1. Introduction
Physical activity has always been present in human history. Its existence was so natural that people could not recognize its importance. In ancient and medieval times, the most important purpose of physical activity was war, and physical education was no different from military training [
1,
2]. In modern times, under the influence of nationalism and with education becoming scientific, physical education developed with the rise of general education and aimed at cognitive, moral, and physical development [
3]. Later, modernized schools played a key role in students’ physical activity, which was placed under the name of physical education. Today, the emerging interest in well-being is emphasizing the role of physical education in student health.
Physical education has recently faced a remarkable change, being especially promoted by the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic. Globally, trends such as the rapid spread of physical activity using non-face-to-face remote systems [
4,
5,
6], verification of health promotion and treatment effects [
7,
8,
9], as well as convergence of physical activity and information and communications technology (ICT) have been observed [
10,
11,
12,
13]. After the pandemic, a new popular trend called “EdTech” has appeared [
14,
15,
16].
Despite the positive aspects of this change, people inevitably faced negative aspects. The biggest drawback is that there is a lack of sufficient amount of physical activity [
17,
18]. Insufficient physical activity caused several problems among various subjects. Notably, the increase in obesity, which threatens student health, has been reported in several studies [
5,
19,
20]. While these studies consistently focused on physical activity and obesity, they did not examine the changes in obesity levels in a large student population at the national level, contemplating the role of physical education for student health from a pedagogical perspective.
Body mass index (BMI), which is the most common index for determining obesity, is calculated by dividing weight by the square of height (㎏/㎡) [
21]. Since the BMI can be measured using only height and weight, it has been widely used as an efficient value for measuring obesity. Recently, research has been exploring the relationship between BMI and employment instability [
22]. Moreover, a relatively long argument is being carried out on the necessity to measure children’s BMI and provide the results to parents during school years [
23].
This study tracked changes in obesity among Korean elementary school students using large-scale national-level data. This is significant in that it targeted a repeated and large number of subjects that could not be included in previous studies. This research is also necessary as it can provide basic data for setting the direction of national policies and future education. Furthermore, the period in which this study was conducted was when non-face-to-face physical education classes had been actively conducted. This study explored changes in obesity during this period to examine the effect of changes in physical education. Furthermore, this was conducted to contemplate the present role and the future direction of physical education.
The data used in this study was obtained from the Physical Activity Promotion System (PAPS) of the Korean government, from 2019 to 2021. The PAPS is a “student health physical fitness evaluation system” led by the Ministry of Education and measures cardiorespiratory endurance, flexibility, quickness, body fat, and muscular strength/endurance of all elementary, middle, and high school students in Korea every year [
24]. It has been used in various studies on student health since it is a highly reliable large-scale survey conducted by a public educational institution [
25,
26].
Therefore, this study seeks to examine how BMI values in Korean elementary schools have changed over the years using a large-scale survey measured repeatedly for 3 years, through which it will provide basic data to diagnose the role of physical education for student health and set future directions. For this purpose, the following research questions were formulated.
First, how did the average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea change according to each year of the study period?
Second, how did the yearly average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea change depending on gender?
Third, how did the yearly average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea change depending on the grade?
2. Materials and Methods
This study aims to explore the role of physical education for student health by examining the changes in the average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea. To this end, this study used the BMI data of Korean elementary school students. BMI was measured as a subfactor of the Physical Activity Promotion System (PAPS) implemented according to the plan established by the Korean Ministry of Education [
25]. The PAPS is a “student health physical fitness evaluation system” implemented every year on 5th and 6th grade elementary school students as well as on all middle school (1st to 3rd year) and high school students (1st to 3rd year) nationwide. Measurements of cardiorespiratory endurance, flexibility, quickness, body fat, and muscular strength/endurance are mandatory, while the precise cardiorespiratory endurance, obesity, and student posture assessments, as well as body self-assessment are optional. BMI is measured as a mandatory element for body fat measurement. The yearly results of the PAPS for elementary, middle, and high schools nationwide are disclosed on the school information disclosure service School Info (
https://www.schoolinfo.go.kr), particularly the male and female BMI averages according to grade . The 2019–2021 PAPS results are disclosed on School Info as of January 2024.
