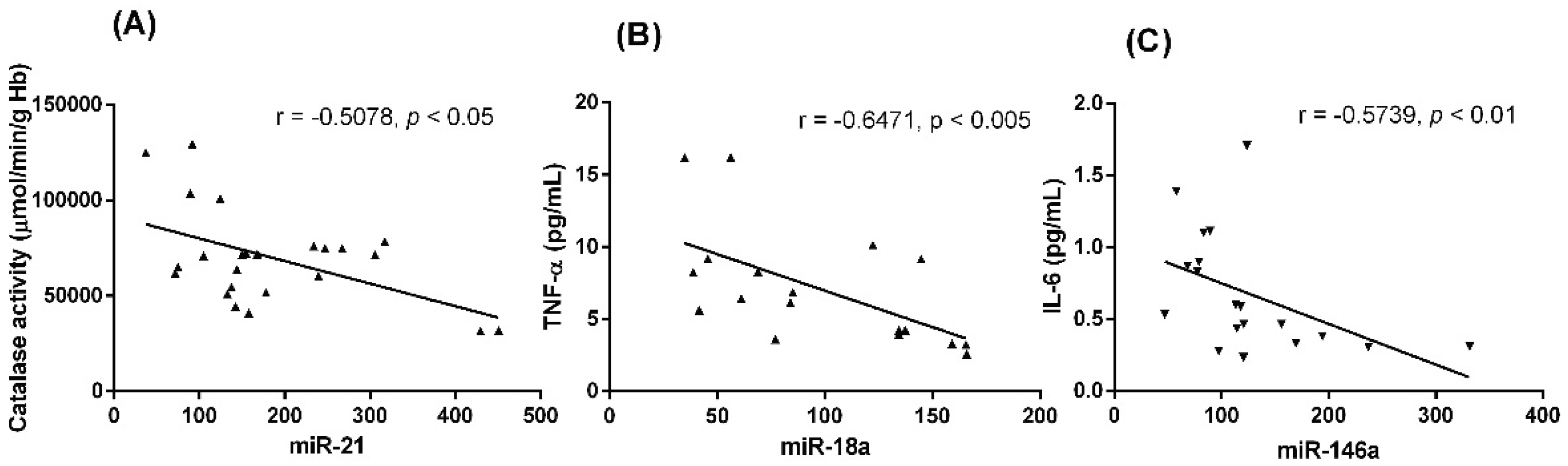
3. Results
3.1. Differential patterns of miRNs expression in MDS patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- G. Garcia-Manero, K.S. Chien, G. Montalban-Bravo, Myelodysplastic syndromes: 2021 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management, Am. J. Hematol. 95 (2020) 1399–1420. [CrossRef]
- D.R. Bond, H.J. Lee, A.K. Enjeti, Unravelling the epigenome of myelodysplastic syndrome: Diagnosis, prognosis, and response to therapy, Cancers (Basel). 12 (2020) 1–25. [CrossRef]
- J.M. Bennett, Changes in the Updated 2016: WHO Classification of the Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Related Myeloid Neoplasms, Clin. Lymphoma, Myeloma Leuk. 16 (2016) 607–609. [CrossRef]
- P. Fenaux, L. Ades, Review of azacitidine trials in Intermediate-2-and High-risk myelodysplastic syndromes, Leuk. Res. 33 (2009) S7–S11. [CrossRef]
- M.D. Jelic, A.D. Mandic, S.M. Maricic, B.U. Srdjenovic, Oxidative stress and its role in cancer, J. Cancer Res. Ther. 17 (2021) 22–28. [CrossRef]
- P. Montes, A. Guerra-Librero, P. García, M.E. Cornejo-Calvo, M.D.S. López, T. de Haro, L. Martínez-Ruiz, G. Escames, D. Acuña-Castroviejo, Effect of 5-Azacitidine Treatment on Redox Status and Inflammatory Condition in MDS Patients, Antioxidants 11 (2022) 1–15. [CrossRef]
- D.P. Bartel, MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function, Cell 116 (2004) 281–297. [CrossRef]
- K. Saliminejad, H.R. Khorram Khorshid, S. Soleymani Fard, S.H. Ghaffari, An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods, J. Cell. Physiol. (2019). [CrossRef]
- C. Chakraborty, A.R. Sharma, G. Sharma, S.S. Lee, The Interplay among miRNAs, Major Cytokines, and Cancer-Related Inflammation, Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 20 (2020) 606–620. [CrossRef]
- J. Lan, Z. Huang, J. Han, J. Shao, C. Huang, Redox regulation of microRNAs in cancer, Cancer Lett. 418 (2018) 250–259. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, W.-L. Ng, P. Wang, L. Tian, E. Werner, H. Wang, P. Doetsch, Y. Wang, MicroRNA-21 Modulates the Levels of Reactive Oxygen Species Levels by Targeting SOD3 and TNFα, Cancer Res 72 (2012) 4707–4713. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang, W. Chen, L. Bai, W. Chen, M.T. Padilla, A.S. Lin, S. Shi, X. Wang, Y. Lin, Receptor-interacting protein 1 increases chemoresistance by maintaining inhibitor of apoptosis protein levels and reducing reactive oxygen species through a microRNA-146a-mediated catalase pathway, J. Biol. Chem. 289 (2014) 5654–5663. [CrossRef]
- Y.A. Veryaskina, S.E. Titov, I.B. Kovynev, S.S. Fedorova, T.I. Pospelova, I.F. Zhimulev, MicroRNAs in the Myelodysplastic Syndrome, Acta Naturae 13 (2021) 4–15. [CrossRef]
- J.S. Choi, M.H. Nam, S.Y. Yoon, S.H. Kang, MicroRNA-194-5p could serve as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in myelodysplastic syndromes, Leuk. Res. 39 (2015) 763–768. [CrossRef]
- A. Pons, B. Nomdedeu, A. Navarro, A. Gaya, B. Gel, T. Diaz, S. Valera, M. Rozman, M. Belkaid, E. Montserrat, M. Monzo, Hematopoiesis-related microRNA expression in myelodysplastic syndromes, Leuk. Lymphoma 50 (2009) 1854–1859. [CrossRef]
