Submitted:
04 March 2024
Posted:
05 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Background
- -
- LR-NC, non-categorizable, due to degraded images
- -
- LR-1, definitely benign,
- -
- LR-2, probably benign, referring to nodules less than 2cm, without any imagistic criteria of malignancy
- -
- LR-3, intermediate probability of malignancy, referring to nodules less than 2 cm with nonrim arterial hyperenhancement or nodules larger than 2cm with arterial iso or hypo-enhancement.
- -
- LR-4, high HCC probability, referring to nodules less than 10mm, with arterial hyperenhancement and one other typical feature or nodules over 20mm with arterial hyperenhancement and no other suggestive features
- -
- LR-5, definite diagnosis of HCC, nodules over 10mm with arterial hyperenhancement and portal washout, or with a 50% size increase in less than 6 months.
- -
- LR-TIV, malignant venous thrombus, with arterial hyperenhancement regardless of the presence of a liver nodule
- -
- LR-M, high malignancy probability, but not HCC, referring to nodules with rim arterial enhancement, peripheral washout, targetoid aspect or infiltrative appearance.
Materials and Methods:
Ethical Statement
Patient Selection
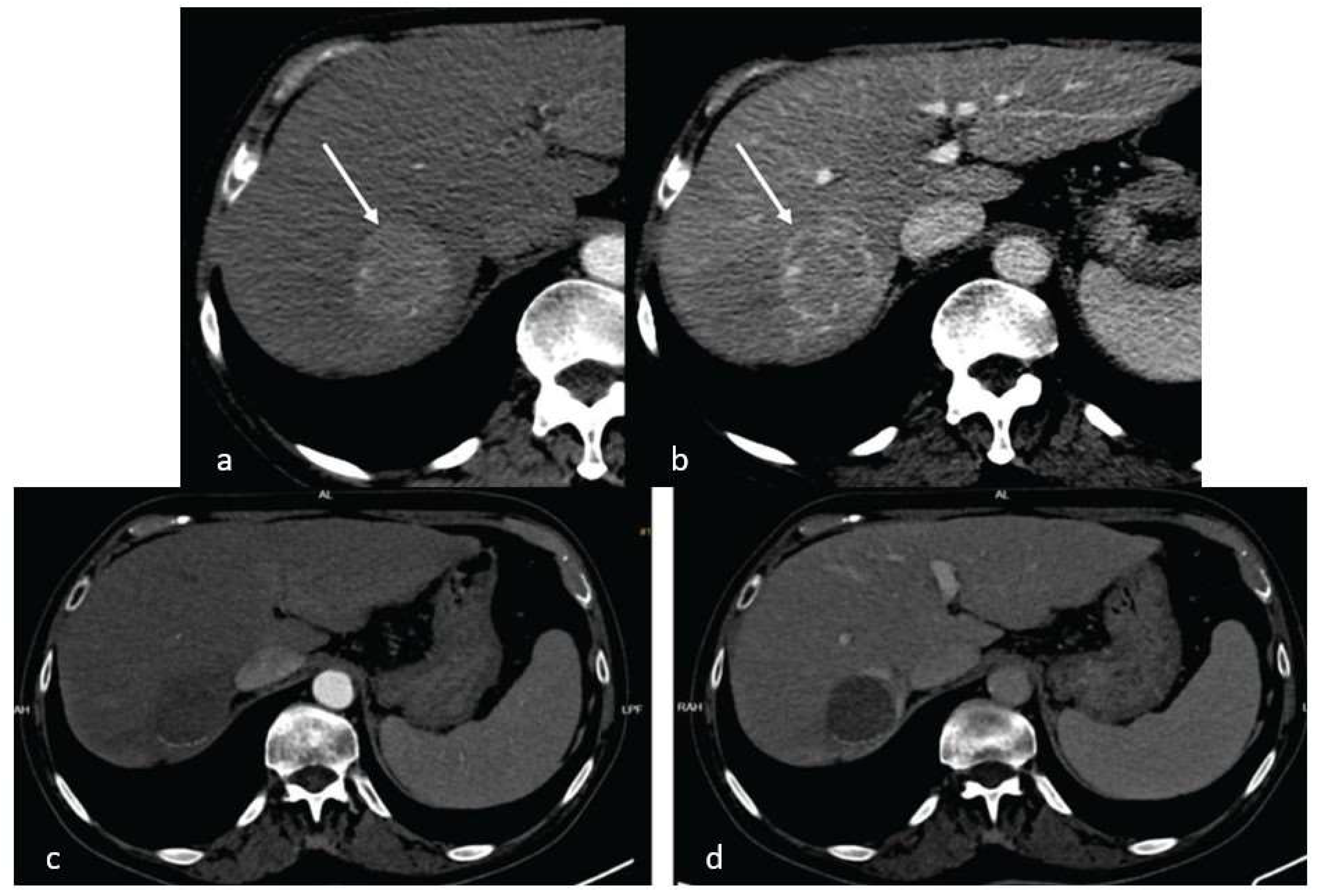
Imaging Techniques
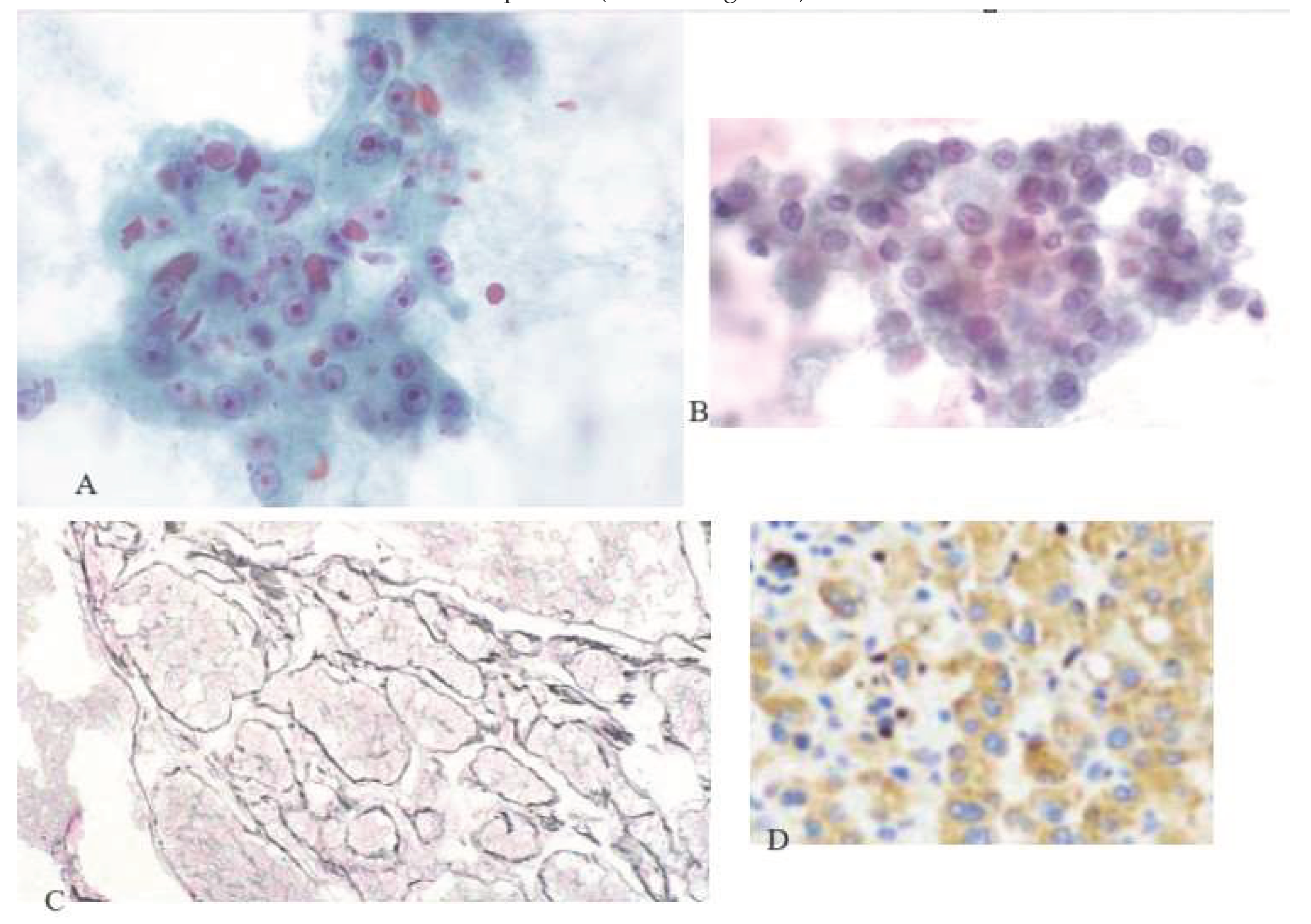
Histology Analysis
Statistical Analysis
Results:
Descriptive Data
Discussion
Conclusion
References
- Lee HM, Lidofsky SD, Taddei TH, Townshend-Bulson LJ. Attacking the public health crisis of hepatocellular carcinoma at its roots. Hepatology. 2023 Apr 1;77(4):1456-1459. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32741. Epub 2022 Oct 11. PMID: 35989555; PMCID: PMC10026951. [CrossRef]
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018 Nov;68(6):394-424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul;70(4):313. PMID: 30207593. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O, Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, Laversanne M, McGlynn KA, Soerjomataram I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec;77(6):1598-1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. Epub 2022 Oct 5. PMID: 36208844; PMCID: PMC9670241. [CrossRef]