2.1. Participants
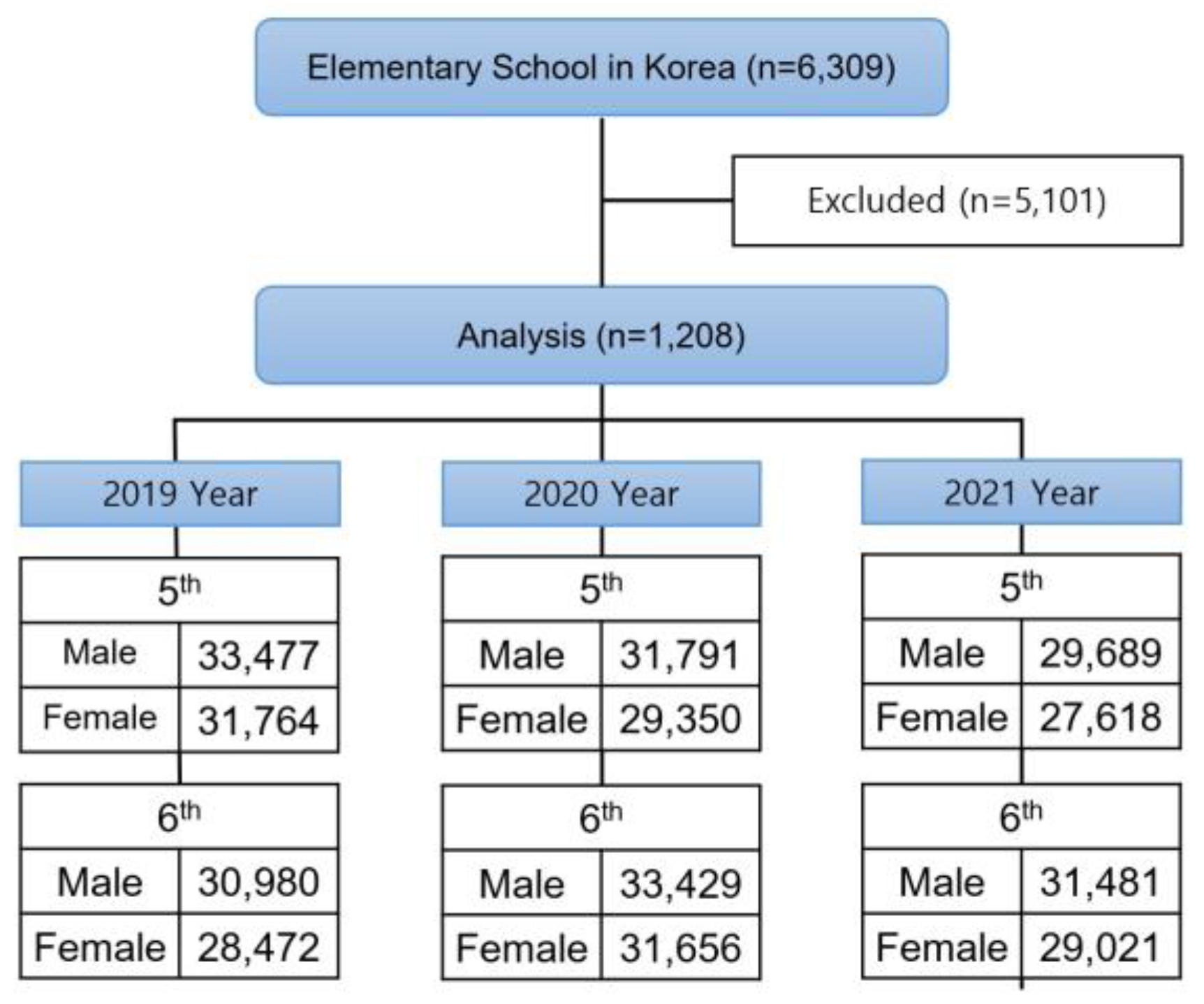
The initial sample population of this study consisted of all 6,309 elementary schools in Korea (as of May 2021). After excluding those with no measured values in even one of the four groups (5th grade male students, 5th grade female students, 6th grade male students, 6th grade female students) for reasons such as not implementing the PAPS due to the COVID-19 pandemic between 2019 and 2021, a total of 1,208 elementary schools remained in the final sample. In 2020–2021, the Korean Ministry of Education allowed schools to autonomously decide whether and when to measure the PAPS, which had been measured every year until then [
24,
25]. The number of students belonging to these schools was 124,693 in 2019, 126,226 in 2020, and 117,809 in 2021; the characteristics of the subjects are as shown in
Table 1. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Korea National University of Education (KNUE-202403-SB-0110-01).
2.2. Items and Measurements
In this study, the measurement tool to compare BMI differences depending on year, gender, and grade was the BMI. It was measured to determine obesity and calculated by dividing weight by the square of height (kg/m
2) [
21]. Elementary schools in Korea enter students’ height and weight into the National Education Information System (NEIS), where the BMI is automatically calculated. The final measurements are provided to students and parents mandatorily after printed out individually. The standard table for the BMI of elementary school students set by the Korean Ministry of Education is shown in
Table 2.
