Submitted:
01 March 2024
Posted:
01 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Optimization Method
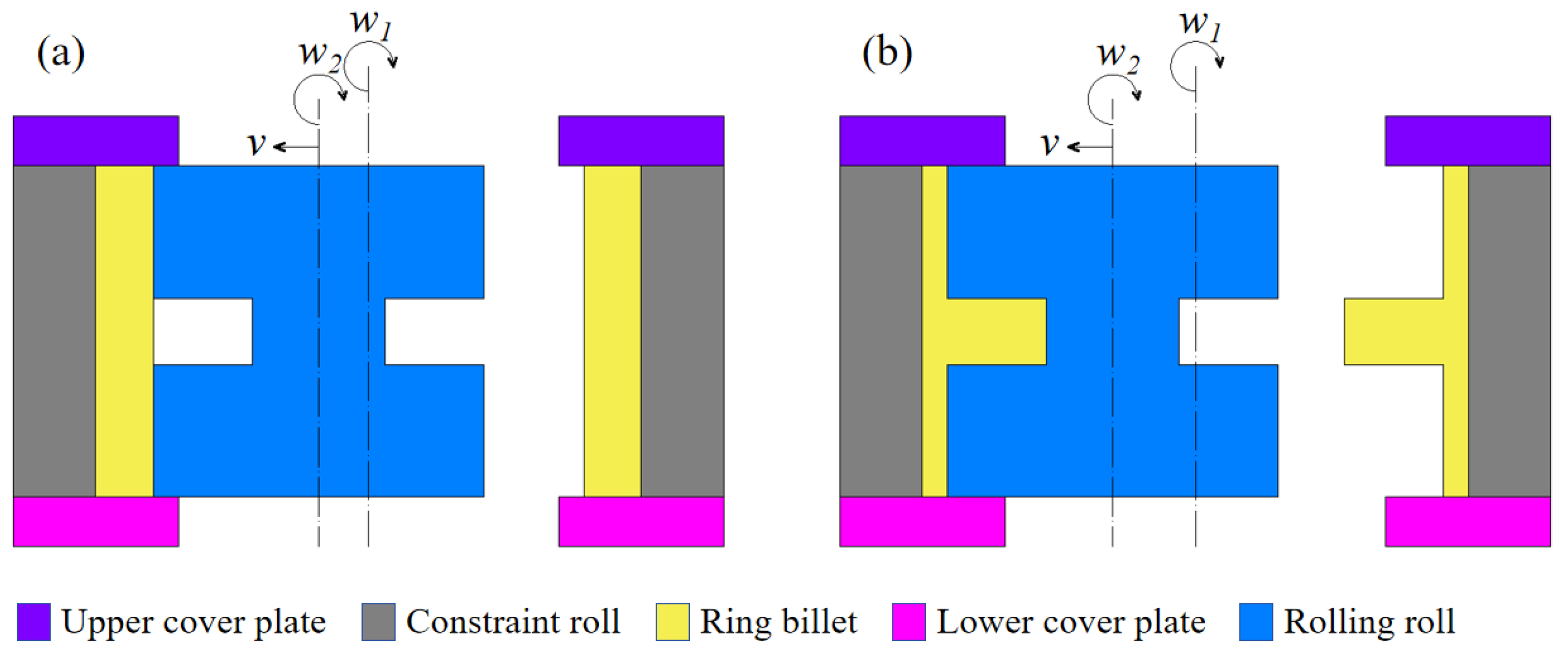
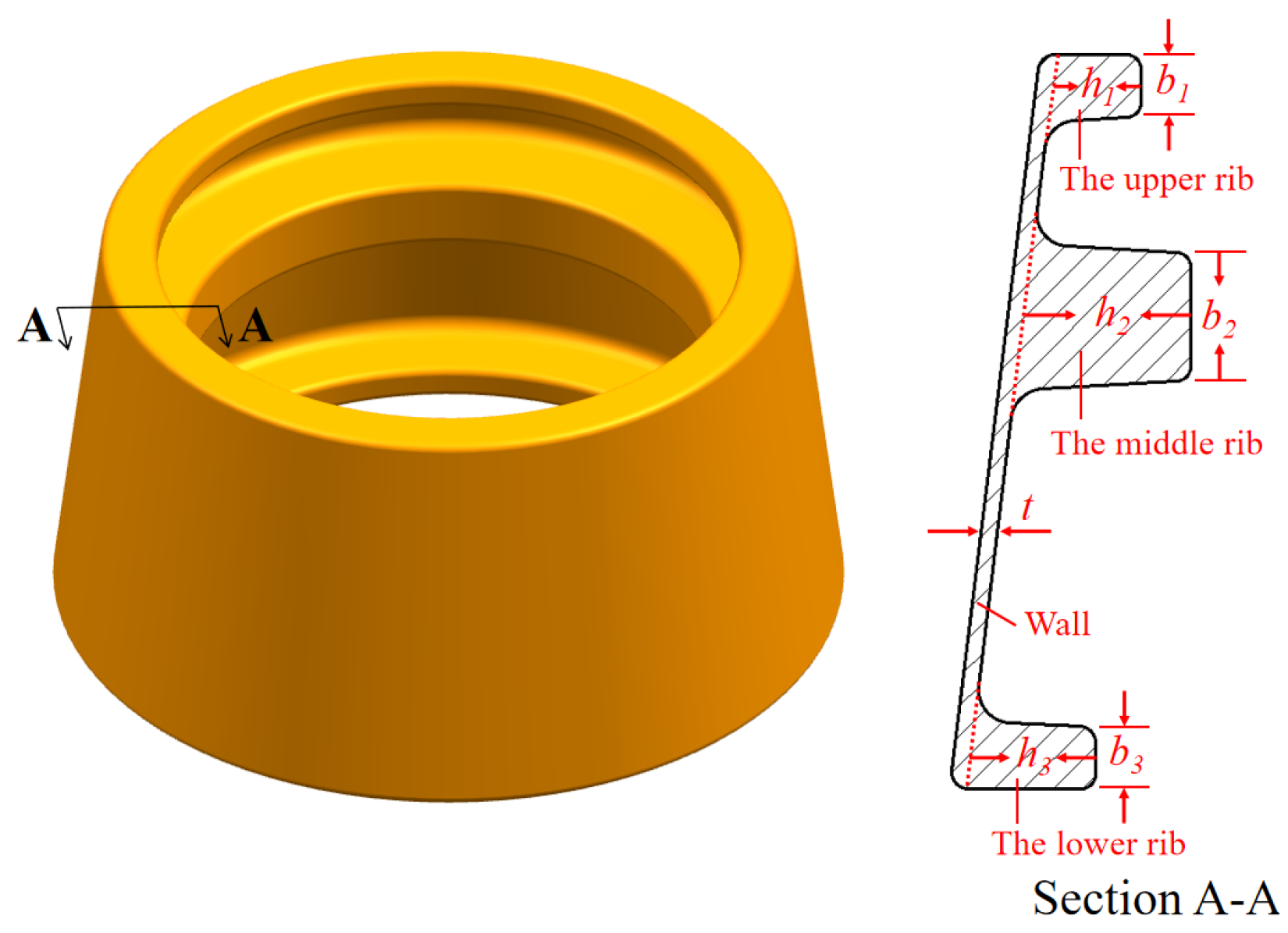
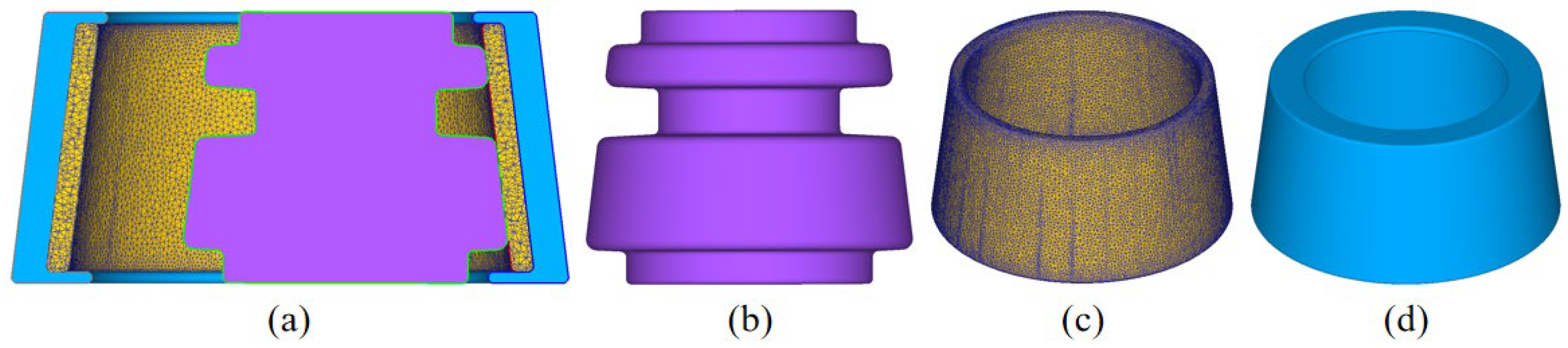
2.1. Establishment of Finite Element Model of Constrained Ring Rolling of AATWCRIHR
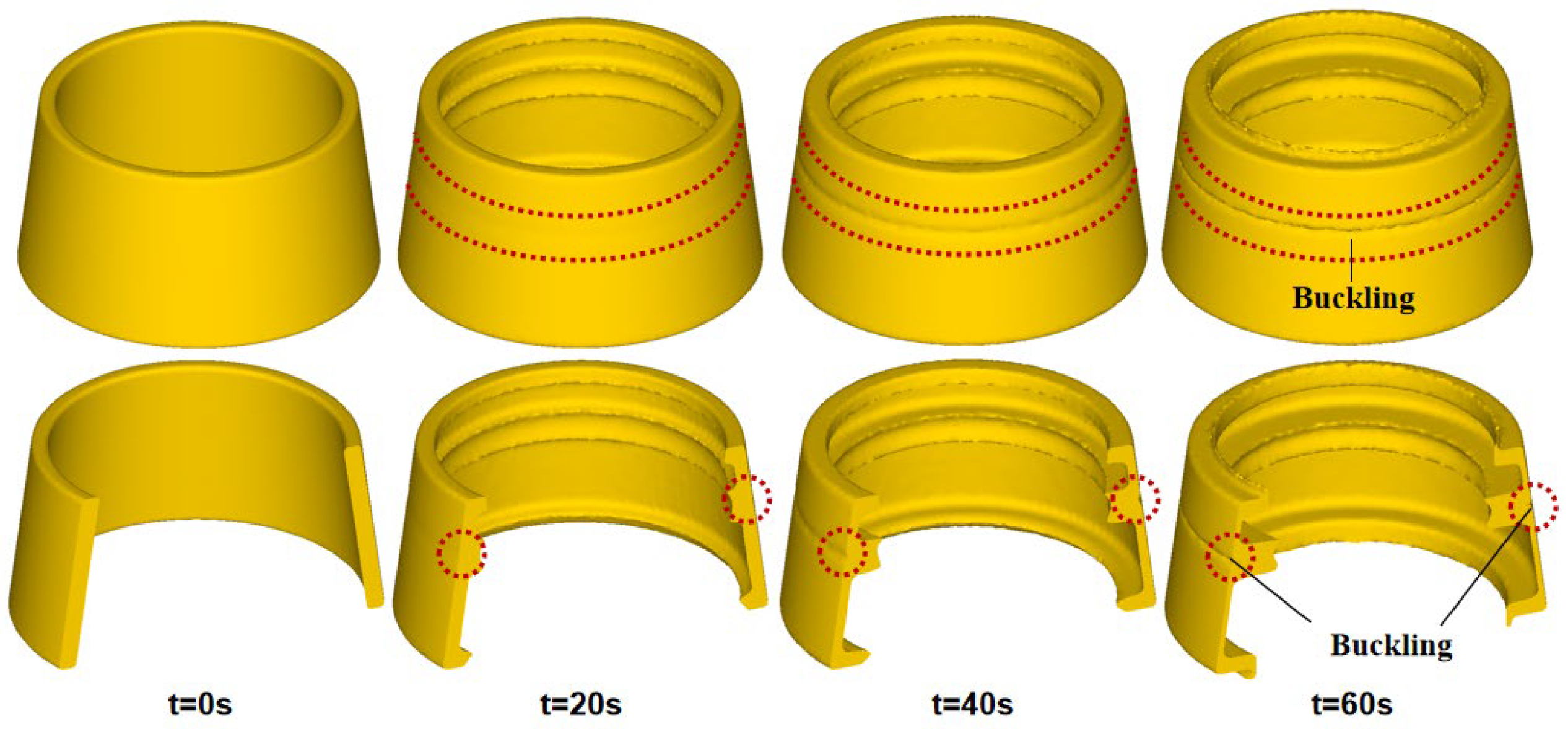
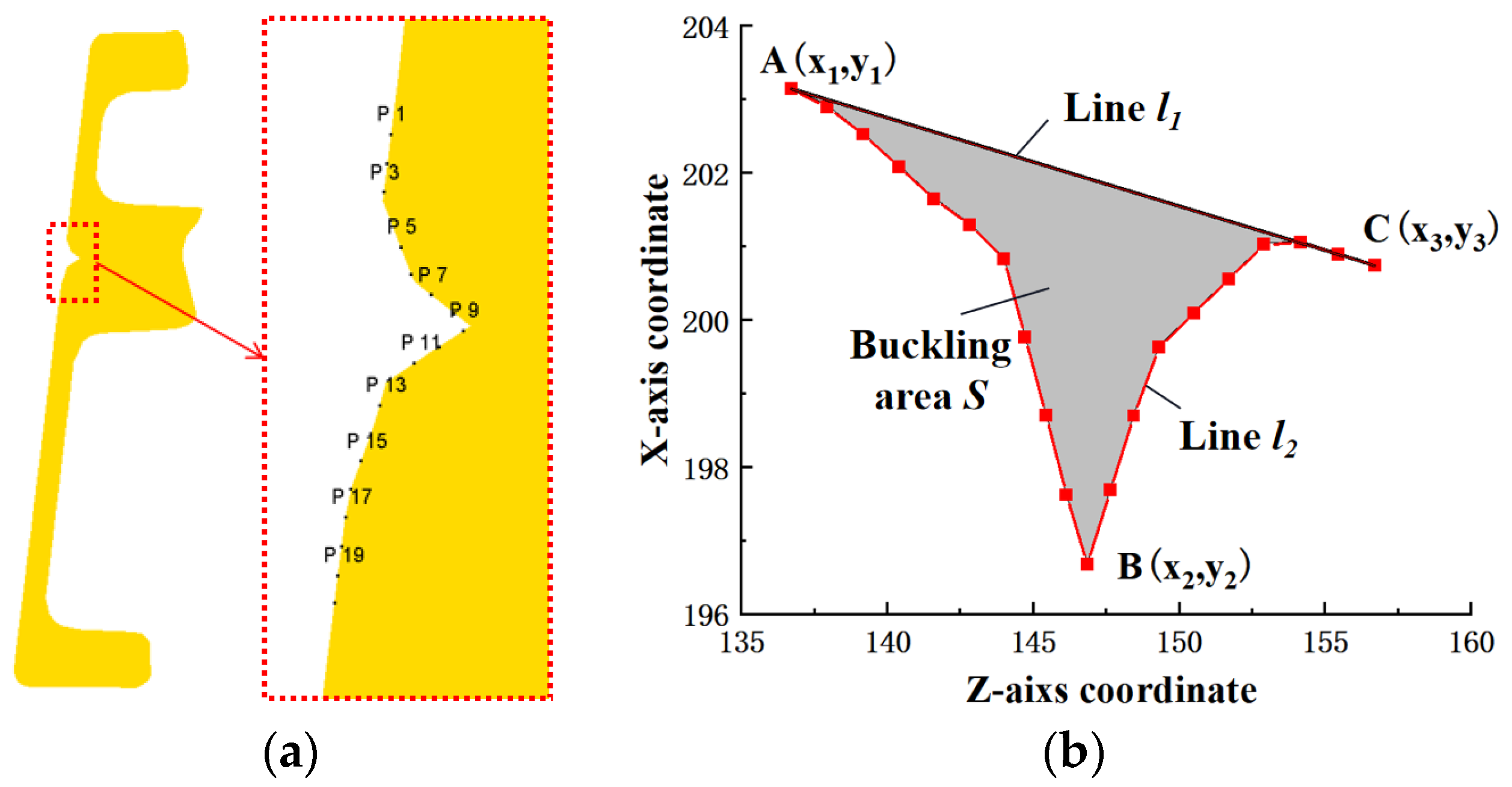
2.2. Evaluation Criteria of Buckling Defect
2.3. Determination of Experimental Scheme
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Orthogonal Experimental Analysis
3.2. Orthogonal Experimental Level Analysis
3.3. Establishment of Response Surface Model
3.4. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
3.5. RSM Analysis
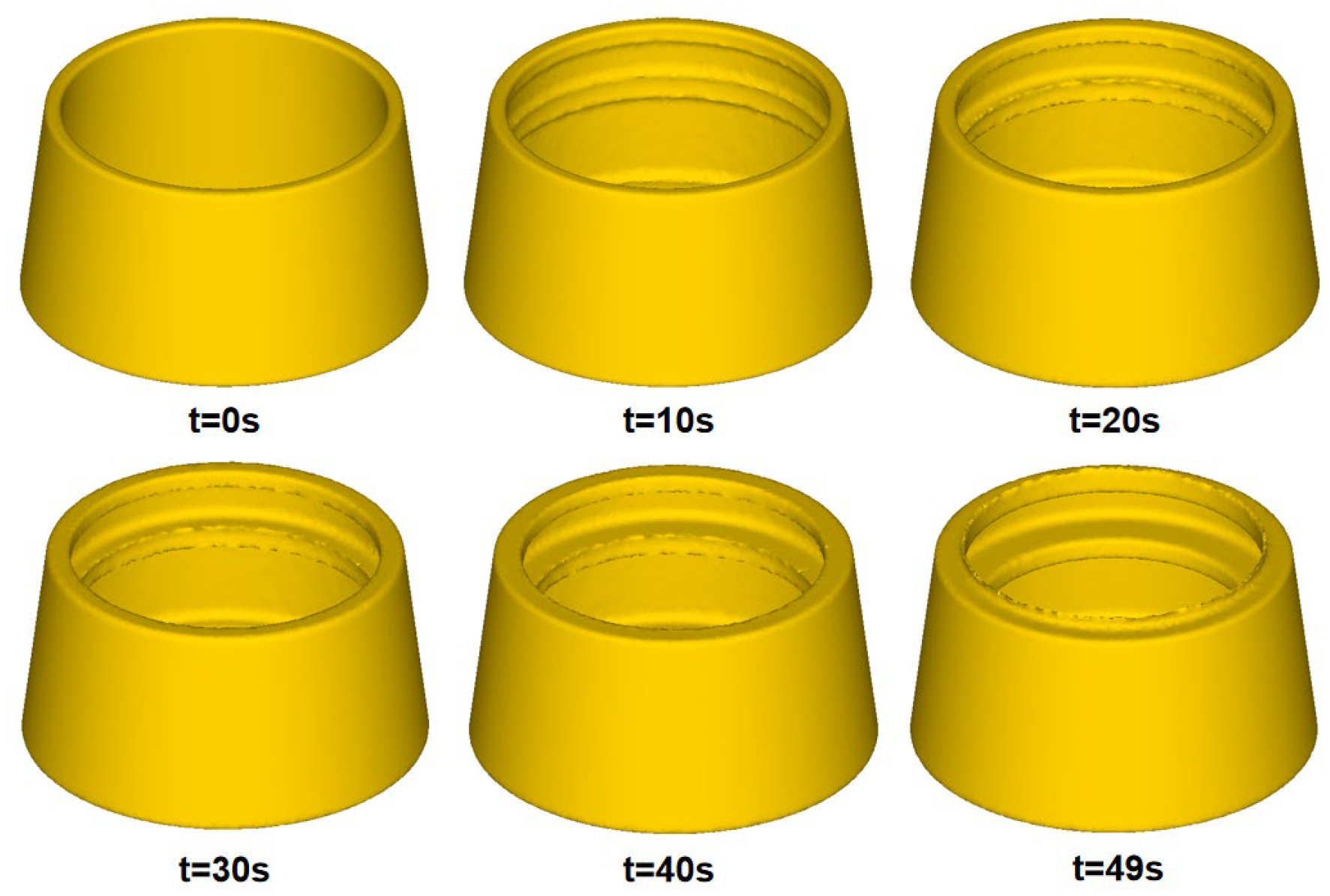
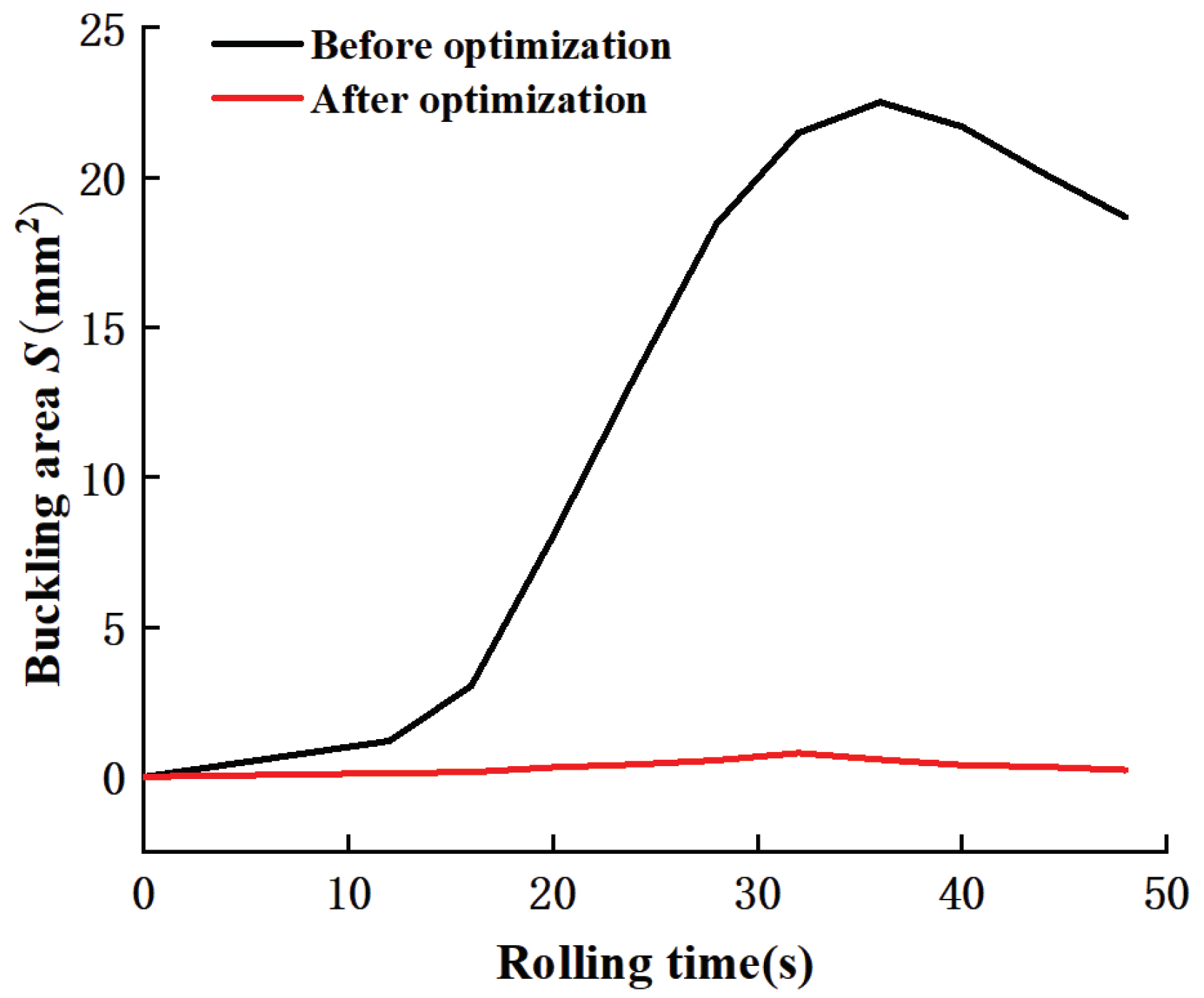
4. Verification Model
5. Conclusions
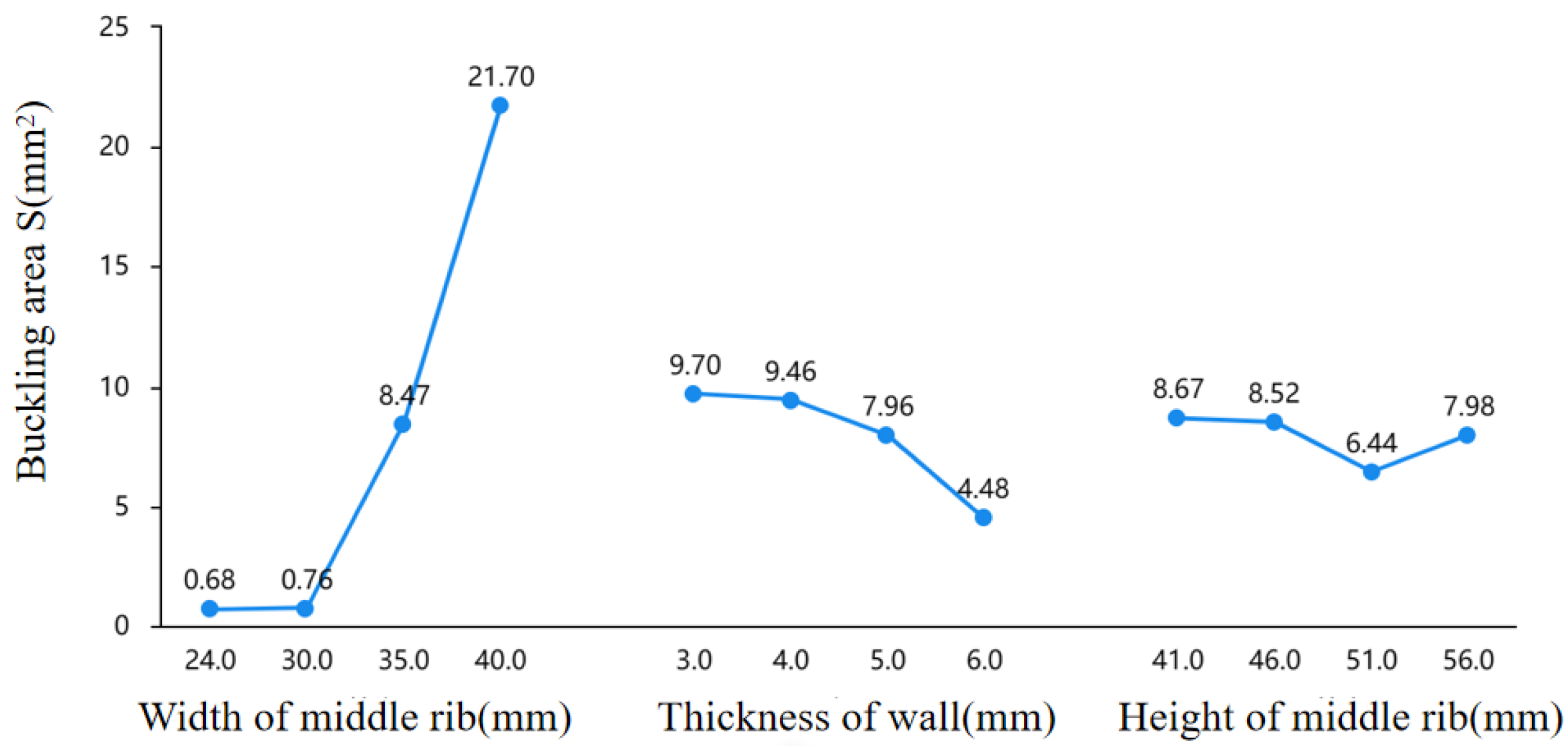
- The degree of influence on buckling defect is the width of the middle rib, the wall thickness and the height of the middle rib in order.