- D.T. Starczynowski, F. Kuchenbauer, B. Argiropoulos, S. Sung, R. Morin, A. Muranyi, M. Hirst, D. Hogge, M. Marra, R.A. Wells, R. Buckstein, W. Lam, R.K. Humphries, A. Karsan, Identification of miR-145 and miR-146a as mediators of the 5q-syndrome phenotype, Nat. Med. 16 (2010) 49–58. [CrossRef]
- T.D. Bhagat, L. Zhou, L. Sokol, R. Kessel, G. Caceres, K. Gundabolu, R. Tamari, S. Gordon, I. Mantzaris, T. Jodlowski, Y. Yu, X. Jing, R. Polineni, K. Bhatia, A. Pellagatti, J. Boultwood, S. Kambhampati, U. Steidl, C. Stein, W. Ju, G. Liu, P. Kenny, A. List, M. Bitzer, A. Verma, miR-21 mediates hematopoietic suppression in MDS by activating TGF-β signaling., Blood 121 (2013) 2875–2881. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, P. Liu, H. Zhu, Y. Xu, C. Ma, X. Dai, L. Huang, Y. Liu, L. Zhang, C. Qin, miR-34a, a microRNA up-regulated in a double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, inhibits bcl2 translation, Brain Res. Bull. 80 (2009) 268–273. [CrossRef]
- M.D. Merkerova, Z. Krejcik, H. Votavova, M. Belickova, A. Vasikova, J. Cermak, Distinctive microRNA expression profiles in CD34 bone marrow cells from patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 19 (2011) 313–319. [CrossRef]
- Y. Choi, E.H. Hur, J.H. Moon, B.K. Goo, D.R. Choi, J.H. Lee, Expression and prognostic significance of microRNAs in Korean patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, Korean J. Intern. Med. 34 (2019) 390–400. [CrossRef]
- F.R. Luly, M. Lévêque, V. Licursi, G. Cimino, C. Martin-Chouly, N. Théret, R. Negri, L. Cavinato, F. Ascenzioni, P. Del Porto, MiR-146a is over-expressed and controls IL-6 production in cystic fibrosis macrophages, Sci. Rep. 9 (2019). [CrossRef]
- K. Das, L.V.M. Rao, The Role of microRNAs in Inflammation, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (2022). [CrossRef]
- G.K. Dipa Bhaumik, Scott, S. Schokrpur, Hiruyeh, C.K. Patil, A. V Orjalo, G.J. Lithgow, J. Campisi, MicroRNAs miR - 146a / b negatively modulate the senescence - associated inflammatory mediators IL - 6 and IL - 8, 1 (2009) 402–411. [CrossRef]
- E. Maffioletti, E. Milanesi, A. Ansari, O. Zanetti, S. Galluzzi, C. Geroldi, M. Gennarelli, L. Bocchio-Chiavetto, miR-146a Plasma Levels Are Not Altered in Alzheimer’s Disease but Correlate With Age and Illness Severity, Front. Aging Neurosci. 11 (2020) 11–14. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jiang, J. Zhou, J. Zhao, D. Hou, H. Zhang, L. Li, D. Zou, J. Hu, Y. Zhang, Z. Jing, MiR-18a-downregulated RORA inhibits the proliferation and tumorigenesis of glioma using the TNF-α-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway, EBioMedicine 52 (2020) 102651. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kim, J.W. Cheong, Y.K. Kim, J.I. Eom, H.K. Jeung, S.J. Kim, D. Hwang, J.S. Kim, H.J. Kim, Y.H. Min, Serum microRNA-21 as a potential biomarker for response to hypomethylating agents in myelodysplastic syndromes, PLoS One 9 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Z. Krejčík, M. Beličková, A. Hruštincová, J. Kléma, Z. Zemanová, K. Michalová, J. Čermák, A. Jonášová, M. Dostálová Merkerová, Aberrant expression of the microRNA cluster in 14q32 is associated with del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome and lenalidomide treatment, Cancer Genet. 208 (2015) 156–161. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