2.3. Procedure and Statistical Analysis
This study used the following procedures to process data. First, frequency analysis was conducted to determine the demographic characteristics of the subjects. Second, repeated measures ANOVA was conducted to explore changes in the average BMI. The statistical significance level was set at p < 0.05 and confidence intervals were modified through the Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons [
25]. As a result of the sphericity test in the process, the interaction effect between average BMI and year failed to meet the sphericity assumption (p < .05), and thus the Greenhouse-Geisser correction was used for effects test [
27]. Statistical significance was set at α = 0.05.
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of data processing. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 18.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
3. Results
Repeated measures ANOVA was conducted to verify changes in the average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea. Changes in the average depending on year and gender, and year and grade were also explored in addition to the year as variables.
3.1. Average MBI Depending on Year, Gender, and Grade
The results showed that the main effect of the year was significant on the average BMI (p < 0.001). Moreover, the interaction effect between gender and year (p < 0.001) and between grade and year (p < 0.01) were also significant. However, the interaction effect between gender, grade, and year was not significant. In other words, the average BMI changed significantly depending on year, gender/year, and grade/year.
Table 3.
Average BMI depending on year, gender, and grade.
Table 3.
Average BMI depending on year, gender, and grade.
| Variable |
Sum of squares |
Degree of freedom |
Mean square |
F |
| Year |
251.156 |
1.992 |
1256.578 |
362.277***
|
| Gender*year |
156.292 |
1.992 |
78.474 |
22.592***
|
| Grade*year |
51.715 |
1.992 |
25.966 |
7.475**
|
| Gender*grade*year |
1.450 |
1.992 |
.727 |
0.210 |
| Error |
33400.220 |
9615.638 |
3.474 |
|
3.2. Average BMI by Year
The results of changes in the average BMI depending on year are as shown in
Table 4. The average BMI increased in 2021 (M = 21.241) compared to 2019 (M = 20.325) and 2020 (M = 20.394; p=0.000). While an increase was observed in 2020 compared to 2019, it was not statistically significant.
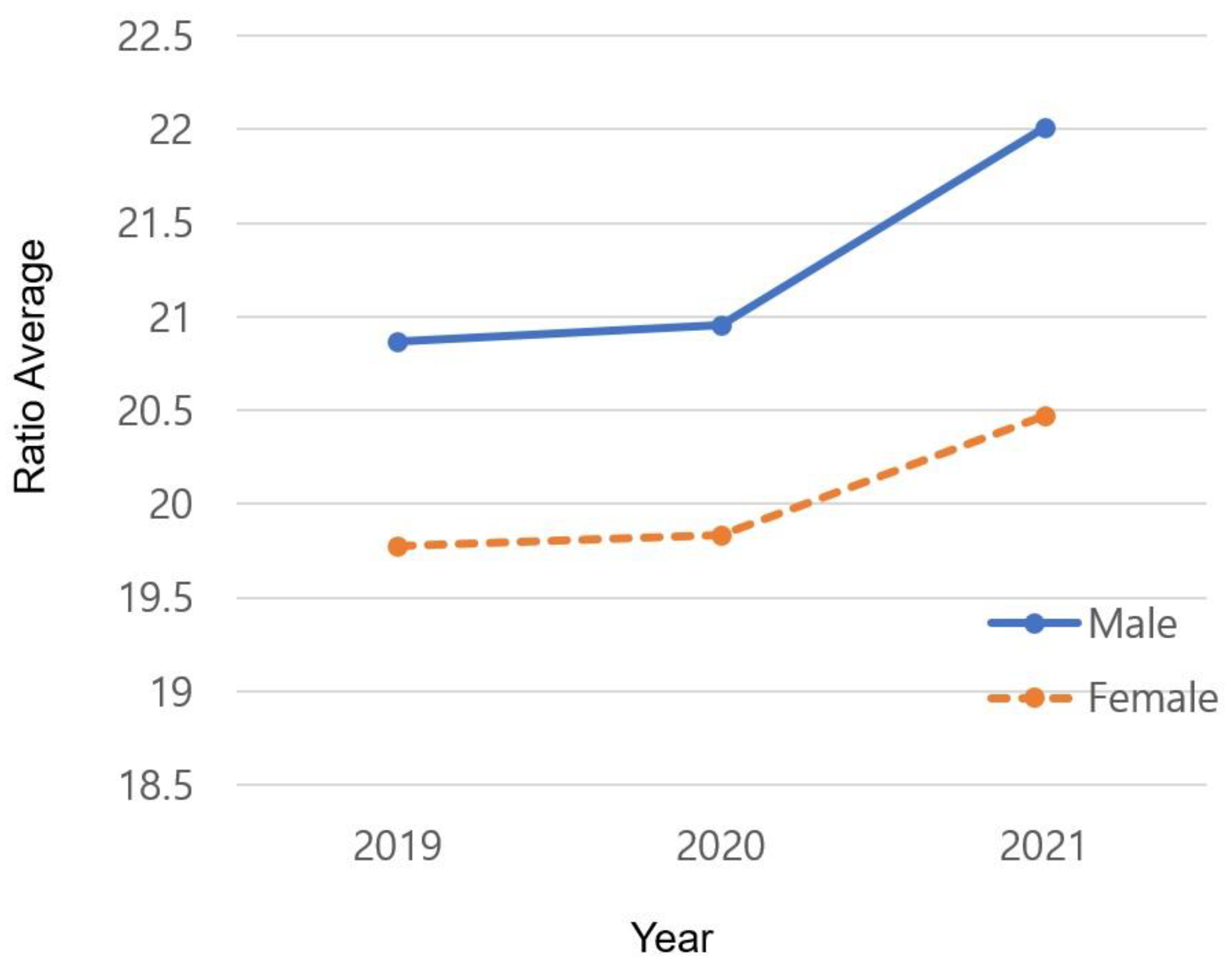
3.3. Average BMI According to Gender and Year
The results of changes in the average depending on gender and year are as shown in
Table 5 and
Figure 2. Male students (M = 20.870) showed a higher average BMI than female students (M = 19.780) in 2019 (p = 0.000). The gap between male (M = 20.952) and female students (M = 19.837) increased in 2020 compared to 2019 (p = 0.000), reaching the largest gap in 2021 (M = 22.012 and M = 20,470, respectively; p = 0.000).