- The buckling area is the smallest and the degree of buckling defect on the back of the middle rib is the lowest when the width of the middle rib is 24 mm, the wall thickness is 6 mm, and the height of the middle rib is 51 mm.
- When the width of the middle rib is larger, the degree of buckling defect becomes more significant with the decrease of the wall thickness. When the width of the middle rib is smaller, the thickness of the wall has little influence on the buckling defect, and the degree of the buckling defect is light.
- The quantitative representation of the buckling defect proposed using the buckling profile S is feasible, and the response surface model can predict the degree of buckling defect at a given geometry dimension of the middle rib and the wall thickness of the conical ring billet by verification.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, D.; Li, G.; Deng, J.; Wang, F. Effect of die structure on extrusion forming of thin-walled component with I-type longitudinal ribs. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 2020, 108, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Fan, X.; Li, H.; Li, S. Flow forming process of thin-walled tubular parts with cross inner ribs. Procedia Manufacturing 2018, 15, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhan, M.; Fan, X.; Zhang, A.; Niu, H.; Bai, D.; Gao, P.; Zheng, Z. A review on manufacturing technologies of thin-walled components with ribs. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University 2022, 40, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Han, X.; Hua, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. Constraining ring rolling of thin-walled conical rings with transverse ribs. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences 2022, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Deng, J.; Qian, D.; Lan, J.; Long, H. Modeling and application of ring stiffness condition for radial-axial ring rolling. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 2016, 110, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y. Multi-objective Optimization of Process Parameters of Aluminium Alloy Rib-web Forgings Based on Orthogonal Experiment. Hot Working Technology 2015, 44, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.; Wright, E.D.; Grandhi, R.V. Preform Die Shape Design in Metal Forming Using an Optimization Method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 1997, 40, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourment, L.; Chenot, J.L. Optimal Design for Non-Steady-State Metal Forming Processes—I. Shape Optimization Method. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 1996, 39, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusiak, J. A technique of tool-shape optimization in large scale problems of metal forming. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 1996, 57, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C. Design and analysis of experiments; John wiley & sons, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gheysarian, A.; Honarpisheh, M. Process Parameters Optimization of the Explosive-Welded Al/Cu Bimetal in the Incremental Sheet Metal Forming Process. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Mechanical Engineering 2018, 43 S1, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, V.; Aryal, A.; Katyal, P.; Goswami, A. Process Parameters Optimization in Single Point Incremental Forming. Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series C 2015, 97, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Cai, G. Optimization of Processing Parameters of Aluminum Alloy Cylindrical Parts Based on Response Surface Method during Hydromechanical Deep Drawing. Metals 2023, 13, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, H.; Ren, M. The Optimization of Welding Spots’ Arrangement in A-Pillar Patchwork Blank Hot Stamping. Metals 2023, 13, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Hua, L. Multi-objective optimization of process parameters for the helical gear precision forging by using Taguchi method. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 2011, 25, 1519–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Hua, L. Process Parameters Optimisation for Helical Gears Precision Forging with Damage Minimization. In 2010 International Conference on Digital Manufacturing & Automation; 2010; pp. 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Anupama Francy, K.; Sai Sudheer, S.V.; Naga Krishna, N.; Gopalakrishnaih, P. Optimization of input process parameters for Al 2024 alloy in cold extrusion process. Materials Today: Proceedings 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, C.; Huang, Y.; Fu, R.; Shao, H. Optimization of numerical parameters and microstructure evolution on 2195 Al–Li alloy extrusion process. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2023, 26, 7694–7706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Tang, L.; Guo, F. Mold design and forming process parameters optimization for passenger vehicle front wing plate. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 2022, 36, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.H.; Sedighi, M.; Mosayebnezhad, J. Numerical and experimental investigation of central cavity formation in aluminum during forward extrusion process. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 2016, 30, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symbol | Factors | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Width of rib/ b2 (mm) | 24 | 30 | 35 | 40 |
| B | Thickness of wall/ t(mm) | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| C | Height of rib/ h2 (mm) | 41 | 46 | 51 | 56 |
| Experiment NO. | A(mm) | B(mm) | C(mm) | S(mm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24 | 3 | 41 | 0.58 |
| 2 | 24 | 4 | 56 | 0.85 |
| 3 | 24 | 5 | 51 | 0.87 |
| 4 | 24 | 6 | 46 | 0.44 |
| 5 | 30 | 3 | 46 | 0.57 |
| 6 | 30 | 4 | 56 | 0.83 |
| 7 | 30 | 5 | 51 | 0.82 |
| 8 | 30 | 6 | 41 | 0.83 |
| 9 | 35 | 3 | 51 | 11.35 |
| 10 | 35 | 4 | 41 | 10.85 |
| 11 | 35 | 5 | 46 | 7.75 |
| 12 | 35 | 6 | 56 | 3.92 |
| 13 | 40 | 3 | 56 | 26.30 |
| 14 | 40 | 4 | 46 | 25.32 |
| 15 | 40 | 5 | 41 | 22.42 |
| 16 | 40 | 6 | 51 | 12.75 |
| K1 | 0.68 | 9.70 | 8.67 | |
| K2 | 0.76 | 9.46 | 8.52 | |
