Submitted:
02 March 2024
Posted:
04 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The S2 subunit sequence has remained very conserved in variants (VOCs)
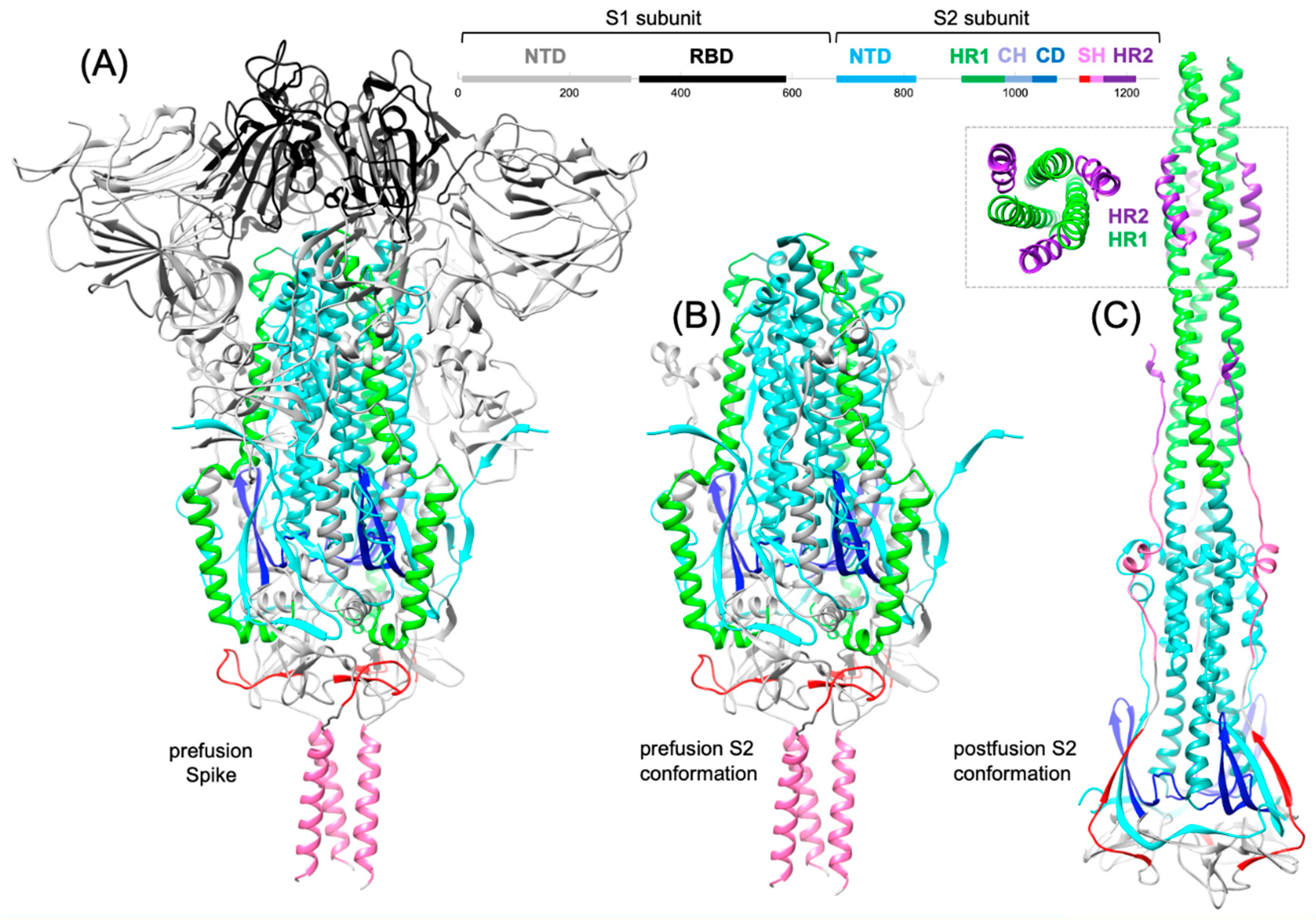
3. Conformational changes and S2 subunit function
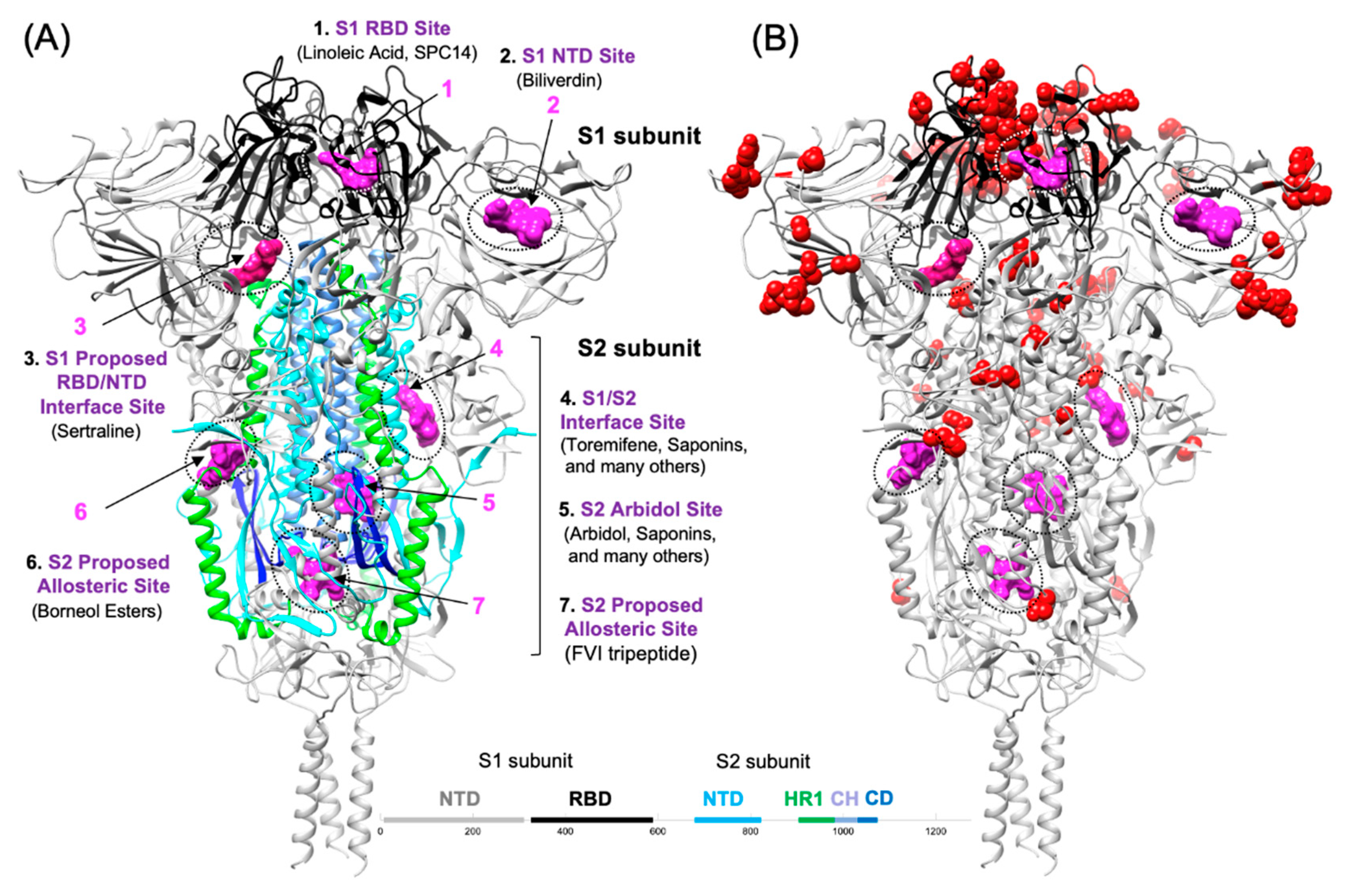
4. Small molecule entry inhibitors of SARS CoV-2 Spike
4.1. S1-targeted small molecule entry inhibitors
4.2. S2-tarteted fusion inhibitors that interfere with HR1-HR2 bundle assembly
4.3. S2-targeted small molecules that interfere with HR1-HR2 bundle assembly
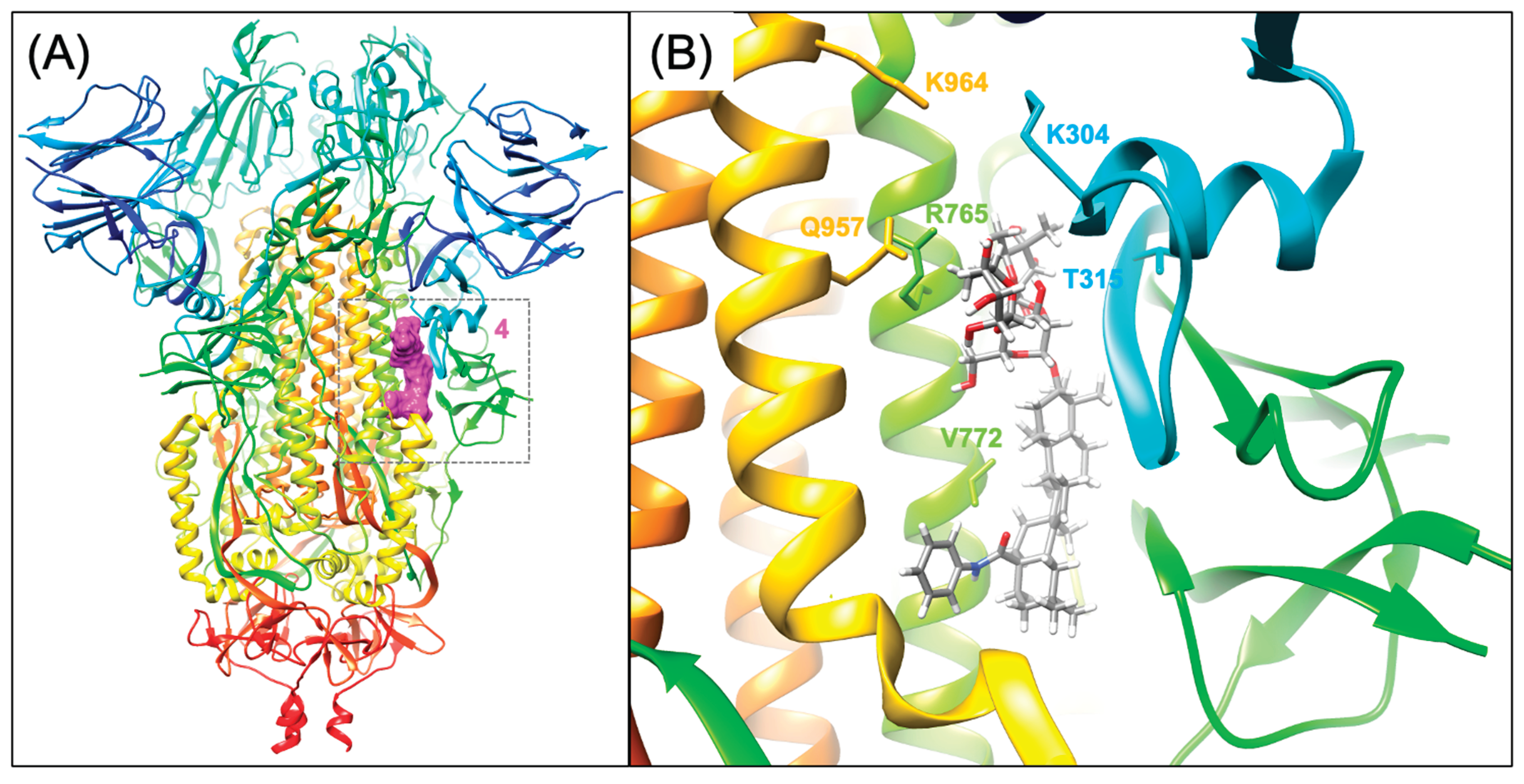
4.4. S2-targeted small molecules that bind to the S2 prefusion conformation