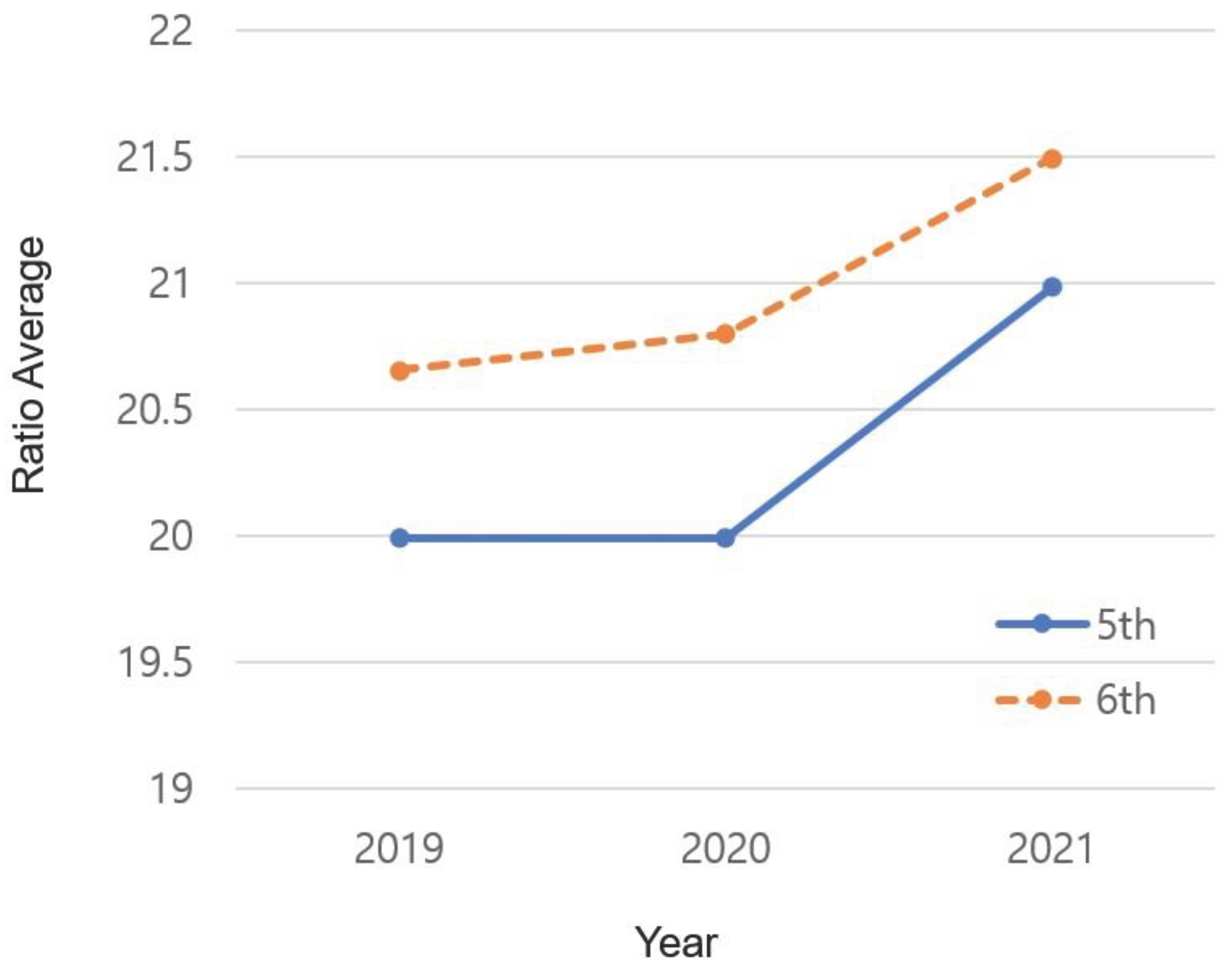
3.4. Average BMI According to Grade and Year
The results of changes in the average BMI by grade and year are as shown in
Table 6 and
Figure 3. In 2019, the average BMI of the 6th grade (M = 20.659) was higher than that of the 5th grade (M = 19.991; p = 0.000). In 2020, the gap between grades increased, compared to 2019 (M = 20.797 and M = 19.992, respectively; p = 0.000). However, in 2021, the gap between the 6th (M = 21.497) and 5th (M = 20.985) grades decreased, showing the smallest gap in 3 years (p = 0.000).