| K3 | 8.47 | 7.69 | 6.44 | |
| K4 | 21.70 | 4.48 | 7.98 | |
| Rang Rs | -21.01 | -5.21 | -2.23 |
| Source | Sum of squares | DOF | Mean square | F-Value | P-Value | Degree of significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 1316.65 | 9 | 146.29 | 104.82 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A | 926.77 | 1 | 926.77 | 664.04 | <0.0001 | |
| B | 47.21 | 1 | 47.21 | 33.83 | 0.0011 | |
| C | 10.96 | 1 | 10.96 | 7.85 | 0.0311 | |
| AB | 38.32 | 1 | 38.32 | 27.46 | 0.0019 | |
| AC | 0.073 | 1 | 0.073 | 0.052 | 0.8269 | |
| BC | 1.206*10-3 | 1 | 1.206*10-3 | 8.640*10-4 | 0.9775 | |
| A2 | 211.28 | 1 | 211.28 | 151.38 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 4.57 | 1 | 4.57 | 3.27 | 0.1205 | |
| C2 | 3.40 | 1 | 3.40 | 2.44 | 0.1695 | |
| Residual error | 8.37 | 6 | 1.40 | |||
| Correlation coefficient R2 | Modified coefficient of determination Radj2 | Model prediction coefficient Rpred2 | S/N Ratio | |||
| 0.9937 | 0.9842 | 0.9355 | 28.303 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