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018 Mar 31;391(10127):1301-1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30010-2. Epub 2018 Jan 5. PMID: 29307467. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018 Jul;69(1):182-236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.019. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Erratum in: J Hepatol. 2019 Apr;70(4):817. PMID: 29628281. [CrossRef]
- Valery PC, Laversanne M, Clark PJ, Petrick JL, McGlynn KA, Bray F. Projections of primary liver cancer to 2030 in 30 countries worldwide. Hepatology. 2018 Feb;67(2):600-611. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29498. Epub 2017 Dec 23. PMID: 28859220; PMCID: PMC5832532. [CrossRef]
- Singal AG, Llovet JM, Yarchoan M, Mehta N, Heimbach JK, Dawson LA, Jou JH, Kulik LM, Agopian VG, Marrero JA, Mendiratta-Lala M, Brown DB, Rilling WS, Goyal L, Wei AC, Taddei TH. AASLD Practice Guidance on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2023 May 22. https://doi.org/10.1097/HEP.0000000000000466. Epub ahead of print. Erratum in: Hepatology. 2023 Oct 16;: PMID: 37199193. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenbrey JR, Gabriel H, Savsani E, Lyshchik A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in HCC diagnosis and assessment of tumor response to locoregional therapies. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Aug;46(8):3579-3595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03059-y. Epub 2021 Apr 7. PMID: 33825927; PMCID: PMC8569604. [CrossRef]
- Matsui O, Kobayashi S, Sanada J, Kouda W, Ryu Y, Kozaka K, Kitao A, Nakamura K, Gabata T. Hepatocelluar nodules in liver cirrhosis: hemodynamic evaluation (angiography-assisted CT) with special reference to multi-step hepatocarcinogenesis. Abdom Imaging. 2011 Jun;36(3):264-72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-011-9685-1. PMID: 21267562; PMCID: PMC3102849. [CrossRef]