4. Discussion
This study investigated changes in the average BMI of a large population consisting of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea over 3 years (2019–2021). Ultimately, this study seeks to diagnose the role of physical education and provide basic data to explore the direction to prepare for future society. Accordingly, the discussions are as follows.
4.1. Interpretation of Findings
4.1.1. Changes in the Average BMI by Year
According to the average BMI results by year, there was no change in 2020 compared to 2019, but there was a significant increase in 2021. Previous studies clarified that the cause of increased obesity lies in decreased physical activity. A comparative study on obese and non-obese children among racially diverse middle school students reported that lack of physical activity was an important factor in maintaining childhood obesity [
28]. There was a negative view of the approach that focused on a healthy diet and physical activity as solutions to overweight and obesity, however, a summary of studies conducted thus far claimed that physical activity and exercise still had potential as solutions to obesity [
29]. Some studies mentioned that the increase in ICT use was a cause for the increase in obesity. It was reported that Finnish adolescents’ use of ICT, such as watching TV, playing digital games, and using computers, was related to the prevalence of overweight and obesity [
19]. To prevent this, adolescents’ exposure to electronic devices must be regulated by their parents [
30].
Notably, the results of this study showed that the BMI increased significantly from 2020 to 2021 compared to from 2019 to 2020. The increase in body fat and decrease in physical fitness showed similar patterns during the same period in previous studies [
25,
31], and the decrease in physical activity was pointed out as the cause. At the time, the decrease in physical activity was due to the social distancing measures and the increase in non-face-to-face learning because of the pandemic, which is one of the options that can be chosen by physical education in the big trend of future education.
Active application of non-face-to-face education and EdTech is an unavoidable trend as part of future education. However, this study clearly revealed that physical education fails to fulfill its role in these environmental changes, and that limiting students’ physical activity may lead to an increase in obesity. Furthermore, since lack of physical activity contributes to various chronic diseases and health complications, it is necessary to increase the amount of physical activity for students at the national level [
32,
33]. In particular, active participation in various forms of physical activity in childhood is an important prerequisite for participation in physical activity in adulthood [
34]. Thus, physical education in public education must establish measures for these changes in a way that can resolve the decline in students’ physical fitness and the increase in obesity.
4.1.2. Changes in the Average BMI Based on Gender and Year
The yearly average BMI results showed differences by gender. This difference gradually increased, reaching its peak in 2021. Furthermore, male students showed a greater increase in BMI than female students. These results are in line with a study [
25] showing that the physical fitness level including body fat of Korean male elementary school students deteriorated more than that of female students during the same period as this study. In addition, many studies reported that limited physical activity had a more negative impact on men than on women [
35,
36]. This is because male students engage in more physical activity than female students [
37,
38]; therefore, the restrictions on physical activity due to COVID-19 had a greater negative impact on male students than female students. According to a study exploring data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) in the United States from 1999 to 2006, among adolescents aged 12 to 19, 16.6% of male and 15.3% of female adolescents participating in recreational sports were obese (based on BMI) [
39]. However, male adolescents not participating in leisure sports showed an obesity rate of 23.6%, whereas female adolescents showed one of 17.0%. In other words, male adolescents showed a greater difference in BMI when not participating in physical activity.
There are also results that are contrary to those of this study. According to previous studies related to ICT use among Finnish adolescents (ages 14, 16, 18, N = 6615), female students showed higher prevalence of overweight and obesity (based on BMI) than male students from watching TV and using computers [
19]. The results imply that male students tend to play more computer games than watch TV compared to female students, and as recently, computer games also involve physical activity, it may affect the amount of physical activity depending on the type of ICT they use.