4.5. Other Proposed Fusion Inhibitor binding sites on the S2 segment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, G.; Rolf Hilgenfeld, R.; Whitley, R.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 449–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, N.D.; Mohan, J.; Kushwaha, B.; Ghazi, T.; Nwabuife, J.C.; Koorbanally, N.; Chuturgoon, A.A. A comprehensive review on the global efforts on vaccines and repurposed drugs for combating COVID-19. Eur J Med Chem. 2023, 260, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsillou, E.; Yu, Y.; Beh, R.C.; Liang, J.J.; Hung, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. Chronicling the 3-year evolution of the COVID-19 pandemic: analysis of disease management, characteristics of major variants, and impacts on pathogenicity. Clin Exp Med. 2023, 23, 3277–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreich, D.M.; Sivapalasingam, S.; Norton, T.; Ali, S.; Gao, H.; Bhore, R.; Xiao, J.; Hooper, A.T.; Hamilton, J.D.; Musser, B.J.; Rofail, D.; Hussein, M.; J, I,; Atmodjo, D.Y.; Perry, C.; Pan, C.; Mahmood, A.; Hosain, R.; Davis, J.D.; Turner, K.C.; Baum, A.; Kyratsous, C.A.; Kim, Y.; Cook, A.; Kampman, W.; Roque-Guerrero, L.; Acloque, G.; Aazami, H.; Cannon, K.; Simón-Campos, J.A.; Bocchini, J.A.; Kowal, B.; DiCioccio, A.T.; Soo, Y.; Geba, G.P.; Stahl, N.; Lipsich, L.; Braunstein, N.; Herman, G.; Yancopoulos, G.D. REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021, 385, e81.
- Takemoto, K. Retrospective Case-Control Study of REGEN-COV (casirivimab and imdevimab) Therapy for Patients with COVID-19 and Cancer Using the United States MarketScan® Database. Oncology. 2023, Sep 4.