- Huang P, Wu F, Hou K, Zhou C, Xiao Y, Wang C, Miao G, Yang C, Zeng M. Diagnostic algorithm for subcentimeter hepatocellular carcinoma using alpha-fetoprotein and imaging features on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol. 2023 Oct 4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-023-10214-0. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37792079. [CrossRef]
- Lee YT, Wang JJ, Zhu Y, Agopian VG, Tseng HR, Yang JD. Diagnostic Criteria and LI-RADS for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021 Aug 5;17(6):409-413. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.1075. PMID: 34386205; PMCID: PMC8340355. [CrossRef]
- Chernyak V, Fowler KJ, Kamaya A, Kielar AZ, Elsayes KM, Bashir MR, Kono Y, Do RK, Mitchell DG, Singal AG, Tang A, Sirlin CB. Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) Version 2018: Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in At-Risk Patients. Radiology. 2018 Dec;289(3):816-830. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018181494. Epub 2018 Sep 25. PMID: 30251931; PMCID: PMC6677371. [CrossRef]
- Tremosini S, Forner A, Boix L, Vilana R, Bianchi L, Reig M, Rimola J, Rodríguez-Lope C, Ayuso C, Solé M, Bruix J. Prospective validation of an immunohistochemical panel (glypican 3, heat shock protein 70 and glutamine synthetase) in liver biopsies for diagnosis of very early hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2012 Oct;61(10):1481-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301862. Epub 2012 Jan 27. PMID: 22287594. [CrossRef]
- Park BV, Gaba RC, Huang YH, Chen YF, Guzman G, Lokken RP. Histology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Association with Clinical Features, Radiological Findings, and Locoregional Therapy Outcomes. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2019 Nov 18;9:52. https://doi.org/10.25259/JCIS_111_2019. PMID: 31819829; PMCID: PMC6884980. [CrossRef]
- Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V, Salem R, Sangro B, Singal AG, Vogel A, Fuster J, Ayuso C, Bruix J. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022 Mar;76(3):681-693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.018. Epub 2021 Nov 19. PMID: 34801630; PMCID: PMC8866082. [CrossRef]