4.1.3. Changes in the Yearly Average BMI by Grade
The average BMI results showed yearly differences depending on grade. While this difference increased slightly in 2020 compared to 2019, it decreased in 2021, showing the smallest difference in three years. This implies that an increase in the period in which physical activity is restricted leads to an increase in BMI regardless of grade and age.
Previous studies suggested various variables that affected obesity. According to a study examining adults in 15 European Union (EU) countries, the prevalence of obesity was higher in men than in women, and in those with lower levels of education. Moreover, less participation in leisure or physical activity led to less interest in physical activity participation, and more time spent sitting at work led to higher obesity rates; further, married couples, widows, and divorced individuals showed a higher prevalence than singles [
40]. Meanwhile, one notable variable in the adolescent group was sleep quality [
41]. According to this study exploring the relationship between sleep quality and obesity among male and female adolescents (ages 11–16), obese adolescents showed shorter sleep duration than non-obese adolescents. Sleep disorders were not correlated with obesity but affected the level of physical activity.
Many previous studies proved that physical activity is a common factor that affects obesity. Although diverse variables may affect obesity, it can be expected that these variables are related to the amount or level of physical activity. In this study, a difference in BMI was observed depending on grade during the first half of the research period (2019–2020); however, this difference decreased in the latter half (2020–2021), indicating that grade did not play a significant role.
4.1.4. Practical Implications of the Study
In summary, the changes in the educational environment during the survey period (2019–2021) reduced physical activity, which increased the average BMI of Korean elementary school students. This was a reminder of how important school physical activity is, and it raised the need to use ICT in a way that involves physical activity in future education [
42]. In particular, the increase in BMI stood out more among male than female students, and the effect depending on grade decreased.
Based on the above, the following suggestions can be made for the role and policy of physical education to prevent the decrease in physical activity due to changes in the future environment.
First, it is necessary to improve the quality and quantity of physical education programs to create a healthy lifestyle for students. Physical education is responsible for nurturing healthy and vibrant citizens [
32], and since these habits are formed from childhood to adolescence, when physical education is introduced [
43], students must be provided with opportunities to participate in physical activity and feel the joy of it so that they can engage in more [
44,
45].
Second, it is necessary to prepare for physical activity even in non-face-to-face situations in case face-to-face physical education cannot be provided due to various environmental constraints. While students can engage in joint physical activity at school, they can engage in individual physical activity at home [
46]. For example, it will be possible to meet the required amount of physical activity for adolescents by measuring and managing the number of steps and amount of exercise using ICT devices and doing exercises or dancing for physical fitness using home games.
Third, parents must pay more attention to their children’s physical activity at home and actively ensure the necessary amount of physical activity for students. As found in previous studies, adolescence is a time when physical activity habits are formed, which is why the role of parents and constant recommendations of physical activity are important so that students can engage in it even at home [
47,
48,
49].
4.1.5. Limitations and Scope for Further Research
Several limitations were found in the process of producing these results, and suggestions for future studies center on these limitations. First, this study was a large-scale project targeting all 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea. Further research should use and compare data by continent, country, and race. Second, this study focused on the gender and grade (5th and 6th grade) of the students. Further research could compare data between regions or lower/middle/upper grades. Third, this study derived objective results using large-scale quantitative data. By understanding the individual context through a qualitative method, it would be possible to gain an in-depth understanding of the impact on physical activity and health of each individual. Last, this study was conducted to explore the role of physical education by examining the changes in the average BMI of elementary school students in the context of a decline in physical activity. The findings of this study are merely a starting point for reestablishing the role of physical education in the future society.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated changes in the average BMI in 1,208 Korean elementary schools using the PAPS data measured in 2019–2021. This was to provide foundational data for discussing not only the present but also the future role of physical education. The findings of this study are as follows.
First, the average BMI of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea significantly increased in 2021 compared to 2019 and 2020. Second, changes in the average BMI by year showed significant differences depending on gender. The difference in the average BMI between men and women gradually increased during the measurement period. Third, changes in the average BMI by year showed significant differences depending on grade. The difference in the average BMI between grades slightly increased in 2020 compared to 2019, but significantly decreased in 2021.
In summary, the obesity of 5th and 6th grade elementary school students in Korea increased in 2019–2021. This may be due to the decrease in students’ physical activity. Male students showed a steeper increase in obesity, regardless of grade.
Experts have argued that the amount of physical activity in students has decreased for various reasons and predicted that it will continue to decrease in the future. Inactive lifestyles at school and increased screen time will lead to a decrease in physical activity, resulting in an increase in obesity and a decrease in physical fitness among students. To prevent this, sufficient discussions must be carried out on how to apply future education such as EdTech and ICT to physical education so that students can continue engaging in physical activity even during changes in the social environment. Furthermore, it is necessary to establish measures to protect the health and physical fitness of students in future education.