- Li, D.; Xu, M.; Hooper, A.T.; Rofail, D.; Mohammadi, K.A.; Chen, Y.; Ali, S.; Norton, T.; Weinreich, D.M.; Musser, B.J.; Hamilton, J.D.; Geba, G.P. Casirivimab + imdevimab accelerates symptom resolution linked to improved COVID-19 outcomes across susceptible antibody and risk profiles. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 12784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuo, C.; Kubota, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kurita, Y.; Nakajima, A. Combined REGN-COV2 Antibody Therapy Immediately Prevented a Patient with Refractory Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis from Contracting SARS-CoV-2 during the Sixth Wave in Japan. Intern Med. 2023, 62, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, S.K.; Tharwat, S.; Hassan, A.H. Comparing the efficacy of regen-cov, remdesivir, and favipiravir in reducing invasive mechanical ventilation need in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. World J Clin Cases 11(26):6105-6121. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somersan-Karakaya, S.; Mylonakis, E.; Mou, J.; Oviedo-Orta, E.; O'Brien, M.P.; Mas Casullo, V.; Mahmood, A.; Hooper, A.T.; Hussein, M.; Ali, S.; Marty, F.M.; Forleo-Neto, E.; Bhore, R.; Hamilton, J.D.; Herman, G.A.; Hirshberg, B.; Weinreich, D.M. Effectiveness of Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Combination in Immunocompromised Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Post Hoc Analysis in a Phase 1/2/3 Double-Blind Trial. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023, 10, ofad211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahakel, H.; Murphy, C.; Frenck Jr, R.W.; Grimley, M.S.; Marsh, R.A.; Paulsen, G.C.; Haslam, D.B.; Phillips, C.L.; Courter, J.; Spearman, P.; Schulert, G.; Danziger-Isakov, L. Single Site Experience of the use of Monoclonal Antibodies for the Treatment of COVID-19 in High-risk Pediatric and Young Adult Patients. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2022, 41, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Teran, C.; Tiruthani, K.; McSweeney, M.; Ma, A.; Pickles, R.; Lai, S.K. Challenges and opportunities for antiviral monoclonal antibodies as COVID-19 therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021, 169, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.M.; Barigye, R.; Saminathan, H. Perspectives on the use and risk of adverse events associated with cytokine-storm targeting antibodies and challenges associated with development of novel monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of COVID-19 clinical cases. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021, 17, 2824–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addetia, A.; Park, Y.J.; Starr, T.; Greaney, A.J.; Sprouse, K.R.; Bowen, J.E.; Tiles, S.W.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; Bloom, J.D.; Corti, D.; Walls, A.C.; Veesler, D. Structural changes in the SARS-CoV-2 spike E406W mutant escaping a clinical monoclonal antibody cocktail. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragonnet-Cronin, M.; Nutalai, R.; Huo, J.; Dijokaite-Guraliuc, A.; Das, R.; Tuekprakhon, A.; Supasa, P.; Liu, C.; Selvaraj, M.; Groves, N.; Hartman, H.; Ellaby, N.; Sutton, J.M.; Bahar, M.W.; Zhou, D.; Fry, E.; Ren, J.; Brown, C.; Klenerman, P.; Dunachie, S.J.; Mongkolsapaya, J.; Hopkins, S.; Chand, M.; Stuart, D.I.; Screaton, G.R.; Rokadiya, S. Generation of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations by monoclonal antibody therapy. Nature Commun. 2023, 14, 3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freidel, M.R.; Armen, R.S. Mapping major SARS-CoV-2 drug targets and assessment of druggability using computational fragment screening: Identification of an allosteric small-molecule binding site on the Nsp13 helicase. PLoS One. 2021, 16, e0246181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.B.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; Péré, H.; Veyer, D.; Puech, J.; Rodary, J.; Baele, G.; Dellicour, S.; Raymenants, J.; Gorissen, S.; Geenen, C.; Vanmechelen, B.; Wawina-Bokalanga, T.; Martí-Carreras, J.; Cuypers, L.; Sève, A.; Hocqueloux, L.; Prazuck, T.; Rey, F.A.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Bruel, T.; Mouquet, H.; André, E.; Schwartz, O. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature. 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Krüger, N.; Schulz, S.; Cossmann, A.; Rocha, C.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Graichen, L.; Moldenhauer, A.S.; Winkler, M.S.; Lier, M.; Dopfer-Jablonka, A.; Jäck, H.M.; Behrens, G.M.N.; Pöhlmann, S. The Omicron variant is highly resistant against antibody-mediated neutralization: Implications for control of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell. 2022, 185, 447–456.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Bruel, T.; Staropoli, I.