- Bruix J, Chan SL, Galle PR, Rimassa L, Sangro B. Systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: An EASL position paper. J Hepatol. 2021 Oct;75(4):960-974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.07.004. Epub 2021 Jul 10. PMID: 34256065. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He Y, Lu M, Che J, Chu Q, Zhang P, Chen Y. Biomarkers and Future Perspectives for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 6;11:716844. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.716844. PMID: 34552872; PMCID: PMC8450565. [CrossRef]
- Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL, Mathurin P, Edeline J, Kudo M, Harding JJ, Merle P, Rosmorduc O, Wyrwicz L, Schott E, Choo SP, Kelley RK, Sieghart W, Assenat E, Zaucha R, Furuse J, Abou-Alfa GK, El-Khoueiry AB, Melero I, Begic D, Chen G, Neely J, Wisniewski T, Tschaika M, Sangro B. Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):77-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00604-5. Epub 2021 Dec 13. PMID: 34914889. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji JH, Ha SY, Lee D, Sankar K, Koltsova EK, Abou-Alfa GK, Yang JD. Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Response in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7640. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24087640. PMID: 37108802; PMCID: PMC10144688. [CrossRef]
- Calderaro J, Rousseau B, Amaddeo G, Mercey M, Charpy C, Costentin C, Luciani A, Zafrani ES, Laurent A, Azoulay D, Lafdil F, Pawlotsky JM. Programmed death ligand 1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship With clinical and pathological features. Hepatology. 2016 Dec;64(6):2038-2046. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28710. Epub 2016 Aug 9. PMID: 27359084. [CrossRef]
- Cheng AL, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux M, Kim TY, Lim HY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, Li D, Verret W, Ma N, Nicholas A, Wang Y, Li L, Zhu AX, Finn RS. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2022 Apr;76(4):862-873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.030. Epub 2021 Dec 11. PMID: 34902530. [CrossRef]
- http://www.casan.ro/casbz/media/pageFiles/201)%20L01XC32.5-ATEZOLIZUMAB%20carcinom%20hepatocelular.pdf.