In the end, school and physical education must be at the heart of such measures. More specifically, physical education must play its role even in educational environments such as non-face-to-face distance learning. This will help recover the health and physical fitness of the increasing number of obese students. Now is the time to discuss and prepare these measures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; methodology, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; data collection, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; analysis, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; investigation, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; writing—review, and editing, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L.; supervision, B.-K.C., S.-W.P., Y.-S.K., and S.-M.L. All authors read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Korea National University of Education (KNUE-202403-SB-0110-01).
Data availability statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data were not publicly available because of the protection of personal information.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the study participants, who generously volunteered to participate in the present study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Boyd, W. The History of Western Education; Adam & Charles Black: London, United Kingdom, 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, B.K. Differences in Self-Rated Health and Physical Activity due to Education Level among Koreans: Understanding Implications of Physical Education. Iran J Public Health 2021, 50, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, N.K. The History of Physical Education and Sport; GS Press: JINJU, South Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.M.; Khoo, S. Non-Face-To-Face Physical Activity Interventions in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2014, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Seo, K.W.; An, K.O. Effects of the Non-Face-To-Face Learning on Health-Related Physical Fitness and Balance in Adolescents According to COVID-19. Exerc Sci 2021, 30, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, O.; Lee, S.; Bae, S.; Makino, K.; Chiba, I.; Harada, K.; Morikawa, M.; Tomida, K.; Shimada, H. Are Non-Face-To-Face Interactions an Effective Strategy for Maintaining Mental and Physical Health? Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2022, 98, 104560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.S.; So, W.Y. The Effects of 24 Weeks of Non-Face-to-Face Home Exercise on Body Composition, Physical Fitness, Cardiovascular Function, and Blood Profiles in Pre-Metabolic Syndrome Korean Adults: A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, Y.; Nonaka, K.; Kuraoka, M.; Murayama, Y.; Murayama, S.; Nemoto, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Matsunaga, H.; Fujita, K.; Murayama, H.; Kobayashi, E. Influence of “Face-To-Face Contact” and “Non-Face-To-Face Contact” on the Subsequent Decline in Self-Rated Health and Mental Health Status of Young, Middle-Aged, and Older Japanese Adults: A Two-Year Prospective Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Adachi, Y.; Adachi, K.; Sato, C. Effects of a Non-Face-To-Face Behavioral Weight-Control Program Among Japanese Overweight Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Behav Med 2010, 17, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kang, S. Development of Curriculum Model Using ICT Content. In Kim, K., Kim, H.Y., Eds.; Information Science and Applications. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Springer Singapore, 2020, pp. 701–705. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Nieto, T.; López-Pastor, V.M.; Palacios-Picos, A. A Combination of Transformative and Authentic Assessment Through ICT in Physical Education. Retos: Nuevas Perspectivas de Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación 2022, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, J.K.V. General Contribution of ICT in Physical Education. IJFMR, 4.
- Hinojo Lucena, F.J.; Lopez Belmonte, J.; Fuentes Cabrera, A.; Trujillo Torres, J.M.; Pozo Sanchez, S. Academic Effects of the Use of Flipped Learning in Physical Education. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.E. Exploration of Educational Possibilities by Four Metaverse Types in Physical Education. Technologies 2022, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Suelves, D.; Ramón-Llin, J.; Gabarda, V. The Role of Technology in Physical Education Teaching in the Wake of the Pandemic. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.H. The Effect of a Virtual Reality-Based Physical Education Program on Physical Fitness among Elementary School Students. Iran J Public Health 2023, 52, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Ciccarelli, M.; Falkmer, T.; Parsons, R. Associations Between Exposure to Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and Reported Discomfort Among Adolescents. Work 2014, 48, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachón-Zagalaz, J.; Zagalaz-Sánchez, M.ª.L.; Arufe-Giráldez, V.; Sanmiguel-Rodríguez, A.; Gonzalez-Valero, G. Physical Activity and Daily Routine Among Children Aged 0–12 During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Spain. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kautiainen, S.; Koivusilta, L.; Lintonen, T.; Virtanen, S.M.; Rimpelä, A. Use of Information and Communication Technology and Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity Among Adolescents. Int J Obes 2005, 29, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, E.A.; Dong, Y.; Dunlop, A.L.; Aschner, J.L.; Stanford, J.B.; Hartert, T.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Hudak, M.L.; Carroll, K.; O’Connor, T.G.; et al. Changes in BMI During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Pediatrics 2022, 150, e2022056552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.H. Nutrition for Health, Fitness and Sport, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: Boston, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nicole, J.M.; Evan, J.A.; Derikk, M.H. Innovative Ways to Use Modern Technology to Enhance, Rather Than Hinder, Physical Activity Among Youth. J Phys Educ Recreat Dance 2015, 86, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.M.; Cole, T.J. What Use is the BMI? Arch Dis Child 2006, 91, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incheon Metroplitan City Office of Education. Physical Activity Promotion System(PAPS) Master Plan. Incheon Metroplitan City Office of Education, 2021.