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Porrot, F.; Maes, P.; Grzelak, L.; Prot, M.; Mougari, S.; Planchais, C.; Puech, J.; Saliba, M.; Sahraoui, R.; Fémy, F.; Morel, N.; Dufloo, J.; Sanjuán, R.; Mouquet, H.; André, E.; Hocqueloux, L.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Veyer, D.; Prazuck, T.; Péré, H.; Schwartz, O. Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies. Nat Commun. 2023, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focosi, D.; McConnell, S.; Sullivan, D.J.; Casadevall, A. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 mutations associated with resistance to therapeutic monoclonal antibodies that emerge after treatment. Drug Resist Updat. 2023, 71, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmam, S.; Vongphayloth, K.; Baquero, E.; Munier, S.; Bonomi, M.; Regnault, B.; Douangboubpha, B.; Karami, Y.; Chrétien, D.; Sanamxay, D.; Xayaphet, V.; Paphaphanh, P.; Lacoste, V.; Somlor, S.; Lakeomany, K.; Phommavanh, N.; Pérot, P.; Dehan, O.; Amara, F.; Donati, F.; Bigot, T.; Nilges, M.; Rey, F.A.; van der Werf, S.; Brey, P.T.; Eloit, M. ; Bat coronaviruses related to SARS-CoV-2 and infectious for human cells. Nature. 2022, 604, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ji, J.; Chen, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, T.; Song, H.; Zhao, R.; Chen, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hughes, A.C.; Holmes, E.C.; Shi, W. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell. 2021, 184, 4380–4391.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Karuppanan, K.; Subramaniam, G. Omicron (BA.1) and sub-variants (BA.1.1, BA.2, and BA.3) of SARS-CoV-2 spike infectivity and pathogenicity: A comparative sequence and structural-based computational assessment. J Med Virol. 2022, 94, 4780–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Delipan, R.; Chakraborty, D.; Kanjo, K.; Singh, R.; Singh, N.; Siddiqui, S.; Tyagi, A.; Jha, V.; Thakur, K.G.; Pandey, R.; Varadarajan, R.; Ringe, R.P. Mutations in S2 subunit of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron spike strongly influence its conformation, fusogenicity, and neutralization sensitivity. J Virol. 2023, 97, e0092223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Cao, Y.; He, B.; Lu, G. Targetable elements in SARS-CoV-2 S2 subunit for the design of pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitors and vaccines. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Wang, H. Spike protein mediated membrane fusion during SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Med Virol. 2023, 95, e28212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Deng, R.; Wong, G.; Lavillette, D.; Meng, G. SARS-CoV-2 spike engagement of ACE2 primes S2' site cleavage and fusion initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022, 119, e2111199119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobelt, R.; Adler, J.; Shaul, Y. The Transmembrane Protease Serine 2 (TMPRSS2) Non-Protease Domains Regulating Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike-Mediated Virus Entry. Viruses. 2023, 15, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, L.; Zhu, G.; Yang, M.; Cao, L.; Xing, X.; Yin, G.; Chan, C.; Qin, C.; Rao, Z.; Wang, X.; Sun, F.; Zhu, Y. Nanometer-resolution in situ structure of the SARS-CoV-2 postfusion spike protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021, 118, e2112703118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, T.; Peng, H.; Sterling, S.M.; Walsh Jr, R.M.; Rawson, S.; Rits-Volloch, S.; Chen, B. Distinct conformational states of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science. 2020, 369, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, C.; White, K.I.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Esquivies, L.; Brunger, A.T. Structural conservation among variants of the SARS-CoV-2 spike postfusion bundle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022, 119, e2119467119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Xu, M.; Pradhan, M.; Gorshkov, K.; Petersen, J.D.; Straus, M.R.; Zhu, W.; Shinn, P.; Guo, H.; Shen, M.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Michael, S.G.; Zimmerberg, J.; Zheng, W.; Whittaker, G.R. Identifying SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitors through Drug Repurposing Screens of SARS-S and MERS-S Pseudotyped Particles. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Shi, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 entry processes: The promising potential and future of host-targeted small-molecule inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2024, 263, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, S.; Kratzel, A.; Barut, G.T.; Lang, R.M.; Moreira, E.A. Thomann, L.; Kelly, J.N.; Thiel, V. SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024, Jan 15.