- Chiang CL, Chan ACY, Chiu KWH, Kong FS. Combined Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy and Checkpoint Inhibition in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Potential Synergistic Treatment Strategy. Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 12;9:1157. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01157. PMID: 31799176; PMCID: PMC6874138. [CrossRef]
- Finn RS. The Role of Liver Biopsy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2016 Oct;12(10):628-630. PMID: 27917077; PMCID: PMC5114505.
- Seeff LB, Everson GT, Morgan TR, Curto TM, Lee WM, Ghany MG, Shiffman ML, Fontana RJ, Di Bisceglie AM, Bonkovsky HL, Dienstag JL; HALT–C Trial Group. Complication rate of percutaneous liver biopsies among persons with advanced chronic liver disease in the HALT-C trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Oct;8(10):877-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2010.03.025. Epub 2010 Apr 1. PMID: 20362695; PMCID: PMC3771318. [CrossRef]
- Midia M, Odedra D, Shuster A, Midia R, Muir J. Predictors of bleeding complications following percutaneous image-guided liver biopsy: a scoping review. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019 Jan;25(1):71-80. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2018.17525. PMID: 30644369; PMCID: PMC6339629. [CrossRef]
- Silva MA, Hegab B, Hyde C, Guo B, Buckels JA, Mirza DF. Needle track seeding following biopsy of liver lesions in the diagnosis of hepatocellular cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 2008 Nov;57(11):1592-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.149062. Epub 2008 Jul 31. PMID: 18669577. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szpakowski JL, Drasin TE, Lyon LL. Rate of seeding with biopsies and ablations of hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. Hepatol Commun. 2017 Sep 29;1(9):841-851. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1089. PMID: 29404497; PMCID: PMC5721456. [CrossRef]
- Liu GJ, Wang W, Lu MD, Xie XY, Xu HX, Xu ZF, Chen LD, Wang Z, Liang JY, Huang Y, Li W, Liu JY. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for the Characterization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2015 Dec;4(4):241-52. https://doi.org/10.1159/000367738. Epub 2015 Oct 21. PMID: 26779444; PMCID: PMC4702012. [CrossRef]
- Wang G, Zhu S, Li X. Comparison of values of CT and MRI imaging in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and analysis of prognostic factors. Oncol Lett. 2019 Jan;17(1):1184-1188. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9690. Epub 2018 Nov 12. PMID: 30655882; PMCID: PMC6312947. [CrossRef]
- Semaan S, Vietti Violi N, Lewis S, Chatterji M, Song C, Besa C, Babb JS, Fiel MI, Schwartz M, Thung S, Sirlin CB, Taouli B. Hepatocellular carcinoma detection in liver cirrhosis: diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced CT vs. MRI with extracellular contrast vs. gadoxetic acid. Eur Radiol. 2020 Feb;30(2):1020-1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06458-4. Epub 2019 Oct 31. PMID: 31673837. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng J, Zheng J, Yang C, Wang R, Zhou Y, Tao YY, Gong XQ, Wang WC, Zhang XM, Yang L. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging to differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 2020 May 7;10(1):7717. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64804-9. PMID: 32382050; PMCID: PMC7206040. [CrossRef]
- Di Tommaso L, Spadaccini M, Donadon M, Personeni N, Elamin A, Aghemo A, Lleo A. Role of liver biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 28;25(40):6041-6052. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6041. PMID: 31686761; PMCID: PMC6824282. [CrossRef]
- Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL, Mathurin P, Edeline J, Kudo M, Harding JJ, Merle P, Rosmorduc O, Wyrwicz L, Schott E, Choo SP, Kelley RK, Sieghart W, Assenat E, Zaucha R, Furuse J, Abou-Alfa GK, El-Khoueiry AB, Melero I, Begic D, Chen G, Neely J, Wisniewski T, Tschaika M, Sangro B. Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):77-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00604-5. Epub 2021 Dec 13. PMID: 34914889. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu AX, Finn RS, Edeline J, Cattan S, Ogasawara S, Palmer D, Verslype C, Zagonel V, Fartoux L, Vogel A, Sarker D, Verset G, Chan SL, Knox J, Daniele B, Webber AL, Ebbinghaus SW, Ma J, Siegel AB, Cheng AL, Kudo M; KEYNOTE-224 investigators. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): a non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Jul;19(7):940-952. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30351-6. Epub 2018 Jun 3. Erratum in: Lancet Oncol. 2018 Sep;19(9):e440. PMID: 29875066. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles T, Eder JP, Fine GD, Braiteh FS, Loriot Y, Cruz C, Bellmunt J, Burris HA, Petrylak DP, Teng SL, Shen X, Boyd Z, Hegde PS, Chen DS, Vogelzang NJ. MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature. 2014 Nov 27;515(7528):558-62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13904. PMID: 25428503. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinovink JW, van Hall T, Ossendorp F, Fransen MF. PD-L1 immune suppression in cancer: Tumor cells or host cells? Oncoimmunology. 2017 May 12;6(7):e1325982. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2017.1325982. PMID: 28811961; PMCID: PMC5543902. [CrossRef]
- Pinato DJ, Mauri FA, Spina P, Cain O, Siddique A, Goldin R, Victor S, Pizio C, Akarca AU, Boldorini RL, Mazzucchelli L, Black JRM, Shetty S, Marafioti T, Sharma R. Clinical implications of heterogeneity in PD-L1 immunohistochemical detection in hepatocellular carcinoma: the Blueprint-HCC study. Br J Cancer. 2019 May;120(11):1033-1036. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0466-x. Epub 2019 May 7. PMID: 31061454; PMCID: PMC6738063. [CrossRef]
- Yi M, Jiao D, Xu H, Liu Q, Zhao W, Han X, Wu K. Biomarkers for predicting efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Mol Cancer. 2018 Aug 23;17(1):129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0864-3. PMID: 30139382; PMCID: PMC6107958. [CrossRef]
- Vilain RE, Menzies AM, Wilmott JS, Kakavand H, Madore J, Guminski A, Liniker E, Kong BY, Cooper AJ, Howle JR, Saw RPM, Jakrot V, Lo S, Thompson JF, Carlino MS, Kefford RF, Long GV, Scolyer RA. Dynamic Changes in PD-L1 Expression and Immune Infiltrates Early During Treatment Predict Response to PD-1 Blockade in Melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;23(17):5024-5033. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0698. Epub 2017 May 16. PMID: 28512174. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallis KS, Makrakis D, Ziogas IA, Tsoulfas G. Immunotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: From clinical trials to real-world data and future advances. World J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jun 24;13(6):448-472. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i6.448. PMID: 35949435; PMCID: PMC9244967. [CrossRef]
- Xia Y, Tang W, Qian X, Li X, Cheng F, Wang K, Zhang F, Zhang C, Li D, Song J, Zhang H, Zhao J, Yao A, Wu X, Wu C, Ji G, Liu X, Zhu F, Qin L, Xiao X, Deng Z, Kong X, Li S, Yu Y, Xi W, Deng W, Qi C, Liu H, Pu L, Wang P, Wang X. Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab plus apatinib during the perioperative period in resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, open label, phase II clinical trial. J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Apr;10(4):e004656. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2022-004656. PMID: 35379737; PMCID: PMC8981365. [CrossRef]