- Chang, B.K. Examining the Degree of Changes in Korean Elementary Schools’ Physical Activity Promotion System Grades amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic. Iran J Public Health 2022, 51, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.S. The Relationship Between Physical Fitness and Academic Achievement Among Adolescent in South Korea. J Phys Ther Sci 2018, 30, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathke, A.C.; Schabenberger, O.; Tobias, R.D.; Madden, L.V. Greenhouse–Geisser Adjustment and the ANOVA-type Statistic: Cousins or Twins? Am Stat 2009, 63, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Kerr, L.M.; Ward, D.S.; Pate, R.R. Physical Activity and Determinants of Physical Activity in Obese and Non-Obese Children. Int J Obes 2001, 25, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, P. The Role of Physical Activity and Exercise in Obesity and Weight Management: Time for Critical Appraisal. J Sport Health Sci 2016, 5, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekra, A.; Rifan, A.; Johara, A.; Ethar, A.; Eman, M.; Reem, A. The Relationship Between Technology Use and Physical Activity Among Typically-Developing Children. Healthcare 2020, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Seo, D-i. ; Lee, S.-M.; Kim, J.-H. Changes in Physical Fitness Among Elementary and Middle School Students in Korea Before and After COVID-19. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19, 11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, T.L.; Kahan, D. Physical Activity, Public Health, and Elementary Schools. Elem Sch J 2008, 108, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, H.W.; Craig, C.L.; Lambert, E.V.; Inoue, S.; Alkandari, J.R.; Leetongin, G.; Kahlmeier, S.; Lancet Physical Activity Series Working Group. The Pandemic of Physical Inactivity: Global Action for Public Health. Lancet 2012, 380, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griggs, G.; Ward, G. Phsical Education in the UK: Disconnections and Reconnections. The Curriculum Journal 2012, 23, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañeda-Babarro, A.; Arbillaga-Etxarri, A.; Gutiérrez-Santamaría, B.; Coca, A. Physical Activity Change During COVID-19 Confinement. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17, 6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallis, J.F. Epidemiology of Physical Activity and Fitness in Children and Adolescents. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1993, 33, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazo-Sayavera, J.; Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; González, S.A.; Tremblay, M.S. Gender Differences in Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior: Results from Over 200,000 Latin-American Children and Adolescents. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0255353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Carreiro da Costa, F. Levels of Physical Activity of Urban Adolescents According to Age and Gender. Int J Sports Sci 2013, 3, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.W.; Perrin, E.M.; Coyne-Beasley, T.; Peterson, C.J.; Skinner, A.C. Reported Sports Participation, Race, Sex, Ethnicity, and Obesity in US Adolescents from NHANES Physical Activity (PAQ_D). Glob Pediatr Health 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.A.; Kearney, J.M.; Kafatos, A.; Paquet, S.; Martínez-Gonzélez, M.A. Variables Independently Associated with Self-Reported Obesity in the European Union. Public Health Nutr 1999, 2, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.K.; Mueller, W.H.; Chan, W.; Meininger, J.C. Is Obesity Associated with Poor Sleep Quality in Adolescents? Am J Hum Biol 2002, 14, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Minami, M.; Yano, E. Body Mass Index, Blood Pressure, and Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Among Permanent and Fixed-Term Workers in the Manufacturing Industry: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchwood, D.; Robert, K.; Pollock, G. Explaining Differences in Sport Participation Rates Among Young Adults: Evidence from the South Caucasus. Eur Phy Educ Rev 2008, 14, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, J.; Hay, J. Children's Involvement in Sport: A Developmental Perspective. In Psychological Foundations of Sport; Silva, J., Stevens, D., Eds.; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.T.; Thomas, J.R. Principles of Motor Development for Elementary School Physical Education. Elem Sch J 2008, 108, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juniu, S. Pedagogical Uses of Technology in Physical Education. J Phys Educ Recreat Dance 2011, 82, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberg, M.A; Pedersen, N.L; Toren, K.; Svartengren, M.; Bäckstrand, B.; Johnsson, T.; Cooper-Kuhn, C.M.; Åberg, N.D.; Nilsson, M.; Kuhn, H.G. Cardiovascular Fitness is Associated with Cognition in Young Adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009, 106, 20906–20911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.; Jacobs, B.; Barber, J.; Eccles, J. Childhood and Adolescent Sports Participation as Predictors of Participation in Sports and Physical Fitness Activities During Young Adulthood. Youth Soc 2004, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, R.E.; Smithe, F.A.; Buzby, J.H. Teach Throwing and Catching to Large Classes. Strategies 1997, 10, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).