- Liu, H.T.; Cheng, T.; Liu, B.Y.; Chi, J.; Shu, T.; Wang, T. Structures of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and applications for novel drug development. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 955648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Goreshnik, I.; Coventry, B.; Case, J.B.; Miller, L.; Kozodoy, L.; Chen, R.E.; Carter, L.; Walls, A.C.; Park, Y.J.; Strauch, E.M.; Stewart, L.; Diamond, M.S.; Veesler, D.; Baker, D. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors. Science. 2020, 370, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Hajjo, R.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Zhong, H.A. An Updated Review on Betacoronavirus Viral Entry Inhibitors: Learning from Past Discoveries to Advance COVID-19 Drug Discovery. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021, 21, 571–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toelzer, C.; Gupta, K.; Yadav, S.K.N.; Borucu, U.; Davidson, A.D.; Williamson, M.K.; Shoemark, D.K.; Garzoni, F.; Staufer, O.; Milligan, R.; Capin, J.; Mulholland, A.J.; Spatz, J.; Fitzgerald, D.; Berger, I.; Schaffitzel, C. Free fatty acid binding pocket in the locked structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Science. 2020, 370, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.; Pye, V.E.; Graham, C.; Muir, L.; Seow, J.; Ng, K.W.; Cook, N.J.; Rees-Spear, C.; Parker, E.; Silva Dos Santos, M.; Rosadas, C.; Susana, A.; Rhy, H.; Nans, A.; Masino, L.; Roustan, C.; Christodoulou, E.; Ulferts, R.; Wrobel, A.G.; Short, C.E.; Fertleman, M.; Sanders, R.W.; Heaney, J.; Spyer, M.; Kjær, S.; Riddell, A.; Malim, M.H.; Beale, R.; MacRae, J.I.; Taylor, G.P.; Nastouli, E.; van Gils, M.J.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Pizzato, M.; McClure, M.O.; Tedder, R.S.; Kassiotis, G.; McCoy, L.E.; Doores, K.J.; Cherepanov, P. SARS-CoV-2 can recruit a heme metabolite to evade antibody immunity. Sci Adv. 2021, 7, eabg7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Meng, F.; Xie, Y.; Wang, W.; Meng, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, T.; Qi, J.; Ni, X.; Zheng, S.; Huang, S.; Huang, N. In Silico Discovery of Small Molecule Modulators Targeting the Achilles' Heel of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. ACS Cent Sci. 2023, 9, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhan, Q.; Wu, D.; Yang, C.; He, X.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wen, M.; Lu, L.; Ma, C.; Guo, J.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Li, L.; Jiang, S.; Pan, X.; Liu, S.; Tan. S. Sertraline Is an Effective SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibitor Targeting the Spike Protein. J Virol. 2022, 96, e0124522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, M.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, S.; Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Parthasarathi, R. Analogue discovery of safer alternatives to HCQ and CQ drugs for SAR-CoV-2 by computational design. Comput Biol Med. 2021, 130:104222.
- Puhl, A.C.; Fritch, E.J.; Lane, T.R.; Tse, L.V.; Yount, B.L.; Sacramento, C.Q.; Fintelman-Rodrigues, N.; Tavella, T.A.; Maranhão Costa, F.T.; Weston, S.; Logue, J.; Frieman, M.; Premkumar, L.; Pearce, K.H.; Hurst, B.L.; Andrade, C.H.; Levi, J.A.; Johnson, N.J.; Kisthardt, S.C.; Scholle, F.; Souza, T.M.L.; Moorman, M.J.; Baric, R.S.; Madrid, P.B.; Ekins, S. Repurposing the Ebola and Marburg Virus Inhibitors Tilorone, Quinacrine, and Pyronaridine: In Vitro Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Potential Mechanisms. ACS Omega. 2021, 6, 7454–7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargantilla, M.; Francés, C.; Adhav, A.; Forcada-Nadal, A.; Martínez-Gualda, B.; Martí-Marí, O.; López-Redondo, M.L.; Melero, R.; Marco-Marín, C.; Gougeard, N.; Espinosa, C.; Rubio-Del-Campo, A.; Ruiz-Partida, R.; Del Pilar Hernández-Sierra, M.; Villamayor-Belinchón, L.; Bravo, J.; Llacer, J.L.; Marina, A.; Rubio, V.; San-Félix, A.; Geller, R.; Pérez-Pérez, M.J. C-2 Thiophenyl Tryptophan Trimers Inhibit Cellular Entry of SARS-CoV-2 through Interaction with the Viral Spike (S) Protein. J Med Chem. 2023, 66, 10432–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattnaik, G.P.; Chakraborty, H. Entry Inhibitors: Efficient Means to Block Viral Infection. J Membr Biol. 2020, 253, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Lan, Q.; Feng, S.; Qi, S.; Bao, L.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; Qin, C.; Sun, F.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lu, L. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Lan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiao, F.; Zhou, J.; Hua, C.; Wang, Q.; Cai, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; Munch, J.; Kirchhoff, F.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Sun, F.; Jiang, S.; Lu, L. Structural and functional basis for pan-CoV fusion inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants with preclinical evaluation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Guo, L., Lin, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, F., Yang, J., Wang, L.; Wen, A.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Yin, K.; Yuan, X.; Yu, C.; He, B.; Cao, Y.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, G. An engineered 5-helix bundle derived from SARS-CoV-2 S2 pre-binds sarbecoviral spike at both serological- and endosomal-pH to inhibit virus entry. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1920–1935.