- Maas M, Beets-Tan R, Gaubert JY, Gomez Munoz F, Habert P, Klompenhouwer LG, Vilares Morgado P, Schaefer N, Cornelis FH, Solomon SB, van der Reijd D, Bilbao JI. Follow-up after radiological intervention in oncology: ECIO-ESOI evidence and consensus-based recommendations for clinical practice. Insights Imaging. 2020 Jul 16;11(1):83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-020-00884-5. PMID: 32676924; PMCID: PMC7366866. [CrossRef]
- Zen C, Zen Y, Mitry RR, Corbeil D, Karbanová J, O'Grady J, Karani J, Kane P, Heaton N, Portmann BC, Quaglia A. Mixed phenotype hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization and liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2011 Aug;17(8):943-54. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.22314. PMID: 21491582. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo FP, Imondi A, Lynch EN, Farinati F. When and how should we perform a biopsy for HCC in patients with liver cirrhosis in 2018? A review. Dig Liver Dis. 2018 Jul;50(7):640-646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Mar 20. PMID: 29636240. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuhu AN, Rahnea-Nita G, Popescu M, Rahnea-Nita RA. Abstract P5-15-22: Evaluation of quality of life in patients with advanced and metastatic breast cancer proposed for palliative chemotherapy and best supportive care versus best supportive care. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, P5-15-22. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.SABCS14-P5-15-22. [CrossRef]
- von Felden J, Karkmann K, Ittrich H, Gil-Ibanez I, Fründt T, Krause J, Lohse AW, Wege H, Schulze K. Sequential Systemic Treatment in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Able to Prolong Median Survival to More than 3 Years in a Selected Real-World Cohort. Visc Med. 2021 Mar;37(2):87-93. https://doi.org/10.1159/000507381. Epub 2020 May 7. PMID: 33981749; PMCID: PMC8077524. [CrossRef]
| No previous interventions (N= 10 patients) |
Previous TACE (N= 9 patients) |
Previous RFA (N= 4 patients) |
|
| Etiology of liver disease | HCV cirrhosis: 2 patients (20%) HBV cirrhosis: 5 patients (50%) NASH cirrhosis: 1 patient (10%) HBV +HDV hepatitis: 2 patients (20%) |
HCV cirrhosis: 5 patients (55.5%) HBV hepatitis: 1 patient (11.1%) HBV + HDV hepatitis: 2 patients (22.2%) NASH cirrhosis: 1 patient (11.1%) |
HCV cirrhosis: 2 patients (50%) HBV hepatitis: 1 patient (25%) HBV cirrhosis: 1 patient (25%) |
| AFP (N: 0 - 8.1 ng/ml) |
380.52 +/- 134.83 | 112.56 +/- 45.24 | 135 +/- 46.13 |
| LI-RADS score | LR- 4: 2 patients (20%) LR- 5: 8 patients (80%) |
LR- 4: 2 patients (22.2%) LR-5: 7 patients (77.7%) |
LR- 4: 1 patient (25%) LR- 5: 3 patients (75%) |
| Number of nodules | 1-3: 8 patients (80%) >3: 2 patients (20%) |
1-3: 6 patients (66.6%) >3: 3 patients (33.3%) |
1-3: 3 patients (75%) >3: 1 patient (25%) |
| Size of nodule of interest | Median 3.5 cm Range 1.6-5.2 cm |
Median 2.4 cm Range 1.8- 3.7 |
Median 2.2 cm Range 2.1-2.5 cm |
| Portal vein invasion | Yes – 4 patients (40%) | Yes- 2 patients (22.2%) | Yes- 0 patients (0%) |
| No previous interventions (N= 10 patients) |
Previous TACE (N= 9 patients) |
Previous RFA (N= 4 patients) |
|
| Edmondson – Steiner | Grade II: 4 patients (40%) Grade III: 5 patients (50%) Grade IV: 1 patient (1%) |
Grade II: 3 patients (33.3%) Grade III: 6 patients (66.6%) |
Grade II: 1 patient (25%) Grade III: 3 patients (75%) |
| PD-L1 expression | 11.6% | 8.7% | 9.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