- Xing, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z.; Shen, X.; Zhou, J.; Xu, L.; Pu, J.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.; Lu, L.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S. A Five-Helix-Based SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Inhibitor Targeting Heptad Repeat 2 Domain against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants of Concern. Viruses. 2022, 14, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, W.; Chen, G.; Dang, B. Novel Engineered SARS-CoV-2 HR1 Trimer Exhibits Improved Potency and Broad-Spectrum Activity against SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants. J Virol. 2022, 96, e0068122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Ma, Y.; Na, H. Structure and Function of the SARS-CoV-2 6-HB Fusion Core and Peptide-Based Fusion Inhibitors: A Review. Curr Med Chem. 2023. Nov 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Pan, X.; Xu, X.; Cheng, C.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Jiang, S.; Xu, W.; Xiao, G.; Liu, S. Salvianolic acid C potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection by blocking the formation of six-helix bundle core of spike protein. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020, 5, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, I.D.; Bhattacharya, P.; Mayilsamy, K.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharje, G.; Das, S.; Aditya, S.; Ghosh, A.; McGill, A.R.; Srikrishnan, S.; Das, A.K.; Basak, A.; Mohapatra, S.S.; Chandran, B.; Bhimsaria, D.; Mohapatra, S.; Roy, A.; Mondal, A. argeting an evolutionarily conserved "E-L-L" motif in spike protein to identify a small molecule fusion inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2. PNAS Nexus. 2022, 1, pgac198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Pan, X.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shang, W.; Niu, X.; Wan, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Xiao, G.; Xu, W. Drug Repurposing of Itraconazole and Estradiol Benzoate against COVID-19 by Blocking SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein-Mediated Membrane Fusion. Adv Ther (Weinh). 2021. 4(5):2000224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Andrianov, A.M.; Wang, L.; Furs, K.V.; Gonchar, A.V.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; Xia, S.; Tuzikov, A.V.; Jiang, S. Repurposing Navitoclax to block SARS-CoV-2 fusion and entry by targeting heptapeptide repeat sequence 1 in S2 protein. J Med Virol. 2023, 95, e29145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Qu, J.; Gui, S.; Li, L.; Li, S. Peptide-based inhibitors hold great promise as the broad-spectrum agents against coronavirus. Front Microbiol. 2023, 19, 1093646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Lan, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiao, F.; Zhou, J.; Hua, C.; Wang, Q.; Cai, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, H.; Sun, G.; Münch, J.; Kirchhoff, F.; Yuan, Z.; Xie, Y.; Sun, F.; Jiang, S.; Lu, L. Structural and functional basis for pan-CoV fusion inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants with preclinical evaluation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021, 6, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cao, R.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.; Deng, F.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Wang, M. The anti-influenza virus drug, arbidol is an efficient inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Chang, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Jiao, T.; Zhao, Z.; Ren, L.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Sharma, L.; Lei, X.; Wang, J. Identification of Potent and Safe Antiviral Therapeutic Candidates Against SARS-CoV-2. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 586572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobrowski, T.; Chen, L.; Eastman, RT.; Itkin, Z.; Shinn, P.; Chen, C.Z.; Guo, H.; Zheng, W.; Michael, S.; Simeonov, A.; Hall, M.D.; Zakharov, A.V.; Muratov, E.N. Synergistic and Antagonistic Drug Combinations against SARS-CoV-2. Mol Ther. 2021, 29, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzorno, A.; Padey, B.; Dubois, J.; Julien, T.; Traversier, A.; Dulière, V.; Brun, P.; Lina, B.; Rosa-Calatrava, M.; Terrier, O. In vitro evaluation of antiviral activity of single and combined repurposable drugs against SARS-CoV-2. Antiviral Res. 2020, 181, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankadari, N. Arbidol: A potential antiviral drug for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 by blocking trimerization of the spike glycoprotein. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2020, 56, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidel, M.R.; Armen, R.S. Modeling the Structure-Activity Relationship of Arbidol Derivatives and Other SARS-CoV-2 Fusion Inhibitors Targeting the S2 Segment of the Spike Protein. J Chem Inf Model. 2021, 61, 5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, A.; Pechalrieu, D.; Jackson, C.B.; Abegg, D.; Choe, H.; Adibekian, A. Clinical Antiviral Drug Arbidol Inhibits Infection by SARS-CoV-2 and Variants through Direct Binding to the Spike Protein. ACS Chem Biol. 2021, 16, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, C.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Song, G. Discovery and structural optimization of 3-O-β-chacotriosyl oleanane-type triterpenoids as potent entry inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 virus infections. Eur J Med Chem. 2021, 215, 113242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curreli, F.; Ahmed, S.; Victor, S.M.B.; Drelich, A.; Panda, S.S.; Altieri, A.; Kurkin, A.K.; Tseng, C.T.K.; Hillyer, C.D.; Debnath., A.K. Discovery of Highly Potent Fusion Inhibitors with Potential Pan-Coronavirus Activity That Effectively Inhibit Major COVID-19 Variants of Concern (VOCs) in Pseudovirus-Based Assays. Viruses. 2021, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curreli, F.; Chau, K.; Tran, T.T.; Nicolau, I.; Ahmed, S.; Das, P.; Hillyer, C.D.; Premenko-Lanier, M.; Debnath, A.K. Discovery of Highly Potent Small Molecule Pan-Coronavirus Fusion Inhibitors. Viruses. 2023, 15, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New substructure filters for removal of pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J Med Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomašić, T.; Mašič, L.P. Rhodanine as a scaffold in drug discovery: a critical review of its biological activities and mechanisms of target modulation. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 549–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musarrat, F.; Chouljenko, V.; Dahal, A.; Nabi, R.; Chouljenko, T.; Jois, S.D.; Kousoulas, K.G. The anti-HIV drug nelfinavir mesylate (Viracept) is a potent inhibitor of cell fusion caused by the SARSCoV-2 spike (S) glycoprotein warranting further evaluation as an antiviral against COVID-19 infections. J Med Virol. 2020, 92, 2087–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.R.; Cheng, F. Repurposing of FDA-Approved Toremifene to Treat COVID-19 by Blocking the Spike Glycoprotein and NSP14 of SARS-CoV-2. J Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4670–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Jan, J.T.; Ma, S.H.; Kuo, C.J.; Juan, H.F.; Cheng, Y.S.E.; Hsu, H.H.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, D.; Brik, A.; Liang, F.S.; Liu, R.S.; Fang, J.M.; Chen, S.T.; Liang, P.H.; Wong, C.H. Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004, 101, 10012–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cheng, C.; Shi, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Huo, L.; Pan, X.; Liu, S.; Song, G. Identification, optimization, and biological evaluation of 3-O-β-chacotriosyl ursolic acid derivatives as novel SARS-CoV-2 entry inhibitors by targeting the prefusion state of spike protein. Eur J Med Chem. 2022, 238, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, J.; Wan, X.; Li, B.; Guan, M.; Ning, X.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Liu, S.; Song, G. Discovery and structural optimization of 3-O-β-Chacotriosyl betulonic acid saponins as potent fusion inhibitors of Omicron virus infections. Bioorg Chem. 2023, 131, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisevich, S.S.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Molecular Modeling of Viral Type I Fusion Proteins: Inhibitors of Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin and the Spike Protein of Coronavirus. Viruses. 2023, 15, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarubaev, V.V.; Pushkina, E.A.; Borisevich, S.S.; Galochkina, A.V.; Garshinina, A.V.; Shtro, A.A.; Egorova, A.A.; Sokolova, A.S.; Khursan, S.L.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Selection of influenza virus resistant to the novel camphor-based antiviral camphecene results in loss of pathogenicity. Virology. 2018, 524, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, A.S.; Yarovaya, O.I.; Baranova, D.V.; Galochkina, A.V.; Shtro, A.A.; Kireeva, M.V.; Borisevich, S.S.; Gatilov, Y.V.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Quaternary ammonium salts based on (-)-borneol as effective inhibitors of influenza virus. Arch Virol. 2021, 166, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarovaya, O.I.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Borisevich, S.S.; Sokolova, A.S.; Gureev, M.A.; Khamitov, E.M.; Rudometova, N.B.; Zybkina, A.V.; Mordvinova, E.D.; Zaykovskaya, A.V.; Rogachev, A.D.; Pyankov, O.V.; Maksyutov, R.A.; Salakhutdinov, N.F. Borneol Ester Derivatives as Entry Inhibitors of a Wide Spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 Viruses. Viruses. 2022, 14, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalathiya, U.; Padariya, M.; Mayordomo, M.; Lisowska, M.; Nicholson, J.; Singh, A.; Baginski, M.; Fahraeus, R.; Carragher, N.; Ball, K.; Haas, J.; Daniels, A.; Hupp, T.R.; Alfaro, J.A. Highly Conserved Homotrimer Cavity Formed by the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein: A Novel Binding Site. J Clin Med. 2020, 9, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannella, C.; Chianese, A.; Greco, G.; Santella, B.; Squillaci, G.; Monti, A.; Doti, N.; Sanna, G.; Manzin, A.; Morana, A.; De Filippis, A.; D'Angelo, G.; Palmieri, F.; Franci, G.; Galdiero., M. Design of Three Residues Peptides against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses. 2022, 14, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




